Treatment Patterns, Testing Practices, and Outcomes in Patients with EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Poland: A Descriptive Analysis of National, Multicenter, Real-World Data from the REFLECT Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Data Sources
2.4. Ethics
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Characteristics of First-Line Therapy
3.3. Characteristics of Second-Line Therapy
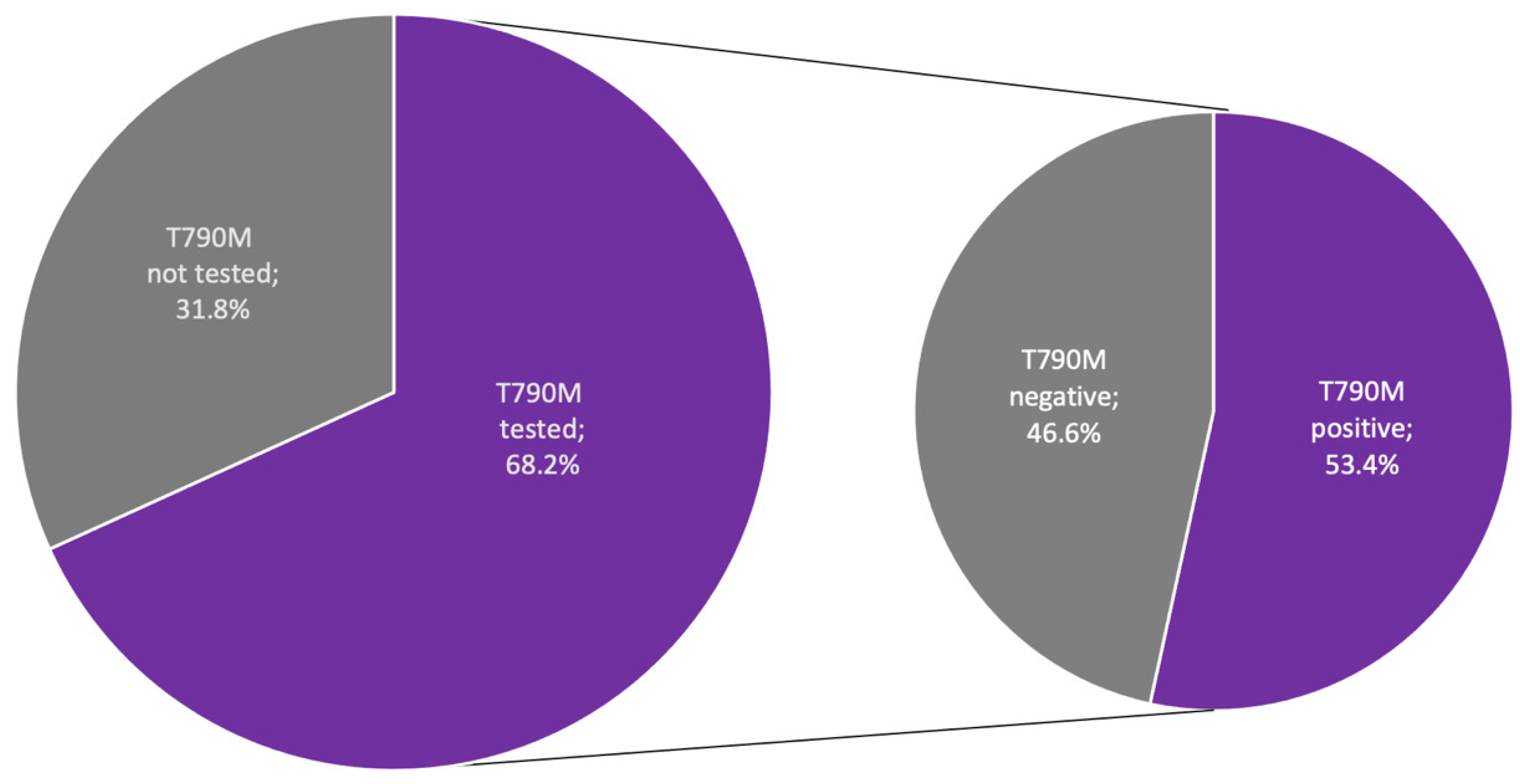
3.4. EGFR Mutation Characteristics
3.5. Brain Metastasis
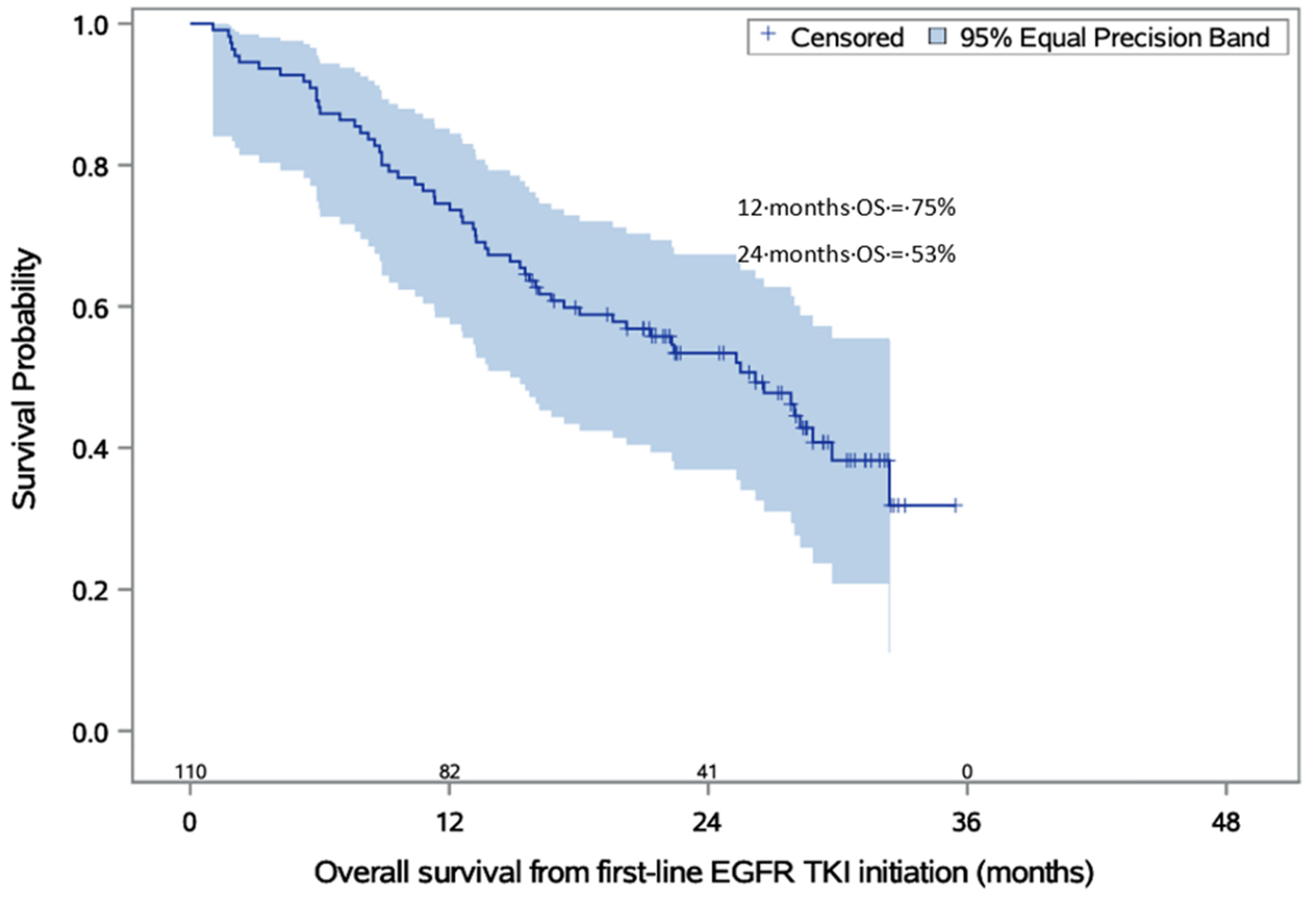
3.6. Overall Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamek, M.; Biernat, W.; Chorostowska-Wynimko, J.; Didkowska, J.A.; Dziadziuszko, K.; Grodzki, T.; Jassem, J.; Kępka, L.; Kowalski, D.; Krawczyk, P.; et al. Lung Cancer in Poland. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gridelli, C.; Rossi, A.; Carbone, D.P.; Guarize, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Mok, T.; Petrella, F.; Spaggiari, L.; Rosell, R. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2015, 1, 15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Assche, K.; Ferdinande, L.; Lievens, Y.; Vandecasteele, K.; Surmont, V. EGFR Mutation Positive Stage IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Treatment Beyond Progression. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Huang, Z.; Han, L.; Gong, Y.; Xie, C. Mechanisms and management of 3rd-generation EGFR-TKI resistance in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Boggon, T.J.; Dayaram, T.; Janne, P.A.; Kocher, O.; Meyerson, M.; Johnson, B.E.; Eck, M.J.; Tenen, D.G.; Halmos, B. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Arcila, M.E.; Sima, C.S.; Riely, G.J.; Chmielecki, J.; Kris, M.G.; Pao, W.; Ladanyi, M.; Miller, V.A. Acquired Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer: Distinct Natural History of Patients with Tumors Harboring the T790M Mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcila, M.E.; Oxnard, G.R.; Nafa, K.; Riely, G.J.; Solomon, S.B.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Pao, W.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M. Rebiopsy of Lung Cancer Patients with Acquired Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors and Enhanced Detection of the T790M Mutation Using a Locked Nucleic Acid-Based Assay. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janne, P.A.; Yang, J.C.; Kim, D.W.; Planchard, D.; Ohe, Y.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Kim, S.-W.; Su, W.-C.; Horn, L. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liam, C.K. Central nervous system activity of first-line osimertinib in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addeo, A.; Hochmair, M.; Janzic, U.; Dudnik, E.; Charpidou, A.; Płużański, A.; Ciuleanu, T.; Donev, I.S.; Elbaz, J.; Aarøe, J.; et al. Treatment patterns, testing practices, and outcomes in the pre-FLAURA era for patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced NSCLC: A retrospective chart review (REFLECT). Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 17588359211059874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadler, E.; Pavilack, M.; Espirito, J.L.; Clark, J.; Fernandes, A. Observational Study of Treatment Patterns in Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer After First-Line EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeneca, A. The EU Approves Tagrisso for 1st-Line Treatment of EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Available online: https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2018/the-eu-approves-tagrisso-for-1st-line-treatment-of-egfr-mutated-non-small-cell-lung-cancer-08062018.html# (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- JRC. ECIS—European Cancer Information System. 2020. Available online: https://ecis.jrc.ec.europa.eu (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Garg, A.; Batra, U.; Choudhary, P.; Jain, D.; Khurana, S.; Malik, P.S.; Muthu, V.; Prasad, K.; Singh, N.; Suri, T.; et al. Clinical predictors of response to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: A real-world multicentric cohort analysis from India. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2020, 44, 100570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, H.; Mori, K.; Minato, K.; Katsura, H.; Taniguchi, K.; Arunachalam, A.; Kothari, S.; Cao, X.; Kato, T. Real-world practice patterns for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Multicenter retrospective cohort study in Japan. Lung Cancer 2017, 8, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reale, M.L.; Chiari, R.; Tiseo, M.; Vitiello, F.; Barbieri, F.; Cortinovis, D.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Finocchiaro, G.; Romano, G.D.; Piovano, P.L.; et al. Be-TeaM: An Italian real-world observational study on second-line therapy for EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients. Lung Cancer 2020, 140, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Appius, A.; Pattipaka, T.; Feyereislova, A.; Cassidy, A.; Ganti, A.K. Real-world management of patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in the USA. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209709. [Google Scholar]
- Planchard, D.; Popat, S.; Kerr, K.; Novello, S.; Smit, E.F.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Mok, T.S.; Reck, M.; Van Schil, P.E.; Hellmann, M.D.; et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. S4), iv192–iv237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, N.H.; Robinson, A.G.; Temin, S.; Baker, S., Jr.; Brahmer, J.R.; Ellis, P.M.; Gaspar, L.E.; Haddad, R.Y.; Hesketh, P.J.; Jain, D.; et al. Therapy for Stage IV Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer With Driver Alterations: ASCO and OH (CCO) Joint Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1040–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Girard, N.; Nagar, S.P.; Griesinger, F.; Roeper, J.; Davis, K.L.; Karimi, P.; Sawyer, W.; Yu, N.; Taylor, A.; et al. European and US Real-World Treatment Patterns in Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Medical Record Review. Drugs Real World Outcomes 2021, 8, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magios, N.; Bozorgmehr, F.; Volckmar, A.L.; Kazdal, D.; Kirchner, M.; Herth, F.J.; Heussel, C.-P.; Eichhorn, F.; Meister, M.; Muley, T.; et al. Real-world implementation of sequential targeted therapies for EGFR-mutated lung cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 1758835921996509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yamamoto, N.; Obyrne, K.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Tsai, C.-M.; Boyer, M.; et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batson, S.; Mitchell, S.A.; Windisch, R.; Damonte, E.; Munk, V.C.; Reguart, N. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor combination therapy in first-line treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 2473–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozawa, T.; Numata, T.; Tamura, T.; Endo, T.; Kaburagi, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamada, H.; Kikuchi, N.; Saito, K.; Inagaki, M.; et al. Prognostic Implication of PD-L1 Expression on Osimertinib Treatment for EGFR-mutated Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2022, 42, 2583–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzi, M.; Ferro, A.; Cecere, F.; Scattolin, D.; Del Conte, A.; Follador, A.; Pilotto, S.; Polo, V.; Santarpia, M.; Chiari, R.; et al. First-Line Osimertinib in Patients with EGFR-Mutant Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Outcome and Safety in the Real World: FLOWER Study. Oncologist 2021, 27, 87-e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, G.; Asahina, H.; Honjo, O.; Sumi, T.; Nakamura, A.; Ito, K.; Kikuchi, H.; Hommura, F.; Honda, R.; Yokoo, K.; et al. First-line osimertinib in elderly patients with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective multicenter study (HOT2002). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, M.; Pasini, L.; Bronte, G.; Delmonte, A.; Cravero, P.; Crinò, L.; Ulivi, P. Role of liquid biopsy in oncogene-addicted non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thress, K.S.; Brant, R.; Carr, T.H.; Dearden, S.; Jenkins, S.; Brown, H.; Hammett, T.; Cantarini, M.; Barrett, J.C. EGFR mutation detection in ctDNA from NSCLC patient plasma: A cross-platform comparison of leading technologies to support the clinical development of AZD9291. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heon, S.; Yeap, B.Y.; Lindeman, N.I.; Joshi, V.A.; Butaney, M.; Britt, G.J.; Costa, D.B.; Rabin, M.S.; Jackman, D.M.; Johnson, B.E. The impact of initial gefitinib or erlotinib versus chemotherapy on central nervous system progression in advanced non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR mutations. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4406–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, S.K.; Chang, J.; Moon, J.W.; Park, I.K.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, B.C. Frequent central nervous system failure after clinical benefit with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in Korean patients with nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Cancer 2010, 116, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omuro, A.M.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Franceschi, E.; Shah, N.; Milton, D.T.; Abrey, L.E. High incidence of disease recurrence in the brain and leptomeninges in patients with nonsmall cell lung carcinoma after response to gefitinib. Cancer 2005, 103, 2344–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, G.; Tsai, C.-M.; Shepherd, F.; Ahn, M.-J.; Bazhenova, L.; Crinò, L.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Morabito, A.; Hodge, R.; et al. CNS response to osimertinib in patients with T790M-positive advanced NSCLC: Pooled data from two phase II trials. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 29, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Ahn, M.-J.; Garassino, M.C.; Han, J.-Y.; Katakami, N.; Kim, H.R.; Hodge, R.; Kaur, P.; Brown, A.P.; Ghiorghiu, D.; et al. CNS Efficacy of Osimertinib in Patients With T790M-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Data from a Randomized Phase III Trial (AURA3). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2702–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reungwetwattana, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Cho, B.C.; Cobo, M.; Cho, E.K.; Bertolini, A.; Bohnet, S.; Zhou, C.; Lee, K.H.; Nogami, N.; et al. CNS Response to Osimertinib Versus Standard Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3290–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, G.; Pocinho, R.; Travancinha, C.; Netto, E.; Roldão, M. Quality of life and radiotherapy in brain metastasis patients. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2012, 17, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kepka, L.; Tyc-Szczepaniak, D.; Osowiecka, K.; Sprawka, A.; Trąbska-Kluch, B.; Czeremszynska, B. Quality of life after whole brain radiotherapy compared with radiosurgery of the tumor bed: Results from a randomized trial. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 20, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.Y.; Na, I.I.; Kim, C.H.; Park, S.; Baek, H.; Yang, S.H. EGFR mutation and brain metastasis in pulmonary adenocarcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, J.; Bonetti, A. Cost-effectiveness of Osimertinib in activating epidermal growth factor receptor gene (EGFR)-mutations in first-line for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021, 4, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines Version 5.2022 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2022).
| Age | Years |
|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | 65.9 (11.44) |
| Gender | n (%) |
| Female | 70 (63.6) |
| Male | 40 (36.4) |
| Smoking status at initial diagnosis | n (%) |
| Current smoker | 6 (5.5) |
| Former smoker | 29 (26.4) |
| Never smoker | 49 (44.5) |
| Not known | 26 (23.6) |
| Histology at initial diagnosis | n (%) |
| Adenocarcinoma | 105 (95.5) |
| Mixed histology | 3 (2.7) |
| Other | 2 (1.8) |
| Tumor stage at initial diagnosis (Stage) | n (%) |
| Early stage (I) | 12 (10.9) |
| Limited regional (II) | 5 (4.5) |
| Locally advanced (IIIA/B) | 12 (10.9) |
| Metastatic (IV) | 81 (73.6) |
| Site of distant metastases | n (%) |
| Adrenal | 9 (8.2) |
| Bone | 34 (30.9) |
| Brain | 20 (18.2) |
| Liver | 13 (11.8) |
| Lung | 45 (40.9) |
| Pleura | 32 (29.1) |
| Other | 13 (11.8) |
| Type of First-Line EGFR-TKI Therapy | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Afatinib | 45 (40.9) |
| Erlotinib | 41 (37.3) |
| Gefitinib | 24 (21.8) |
| Discontinuation of first-line EGFR-TKI therapy | n (%) |
| Yes | 90 (81.8) |
| No | 20 (18.2) |
| Reason for discontinuation of first-line EGFR-TKI therapy | n (%) |
| Radiological progression | 62 (56.4) |
| Clinical progression | 14 (12.7) |
| Death | 8 (7.3) |
| Other reason | 6 (5.5) |
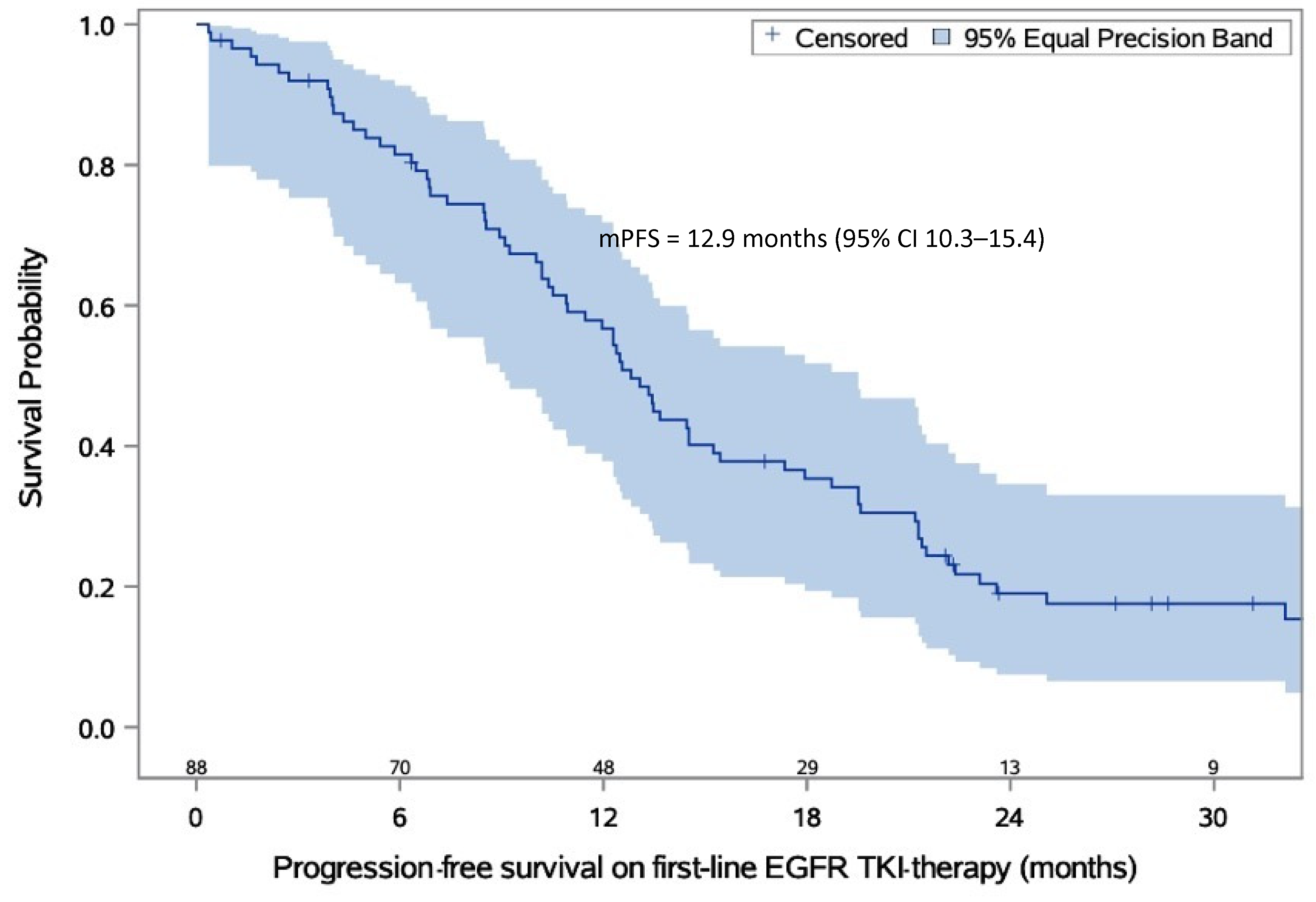
| PFS on first-line EGFR-TKI therapy | Months |
| Minimum time to event | 1.0 |
| Maximum time to event | 23.0 |
| Median (95% CI) | 12.9 (10.3–15.4) |
| Type of Second-Line EGFR-TKI Therapy | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Osimertinib | 31 (57.4) |
| Chemotherapy | 23 (42.6) |
| Cytotoxic agents | n (%) |
| Cisplatin/carboplatin + pemetrexed | 15 (27.8) |
| Carboplatin + paclitaxel | 1 (1.9) |
| Vinorelbine | 4 (7.4) |
| Gemcitabine | 1 (1.9) |
| Discontinuation of second-line therapy | n (%) |
| Yes | 39 (72.2) |
| No | 15 (27.8) |
| Reason for discontinuation of second-line therapy | n (%) |
| Radiological progression | 19 (35.2) |
| Clinical progression | 5 (9.3) |
| Death | 5 (9.3) |
| Other reason | 9 (16.7) |
| Not known | 1 (1.9) |
| Time between the start of first-line EGFR-TKI therapy and the start of second-line therapy | Months |
| Mean (SD) | 13.87 (6.47) |
| Median | 13.57 |
| Minimum, Maximum | 1.3, 26.7 |
| Time between Initial NSCLC Diagnosis and EGFR Mutation Testing | Months |
|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | 4.28 (11.75) |
| Median | 0.62 |
| Type of identified EGFR mutation | n (%) |
| Exon 19 deletion | 56 (50.9) |
| L858R mutation | 42 (38.2) |
| Other EGFR mutation | 12 (10.9) |
| Time to Death from First Diagnosis of Locally Advanced or Metastatic Disease | Months |
|---|---|
| Minimum time to event | 2.0 |
| Maximum time to event | 33.0 |
| Median (95% CI) | 27.3 (18.1–31.9) |
| Time to death from start of first-line EGFR-TKI therapy | Months |
| Minimum time to event | 1.0 |
| Maximum time to event | 32.0 |
| Median (95% CI) | 26.2 (18.0–29.7) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pluzanski, A.; Bryl, M.; Chmielewska, I.; Czyzewicz, G.; Luboch-Kowal, J.; Wrona, A.; Samborska, A.; Krzakowski, M. Treatment Patterns, Testing Practices, and Outcomes in Patients with EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Poland: A Descriptive Analysis of National, Multicenter, Real-World Data from the REFLECT Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051581
Pluzanski A, Bryl M, Chmielewska I, Czyzewicz G, Luboch-Kowal J, Wrona A, Samborska A, Krzakowski M. Treatment Patterns, Testing Practices, and Outcomes in Patients with EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Poland: A Descriptive Analysis of National, Multicenter, Real-World Data from the REFLECT Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(5):1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051581
Chicago/Turabian StylePluzanski, Adam, Maciej Bryl, Izabela Chmielewska, Grzegorz Czyzewicz, Joanna Luboch-Kowal, Anna Wrona, Agnieszka Samborska, and Maciej Krzakowski. 2023. "Treatment Patterns, Testing Practices, and Outcomes in Patients with EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Poland: A Descriptive Analysis of National, Multicenter, Real-World Data from the REFLECT Study" Cancers 15, no. 5: 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051581
APA StylePluzanski, A., Bryl, M., Chmielewska, I., Czyzewicz, G., Luboch-Kowal, J., Wrona, A., Samborska, A., & Krzakowski, M. (2023). Treatment Patterns, Testing Practices, and Outcomes in Patients with EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Poland: A Descriptive Analysis of National, Multicenter, Real-World Data from the REFLECT Study. Cancers, 15(5), 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051581






