Frequency of Peripheral CD8+ T Cells Expressing Chemo-Attractant Receptors CCR1, 4 and 5 Increases in NPC Patients with EBV Clearance upon Radiotherapy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Eligibility and Collection of Biomaterials
2.2. Definition of Plasma EBV DNA Clearance
2.3. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.4. T-Cell Subset Clustering and Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projections
2.5. Quantification of Chemo Attractants
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient and Study Characteristics
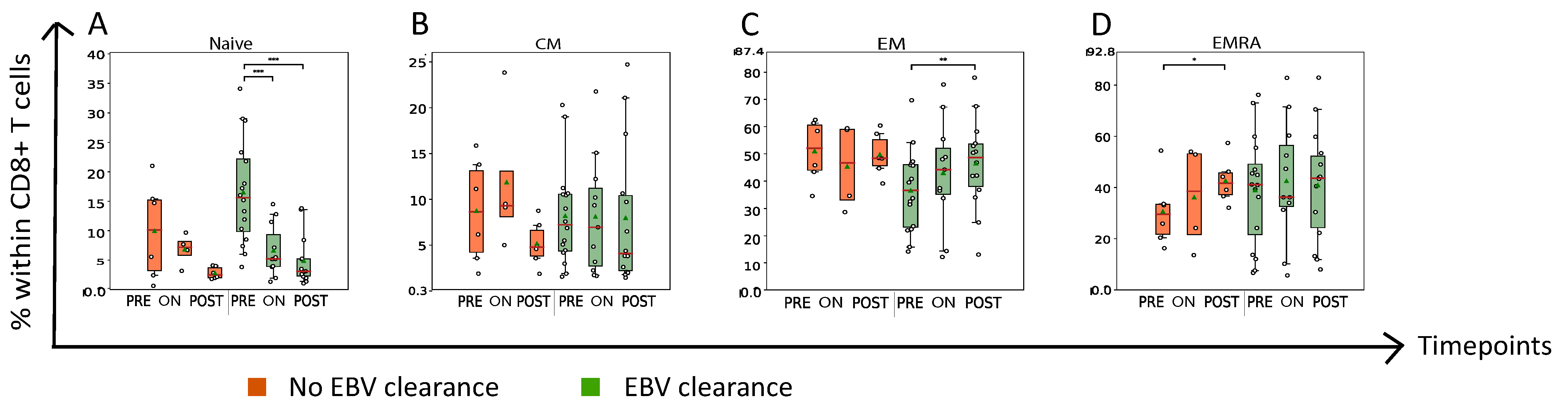
3.2. Nasopharyngeal Cancer Patients with Plasma EBV DNA Clearance Exhibit Lower Abundance of Circulating PD1+CD8+ T Cells On- and Post-RT When Compared to Patients without Plasma EBV DNA Clearance
3.3. Nasopharyngeal Cancer Patients with Plasma EBV DNA Clearance Had a Late Rise in the Abundance of OX40+ CD8+ T Cells during RT
3.4. Nasopharyngeal Cancer Patients with Plasma EBV DNA Clearance Demonstrate an Early and Profound Rise in the Abundance of CCR1+, CCR4+ and/or CCR5+CD8+ T Cells during RT
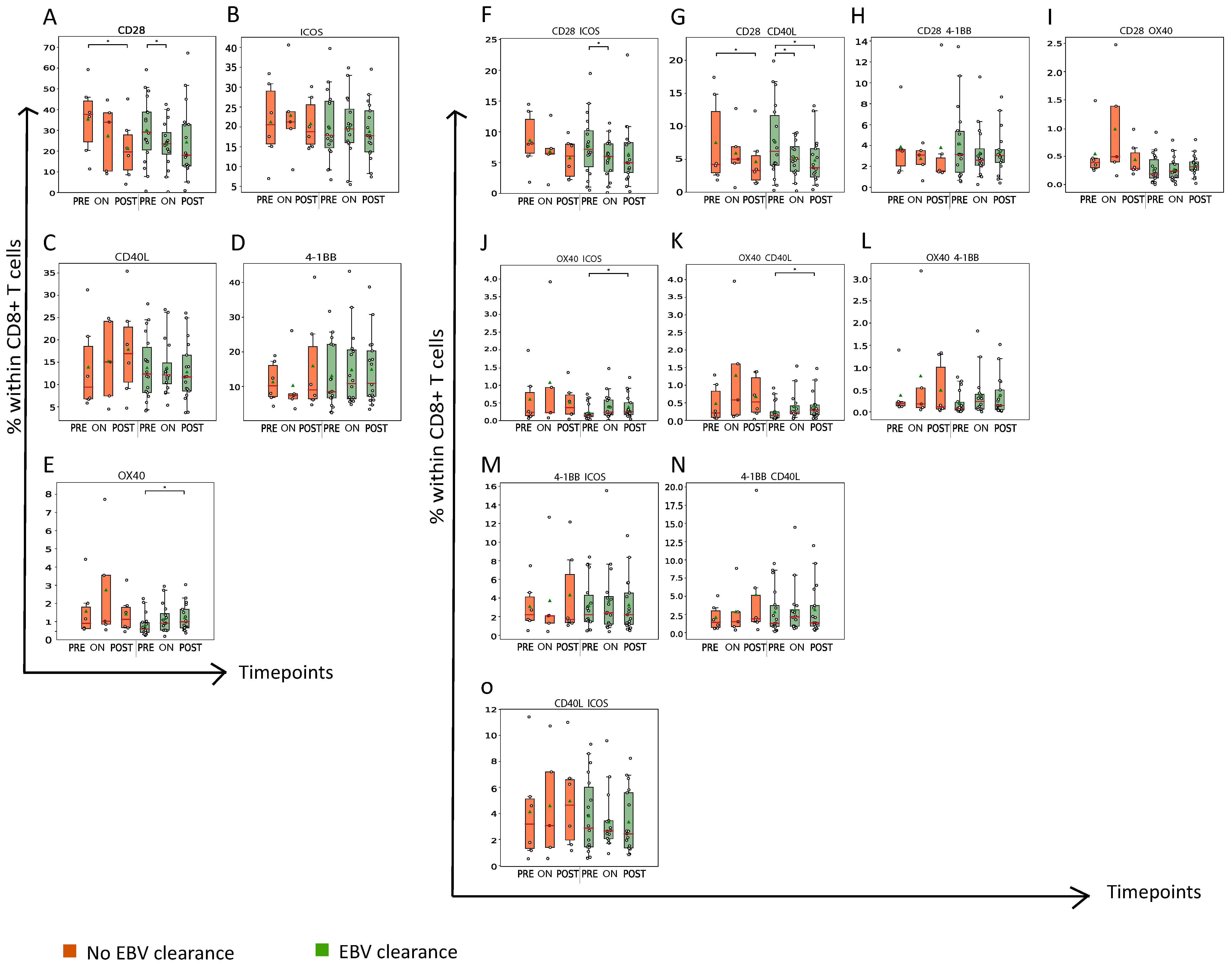
3.5. Abundance of CCR1, CCR4 and/or CCR5+CD8+ T Cells Is Associated with Presence of Mature OX40+CD8+ T Cells
3.6. Patients without NPC Recurrence Showed Differential Presence of Markers of T-Cell Chemotaxis When Compared to Patients with NPC Recurrence
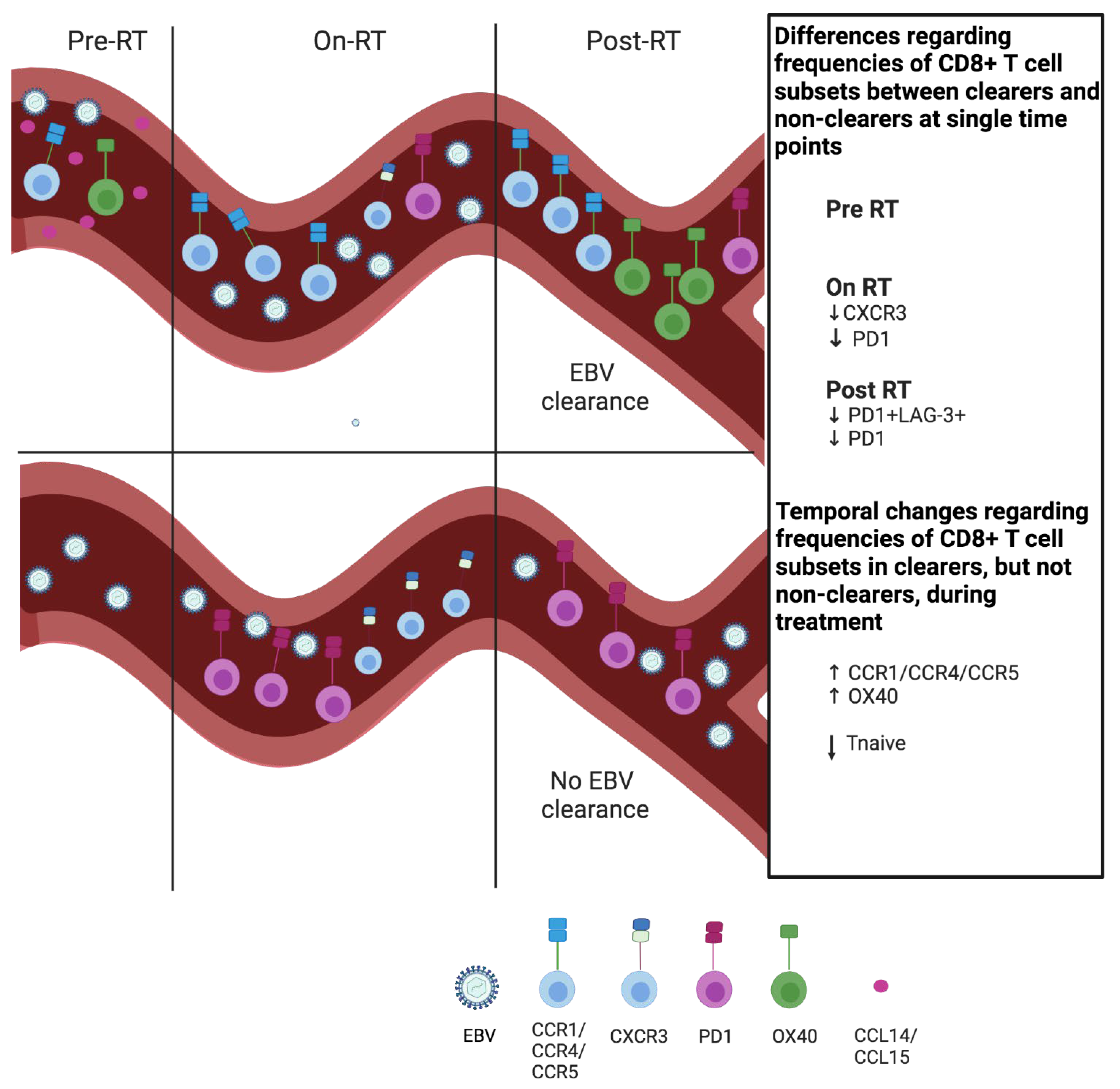
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsao, S.W.; Tsang, C.M.; Lo, K.W. Epstein-barr virus infection and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.-P.; Xie, F.-Y.; Liu, L.-Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, L.-L.; Liao, X.-B.; Xu, H.-Y.; Chen, L.; Lai, S.-Z.; et al. Re-Evaluation of 6th Edition of AJCC Staging System for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and Proposed Improvement Based on Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 73, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Hu, G.-Q.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, X.-D.; Yang, K.-Y.; Jin, F.; Shi, M.; Chen, Y.P.; Hu, W.-H.; et al. Gemcitabine and Cisplatin Induction Chemotherapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-P.; Ismaila, N.; Chua, M.L.K.; Colevas, A.D.; Haddad, R.; Huang, S.H.; Wee, J.T.S.; Whitley, A.C.; Yi, J.-L.; Yom, S.S.; et al. Chemotherapy in Combination with Radiotherapy for Definitive-Intent Treatment of Stage II-IVA Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: CSCO and ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 840–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.W.; Ma, B.; Ng, W.T.; Chan, A.T. Management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Current practice and future perspective. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3356–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-Q.; Pan, S.-M.; Liang, S.-X.; Han, Y.-S.; Chen, H.-B.; Li, J.-C. Research status and prospects of biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the era of high-throughput omics (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 58, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.A. Plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA as a biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.K.J.; Chan, K.C.A.; Lo, Y.M.D. Plasma Epstein–Barr virus DNA as an archetypal circulating tumour DNA marker. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, K.; Yi, B. Molecular Prognostic Value of Circulating Epstein-Barr Viral DNA in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of 27,235 Cases in the Endemic Area of Southeast Asia. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomarkers 2019, 23, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berele, B.A.; Cai, Y.; Yang, G. Prognostic Value of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients: Meta-Analysis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211034265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yin, J.-H.; Li, W.-F.; Li, H.-J.; Chen, D.-P.; Zhang, C.-J.; Lv, J.-W.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Li, X.-M.; Li, J.-Y.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals regulators underlying immune cell diversity and immune subtypes associated with prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 1024–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; He, S.; Wang, X.-L.; Peng, W.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Chi, D.-M.; Chen, J.-R.; Han, B.-W.; Lin, G.-W.; Li, Y.-Q.; et al. Tumour heterogeneity and intercellular networks of nasopharyngeal carcinoma at single cell resolution. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Kwong, D.L.-W.; Dai, W.; Wu, P.; Li, S.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Fang, X.; Liu, L.; et al. Comprehensive single-cell sequencing reveals the stromal dynamics and tumor-specific characteristics in the microenvironment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-P.; Lv, J.-W.; Mao, Y.-P.; Li, X.-M.; Li, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.-Q.; He, Q.-M.; Yang, X.-J.; et al. Unraveling tumour microenvironment heterogeneity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma identifies biologically distinct immune subtypes predicting prognosis and immunotherapy responses. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.-L.; Bian, L.-J.; Liu, Z.-X.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Sun, X.-S.; Sun, R.; Luo, D.-H.; Li, X.-Y.; Xiao, B.-B.; Yan, J.-J.; et al. Development and validation of the immune signature to predict distant metastasis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 8, e000205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Chung, G.T.Y.; Lui, V.W.Y.; To, K.-F.; Ma, B.B.Y.; Chow, C.; Woo, J.K.S.; Yip, K.Y.; Seo, J.; Hui, E.P.; et al. Exome and genome sequencing of nasopharynx cancer identifies NF-κB pathway activating mutations. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.C.W.; Hui, E.P.; Lo, K.-W.; Lam, W.K.J.; Johnson, D.; Li, L.; Tao, Q.; Chan, K.C.A.; To, K.-F.; King, A.D.; et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An evolving paradigm. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, G.T.-Y.; Lou, W.P.-K.; Chow, C.; To, K.-F.; Choy, K.-W.; Leung, A.W.-C.; Tong, C.Y.-K.; Yuen, J.W.-F.; Ko, C.-W.; Yip, T.T.-C.; et al. Constitutive activation of distinct NF-κB signals in EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2013, 231, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.-T.; Ye, S.-B.; Liu, Y.-N.; He, J.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Mai, H.-Q.; Zhang, C.-X.; Cui, J.; Zhang, X.-S.; Busson, P.; et al. LMP1-mediated glycolysis induces myeloid-derived suppressor cell expansion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLOS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Luo, Y.; Deng, R.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, F.; Lu, J.; Li, X. EBV-EBNA1 constructs an immunosuppressive microenvironment for nasopharyngeal carcinoma by promoting the chemoattraction of Treg cells. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.; Zhang, N.; Huang, Q.; Ge, C.; Li, Q.; Li, S.; Weng, K.; Guo, Q.; Sui, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Association of Epstein-Barr virus infection with peripheral immune parameters and clinical outcome in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.M.; Chan, L.Y.; Lo, K.W.; Leung, S.F.; Zhang, J.; Chan, A.T.C.; Lee, J.C.; Hjelm, N.M.; Johnson, P.J.; Huang, D.P. Quantitative analysis of cell-free Epstein-Barr virus DNA in plasma of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res 1999, 59, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rijnders, M.; Balcioglu, H.E.; Robbrecht, D.G.; Oostvogels, A.A.; Wijers, R.; Aarts, M.J.; Hamberg, P.; van Leenders, G.J.; Nakauma-González, J.A.; Voortman, J.; et al. Anti–PD-1 Efficacy in Patients with Metastatic Urothelial Cancer Associates with Intratumoral Juxtaposition of T Helper-Type 1 and CD8+ T cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunert, A.; Basak, E.A.; Hurkmans, D.P.; Balcioglu, H.E.; Klaver, Y.; Van Brakel, M.; Oostvogels, A.A.M.; Lamers, C.H.J.; Bins, S.; Koolen, S.; et al. CD45RA+CCR7− CD8 T cells lacking co-stimulatory receptors demonstrate enhanced frequency in peripheral blood of NSCLC patients responding to nivolumab. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, A.H.; Pauken, K.E. The diverse functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 18, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, F.; Pan, Q.; Phiphatwatchara, P.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, H. The promising immune checkpoint LAG-3: From tumor microenvironment to cancer immunotherapy. Genes Cancer 2018, 9, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graydon, C.G.; Mohideen, S.; Fowke, K.R. LAG3′s Enigmatic Mechanism of Action. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, A.E.; Kovacsovics-Bankowski, M.; Weinberg, A.D. The TNFRs OX40, 4-1BB, and CD40 as targets for cancer immunotherapy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L. Therapeutic strategies for the costimulatory molecule OX40 in T-cell-mediated immunity. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 10, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Raemdonck, K.; Van den Steen, P.E.; Liekens, S.; Van Damme, J.; Struyf, S. CXCR3 ligands in disease and therapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeta, V.M.; Massara, M.; Capucetti, A.; Bonecchi, R. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: New targets for cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshie, O.; Matsushima, K. CCR4 and its ligands: From bench to bedside. Int. Immunol. 2014, 27, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, R. Clinical Application of Anti-CCR4 Monoclonal Antibody. Oncology 2015, 89 (Suppl. S1), 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldinucci, D.; Borghese, C.; Casagrande, N. The CCL5/CCR5 Axis in Cancer Progression. Cancers 2020, 12, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halama, N.; Zoernig, I.; Berthel, A.; Kahlert, C.; Klupp, F.; Suarez-Carmona, M.; Suetterlin, T.; Brand, K.; Krauss, J.; Lasitschka, F.; et al. Tumoral Immune Cell Exploitation in Colorectal Cancer Metastases Can Be Targeted Effectively by Anti-CCR5 Therapy in Cancer Patients. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, E.L.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Soo, K.-C.; Wee, J.T.S.; Chua, M.L.K. Combinatorial strategies of radiotherapy and immunotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, M.; Patin, E.C.; Pedersen, M.; Wilkins, A.; Dillon, M.T.; Melcher, A.A.; Harrington, K.J. Inflammatory microenvironment remodelling by tumour cells after radiotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Wei, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, K.; Huang, W.; Liu, H.; Li, B. Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 is closely correlated with clinical outcome in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2015, 37, 6099–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Li, R.; Chen, M.-Y.; Yu, C.; Tang, L.-Q.; Liu, Y.-M.; Li, J.-P.; Liu, Y.-N.; Luo, Y.-L.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis defines the interplay between tumor cells, viral infection, and the microenvironment in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 950–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; MacIsaac, K.D.; Zhou, T.; Huang, P.-Y.; Xin, C.; Dobson, J.R.; Yu, K.; Chiang, D.Y.; Fan, Y.; Pelletier, M.; et al. Genomic analysis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma reveals TME-based subtypes. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.; Zeng, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Xie, B.; Sun, L.-Q. Radiation-Enhanced Expression of CCL22 in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma is Associated with CCR4+ CD8 T Cell Recruitment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 108, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, T.; Takiguchi, M. Human memory CCR4+CD8+ T cell subset has the ability to produce multiple cytokines. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.B.Y.; Lim, W.-T.; Goh, B.-C.; Hui, E.P.; Lo, K.-W.; Pettinger, A.; Foster, N.R.; Riess, J.W.; Agulnik, M.; Chang, A.Y.C.; et al. Antitumor activity of nivolumab in recurrent and metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An international, multicenter study of the mayo clinic phase 2 consortium (NCI-9742). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkins, D.R.; Haddad, R.I. Clinical trial data of Anti–PD-1/PD-L1 therapy for recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2022, 109, 102428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.-L.; Liu, S.; Wang, G.-N.; Zheng, S.-H.; Ding, S.-R.; Tao, Y.-L.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.-R.; Yang, X.; Chang, H.; et al. The prognostic significance of PD-L1 and PD-1 expression in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, F.; Ai, P. Combined Association of Tumoral PD-L1 Expression and Pretreatment Presence of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA With Risk Stratification and Prognosis of Patients With Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 791411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, R.; Xiang, W.; Marlier, D.; Au, V.B.; Ching, Q.; Wu, L.X.; Guan, R.; Lee, B.; Chia, W.-K.; Wang, W.-W.; et al. Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Underpin Resistance to Adoptive T Cell Therapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; Jia, K.; Wang, H.; Zhou, C.; He, Y. OX40 (CD134) and OX40 ligand, important immune checkpoints in cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 7347–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahiliani, V.; Hutchinson, T.E.; Abboud, G.; Croft, M.; Salek-Ardakani, S. OX40 Cooperates with ICOS To Amplify Follicular Th Cell Development and Germinal Center Reactions during Infection. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyrend, G.; van der Sluis, T.; van der Gracht, E.; Abdelaal, T.; Jochems, S.; Belderbos, R.; Wesselink, T.; van Duikeren, S.; van Haften, F.; Redeker, A.; et al. OX40 Agonism Enhances Efficacy of PD-L1 Checkpoint Blockade by Shifting the Cytotoxic T Cell Differentiation Spectrum. SSRN Electron. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhen, R.; Ballesteros-Merino, C.; Frye, A.K.; Tran, E.; Rajamanickam, V.; Chang, S.-C.; Koguchi, Y.; Bifulco, C.B.; Bernard, B.; Leidner, R.S.; et al. Neoadjuvant anti-OX40 (MEDI6469) therapy in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma activates and expands antigen-specific tumor-infiltrating T cells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Wang, C.-P.; Lin, P.-H.; Yang, T.-L.; Lou, P.-J.; Ko, J.-Y.; Wu, C.-T.; Chang, Y.-L. The immunologic advantage of recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma from the viewpoint of Galectin-9/Tim-3-related changes in the tumour microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Cohort 1 | ||
| Age, median (range) | 51 (30–67) | |
| Sex, n | ||
| Male | 20 | |
| Female | 4 | |
| Tumor stage, n | ||
| I | 3 | |
| II | 3 | |
| III | 11 | |
| IVA | 7 | |
| Treatment | ||
| Induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy | 5 | |
| Concurrent chemoradiotherapy | 21 | |
| Radiotherapy | 3 | |
| Cohort 2 | ||
| Age, median (range) | 55 (33–68) | |
| Sex, n | ||
| Male | 21 | |
| Female | 7 | |
| Tumor stage, n * | ||
| I | 1 | |
| II | 5 | |
| III | 11 | |
| IVA | 5 | |
| Treatment | ||
| Induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy | 7 | |
| Concurrent chemoradiotherapy | 21 | |
| Radiotherapy | 5 | |
| Marker | Expression | Ligand | Immune Function | Therapeutic Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD-1 [25] | Expressed by different immune and myeloid cells | PD-L1 | Inhibits TCR-CD3z and CD28 signaling via recruitment of phosphatases. | Antibodies targeting PD1 are standard of care for multiple cancer types |
| LAG3 [26,27] | Expressed by different immune cells | MHC-II | Inhibits early steps of TCR signaling, such as NFAT activation | Antibodies targeting LAG3 to treat multiple tumor types are currently tested in clinical trials |
| OX40 [28,29] | Expressed by CD4+ and CCD8+ T cells | OX40L | Promotes survival and memory generation of CD4+ T cells and suppresses regulatory T-cell activation by antagonizing TGF β signaling | Agonistic antibody-targeting OX40 resulted in enhanced recruitment of antigen-reactive T cells into HNSCC tumor in a clinical trial |
| CXCR3 [30] | Expressed by different immune and myeloid cells | CXCL9/10/11/13 | Enhances recruitment and migration of T cells | No clinical trials yet that target CXCR3 |
| CCR1 [31] | CCL3/4/5/8/13/14/15/23 | Enhances recruitment of T cells and suppressive macrophages | No clinical trials yet that target CCR1 | |
| CCR4 [32,33] | CCL3/5/17/22 | Enhances recruitment of T cells and, in the case of the CCR4-CCL22 axis, mediates suppression by regulatory T cells | CCR4 antagonist blocks CCR4-expressing regulatory T cells for treatment of T-cell leukemia | |
| CCR5 [34,35] | CCL2/3/4/5/8/11/13/14 | Enhances recruitment of T cells, and constitutes an entry receptor of HIV. Activates calcium signaling and PI3K pathway to induce survival | CCR5 antagonist repolarizes macrophages to induce an anti-tumor effect in colorectal cancer patients. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahajan, S.; Balcioglu, H.E.; Oostvogels, A.; Dik, W.A.; Chan, K.C.A.; Lo, K.-W.; Hui, E.P.; Tsang, A.; Tong, J.; Lam, W.K.J.; et al. Frequency of Peripheral CD8+ T Cells Expressing Chemo-Attractant Receptors CCR1, 4 and 5 Increases in NPC Patients with EBV Clearance upon Radiotherapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061887
Mahajan S, Balcioglu HE, Oostvogels A, Dik WA, Chan KCA, Lo K-W, Hui EP, Tsang A, Tong J, Lam WKJ, et al. Frequency of Peripheral CD8+ T Cells Expressing Chemo-Attractant Receptors CCR1, 4 and 5 Increases in NPC Patients with EBV Clearance upon Radiotherapy. Cancers. 2023; 15(6):1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061887
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahajan, Shweta, Hayri E. Balcioglu, Astrid Oostvogels, Willem A. Dik, K. C. Allen Chan, Kwok-Wai Lo, Edwin P. Hui, Anna Tsang, Joanna Tong, Wai Kei Jacky Lam, and et al. 2023. "Frequency of Peripheral CD8+ T Cells Expressing Chemo-Attractant Receptors CCR1, 4 and 5 Increases in NPC Patients with EBV Clearance upon Radiotherapy" Cancers 15, no. 6: 1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061887
APA StyleMahajan, S., Balcioglu, H. E., Oostvogels, A., Dik, W. A., Chan, K. C. A., Lo, K.-W., Hui, E. P., Tsang, A., Tong, J., Lam, W. K. J., Wong, K., Chan, A. T. C., Ma, B. B. Y., & Debets, R. (2023). Frequency of Peripheral CD8+ T Cells Expressing Chemo-Attractant Receptors CCR1, 4 and 5 Increases in NPC Patients with EBV Clearance upon Radiotherapy. Cancers, 15(6), 1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061887








