Prognostic Impact of Metastatic Site in Patients Receiving First-Line Sorafenib Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of the Study
2.2. Baseline and Re-Evaluation
2.3. Management of Sorafenib
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
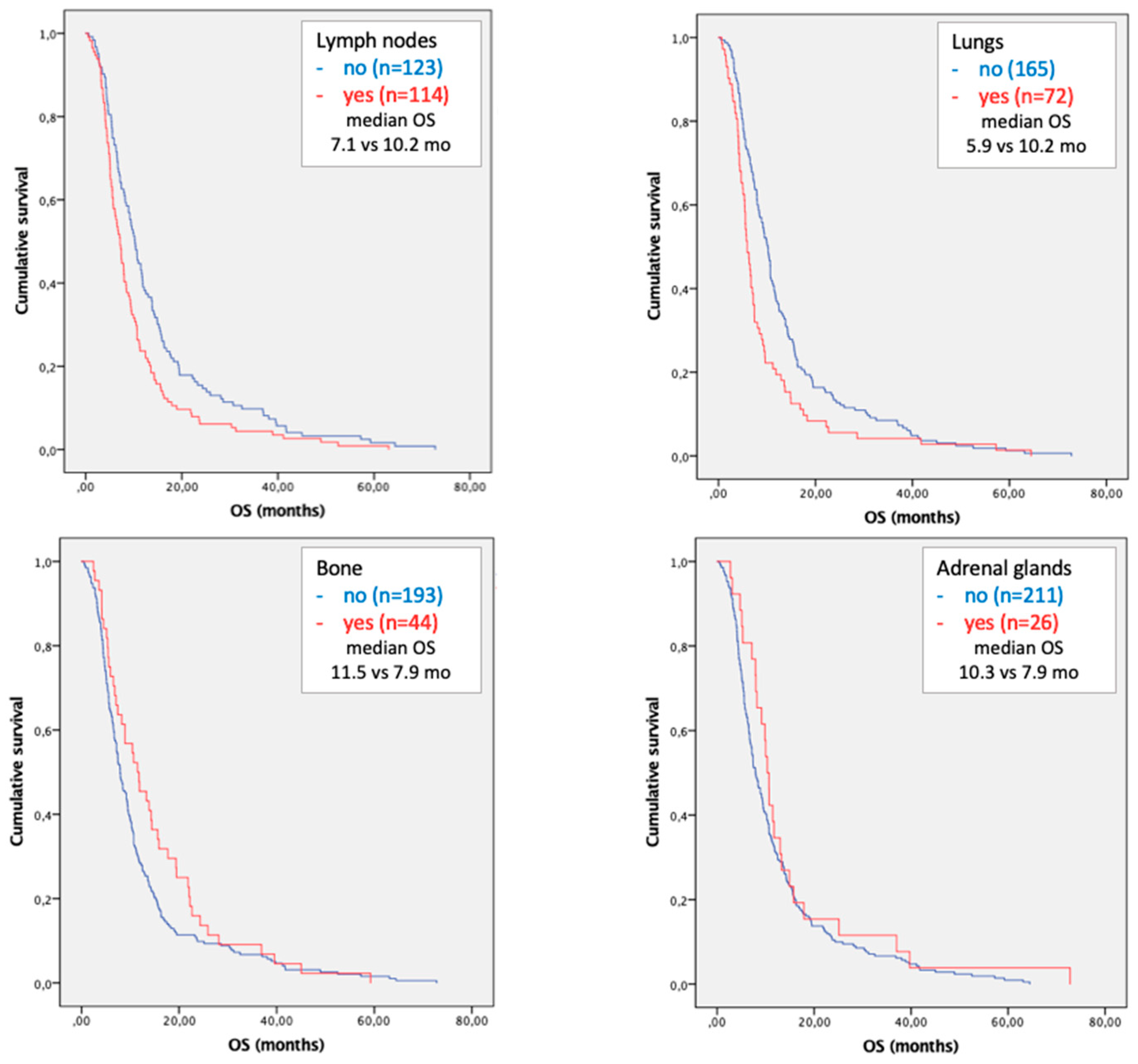
3.2. Survival Analysis
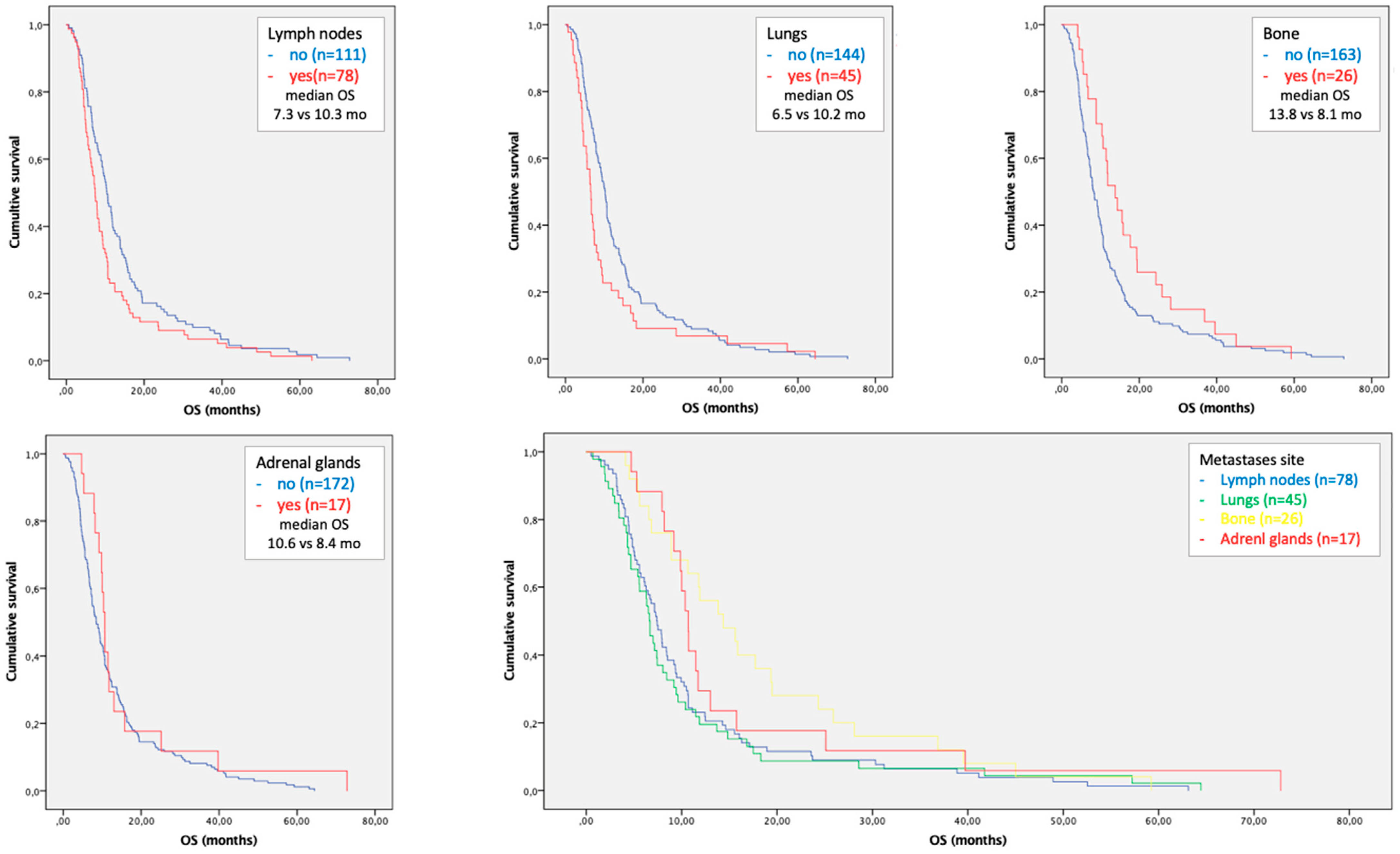
3.3. Subgroup Analysis in Patients with Single Site of Metastases
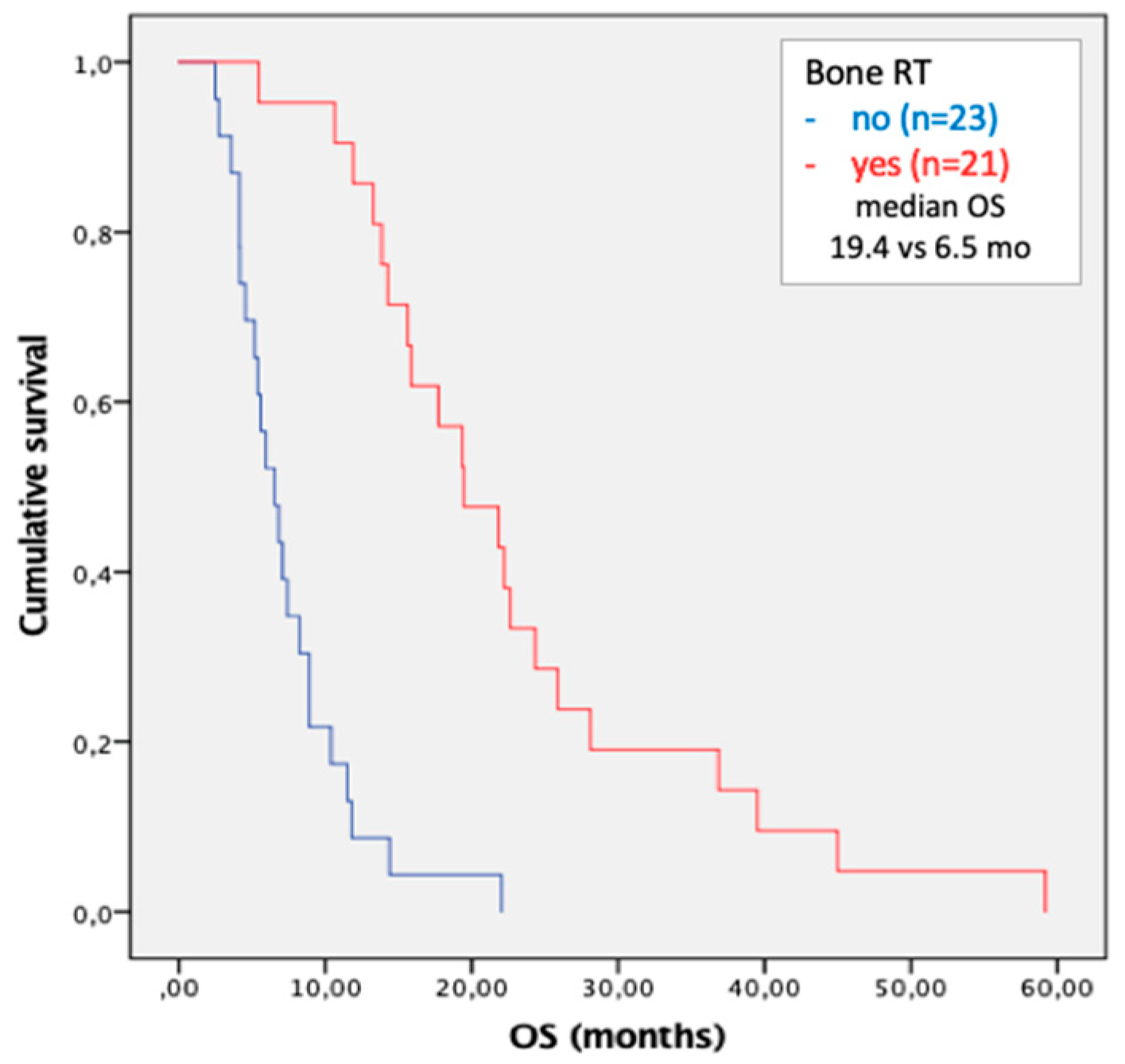
3.4. Metastases Focused Combination Treatments
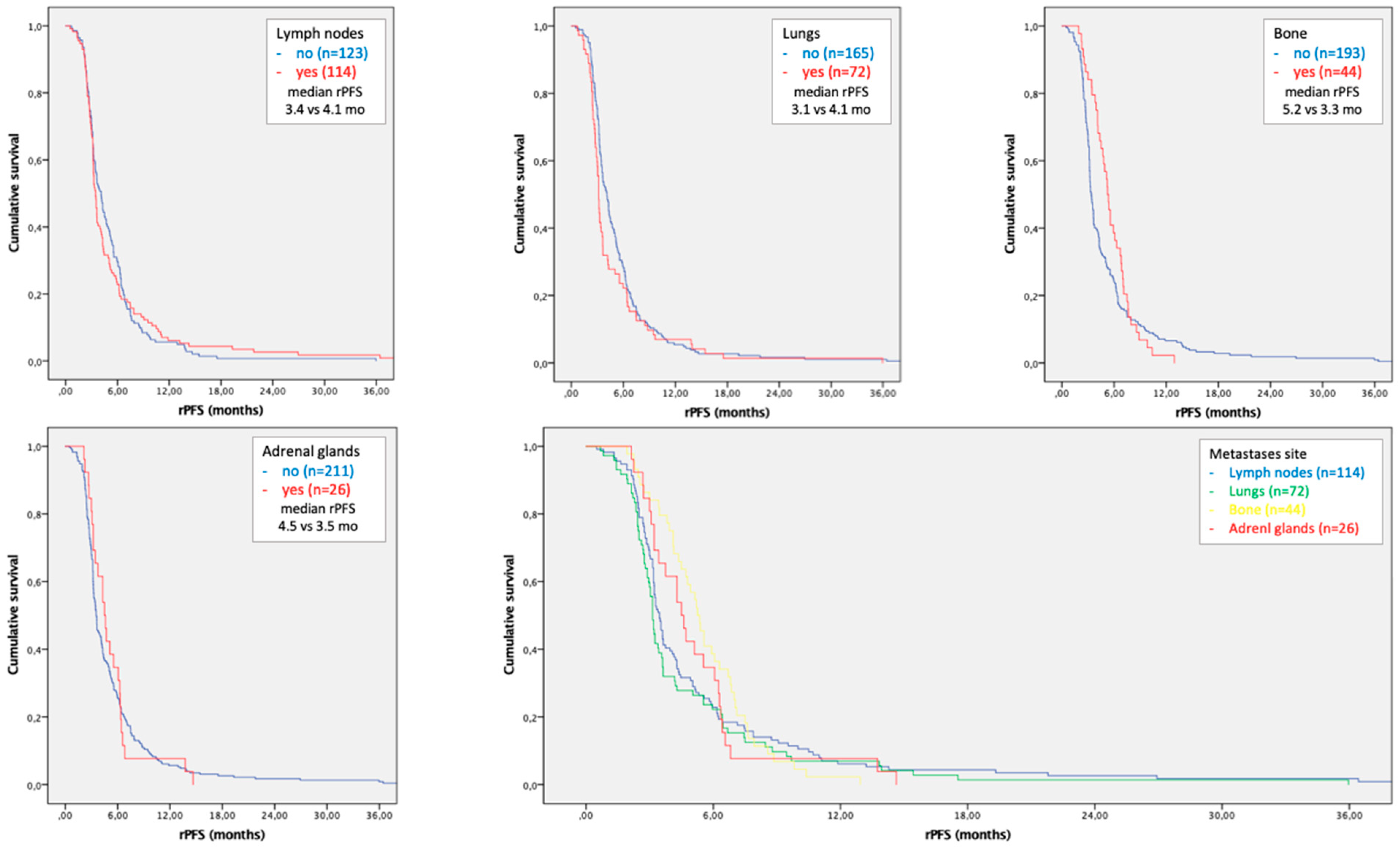
3.5. Time to Progression According to Site of Metastases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Kulik, L.M.; Finn, R.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Zhu, A.X.; Murad, M.H.; Marrero, J.A. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.-H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.-W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.-H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Meyer, T.; Cheng, A.-L.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Rimassa, L.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Cicin, I.; Merle, P.; Chen, Y.; Park, J.-W.; et al. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced and Progressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uka, K. Clinical features and prognosis of patients with extrahepatic metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlageter, M.; Quagliata, L.; Matter, M.; Perrina, V.; Tornillo, L.; Terracciano, L. Clinicopathological Features and Metastatic Pattern of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Autopsy Study of 398 Patients. Pathobiology 2016, 83, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iavarone, M.; Cabibbo, G.; Piscaglia, F.; Zavaglia, C.; Grieco, A.; Villa, E.; Cammà, C.; Colombo, M. Field-practice study of sorafenib therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective multicenter study in Italy. Hepatology 2011, 54, 2055–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovoli, F.; Ielasi, L.; Gardini, A.C.; Granito, A.; Foschi, F.G.; Rovesti, G.; Negrini, G.; Orsi, G.; Renzulli, M.; Piscaglia, F. Management of adverse events with tailored sorafenib dosing prolongs survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Cheng, A.L.; Meinhardt, G.; Nakajima, K.; De Sanctis, Y.; Llovet, J. Prognostic factors and predictors of sorafenib benefit in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis of two phase III studies. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, M.; Torres, F.; Rodriguez-Lope, C.; Forner, A.; Llarch, N.; Rimola, J.; Darnell, A.; Ríos, J.; Ayuso, C.; Bruix, J. Early dermatologic adverse events predict better outcome in HCC patients treated with sorafenib. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, V.; Tovoli, F.; Casadei-Gardini, A.; Di Costanzo, G.G.; Magini, G.; Sacco, R.; Pressiani, T.; Trevisani, F.; Rimini, M.; Tortora, R.; et al. Comparison of Prognostic Scores in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sorafenib. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2021, 12, e00286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.; Tanaka, M.; Kuromatsu, R.; Nagamatsu, H.; Tajiri, N.; Satani, M.; Niizeki, T.; Aino, H.; Okamura, S.; Iwamoto, H.; et al. Sorafenib for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with extrahepatic metastasis: A prospective multicenter cohort study. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. Assessment of Liver Function in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A New Evidence-Based Approach—The ALBI Grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, G.; Tovoli, F.; Dadduzio, V.; Vivaldi, C.; Brunetti, O.; Ielasi, L.; Conti, F.; Rovesti, G.; Gramantieri, L.; Rizzato, M.D.; et al. Prognostic Role of Blood Eosinophil Count in Patients with Sorafenib-Treated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Target. Oncol. 2020, 15, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lué, A.; Serrano, M.T.; Bustamante, F.J.; Iñarrairaegui, M.; Arenas, J.I.; Testillano, M.; Lorente, S.; Gil, C.; de la Torre, M.; Gomez, A.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts survival in European patients with hepatocellular carcinoma administered sorafenib. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 103077–103086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Cheng, B.B.; Ling, C. Prognostic Role of Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Different BCLC Stages: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterol Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 5670949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadei Gardini, A.; Faloppi, L.; De Matteis, S.; Foschi, F.G.; Silvestris, N.; Tovoli, F.; Palmieri, V.; Marisi, G.; Brunetti, O.; Umberto, V.-G.; et al. Metformin and insulin impact on clinical outcome in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma receiving sorafenib: Validation study and biological rationale. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 86, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ielasi, L.; Tovoli, F.; Tonnini, M.; Tortora, R.; Magini, G.; Sacco, R.; Pressiani, T.; Trevisani, F.; Sansone, V.; Marasco, G.; et al. Beneficial Prognostic Effects of Aspirin in Patients Receiving Sorafenib for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Tale of Multiple Confounders. Cancers 2021, 13, 6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Zhao, X.; Lu, Z.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, X. Correlation and Survival Analysis of Distant Metastasis Site and Prognosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 652768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.F.; Chong, S.W.; Huang, C.W.; Hsu, H.Y.; Pan, K.T.; Hung, C.F.; Wu, T.H.; Lee, C.W.; Hsieh, C.H.; Wang, C.T.; et al. Differential Response to Sorafenib Administration for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.I.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.; Jung, Y.J.; Chie, E.K. Role of radiotherapy in Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage C hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 37, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goio, E.; Ielasi, L.; Benevento, F.; Renzulli, M.; Tovoli, F. Long-lasting remission in a metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma patient after combined regorafenib therapy and surgery. Hepatic Oncol. 2020, 7, HEP24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Gaede, S.; Louie, A.V.; Haasbeek, C.; Mulroy, L.; Lock, M.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Yaremko, B.P.; et al. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for the Comprehensive Treatment of Oligometastatic Cancers: Long-Term Results of the SABR-COMET Phase II Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2830–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Park, S.; Rim, C.H.; Choi, C.; Seong, J. Improved oncologic outcomes by ablative radiotherapy in patients with bone metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielasi, L.; Stefanini, B.; Piscaglia, F.; Granito, A.; Tovoli, F. A Case of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Bone Metastases Managed with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Aggressive Palliative Radiation Therapy: Role of Combination Therapy for Extending Survival. Gastroenterol. Insights 2023, 14, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Forgione, A.; Marinelli, S.; Renzulli, M.; Ielasi, L.; Sansone, V.; Benevento, F.; Piscaglia, F.; Tovoli, F. Experience with regorafenib in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 17562848211016959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ielasi, L.; Sansone, V.; Granito, A.; Benevento, F.; De Lorenzo, S.; Tovoli, F. An update of treatments of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients refractory to sorafenib. Drugs Today 2018, 54, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ielasi, L.; Sansone, V.; Forgione, A.; Granito, A.; Benevento, F.; Tovoli, F. An update on atezolizumab for hepatocellular carcinoma. Drugs Today 2021, 57, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanini, B.; Bucci, L.; Santi, V.; Reggidori, N.; Rampoldi, D.; Lani, L.; Granito, A.; Sangiovanni, A.; Cabibbo, G.; Farinati, F.; et al. Potential feasibility of atezolizumab-bevacizumab therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with tyrosine-kinase inhibitors. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 54, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovoli, F.; Pallotta, D.P.; Sansone, V.; Iavarone, M.; De Giorgio, M.; Ielasi, L.; Di Costanzo, G.G.; Giuffrida, P.; Sacco, R.; Pressiani, T.; et al. Outcomes of Sorafenib for Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Liver Transplantation in the Era of Combined and Sequential Treatments. Transplantation 2023, 107, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimini, M.; Rimassa, L.; Ueshima, K.; Burgio, V.; Shigeo, S.; Tada, T.; Suda, G.; Yoo, C.; Cheon, J.; Pinato, D.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus lenvatinib or sorafenib in non-viral unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: An international propensity score matching analysis. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | EHS (n = 237) | All w/o EHS (n = 475) | p | BCLC-C w/o EHS (n = 311) | p | BCLC-B (n = 164) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex | 202 (85.2%) | 398 (83.8%) | 0.637 | 264 (84.9%) | 0.951 | 134 (85.2%) | 0.355 |
| Age | 67.6 ± 11.5 | 67.8 ± 9.8 | 0.825 | 66.7 ± 10.4 | 0.374 | 69.7 ± 11.5 | 0.056 |
| Viral etiology | 165 (69.6%) | 349 (73.5%) | 0.281 | 231 (74.3%) | 0.224 | 118 (69.6%) | 0.630 |
| Child-Pugh B | 11 (4.6%) | 47 (9.9%) | 0.014 | 40 (12.9%) | 0.001 | 7 (4.6%) | 0.792 |
| ALBI > 1 | 154 (65.0%) | 381 (80.2%) | <0.001 | 251 (80.7%) | <0.001 | 130 (65.0%) | 0.003 |
| AFP > 400 ng/mL | 76 (32.1%) | 156 (32.8%) | 0.841 | 116 (37.3%) | 0.209 | 40 (32.1%) | 0.115 |
| ITB > 50% | 69 (29.1%) | 149 (31.4%) | 0.545 | 106 (34.1%) | 0.245 | 43 (29.1%) | 0.628 |
| ECOG-PS > 0 | 60 (25.3%) | 126 (26.5%) | 0.743 | 126 (26.5%) | 0.743 | N.A. | - |
| MVI | 78 (32.9%) | 232 (48.8%) | <0.001 | 232 (48.8%) | <0.001 | N.A. | - |
| Variable | Yes (n = 114) | Lymph Nodes No (n = 123) | p | Yes (n = 72) | Lungs No (n = 165) | p |
| Male sex | 93 (81.5%) | 109 (88.6%) | 0.108 | 61 (84.7%) | 141 (85.4%) | 0.845 |
| Age | 67.7 ± 12.5 | 67.6 ± 10.6 | 0.955 | 66.7 ± 9.8 | 68.0 ± 12.2 | 0.436 |
| Viral etiology | 81 (71.0%) | 84 (68.2%) | 0.673 | 46 (63.8%) | 119 (72.1%) | 0.062 |
| Child-Pugh B | 5 (4.3%) | 6 (4.8%) | 1.000 | 5 (6.9%) | 6 (3.6%) | 0.316 |
| ALBI > 1 | 81 (71.0%) | 73 (59.3%) | 0.070 | 44 (61.1%) | 110 (66.6%) | 0.449 |
| AFP > 400 ng/mL | 36 (31.5%) | 40 (32.5%) | 0.890 | 24 (33.3%) | 52 (31.5%) | 0.880 |
| ITB > 50% | 33 (28.9%) | 36 (29.2) | 0.984 | 20 (27.7%) | 49 (29.6%) | 0.874 |
| ECOG-PS > 0 | 23 (20.1%) | 37 (30.0%) | 0.100 | 20 (27.7%) | 40 (24.2%) | 0.627 |
| MVI | 44 (38.5%) | 34 (27.6%) | 0.090 | 25 (34.7%) | 53 (32.1%) | 0.764 |
| Variable | Yes (n = 44) | Bone No (n = 193) | p | Yes (n = 26) | Adrenal Glands No (n = 211) | p |
| Male sex | 41 (93.1%) | 161 (83.4%) | 0.155 | 25 (96.1%) | 177 (83.8%) | 0.141 |
| Age | 68.4 ± 9.6 | 67.4 ± 11.9 | 0.618 | 67.3 ± 10.6 | 67.7 ± 11.7 | 0.867 |
| Viral etiology | 34 (77.2%) | 131 (67.8%) | 0.277 | 20 (76.9%) | 145 (68.7%) | 0.134 |
| Child-Pugh B | 3 (6.8%) | 8 (4.1%) | 0.433 | 1 (3.8%) | 10 (4.7%) | 1.000 |
| ALBI > 1 | 26 (59.0%) | 128 (66.3%) | 0.293 | 15 (57.6%) | 139 (65.8%) | 0.375 |
| AFP > 400 ng/mL | 16 (36.3%) | 60 (31.0%) | 0.592 | 7 (26.9%) | 69 (32.7%) | 0.659 |
| ITB > 50% | 10 (22.7%) | 59 (30.5) | 0.341 | 6 (23.0%) | 63 (29.8%) | 0.813 |
| ECOG-PS > 0 | 15 (34.0%) | 45 (23.3%) | 0.204 | 5 (19.2%) | 55 (26.0%) | 0.633 |
| MVI | 9 (20.4%) | 69 (35.7%) | 0.053 | 7 (26.9%) | 71 (33.6%) | 0.659 |
| Variable | Univariate HR (95% CI) | p | Multivariate HR (95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex | 1.089 (0.758–1.564) | 0.644 | ||
| Viral etiology | 0.918 (0.695–1.212) | 0.546 | ||
| Child-Pugh B | 3.615 (1.952–6.696) | <0.001 | 3.105 (1.538–6.268) | 0.002 |
| ALBI > 1 | 1.367 (1.038–1.801) | 0.026 | 1.216 (0.904–1.637) | 0.196 |
| AFP > 400 ng/mL | 1.478 (1.120–1.950) | 0.006 | 1.396 (1.033–1.887) | 0.030 |
| ITB > 50% | 1.550 (1.550–2.080) | 0.003 | 1.543 (1.130–2.109) | 0.006 |
| ECOG-PS > 0 | 1.552 (1.152–2.092) | 0.004 | 1.288 (0.926–1.791) | 0.133 |
| MVI | 2.014 (1.522–2.080) | <0.001 | 1.770 (1.301–2.409) | <0.001 |
| DAEs | 0.759 (0.579–0.971) | 0.029 | 0.755 (0.573–0.994) | 0.045 |
| Lymph nodes | 1.487 (1.149–1.925) | 0.003 | 1.545 (1.127–2.117) | 0.007 |
| Lungs | 1.569 (1.186–2.075) | 0.002 | 2.110 (1.484–2.999) | <0.001 |
| Bone | 0.759 (0.546–1.055) | 0.100 | ||
| Adrenal glands | 0.768 (0.506–1.164) | 0.213 | ||
| Multiple sites | 1.505 (1.0.91–2.075) | 0.013 | 1.041 (0.702–1.544) | 0.842 |
| Variable | Univariate HR (95% CI) | p | Multivariate HR (95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex | 1.079 (0.723–1.609) | 0.710 | ||
| Viral etiology | 0.921 (0.672–1.262) | 0.610 | ||
| Child-Pugh B | 5.356 (2.577–11.131) | <0.001 | 6.326 (2.696–14.843) | <0.001 |
| ALBI > 1 | 1.423 (1.045–1.939) | 0.025 | 1.291 (0.913–1.825) | 0.148 |
| AFP > 400 ng/mL | 1.500 (1.098–2.048) | 0.011 | 1.464 (1.046–2.049) | 0.026 |
| ITB > 50% | 1.580 (1.140–2.191) | 0.006 | 1.614 (1.130–2.307) | 0.009 |
| ECOG-PS > 0 | 1.587 (1.133–2.222) | 0.007 | 1.311 (0.905–1.898) | 0.152 |
| MVI | 1.963 (1.434–2.686) | <0.001 | 1.770 (1.251–2.503) | 0.001 |
| DAEs | 0.780 (0.584–1.042) | 0.093 | 0.755 (0.573–0.994) | 0.045 |
| Lymph nodes | 1.411 (1.054–1.890) | 0.021 | 1.645 (1.078–2.509) | 0.021 |
| Lungs | 1.431 (1.018–2.013) | 0.039 | 2.182 (1.331–3.578) | 0.002 |
| Bone | 0.663 (0.440–0.998) | 0.049 | 1.018 (0.586–1.766) | 0.950 |
| Adrenal glands | 0.727 (0.434–1.218) | 0.226 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ielasi, L.; Tovoli, F.; Tonnini, M.; Stefanini, B.; Tortora, R.; Magini, G.; Sacco, R.; Pressiani, T.; Trevisani, F.; Garajová, I.; et al. Prognostic Impact of Metastatic Site in Patients Receiving First-Line Sorafenib Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051523
Ielasi L, Tovoli F, Tonnini M, Stefanini B, Tortora R, Magini G, Sacco R, Pressiani T, Trevisani F, Garajová I, et al. Prognostic Impact of Metastatic Site in Patients Receiving First-Line Sorafenib Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(5):1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051523
Chicago/Turabian StyleIelasi, Luca, Francesco Tovoli, Matteo Tonnini, Bernardo Stefanini, Raffaella Tortora, Giulia Magini, Rodolfo Sacco, Tiziana Pressiani, Franco Trevisani, Ingrid Garajová, and et al. 2023. "Prognostic Impact of Metastatic Site in Patients Receiving First-Line Sorafenib Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 15, no. 5: 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051523
APA StyleIelasi, L., Tovoli, F., Tonnini, M., Stefanini, B., Tortora, R., Magini, G., Sacco, R., Pressiani, T., Trevisani, F., Garajová, I., Piscaglia, F., & Granito, A. (2023). Prognostic Impact of Metastatic Site in Patients Receiving First-Line Sorafenib Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 15(5), 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051523









