Liquid Biopsies, Novel Approaches and Future Directions
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CTCs
2.1. Enrichment and Isolation of CTCs
| Marker | Assay Relevance | Disease | Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERBB2 | Prognostic/guiding therapy | Breast cancer | CellSearch | First-line ERBB2-targeted therapy for metastatic breast cancer appears to reduce CTC levels more than endocrine or chemotherapeutic therapy; anti-ERBB2 therapy appears to be linked with lower total CTC levels. | Retrospective analysis. The small number of patients with progressive disease highlights the implicit difficulties in analyzing the rate of CTC-positive cases. | [43] |
| PDL-1 | Guiding therapy | Breast cancer | CellSearch | CTC and platelet PD-L1 expression might be used to determine which patients should be treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors and as a pharmacodynamic biomarker during therapy. | The CellSearch platform might potentially disrupt CTC doublets and clusters, underestimating their biological/prognostic effect compared with other assays. | [44] |
| EpCAM | Prognostic | Metastatic breast cancer | CellSearch | CTC counts as independent prognostic factor. CTC testing is more repeatable than radiology and detects progression earlier. | The findings of the study do not support the use of the test as a screening tool for detecting new primary or metastatic breast cancer. | [45,46,47] |
| Nonmetastatic primary breast cancer | Laser scanning cytometry | A rise in CTC counts of more than ten-fold at the conclusion of therapy is significantly predictive of recurrence. | The relationship among CTC number and therapeutic efficacy may change amongst patients. | [48] | ||
| CellSearch | CTCs are considered an independent prognostic factor. | CTC detected only in 24% of patients studied. | [49,50] | |||
| Non-small-cell lung cancer | CellSearch | CTC reduction as an early indicator of therapeutic response. | Biomarkers’ predictive or prognostic value cannot be differentiated. | [51] | ||
| Small-cell lung cancer | CellSearch and ISET | CTC isolation using ISET is dependent on cellular size and independent of any cellular marker. | NA | [52] | ||
| Metastatic colorectal cancer | CellSearch | CTC count as independent prognostic factor. | Overall CTC yield is less than in other epithelial malignancies such as breast cancer. | [53] | ||
| Non metastatic colorectal cancer | CellSearch | CTC count as independent prognostic factor. | It is uncertain if CTCs discovered are precursors of metastatic lesions or if CTCs arise from metastases and are just a marker of overall disease burden. | [54] | ||
| Hepatocellural cancer | CellSearch and EpCAM-based immunoenrichment and FACS | The study demonstrated the feasibility of utilizing CTC-derived DNA for next-generation sequencing. | NA | [55] | ||
| Castration-resistant prostate cancer | CellSearch | At all time points, CTC numbers predicted OS better than PSA decrement methods. | NA | [56,57] | ||
| ALK | Predictive | Lung adenocarcinoma | ISET-ICC/FISH | Noninvasive real-time monitoring of targeted treatment is a possibility. | NA | [58] |
| ASGR1 | Prognostic | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Antibody-coated magnetic beads based separation | In terms of specificity and sensitivity, CTC detection exceeds AFP mRNA. | Comparison with other studies is problematic owing to the unique technique utilized. | [59] |
| PSA, PSMA, PSCA, KRT19 | Prognostic | Prostate cancer | RT-PCR | High sensitivity of RT-PCR. | False positive and false negative results are possible. | [60] |
| Pan-cytokeratin, AR-V7, CD45 | Prognostic/predictive | Metastatic castration-resistant prostate carcinoma | AdnaTest | Taxanes as chemotherapeutic drugs of choice for individuals with androgen receptor signaling blocker resistance (based on CTC AR-V7 positivity). | Due to the small sample size, multivariable analysis to connect AR-V7 status with prognosis and define subpopulations was not possible. | [61] |
| Epic AR-V7 Test | Stratification for CTH based on taxanes in mCRPC CTC AR-V7+. | NA | [62,63] | |||
| Tyrosinase | Prognostic | Malignant melanoma | RT-PCR | CTC count as independent prognostic factor. | NA | [64] |
| MART1, MAGE-A3, and PAX3 | Prognostic | Malignant melanoma | RT-PCR | CTC count as independent prognostic factor. | The presence of CTCs was not related to any of the identified clinical prognostic indicators. | [65] |
2.2. Detection of CTCs
2.3. Characterization of CTCs and Analytical Technologies
3. ctDNA
3.1. Detection of ctDNA and Current Limitations
| Cancer | Markers | Technique | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ctDNA | Breast | ERBB2, BRCA1, TP53, PIK3CA | NGS Tam-Seq | [126] [127] |
| Colorectal | BRAF, KRAS, APC, TP53, CEA, and SEPTIN9 | Sanger Sequencing, Epi proColon Assay | [126] | |
| Gastric | ERBB2, FGFR1, CDH1, PIK3CA, MET, KDR, TP53, and TFDP-1 | qPCR CellSearch | [126] [128] | |
| Gliomas | IDH1, EGFR, KRAS, MGMT | qRT-PCR, ddPCR, BEAMing | [129] | |
| Head and neck | TP53, PIK3CA, NOTCH1, FBXW7, CDKN2A, NRAS and HRAS | NGS | [130,131] | |
| Hepatocellural | TP53, CTNNB1, PTEN, CDKN2, ARID1A, MET, CDK6, EGFR, MYC, BRAF, RAF1, FGFR1, CCNE1, PIK3CA and ERBB2 | Sanger Sequencing, Mass Spectrometry, qPCR | [126] | |
| Lung | EGFR, ALK, BRAF, KRAS, ERBB2, PIK3CA, FGFR1, KRAS, ROS1, MET, RET and TP53 | NGS ddPCR | [132,133,134] | |
| Pancreatic | KRAS, BRAF | NGS ddPCR WES | [131,135,136] | |
| Prostate | TP53, RB1, PTEN, AR, FOXA1, MYC, ERG, PIK3CA, and WNT1 | CellSearch | [137] | |
| RNA | Colorectal | miR-548c-5p, miR-21, CRNDE-h, lncRNA GAS5, miR-19, miR-221, lncRNA 91H, miR-23a, miR-1224-5p, miR-6803, Let-7a, miR-1229 | qRT-PCR | [138,139,140,141] |
| Gastric | lncUEGC1, lncUEGC2, HOTTIP, ZFAS1, miR-423-5p, miR-451, miR23b | qRT-PCR | [142,143,144,145] | |
| Pancreatic | MiR-125b-5p, miR-21, circPDE8A, miR-451a, miR-191, miR-17-5p | qRT-PCR | [146,147,148] | |
| Liver | hnRNPH1, LINC00161, LINC00635, TERT, miR-638, miR-125b, miR-93 | qRT-PCR | [149,150,151] | |
| Laryngeal | HOTAIR | qRT-PCR | [152] | |
| Prostate | MiR-1290, miR-375, miR-125, miR-19b, SAP30L-AS1, SChLAP1, LincRNA-p21 | qRT-PCR | [153,154] | |
| Ovarian | miR-200a, miR-200b, miR-200c, miR-21, miR-100, miR-326 | PCR, qRT-PCR | [155] | |
| Lung | miR-451a, miR-23b-3p, miR-21-5p, miR-10b-5p, MALAT-1 | qRT-PCR | [156,157] | |
| Multiple Myeloma | let-7b, let-7e, miR-106a, miR-106b, miR-155, miR-16, miR-17, miR-18a, miR-20a | qRT-PCR | [158] | |
| Glioma | miR-301a | qRT-PCR | [159] | |
| Glioblastoma | RNU6 | qRT-PCR | [160] | |
| EVs proteins | Colorectal | CPNE3, GPC1 | ELISA | [161,162] |
| Pancreatic | GPC1 | Flow cytometry | [163] | |
| Lung | CD171, 14-3-3ζ, Flotilin 1, HER3, GRP78 | ELISA | [164,165] | |
| Ovarian | ephrin A2 | ELISA | [166] | |
| Prostate | ADIRF, TMEM256 | Mass spectrometry | [167] | |
| Melanoma | exo-MIA, exo-5100B | ELISA | [168] | |
| Bladder | TACSTD2 | ELISA | [169] | |
| Breast | ERBB2, BCRP, Fibronectin, Periostin, Del-1 | Flow cytometry ELISA | [170,171,172] |
3.2. Clinical Applications
3.3. ctDNA in Other Biofluids
4. ctRNA
Clinical Applications and Limitations
5. Extracellular Vesicles (EVs)
5.1. Isolation of EVs
5.2. Clinical Applications
6. Proteomics
6.1. Mass Spectrometry
6.2. Antibody/Antigen Arrays
6.3. Aptamer-Based Assays
6.4. Proximity Extension Assay (PEA)
6.5. Reverse Phase Protein Arrays (RPPA)
7. Metabolomics
8. Future Directions
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martins, I.; Ribeiro, I.P.; Jorge, J.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Sarmento-Ribeiro, A.B.; Melo, J.B.; Carreira, I.M. Liquid Biopsies: Applications for Cancer Diagnosis and Monitoring. Genes 2021, 12, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rubis, G.; Rajeev Krishnan, S.; Bebawy, M. Liquid Biopsies in Cancer Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Prognosis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Hurley, J.; Roberts, D.; Chakrabortty, S.K.; Enderle, D.; Noerholm, M.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J.K. Exosome-Based Liquid Biopsies in Cancer: Opportunities and Challenges. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Li, P.; Gong, J.; Tan, H.; Ma, J. Urinary Cell-Free DNA as a Prognostic Marker for KRAS-Positive Advanced-Stage NSCLC. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 20, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Liquid Biopsy: From Discovery to Clinical Application. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 858–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In ‘t Veld, S.G.J.G.; Wurdinger, T. Tumor-Educated Platelets. Blood 2019, 133, 2359–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A.; Lim, A.R.; Ghajar, C.M. Circulating and Disseminated Tumor Cells: Harbingers or Initiators of Metastasis? Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix-Panabières, C. EPISPOT Assay: Detection of Viable DTCs/CTCs in Solid Tumor Patients. In Minimal Residual Disease and Circulating Tumor Cells in Breast Cancer; Recent Results in Cancer, Research; Ignatiadis, M., Sotiriou, C., Pantel, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 69–76. ISBN 978-3-642-28160-0. [Google Scholar]
- Maisano, D.; Mimmi, S.; Dattilo, V.; Marino, F.; Gentile, M.; Vecchio, E.; Fiume, G.; Nisticò, N.; Aloisio, A.; de Santo, M.P.; et al. A novel phage display based platform for exosome diversity characterization. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 2998–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozar, T.; Gersak, K.; Cemazar, M.; Kuhar, C.G.; Jesenko, T. The Biology and Clinical Potential of Circulating Tumor Cells. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D.; Tamma, R.; Annese, T. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer: A Historical Overview. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Gomez, S.J.; Maziveyi, M.; Alahari, S.K. Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through Epigenetic and Post-Translational Modifications. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, J.M.; Wagner, M.S.; Sousa-Squiavinato, A.C.; de Freitas-Junior, J.C.; de Araújo, W.M.; Tessmann, J.W.; Rocha, M.R. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Exon. Publ. 2022, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.-L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Tesic Mark, M.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour Exosome Integrins Determine Organotropic Metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canel, M.; Serrels, A.; Frame, M.C.; Brunton, V.G. E-Cadherin-Integrin Crosstalk in Cancer Invasion and Metastasis. J. Cell. Sci. 2013, 126, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Capua, D.; Bracken-Clarke, D.; Ronan, K.; Baird, A.-M.; Finn, S. The Liquid Biopsy for Lung Cancer: State of the Art, Limitations and Future Developments. Cancers 2021, 13, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantel, K.; Alix-Panabières, C. Liquid Biopsy and Minimal Residual Disease—Latest Advances and Implications for Cure. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, A.; Tzanikou, E.; Lianidou, E. The Potential of Liquid Biopsy in the Management of Cancer Patients. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 84, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Zhuang, R.; Long, M.; Pavlovic, M.; Kang, Y.; Ilyas, A.; Asghar, W. Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation, Culture, and Downstream Molecular Analysis. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Pohlmann, P.R.; Isaacs, C.; Weinberg, B.A.; He, A.R.; Schlegel, R.; Agarwal, S. Circulating Tumor Cells: Technologies and Their Clinical Potential in Cancer Metastasis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ji, F.; Wang, L. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells: Opportunities and Challenges. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalik, A.; Kowalewska, M.; Góźdź, S. Current Approaches for Avoiding the Limitations of Circulating Tumor Cells Detection Methods—Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Solid Tumors. Transl. Res. 2017, 185, 58–84.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SMART. Available online: https://smart.servier.com/ (accessed on 18 January 2023).
- Deng, Z.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Shi, D. Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. eBioMedicine 2022, 83, 104237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gires, O.; Pan, M.; Schinke, H.; Canis, M.; Baeuerle, P.A. Expression and Function of Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule EpCAM: Where Are We after 40 Years? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 969–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Mader, S.; Pantel, K. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Circulating Tumor Cells. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami-S, Z.; Cortés-Hernández, L.E.; Alix-Panabières, C. Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule: An Anchor to Isolate Clinically Relevant Circulating Tumor Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riethdorf, S.; O’Flaherty, L.; Hille, C.; Pantel, K. Clinical Applications of the CellSearch Platform in Cancer Patients. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 125, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnaga, T.; Takei, Y.; Nagata, T.; Shimada, Y. Highly Efficient Capture of Cancer Cells Expressing EGFR by Microfluidic Methods Based on Antigen-Antibody Association. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thege, F.I.; Lannin, T.B.; Saha, T.N.; Tsai, S.; Kochman, M.L.; Hollingsworth, M.A.; Rhim, A.D.; Kirby, B.J. Microfluidic Immunocapture of Circulating Pancreatic Cells Using Parallel EpCAM and MUC1 Capture: Characterization, Optimization and Downstream Analysis. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Heliebi, A.; Hille, C.; Laxman, N.; Svedlund, J.; Haudum, C.; Ercan, E.; Kroneis, T.; Chen, S.; Smolle, M.; Rossmann, C.; et al. In Situ Detection and Quantification of AR-V7, AR-FL, PSA, and KRAS Point Mutations in Circulating Tumor Cells. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, K.-A.; Lee, T.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, H.-I. Two-Stage Microfluidic Chip for Selective Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-L.; Tang, M.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Qi, C.-B.; Hu, J.; Ma, X.-Y.; Pang, D.-W. Chip-Assisted Single-Cell Biomarker Profiling of Heterogeneous Circulating Tumor Cells Using Multifunctional Nanospheres. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 10518–10526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, C.; Larios, J.M.; Muñiz, M.C.; Aung, K.; Cannell, E.M.; Darga, E.P.; Kidwell, K.M.; Thomas, D.G.; Tokudome, N.; Brown, M.E.; et al. Heterogeneous Estrogen Receptor Expression in Circulating Tumor Cells Suggests Diverse Mechanisms of Fulvestrant Resistance. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapanotti, M.C.; Campione, E.; Suarez Viguria, T.M.; Spallone, G.; Costanza, G.; Rossi, P.; Orlandi, A.; Valenti, P.; Bernardini, S.; Bianchi, L. Stem–Mesenchymal Signature Cell Genes Detected in Heterogeneous Circulating Melanoma Cells Correlate With Disease Stage in Melanoma Patients. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, J.C.-H.; Wu, T.M.-H.; Hsieh, J.C.-H.; Wu, T.M.-H. The Selection Strategy for Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) Isolation and Enumeration: Technical Features, Methods, and Clinical Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-953-51-2631-7. [Google Scholar]
- Habli, Z.; AlChamaa, W.; Saab, R.; Kadara, H.; Khraiche, M.L. Circulating Tumor Cell Detection Technologies and Clinical Utility: Challenges and Opportunities. Cancers 2020, 12, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Toom, E.E.; Verdone, J.E.; Gorin, M.A.; Pienta, K.J. Technical Challenges in the Isolation and Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 62754–62766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.-Y.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Wu, M.-H. The Combination of Immunomagnetic Bead-Based Cell Isolation and Optically Induced Dielectrophoresis (ODEP)-Based Microfluidic Device for the Negative Selection-Based Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs). Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Pei, R. High-Purity Capture of CTCs Based on Micro-Beads Enhanced Isolation by Size of Epithelial Tumor Cells (ISET) Method. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarioglu, A.F.; Aceto, N.; Kojic, N.; Donaldson, M.C.; Zeinali, M.; Hamza, B.; Engstrom, A.; Zhu, H.; Sundaresan, T.K.; Miyamoto, D.T.; et al. A Microfluidic Device for Label-Free, Physical Capture of Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkountela, S.; Castro-Giner, F.; Szczerba, B.M.; Vetter, M.; Landin, J.; Scherrer, R.; Krol, I.; Scheidmann, M.C.; Beisel, C.; Stirnimann, C.U.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Clustering Shapes DNA Methylation to Enable Metastasis Seeding. Cell 2019, 176, 98–112.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, T.M.; Riethdorf, S.; Fremd, C.; Feisst, M.; Nees, J.; Fischer, C.; Hartkopf, A.D.; Pantel, K.; Trumpp, A.; Schütz, F.; et al. HER2-Targeted Therapy Influences CTC Status in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 182, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, C.; Miao, J.; Dolce, E.M.; Darga, E.P.; Repollet, M.I.; Doyle, G.V.; Gralow, J.R.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Smerage, J.B.; Barlow, W.E.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer: A SWOG S0500 Translational Medicine Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6089–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Reuben, J.M.; Doyle, G.V.; Allard, W.J.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells, Disease Progression, and Survival in Metastatic Breast Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidard, F.-C.; Peeters, D.J.; Fehm, T.; Nolé, F.; Gisbert-Criado, R.; Mavroudis, D.; Grisanti, S.; Generali, D.; Garcia-Saenz, J.A.; Stebbing, J.; et al. Clinical Validity of Circulating Tumour Cells in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of Individual Patient Data. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, G.T.; Cristofanilli, M.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Borden, E.; Miller, M.C.; Matera, J.; Repollet, M.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells versus Imaging—Predicting Overall Survival in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6403–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachmann, K.; Camara, O.; Kavallaris, A.; Krauspe, S.; Malarski, N.; Gajda, M.; Kroll, T.; Jörke, C.; Hammer, U.; Altendorf-Hofmann, A.; et al. Monitoring the Response of Circulating Epithelial Tumor Cells to Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Allows Detection of Patients at Risk of Early Relapse. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucci, A.; Hall, C.S.; Lodhi, A.K.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Anderson, A.E.; Xiao, L.; Bedrosian, I.; Kuerer, H.M.; Krishnamurthy, S. Circulating Tumour Cells in Non-Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Prospective Study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smerage, J.B.; Barlow, W.E.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Winer, E.P.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Srkalovic, G.; Tejwani, S.; Schott, A.F.; O’Rourke, M.A.; Lew, D.L.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells and Response to Chemotherapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer: SWOG S0500. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3483–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punnoose, E.A.; Atwal, S.; Liu, W.; Raja, R.; Fine, B.M.; Hughes, B.G.M.; Hicks, R.J.; Hampton, G.M.; Amler, L.C.; Pirzkall, A.; et al. Evaluation of Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Tumor DNA in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Association with Clinical Endpoints in a Phase II Clinical Trial of Pertuzumab and Erlotinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.-M.; Krebs, M.G.; Lancashire, L.; Sloane, R.; Backen, A.; Swain, R.K.; Priest, L.J.C.; Greystoke, A.; Zhou, C.; Morris, K.; et al. Clinical Significance and Molecular Characteristics of Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Tumor Microemboli in Patients With Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Punt, C.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.; Sabbath, K.; Gabrail, N.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Cohen SJ, Punt CJA, Iannotti N, Saidman BH, Sabbath KD, Gabrail NY, Picus J, Morse M, Mitchell E, Miller MC, Doyle GV, Tissing H, Terstappen LWMM, Meropol NJRelationship of Circulating Tumor Cells to Tumor Response, Progression-Free Survival, and Overall Survival in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bork, U.; Rahbari, N.N.; Schölch, S.; Reissfelder, C.; Kahlert, C.; Büchler, M.W.; Weitz, J.; Koch, M. Circulating Tumour Cells and Outcome in Non-Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Prospective Study. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, R.K.; Magbanua, M.J.M.; Butler, T.M.; Collisson, E.A.; Hwang, J.; Sidiropoulos, N.; Evason, K.; McWhirter, R.M.; Hameed, B.; Wayne, E.M.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Pilot Study of Detection, Enumeration, and next-Generation Sequencing in Cases and Controls. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okegawa, T.; Itaya, N.; Hara, H.; Tambo, M.; Nutahara, K. Circulating Tumor Cells as a Biomarker Predictive of Sensitivity to Docetaxel Chemotherapy in Patients with Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 6705–6710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Bono, J.S.; Scher, H.I.; Montgomery, R.B.; Parker, C.; Miller, M.C.; Tissing, H.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.W.M.; Pienta, K.J.; Raghavan, D. Circulating Tumor Cells Predict Survival Benefit from Treatment in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6302–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, M.; Long, E.; Butori, C.; Hofman, V.; Coelle, C.; Mauro, V.; Zahaf, K.; Marquette, C.H.; Mouroux, J.; Paterlini-Bréchot, P.; et al. ALK-Gene Rearrangement: A Comparative Analysis on Circulating Tumour Cells and Tumour Tissue from Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2907–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Cao, L.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.-F.; Qian, H.-H.; Kang, X.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, J.; Shi, L.-H.; et al. Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using a Novel Cell Separation Strategy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3783–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteleakou, Z.; Lembessis, P.; Sourla, A.; Pissimissis, N.; Polyzos, A.; Deliveliotis, C.; Koutsilieris, M. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells in Prostate Cancer Patients: Methodological Pitfalls and Clinical Relevance. Mol. Med. 2009, 15, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Lu, C.; Luber, B.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Nakazawa, M.; Nadal, R.; Paller, C.J.; Denmeade, S.R.; Carducci, M.A.; et al. Androgen Receptor Splice Variant 7 and Efficacy of Taxane Chemotherapy in Patients With Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, H.I.; Lu, D.; Schreiber, N.A.; Louw, J.; Graf, R.P.; Vargas, H.A.; Johnson, A.; Jendrisak, A.; Bambury, R.; Danila, D.; et al. Association of AR-V7 on Circulating Tumor Cells as a Treatment-Specific Biomarker With Outcomes and Survival in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, H.I.; Graf, R.P.; Schreiber, N.A.; McLaughlin, B.; Jendrisak, A.; Wang, Y.; Lee, J.; Greene, S.; Krupa, R.; Lu, D.; et al. Phenotypic Heterogeneity of Circulating Tumor Cells Informs Clinical Decisions between AR Signaling Inhibitors and Taxanes in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5687–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proebstle, T.M.; Jiang, W.; Högel, J.; Keilholz, U.; Weber, L.; Voit, C. Correlation of Positive RT-PCR for Tyrosinase in Peripheral Blood of Malignant Melanoma Patients with Clinical Stage, Survival and Other Risk Factors. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshimoto, S.; Faries, M.B.; Morton, D.L.; Shingai, T.; Kuo, C.; Wang, H.; Elashoff, R.; Mozzillo, N.; Kelley, M.C.; Thompson, J.F.; et al. Assessment of Prognostic Circulating Tumor Cells in a Phase III Trial of Adjuvant Immunotherapy After Complete Resection of Stage IV Melanoma. Ann. Surg. 2012, 255, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Challenges in Circulating Tumour Cell Research. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swennenhuis, J.F.; van Dalum, G.; Zeune, L.L.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Improving the CellSearch® System. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn 2016, 16, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, M.T.; Calleja, L.R.; Chalopin, A.; Ory, B.; Heymann, D. Circulating Tumor Cells: A Review of Non-EpCAM-Based Approaches for Cell Enrichment and Isolation. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Balasubramanian, P.; Chen, A.P.; Kummar, S.; Evrard, Y.A.; Kinders, R.J. Promise and Limits of the CellSearch Platform for Evaluating Pharmacodynamics in Circulating Tumor Cells. Semin. Oncol. 2016, 43, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, F.; Rotunno, G.; Salvianti, F.; Galardi, F.; Pestrin, M.; Gabellini, S.; Simi, L.; Mancini, I.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Pazzagli, M.; et al. Mutational Analysis of Single Circulating Tumor Cells by next Generation Sequencing in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 26107–26119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethig, R. Review Article-Dielectrophoresis: Status of the Theory, Technology, and Applications. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 022811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshareef, M.; Metrakos, N.; Juarez Perez, E.; Azer, F.; Yang, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, G. Separation of Tumor Cells with Dielectrophoresis-Based Microfluidic Chip. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 011803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, N.; Dulmage, K.; Pletcher, C.H.; Wang, L.; DeMuth, W.; Sen, M.; Balli, D.; Yee, S.S.; Sa, S.; Tong, F.; et al. An Integrated Flow Cytometry-Based Platform for Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Circulating Tumor Single Cells and Clusters. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magbanua, M.J.M.; Park, J.W. Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells by Immunomagnetic Enrichment and Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (IE/FACS) for Molecular Profiling. Methods 2013, 64, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eifler, R.L.; Lind, J.; Falkenhagen, D.; Weber, V.; Fischer, M.B.; Zeillinger, R. Enrichment of Circulating Tumor Cells from a Large Blood Volume Using Leukapheresis and Elutriation: Proof of Concept. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2011, 80, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-K.; Kim, G.-S.; Wu, Y.; Kim, D.-J.; Lu, Y.; Kwak, M.; Han, L.; Hyung, J.-H.; Seol, J.-K.; Sander, C.; et al. Nanowire Substrate-Based Laser Scanning Cytometry for Quantitation of Circulating Tumor Cells. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2697–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastoraki, S.; Strati, A.; Tzanikou, E.; Chimonidou, M.; Politaki, E.; Voutsina, A.; Psyrri, A.; Georgoulias, V.; Lianidou, E. ESR1 Methylation: A Liquid Biopsy-Based Epigenetic Assay for the Follow-up of Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer Receiving Endocrine Treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Siddiqi, S.; Ahmed, S.; Hands, R.; Dorudi, S. Quantification of Cytokeratin 20, Carcinoembryonic Antigen and Guanylyl Cyclase C MRNA Levels in Lymph Nodes May Not Predict Treatment Failure in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 108, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHANG, B.; XU, C.-W.; SHAO, Y.; WANG, H.-T.; WU, Y.-F.; SONG, Y.-Y.; LI, X.-B.; ZHANG, Z.; WANG, W.-J.; LI, L.-Q.; et al. Comparison of Droplet Digital PCR and Conventional Quantitative PCR for Measuring EGFR Gene Mutation. Exp. Med. 2015, 9, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siravegna, G.; Bardelli, A. Minimal Residual Disease in Breast Cancer: In Blood Veritas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2505–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindson, B.J.; Ness, K.D.; Masquelier, D.A.; Belgrader, P.; Heredia, N.J.; Makarewicz, A.J.; Bright, I.J.; Lucero, M.Y.; Hiddessen, A.L.; Legler, T.C.; et al. High-Throughput Droplet Digital PCR System for Absolute Quantitation of DNA Copy Number. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8604–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, A.; Cayrefourcq, L.; Mazel, M.; Alix-Panabières, C. EpCAM-Independent Enrichment and Detection of Viable Circulating Tumor Cells Using the EPISPOT Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1634, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyer, K.; Doineau, R.C.L.; Castrillon, C.E.; Briseño-Roa, L.; Menrath, V.; Mottet, G.; England, P.; Godina, A.; Brient-Litzler, E.; Nizak, C.; et al. Single-Cell Deep Phenotyping of IgG-Secreting Cells for High-Resolution Immune Monitoring. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millner, L.M.; Linder, M.W.; Valdes, R. Circulating Tumor Cells: A Review of Present Methods and the Need to Identify Heterogeneous Phenotypes. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci 2013, 43, 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez, J.-M.; Fehm, T.; Orsini, M.; Cayrefourcq, L.; Maudelonde, T.; Pantel, K.; Alix-Panabières, C. Prognostic Relevance of Viable Circulating Tumor Cells Detected by EPISPOT in Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients. Clin. Chem. 2014, 60, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Inman, A.O.; Zhang, L.W. Limitations and Relative Utility of Screening Assays to Assess Engineered Nanoparticle Toxicity in a Human Cell Line. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2009, 234, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catelain, C.; Pailler, E.; Oulhen, M.; Faugeroux, V.; Pommier, A.-L.; Farace, F. Detection of Gene Rearrangements in Circulating Tumor Cells: Examples of ALK-, ROS1-, RET-Rearrangements in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and ERG-Rearrangements in Prostate Cancer. In Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Circulating Tumor Cells; Advances in Experimental Medicine and, Biology; Magbanua, M.J.M., Park, J.W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 169–179. ISBN 978-3-319-55947-6. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, L.; Rothwell, D.G.; Mesquita, B.; Smowton, C.; Leong, H.S.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, F.; Li, Y.; Burt, D.J.; Antonello, J.; Morrow, C.J.; et al. Molecular Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells Identifies Distinct Copy-Number Profiles in Patients with Chemosensitive and Chemorefractory Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohr, J.G.; Adalsteinsson, V.A.; Cibulskis, K.; Choudhury, A.D.; Rosenberg, M.; Cruz-Gordillo, P.; Francis, J.M.; Zhang, C.-Z.; Shalek, A.K.; Satija, R.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing of Circulating Tumor Cells Provides a Window into Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babayan, A.; Alawi, M.; Gormley, M.; Müller, V.; Wikman, H.; McMullin, R.P.; Smirnov, D.A.; Li, W.; Geffken, M.; Pantel, K.; et al. Comparative Study of Whole Genome Amplification and next Generation Sequencing Performance of Single Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56066–56080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, W.; Fan, A.; Tran, T.; Danila, D.C.; Keys, D.; Schwartz, M.; Ionescu-Zanetti, C. Mutational Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells Using a Novel Microfluidic Collection Device and QPCR Assay. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 6, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, D.T.; Wittner, B.S.; Ligorio, M.; Jordan, N.V.; Shah, A.M.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Aceto, N.; Bersani, F.; Brannigan, B.W.; Xega, K.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Identifies Extracellular Matrix Gene Expression by Pancreatic Circulating Tumor Cells. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1905–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorges, T.M.; Kuske, A.; Röck, K.; Mauermann, O.; Müller, V.; Peine, S.; Verpoort, K.; Novosadova, V.; Kubista, M.; Riethdorf, S.; et al. Accession of Tumor Heterogeneity by Multiplex Transcriptome Profiling of Single Circulating Tumor Cells. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, N.V.; Bardia, A.; Wittner, B.S.; Benes, C.; Ligorio, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, M.; Sundaresan, T.K.; Licausi, J.A.; Desai, R.; et al. HER2 Expression Identifies Dynamic Functional States within Circulating Breast Cancer Cells. Nature 2016, 537, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.C.M.; Massie, C.; Garcia-Corbacho, J.; Mouliere, F.; Brenton, J.D.; Caldas, C.; Pacey, S.; Baird, R.; Rosenfeld, N. Liquid Biopsies Come of Age: Towards Implementation of Circulating Tumour DNA. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plagnol, V.; Woodhouse, S.; Howarth, K.; Lensing, S.; Smith, M.; Epstein, M.; Madi, M.; Smalley, S.; Leroy, C.; Hinton, J.; et al. Analytical Validation of a next Generation Sequencing Liquid Biopsy Assay for High Sensitivity Broad Molecular Profiling. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobek, V.; Gurlich, R.; Eliasova, P.; Kolostova, K. Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Cancer Patients: Enrichment and Cultivation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 17163–17170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinen, L.T.D.; Mello, C.A.L.; Abdallah, E.A.; Ocea, L.M.; Buim, M.E.; Breve, N.M.; Gasparini, J.L.; Fanelli, M.F.; Paterlini-Bréchot, P. Isolation, Detection, and Immunomorphological Characterization of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) from Patients with Different Types of Sarcoma Using Isolation by Size of Tumor Cells: A Window on Sarcoma-Cell Invasion. Onco Targets Ther. 2014, 7, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nature Communications. Profiling Protein Expression in Circulating Tumour Cells Using Microfluidic Western Blotting. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms14622 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Baselga, J. Targeting the Phosphoinositide-3 (PI3) Kinase Pathway in Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2011, 16 (Suppl. 1), 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Cayrefourcq, L.; Mazard, T.; Maudelonde, T.; Assenat, E.; Assou, S. Molecular Portrait of Metastasis-Competent Circulating Tumor Cells in Colon Cancer Reveals the Crucial Role of Genes Regulating Energy Metabolism and DNA Repair. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, A.; Cayrefourcq, L.; Mazard, T.; Babayan, A.; Lamy, P.-J.; Assou, S.; Assenat, E.; Pantel, K.; Alix-Panabières, C. Autologous Cell Lines from Circulating Colon Cancer Cells Captured from Sequential Liquid Biopsies as Model to Study Therapy-Driven Tumor Changes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccelli, I.; Schneeweiss, A.; Riethdorf, S.; Stenzinger, A.; Schillert, A.; Vogel, V.; Klein, C.; Saini, M.; Bäuerle, T.; Wallwiener, M.; et al. Identification of a Population of Blood Circulating Tumor Cells from Breast Cancer Patients That Initiates Metastasis in a Xenograft Assay. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson, C.L.; Morrow, C.J.; Li, Y.; Metcalf, R.L.; Rothwell, D.G.; Trapani, F.; Polanski, R.; Burt, D.J.; Simpson, K.L.; Morris, K.; et al. Tumorigenicity and Genetic Profiling of Circulating Tumor Cells in Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, D.; Lawson, A.R.J.; Howarth, K.; Madi, M.; Durham, B.; Smalley, S.; Calaway, J.; Blais, S.; Jones, G.; Clark, J.; et al. Development of a Highly Sensitive Liquid Biopsy Platform to Detect Clinically-Relevant Cancer Mutations at Low Allele Fractions in Cell-Free DNA. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvianti, F.; Giuliani, C.; Petrone, L.; Mancini, I.; Vezzosi, V.; Pupilli, C.; Pinzani, P. Integrity and Quantity of Total Cell-Free DNA in the Diagnosis of Thyroid Cancer: Correlation with Cytological Classification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Brown, H.; Tabak, J.; Fang, Z.; Tertre, M.C.D.; McNamara, S.; Gambaro, K.; Batist, G.; Buell, J.F. Multiplexed Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Cell-Free DNA Assay as a Potential Method to Monitor Stage IV Colorectal Cancer. Surgery 2019, 166, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Mao, F.; Shi, L.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, M. Urinary Measurement of Circulating Tumor DNA for Treatment Monitoring and Prognosis of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 57, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, J.; Cui, L.; Liu, Y. Urinary Circulating DNA Detection for Dynamic Tracking of EGFR Mutations for NSCLC Patients Treated with EGFR-TKIs. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 19, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Han, L.; Yuan, J.; Sun, Y. Circulating Tumor Cell Free DNA from Plasma and Urine in the Clinical Management of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Biomark 2020, 27, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, S.A.; Shanmugam, A.; Chougule, A.; Sridharan, S.; Prabhash, K.; Arya, A.; Chaubey, A.; Hariharan, A.; Kolekar, P.; Sen, M.; et al. Analysis of Solid Tumor Mutation Profiles in Liquid Biopsy. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 5439–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, S.; Zhan, T.; Betge, J.; Rauscher, B.; Belle, S.; Gutting, T.; Schulte, N.; Jesenofsky, R.; Härtel, N.; Gaiser, T.; et al. Detection of Mutational Patterns in Cell-Free DNA of Colorectal Cancer by Custom Amplicon Sequencing. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 1669–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisetsky, D.S.; Fairhurst, A.-M. The Origin of Extracellular DNA during the Clearance of Dead and Dying Cells. Autoimmunity 2007, 40, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braig, D.; Becherer, C.; Bickert, C.; Braig, M.; Claus, R.; Eisenhardt, A.E.; Heinz, J.; Scholber, J.; Herget, G.W.; Bronsert, P.; et al. Genotyping of Circulating Cell-Free DNA Enables Noninvasive Tumor Detection in Myxoid Liposarcomas. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitzer, E.; Haque, I.S.; Roberts, C.E.S.; Speicher, M.R. Current and Future Perspectives of Liquid Biopsies in Genomics-Driven Oncology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwapisz, D. The First Liquid Biopsy Test Approved. Is It a New Era of Mutation Testing for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer? Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, F.; Schmidt, K.; Choti, M.A.; Romans, K.; Goodman, S.; Li, M.; Thornton, K.; Agrawal, N.; Sokoll, L.; Szabo, S.A.; et al. Circulating Mutant DNA to Assess Tumor Dynamics. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbreteau, G.; Vallée, A.; Knol, A.-C.; Théoleyre, S.; Quéreux, G.; Varey, E.; Khammari, A.; Dréno, B.; Denis, M.G. Quantitative Monitoring of Circulating Tumor DNA Predicts Response of Cutaneous Metastatic Melanoma to Anti-PD1 Immunotherapy. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 25265–25276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Muto, Y.; Ichida, K.; Fukui, T.; Kakizawa, N.; Ishikawa, H.; Watanabe, F.; Hasegawa, F.; Saito, M.; et al. Monitoring Circulating Tumor DNA Revealed Dynamic Changes in KRAS Status in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 24398–24413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Foncillas, J.; Alba, E.; Aranda, E.; Díaz-Rubio, E.; López-López, R.; Tabernero, J.; Vivancos, A. Incorporating BEAMing Technology as a Liquid Biopsy into Clinical Practice for the Management of Colorectal Cancer Patients: An Expert Taskforce Review. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2943–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.M.; Bratman, S.V.; To, J.; Wynne, J.F.; Eclov, N.C.W.; Modlin, L.A.; Liu, C.L.; Neal, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A.; Merritt, R.E.; et al. An Ultrasensitive Method for Quantitating Circulating Tumor DNA with Broad Patient Coverage. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitzer, E.; Perakis, S.; Geigl, J.B.; Speicher, M.R. The Potential of Liquid Biopsies for the Early Detection of Cancer. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.D.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Thoburn, C.; Afsari, B.; Danilova, L.; Douville, C.; Javed, A.A.; Wong, F.; Mattox, A.; et al. Detection and Localization of Surgically Resectable Cancers with a Multi-Analyte Blood Test. Science 2018, 359, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, S.; Lemmens, L.; Koessler, T.; Blouin, J.-L.; Nouspikel, T. Circulating Tumoral DNA: Preanalytical Validation and Quality Control in a Diagnostic Laboratory. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 542, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-J.; Park, J.; Sunkara, V.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, K.; Kim, M.-H.; Cho, Y.-K. Fully Automated, on-Site Isolation of CfDNA from Whole Blood for Cancer Therapy Monitoring. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathai, R.A.; Vidya, R.V.S.; Reddy, B.S.; Thomas, L.; Udupa, K.; Kolesar, J.; Rao, M. Potential Utility of Liquid Biopsy as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Tool for the Assessment of Solid Tumors: Implications in the Precision Oncology. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nik-Zainal, S.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Wedge, D.C.; Van Loo, P.; Greenman, C.D.; Raine, K.; Jones, D.; Hinton, J.; Marshall, J.; Stebbings, L.A.; et al. Mutational Processes Molding the Genomes of 21 Breast Cancers. Cell 2012, 149, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, T.; Yashiro, M. Precision Medicine for Gastrointestinal Cancer: Recent Progress and Future Perspective. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachariah, M.A.; Oliveira-Costa, J.P.; Carter, B.S.; Stott, S.L.; Nahed, B.V. Blood-Based Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Gliomas. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Springer, S.; Mulvey, C.L.; Silliman, N.; Schaefer, J.; Sausen, M.; James, N.; Rettig, E.M.; Guo, T.; Pickering, C.R.; et al. Detection of Somatic Mutations and HPV in the Saliva and Plasma of Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 293ra104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.-H.; Xu, H.-X.; Zhang, S.-R.; Xu, J.-Z.; Li, S.; Gao, H.-L.; Jin, W.; Wang, W.-Q.; Wu, C.-T.; Ni, Q.-X.; et al. The Significance of Liquid Biopsy in Pancreatic Cancer. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3417–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Re, M.; Biasco, E.; Crucitta, S.; Derosa, L.; Rofi, E.; Orlandini, C.; Miccoli, M.; Galli, L.; Falcone, A.; Jenster, G.W.; et al. The Detection of Androgen Receptor Splice Variant 7 in Plasma-Derived Exosomal RNA Strongly Predicts Resistance to Hormonal Therapy in Metastatic Prostate Cancer Patients. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couraud, S.; Vaca-Paniagua, F.; Villar, S.; Oliver, J.; Schuster, T.; Blanché, H.; Girard, N.; Trédaniel, J.; Guilleminault, L.; Gervais, R.; et al. Noninvasive Diagnosis of Actionable Mutations by Deep Sequencing of Circulating Free DNA in Lung Cancer from Never-Smokers: A Proof-of-Concept Study from BioCAST/IFCT-1002. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4613–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighl, N.B.; Page, R.D.; Raymond, V.M.; Daniel, D.B.; Divers, S.G.; Reckamp, K.L.; Villalona-Calero, M.A.; Dix, D.; Odegaard, J.I.; Lanman, R.B.; et al. Clinical Utility of Comprehensive Cell-Free DNA Analysis to Identify Genomic Biomarkers in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4691–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Bi, J.; Bao, L. Genetic Profiling of Cancer with Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis. J. Genet. Genom. 2018, 45, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkiewicz, A.K.; McMillan, E.A.; Balaji, U.; Baek, G.; Lin, W.-C.; Mansour, J.; Mollaee, M.; Wagner, K.-U.; Koduru, P.; Yopp, A.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing of Pancreatic Cancer Defines Genetic Diversity and Therapeutic Targets. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodara, E.; Morrison, G.; Cunha, A.; Zainfeld, D.; Xu, T.; Xu, Y.; Dempsey, P.W.; Pagano, P.C.; Bischoff, F.; Khurana, A.; et al. Multiparametric Liquid Biopsy Analysis in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e125529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, X.; Gao, S.; Jing, F.; Yang, Y.; Du, L.; Zheng, G.; Li, P.; Li, C.; Wang, C. Exosomal Long Noncoding RNA CRNDE-h as a Novel Serum-Based Biomarker for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 85551–85563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Meng, T.; Yang, X.-H.; Sayim, P.; Lei, C.; Jin, B.; Ge, L.; Wang, H.-J. Prognostic and Predictive Value of Long Non-Coding RNA GAS5 and MircoRNA-221 in Colorectal Cancer and Their Effects on Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 22, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.-Y.; Gu, R.-H.; Yan, B. Downregulation of Exosome-Encapsulated MiR-548c-5p Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 120, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Liu, X.; He, B.; Nie, Z.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, P.; Wang, S. Exosomal LncRNA 91H Is Associated with Poor Development in Colorectal Cancer by Modifying HNRNPK Expression. Cancer Cell. Int. 2018, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-Y.; Yang, L.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, L.; Chen, M.-L.; Zhao, Z.-H.; Ye, G.-D.; Luo, Q.-C.; Lv, P.-Y.; Guo, Q.-W.; et al. Tumor-Originated Exosomal LncUEGC1 as a Circulating Biomarker for Early-Stage Gastric Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Exosomal Long Noncoding RNA HOTTIP as Potential Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker Test for Gastric Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, R.; Wang, C.; Qiu, J.; Ren, B.; You, L. Early Screening and Diagnosis Strategies of Pancreatic Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 1257–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumata, Y.; Iinuma, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Tsukahara, D.; Midorikawa, H.; Igarashi, Y.; Soeda, N.; Kiyokawa, T.; Horikawa, M.; Fukushima, R. Exosome-encapsulated MicroRNA-23b as a Minimally Invasive Liquid Biomarker for the Prediction of Recurrence and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer Patients in Each Tumor Stage. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Fujiya, M.; Konishi, H.; Sasajima, J.; Fujibayashi, S.; Hayashi, A.; Utsumi, T.; Sato, H.; Iwama, T.; Ijiri, M.; et al. An Elevated Expression of Serum Exosomal MicroRNA-191, - 21, -451a of Pancreatic Neoplasm Is Considered to Be Efficient Diagnostic Marker. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Lu, Z.; Wang, T.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Miao, Y. Plasma MiRNAs in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer: A MiRNA Expression Analysis. Gene 2018, 673, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yanfang, W.; Li, J.; Jiang, P.; Peng, T.; Chen, K.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhen, P.; Zhu, J.; et al. Tumor-Released Exosomal Circular RNA PDE8A Promotes Invasive Growth via the MiR-338/MACC1/MET Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 432, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Serum Exosomal HnRNPH1 MRNA as a Novel Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Su, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, M.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Bai, T.; Dong, L.; Wei, C.; et al. Serum and Exosome Long Non Coding RNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 2631–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, R.; Qin, L. Exosomal MiR-93 Promotes Proliferation and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Directly Inhibiting TIMP2/TP53INP1/CDKN1A. BioChem. Biophys Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, H.; Liu, M.; Tian, L. Combined Detection of Serum Exosomal MiR-21 and HOTAIR as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yuan, T.; Liang, M.; Du, M.; Xia, S.; Dittmar, R.; Wang, D.; See, W.; Costello, B.A.; Quevedo, F.; et al. Exosomal MiR-1290 and MiR-375 as Prognostic Markers in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Ji, J.; Wang, B.-C.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z.-H.; Wang, K.; Luo, C.-L.; Zhang, W.-W.; Wang, F.-B.; Zhang, X.-L. Tumor-Derived Exosomal Long Noncoding RNAs as Promising Diagnostic Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer. Cell. Physiol. BioChem. 2018, 46, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Stevic, I.; Müller, V.; Ni, Q.; Oliveira-Ferrer, L.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Exosomal MicroRNAs as Tumor Markers in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, S.; Xie, W.; Li, C.; Hu, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, N.; Wu, L.; Bai, L.; et al. Circulating Exosomal MicroRNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 13048–13058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Ming, H. Serum Long Non Coding RNA MALAT-1 Protected by Exosomes Is up-Regulated and Promotes Cell Proliferation and Migration in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. BioChem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 490, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manier, S.; Liu, C.-J.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Park, J.; Shi, J.; Campigotto, F.; Salem, K.Z.; Huynh, D.; Glavey, S.V.; Rivotto, B.; et al. Prognostic Role of Circulating Exosomal MiRNAs in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2017, 129, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, F.; Qing, Q.; Pan, Q.; Hu, M.; Yu, H.; Yue, X. Serum Exosomal MiR-301a as a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Human Glioma. Cell. Oncol. 2018, 41, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manterola, L.; Guruceaga, E.; Gállego Pérez-Larraya, J.; González-Huarriz, M.; Jauregui, P.; Tejada, S.; Diez-Valle, R.; Segura, V.; Samprón, N.; Barrena, C.; et al. A Small Noncoding RNA Signature Found in Exosomes of GBM Patient Serum as a Diagnostic Tool. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ng, T.K.; Zhao, C.; Gan, Q.; Gu, X.; Xiang, J. Circulating Exosomal CPNE3 as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Colorectal Cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 1416–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, B.; Ren, C.; Chen, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhou, L.; Peng, Z.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. The Clinical Significance of Circulating GPC1 Positive Exosomes and Its Regulative MiRNAs in Colon Cancer Patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 101189–101202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, S.A.; Luecke, L.B.; Kahlert, C.; Fernandez, A.F.; Gammon, S.T.; Kaye, J.; LeBleu, V.S.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Weitz, J.; Rahbari, N.; et al. Glypican1 Identifies Cancer Exosomes and Facilitates Early Detection of Cancer. Nature 2015, 523, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandfeld-Paulsen, B.; Aggerholm-Pedersen, N.; Bæk, R.; Jakobsen, K.R.; Meldgaard, P.; Folkersen, B.H.; Rasmussen, T.R.; Varming, K.; Jørgensen, M.M.; Sorensen, B.S. Exosomal Proteins as Prognostic Biomarkers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Sun, S.G.; Lu, Z.L.; He, J. Diagnostic value of protein markers in plasma exosomes of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2018, 40, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, W.; Yin, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, H.; Cai, C.; Li, P.; Huang, L.; Ma, P. Exosomal EphrinA2 Derived from Serum as a Potential Biomarker for Prostate Cancer. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 2659–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Øverbye, A.; Skotland, T.; Koehler, C.J.; Thiede, B.; Seierstad, T.; Berge, V.; Sandvig, K.; Llorente, A. Identification of Prostate Cancer Biomarkers in Urinary Exosomes. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 30357–30376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alegre, E.; Zubiri, L.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; González-Cao, M.; Soria, L.; Martín-Algarra, S.; González, A. Circulating Melanoma Exosomes as Diagnostic and Prognosis Biomarkers. Clin. Chim Acta 2016, 454, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-L.; Lai, Y.-F.; Tang, P.; Chien, K.-Y.; Yu, J.-S.; Tsai, C.-H.; Chen, H.-W.; Wu, C.-C.; Chung, T.; Hsu, C.-W.; et al. Comparative and Targeted Proteomic Analyses of Urinary Microparticles from Bladder Cancer and Hernia Patients. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 5611–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, P.-G.; Lee, J.-E.; Cho, Y.-E.; Lee, S.J.; Chae, Y.S.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, I.-S.; Park, H.Y.; Baek, M.-C. Fibronectin on Circulating Extracellular Vesicles as a Liquid Biopsy to Detect Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40189–40199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciravolo, V.; Huber, V.; Ghedini, G.C.; Venturelli, E.; Bianchi, F.; Campiglio, M.; Morelli, D.; Villa, A.; Mina, P.D.; Menard, S.; et al. Potential Role of HER2-Overexpressing Exosomes in Countering Trastuzumab-Based Therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHEN, Y.; WANG, L.; ZHU, Y.; CHEN, Z.; QI, X.; JIN, L.; JIN, J.; HUA, D.; MA, X. Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP)-Containing Circulating Microvesicles Contribute to Chemoresistance in Breast Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 3742–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-Villanueva, M.; Hidalgo-Pérez, L.; Rios-Romero, M.; Cedro-Tanda, A.; Ruiz-Villavicencio, C.A.; Page, K.; Hastings, R.; Fernandez-Garcia, D.; Allsopp, R.; Fonseca-Montaño, M.A.; et al. Cell-Free DNA Analysis in Current Cancer Clinical Trials: A Review. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, J.-C.; Belloum, Y.; Deitert, B.; Sementsov, M.; Heidrich, I.; Gebhardt, C.; Keller, L.; Pantel, K. Current and Future Clinical Applications of CtDNA in Immuno-Oncology. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, E.; Winter, C.; George, A.; Chen, Y.; Howlin, J.; Tang, M.-H.E.; Dahlgren, M.; Schulz, R.; Grabau, D.; van Westen, D.; et al. Serial Monitoring of Circulating Tumor DNA in Patients with Primary Breast Cancer for Detection of Occult Metastatic Disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, C.A.; Gale, D.; Piskorz, A.M.; Biggs, H.; Hodgkin, C.; Addley, H.; Freeman, S.; Moyle, P.; Sala, E.; Sayal, K.; et al. Exploratory Analysis of TP53 Mutations in Circulating Tumour DNA as Biomarkers of Treatment Response for Patients with Relapsed High-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, J.; Wang, Y.; Tomasetti, C.; Li, L.; Springer, S.; Kinde, I.; Silliman, N.; Tacey, M.; Wong, H.-L.; Christie, M.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis Detects Minimal Residual Disease and Predicts Recurrence in Patients with Stage II Colon Cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, ra92–ra346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, Y.N.; Dhillon, S. Epi ProColon® 2.0 CE: A Blood-Based Screening Test for Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Diagn 2017, 21, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avogbe, P.H.; Manel, A.; Vian, E.; Durand, G.; Forey, N.; Voegele, C.; Zvereva, M.; Hosen, M.I.; Meziani, S.; De Tilly, B.; et al. Urinary TERT Promoter Mutations as Non-Invasive Biomarkers for the Comprehensive Detection of Urothelial Cancer. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mattos-Arruda, L.; Mayor, R.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Weigelt, B.; Martínez-Ricarte, F.; Torrejon, D.; Oliveira, M.; Arias, A.; Raventos, C.; Tang, J.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid-Derived Circulating Tumour DNA Better Represents the Genomic Alterations of Brain Tumours than Plasma. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.G.; Moser, T.; Mouliere, F.; Field-Rayner, J.; Eldridge, M.; Riediger, A.L.; Chandrananda, D.; Heider, K.; Wan, J.C.M.; Warren, A.Y.; et al. Comprehensive Characterization of Cell-Free Tumor DNA in Plasma and Urine of Patients with Renal Tumors. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, N.B.; Ng, E.K.; Lo, Y.D. Stability of Endogenous and Added RNA in Blood Specimens, Serum, and Plasma. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Chevillet, J.R.; Kroh, E.M.; Ruf, I.K.; Pritchard, C.C.; Gibson, D.F.; Mitchell, P.S.; Bennett, C.F.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Stirewalt, D.L.; et al. Argonaute2 Complexes Carry a Population of Circulating MicroRNAs Independent of Vesicles in Human Plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischhacker, M.; Schmidt, B. Circulating Nucleic Acids (CNAs) and Cancer—A Survey. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Rev. Cancer 2007, 1775, 181–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, K.L.; Sanda, M.G.; Moreno, C.S. RNA Biomarkers to Facilitate the Identification of Aggressive Prostate Cancer. Mol. Asp. Med. 2015, 45, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaporozhchenko, I.A.; Ponomaryova, A.A.; Rykova, E.Y.; Laktionov, P.P. The Potential of Circulating Cell-Free RNA as a Cancer Biomarker: Challenges and Opportunities. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 18, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sestini, S.; Boeri, M.; Marchiano, A.; Pelosi, G.; Galeone, C.; Verri, C.; Suatoni, P.; Sverzellati, N.; La Vecchia, C.; Sozzi, G.; et al. Circulating MicroRNA Signature as Liquid-Biopsy to Monitor Lung Cancer in Low-Dose Computed Tomography Screening. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 32868–32877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okajima, W.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Miyamae, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Hirajima, S.; Ohashi, T.; Imamura, T.; Kiuchi, J.; Arita, T.; et al. Circulating MicroRNA Profiles in Plasma: Identification of MiR-224 as a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Independent of Hepatic Function. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 53820–53836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endzeliņš, E.; Berger, A.; Melne, V.; Bajo-Santos, C.; Soboļevska, K.; Ābols, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Šantare, D.; Rudņickiha, A.; Lietuvietis, V.; et al. Detection of Circulating MiRNAs: Comparative Analysis of Extracellular Vesicle-Incorporated MiRNAs and Cell-Free MiRNAs in Whole Plasma of Prostate Cancer Patients. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-F.; Hannafon, B.N.; Zhao, Y.D.; Postier, R.G.; Ding, W.-Q. Plasma Exosome MiR-196a and MiR-1246 Are Potential Indicators of Localized Pancreatic Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 77028–77040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Fei, S.; Chen, D.; Cai, X.; Liu, L.; Lin, B.; Su, H.; Zhao, L.; et al. Evaluation of Tumor-Derived Exosomal MiRNA as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Early-Stage Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Next-Generation Sequencing. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5311–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, A.; Imbrucè, P.; Gardenghi, B.; Belli, L.; Agushi, R.; Tamanini, A.; Munari, S.; Bossi, A.M.; Scambi, I.; Benati, D.; et al. A MicroRNA Signature from Serum Exosomes of Patients with Glioma as Complementary Diagnostic Biomarker. J. NeuroOncol. 2018, 136, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.-X.; Li, Y.-M.; Ye, M.; Guo, Y.-Y.; Li, Q.-W.; Peng, X.-M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.-F.; Zhao, H.-X.; Zhang, H.; et al. KRAS and BRAF Mutations in Serum Exosomes from Patients with Colorectal Cancer in a Chinese Population. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3608–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manda, S.V.; Kataria, Y.; Tatireddy, B.R.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Ratnam, B.G.; Lath, R.; Ranjan, A.; Ray, A. Exosomes as a Biomarker Platform for Detecting Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor–Positive High-Grade Gliomas. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, C.; Giménez-Capitán, A.; Karachaliou, N.; Pérez-Rosado, A.; Viteri, S.; Morales-Espinosa, D.; Rosell, R. Fusion Gene and Splice Variant Analyses in Liquid Biopsies of Lung Cancer Patients. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, T.; Miao, M.; Qin, L.; Wang, B.; Ye, G.; Xiao, B.; Guo, J. Plasma Long Noncoding RNA Protected by Exosomes as a Potential Stable Biomarker for Gastric Cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 2007–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Lin, W.; Qi, P.; Xu, M.; Wu, X.; Ni, S.; Huang, D.; Weng, W.; Tan, C.; Sheng, W.; et al. Circulating Long RNAs in Serum Extracellular Vesicles: Their Characterization and Potential Application as Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2016, 25, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Shi, H.; Xi, H.; Wu, X.; Cui, J.; Gao, Y.; Liang, W.; Hu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Genome-Wide LncRNA Microarray Profiling Identifies Novel Circulating LncRNAs for Detection of Gastric Cancer. Theranostics 2017, 7, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sourvinou, I.S.; Markou, A.; Lianidou, E.S. Quantification of Circulating MiRNAs in Plasma: Effect of Preanalytical and Analytical Parameters on Their Isolation and Stability. J. Mol. Diagn. 2013, 15, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.; Bebawy, M. Proteins Regulating Microvesicle Biogenesis and Multidrug Resistance in Cancer. Proteomics 2019, 19, 1800165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding Light on the Cell Biology of Extracellular Vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Tang, W.H. Exosomes: Biogenesis, Biologic Function and Clinical Potential. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, B.M.; Prieto, M.; Silva, L.C. Ceramide: A Simple Sphingolipid with Unique Biophysical Properties. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 54, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The Biology, Function, and Biomedical Applications of Exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R. The Biology and Function of Exosomes in Cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Gu, J.; Jiang, P.; Qian, H.; Xu, W.; Zhang, X. Exosomes in Gastric Cancer: Roles, Mechanisms, and Applications. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, A.; Tovar-Camargo, O.A.; Toden, S. Exosomal MicroRNA Biomarkers: Emerging Frontiers in Colorectal and Other Human Cancers. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn 2016, 16, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baassiri, A.; Nassar, F.; Mukherji, D.; Shamseddine, A.; Nasr, R.; Temraz, S. Exosomal Non Coding RNA in LIQUID Biopsies as a Promising Biomarker for Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2020, 21, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, A.; Buschmann, D.; Byrd, J.B.; Carter, D.R.F.; Cheng, L.; Compton, C.; Daaboul, G.; Devitt, A.; Falcon-Perez, J.M.; Gardiner, C.; et al. Summary of the ISEV Workshop on Extracellular Vesicles as Disease Biomarkers, Held in Birmingham, UK, during December 2017. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1473707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.; Wildman, D.E. Extracellular Vesicles and the Promise of Continuous Liquid Biopsies. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2018, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, K.; Jo, A.; Giedt, J.; Vinegoni, C.; Yang, K.S.; Peruzzi, P.; Chiocca, E.A.; Breakefield, X.O.; Lee, H.; Weissleder, R. Characterization of Single Microvesicles in Plasma from Glioblastoma Patients. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deun, J.; Mestdagh, P.; Sormunen, R.; Cocquyt, V.; Vermaelen, K.; Vandesompele, J.; Bracke, M.; De Wever, O.; Hendrix, A. The Impact of Disparate Isolation Methods for Extracellular Vesicles on Downstream RNA Profiling. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 24858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyai, T.; Herczeg, K.; Onódi, Z.; Voszka, I.; Módos, K.; Marton, N.; Nagy, G.; Mäger, I.; Wood, M.J.; El Andaloussi, S.; et al. Isolation of Exosomes from Blood Plasma: Qualitative and Quantitative Comparison of Ultracentrifugation and Size Exclusion Chromatography Methods. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.D.; Shah, S. Methods of Isolating Extracellular Vesicles Impact Down-Stream Analyses of Their Cargoes. Methods 2015, 87, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sódar, B.W.; Kittel, Á.; Pálóczi, K.; Vukman, K.V.; Osteikoetxea, X.; Szabó-Taylor, K.; Németh, A.; Sperlágh, B.; Baranyai, T.; Giricz, Z.; et al. Low-Density Lipoprotein Mimics Blood Plasma-Derived Exosomes and Microvesicles during Isolation and Detection. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Ishikawa, N.; Tatsuguchi, A.; Saichi, N.; Fujii, R.; Nakagawa, H. Antibody-Coupled Monolithic Silica Microtips for Highthroughput Molecular Profiling of Circulating Exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Luo, J.; Wang, S. Recent Progress in Isolation and Detection of Extracellular Vesicles for Cancer Diagnostics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.M.; Vyas, A.D.; Qiu, Y.; Messer, K.S.; White, R.; Heller, M.J. Integrated Analysis of Exosomal Protein Biomarkers on Alternating Current Electrokinetic Chips Enables Rapid Detection of Pancreatic Cancer in Patient Blood. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3311–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Fine, D.; Schmulen, J.; Hu, Y.; Godin, B.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, X. Ciliated Micropillars for the Microfluidic-Based Isolation of Nanoscale Lipid Vesicles. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2879–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Kanwar, S.; James Dunlay, C.; Simeone, D.; Nagrath, S. Microfluidic Device (ExoChip) for on-Chip Isolation, Quantification and Characterization of Circulating Exosomes. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, H.M.; Kharel, S.; Dalan, R.; Chen, Z.J.; Tan, K.K.; Boehm, B.O.; Loo, S.C.J.; Hou, H.W. Rapid Purification of Sub-Micrometer Particles for Enhanced Drug Release and Microvesicles Isolation. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.T.; Kim, J.; Jang, S.C.; Choi, E.-J.; Gho, Y.S.; Park, J. Microfluidic Filtration System to Isolate Extracellular Vesicles from Blood. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 5202–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, J.Z.; Lee, Y.; Vader, P.; Mäger, I.; Johansson, H.J.; Heusermann, W.; Wiklander, O.P.B.; Hällbrink, M.; Seow, Y.; Bultema, J.J.; et al. Ultrafiltration with Size-Exclusion Liquid Chromatography for High Yield Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles Preserving Intact Biophysical and Functional Properties. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumans, F.A.W.; Gool, E.L.; Nieuwland, R. Bulk Immunoassays for Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles. Platelets 2017, 28, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriachek, K.; Islam, M.N.; Möller, A.; Salomon, C.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Hossain, M.S.A.; Yamauchi, Y.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. Biological Functions and Current Advances in Isolation and Detection Strategies for Exosome Nanovesicles. Small 2018, 14, 1702153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Romero, N.; Esteban-Rubio, S.; Rackov, G.; Carrión-Navarro, J.; Belda-Iniesta, C.; Ayuso-Sacido, A. Extracellular Vesicles Compartment in Liquid Biopsies: Clinical Application. Mol. Asp. Med. 2018, 60, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrano, V.; Royo, F.; Peinado, H.; Loizaga-Iriarte, A.; Unda, M.; Falcón-Perez, J.M.; Carracedo, A. Vesicle-MaNiA: Extracellular Vesicles in Liquid Biopsy and Cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshishian, H.; Burgess, M.W.; Specht, H.; Wallace, L.; Clauser, K.R.; Gillette, M.A.; Carr, S.A. Quantitative, Multiplexed Workflow for Deep Analysis of Human Blood Plasma and Biomarker Discovery by Mass Spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 1683–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Wang, N.; Ji, N.; Chen, Z.-S. Proteomics Technologies for Cancer Liquid Biopsies. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelio, I.; Bertolo, R.; Bove, P.; Buonomo, O.C.; Candi, E.; Chiocchi, M.; Cipriani, C.; Di Daniele, N.; Ganini, C.; Juhl, H.; et al. Liquid Biopsies and Cancer Omics. Cell. Death Discov. 2020, 6, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macklin, A.; Khan, S.; Kislinger, T. Recent Advances in Mass Spectrometry Based Clinical Proteomics: Applications to Cancer Research. Clin. Proteom. 2020, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Loo, J.A.; Wong, D.T. Human Body Fluid Proteome Analysis. Proteomics 2006, 6, 6326–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.L.; Polanski, M.; Pieper, R.; Gatlin, T.; Tirumalai, R.S.; Conrads, T.P.; Veenstra, T.D.; Adkins, J.N.; Pounds, J.G.; Fagan, R.; et al. The Human Plasma Proteome: A Nonredundant List Developed by Combination of Four Separate Sources. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2004, 3, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.L.; Xiao, C.; Fu, G.; Wang, X.; Li, L. Identification of Potential Serum Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Using a Functional Proteomics Technology. Biomark. Res. 2017, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worst, T.S.; Von Hardenberg, J.; Gross, J.C.; Erben, P.; Schnölzer, M.; Hausser, I.; Bugert, P.; Michel, M.S.; Boutros, M. Database-Augmented Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Exosomes Identifies Claudin 3 as a Putative Prostate Cancer Biomarker *. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2017, 16, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttenhain, R.; Choi, M.; de la Fuente, L.M.; Oehl, K.; Chang, C.-Y.; Zimmermann, A.-K.; Malander, S.; Olsson, H.; Surinova, S.; Clough, T.; et al. A Targeted Mass Spectrometry Strategy for Developing Proteomic Biomarkers: A Case Study of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer *[S]. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 1836–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöström, M.; Ossola, R.; Breslin, T.; Rinner, O.; Malmström, L.; Schmidt, A.; Aebersold, R.; Malmström, J.; Niméus, E. A Combined Shotgun and Targeted Mass Spectrometry Strategy for Breast Cancer Biomarker Discovery. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2807–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reslova, N.; Michna, V.; Kasny, M.; Mikel, P.; Kralik, P. XMAP Technology: Applications in Detection of Pathogens. Front. MicroBiol. 2017, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Schneiderhan-Marra, N.; Joos, T.O. Protein Microarrays for Personalized Medicine. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, J.G.; Blackburn, J.M. Advances in the Development of Human Protein Microarrays. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2017, 14, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syu, G.-D.; Dunn, J.; Zhu, H. Developments and Applications of Functional Protein Microarrays. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2020, 19, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Fu, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liang, C. Advances in Aptamer-Based Biomarker Discovery. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 659760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, E.N.; Gold, L.; Lawn, R.M.; Walker, J.J.; Zichi, D. High-Content Affinity-Based Proteomics: Unlocking Protein Biomarker Discovery. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 10, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lollo, B.; Steele, F.; Gold, L. Beyond Antibodies: New Affinity Reagents to Unlock the Proteome. Proteomics 2014, 14, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, I.-T.; Li, X.; Yadikar, H.A.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Lyu, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, K.K.; Tan, W. Identification and Characterization of DNA Aptamers Specific for Phosphorylation Epitopes of Tau Protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 14314–14323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landegren, U.; Hammond, M. Cancer Diagnostics Based on Plasma Protein Biomarkers: Hard Times but Great Expectations. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assarsson, E.; Lundberg, M.; Holmquist, G.; Björkesten, J.; Thorsen, S.B.; Ekman, D.; Eriksson, A.; Rennel Dickens, E.; Ohlsson, S.; Edfeldt, G.; et al. Homogenous 96-Plex PEA Immunoassay Exhibiting High Sensitivity, Specificity, and Excellent Scalability. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petricoin, E.; Wulfkuhle, J.; Howard, M.; Pierobon, M.; Espina, V.; Luchini, A.; Liotta, L.A. RPPA: Origins, Transition to a Validated Clinical Research Tool, and Next Generations of the Technology. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1188, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbani, R.; Becker, K.-F.; Carragher, N.; Goldstein, T.; de Koning, L.; Korf, U.; Liotta, L.; Mills, G.B.; Nishizuka, S.S.; Pawlak, M.; et al. Realizing the Promise of Reverse Phase Protein Arrays for Clinical, Translational, and Basic Research: A Workshop Report: The RPPA (Reverse Phase Protein Array) Society. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 1625–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocan, T.; Simão, A.L.; Castro, R.E.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Słomka, A.; Wang, B.; Strassburg, C.; Wöhler, A.; Willms, A.G.; Kornek, M. Liquid Biopsies in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Are We Winning? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascale, R.M.; Calvisi, D.F.; Simile, M.M.; Feo, C.F.; Feo, F. The Warburg Effect 97 Years after Its Discovery. Cancers 2020, 12, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beger, R.D.; Dunn, W.; Schmidt, M.A.; Gross, S.S.; Kirwan, J.A.; Cascante, M.; Brennan, L.; Wishart, D.S.; Oresic, M.; Hankemeier, T.; et al. Metabolomics Enables Precision Medicine: “A White Paper, Community Perspective”. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Zhou, R.; Yu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Bin, J.; Liao, Y.; Rao, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Gene Expression Profiles for a Prognostic Immunoscore in Gastric Cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Ye, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhou, R.; Fan, X.; Wang, G.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, M.; et al. Macrophage Correlates with Immunophenotype and Predicts Anti-PD-L1 Response of Urothelial Cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 7002–7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Covarrubias, V.; Martínez-Martínez, E.; del Bosque-Plata, L. The Potential of Metabolomics in Biomedical Applications. Metabolites 2022, 12, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erben, V.; Poschet, G.; Schrotz-King, P.; Brenner, H. Comparing Metabolomics Profiles in Various Types of Liquid Biopsies among Screening Participants with and without Advanced Colorectal Neoplasms. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed Minimum Reporting Standards for Chemical Analysis Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocan-Cartita, C.A.; Jurj, A.; Buse, M.; Gulei, D.; Braicu, C.; Raduly, L.; Cojocneanu, R.; Pruteanu, L.L.; Iuga, C.A.; Coza, O.; et al. The Relevance of Mass Spectrometry Analysis for Personalized Medicine through Its Successful Application in Cancer “Omics”. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons-Belda, O.D.; Fernandez-Uriarte, A.; Diamandis, E.P. Can Circulating Tumor DNA Support a Successful Screening Test for Early Cancer Detection? The Grail Paradigm. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammerlaan, W.; Betsou, F. Biospecimen Science of Blood for CfDNA Genetic Analyses. Curr. PathoBiol. Rep. 2019, 7, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Tan, W.; Ma, J. Circulating Tumor Cells and DNA for Real-Time EGFR Detection and Monitoring of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Future Oncol. 2017, 13, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.H.; Cunningham, D.; Werner, B.; Vlachogiannis, G.; Spiteri, I.; Heide, T.; Mateos, J.F.; Vatsiou, A.; Lampis, A.; Damavandi, M.D.; et al. Longitudinal Liquid Biopsy and Mathematical Modeling of Clonal Evolution Forecast Time to Treatment Failure in the PROSPECT-C Phase II Colorectal Cancer Clinical Trial. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1270–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Cao, Y.; MacLeay, A.; Lennerz, J.K.; Baig, A.; Frazier, R.P.; Lee, J.; Hu, K.; Pacula, M.; Meneses, E.; et al. Clinical Validation of a Cell-Free DNA Gene Panel. J. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 21, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Garcia, D.; Hills, A.; Page, K.; Hastings, R.K.; Toghill, B.; Goddard, K.S.; Ion, C.; Ogle, O.; Boydell, A.R.; Gleason, K.; et al. Plasma Cell-Free DNA (CfDNA) as a Predictive and Prognostic Marker in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Si, D.; Xiu, D.; Zhong, L. Metabolomics Identifies Serum and Exosomes Metabolite Markers of Pancreatic Cancer. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meo, A.; Bartlett, J.; Cheng, Y.; Pasic, M.D.; Yousef, G.M. Liquid Biopsy: A Step Forward towards Precision Medicine in Urologic Malignancies. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrera, A.; von Toerne, C.; Behler, J.; Huth, C.; Thorand, B.; Hilgendorff, A.; Hauck, S.M. Multiplatform Approach for Plasma Proteomics: Complementarity of Olink Proximity Extension Assay Technology to Mass Spectrometry-Based Protein Profiling. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, M.; Gies, A.; Weigl, K.; Tikk, K.; Benner, A.; Schrotz-King, P.; Borchers, C.H.; Brenner, H. Evaluation and Validation of Plasma Proteins Using Two Different Protein Detection Methods for Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, A.-D.; Thielert, M.; Vasilopoulou, C.; Ammar, C.; Coscia, F.; Mund, A.; Hoerning, O.B.; Bache, N.; Apalategui, A.; Lubeck, M.; et al. Ultra-High Sensitivity Mass Spectrometry Quantifies Single-Cell Proteome Changes upon Perturbation. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2022, 18, e10798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, J.J.; Fan, R. Single-Cell Protein Secretion Detection and Profiling. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 12, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
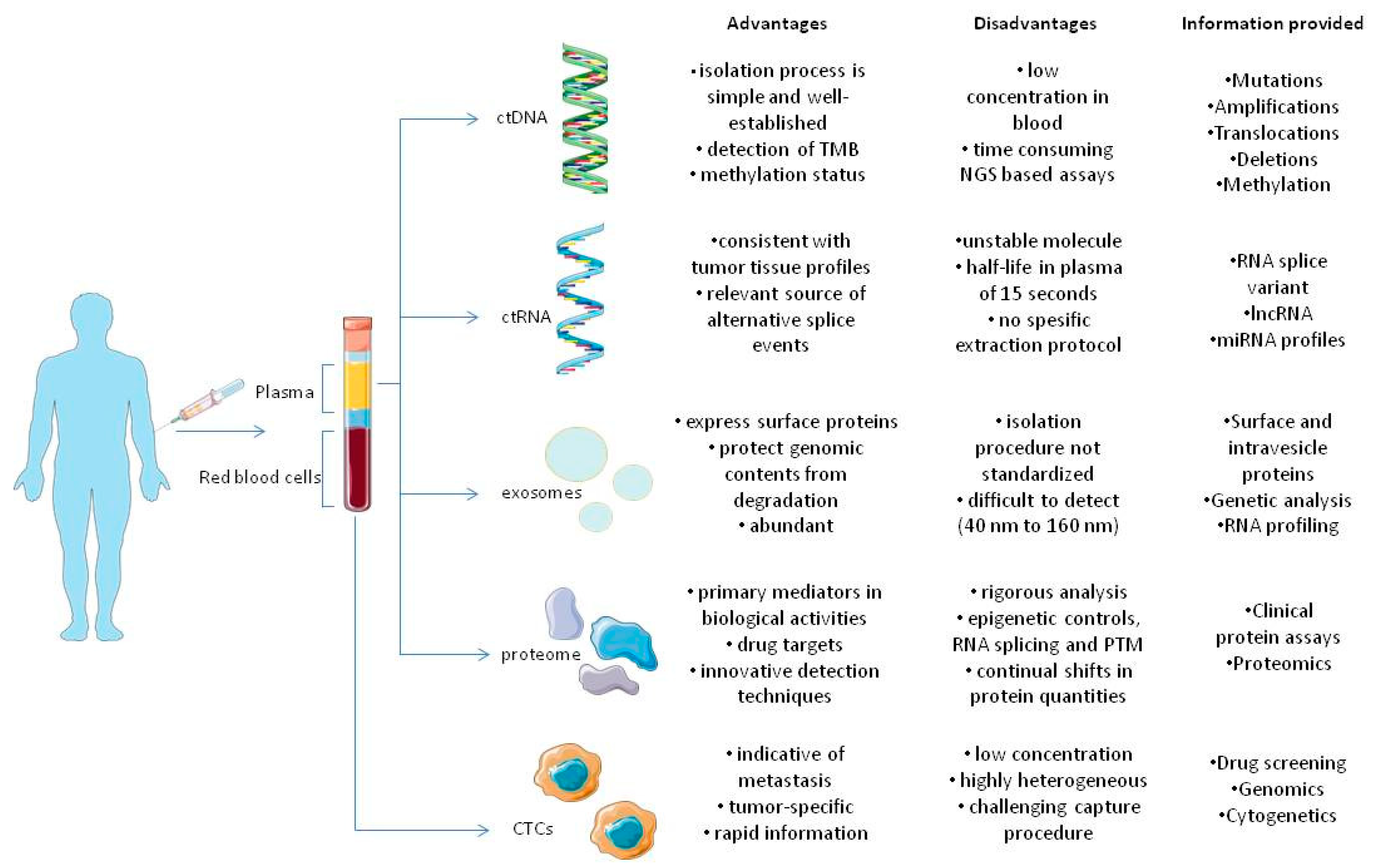
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Armakolas, A.; Kotsari, M.; Koskinas, J. Liquid Biopsies, Novel Approaches and Future Directions. Cancers 2023, 15, 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051579
Armakolas A, Kotsari M, Koskinas J. Liquid Biopsies, Novel Approaches and Future Directions. Cancers. 2023; 15(5):1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051579
Chicago/Turabian StyleArmakolas, Athanasios, Maria Kotsari, and John Koskinas. 2023. "Liquid Biopsies, Novel Approaches and Future Directions" Cancers 15, no. 5: 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051579
APA StyleArmakolas, A., Kotsari, M., & Koskinas, J. (2023). Liquid Biopsies, Novel Approaches and Future Directions. Cancers, 15(5), 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051579






