The Prognostic Value of the Serum Level of C-Reactive Protein for Survival of Children with Ewing’s Sarcoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fabbri, N.; Manfrini, M. Atlas of Musculoskeletal Tumors and Tumorlike Lesions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünewald, T.G.P.; Cidre-Aranaz, F.; Surdez, D.; Tomazou, E.M.; De Álava, E.; Kovar, H.; Sorensen, P.H.; Delattre, O.; Dirksen, U. Ewing Sarcoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picci, P.; Manfrini, M.; Donati, D.M.; Gambarotti, M.; Righi, A.; Vanel, D.; Paolo, A.; Tos, D. Diagnosis of Musculoskeletal Tumors and Tumor-like Conditions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; ISBN 9783030296759. [Google Scholar]
- Riggi, N.; Suvà, M.L.; Stamenkovic, I. Ewing’s Sarcoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbaraglia, M.; Righi, A.; Gambarotti, M.; Dei Tos, A.P. Ewing Sarcoma and Ewing-like Tumors. Virchows Arch. 2020, 476, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanacci, M. Bone and Soft Tissue Tumor; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bacci, G.; Longhi, A.; Ferrari, S.; Mercuri, M.; Versari, M.; Bertoni, F. Prognostic Factors in Non-Metastatic Ewing’s Sarcoma Tumor of Bone: An Analysis of 579 Patients Treated at a Single Institution with Adjuvant or Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy between 1972 and 1998. Acta Oncol. 2006, 45, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakiewicz, P.I.; Hutterer, G.C.; Trinh, Q.D.; Jeldres, C.; Perrotte, P.; Gallina, A.; Tostain, J.; Patard, J.J. C-Reactive Protein Is an Informative Predictor of Renal Cell Carcinoma-Specific Mortality: A European Study of 313 Patients. Cancer 2007, 110, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Oh, S.Y.; Kwon, H.C.; Lee, S.; Kwon, K.A.; Kim, B.G.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, J.S.; Kim, M.C.; et al. Clinical Significances of Preoperative Serum Interleukin-6 and C-Reactive Protein Level in Operable Gastric Cancer. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, D.C.; Canna, K.; McArdle, C.S. Systemic Inflammatory Response Predicts Survival Following Curative Resection of Colorectal Cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2003, 90, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.R.; Li, H.; Kraft, P.; Kurth, T.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Stampfer, M.J.; Ma, J.; Mucci, L.A. Circulating Prediagnostic Interleukin-6 and C-Reactive Protein and Prostate Cancer Incidence and Mortality. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2683–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maretty-Kongstad, K.; Aggerholm-Pedersen, N.; Keller, J.; Safwat, A. A Validated Prognostic Biomarker Score for Adult Patients with Nonmetastatic Soft Tissue Sarcomas of the Trunk and Extremities. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Grimer, R.J.; Gaston, C.L.; Watanuki, M.; Sudo, A.; Jeys, L. The Prognostic Value of the Serum Level of C-Reactive Protein for the Survival of Patients with a Primary Sarcoma of Bone. Bone Jt. J. 2013, 95-B, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Grimer, R.; Gaston, C.; Francis, M.; Charman, J.; Graunt, P.; Uchida, A.; Sudo, A.; Jeys, L. The Value of C-Reactive Protein and Comorbidity in Predicting Survival of Patients with High Grade Soft Tissue Sarcoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Matsumine, A.; Asanuma, K.; Matsubara, T.; Sudo, A. The Role of C-Reactive Protein in Predicting Post-Metastatic Survival of Patients with Metastatic Bone and Soft Tissue Sarcoma. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 7515–7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong-Jiang, L.; Yang, X.; Wen-Biao, Z.; Yi, C.; Wang, F.; Li, P. Clinical Implications of Six Inflammatory Biomarkers as Prognostic Indicators in Ewing Sarcoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2017, 9, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Lou, Y.; Sun, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Huang, Q.; Wan, W.; Xiao, J. Establishment of a Nomogram-Based Model for Predicting the Prognostic Value of Inflammatory Biomarkers and Preoperative D-Dimer Level in Spinal Ewing’s Sarcoma Family Tumors: A Retrospective Study of 83 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2019, 121, e104–e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Baldo, G.; Abbas, R.; De Ioris, M.A.; Di Ruscio, V.; Alessi, I.; Miele, E.; Mastronuzzi, A.; Milano, G.M. The Prognostic Role of the C-Reactive Protein and Serum Lactate Dehydrogenase in a Pediatric Series of Bone Ewing Sarcoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consalvo, S.; Hinterwimmer, F.; Harrasser, N.; Lenze, U.; Matziolis, G.; von Eisenhart-Rothe, R.; Knebel, C. C-Reactive Protein Pretreatment-Level Evaluation for Ewing’s Sarcoma Prognosis Assessment-A 15-Year Retrospective Single-Centre Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggerholm-Pedersen, N.; Maretty-Kongstad, K.; Keller, J.; Baerentzen, S.; Safwat, A. The Prognostic Value of Serum Biomarkers in Localized Bone Sarcoma. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 9, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, N.; Hawkins, D.S.; Dirksen, U.; Lewis, I.J.; Ferrari, S.; Le Deley, M.C.; Kovar, H.; Grimer, R.; Whelan, J.; Claude, L.; et al. Ewing Sarcoma: Current Management and Future Approaches through Collaboration. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3036–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göbel, V.; Jürgens, H.; Etspüler, G.; Kemperdick, H.; Jungblut, R.M.; Stienen, U.; Göbel, U. Prognostic Significance of Tumor Volume in Localized Ewing’s Sarcoma of Bone in Children and Adolescents. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1987, 113, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Matsumine, A.; Matsubara, T.; Asanuma, K.; Uchida, A.; Sudo, A. The Combined Use of the Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio and C-Reactive Protein Level as Prognostic Predictors in Adult Patients with Soft Tissue Sarcoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 108, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errani, C.; Cosentino, M.; Ciani, G.; Ferra, L.; Alfaro, P.A.; Bordini, B.; Donati, D.M. C-Reactive Protein and Tumour Diagnosis Predict Survival in Patients Treated Surgically for Long Bone Metastases. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.D.; Burchill, S.A.; Abrams, K.R.; Heney, D.; Sutton, A.J.; Jones, D.R.; Lambert, P.C.; Young, B.; Wailoo, A.J.; Lewis, I.J. A Systematic Review of Molecular and Biological Markers in Tumours of the Ewing’s Sarcoma Family. Eur. J. Cancer 2003, 39, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avnet, S.; Di Pompo, G.; Lemma, S.; Baldini, N. Cause and Effect of Microenvironmental Acidosis on Bone Metastases. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019, 38, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pompo, G.; Lemma, S.; Canti, L.; Rucci, N.; Ponzetti, M.; Errani, C.; Donati, D.M.; Russell, S.; Gillies, R.; Chano, T.; et al. Intratumoral Acidosis Fosters Cancer-Induced Bone Pain through the Activation of the Mesenchymal Tumor-Associated Stroma in Bone Metastasis from Breast Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 54478–54496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proctor, M.J.; Morrison, D.S.; Talwar, D.; Balmer, S.M.; O’Reilly, D.S.J.; Foulis, A.K.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C. An Inflammation-Based Prognostic Score (MGPS) Predicts Cancer Survival Independent of Tumour Site: A Glasgow Inflammation Outcome Study. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.Z. Inflammation Fires up Cancer Metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 47, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobusch, G.M.; Bodner, F.; Walzer, S.; Marculescu, R.; Funovics, P.T.; Sulzbacher, I.; Windhager, R.; Panotopoulos, J. C-Reactive Protein as a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Chordoma of Lumbar Spine and Sacrum--a Single Center Pilot Study. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.P.; Rubal; Banipal, R.P.S.; Vashistha, R.; Dhiman, M.; Munshi, A. Association of Elevated Levels of C-Reactive Protein with Breast Cancer, Breast Cancer Subtypes, and Poor Outcome. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2019, 43, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Luo, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z. Prognostic Value of C-Reactive Protein Levels in Patients with Bone Neoplasms: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemecek, E.; Funovics, P.T.; Hobusch, G.M.; Lang, S.; Willegger, M.; Sevelda, F.; Brodowicz, T.; Stihsen, C.; Windhager, R.; Panotopoulos, J. C-Reactive Protein: An Independent Predictor for Dedifferentiated Chondrosarcoma. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 2797–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Localized | Metastatic | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (n) | 108 | 43 | 151 |
| Gender (n) | |||
| Male | 79 (73.1%) | 32 (74.4%) | 111 (73.5%) |
| Female | 29 (26.9%) | 11 (25.6%) | 40 (26.5%) |
| Age (years) | 12.7 (3–18) | 13.9 (6–18) | 13.1 (3–18) |
| Tumor location (n) | |||
| Extremities | 81 (75.0%) | 26 (60.5%) | 107 (70.9%) |
| Trunk | 27 (25.0%) | 17 (39.5%) | 44 (29.1%) |
| Tumor size (n) | |||
| >200 mL | 31 (28.7%) | 29 (67.4%) | 60 (39.7%) |
| <200 mL | 70 (64.8%) | 9 (20.9%) | 79 (52.3) |
| missing | 7 (6.5%) | 5 (11.7%) | 12 (7.9%) |
| Surgery (n) | |||
| Yes | 95 (88.0%) | 19 (44.2%) | 114 (75.5%) |
| No | 13 (22.0%) | 24 (55.8%) | 37 (24.5%) |
| Radiotherapy (n) | |||
| None | 83 (76.9%) | 15 (34.9%) | 98 (64.9%) |
| Exclusive | 13 (12.0%) | 21 (48.8%) | 34 (22.5%) |
| Before surgery | 6 (5.5%) | 2 (4.6%) | 8 (5.3%) |
| Adjuvant | 6 (5.5%) | 5 (11.6%) | 11 (7.3%) |
| Neoajuvant CHT (n) | |||
| Yes | 108 (100%) | 42 (97.7%) | 150 (99.3%) |
| No | 0 | 1 (2.3%) | 1 (0.7%) |
| Localized | Metastatic | Overall | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Raised CRP | Normal CRP | p-Value | Raised CRP | Normal CRP | p-Value | Raised CRP | Normal CRP | p-Value |
| n. Patients (%) | 37 | 60 | p = 0.025 (Proportion Z-Test) | 28 | 12 | p = 0.017 (Proportion Z-Test) | 65 (43.0) | 72 (47.7) | p = 0.608 (Proportion Z-Test) |
| Gender n. (%) | p = 0.238 (Fisher’s Exact Test) | p = 1.000 (Fisher’s Exact Test) | p = 0.249 (Fisher’s Exact Test) | ||||||
| Male | 30 (81.1) | 41 (68.3) | 21 (75.0) | 9 (75.0) | 51 (78.5) | 50 (69.4) | |||
| Female | 7 (18.9) | 19 (31.7) | 7 (25.0) | 3 (25.0) | 14 (21.5) | 22 (30.6) | |||
| Mean age (min-max) | 13.4 (3.0–18.0) | 12.4 (3.0–18.0) | p = 0.224 (t-Test) | 14.5 (6.0–18.0) | 12.3 (6.0–18.0) | p = 0.055 (t-Test) | 13.8 (3.0–18.0) | 12.3 (3.0–18.0) | p = 0.021 (t-Test) |
| n. Tumor location (%) | p = 0.020 (Fisher’s Exact Test) | p = 0.152 (Fisher’s Exact Test) | p < 0.001 (Fisher’s Exact Test) | ||||||
| Extremities | 24 (64.9) | 52 (86.7) | 15 (53.6) | 10 (83.3) | 39 (60.0) | 62 (86.1) | |||
| Trunk | 13 (35.1) | 8 (13.3) | 13 (46.4) | 2 (16.7) | 26 (40.0) | 10 (13.9) | |||
| Tumor size | p = 0.004 (Fisher’s Exact Test) | p = 0.027 (Fisher’s Exact Test) | p < 0.001 (Fisher’s Exact Test) | ||||||
| >200 mL | 16 (43.2) | 10 (16.7) | 22 (78.6) | 5 (41.7) | 38 (58.5) | 15 (20.8) | |||
| <200 mL | 18 (48.6) | 46 (76.7) | 3 (10.7) | 5 (41.7) | 21 (32.3) | 51 (70.8) | |||
| Localized | Metastatic | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathological CRP | Normal CRP | Log Rank Test | Raised CRP | Pathological CRP | Log Rank Test | |
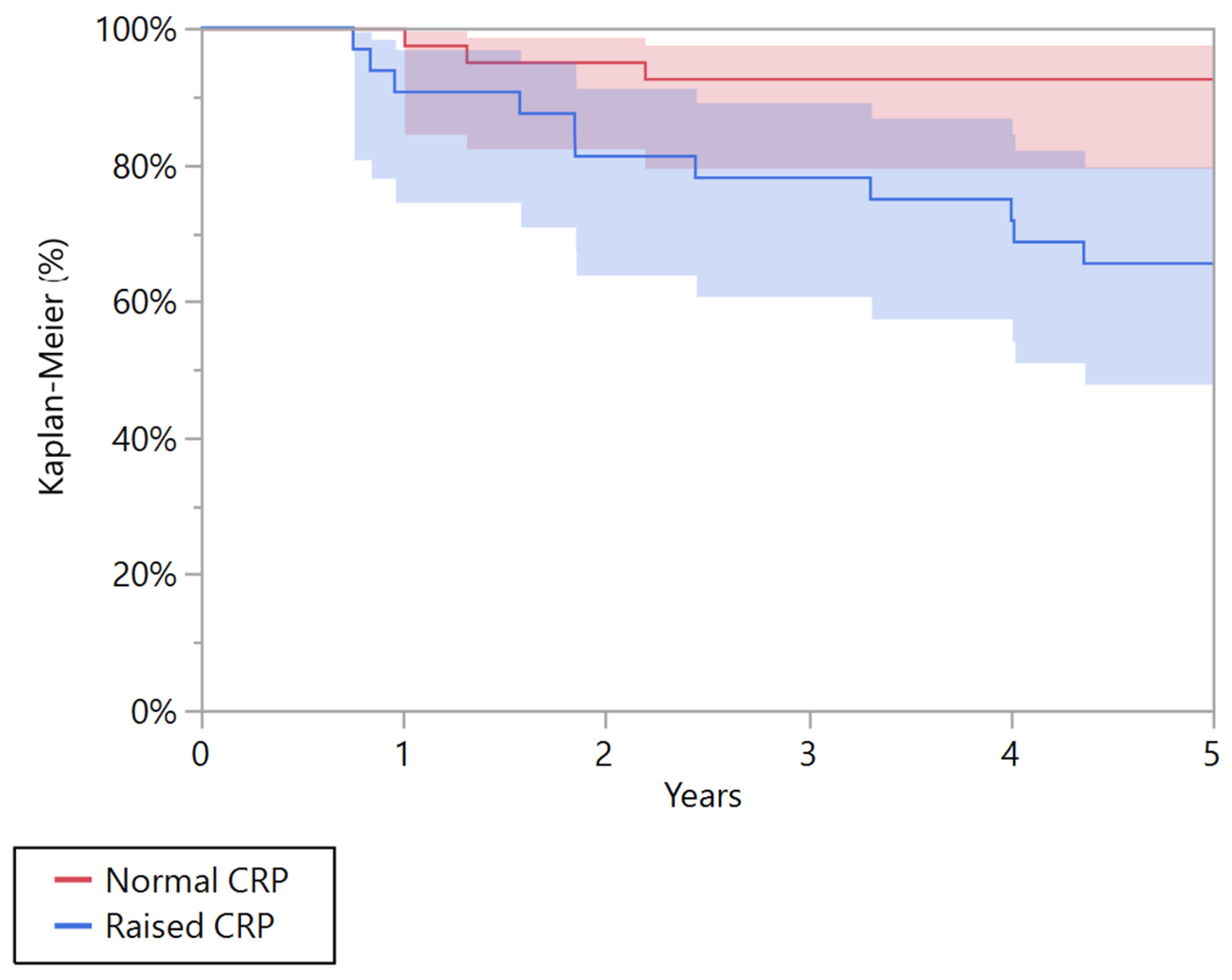
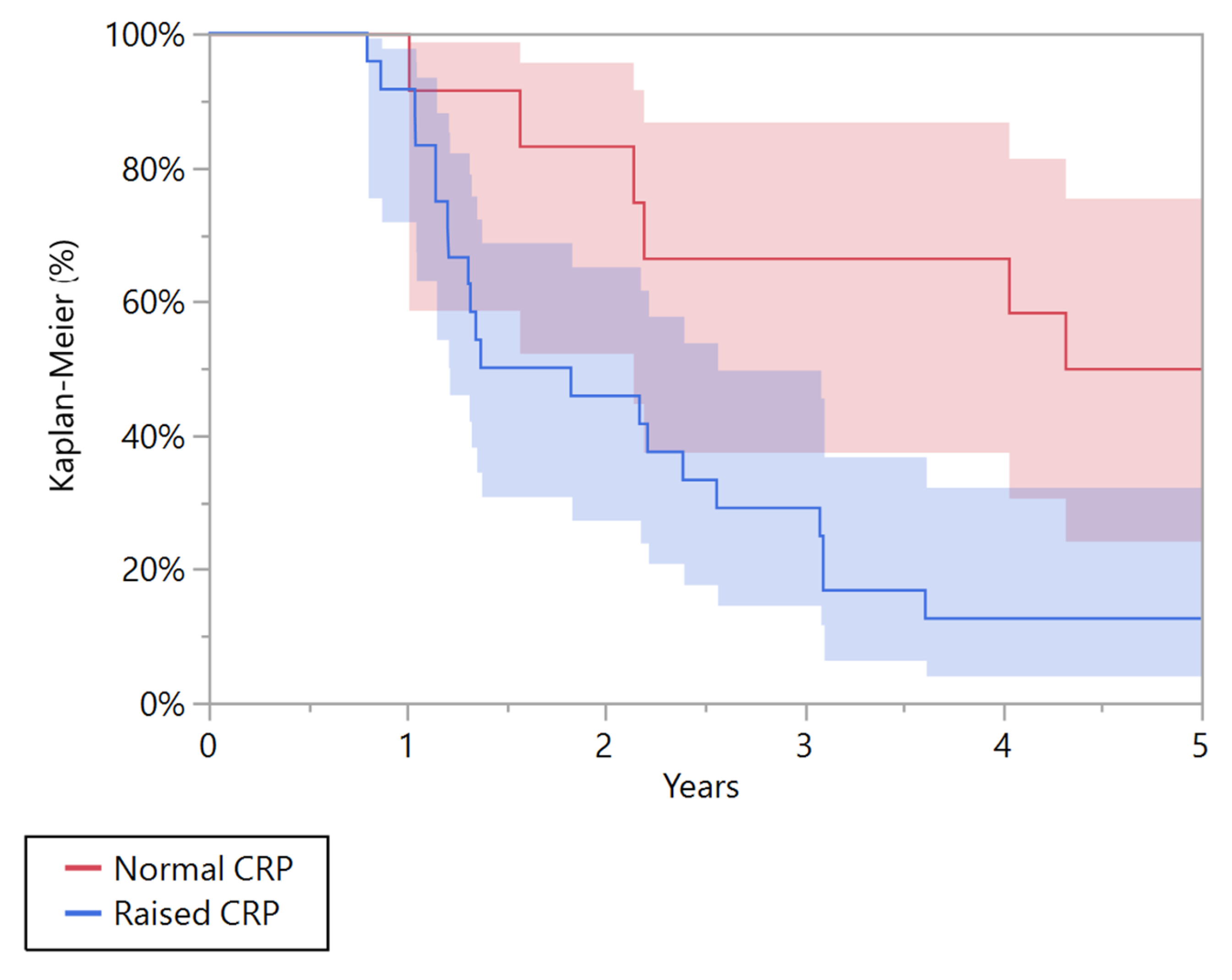
| 5 years overall survival (95% CI) | 65.6% (47.9–79.8) | 92.7% (79.6–97.6) | 0.004 | 12.5% (4.1–32.4) | 50.0% (24.4–75.6) | 0.010 |
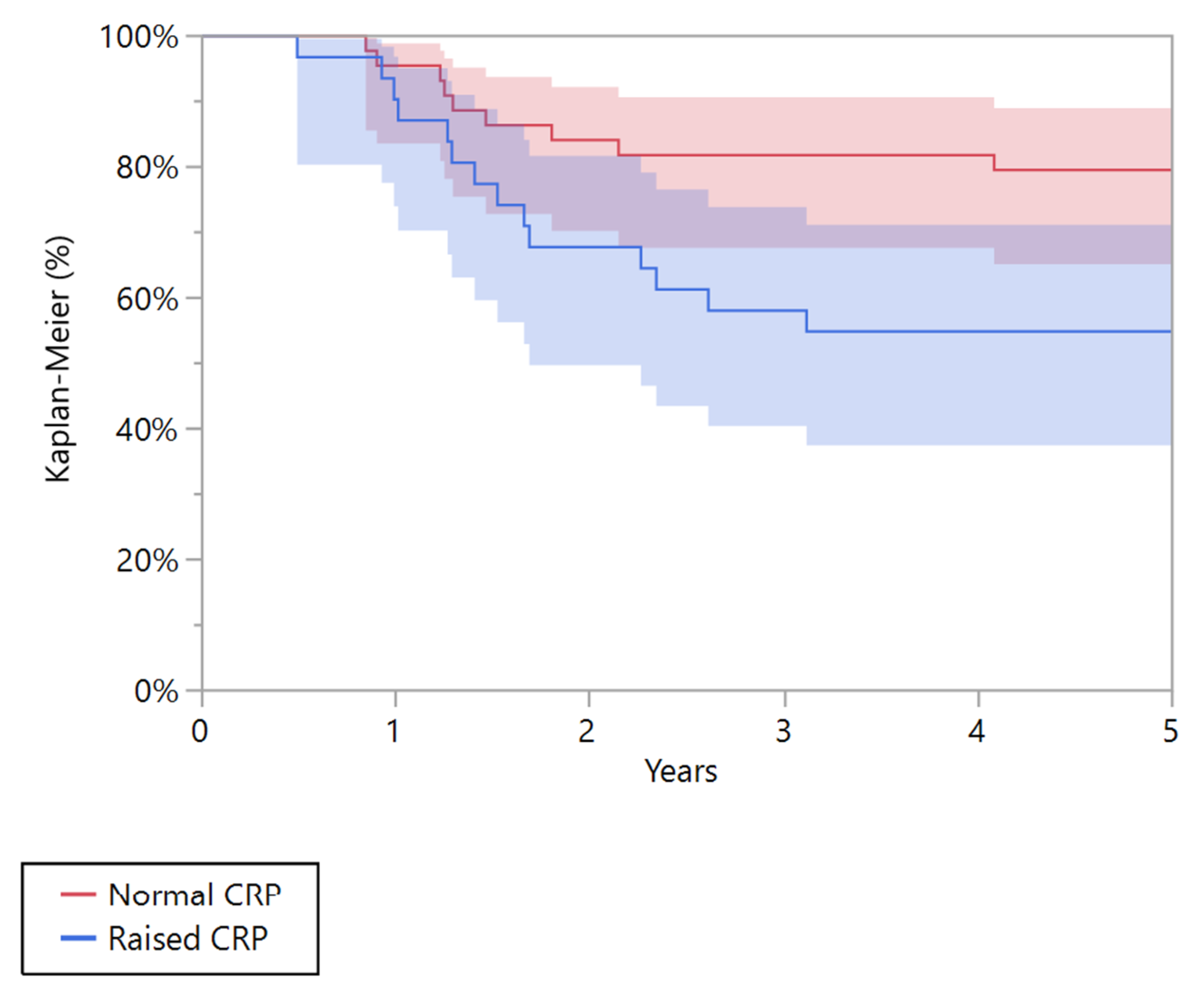
| 5 years recurrence-free survival (95% CI) | 54.8% (37.4–71.1) | 79.5% (65.1–89.0) | 0.024 | 13.0% (4.3–33.5) | 45.5% (20.3–73.2) | 0.076 |
| Variables | n | Death in 5 Years | p-Value (Log-Rank Test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.771 | ||
| Male | 70 | 16 | |
| Female | 19 | 5 | |
| Tumor location (n) | 0.595 | ||
| Extremities | 75 | 17 | |
| Trunk | 14 | 4 | |
| Tumor size | 0.309 | ||
| >200 mL | 30 | 8 | |
| <200 mL | 49 | 9 | |
| CRP | 0.003 | ||
| Pathological | 34 | 14 | |
| Normal | 47 | 6 | |
| Monocyte count | 0.482 | ||
| Raised | 50 | 13 | |
| Normal | 39 | 8 | |
| Neutrophile count | 0.445 | ||
| Raised | 8 | 3 | |
| Normal | 80 | 18 | |
| Lymphocyte count | 0.199 | ||
| Raised | 16 | 3 | |
| Normal | 73 | 18 | |
| Haemoglobin | 0.570 | ||
| Low | 22 | 6 | |
| Normal | 67 | 15 | |
| LDH | 0.264 | ||
| Raised | 22 | 7 | |
| Normal | 54 | 14 | |
| ALP | 0.993 | ||
| Raised | 9 | 2 | |
| Normal | 80 | 19 | |
| NLR | 0.054 | ||
| Raised | 34 | 12 | |
| Normal | 55 | 9 | |
| PLR | 0.634 | ||
| Raised | 55 | 14 | |
| Normal | 34 | 7 | |
| Radiotherapy | 0.010 | ||
| Yes | 15 | 7 | |
| No | 74 | 14 | |
| Metastasis at diagnosis | <0.0001 | ||
| Yes | 19 | 11 | |
| No | 70 | 10 |
| Variables | HR (95% CI) | p-Value (Log-Rank Test) |
|---|---|---|
| Metastasis at diagnosis | 4.27 (1.58–11.47) | 0.004 |
| Radiotherapy | 1.7 (0.57–4.86) | 0.310 |
| Pathological CRP | 3.67 (1.46–10.42) | 0.005 |
| Variables | n | Recurrence in 5 Years | p-Value (Log-Rank Test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.999 | ||
| Male | 74 | 27 | |
| Female | 20 | 7 | |
| Tumor location (n) | 0.184 | ||
| Extremities | 79 | 27 | |
| Trunk | 15 | 7 | |
| Tumor size | 0.736 | ||
| >200 mL | 31 | 11 | |
| <200 mL | 41 | 17 | |
| CRP | 0.002 | ||
| Pathological | 35 | 19 | |
| Normal | 49 | 11 | |
| Monocyte count | 0.531 | ||
| Raised | 52 | 20 | |
| Normal | 42 | 14 | |
| Neutrophile count | 0.305 | ||
| Raised | 10 | 5 | |
| Normal | 84 | 29 | |
| Lymphocyte count | 0.467 | ||
| Raised | 6 | 3 | |
| Normal | 88 | 31 | |
| Haemoglobin | 0.955 | ||
| Low | 23 | 8 | |
| Normal | 71 | 26 | |
| LDH | 0.576 | ||
| Raised | 23 | 9 | |
| Normal | 66 | 23 | |
| ALP | 0.995 | ||
| Raised | 9 | 3 | |
| Normal | 85 | 31 | |
| NLR | 0.026 | ||
| Raised | 36 | 18 | |
| Normal | 58 | 16 | |
| PLR | 0.803 | ||
| Raised | 57 | 21 | |
| Normal | 37 | 13 | |
| Radiotherapy | 0.050 | ||
| Yes | 17 | 9 | |
| No | 77 | 25 | |
| Metastasis at diagnosis | 0.001 | ||
| Yes | 19 | 12 | |
| No | 75 | 22 |
| Variables | HR (95% CI) | p-Value (Log-Rank Test) |
|---|---|---|
| Metastasis ad diagnosis | 2.56 (1.13–5.55) | 0.024 |
| Radiotherapy | 1.86 (0.69–4.49) | 0.201 |
| Pathological CRP | 2.66 (1.23–6.01) | 0.012 |
| NRL | 1.72 (0.79–3.74) | 0.165 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Errani, C.; Traversari, M.; Cosentino, M.; Manfrini, M.; Basoli, S.; Tsukamoto, S.; Mavrogenis, A.F.; Bordini, B.; Donati, D.M. The Prognostic Value of the Serum Level of C-Reactive Protein for Survival of Children with Ewing’s Sarcoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051573
Errani C, Traversari M, Cosentino M, Manfrini M, Basoli S, Tsukamoto S, Mavrogenis AF, Bordini B, Donati DM. The Prognostic Value of the Serum Level of C-Reactive Protein for Survival of Children with Ewing’s Sarcoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(5):1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051573
Chicago/Turabian StyleErrani, Costantino, Matteo Traversari, Monica Cosentino, Marco Manfrini, Stefano Basoli, Shinji Tsukamoto, Andreas F. Mavrogenis, Barbara Bordini, and Davide Maria Donati. 2023. "The Prognostic Value of the Serum Level of C-Reactive Protein for Survival of Children with Ewing’s Sarcoma" Cancers 15, no. 5: 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051573
APA StyleErrani, C., Traversari, M., Cosentino, M., Manfrini, M., Basoli, S., Tsukamoto, S., Mavrogenis, A. F., Bordini, B., & Donati, D. M. (2023). The Prognostic Value of the Serum Level of C-Reactive Protein for Survival of Children with Ewing’s Sarcoma. Cancers, 15(5), 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051573









