The Influence of the Normal Mammary Microenvironment on Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Breast Cancer
1.2. HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
1.3. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
1.4. Mammary Gland Development
1.5. Mammary Gland Stem Cell Niche
2. Cell Redirection
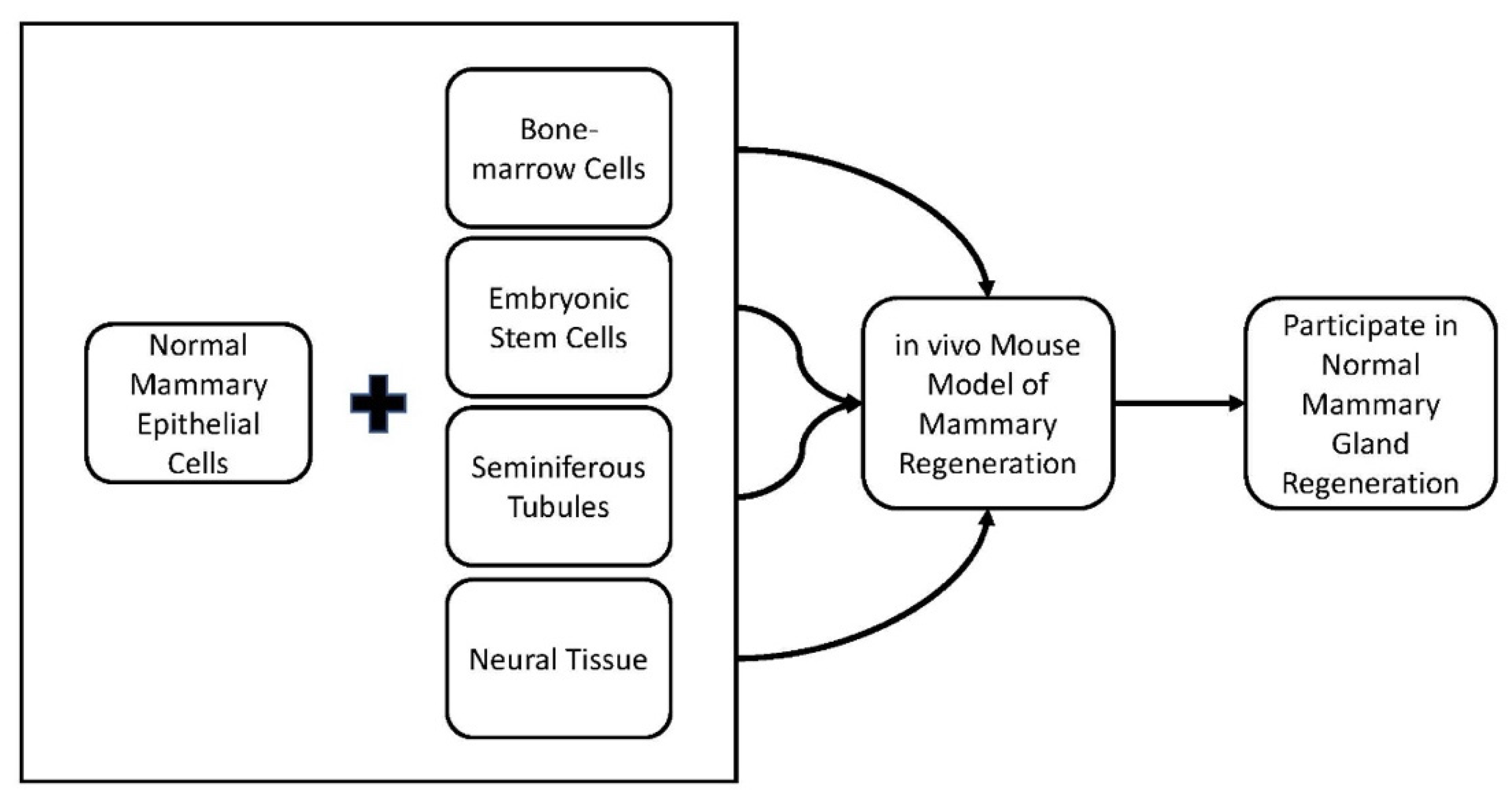
2.1. Cell Redirection by Mammary Microenvironments In Vivo
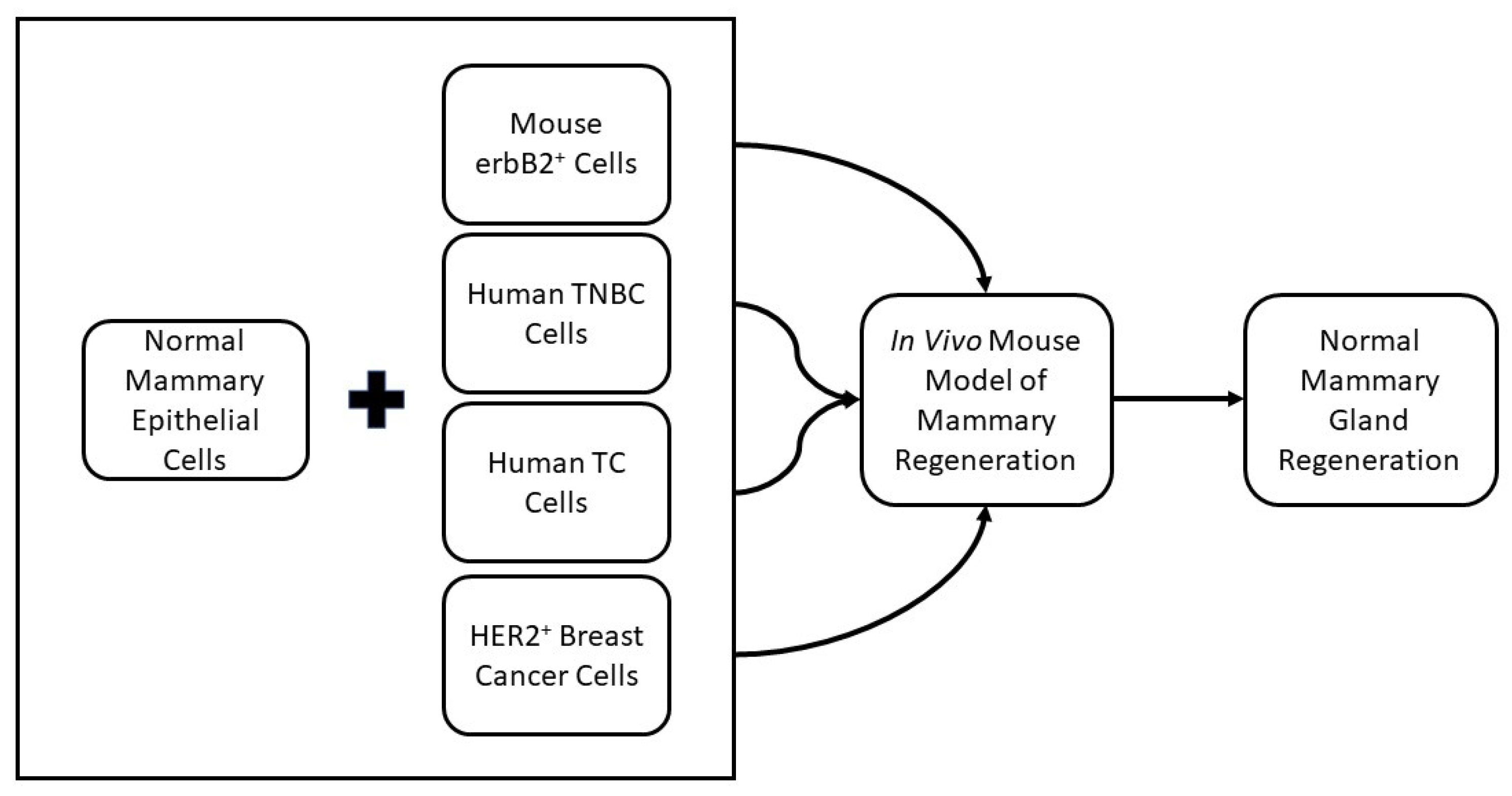
2.2. Cancer Cell Redirection
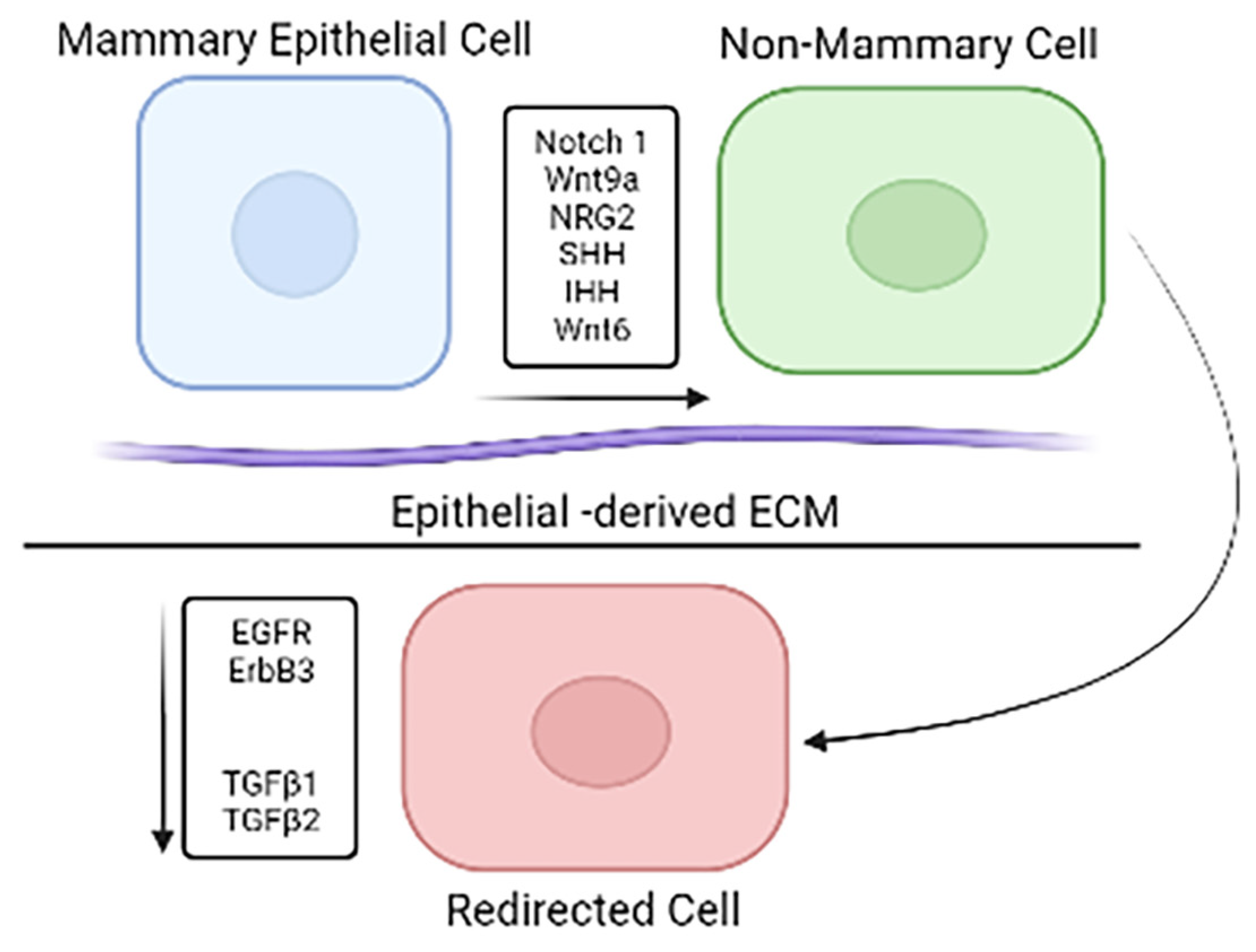
2.3. Differential Gene Expression in Mouse Mammary Microenvironment In Vitro
2.4. Cell Redirection by Mammary Microenvironment In Vitro
2.5. Phenotypic Changes Induced through In Vitro Redirection
2.6. Gene Expression Profile Changes In Vitro Redirection
3. Conclusions
4. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitt, S.J. Classification and prognosis of invasive breast cancer: From morphology to molecular taxonomy. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, S60–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehraj, U.; Dar, A.H.; Wani, N.A.; Mir, M.A. Tumor microenvironment promotes breast cancer chemoresistance. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieduwilt, M.J.; Moasser, M.M. The epidermal growth factor receptor family: Biology driving targeted therapeutics. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1566–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus-Porta, D.; Beerli, R.R.; Daly, J.M.; Hynes, N.E. ErbB-2, the preferred heterodimerization partner of all ErbB receptors, is a mediator of lateral signaling. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteaga, C.L.; Sliwkowski, M.X.; Osborne, C.K.; Perez, E.A.; Puglisi, F.; Gianni, L. Treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer: Current status and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 9, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, C.E.; Forster, J.; Lindquist, D.; Chan, S.; Romieu, C.G.; Pienkowski, T.; Jagiello-Gruszfeld, A.; Crown, J.; Chan, A.; Kaufman, B.; et al. Lapatinib plus Capecitabine for HER2-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, R.H.; Kaklamani, V.G. HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Drugs 2007, 67, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshani, A.; Rezaei, Z.; Safarpour, H.; Sabri, M.; Mir, A.; Sanati, M.A.; Vahidian, F.; Moghadam, A.G.; Aghadoukht, A.; Hajiasgharzadeh, K.; et al. Overcoming trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer using combination therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 235, 3142–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Minden, A. Current Molecular Combination Therapies Used for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias, H.; Hinck, L. Mammary gland development. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2012, 1, 533–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassiotou, F.; Geddes, D. Anatomy of the human mammary gland: Current status of knowledge. Clin. Anat. 2012, 26, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, A.C.; Fu, N.Y.; Lindeman, G.J.; Visvader, J.E. In situ identification of bipotent stem cells in the mammary gland. Nature 2014, 506, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank-Kamenetskii, A.; Booth, B.W. Redirecting Normal and Cancer Stem Cells to a Mammary Epithelial Cell Fate. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2019, 24, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank-Kamenetskii, A.; Mook, J.; Reeves, M.; Boulanger, C.A.; Meyer, T.J.; Ragle, L.; Jordan, H.C.; Smith, G.H.; Booth, B.W. Induction of phenotypic changes in HER2-postive breast cancer cells in vivo and in vitro. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 2919–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, B.W.; Boulanger, C.A.; Anderson, L.H.; Smith, G.H. The normal mammary microenvironment suppresses the tumorigenic phenotype of mouse mammary tumor virus-neu-transformed mammary tumor cells. Oncogene 2010, 30, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landskroner-Eiger, S.; Park, J.; Israel, D.; Pollard, J.W.; Scherer, P.E. Morphogenesis of the developing mammary gland: Stage-dependent impact of adipocytes. Dev. Biol. 2010, 344, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couldrey, C.; Moitra, J.; Vinson, C.; Anver, M.; Nagashima, K.; Green, J. Adipose tissue: A vital in vivo role in mammary gland development but not differentiation. Dev. Dyn. 2002, 223, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisken, C.; Park, S.; Vass, T.; Lydon, J.P.; O’Malley, B.W.; Weinberg, R.A. A paracrine role for the epithelial progesterone receptor in mammary gland development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5076–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.A.; Nusse, R. Wnt Proteins Are Self-Renewal Factors for Mammary Stem Cells and Promote Their Long-Term Expansion in Culture. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, R.D.; Smith, G.H. A potential mechanism for extracellular matrix induction of breast cancer cell normality. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaks, V.; Kong, N.; Werb, Z. The Cancer Stem Cell Niche: How Essential Is the Niche in Regulating Stemness of Tumor Cells? Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulanger, C.A.; Mack, D.L.; Booth, B.W.; Smith, G.H. Interaction with the mammary microenvironment redirects spermatogenic cell fate in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3871–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, B.W.; Mack, D.L.; Androutsellis-Theotokis, A.; McKay, R.D.G.; Boulanger, C.A.; Smith, G.H. The mammary microenvironment alters the differentiation repertoire of neural stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14891–14896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, C.A.; Bruno, R.D.; Mack, D.L.; Gonzales, M.; Castro, N.P.; Salomon, D.S.; Smith, G.H. Embryonic Stem Cells Are Redirected to Non-Tumorigenic Epithelial Cell Fate by Interaction with the Mammary Microenvironment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulanger, C.A.; Bruno, R.D.; Rosu-Myles, M.; Smith, G.H. The Mouse Mammary Microenvironment Redirects Mesoderm-Derived Bone Marrow Cells to a Mammary Epithelial Progenitor Cell Fate. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.D.; Triplett, A.A.; Oh, K.B.; Smith, G.H.; Wagner, K.-U. Parity-induced mammary epithelial cells facilitate tumorigenesis in MMTV-neu transgenic mice. Oncogene 2004, 23, 6980–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, R.D.; Smith, G.H. Reprogramming non-mammary and cancer cells in the developing mouse mammary gland. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketo, M.; Schroeder, A.C.; Mobraaten, L.E.; Gunning, K.B.; Hanten, G.; Fox, R.R.; Roderick, T.H.; Stewart, C.L.; Lilly, F.; Hansen, C.T. FVB/N: An inbred mouse strain preferable for transgenic analyses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2065–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussard, K.M.; Smith, G.H. Human Breast Cancer Cells Are Redirected to Mammary Epithelial Cells upon Interaction with the Regenerating Mammary Gland Microenvironment In-Vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussard, K.M.; Boulanger, C.A.; Booth, B.W.; Bruno, R.D.; Smith, G.H. Reprogramming Human Cancer Cells in the Mouse Mammary Gland. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6336–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.P.; Raafat, A.; Feltracco, J.A.; Blanding, W.M.; Booth, B.W. Differential Gene Expression in Nuclear Label-Retaining Cells in the Developing Mouse Mammary Gland. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.P.; Blanding, W.M.; Feltracco, J.A.; Booth, B.W. Validation of an in vitro model of erbB2+ cancer cell redirection. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2015, 51, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, K.; Feltus, F.A.; Park, J.P.; Coissieux, M.-M.; Chang, C.; Chan, V.B.S.; Bentires-Alj, M.; Booth, B.W. Cancer cell redirection biomarker discovery using a mutual information approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmucker, H.S.; Park, J.P.; Coissieux, M.-M.; Bentires-Alj, M.; Feltus, F.A.; Booth, B.W. RNA Expression Profiling Reveals Differentially Regulated Growth Factor and Receptor Expression in Redirected Cancer Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2017, 26, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, R.D.; Fleming, J.M.; George, A.L.; Boulanger, C.A.; Schedin, P.; Smith, G.H. Mammary extracellular matrix directs differentiation of testicular and embryonic stem cells to form functional mammary glands in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cells Transplanted | Ratio of Cancer Cells:MECs | # Positive Takes/# Implants | # Cancer Cell Takes/# Positive Takes | % Tumors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse erbB2+ Cancer Cells Only | Cancer only | 0/18 | 0/0 | 100 |
| Mouse erbB2+ Cancer Cells with MECs | 1:50 | 15/16 | 15/15 | 6.25 |
| Human TC Cells Only | Cancer only | 0/6 | 0/0 | 33.3 |
| Human TC Cells with MECs | 1:50 | 10/12 | 10/10 | 0 |
| Human TNBC Cells with MECs | 1:5 | 5/20 | 5/5 | 50 |
| Human TNBC Cells with MECs | 1:50 | 10/16 | 10/10 | 0 |
| HER2+ Breast Cancer Cells Only | Cancer only | 0/4 | 0/0 | 100 |
| HER2+ Breast Cancer Cells with MECs | 1:50 | 2/4 | 2/4 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campbell, C.J.; Booth, B.W. The Influence of the Normal Mammary Microenvironment on Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2023, 15, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030576
Campbell CJ, Booth BW. The Influence of the Normal Mammary Microenvironment on Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030576
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampbell, Caroline J., and Brian W. Booth. 2023. "The Influence of the Normal Mammary Microenvironment on Breast Cancer Cells" Cancers 15, no. 3: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030576
APA StyleCampbell, C. J., & Booth, B. W. (2023). The Influence of the Normal Mammary Microenvironment on Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers, 15(3), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030576








