HNRNPA2B1-Mediated MicroRNA-92a Upregulation and Section Acts as a Promising Noninvasive Diagnostic Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Meta-Analysis and Statistical Analysis
2.2. Recruitment of Volunteers for Prospective Studies
2.3. MiRNA Extraction and qPCR in Stool Samples
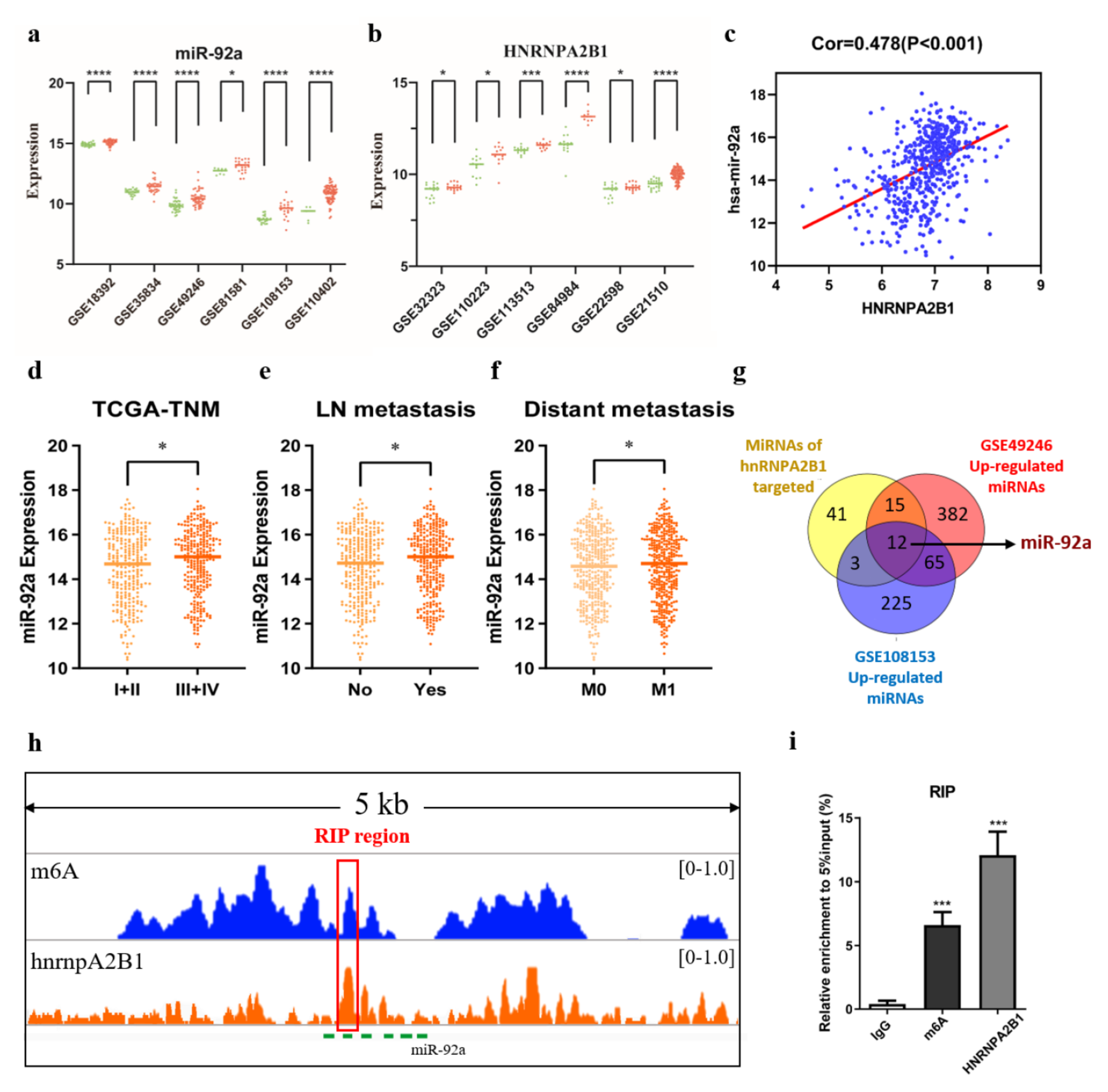
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis of CRC Datasets
2.5. Cell Culture In Vitro
2.6. m6A RNA Methylation Assay
2.7. RNA Immunoprecipitation Assay
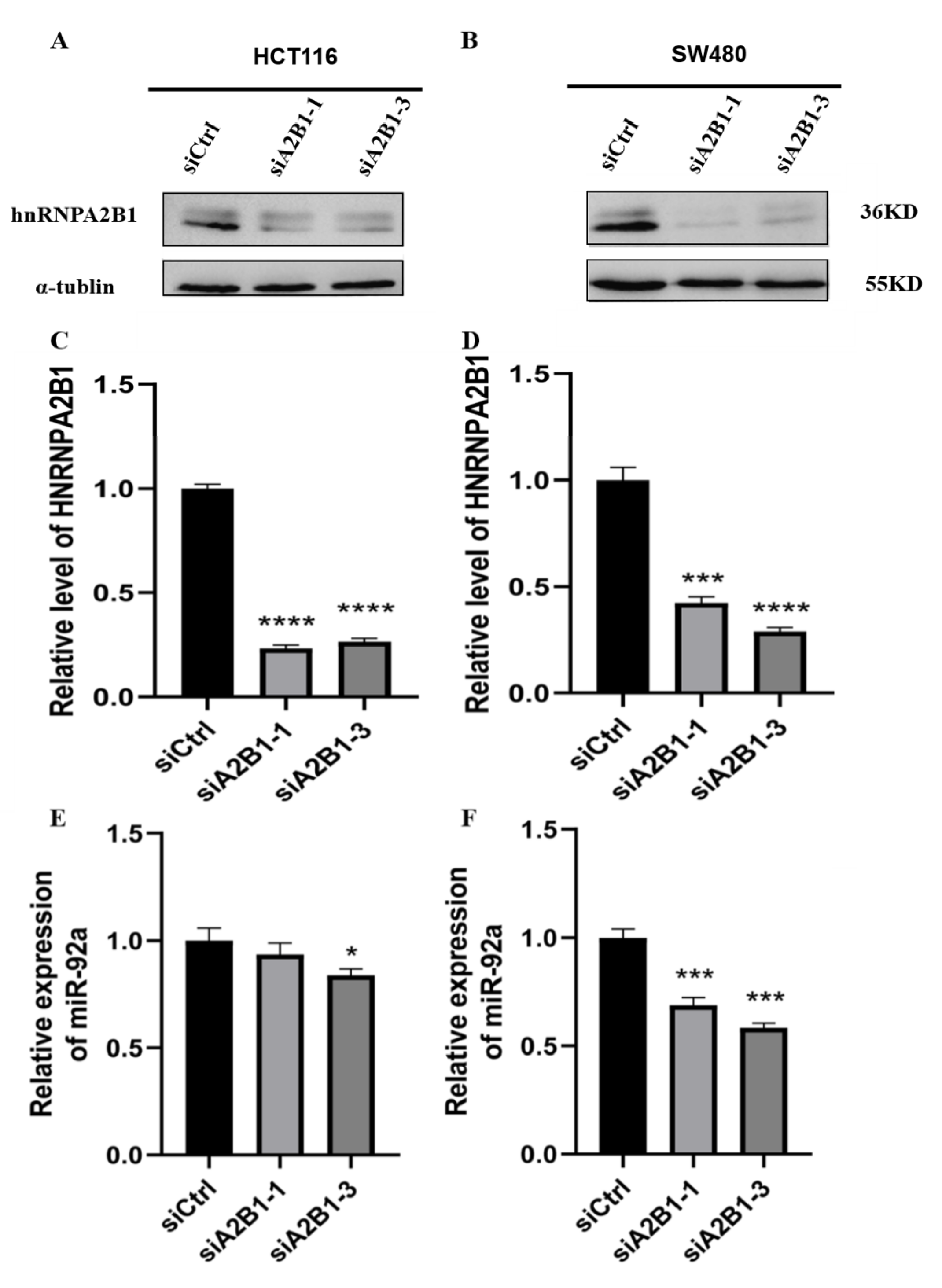
2.8. SiRNA Transfection
2.9. Secreting miRNA Isolation
2.10. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and RT-qPCR
2.11. Western Blot Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MiR-92a Was Differentially Expressed among Tissue, Blood, and Stool Sample Types in CRC
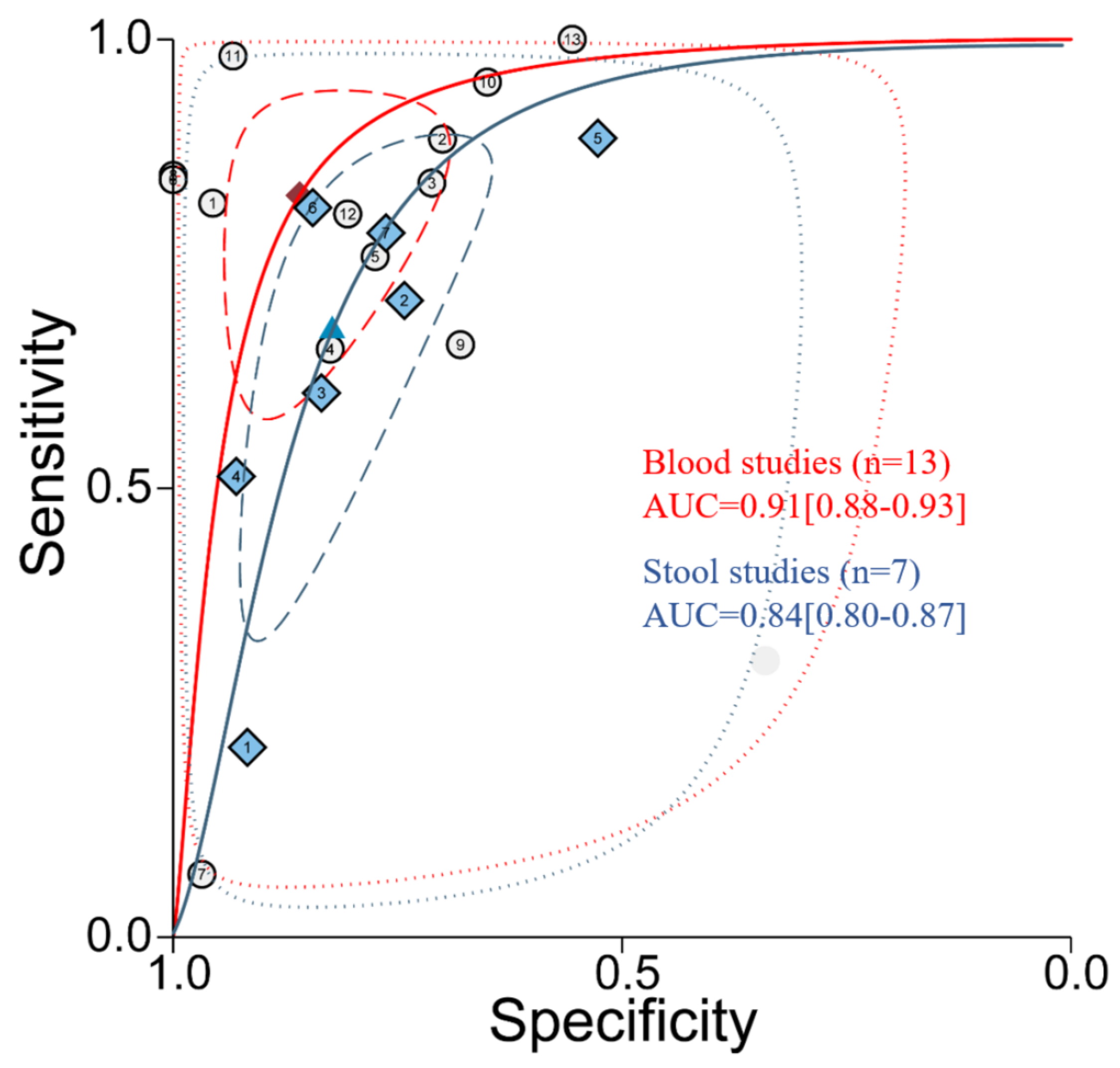
3.2. Diagnostic Accuracy of miR-92a Based on Plasma/Serum Appears Better than Stool Samples
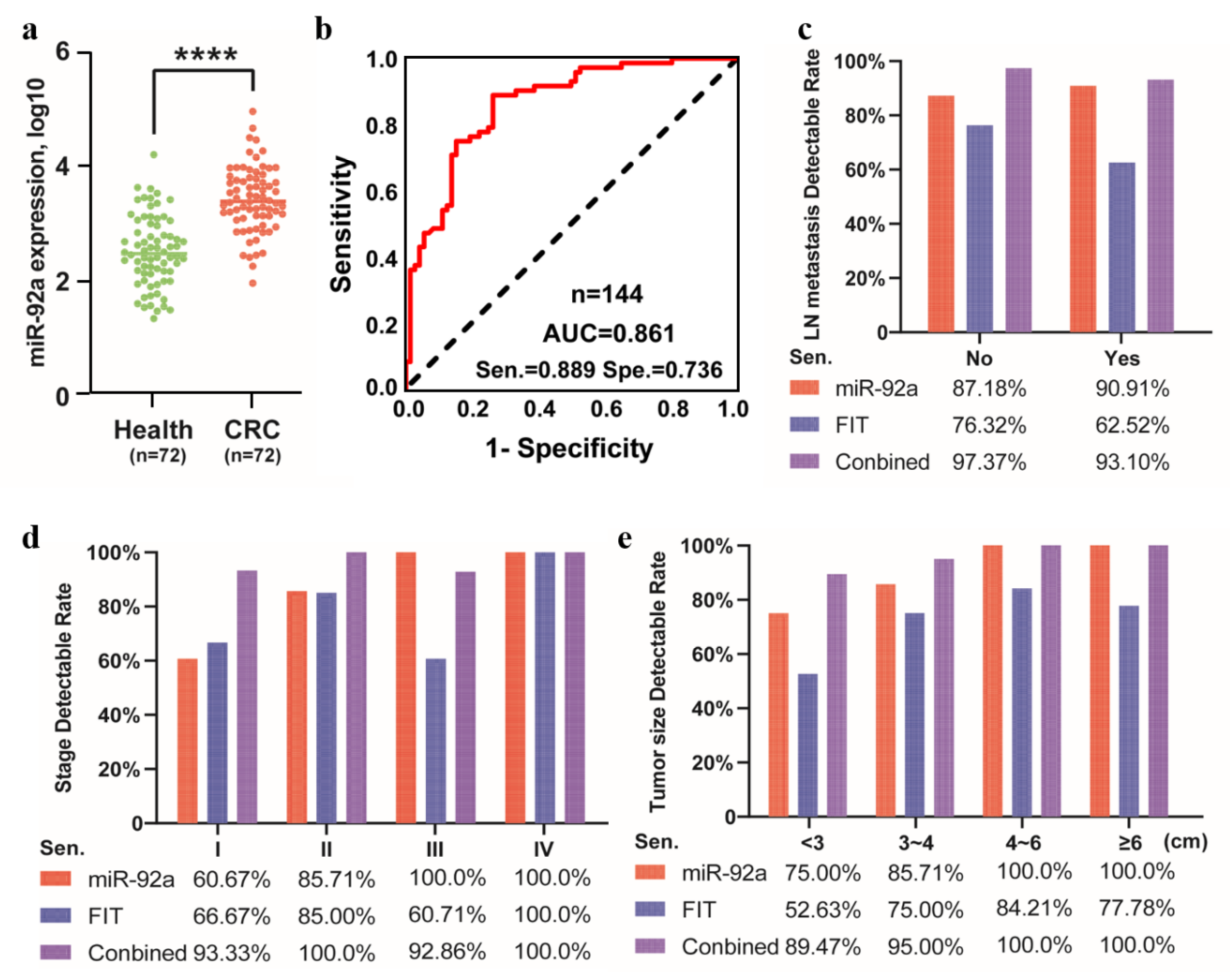
3.3. MiR-92a as a Potential Biomarker in the Independent Prospective Data from Stool Samples
3.4. HNRNPA2B1 May Regulate miR-92a through m6A Modification in Colorectal Cancer
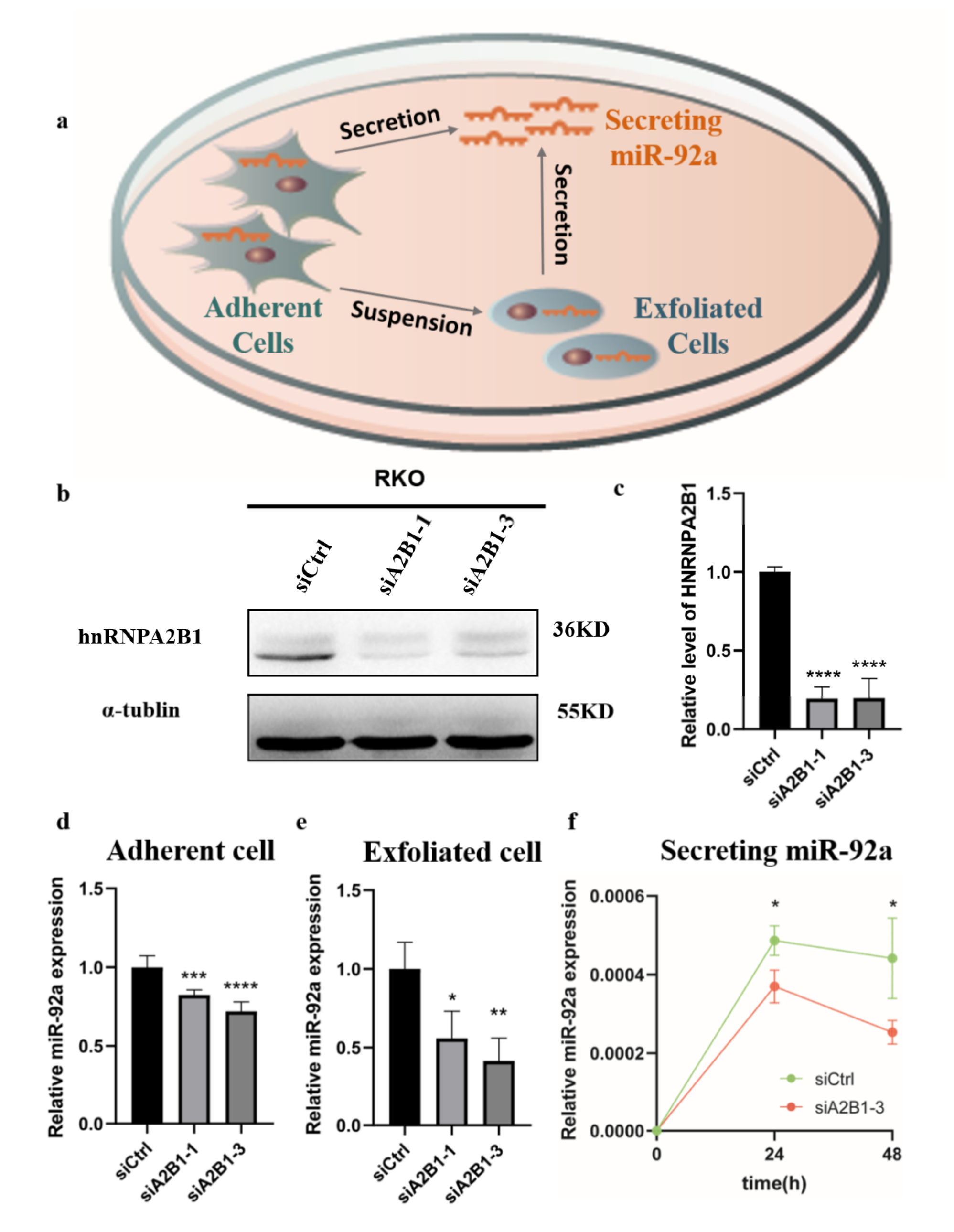
3.5. HNRNPA2B1 May Regulate the Expression and Secretion of miR-92a In Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Characteristics | Health | CRC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Mean ± SD | 50.46 ± 13.68 | 59.90 ± 11.00 |
| Sex | Male | 35 | 47 |
| Female | 37 | 25 | |
| Total | 72 | 72 | |
| Characteristics | CRC | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Cases | miR-92a Positive (n) | Sensitivity (%) | |
| Age, year | |||
| Mean ± SD | 59.90 ± 11.00 | ||
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 47 | 38 | 80.85 |
| Female | 25 | 20 | 80.00 |
| Family history of cancers | |||
| Yes | 18 | 17 | 94.44 |
| No/unknown | 54 | 41 | 75.93 |
| Histological type | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 54 | 42 | 77.78 |
| Mucinous | 7 | 6 | 85.71 |
| Others | 11 | 10 | 90.91 |
| Location | |||
| left | 9 | 7 | 77.78 |
| right | 63 | 51 | 80.95 |
| LN metastasis | |||
| Yes | 33 | 28 | 84.85 |
| No/unknown | 39 | 30 | 76.92 |
| Stage | |||
| I & II | 36 | 27 | 75.00 |
| III & IV | 36 | 31 | 86.11 |
| Differentiation | |||
| High | 2 | 1 | 50.00 |
| Moderate | 46 | 38 | 82.61 |
| Poor | 18 | 15 | 83.33 |
| Unknown | 6 | 4 | 66.67 |
Appendix B. Materials and Methods
Appendix B.1. Search Terms
Appendix B.2. Eligibility Criteria
Appendix B.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Appendix B.4. GEO Datasets
| HNRNPA2B1 GEO_ID | miR-92a GEO_ID |
|---|---|
| GSE32323 | GSE18392 |
| GSE110223 | GSE35834 |
| GSE113513 | GSE49246 |
| GSE84984 | GSE81581 |
| GSE22598 | GSE108153 |
| GSE21510 | GSE110402 |
Appendix B.5. SiRNA and RT-qPCR Primers
| Gene | Sense (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| hs-HNRNPA2B1-si-1 | GGACCAGGAAGUAACUUUAdTdT |
| UAAAGUUACUUCCUGGUCCdTdT | |
| hs-HNRNPA2B1-si-3 | GGCUUUGUCUAGACAAGAAdTdT |
| UUCUUGUCUAGACAAAGCCdTdT | |
| GAPDH-Fwd | TGACAACTTTGGTATCGTGGAAGG |
| GAPDH-Rev | AGGGATGATGTTCTGGAGAGCC |
| hnRNPA2B1-Fwd | ATTGATGGGAGAGTAGTTGAGCC |
| hnRNPA2B1-Rev | AATTCCGCCAACAAACAGCTT |
| miR-92-Fwd | TATTGCACTTGTCCCGGCCTG |
| Universal-Rev | GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT |
| m6A-RIP-Fwd | AAGGCACTTGTAGCATTATG |
| m6A-RIP-Rev | CCAGAAGGAGCACTTAGG |
| 18S-Fwd | GTAACCCGTTGAACCCCATT |
| 18S-Rev | CCATCCAATCGGTAGTAGCG |
| U6-Fwd | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| U6-Rev | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Geest, L.G.; Lam-Boer, J.; Koopman, M.; Verhoef, C.; Elferink, M.A.; de Wilt, J.H. Nationwide trends in incidence, treatment and survival of colorectal cancer patients with synchronous metastases. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2015, 32, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, T.; Yoshida, N.; Sadakari, Y.; Iwanaga, A.; Nakane, H.; Okawara, K.; Endo, K.; Kaneshiro, K.; Hirokata, G.; Aoyagi, T.; et al. Colorectal cancer surgery in elderly patients 80 years and older: A comparison with younger age groups. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 13, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osseis, M.; Nehmeh, W.A.; Rassy, N.; Derienne, J.; Noun, R.; Salloum, C.; Rassy, E.; Boussios, S.; Azoulay, D. Surgery for T4 Colorectal Cancer in Older Patients: Determinants of Outcomes. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Shi, K.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.; Song, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, W. Effect of exosomal miRNA on cancer biology and clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Guan, X.; Sun, Y.; Mi, J.; Shu, X.; Liu, F.; Li, C. miR-92a family and their target genes in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 323, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, Z. Serum miR-92a-1 is a novel diagnostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 8363–8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Chang, Y.S.; Tsai, W.S.; You, J.F.; Lin, G.P.; Chen, T.W.; Chen, J.S.; Chan, E.C. MicroRNA-223 and microRNA-92a in stool and plasma samples act as complementary biomarkers to increase colorectal cancer detection. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10663–10675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Dominissini, D.; Rechavi, G.; He, C. Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible m⁶A RNA methylation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gan, M.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, J.; Zhang, H.; Lai, M. Methyl CpG binding protein 2 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by regulating N(6)-methyladenosine methylation through methyltransferase-like 14. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 3243–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, C.R.; Goodarzi, H.; Lee, H.; Liu, X.; Tavazoie, S.; Tavazoie, S.F. HNRNPA2B1 Is a Mediator of m(6)A-Dependent Nuclear RNA Processing Events. Cell 2015, 162, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, J.; Lou, X.; Li, Y.; Qian, B.; Xu, D.; Wu, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhang, D.; Cui, W. HNRNPA2B1 Affects the Prognosis of Esophageal Cancer by Regulating the miR-17-92 Cluster. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 658642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Otterbein, L.E.; Jin, Y. Caveolin-1 selectively regulates microRNA sorting into microvesicles after noxious stimuli. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 2202–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.Y.; Yu, Y.; Cao, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zhang, X.X. Systematic Profiling of Exosomal Small RNA Epigenetic Modifications by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 14907–14911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Ning, J.; Liu, W.; Li, K.; Qian, B.; Xu, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cui, W. YTHDF1 Promotes Cyclin B1 Translation through m(6)A Modulation and Contributes to the Poor Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma with KRAS/TP53 Co-Mutation. Cells 2021, 10, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giráldez, M.D.; Lozano, J.J.; Ramírez, G.; Hijona, E.; Bujanda, L.; Castells, A.; Gironella, M. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of colorectal cancer: Results from a genome-wide profiling and validation study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 681–688.e683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.A.; El-Din Abd El-Rehim, A.S.; Mohammed Kholef, E.F.; Abd-Elgwad Elsewify, W. Potential role of plasma miR-21 and miR-92a in distinguishing between irritable bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, and colorectal cancer. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2020, 13, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, E.K.; Chong, W.W.; Jin, H.; Lam, E.K.; Shin, V.Y.; Yu, J.; Poon, T.C.; Ng, S.S.; Sung, J.J. Differential expression of microRNAs in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer: A potential marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gut 2009, 58, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, D.; Ni, S.; Peng, Z.; Sheng, W.; Du, X. Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, Y.; Yasunaga, M.; Takahashi, A.; Kuroda, J.; Moriya, Y.; Akasu, T.; Fujita, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Baba, H.; Matsumura, Y. MicroRNA expression profiling of exfoliated colonocytes isolated from feces for colorectal cancer screening. Cancer Prev. Res. 2010, 3, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.W.; Ng, S.S.; Dong, Y.J.; Ng, S.C.; Leung, W.W.; Lee, C.W.; Wong, Y.N.; Chan, F.K.; Yu, J.; Sung, J.J. Detection of miR-92a and miR-21 in stool samples as potential screening biomarkers for colorectal cancer and polyps. Gut 2011, 61, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Zhou, Z.G.; Chen, R.; Wang, M.J.; Zhou, B.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.F. Serum miR-21 and miR-92a as biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2013, 34, 2175–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Bayaxi, N.; Li, J.; Verhaegh, W.; Janevski, A.; Varadan, V.; Ren, Y.; Merkle, D.; Meng, X.; et al. A microRNA panel to discriminate carcinomas from high-grade intraepithelial neoplasms in colonoscopy biopsy tissue. Gut 2012, 62, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, X.; Lin, L. Values of fecal microRNA-141, -17-3p and -92a-3p in the diagnosis and prognostic evaluation of colorectal cancer. Tumor 2016, 36, 901–907. [Google Scholar]
- Elshafei, A.; Shaker, O.; Abd El-Motaal, O.; Salman, T. The expression profiling of serum miR-92a, miR-375, and miR-760 in colorectal cancer: An Egyptian study. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317705765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.H.; Cho, Y.S.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, S.S.; Chae, H.S. Stool-Based miR-92a and miR-144* as Noninvasive Biomarkers for Colorectal Cancer Screening. Oncology 2019, 97, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Wu, Y.; Ji, M.; Zhang, S. Combined Plasma MicroRNA and Fecal Occult Blood Tests in Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Lab. 2019, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brînzan, C.; Aşchie, M.; Cozaru, G.; Dumitru, E.; Mitroi, A. The diagnostic value of miR-92a, -143, and -145 expression levels in patients with colorectal adenocarcinoma from Romania. Medicine 2020, 99, e21895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elaguizy, M.; Sheta, M.; Ibrahim, N.; Eltaweel, A.; Mostafa, A. Serum microRNA-18a, microRNA-21 and microRNA-92a as diagnostic markers in colorectal cancer patients. J. BUON 2020, 25, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Earle, J.S.; Luthra, R.; Romans, A.; Abraham, R.; Ensor, J.; Yao, H.; Hamilton, S.R. Association of microRNA expression with microsatellite instability status in colorectal adenocarcinoma. J. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 12, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Z. Application of microarray chip to analyze the differential expression of miRNA in colon cancer tissues. J. Sichuan Univ. 2011, 344–348. [Google Scholar]
- Nishida, N.; Nagahara, M.; Sato, T.; Mimori, K.; Sudo, T.; Tanaka, F.; Shibata, K.; Ishii, H.; Sugihara, K.; Doki, Y.; et al. Microarray analysis of colorectal cancer stromal tissue reveals upregulation of two oncogenic miRNA clusters. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3054–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, M.; Statello, L.; Maugeri, M.; Majorana, A.; Barbagallo, D.; Salito, L.; Sammito, M.; Santonocito, M.; Angelica, R.; Cavallaro, A.; et al. Specific alterations of the microRNA transcriptome and global network structure in colorectal cancer after treatment with MAPK/ERK inhibitors. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 1421–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerincx, M.; Sie, D.L.; van de Wiel, M.A.; van Grieken, N.C.; Burggraaf, J.D.; Dekker, H.; Eijk, P.P.; Ylstra, B.; Verhoef, C.; Meijer, G.A.; et al. MiR expression profiles of paired primary colorectal cancer and metastases by next-generation sequencing. Oncogenesis 2015, 4, e170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sheikh, Y.A.; Ghneim, H.K.; Softa, K.I.; Al-Jobran, A.A.; Al-Obeed, O.; Mohamed, M.A.; Abdulla, M.; Aboul-Soud, M.A. Expression profiling of selected microRNA signatures in plasma and tissues of Saudi colorectal cancer patients by qPCR. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, R.K.; Novotny, G.W.; Klarskov, L.L.; Christensen, I.J.; Riis, L.B.; Høgdall, E. Intra-tumor heterogeneity of microRNA-92a, microRNA-375 and microRNA-424 in colorectal cancer. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2016, 100, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uratani, R.; Toiyama, Y.; Kitajima, T.; Kawamura, M.; Hiro, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Mohri, Y.; Mori, T.; et al. Diagnostic Potential of Cell-Free and Exosomal MicroRNAs in the Identification of Patients with High-Risk Colorectal Adenomas. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, M.L.; Mullany, L.E.; Sakoda, L.C.; Wolff, R.K.; Samowitz, W.S.; Herrick, J.S. Dysregulated genes and miRNAs in the apoptosis pathway in colorectal cancer patients. Apoptosis 2018, 23, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.; Fawzy, A.; Akel, S.Y.; Gamal, H.; Elshimy, R.A.A. Evaluation of microRNA 92a Expression and Its Target Protein Bim in Colorectal Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 23, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellizar, A.; Refuerzo, V.; Ramos, J.D.; Albano, P.M. Expression of specific microRNAs in tissue and plasma in colorectal cancer. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Han, J.; Park, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, E.S.; Cha, B.S.; Park, K.S. DNA barcode-based detection of exosomal microRNAs using nucleic acid lateral flow assays for the diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Talanta 2022, 242, 123306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; He, W.; Chen, M.; Zhao, L.; Shao, J.; Xu, G.; Lin, S.; Liu, R.; Li, B.; Lv, H.; et al. Non-invasive stool miR-92a test for colorectal cancer screening: A multicenter retrospective clinical study. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2023. in publication stage. [Google Scholar]
- Olenius, T.; Koskenvuo, L.; Koskensalo, S.; Lepistö, A.; Böckelman, C. Long-term survival among colorectal cancer patients in Finland, 1991–2015: A nationwide population-based registry study. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepus, M.; Yau, T.O. Non-Invasive Colorectal Cancer Screening: An Overview. Gastrointest. Tumors 2020, 7, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussios, S.; Ozturk, M.A.; Moschetta, M.; Karathanasi, A.; Zakynthinakis-Kyriakou, N.; Katsanos, K.H.; Christodoulou, D.K.; Pavlidis, N. The Developing Story of Predictive Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2019, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedaeinia, R.; Manian, M.; Jazayeri, M.H.; Ranjbar, M.; Salehi, R.; Sharifi, M.; Mohaghegh, F.; Goli, M.; Jahednia, S.H.; Avan, A.; et al. Circulating exosomes and exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers in gastrointestinal cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Leung, L.L.; Mak, C.S.L.; Wang, X.; Chan, W.S.; Hui, L.M.N.; Tang, H.W.M.; Siu, M.K.Y.; Sharma, R.; Xu, D.; et al. Tumor-secreted exosomal miR-141 activates tumor-stroma interactions and controls premetastatic niche formation in ovarian cancer metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, A.; Balaguer, F.; Shen, Y.; Nagasaka, T.; Lozano, J.J.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Fecal MicroRNAs as novel biomarkers for colon cancer screening. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 1766–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.E.; Ahmed, N.C.; Vos, P.W.; Bonnerup, C.; Atkins, J.N.; Casey, M.; Nuovo, G.J.; Naziri, W.; Wiley, J.E.; Mota, H.; et al. Diagnostic microRNA markers to screen for sporadic human colon cancer in stool: I. Proof of principle. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2013, 10, 93–113. [Google Scholar]
- Voigt, A.Y.; Costea, P.I.; Kultima, J.R.; Li, S.S.; Zeller, G.; Sunagawa, S.; Bork, P. Temporal and technical variability of human gut metagenomes. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Sánchez-Cabo, F.; Pérez-Hernández, D.; Vázquez, J.; Martin-Cofreces, N.; Martinez-Herrera, D.J.; Pascual-Montano, A.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Grady, T.; Njock, M.S.; Lion, M.; Bruyr, J.; Mariavelle, E.; Galvan, B.; Boeckx, A.; Struman, I.; Dequiedt, F. Sorting and packaging of RNA into extracellular vesicles shape intracellular transcript levels. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Shu, Y.; He, J.; Gao, W. Interaction between N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) modification and noncoding RNAs in cancer. Mol. Cancer. 2020, 19, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abner, J.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Clement, M.A.; Hinger, S.A.; Allen, R.M.; Liu, X.; Kellner, S.; Wu, J.; Karijolich, J.; Liu, Q.; et al. Depletion of METTL3 alters cellular and extracellular levels of miRNAs containing m(6)A consensus sequences. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, C.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Guo, Y. microRNA-96 promotes occurrence and progression of colorectal cancer via regulation of the AMPKα2-FTO-m6A/MYC axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Song, W.; Xu, X.; Zhao, X.; Yang, L. IGF2BP2 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and survival through interfering with RAF-1 degradation by miR-195. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, N.; Jiao, X.; Wang, C.; Sun, W.; He, Y.; Ren, G.; Huang, S.; Li, M.; Chang, Y.; et al. Downregulation of microRNA-6125 promotes colorectal cancer growth through YTHDF2-dependent recognition of N6-methyladenosine-modified GSK3β. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Source | Author | Year | Region | Case/Control | Fold Change | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tissue | 744/635 | 2.64 ± 1.30 | <0.0001 | |||
| Ng et al. [18] | 2009 | China | 5/5 | 2.58 | <0.05 | |
| Earle et al. [30] | 2010 | USA | 55/55 | 1.75 | <0.0001 | |
| Koga et al. [20] | 2010 | Japan | 31/31 | 1.81 | 0.01 | |
| Ma et al. [31] | 2011 | China | 12/12 | 1.17 | <0.05 | |
| Wu et al. [21] | 2011 | China | 40/40 | 2.18 | <0.0001 | |
| Wang et al. [23] | 2012 | China | 57/15 | 2 | <0.0001 | |
| Nishida et al. [32] | 2012 | Japan | 13/4 | 2.8842 | <0.0001 | |
| Ragusa et al. [33] | 2012 | Italy | 22/5 | up 1 | <0.05 | |
| Neerincx et al. [34] | 2015 | Holland | 40/23 | 1.866 | <0.0001 | |
| Al-Sheikh et al. [35] | 2016 | Saudi Arabia | 20/20 | 2.6 | <0.01 | |
| Jepsen et al. [36] | 2016 | Denmark | 9/3 | 1.68 | 0.002 | |
| Uratani et al. [37] | 2016 | USA | 19/20 | up | <0.001 | |
| Slattery et al. [38] | 2018 | USA | 217/217 | 2.95 | 0.0009 | |
| Chang et al. [8] | 2016 | China | 62/62 | 1.9 | <0.001 | |
| Brînzan et al. [28] | 2020 | Romania | 82/82 | 2.32 | <0.001 | |
| Fellizar et al. [40] | 2022 | Philippines | 41/41 | 7.41 | <0.001 | |
| Stool | 766/721 | 5.07 ± 3.07 | <0.0001 | |||
| Koga et al. [20] | 2010 | Japan | 197/119 | 8.3 | <0.0001 | |
| Wu et al. [21] | 2011 | China | 88/101 | up | <0.0001 | |
| Chang et al. [8] | 2016 | China | 62/62 | 3.48 | <0.0001 | |
| Xue et al. [24] | 2016 | China | 50/50 | 1.08 | <0.01 | |
| Choi et al. [26] | 2019 | Korea | 29/29 | 2.12 | 0.001 | |
| Xu et al. [42] | 2022 | China | 340/360 | 1.33 | <0.0001 | |
| Blood | 835/598 | 28.42 ± 49.09 | <0.0001 | |||
| Ng et al. [18] | 2009 | China | 5/5 | 4.45 | <0.05 | |
| Huang et al. [19] | 2010 | China | 100/59 | up | <0.0001 | |
| Giráldez et al. [16] | 2013 | Spain | 21/20 | 1.83 | 0.0437 | |
| Liu et al. [22] | 2013 | China | 200/80 | up | <0.05 | |
| Chang et al. [8] | 2016 | China | 62/62 | 2.85 | <0.0001 | |
| Elshafei et al. [25] | 2017 | Egypt | 64/27 | 3.38 | <0.0001 | |
| Luo et al. [27] | 2019 | China | 57/125 | up | 0.007 | |
| Shi et al. [7] | 2020 | China | 148/68 | up | <0.001 | |
| Hassan et al. [17] | 2020 | Egypt | 33/30 | 158.83 | <0.05 | |
| Elaguizy et al. [29] | 2020 | Egypt | 50/50 | 1.879 | 0.003 | |
| Zaki et al. [39] | 2022 | Egypt | 54/15 | 62.2 | <0.001 | |
| Fellizar et al. [40] | 2022 | Philippines | 36/36 | 2.5 | <0.001 | |
| Kim et al. [41] | 2022 | Korea | 5/21 | up | <0.001 |
| Sample Source | Author | Year | Specimen | Case/Control | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood | 920/650 | 0.910 | |||
| Ng et al. [18] | 2009 | plasma | 90/50 | 0.885 | |
| Huang et al. [19] | 2010 | plasma | 100/59 | 0.838 | |
| Giráldez et al. [16] | 2013 | plasma | 21/20 | 0.857 | |
| Liu et al. [22] | 2013 | serum | 200/80 | 0.786 | |
| Chang et al. [8] | 2016 | plasma | 62/62 | 0.833 | |
| Elshafei et al. [25] | 2017 | serum | 64/27 | 0.844 | |
| Luo et al. [27] | 2019 | plasma | 57/125 | 0.603 | |
| Shi et al. [7] | 2020 | serum | 148/68 | 0.914 | |
| Hassan et al. [17] | 2020 | plasma | 33/37 | 0.887 | |
| Elaguizy et al. [29] | 2020 | serum | 50/50 | 0.672 | |
| Zaki et al. [39] | 2022 | plasma | 54/15 | 0.994 | |
| Fellizar et al. [40] | 2022 | plasma | 36/36 | 0.760 | |
| Kim et al. [41] | 2022 | plasma | 5/21 | 0.895 | |
| Stool | 838/793 | 0.840 | |||
| Koga et al. [20] | 2010 | stool | 197/119 | NA | |
| Wu et al. [21] | 2011 | stool | 88/101 | 0.780 | |
| Chang et al. [8] | 2016 | stool | 62/62 | 0.739 | |
| Xue et al. [24] | 2016 | stool | 50/50 | 0.789 | |
| Choi et al. [26] | 2019 | stool | 29/29 | 0.760 | |
| Xu et al. [42] | 2022 | stool | 340/360 | 0.870 | |
| Li et al. | 2022 | stool | 72/72 | 0.861 |
| Studies | Pooled Sensitivity (95% CI) | Pooled Specificity (95% CI) | Pooled Odds Ratio (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood | 0.83 (0.67–0.92) | 0.86 (0.75–0.92) | 28.98 (11.67–71.92) |
| Stool | 0.68 (0.48–0.83) | 0.81 (0.72–0.88) | 9.34 (5.34–16.34) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Li, K.; Lou, X.; Wu, Y.; Seery, S.; Xu, D.; Pei, Y.; Qian, B.; Wu, Y.; Liang, S.; et al. HNRNPA2B1-Mediated MicroRNA-92a Upregulation and Section Acts as a Promising Noninvasive Diagnostic Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051367
Li Y, Li K, Lou X, Wu Y, Seery S, Xu D, Pei Y, Qian B, Wu Y, Liang S, et al. HNRNPA2B1-Mediated MicroRNA-92a Upregulation and Section Acts as a Promising Noninvasive Diagnostic Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051367
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yiling, Kexin Li, Xiaoying Lou, Yue Wu, Samuel Seery, Danfei Xu, Yuqing Pei, Benheng Qian, Yuxin Wu, Shuang Liang, and et al. 2023. "HNRNPA2B1-Mediated MicroRNA-92a Upregulation and Section Acts as a Promising Noninvasive Diagnostic Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051367
APA StyleLi, Y., Li, K., Lou, X., Wu, Y., Seery, S., Xu, D., Pei, Y., Qian, B., Wu, Y., Liang, S., Wu, K., & Cui, W. (2023). HNRNPA2B1-Mediated MicroRNA-92a Upregulation and Section Acts as a Promising Noninvasive Diagnostic Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers, 15(4), 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051367





