EF-24, a Curcumin Analog, Inhibits Cancer Cell Invasion in Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through Transcriptional Suppression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Gene Expression
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. NPC Cell Culture and Reagents
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Wound Healing Assay
2.4. Cell Migration and Invasion Assay
2.5. Gelatin Zymography
2.6. Immunoblotting and Immunofluorescence
2.7. Quantitative PCR
2.8. Reporter Assay
2.9. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
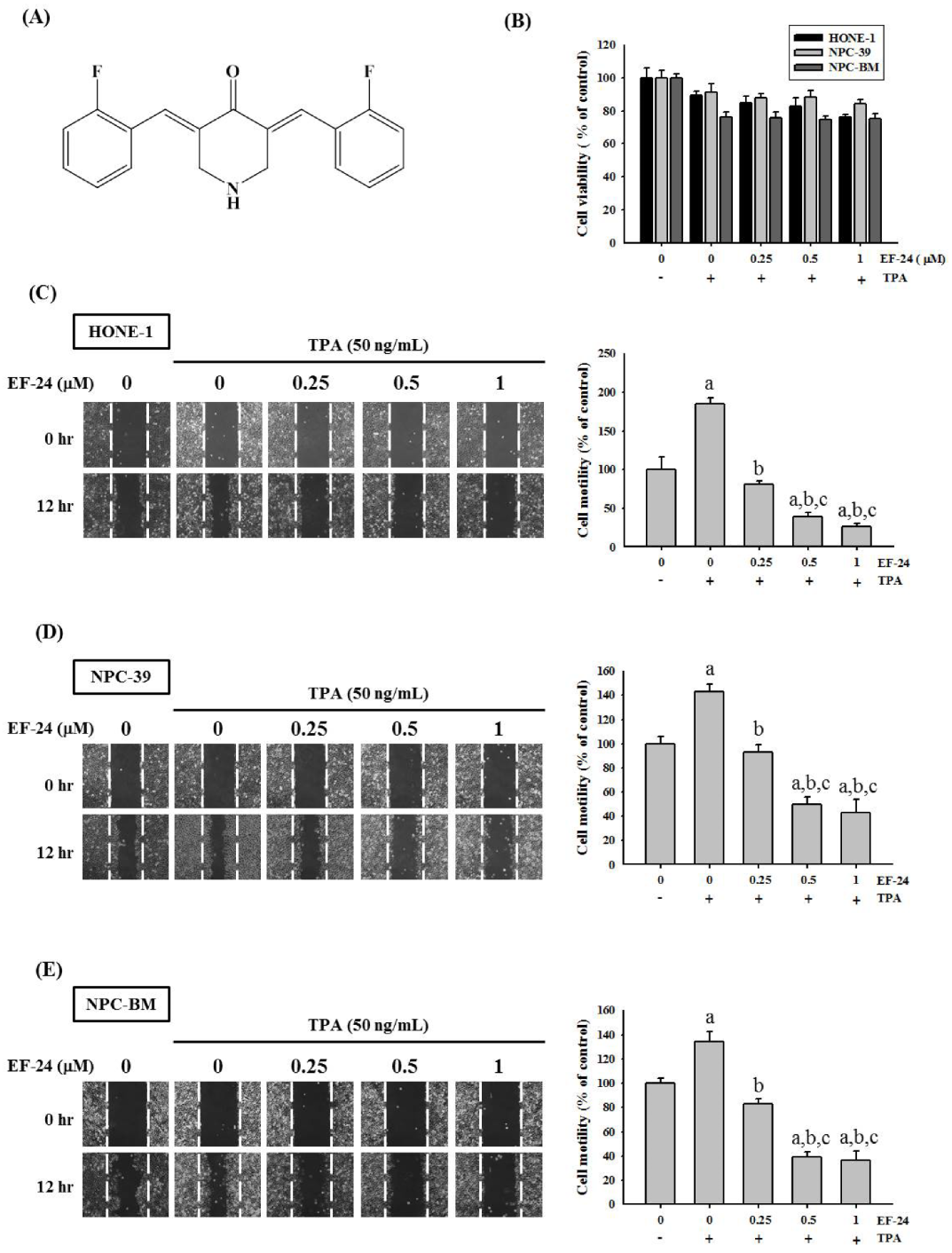
3.1. EF-24 Restricted Cell Motility and Invasion but Not Cell Viability in TPA-Induced NPC Cells
3.2. EF-24 Represses the Activity and Expression of MMP-9 in NPC
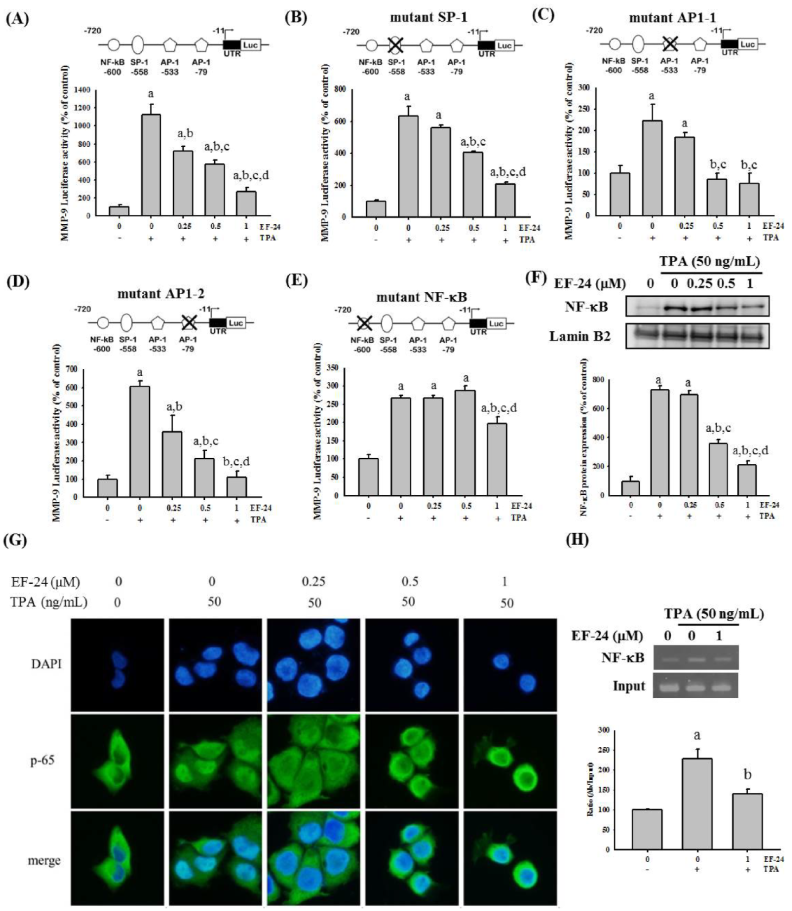
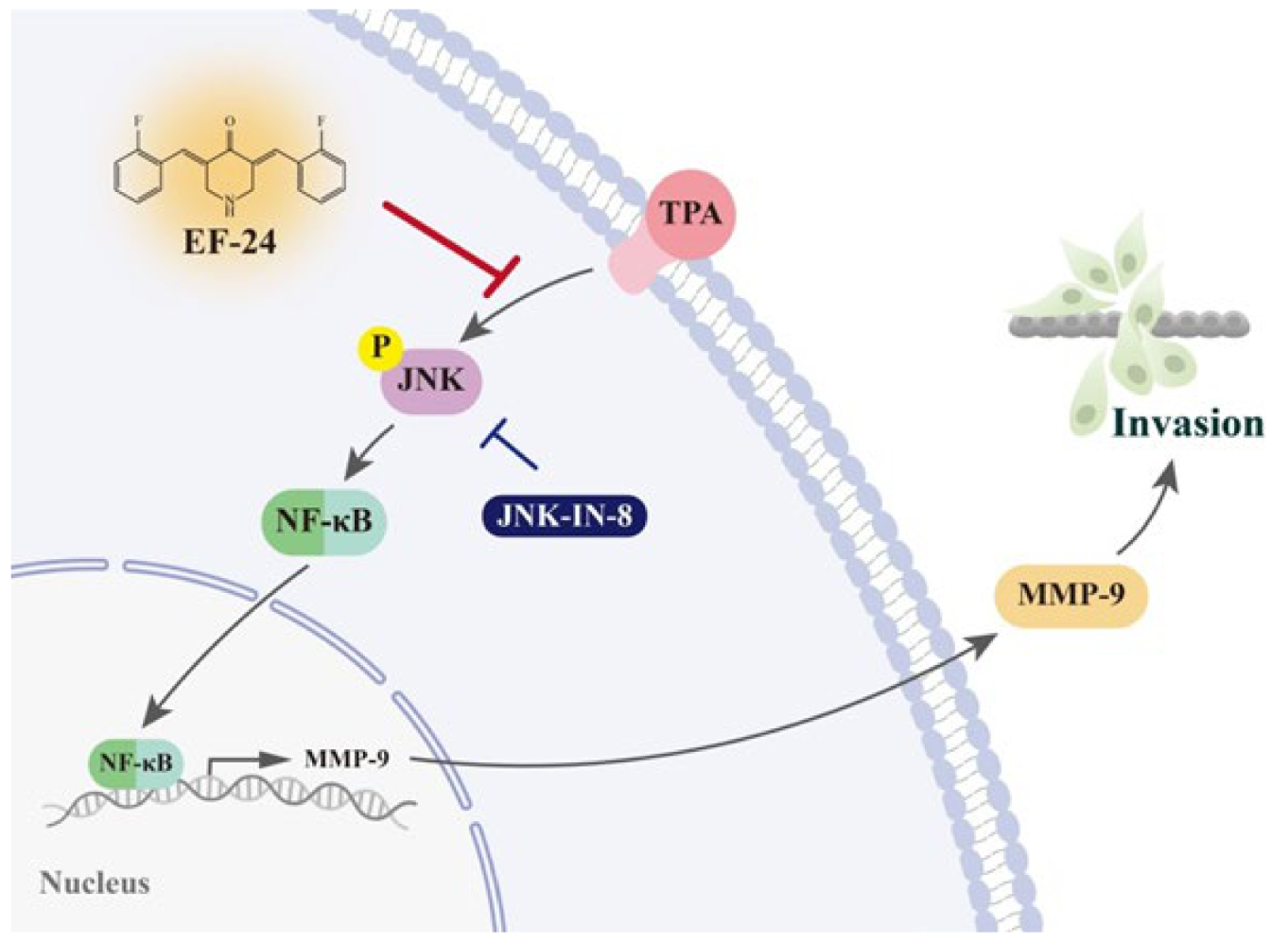
3.3. EF-24 Negatively Regulates the Transcription of MMP-9 Gene by Interfering with Nuclear Translocation of NF-κB
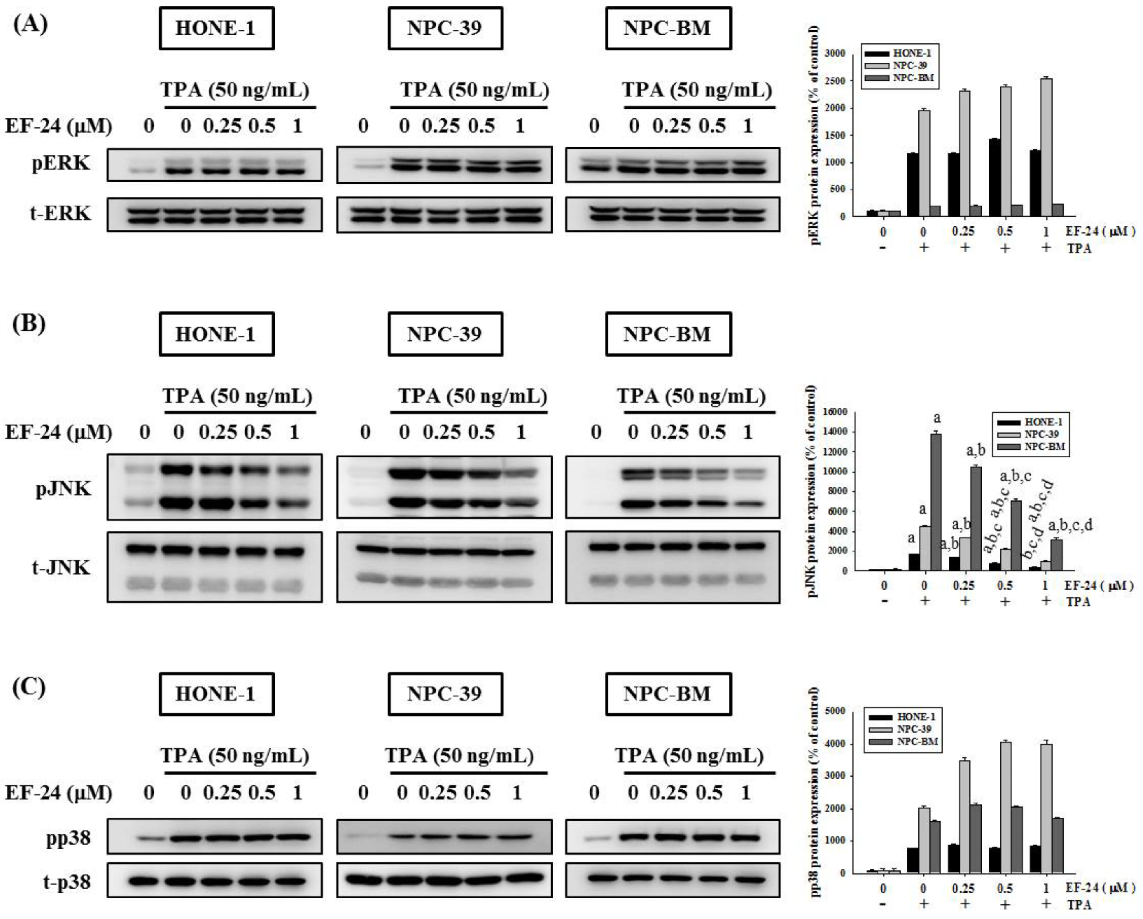
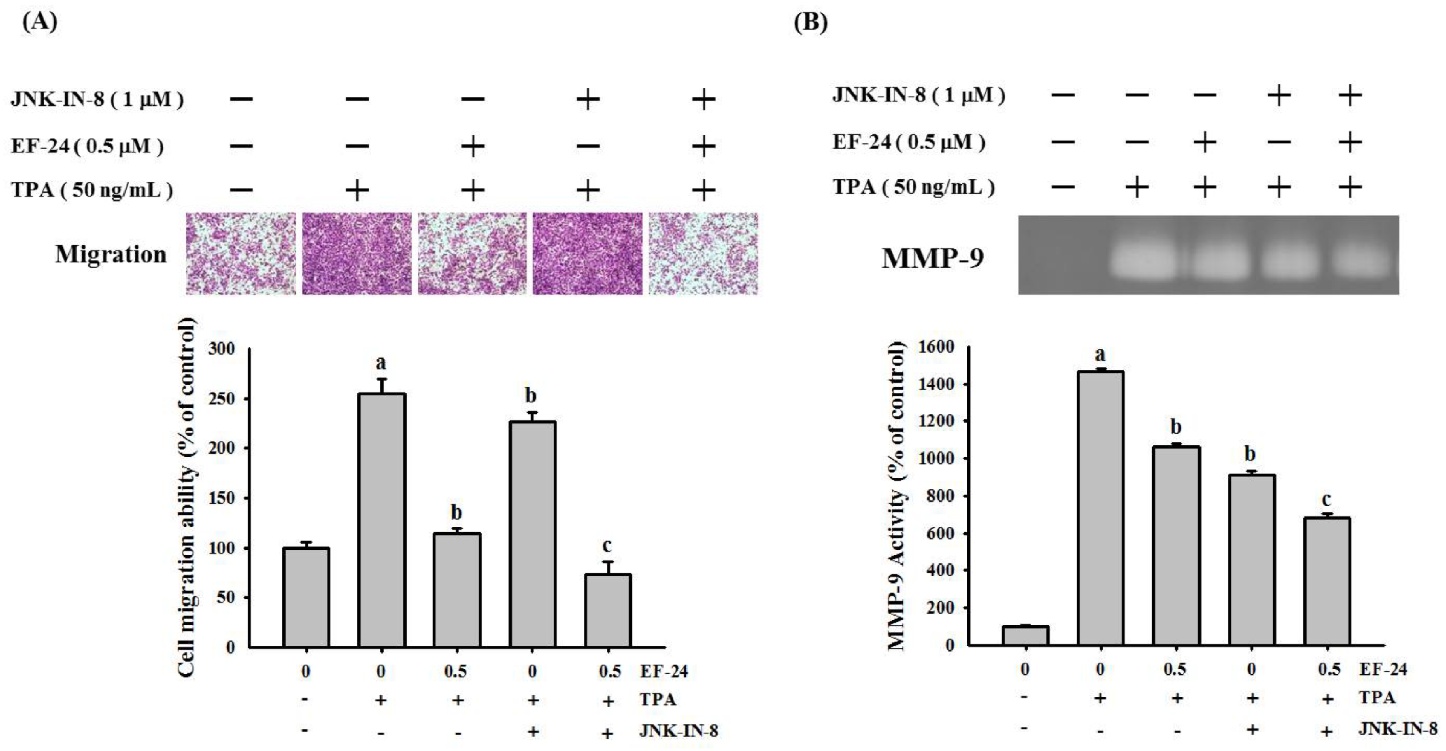
3.4. EF-24 Inhibits JNK Signaling Pathway in NPC Invasion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H.; Yin, X.; Mao, Y.; Chen, M.; Tang, Q.; Yan, S. The global burden of nasopharyngeal carcinoma from 2009 to 2019: An observational study based on the global burden of disease study 2019. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 1519–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, M.L.K.; Wee, J.T.S.; Hui, E.P.; Chan, A.T.C. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 2016, 387, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.N.; Luo, J.W.; Gao, L.; Yi, J.L.; Huang, X.D.; Wang, K.; Zhang, S.P.; Qu, Y.; Li, S.Y.; Cai, W.M.; et al. Clinical outcomes and patterns of failure after intensity-modulated radiotherapy for t4 nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, K.H.; Ngan, R.K.C.; Ng, A.W.Y.; Poon, D.M.C.; Ng, W.T.; Yuen, K.T.; Lee, V.H.F.; Tung, S.Y.; Chan, A.T.C.; Sze, H.C.K.; et al. Treatment outcomes of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in modern era after intensity modulated radiotherapy (imrt) in hong kong: A report of 3328 patients (hknpcsg 1301 study). Oral Oncol. 2018, 77, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razak, A.R.; Siu, L.L.; Liu, F.F.; Ito, E.; O’Sullivan, B.; Chan, K. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: The next challenges. Eur J. Cancer 2010, 46, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda, M.; den Hollander, P.; Kuburich, N.A.; Rosen, J.M.; Mani, S.A. Mechanisms of cancer metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 87, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.C.; Hsieh, M.J.; Yang, W.E.; Chung, W.H.; Reiter, R.J.; Yang, S.F. Cancer metastasis: Mechanisms of inhibition by melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 62, e12370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, J.A.; Pollard, J.W. Microenvironmental regulation of metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, A.F.; Groom, A.C.; MacDonald, I.C. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reymond, N.; d’Agua, B.B.; Ridley, A.J. Crossing the endothelial barrier during metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, J.; Fares, M.Y.; Khachfe, H.H.; Salhab, H.A.; Fares, Y. Molecular principles of metastasis: A hallmark of cancer revisited. Signal. Transduct Target. Ther 2020, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griner, E.M.; Kazanietz, M.G. Protein kinase c and other diacylglycerol effectors in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.E.; Skilton, G.; Alonso, D.F.; Kazanietz, M.G. The role of protein kinase c and novel phorbol ester receptors in tumor cell invasion and metastasis (review). Oncol. Rep. 1999, 6, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.; Benedetti, L.G.; Abera, M.B.; Wang, H.; Abba, M.; Kazanietz, M.G. Protein kinase c and cancer: What we know and what we do not. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5225–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.C.; Yeh, C.M.; Lin, C.W.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Chuang, C.Y.; Tang, C.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Yang, S.F. A novel melatonin-regulated lncrna suppresses tpa-induced oral cancer cell motility through replenishing prune2 expression. J. Pineal Res. 2021, 71, e12760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.M.; Lin, C.W.; Yang, J.S.; Yang, W.E.; Su, S.C.; Yang, S.F. Melatonin inhibits tpa-induced oral cancer cell migration by suppressing matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation through the histone acetylation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 21952–21967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.J.; Huang, S.Y.; Zhou, D.D.; Xiong, R.G.; Zhao, C.N.; Fang, A.P.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, H.B.; Zhu, H.L. Effects and mechanisms of curcumin for the prevention and management of cancers: An updated review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.H.; Lu, P.W.; Lin, C.W.; Yang, S.F. Curcumin in human osteosarcoma: From analogs to carriers. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.H.; Lu, P.W.; Lu, E.W.; Lin, C.W.; Yang, S.F. Curcumin and its analogs and carriers: Potential therapeutic strategies for human osteosarcoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 1241–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Newman, R.A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Bioavailability of curcumin: Problems and promises. Mol. Pharm 2007, 4, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghadani, R.; Naidu, R. Curcumin as an enhancer of therapeutic efficiency of chemotherapy drugs in breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khudhayer Oglah, M.; Fakri Mustafa, Y. Curcumin analogs: Synthesis and biological activities. Med. Chem. Res. 2020, 29, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, A.J.; Mirzaei, S.; Mahabady, M.K.; Hashemi, F.; Zabolian, A.; Hashemi, F.; Raee, P.; Aghamiri, S.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Aref, A.R.; et al. Curcumin and its derivatives in cancer therapy: Potentiating antitumor activity of cisplatin and reducing side effects. Phytother Res. 2022, 36, 189–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki Dizaj, S.; Alipour, M.; Dalir Abdolahinia, E.; Ahmadian, E.; Eftekhari, A.; Forouhandeh, H.; Rahbar Saadat, Y.; Sharifi, S.; Zununi Vahed, S. Curcumin nanoformulations: Beneficial nanomedicine against cancer. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 1156–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.W.; Hsieh, M.J.; Ju, P.C.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Su, C.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Yang, S.F.; Lin, C.W. Curcumin analog ho-3867 triggers apoptotic pathways through activating jnk1/2 signalling in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 2273–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, M.H.; Shih, P.C.; Ding, Y.F.; Chen, L.H.; Hsieh, F.K.; Tsai, M.Y.; Li, P.Y.; Lin, C.W.; Yang, S.F. Curcumin analog, go-y078, induces ho-1 transactivation-mediated apoptotic cell death of oral cancer cells by triggering mapk pathways and ap-1 DNA-binding activity. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2022, 26, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.W.; Chou, C.H.; Yang, J.S.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Tsai, M.Y.; Lu, K.H.; Yang, S.F. Ho-3867 induces apoptosis via the jnk signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.W.; Lin, R.C.; Yang, J.S.; Lu, E.W.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Tsai, M.Y.; Lu, K.H.; Yang, S.F. Go-y078, a curcumin analog, induces both apoptotic pathways in human osteosarcoma cells via activation of jnk and p38 signaling. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.K.; Ferstl, E.M.; Davis, M.C.; Herold, M.; Kurtkaya, S.; Camalier, R.F.; Hollingshead, M.G.; Kaur, G.; Sausville, E.A.; Rickles, F.R.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel curcumin analogs as anti-cancer and anti-angiogenesis agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 3871–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertazza, L.; Barollo, S.; Mari, M.E.; Faccio, I.; Zorzan, M.; Redaelli, M.; Rubin, B.; Armanini, D.; Mian, C.; Pezzani, R. Biological effects of ef24, a curcumin derivative, alone or combined with mitotane in adrenocortical tumor cell lines. Molecules 2019, 24, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasinski, A.L.; Du, Y.; Thomas, S.L.; Zhao, J.; Sun, S.Y.; Khuri, F.R.; Wang, C.Y.; Shoji, M.; Sun, A.; Snyder, J.P.; et al. Inhibition of ikappab kinase-nuclear factor-kappab signaling pathway by 3,5-bis(2-flurobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one (ef24), a novel monoketone analog of curcumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.L.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Lou, B.; Du, Y.; Purcell, J.; Snyder, J.P.; Khuri, F.R.; Liotta, D.; Fu, H. Activation of the p38 pathway by a novel monoketone curcumin analog, ef24, suggests a potential combination strategy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Ho, Y.C.; Lin, C.W.; Hsin, M.C.; Wang, P.H.; Tang, Y.C.; Yang, S.F.; Hsiao, Y.H. Ef-24 inhibits tpa-induced cellular migration and mmp-9 expression through the p38 signaling pathway in cervical cancer cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 38, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zheng, T.; Song, R.; Wang, J.; Yin, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Tian, L.; Fang, X.; Meng, X.; et al. Hypoxia-mediated sorafenib resistance can be overcome by ef24 through von hippel-lindau tumor suppressor-dependent hif-1alpha inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Ben, W.; Yang, Y.; Ning, N.; Lu, M.; Guan, Y. Therapeutic role of ef24 targeting glucose transporter 1-mediated metabolism and metastasis in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalova, R.; Zhelev, Z.; Shibata, S.; Nikolova, B.; Aoki, I.; Higashi, T. Impressive suppression of colon cancer growth by triple combination sn38/ef24/melatonin: "Oncogenic" versus "onco-suppressive" reactive oxygen species. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 5449–5458. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez Gaspar, V.; McMorrow, T. The curcuminoid ef24 in combination with trail reduces human renal cancer cell migration by decreasing mmp-2/mmp-9 activity through a reduction in h2o2. Int J. Mol. Sci 2023, 24, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.K.; Perng, Y.P.; Shen, Y.C.; Chung, P.J.; Chang, Y.S.; Wang, C.H. Chromosomal abnormalities of a new nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line (npc-bm1) derived from a bone marrow metastatic lesion. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1998, 103, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.H.; Su, S.C.; Lin, C.W.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Chien, M.H.; Reiter, R.J.; Yang, S.F. Melatonin attenuates osteosarcoma cell invasion by suppression of c-c motif chemokine ligand 24 through inhibition of the c-jun n-terminal kinase pathway. J. Pineal Res. 2018, 65, e12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.J.; Yeh, C.B.; Chiou, H.L.; Hsieh, M.C.; Yang, S.F. Dioscorea nipponica attenuates migration and invasion by inhibition of urokinase-type plasminogen activator through involving pi3k/akt and transcriptional inhibition of nf-[formula: See text]b and sp-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Su, C.W.; Wang, P.H.; Lu, Y.T.; Ho, Y.T.; Yang, S.F.; Hsin, C.H.; Lin, C.W. Dihydromyricetin inhibits cancer cell migration and matrix metalloproteinases-2 expression in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma through extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway. Environ. Toxicol 2022, 37, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.P.; Lin, C.W.; Huang, C.C.; Lu, Y.T.; Ho, Y.T.; Yang, S.F.; Hsin, C.H. Lipocalin 2 reduces met levels by inhibiting mek/erk signaling to inhibit nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell migration. Cancers 2022, 14, 5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.W.; Chou, Y.E.; Chiou, H.L.; Chen, M.K.; Yang, W.E.; Hsieh, M.J.; Yang, S.F. Pterostilbene suppresses oral cancer cell invasion by inhibiting mmp-2 expression. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 18, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.W.; Hua, K.T.; Kao, H.J.; Chi, C.C.; Wei, L.H.; Johansson, G.; Shiah, S.G.; Chen, P.S.; Jeng, Y.M.; Cheng, T.Y.; et al. H3k9 histone methyltransferase g9a promotes lung cancer invasion and metastasis by silencing the cell adhesion molecule ep-cam. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7830–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.T.; Tan, C.T.; Johansson, G.; Lee, J.M.; Yang, P.W.; Lu, H.Y.; Chen, C.K.; Su, J.L.; Chen, P.B.; Wu, Y.L.; et al. N-α-acetyltransferase 10 protein suppresses cancer cell metastasis by binding pix proteins and inhibiting cdc42/rac1 activity. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsin, M.C.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Wang, P.H.; Ko, J.L.; Hsin, I.L.; Yang, S.F. Hispolon suppresses metastasis via autophagic degradation of cathepsin s in cervical cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.Y.; Lin, C.W.; Chien, M.H.; Reiter, R.J.; Su, S.C.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Yang, S.F. Melatonin suppresses tpa-induced metastasis by downregulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression through jnk/sp-1 signaling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.W.; Chang, Y.C.; Chien, M.H.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Chen, M.K.; Lin, C.W.; Yang, S.F. Loss of timp3 by promoter methylation of sp1 binding site promotes oral cancer metastasis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barillari, G. The impact of matrix metalloproteinase-9 on the sequential steps of the metastatic process. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, K.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Daneshkhah, A.; Abolfathi, S.; Salari, N.; Mohammadi, M.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Shabani, S. Clinical effects of curcumin in enhancing cancer therapy: A systematic review. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Chakrabarti, J.; Banerji, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Das, B.R. Curcumin, a potential inhibitor of mmp-2 in human laryngeal squamous carcinoma cells hep2. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2006, 25, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.C.; Chen, G.W.; Lin, J.G.; Wu, L.T.; Chung, J.G. Curcumin inhibits cell migration of human colon cancer colo 205 cells through the inhibition of nuclear factor kappa b /p65 and down-regulates cyclooxygenase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-2 expressions. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Banerji, A.; Chakrabarti, J.; Mitra, A.; Chatterjee, A. Effect of curcumin on gelatinase a (mmp-2) activity in b16f10 melanoma cells. Cancer Lett 2004, 211, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.I.; Ke, Y.F.; Ko, Y.C.; Lin, J.K. Curcumin inhibits sk-hep-1 hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion in vitro and suppresses matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion. Oncology 1998, 55, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmeier, B.; Nerlich, A.G.; Iancu, C.M.; Cilli, M.; Schleicher, E.; Vene, R.; Dell’Eva, R.; Jochum, M.; Albini, A.; Pfeffer, U. The chemopreventive polyphenol curcumin prevents hematogenous breast cancer metastases in immunodeficient mice. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 19, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, W.; Hu, G.; Sun, H.; Kong, Q. Bioactivities of ef24, a novel curcumin analog: A review. Front. Oncol 2018, 8, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.L.; Zhong, D.; Zhou, W.; Malik, S.; Liotta, D.; Snyder, J.P.; Hamel, E.; Giannakakou, P. Ef24, a novel curcumin analog, disrupts the microtubule cytoskeleton and inhibits hif-1. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Noh, E.M.; Kwon, K.B.; Kim, J.S.; You, Y.O.; Hwang, J.K.; Hwang, B.M.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Curcumin suppresses the tpa-induced invasion through inhibition of pkcalpha-dependent mmp-expression in mcf-7 human breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.B.; Nabha, S.M.; Atanaskova, N. Role of map kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tu, C.; Ma, Y.; Ye, P.; Shao, X.; Yang, Z.; Fang, Y. Curcumin analog ef24 induces apoptosis and downregulates the mitogen activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated signaling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 4927–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.I.; Sham, J.S. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 2005, 365, 2041–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, S.-C.; Hsin, C.-H.; Lu, Y.-T.; Chuang, C.-Y.; Ho, Y.-T.; Yeh, F.-L.; Yang, S.-F.; Lin, C.-W. EF-24, a Curcumin Analog, Inhibits Cancer Cell Invasion in Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through Transcriptional Suppression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Gene Expression. Cancers 2023, 15, 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051552
Su S-C, Hsin C-H, Lu Y-T, Chuang C-Y, Ho Y-T, Yeh F-L, Yang S-F, Lin C-W. EF-24, a Curcumin Analog, Inhibits Cancer Cell Invasion in Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through Transcriptional Suppression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Gene Expression. Cancers. 2023; 15(5):1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051552
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Shih-Chi, Chung-Han Hsin, Yen-Ting Lu, Chun-Yi Chuang, Yu-Ting Ho, Fang-Ling Yeh, Shun-Fa Yang, and Chiao-Wen Lin. 2023. "EF-24, a Curcumin Analog, Inhibits Cancer Cell Invasion in Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through Transcriptional Suppression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Gene Expression" Cancers 15, no. 5: 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051552
APA StyleSu, S.-C., Hsin, C.-H., Lu, Y.-T., Chuang, C.-Y., Ho, Y.-T., Yeh, F.-L., Yang, S.-F., & Lin, C.-W. (2023). EF-24, a Curcumin Analog, Inhibits Cancer Cell Invasion in Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through Transcriptional Suppression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Gene Expression. Cancers, 15(5), 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051552





