The Targeted Degradation of BRAF V600E Reveals the Mechanisms of Resistance to BRAF-Targeted Treatments in Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines, Media, and Drugs
2.2. Cell Culture and Viability Assays
2.3. Curve Fitting by the Hill Equation
2.4. Time Course Experiments
2.5. Cell Treatments and Western Blots
3. Results
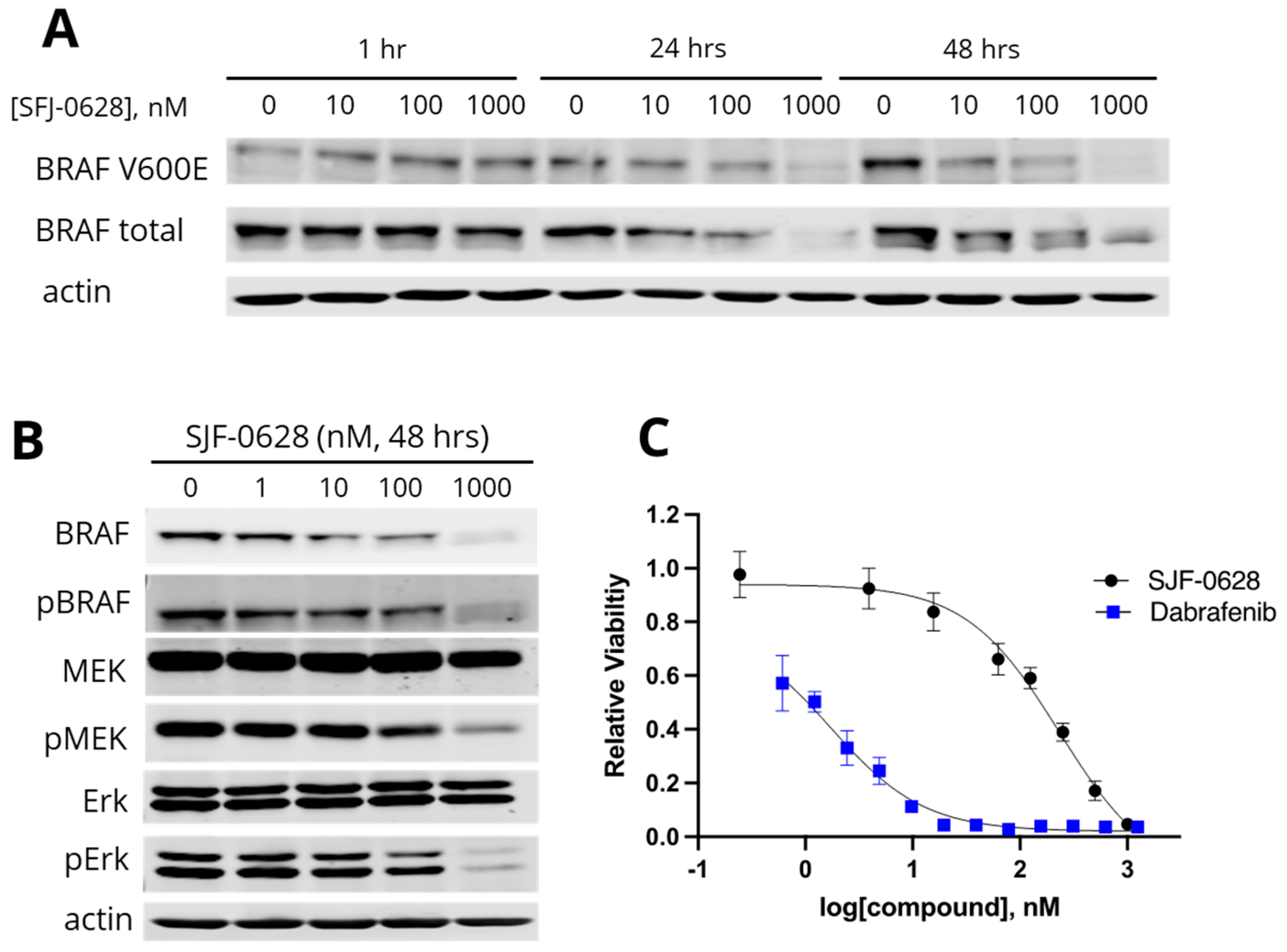
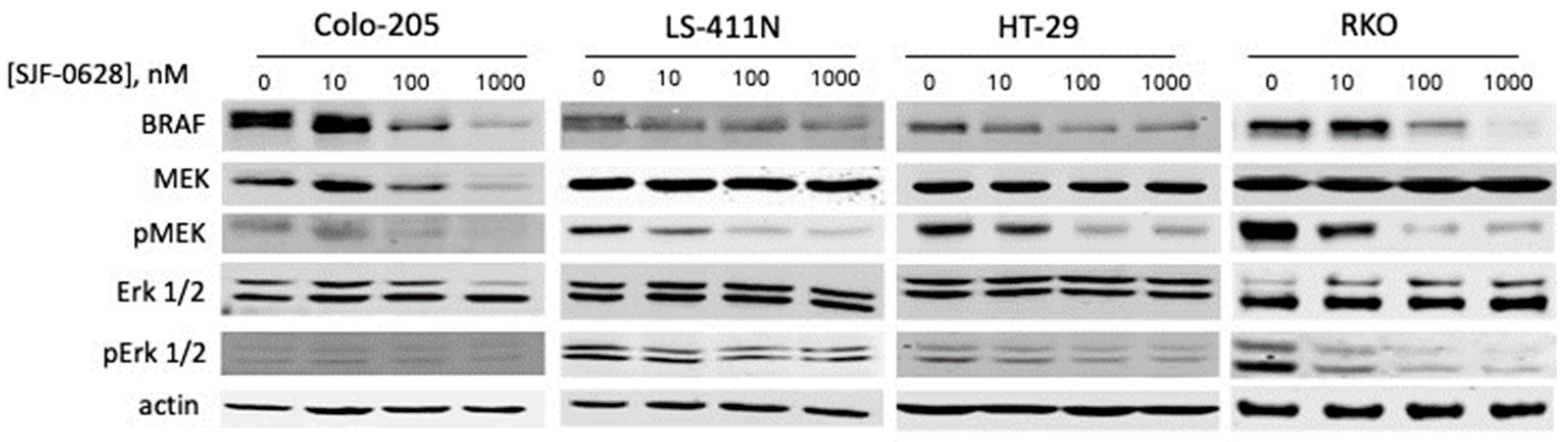
3.1. Treatment with SJF-0628 Caused Specific Degradation of BRAF in All Cell Lines
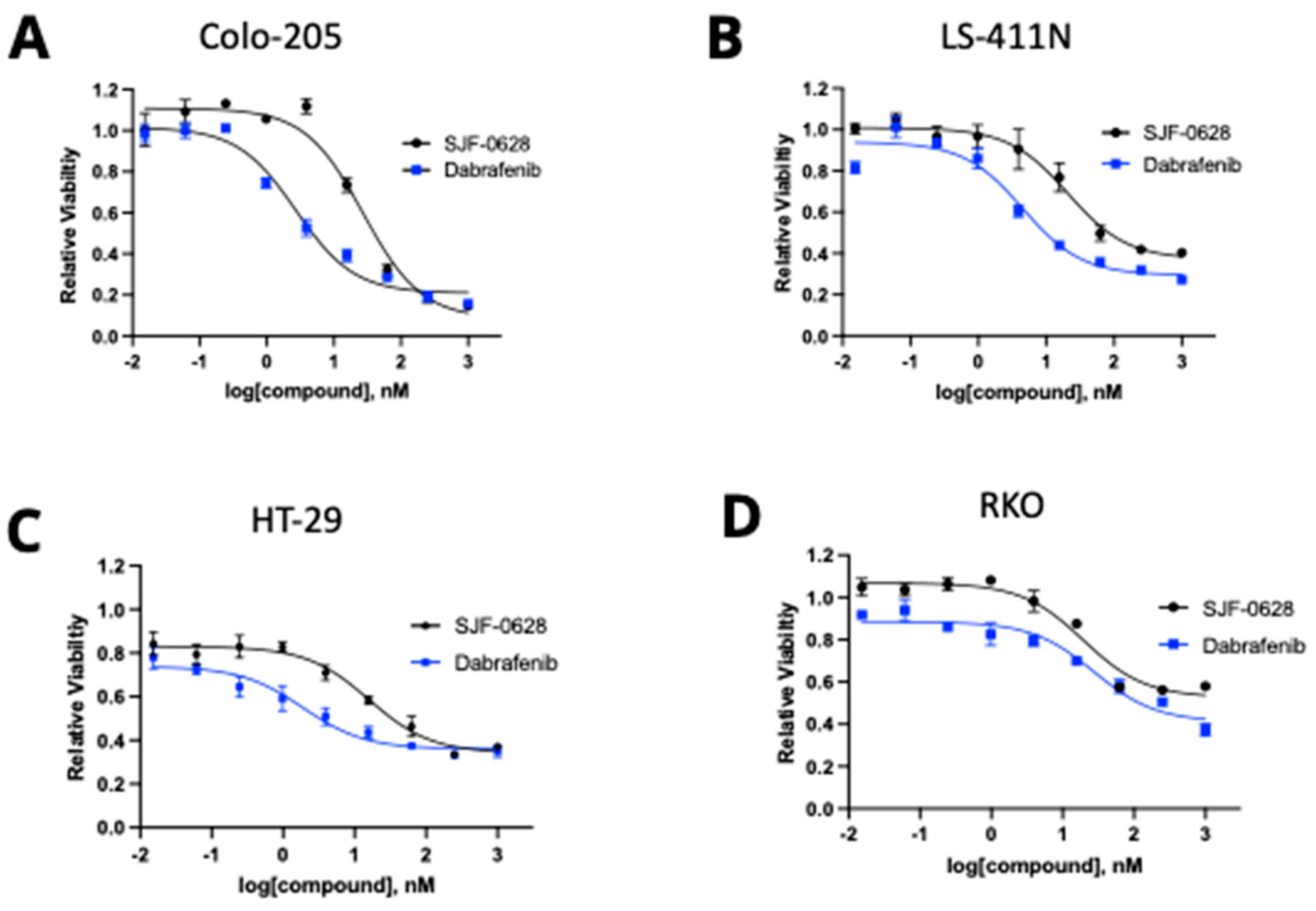
3.2. Treatment with SJF-0628 and the BRAF Inhibitor Dabrafenib Caused Cell Line-Dependent Effects on Cell Viability
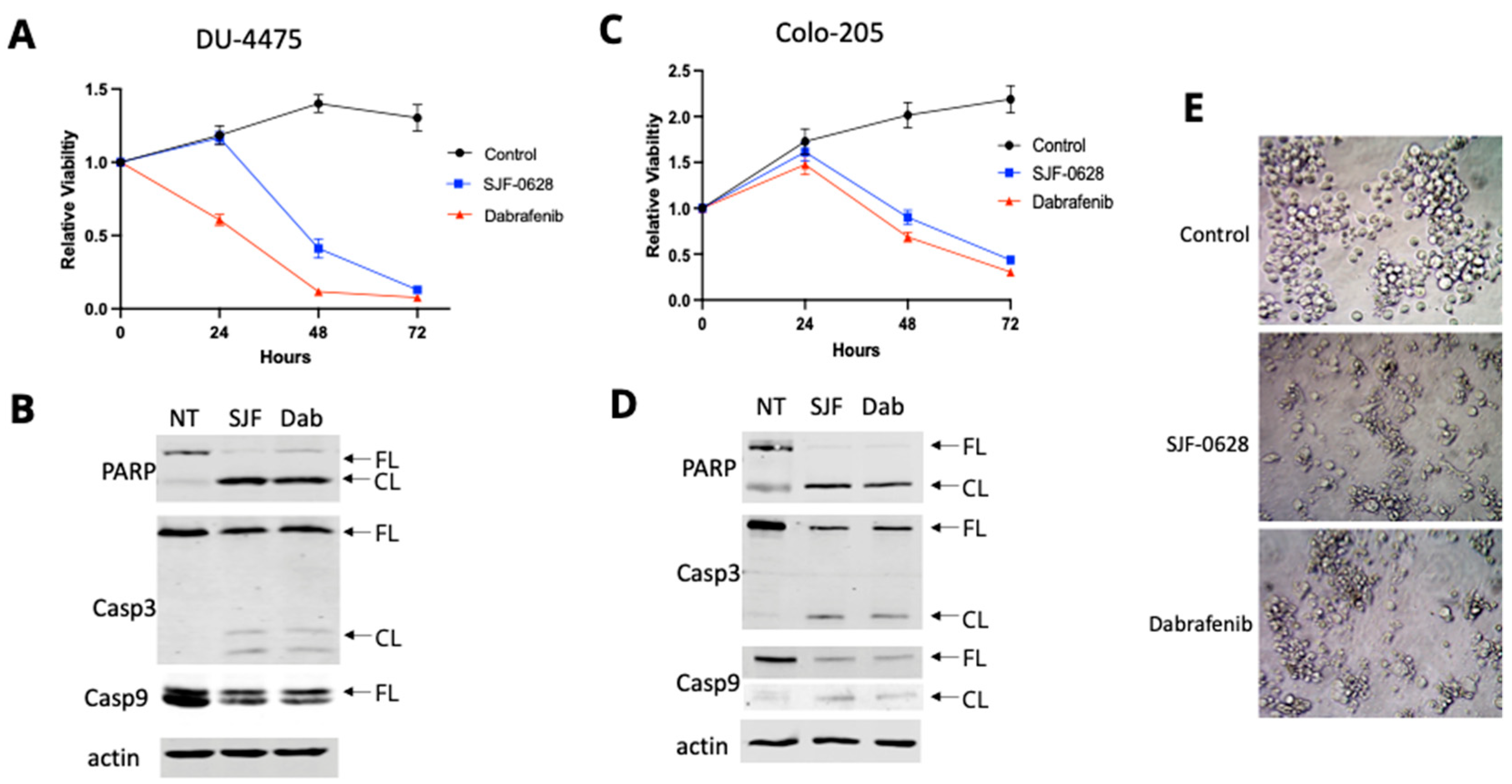
3.3. Treatment with SJF-0628 Causes Cell Apoptosis in DU-4475 and Colo-205 Cancer Cells
3.4. HT-29 and RKO Are Multi-Driver Cancer Cell Lines and Are Not Lethally Inhibited by BRAF Degradation or Inhibition
4. Discussion
4.1. SJF-0628 Causes Specific Degradation of BRAF V600E in CRC and TNBC Cancer Cells
4.2. DU-4475 and Colo-205 Are BRAF V600E-Dependent Mono-Driver Cancer Cell Lines
4.3. Most CRC Cells Are Not Killed by BRAF Degradation or Inhibition Due to Their Multi-Driver Nature
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Durrant, D.E.; Morrison, D.K. Targeting the Raf kinases in human cancer: The Raf dimer dilemma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, H.; Bignell, G.R.; Cox, C.; Stephens, P.; Edkins, S.; Clegg, S.; Teague, J.; Woffendin, H.; Garnett, M.J.; Bottomley, W.; et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 2002, 417, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.R.; Chen, L.; Wei, Y.; Yu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Jiao, B.; Shi, T.; Sun, L.; Xu, Y.; et al. Discovery of Selective Small Molecule Degraders of BRAF-V600E. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 4069–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, H.; Therrien, M. Regulation of RAF protein kinases in ERK signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauri, G.; Bonazzina, E.; Amatu, A.; Tosi, F.; Bencardino, K.; Gori, V.; Massihnia, D.; Cipani, T.; Spina, F.; Ghezzi, S.; et al. The Evolutionary Landscape of Treatment for. Cancers 2021, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, J.G.B.; Otterson, G.A. Agents to treat. Drugs Context 2019, 8, 212566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López de Sá, A.; de Luna, A.; Antoñanzas, M.; García-Barberán, V.; Moreno-Anton, F.; García-Sáenz, J.A. Case report: Clinical success targeting BRAF-mutated, hormone receptor positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer patient with BRAF-inhibitor plus MEK-inhibitor. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 997346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capper, D.; Berghoff, A.S.; Magerle, M.; Ilhan, A.; Wöhrer, A.; Hackl, M.; Pichler, J.; Pusch, S.; Meyer, J.; Habel, A.; et al. Immunohistochemical testing of BRAF V600E status in 1120 tumor tissue samples of patients with brain metastases. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiacci, E.; Trifonov, V.; Schiavoni, G.; Holmes, A.; Kern, W.; Martelli, M.P.; Pucciarini, A.; Bigerna, B.; Pacini, R.; Wells, V.A.; et al. BRAF mutations in hairy-cell leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2305–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustgi, A.K. BRAF: A driver of the serrated pathway in colon cancer. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, G.C.; Chapdelaine, A.G.; Ayrapetov, M.K.; Sun, G. Identification of Lethal Inhibitors and Inhibitor Combinations for Mono-Driver versus Multi-Driver Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, A.; Wu, W.; Bivona, T.G. Targeting Oncogenic BRAF: Past, Present, and Future. Cancers 2019, 11, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollag, G.; Hirth, P.; Tsai, J.; Zhang, J.; Ibrahim, P.N.; Cho, H.; Spevak, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Habets, G.; et al. Clinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor needs broad target blockade in BRAF-mutant melanoma. Nature 2010, 467, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschild, A.; Grob, J.J.; Demidov, L.V.; Jouary, T.; Gutzmer, R.; Millward, M.; Rutkowski, P.; Blank, C.U.; Miller, W.H.; Kaempgen, E.; et al. Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: A multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelblinger, P.; Thuerigen, O.; Dummer, R. Development of encorafenib for BRAF-mutated advanced melanoma. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.B.; Hauschild, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.B.; Ascierto, P.; Larkin, J.; Dummer, R.; Garbe, C.; Testori, A.; Maio, M.; et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorenko, I.V.; Paraiso, K.H.; Smalley, K.S. Acquired and intrinsic BRAF inhibitor resistance in BRAF V600E mutant melanoma. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosman, J.A.; Kim, K.B.; Schuchter, L.; Gonzalez, R.; Pavlick, A.C.; Weber, J.S.; McArthur, G.A.; Hutson, T.E.; Moschos, S.J.; Flaherty, K.T.; et al. Survival in BRAF V600-mutant advanced melanoma treated with vemurafenib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahallad, A.; Sun, C.; Huang, S.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Salazar, R.; Zecchin, D.; Beijersbergen, R.L.; Bardelli, A.; Bernards, R. Unresponsiveness of colon cancer to BRAF(V600E) inhibition through feedback activation of EGFR. Nature 2012, 483, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, J.; Vultur, A.; Lee, J.T.; Somasundaram, R.; Fukunaga-Kalabis, M.; Cipolla, A.K.; Wubbenhorst, B.; Xu, X.; Gimotty, P.A.; Kee, D.; et al. Acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors mediated by a RAF kinase switch in melanoma can be overcome by cotargeting MEK and IGF-1R/PI3K. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Suzuki, M.; Kawachi, H.; Low, S.K.; Oh-Hara, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Fujita, N.; Nagayama, S.; Katayama, R. Acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors is mediated by BRAF splicing variants in BRAF V600E mutation-positive colorectal neuroendocrine carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2022, 543, 215799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannessen, C.M.; Boehm, J.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Thomas, S.R.; Wardwell, L.; Johnson, L.A.; Emery, C.M.; Stransky, N.; Cogdill, A.P.; Barretina, J.; et al. COT drives resistance to RAF inhibition through MAP kinase pathway reactivation. Nature 2010, 468, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahronian, L.G.; Sennott, E.M.; Van Allen, E.M.; Wagle, N.; Kwak, E.L.; Faris, J.E.; Godfrey, J.T.; Nishimura, K.; Lynch, K.D.; Mermel, C.H.; et al. Clinical Acquired Resistance to RAF Inhibitor Combinations in BRAF-Mutant Colorectal Cancer through MAPK Pathway Alterations. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Torres, N.M.; Tao, A.; Gao, Y.; Luo, L.; Li, Q.; de Stanchina, E.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Solit, D.B.; Poulikakos, P.I.; et al. BRAF Mutants Evade ERK-Dependent Feedback by Different Mechanisms that Determine Their Sensitivity to Pharmacologic Inhibition. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.T.; Infante, J.R.; Daud, A.; Gonzalez, R.; Kefford, R.F.; Sosman, J.; Hamid, O.; Schuchter, L.; Cebon, J.; Ibrahim, N.; et al. Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition in melanoma with BRAF V600 mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1694–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Grob, J.J.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Karaszewska, B.; Hauschild, A.; Levchenko, E.; Chiarion Sileni, V.; Schachter, J.; Garbe, C.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes with Dabrafenib plus Trametinib in Metastatic Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Atreya, C.E.; Falchook, G.S.; Kwak, E.L.; Ryan, D.P.; Bendell, J.C.; Hamid, O.; Messersmith, W.A.; Daud, A.; Kurzrock, R.; et al. Combined BRAF and MEK Inhibition With Dabrafenib and Trametinib in BRAF V600-Mutant Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 4023–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Ebi, H.; Turke, A.B.; Coffee, E.M.; Nishino, M.; Cogdill, A.P.; Brown, R.D.; Della Pelle, P.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Hung, K.E.; et al. EGFR-mediated re-activation of MAPK signaling contributes to insensitivity of BRAF mutant colorectal cancers to RAF inhibition with vemurafenib. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Bergethon, K.; Iafrate, A.J.; Settleman, J.; Engelman, J.A. BRAF gene amplification can promote acquired resistance to MEK inhibitors in cancer cells harboring the BRAF V600E mutation. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopetz, S.; Grothey, A.; Yaeger, R.; Van Cutsem, E.; Desai, J.; Yoshino, T.; Wasan, H.; Ciardiello, F.; Loupakis, F.; Hong, Y.S.; et al. Encorafenib, Binimetinib, and Cetuximab in BRAF V600E-Mutated Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1632–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, R.B.; André, T.; Atreya, C.E.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Yoshino, T.; Bendell, J.C.; Hollebecque, A.; McRee, A.J.; Siena, S.; Middleton, G.; et al. Combined BRAF, EGFR, and MEK Inhibition in Patients with BRAF(V600E)-Mutant Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 428–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Békés, M.; Langley, D.R.; Crews, C.M. PROTAC targeted protein degraders: The past is prologue. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salami, J.; Crews, C.M. Waste disposal-An attractive strategy for cancer therapy. Science 2017, 355, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, A.C.; Crews, C.M. Induced protein degradation: An emerging drug discovery paradigm. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.M.; Kim, K.B.; Kumagai, A.; Mercurio, F.; Crews, C.M.; Deshaies, R.J. Protacs: Chimeric molecules that target proteins to the Skp1-Cullin-F box complex for ubiquitination and degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8554–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabi, S.; Jaime-Figueroa, S.; Yao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Hines, J.; Samarasinghe, K.T.G.; Vogt, L.; Rosen, N.; Crews, C.M. Mutant-selective degradation by BRAF-targeting PROTACs. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasetti, C.; Marchionni, L.; Nowak, M.A.; Parmigiani, G.; Vogelstein, B. Only three driver gene mutations are required for the development of lung and colorectal cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelstein, B.; Papadopoulos, N.; Velculescu, V.E.; Zhou, S.; Diaz, L.A.; Kinzler, K.W. Cancer genome landscapes. Science 2013, 339, 1546–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martincorena, I.; Raine, K.M.; Gerstung, M.; Dawson, K.J.; Haase, K.; Van Loo, P.; Davies, H.; Stratton, M.R.; Campbell, P.J. Universal Patterns of Selection in Cancer and Somatic Tissues. Cell 2017, 171, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, L.; Yang, T.; Cohen, P.S.; Sun, G. Biphasic Mathematical Model of Cell-Drug Interaction That Separates Target-Specific and Off-Target Inhibition and Suggests Potent Targeted Drug Combinations for Multi-Driver Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Flaherty, K.T. BRAF targeted therapy changes the treatment paradigm in melanoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasband, W.S. ImageJ; U. S. National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1997–2018; 1.53k. [Google Scholar]
- Tate, J.G.; Bamford, S.; Jubb, H.C.; Sondka, Z.; Beare, D.M.; Bindal, N.; Boutselakis, H.; Cole, C.G.; Creatore, C.; Dawson, E.; et al. COSMIC: The Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D941–D947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnaby, W.; Koegl, M.; Roy, M.J.; Whitworth, C.; Diers, E.; Trainor, N.; Zollman, D.; Steurer, S.; Karolyi-Oezguer, J.; Riedmueller, C.; et al. BAF complex vulnerabilities in cancer demonstrated via structure-based PROTAC design. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langlois, A.J.; Holder, W.D.; Iglehart, J.D.; Nelson-Rees, W.A.; Wells, S.A.; Bolognesi, D.P. Morphological and biochemical properties of a new human breast cancer cell line. Cancer Res. 1979, 39, 2604–2613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riaz, M.; van Jaarsveld, M.T.; Hollestelle, A.; Prager-van der Smissen, W.J.; Heine, A.A.; Boersma, A.W.; Liu, J.; Helmijr, J.; Ozturk, B.; Smid, M.; et al. miRNA expression profiling of 51 human breast cancer cell lines reveals subtype and driver mutation-specific miRNAs. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windham, T.C.; Parikh, N.U.; Siwak, D.R.; Summy, J.M.; McConkey, D.J.; Kraker, A.J.; Gallick, G.E. Src activation regulates anoikis in human colon tumor cell lines. Oncogene 2002, 21, 7797–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuels, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bardelli, A.; Silliman, N.; Ptak, J.; Szabo, S.; Yan, H.; Gazdar, A.; Powell, S.M.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 2004, 304, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, Y.; Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Schmidt-Kittler, O.; Cummins, J.M.; Delong, L.; Cheong, I.; Rago, C.; Huso, D.L.; Lengauer, C.; Kinzler, K.W.; et al. Mutant PIK3CA promotes cell growth and invasion of human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Bader, A.G.; Vogt, P.K. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mutations identified in human cancer are oncogenic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Kakegawa, J.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hantani, Y.; Okajima, N.; Sakai, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Nakamura, M. Identification and characterization of a novel chemotype MEK inhibitor able to alter the phosphorylation state of MEK1/2. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.M.; Real, A.M.; Marsiglia, W.M.; Chow, A.; Duffy, M.E.; Yerabolu, J.R.; Scopton, A.P.; Dar, A.C. Structural basis for the action of the drug trametinib at KSR-bound MEK. Nature 2020, 588, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Del Pino, G.L.; Li, K.; Park, E.; Schmoker, A.M.; Ha, B.H.; Eck, M.J. Allosteric MEK inhibitors act on BRAF/MEK complexes to block MEK activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2107207118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, I.B. Cancer. Addiction to oncogenes—The Achilles heal of cancer. Science 2002, 297, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, I.B.; Joe, A.K. Mechanisms of disease: Oncogene addiction—A rationale for molecular targeting in cancer therapy. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2006, 3, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pircher, M.; Winder, T.; Trojan, A. Response to Vemurafenib in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Harbouring a BRAF V600E Mutation: A Case Report and Electronically Captured Patient-Reported Outcome. Case Rep. Oncol. 2021, 14, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, T.; Noguchi, E.; Yoshida, M.; Mori, T.; Tanioka, M.; Sudo, K.; Shimomura, A.; Yonemori, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tamura, K. Response to Dabrafenib and Trametinib of a Patient with Metaplastic Breast Carcinoma Harboring a BRAF V600E Mutation. Case Rep. Oncol. Med. 2020, 2020, 2518383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lu, Q.; Jiang, K.; Hong, R.; Wang, S.; Xu, F. BRAF V600E Mutation in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Case Report and Literature Review. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2022, 45, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druker, B.J. Translation of the Philadelphia chromosome into therapy for CML. Blood 2008, 112, 4808–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, D.E. EGFR Inhibition in the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Drug Dev. Res. 2008, 69, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Z.; Raut, C.P. Targeted therapy and personalized medicine in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Drug resistance, mechanisms, and treatment strategies. Onco. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 5123–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
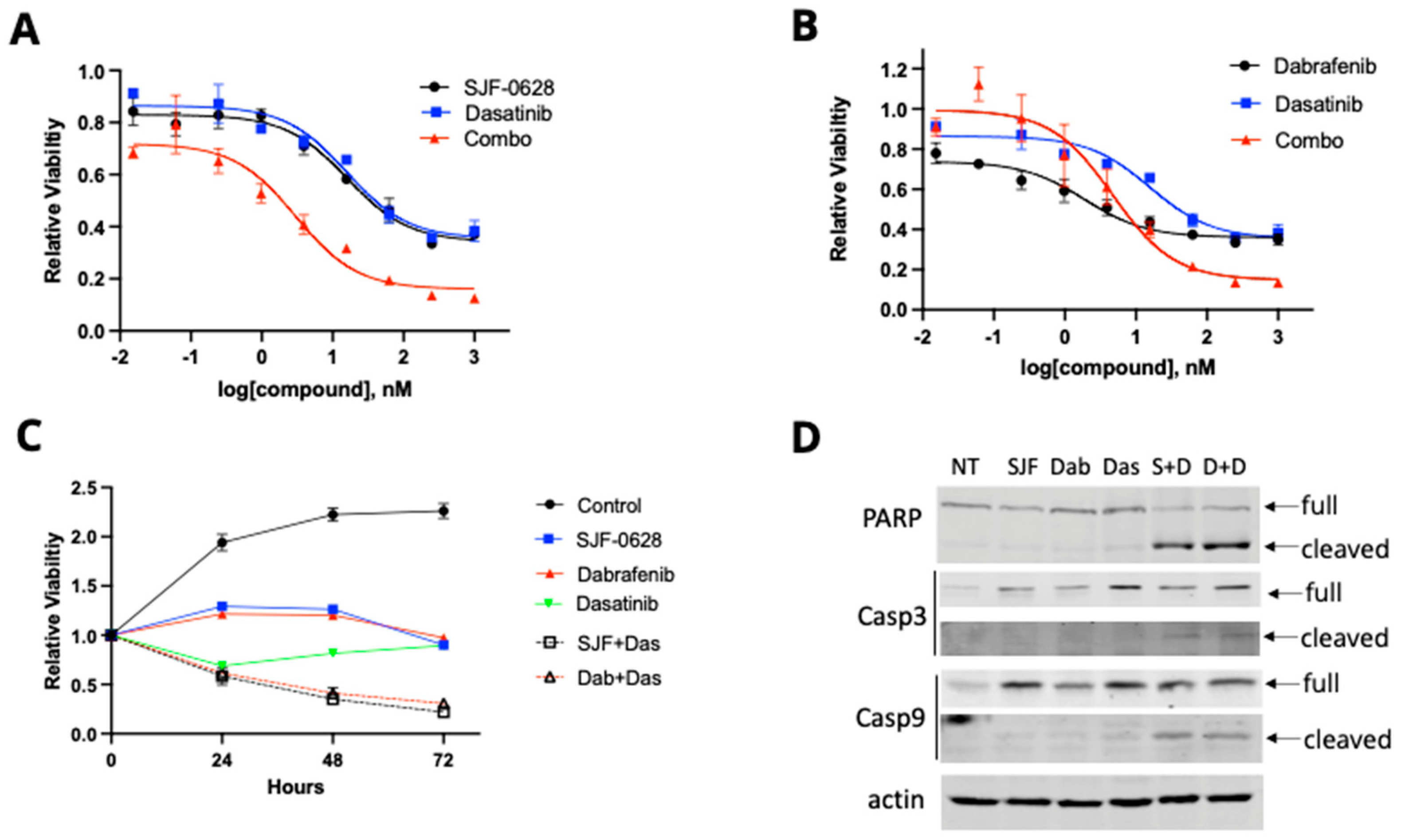
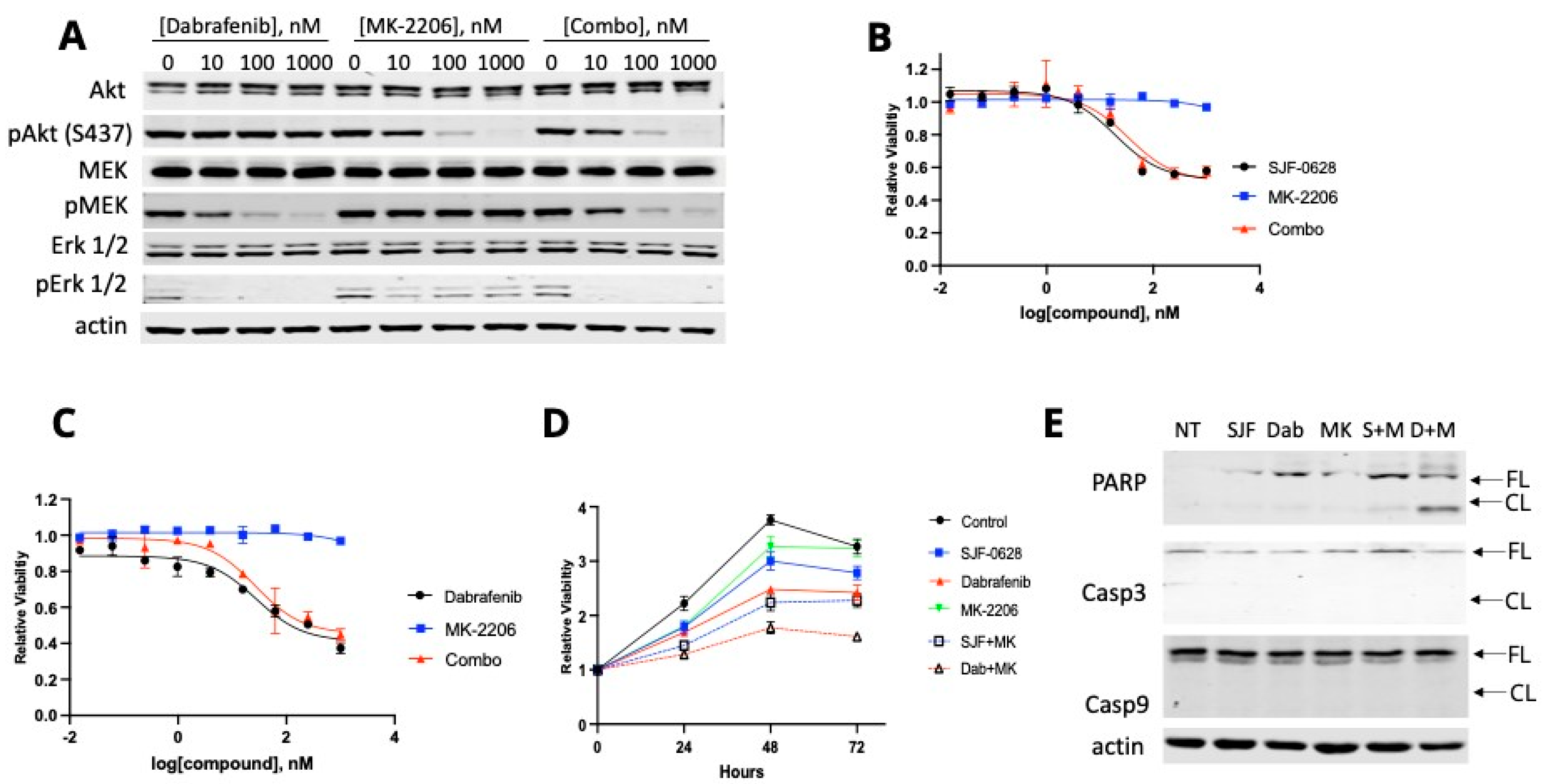
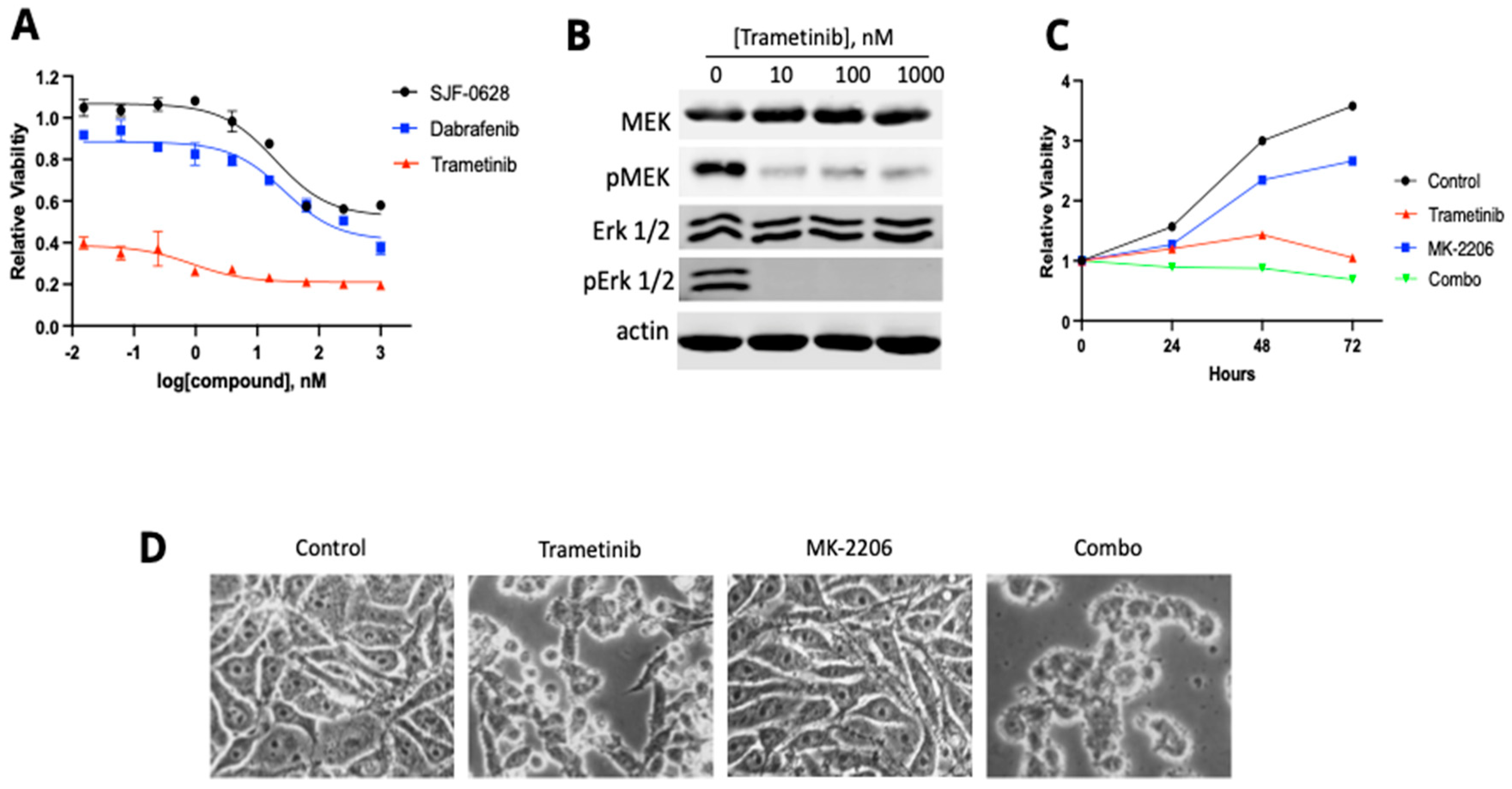
| Cell Line | Tumor Type | BRAF V600E Genotype | Other Drivers | Cancer Mutations | Total Mutations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DU-4475 | TNBC | Heterozygous | None | 50 | 387 |
| Colo-205 | CRC | Heterozygous | None | 42 | 312 |
| LS-411N | CRC | Heterozygous | Unknown | 567 | 7141 |
| HT-29 | CRC | Heterozygous | Src | 24 | 676 |
| RKO | CRC | Heterozygous | PI3K, others | 155 | 4762 |
| Cell Line | IC50 (nM) | Imax (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SJF-0628 | Dabrafenib | SJF-0628 | Dabrafenib | |
| DU-4475 | 163 ± 8.2 | 2.4 ± 0.5 | 91.5 ± 3.4 | 98.0 ± 0.25 * |
| Colo-205 | 37.6 ± 6.0 | 7.9 ± 4.1 | 85.2 ± 0.3 | 86.3 ± 2.9 |
| LS-411N | 96.3 ± 15.2 | 4.4 ± 2.5 | 65.2 ± 10.0 | 63.7 ± 8.0 |
| HT-29 | 53.6 ± 5.4 | 3.82 ± 2.3 | 63.0 ± 1.2 | 65.6 ± 2.9 |
| RKO | <1 µM | <1 µM | 42.0 ± 0.2 | 62.8 ± 0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chapdelaine, A.G.; Ku, G.C.; Sun, G.; Ayrapetov, M.K. The Targeted Degradation of BRAF V600E Reveals the Mechanisms of Resistance to BRAF-Targeted Treatments in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers 2023, 15, 5805. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245805
Chapdelaine AG, Ku GC, Sun G, Ayrapetov MK. The Targeted Degradation of BRAF V600E Reveals the Mechanisms of Resistance to BRAF-Targeted Treatments in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2023; 15(24):5805. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245805
Chicago/Turabian StyleChapdelaine, Abygail G., Geng Chia Ku, Gongqin Sun, and Marina K. Ayrapetov. 2023. "The Targeted Degradation of BRAF V600E Reveals the Mechanisms of Resistance to BRAF-Targeted Treatments in Colorectal Cancer Cells" Cancers 15, no. 24: 5805. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245805
APA StyleChapdelaine, A. G., Ku, G. C., Sun, G., & Ayrapetov, M. K. (2023). The Targeted Degradation of BRAF V600E Reveals the Mechanisms of Resistance to BRAF-Targeted Treatments in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers, 15(24), 5805. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245805





