Mapping Resection Progress by Tool-Tip Tracking during Brain Tumor Surgery for Real-Time Estimation of Residual Tumor
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Preoperative Planning
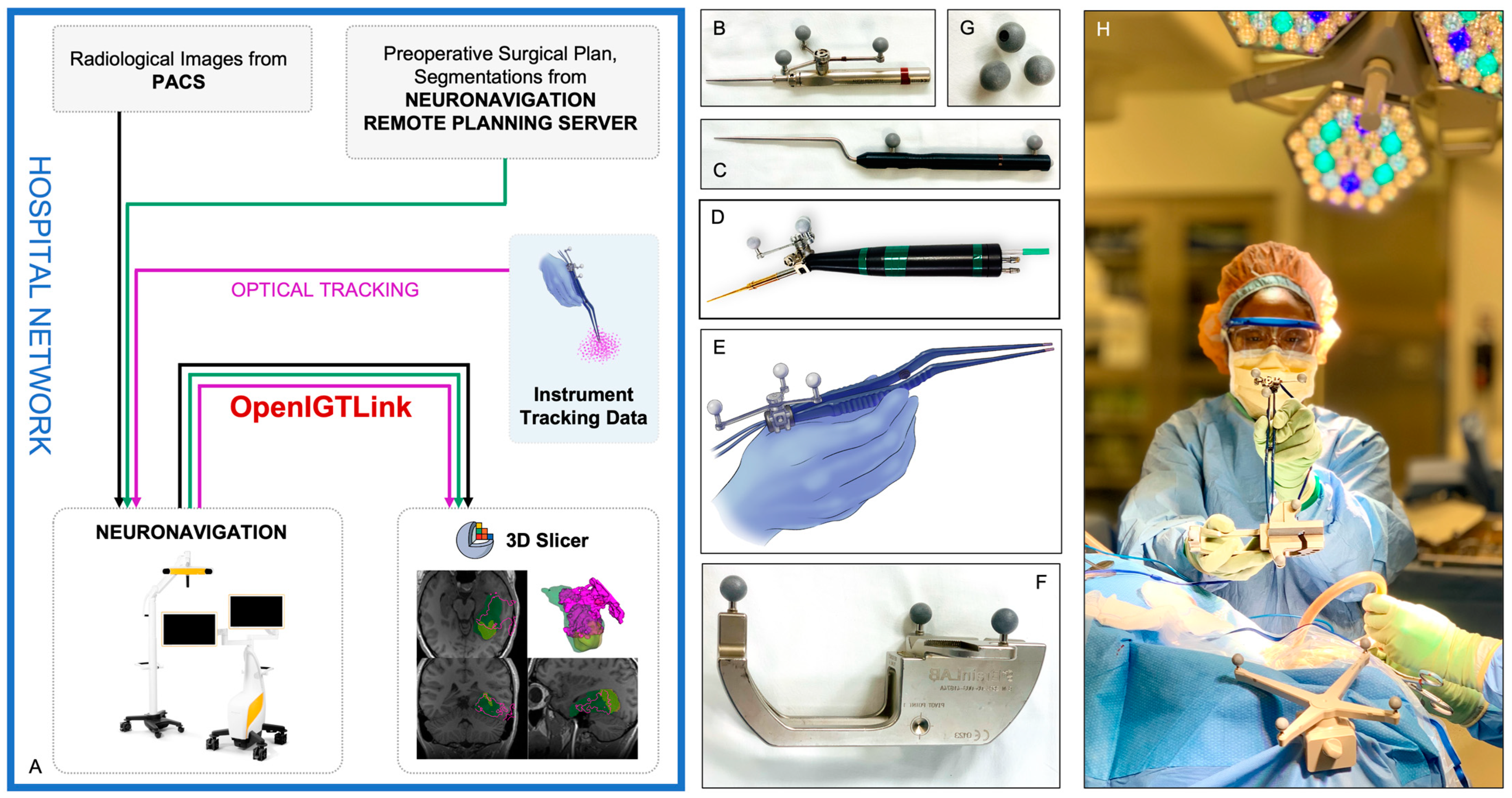
2.3. Neuronavigation and Instrument Tracking
2.4. Data Collection and Visualization of Resection Progress
2.5. Intraoperative Imaging
2.6. Postoperative Data Analysis
2.7. Additional Clinical Descriptors and Metadata
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Clinical and Surgical Descriptors
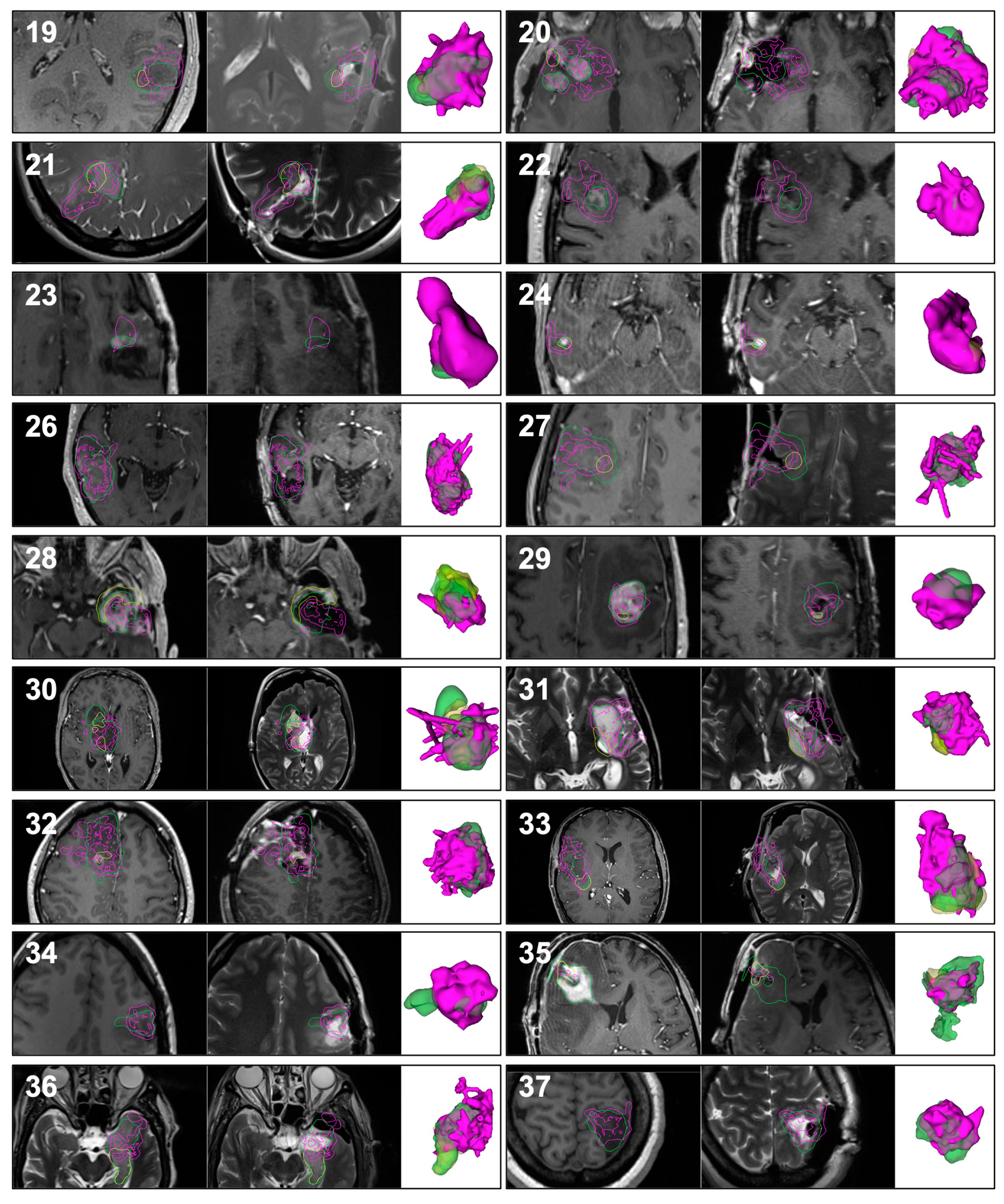
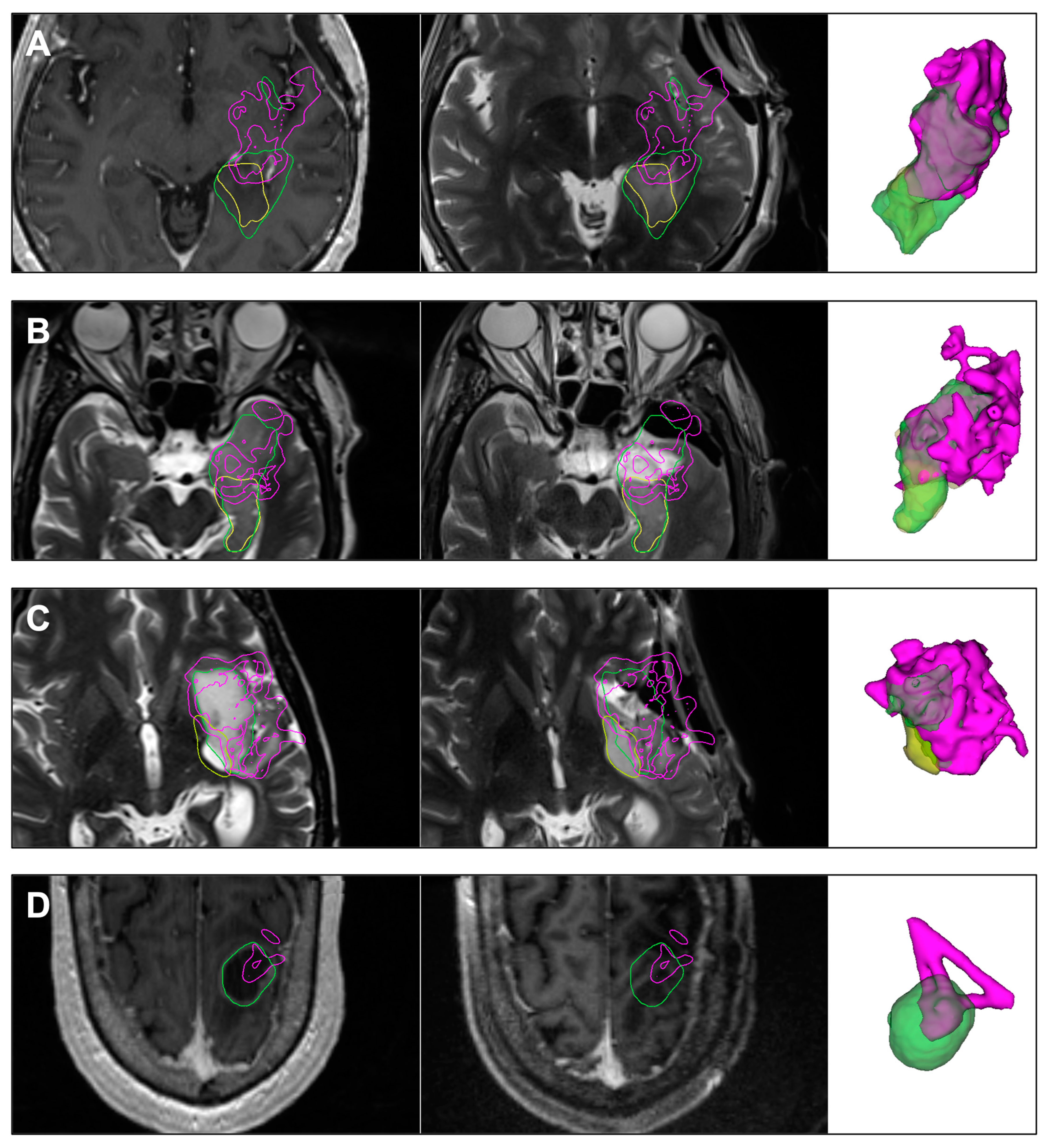
3.2. Qualitative Results
3.2.1. Case 7
3.2.2. Case 31
3.3. Quantitative Results
4. Discussion
4.1. System Compatibility and Generalizability
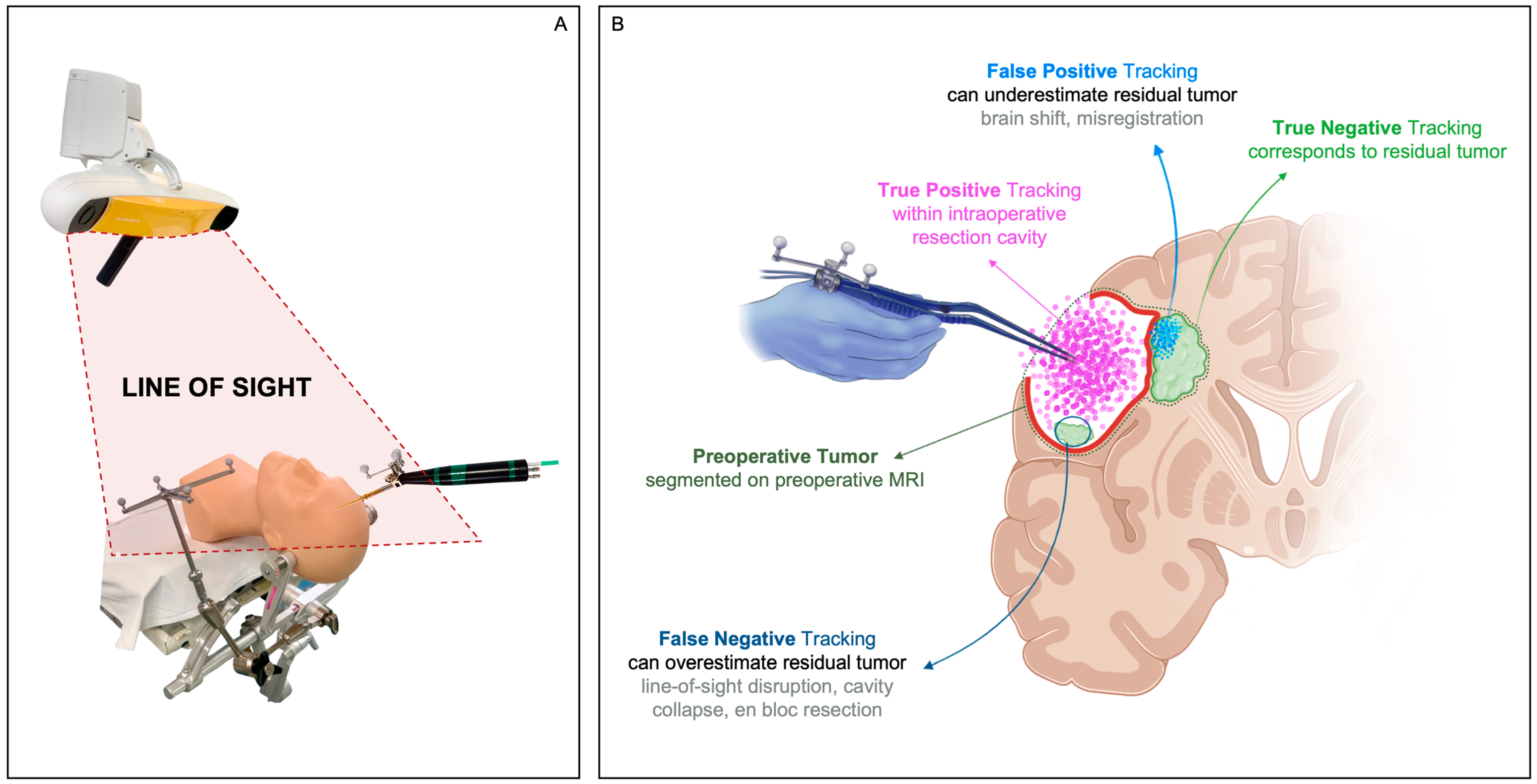
4.2. Line-of-Sight
4.3. Choice of Tracked Surgical Instrument
4.4. Instrument Tracking Arrays
4.5. User Interface
4.6. Brain Shift
4.7. Extrapolation to Other Pathologies and Subspecialties
4.8. Neurosurgical Education
4.9. Alternative to iMRI
4.10. Advancements from Prior Studies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


| Case ID | Preoperative Tumor Volume (cm3) | Residual Tumor Volume (cm3) | Tumor Resected Based on iMRI (%) | Tumor Resected Based on Tool-Tip Tracking (%) | False Positive Tracking (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 33.5 | 14.7 | 56.1 | 46.5 | 3.5 |
| 2 | 36.8 | 3.1 | 91.6 | 60.1 | 16.6 |
| 3 | 13.0 | 4.4 | 65.7 | 63.7 | 6.25 |
| 4 | 38.1 | 0.3 | 99.3 | 57.6 | 3.1 |
| 5 | 6.3 | 2.5 | 60.0 | 50.1 | 14.6 |
| 6 | 6.5 | 3.7 | 42.6 | 46.2 | 5.8 |
| 7 | 35.3 | 12.3 | 65.1 | 50.8 | 7.3 |
| 8 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 40.25 | 0 |
| 9 | 4.9 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 15.22 | 0 |
| 10 | 8.6 | 5.1 | 40.2 | 66.5 | 6.3 |
| 11 | 6.3 | 0.2 | 97.3 | 72.5 | 4.4 |
| 12 | 28.9 | 3.8 | 86.7 | 55.4 | 12.6 |
| 13 | 8.7 | 2.5 | 71.1 | 52.1 | 1.5 |
| 14 | 28.9 | 2.9 | 89.9 | 41.5 | 10.3 |
| 15 | 16.4 | 2.8 | 82.8 | 62.3 | 30.4 |
| 16 | 48.1 | 8.6 | 82.1 | 60.4 | 7.7 |
| 17 | 9.4 | 3.2 | 66.3 | 83.5 | 47.9 |
| 18 | 86.2 | 2.4 | 97.2 | 72.8 | 42.9 |
| 19 | 10.5 | 0.4 | 96.1 | 69.5 | 10.1 |
| 20 | 38.0 | 4.5 | 88.1 | 64.2 | 33.2 |
| 21 | 11.9 | 6.0 | 50.0 | 68.6 | 37.9 |
| 22 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 99.7 | 0 |
| 23 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 44.7 | 0 |
| 24 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 98 | 0 |
| 25 | 35.5 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 78.4 | 0 |
| 26 | 19.7 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 85.3 | 0 |
| 27 | 30.3 | 0.6 | 97.9 | 67.7 | 17.5 |
| 28 | 16.4 | 9.4 | 42.9 | 56.3 | 6.8 |
| 29 | 7.7 | 0.3 | 96.0 | 55.6 | 38.7 |
| 30 | 40.9 | 6.4 | 84.4 | 50.3 | 10.9 |
| 31 | 14.7 | 3.7 | 75.1 | 75.2 | 3.9 |
| 32 | 57.9 | 2.0 | 96.5 | 69 | 40.4 |
| 33 | 20.4 | 9.7 | 52.6 | 58.3 | 13.5 |
| 34 | 4.7 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 69.8 | 0 |
| 35 | 37.0 | 1.1 | 97.0 | 41.3 | 1.5 |
| 36 | 18.4 | 10.1 | 45.0 | 56.5 | 13.5 |
| 37 | 9.9 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 71.2 | 0 |
| 38 | 19.8 | 18.2 | 7.7 | 45.7 | 7 |
| 39 | 17.5 | 5.3 | 69.9 | 78 | 14.8 |
| 40 | 8.2 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 53.1 | 0 |
| 41 | 11.8 | 5.3 | 55.0 | 76.4 | 29 |
| 42 | 23.5 | 7.5 | 68.1 | 84.5 | 13 |
| 43 | 27.2 | 4.5 | 83.6 | 64.4 | 21.1 |
| 44 | 42.8 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 44.7 | 0 |
| Case ID | Age/Sex | Race | Laterality, Anatomic Compartments | Eloquence | Cystic | Enhancing | Non-enhancing | Ventricle Opened? | Cistern Opened? | Brain Shift | GTR | Residual Location | Pathology | WHO Grade | MIB-1 Index | MGMT Promoter | IDH Mutation | 1p/19q Status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 43/F | White | R | Temporal, Mesial Temporal, Thalamic | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Thalamus | Glioblastoma | 4 | 5.46% | Methylated | - | Retained |
| 2 | 26/M | White | L | Frontal, Insular, Temporal | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Superior, Frontal | Anaplastic Astrocytoma | 3 | 5% | Partially Methylated | + | Retained |
| 3 | 38/M | White | R | Insular | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Anterior, Posterior | Diffuse Astrocytoma | 2 | 2% | Unmethylated | + | Retained |
| 4 | 62/M | White | R | Frontal, Insular, Temporal | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | None | Glioblastoma | 4 | Unmethylated | - | Retained | |
| 5 | 42/M | White | R | Frontal, Insular, Temporal | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Medial, Anterior, Superior | Oligodendroglioma | 2 | 1% | Methylated | + | Co-deleted |
| 6 | 52/F | White | L | Frontal, SMA | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Anterior, Lateral, Inferior, Posterior | Glioblastoma | 4 | >80% | Unmethylated | - | Pending |
| 7 | 28/M | White | L | Mesial Temporal | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Superior, Posterior, Medial, Anterior | Anaplastic Astrocytoma | 3 | 10% | Methylated | + | Retained |
| 8 | 45/F | White | R | Frontal, Parietal | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | None | Oligodendroglioma | 2 | 0.68% | Methylated | + | Co-deleted |
| 9 | 58/M | White | B | Multifocal (Frontal, Parietal, Occipital) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | Right Basal Frontal, Right Frontal, Right Occipital | Metastatic Carcinoma from Lung Primary | |||||
| 10 | 49/F | White | B | Frontal | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Anterior, Medial | Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma | 3 | 3.70% | Unknown | + | Co-deleted |
| 11 | 33/F | White | L | Parietal | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | None | Low-grade Glioma | 7% | Methylated | - | Retained | |
| 12 | 59/F | White | L | Temporal, Mesial Temporal, Thalamic | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Medial, Posterior | Glioblastoma | 4 | Unmethylated | - | Retained | |
| 13 | 61/F | White | L | Temporal, Mesial Temporal, Capsular | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Temporal, Internal Capsule | Glioblastoma | 4 | 30% | Unmethylated | - | Retained |
| 14 | 24/M | White | L | Temporal, Insular | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Medial, Lateral, Posterior, Inferior | Low-grade Glioma/Glioneural Tumor | 2 | 10% | - | Retained | |
| 15 | 64/F | White | R | Frontal, Parietal | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Anterior, Medial, Inferior | Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma | 3 | 30% | Methylated | + | Co-deleted |
| 16 | 25/M | White | R | Frontal, Insular, Temporal | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Insula, Amygdala, Frontal | Glioblastoma | 4 | 15% | Unmethylated | + | Retained |
| 17 | 53/F | White | L | Frontal, SMA | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Posterior, Lateral, Inferior, Anterior | Glioblastoma | 4 | >80% | Unmethylated | - | Retained |
| 18 | 51/M | White | L | Frontal, Temporal | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Frontal Operculum | Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma | 3 | Methylated | + | Co-deleted | |
| 19 | 30/M | Asian | L | Temporal | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | None | Oligodendroglioma | 2 | 10% | Methylated | + | Co-deleted |
| 20 | 52/F | White | R | Frontal, Temporal | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | None | Metastatic Breast Carcinoma | |||||
| 21 | 36/F | White | R | Occipital | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Lateral | Oligodendroglioma | 2 | 4% | Methylated | + | Co-deleted |
| 22 | 61/M | White | R | Frontal, SMA | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | Lateral | Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma | 3 | <2% | Methylated | + | Co-deleted |
| 23 | 40/M | White | L | Frontal | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | None | Astrocytoma | 4 | <3% | Methylated | + | Retained |
| 24 | 43/F | White | R | Temporal | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Medial | Abnormally Thickened Blood Vessels and Chronic Inflammatory Infiltrate | |||||
| 25, 26 | 72/M | White | R | Temporal | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | Anterior | Glioblastoma | 4 | Methylated | - | Retained | |
| 27 | 63/F | White | R | Frontal | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Posterior, Medial | Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma | 3 | 16% | Methylated | + | Co-deleted |
| 28 | 50/M | White | L | Temporal, Mesial Temporal, Insular | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Insula | Glioblastoma | 4 | Unmethylated | - | Retained | |
| 29 | 70/M | White | L | Frontal | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | Posterior | Metastatic Melanoma | |||||
| 30 | 46/F | White | R | Thalamus, Caudate | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Inferolateral Thalamus | Glioblastoma | 4 | 5% | Methylated | - | |
| 31 | 45/M | White | L | Frontal, Insular, Temporal, Mesial Temporal | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Temporal, Insula | Astrocytoma | 3 | 2% | Unmethylated | + | Retained |
| 32 | 24/F | Asian | R | Frontal, SMA | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Posterior, Inferior | Astrocytoma | 4 | Methylated | + | Retained | |
| 33 | 26/F | Declined | R | Temporal, Insular | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Insula, Temporal | Oligodendroglioma | 2 | 2% | Partially Methylated | + | Co-deleted |
| 34 | 31/F | White | L | Frontal | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Left Frontal Medial and Inferior | Astrocytoma | 3 | 15% | Partially Methylated | + | Retained |
| 35 | 66/F | White | L | Frontal, Temporal | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | None | Metastatic Poorly Differentiated Carcinoma | |||||
| 36 | 62/M | White | L | Temporal, Mesial Temporal | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Temporal, Amygdala, Hippocampus, Insula | Diffuse Glioma | >2 | 2-3% | Partially Methylated | - | Retained |
| 37 | 32/F | African American | L | Parietal | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | None | Astrocytoma | 2 | 2% | Methylated | + | Retained |
| 38 | 69/M | White | L | Frontal, Insular, Mesial Temporal | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Amygdala, Anterior and Posterior insula | Glioblastoma | 4 | Methylated | - | Retained | |
| 39 | 66/F | White | R | Frontal, SMA | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Anterior, Medial, Posterior, Inferior | Glioblastoma | 4 | >50% | Unmethylated | - | Retained |
| 40 | 43/M | Asian | R | Frontal, Insular, Temporal | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | None | Astrocytoma | 2 | 3% | Methylated | + | Retained |
| 41 | 60/M | White | L | Frontal | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | None | Metastatic Melanoma | |||||
| 42 | 30/M | White | R | Temporal, Insular | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Posterior, Anterior | Astrocytoma | 2 | 5-10% | Unmethylated | + | Retained |
| 43 | 42/F | White | L | Frontal, Insular, Temporal | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Small Segment of Anterior Superior Insular Gyrus, Segment of the Posterior Insula and the Posterior Superior Temporal Segment of the tumor | Oligodendroglioma | 2 | 5% | Methylated | + | |
| 44 | 70/M | White | L | Parietal, Temporal | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | Posterior, Inferior | Metastatic Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor | |||||
References
- Brown, T.J.; Brennan, M.C.; Li, M.; Church, E.W.; Brandmeir, N.J.; Rakszawski, K.L.; Patel, A.S.; Rizk, E.B.; Suki, D.; Sawaya, R.; et al. Association of the Extent of Resection with Survival in Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orringer, D.; Lau, D.; Khatri, S.; Zamora-Berridi, G.J.; Zhang, K.; Wu, C.; Chaudhary, N.; Sagher, O. Extent of Resection in Patients with Glioblastoma: Limiting Factors, Perception of Resectability, and Effect on Survival. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 117, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanai, N.; Polley, M.-Y.; McDermott, M.W.; Parsa, A.T.; Berger, M.S. An Extent of Resection Threshold for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastomas. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, D.C.D.A.; Juvekar, P.; Tie, Y.; Jowkar, N.; Pieper, S.; Wells, W.M.; Bi, W.L.; Golby, A.; Frisken, S.; Kapur, T. Challenges and Opportunities of Intraoperative 3D Ultrasound with Neuronavigation in Relation to Intraoperative MRI. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 656519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orringer, D.A.; Golby, A.; Jolesz, F. Neuronavigation in the Surgical Management of Brain Tumors: Current and Future Trends. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2012, 9, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, A.; Black, P.M.; Gering, D.T.; Westin, C.F.; Mehta, V.; Pergolizzi, R.S., Jr.; Ferrant, M.; Warfield, S.K.; Hata, N.; Schwartz, R.B.; et al. Serial Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Brain Shift. Neurosurgery 2001, 48, 787–797; discussion 797–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimsky, C.; Ganslandt, O.; Cerny, S.; Hastreiter, P.; Greiner, G.; Fahlbusch, R. Quantification Of, Visualization Of, and Compensation for Brain Shift Using Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 1070–1079; discussion 1079–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosteiro, A.; Di Somma, A.; Ramos, P.R.; Ferrés, A.; De Rosa, A.; González-Ortiz, S.; Enseñat, J.; González, J.J. Is Intraoperative Ultrasound More Efficient than Magnetic Resonance in Neurosurgical Oncology? An Exploratory Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1016264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.S.; Sylvester, P.T.; Yahanda, A.T.; Vellimana, A.K.; Dunn, G.P.; Evans, J.; Rich, K.M.; Dowling, J.L.; Leuthardt, E.C.; Dacey, R.G.; et al. Intraoperative MRI for Newly Diagnosed Supratentorial Glioblastoma: A Multicenter-Registry Comparative Study to Conventional Surgery. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 135, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisken, S.F.; Juvekar, P.R.; Bi, W.L.; Golby, A.J. Mapping the Progression of Resection Continuously during Brain Tumor Surgery. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2021: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021; Volume 11598, pp. 362–372. [Google Scholar]
- Frisken, S.F.; Perry, R.N.; Rockwood, A.P.; Jones, T.R. Adaptively Sampled Distance Fields: A General Representation of Shape for Computer Graphics. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–28 July 2000; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA; Addison-Wesley Publishing Co.: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Tempany, C.M.C.; Jayender, J.; Kapur, T.; Bueno, R.; Golby, A.; Agar, N.; Jolesz, F.A. Multimodal Imaging for Improved Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancers. Cancer 2015, 121, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugler, J.P., 3rd. Optimized Three-Dimensional Fast-Spin-Echo MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 39, 745–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavdas, E.; Mavroidis, P.; Kostopoulos, S.; Glotsos, D.; Roka, V.; Topalzikis, T.; Bakas, A.; Oikonomou, G.; Papanikolaou, N.; Batsikas, G.; et al. Improvement of Image Quality Using BLADE Sequences in Brain MR Imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 31, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, M.; Gambarota, G.; Kober, T.; Krueger, G.; Erritzoe, D.; Marques, J.P.; Newbould, R. Fluid and White Matter Suppression with the MP2RAGE Sequence. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 35, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, J.; Fischer, G.S.; Papademetris, X.; Yaniv, Z.; Ibanez, L.; Cheng, P.; Liu, H.; Blevins, J.; Arata, J.; Golby, A.J.; et al. OpenIGTLink: An Open Network Protocol for Image-Guided Therapy Environment. Int. J. Med. Robot. 2009, 5, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikinis, R.; Pieper, S.D.; Vosburgh, K.G. 3D Slicer: A Platform for Subject-Specific Image Analysis, Visualization, and Clinical Support. In Intraoperative Imaging and Image-Guided Therapy; Jolesz, F.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 277–289. ISBN 9781461476573. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, E.; Lane, M.; Sagher, O. Eloquent: History of a Word’s Adoption into the Neurosurgical Lexicon. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasso, A.; Heffter, T.; Rankin, A.; Pinter, C.; Ungi, T.; Fichtinger, G. PLUS: Open-Source Toolkit for Ultrasound-Guided Intervention Systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 2527–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, É.; Horvath, S.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Allemang, D.; Gerber, S.; Juvekar, P.; Torio, E.; Kapur, T.; Pieper, S.; Pujol, S.; et al. NousNav: A Low-Cost Neuronavigation System for Deployment in Lower-Resource Settings. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2022, 17, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Narayanan, M.D.K.; Umana, G.E.; Montemurro, N.; Chaurasia, B.; Deora, H. Virtual Reality in Neurosurgery: Beyond Neurosurgical Planning. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Maruyama, T.; Konishi, Y.; Masamune, K.; Muragaki, Y. Reliability of Residual Tumor Estimation Based on Navigation Log. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2020, 60, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Muragaki, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Hashizume, M.; Iseki, H. A Neurosurgical Navigation System Based on Intraoperative Tumour Remnant Estimation. J. Robot. Surg. 2007, 1, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisken, S.; Luo, J.; Haouchine, N.; Pieper, S.; Wang, Y.; Wells, W.M.; Golby, A.J. Incorporating Uncertainty into Path Planning for Minimally Invasive Robotic Neurosurgery. IEEE Transactions on Medical Robotics and Bionics 2022, 4, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woerdeman, P.A.; Willems, P.W.A.; Noordmans, H.J.; van der Sprenkel, J.W.B. The Analysis of Intraoperative Neurosurgical Instrument Movement Using a Navigation Log-File. Int. J. Med. Robot. 2006, 2, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variables | Median [IQR], Mean ± SD, % (n) |
|---|---|
| Demographics | |
| Age | 46 [31–61] |
| Sex | |
| Female | 47.6% (20) |
| Male | 52.4% (22) |
| Race | |
| White | 88.1% (37) |
| Asian | 7.1% (3) |
| African American | 2.4% (1) |
| Pathology | |
| Gliomas | 84% (35) |
| Glioblastoma | 26.4% (11) |
| Astrocytoma | 19.2% (8) |
| Oligodendroglioma | 14.4% (6) |
| Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma | 12.0% (5) |
| Anaplastic Astrocytoma | 4.8% (2) |
| Others | 7.2% (3) |
| Metastases | 14.4% (6) |
| Other | 2.4% (1) |
| Variables | Median [IQR], Mean ± SD, % (n) |
|---|---|
| Preoperative MRI | |
| Laterality | |
| Left | 50.0% (22) |
| Right | 45.5% (20) |
| Bilateral | 4.5% (2) |
| Previous cranial surgery | |
| Yes | 65.9% (29) |
| No | 34.1% (15) |
| Resection cavity | |
| Yes | 40.9% (18) |
| No | 59.1% (26) |
| Anatomic compartments | |
| Frontal | 56.8% (25) |
| Temporal | 52.3% (23) |
| Insular | 27.3% (12) |
| Limbic | 20.5% (9) |
| Parietal | 13.6% (6) |
| Occipital | 4.5% (2) |
| Basal ganglia | 4.5% (2) |
| Components | |
| Cystic | 36.4% (16) |
| Enhancing | 56.8% (25) |
| Non-enhancing | 77.3% (34) |
| Eloquence | |
| Yes | 63.6% (28) |
| No | 36.4% (16) |
| Intraoperative findings and iMRI | |
| Opening of ventricle | |
| Yes | 38.6% (17) |
| No | 61.4% (27) |
| Opening of basal cisterns | |
| Yes | 34.1% (15) |
| No | 65.9% (29) |
| Brain shift | |
| Yes | 63.6% (28) |
| No | 36.4% (16) |
| Gross total resection | |
| Yes | 22.7% (10) |
| No | 77.3% (34) |
| Preoperative Tumor Volume (cm3) | Residual Tumor Volume (cm3) | Tumor Resected Based on iMRI (%) | Tumor Resected Based on Tool-Tip Tracking (%) | False Positive Tracking (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 21.1 | 3.9 | 79.1 | 61.5 | 16.2 |
| Median | 16.4 | 2.9 | 86.7 | 60.4 | 12.6 |
| Minimum | 0.1 | 0.0 | 7.7 | 15.2 | 1.5 |
| Maximum | 86.2 | 18.2 | 100.0 | 99.7 | 47.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juvekar, P.; Torio, E.; Bi, W.L.; Bastos, D.C.D.A.; Golby, A.J.; Frisken, S.F. Mapping Resection Progress by Tool-Tip Tracking during Brain Tumor Surgery for Real-Time Estimation of Residual Tumor. Cancers 2023, 15, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030825
Juvekar P, Torio E, Bi WL, Bastos DCDA, Golby AJ, Frisken SF. Mapping Resection Progress by Tool-Tip Tracking during Brain Tumor Surgery for Real-Time Estimation of Residual Tumor. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):825. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030825
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuvekar, Parikshit, Erickson Torio, Wenya Linda Bi, Dhiego Chaves De Almeida Bastos, Alexandra J. Golby, and Sarah F. Frisken. 2023. "Mapping Resection Progress by Tool-Tip Tracking during Brain Tumor Surgery for Real-Time Estimation of Residual Tumor" Cancers 15, no. 3: 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030825
APA StyleJuvekar, P., Torio, E., Bi, W. L., Bastos, D. C. D. A., Golby, A. J., & Frisken, S. F. (2023). Mapping Resection Progress by Tool-Tip Tracking during Brain Tumor Surgery for Real-Time Estimation of Residual Tumor. Cancers, 15(3), 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030825





