Favorable Conditions for the Detection of EGFR T790M Mutation Using Plasma Sample in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
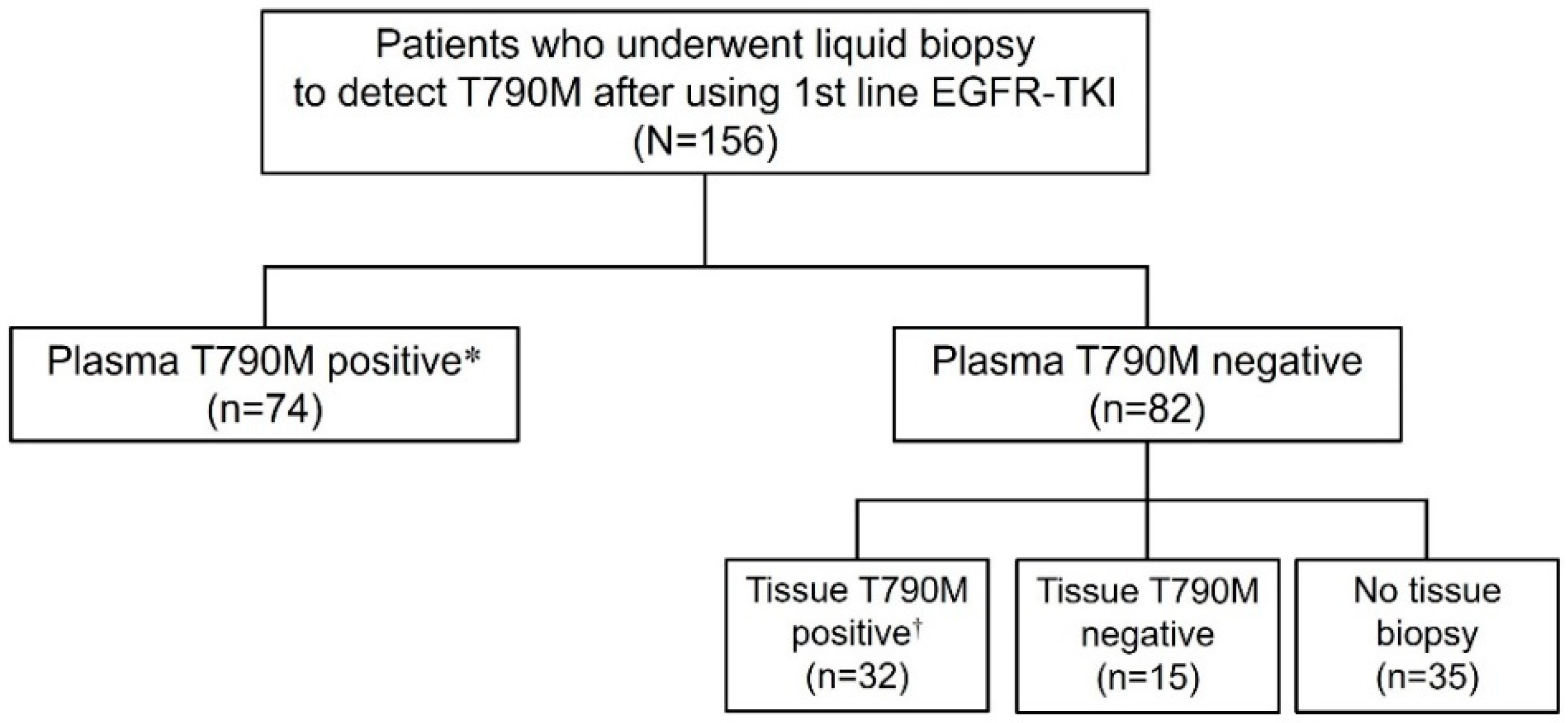
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Groups
2.3. Tissue Acquisition Methods
2.4. T790M-Resistant Mutation Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Participants
3.2. EGFR Mutation Status on Secondary Biopsy
3.3. Treatment-Related Parameters
3.4. Reassessment of Clinical Stage and Metastatic Organs
3.5. Favorable Factors for T790M Mutation Detection Using Plasma Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Economopoulou, P.; Mountzios, G. The emerging treatment landscape of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, L.A. Update on liquid biopsy in clinical management of non-small cell lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 5097–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Mok, T.S.; Han, J.Y.; Ahn, M.J.; Delmonte, A.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Kim, S.W.; Shepherd, F.A.; Laskin, J.; He, Y.; et al. Osimertinib versus platinum-pemetrexed for patients with EGFR T790M advanced NSCLC and progression on a prior EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor: AURA3 overall survival analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.J.; Cardarella, S.; Lydon, C.A.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Jackman, D.M.; Janne, P.A.; Johnson, B.E. Five-Year Survival in EGFR-Mutant Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma Treated with EGFR-TKIs. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.G.; Shih, J.Y. Management of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.C.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, E.K.; Lee, Y.G.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, G.W.; Lee, J.S.; et al. A Phase 1/2 Study of Lazertinib 240 mg in Patients with Advanced EGFR T790M-Positive NSCLC after Previous EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, F.; Kimura, M.; Yano, Y.; Mori, M.; Suzuki, H.; Hirashima, T.; Ihara, S.; Komuta, K.; Shiroyama, T.; Nagatomo, I.; et al. Real-world osimertinib for EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer with acquired T790M mutation. Future Oncol. 2020, 16, 1537–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.J.; Chang, J.W.; Chang, C.F.; Huang, C.Y.; Yang, C.T.; Kuo, C.S.; Fang, Y.F.; Hsu, P.C.; Wu, C.E. Impact of T790M Mutation Status on Later-Line Osimertinib Treatment in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Cancers 2022, 14, 5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uozu, S.; Imaizumi, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Goto, Y.; Kawada, K.; Minezawa, T.; Okamura, T.; Akao, K.; Hayashi, M.; Isogai, S.; et al. Feasibility of tissue re-biopsy in non-small cell lung cancers resistant to previous epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapies. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Shaw, A.T. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (Version 1.2023). 2023. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Kim, H.; Chae, K.J.; Yoon, S.H.; Kim, M.; Keam, B.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, D.W.; Goo, J.M.; Park, C.M. Repeat biopsy of patients with acquired resistance to EGFR TKIs: Implications of biopsy-related factors on T790M mutation detection. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosaki, K.; Satouchi, M.; Kurata, T.; Yoshida, T.; Okamoto, I.; Katakami, N.; Imamura, F.; Tanaka, K.; Yamane, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Re-biopsy status among non-small cell lung cancer patients in Japan: A retrospective study. Lung Cancer 2016, 101, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, K.; Miura, S.; Watanabe, S.; Shoji, S.; Koshio, J.; Hayashi, Y.; Ishikawa, D.; Sato, K.; Miyabayashi, T.; Okajima, M.; et al. Observational study of rebiopsy in EGFR-TKI-resistant patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced NSCLC. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochmair, M.J.; Buder, A.; Schwab, S.; Burghuber, O.C.; Prosch, H.; Hilbe, W.; Cseh, A.; Fritz, R.; Filipits, M. Liquid-Biopsy-Based Identification of EGFR T790M Mutation-Mediated Resistance to Afatinib Treatment in Patients with Advanced EGFR Mutation-Positive NSCLC, and Subsequent Response to Osimertinib. Target. Oncol. 2019, 14, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Nagakura, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Kubo, S.; Tanaka, K.; Watanabe, K.; Horita, N.; Hara, Y.; Nishikawa, M.; Miura, K.; et al. Liquid biopsy for detecting epidermal growth factor receptor mutation among patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with afatinib: A multicenter prospective study. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueoka-Aragane, N.; Sato, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Ide, M.; Yokoo, M.; Nagano, Y.; Sueoka, E.; Okada, S.; Kimura, S. Correlation between plasma DNA and tumor status in an animal model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulivi, P.; Petracci, E.; Canale, M.; Priano, I.; Capelli, L.; Calistri, D.; Chiadini, E.; Cravero, P.; Rossi, A.; Delmonte, A.; et al. Liquid Biopsy for EGFR Mutation Analysis in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: Thoughts Drawn from a Real-Life Experience. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Tan, D.; Yang, J.C.; Ahn, M.J.; Batra, U.; Cho, B.C.; Cornelio, G.; Lim, T.; Mok, T.; Prabhash, K.; et al. Expert consensus recommendations on biomarker testing in metastatic and non-metastatic non-small cell lung cancer in Asia. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.S.; Chung, J.H.; Kim, L.; Chang, S.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, G.K.; Jung, S.H.; Jang, S.J. Guideline Recommendations for EGFR Mutation Testing in Lung Cancer: Proposal of the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group. Korean J. Pathol. 2013, 47, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindeman, N.I.; Cagle, P.T.; Aisner, D.L.; Arcila, M.E.; Beasley, M.B.; Bernicker, E.H.; Colasacco, C.; Dacic, S.; Hirsch, F.R.; Kerr, K.; et al. Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment with Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Guideline From the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the Association for Molecular Pathology. J. Mol. Diagn. JMD 2018, 20, 129–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Overall Group (N = 106) | Plasma Positive Group (n = 74) | Plasma False Negative Group (n = 32) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 67 ± 10 | 68 ± 9 | 65 ± 13 | 0.191 |
| Male gender | 57 (54) | 37 (50) | 20 (63) | 0.331 |
| ECOG performance status | 0.768 | |||
| 0 | 60 (56) | 42 (57) | 18 (56) | |
| 1 | 42 (40) | 28 (38) | 14 (44) | |
| ≥2 | 4 (4) | 4 (5) | 0 (0) | |
| Smoking status | 0.626 | |||
| Never smoker | 65 (61) | 47 (64) | 18 (56) | |
| Ever smoker | 41 (39) | 27 (36) | 14 (44) | |
| EGFR mutation status | 0.601 | |||
| 19del | 62 (58) | 45 (60) | 17 (53) | |
| L858R | 44 (42) | 29 (40) | 15 (47) | |
| Initial stage * | 0.001 | |||
| I | 5 (5) | 3 (4) | 2 (6) | |
| II | 2 (2) | 2 (3) | 0 (0) | |
| III | 15 (14) | 7 (9) | 8 (25) | |
| IV | 84 (79) | 62 (84) | 22 (69) |
| Plasma Positive Group (n = 74) | Plasma False Negative Group (n = 32) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 19del + T790M | 46 (47) | Wild type | 18 (28) |
| L858R + T790M | 30 (31) | 19del + T790M | 17 (27) |
| 19del | 9 (9) | L858R + T790M | 15 (23) |
| L858R | 6 (6) | 19del | 8 (13) |
| T790M | 4 (4) | L858R | 6 (9) |
| Wild type | 1 (1) | ||
| 9del + L858R + T790M | 1 (1) | ||
| L861Q + T790M | 1 (1) |
| Plasma Positive Group (n = 74) | Plasma False Negative Group (n = 32) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial TKI | 0.361 | ||
| Gefitinib | 22 (29) | 7 (22) | |
| Erlotinib | 10 (14) | 2 (6) | |
| Afatinib | 42 (57) | 23 (72) | |
| Duration of first TKI, months | 19 ± 14 | 24 ± 22 | 0.179 |
| First response to initial TKI * | 0.834 | ||
| Partial response | 42 (57) | 19 (59) | |
| Stable disease | 32 (43) | 13 (41) | |
| Best response to initial TKI * | 0.440 | ||
| Partial response | 43 (58) | 19 (59) | |
| Stable disease | 31 (42) | 13 (41) |
| Plasma Positive Group (n = 74) | Plasma False Negative Group (n = 32) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T stage | 0.630 | ||
| 0 | 6 (8) | 3 (9) | |
| 1 | 14 (19) | 5 (16) | |
| 2 | 21 (28) | 10 (31) | |
| 3 | 7 (10) | 6 (19) | |
| 4 | 26 (35) | 8 (25) | |
| N stage | 0.685 | ||
| 0 | 18 (24) | 7 (22) | |
| 1 | 8 (11) | 4 (12) | |
| 2 | 19 (26) | 5 (16) | |
| 3 | 29 (39) | 16 (50) | |
| M stage | 0.239 | ||
| 0 | 4 (5) | 4 (13) | |
| 1 | 70 (95) | 28 (87) | |
| Clinical stage | 0.239 | ||
| III | 4 (5) | 4 (13) | |
| IV | 70 (95) | 28 (87) | |
| Number of metastatic organs | 0.028 | ||
| 1 | 8 (11) | 2 (6) | |
| 2 | 15 (20) | 10 (30) | |
| 3 | 24 (32) | 13 (38) | |
| ≥4 | 27 (37) | 5 (15) |
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Sex, female | 0.60 (0.25–1.39) | 0.238 | 0.67 (0.24–1.81) | 0.427 |
| Age, years | 1.03 (0.99–1.08) | 0.135 | 1.03 (0.99–1.08) | 0.197 |
| Smoking status, ever smoker | 0.74 (0.32–1.73) | 0.482 | ||
| Pleural effusion, yes | 0.66 (0.28–1.58) | 0.342 | ||
| Histologic type, non-squamous | 0.76 (0.04–6.23) | 0.818 | ||
| Metastatic organs ≥ 3 at initial diagnosis, yes | 3.30 (1.28–9.72) | 0.019 | 3.71 (1.38–11.50) | 0.014 |
| Metastatic organs ≥ 3 at re-biopsy, yes | 1.72 (0.73–4.06) | 0.211 | 1.97 (0.80–4.87) | 0.139 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, I.; Seol, H.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, M.-H.; Lee, M.K.; Eom, J.S. Favorable Conditions for the Detection of EGFR T790M Mutation Using Plasma Sample in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051445
Kim I, Seol HY, Kim SH, Kim M-H, Lee MK, Eom JS. Favorable Conditions for the Detection of EGFR T790M Mutation Using Plasma Sample in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(5):1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051445
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Insu, Hee Yun Seol, Soo Han Kim, Mi-Hyun Kim, Min Ki Lee, and Jung Seop Eom. 2023. "Favorable Conditions for the Detection of EGFR T790M Mutation Using Plasma Sample in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 5: 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051445
APA StyleKim, I., Seol, H. Y., Kim, S. H., Kim, M.-H., Lee, M. K., & Eom, J. S. (2023). Favorable Conditions for the Detection of EGFR T790M Mutation Using Plasma Sample in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers, 15(5), 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051445






