Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast: A Comprehensive Review with Translational Insights
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathogenesis
3. ILC Histological Subtypes
4. Immunohistochemistry
5. Molecular Alterations in Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
5.1. CDH1 Mutations
5.2. Mutations of the PI3K/Akt Pathway
5.3. IGF1 Pathway
5.4. ERBB2 Mutations
5.5. Fibroblast Growth Factor Signaling
5.6. Endocrine Resistance and Fox A1 Amplification
5.7. ESR 1 Mutations
5.8. APOBEC and Tumor Mutational Burden
5.9. Germline Mutations
6. Gene Expression Profiling Tests
Lobsig
7. Tumor Microenvironment in ILC
8. ILC Radiology Aspects
9. Current Treatment Approaches
9.1. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
9.2. Surgery
9.3. Adjuvant Radiotherapy
9.4. Endocrine Therapy and CDK4/6 Inhibitors
9.5. Adjuvant Chemotherapy
9.6. HER-2 Targeted Therapies
9.7. Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor and Therapies
9.8. Treatment Schema
10. Important Clinical Trials Specific to ILC
- Trials researching the biology of ILC:
- LobularCard Trial: In this cross-sectional retrospective study, the population of interest is patients with LCIS and ILC. CDH1 is the unique mutation in ILCs; however, the germline mutation frequency is much less, and, hence, this trial aims to find out other genes associated with lobular breast cancer predisposition, using a panel of 113 genes in the “Illumina” protocol [115]. Thus, this will help in better understanding the disease, especially early-onset ILC.
- CDH1 Germline Mutations in Lobular Breast Cancer: Hereditary CDH1 germline mutations are associated with lobular carcinoma and associated hereditary diffuse gastric cancer. However, a few subsets of patients (<45 years) without hereditary diffuse gastric cancer also present with lobular cancer. Thus, this trial aims to investigate the prevalence of CDH1 in this specific population of women with early onset (<45 or <50) in situ or ILBC, bilateral LBC, or LBC with no family history of HDGC. Thus, this study might help in finding and better understanding the role of CDH1 as a susceptibility gene in lobular cancers [245].
- Drug intervention trials in ILC
- Early-stage ILC:
- (a)
- Palbociclib and Endocrine Therapy for Lobular Breast Cancer Preoperative Study (PELOPS) [209]: CDK4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy have shown promising results in HR+ breast cancer. In this randomized phase 2 trial studying ILC specifically, the patients are randomized to Tamoxifen versus Letrozole in the window phase, and the Ki67 score is measured in subsequent biopsies. The treatment phase includes patients who are randomized to tamoxifen plus palbociclib (CDK4/6 INHIBITOR) versus letrozole plus palbociclib.
- (b)
- Translational Breast Cancer Research Consortium 037 (TBCRC037) [246]: This is a randomized trial which studied neoadjuvant endocrine treatment strategies in postmenopausal woman with early-stage ILC. The study aims to find the efficacy of the most prevalent neoadjuvant therapies, viz., Tamoxifen, Anastrazole, and Fulvestrant, when given for a period of 21–24 days. The endpoint was measured by evaluating the Ki67 score.
- (c)
- Neoadjuvant Study of Targeting ROS1 in Combination with Endocrine Therapy in Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast (ROSALINE): Inhibitors of ROS 1 have been found effective in CDH1 tumors in preclinical studies (synthetic lethality) [73]. This trial is a neoadjuvant, single-arm, nonrandomized trial exploring the role of Entrectinib (ROS1 inhibitor) + letrozole in patients with early-stage ILC preoperatively, thus having the advantage of testing this treatment regimen in “treatment-naïve” tumors.
- Metastatic ILC:
- (a)
- MutHer II: In this single-arm multicohort phase 2 trial, the efficacy of Neratinib (irreversible pan-HER tyrosine kinase inhibitor) was evaluated in metastatic breast cancer patients with Her 2 mutations and not Her 2 amplifications. Although this trial was not ILC specific, they showed a 38% clinical benefit rate in fulvestrant-treated cases. Also, the clinical benefit rate was positively associated with ILC histology with Her 2 mutations, thus implying that this therapy may be more sensitive for such cases of ILC.
- (b)
- Crizotinib in Lobular Breast, Diffuse Gastric, and Triple Negative Lobular Breast Cancer or CDH1-mutated Solid Tumours (ROLo) [75]: This is a nonrandomized phase 2 study evaluating the role of a newer ROS1 inhibitor Crizotinib with fulvestrant in patients with E-cadherin defective, ER+ advanced, or metastatic lobular breast cancer.
11. Future Perspectives
12. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.I.; Anderson, B.O.; Daling, J.R.; Moe, R.E. Trends in incidence rates of invasive lobular and ductal breast carcinoma. JAMA 2003, 289, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouabbi, J.A.; Hassan, A.; Lim, B.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Tripathy, D.; Layman, R.M. Invasive lobular carcinoma: An understudied emergent subtype of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 193, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakha, E.A.; Ellis, I.O. Lobular breast carcinoma and its variants. In Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Biglia, N.; Mariani, L.; Sgro, L.; Mininanni, P.; Moggio, G.; Sismondi, P. Increased incidence of lobular breast cancer in women treated with hormone replacement therapy: Implications for diagnosis, surgical and medical treatment. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2007, 14, 549–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daling, J.R.; Malone, K.E.; Doody, D.R.; Voigt, L.F.; Bernstein, L.; Coates, R.J.; Marchbanks, P.A.; Norman, S.A.; Weiss, L.K.; Ursin, G. Relation of regimens of combined hormone replacement therapy to lobular, ductal, and other histologic types of breast carcinoma. Cancer Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 2002, 95, 2455–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colditz, G.A.; Hankinson, S.E.; Hunter, D.J.; Willett, W.C.; Manson, J.E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Hennekens, C.; Rosner, B.; Speizer, F.E. The use of estrogens and progestins and the risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veer, P.V.; Kok, F.J.; Hermus, R.J.; Sturmans, F. Alcohol dose, frequency and age at first exposure in relation to the risk of breast cancer. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1989, 18, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriello, G.; Gatza, M.L.; Beck, A.H.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Rhie, S.K.; Pastore, A.; Zhang, H.; McLellan, M.; Yau, C.; Kandoth, C.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Portraits of Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCart Reed, A.E.; Kalinowski, L.; Simpson, P.T.; Lakhani, S.R. Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: The increasing importance of this special subtype. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, K.H.; Brogi, E.; Ellis, I.; Fox, S.; Morris, E.; Sahin, A.; Salgado, R.; Sapino, A.; Sasano, H.; Schnitt, S. WHO Classification of Tumours: Breast Tumours; IARC Library Catalguing-in-Publication Data: Lyon, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Arpino, G.; Bardou, V.J.; Clark, G.M.; Elledge, R.M. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: Tumor characteristics and clinical outcome. Breast Cancer Res. 2004, 6, R149–R156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Juang, Y.-L.; Jeng, Y.-M. Frequent alterations of HER2 through mutation, amplification, or overexpression in pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 150, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, P.; Reis-Filho, J.; Lambros, M.; Jones, C.; Steele, D.; Mackay, A.; Iravani, M.; Fenwick, K.; Dexter, T.; Jones, A. Molecular profiling pleomorphic lobular carcinomas of the breast: Evidence for a common molecular genetic pathway with classic lobular carcinomas. J. Pathol. J. Pathol. Soc. Great Br. Irel. 2008, 215, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestalozzi, B.C.; Zahrieh, D.; Mallon, E.; Gusterson, B.A.; Price, K.N.; Gelber, R.D.; Holmberg, S.B.; Lindtner, J.; Snyder, R.; Thürlimann, B. Distinct clinical and prognostic features of infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: Combined results of 15 International Breast Cancer Study Group clinical trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3006–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlicot, S.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Medioni, J.; Genin, P.; Rosty, C.; Sigal-Zafrani, B.; Freneaux, P.; Jouve, M.; Thiery, J.-P.; Sastre-Garau, X. Wide metastatic spreading in infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, M.; Howell, A.; Chrissohou, M.; Swindell, R.; Hudson, M.; Sellwood, R. A comparison of the metastatic pattern of infiltrating lobular carcinoma and infiltrating duct carcinoma of the breast. Br. J. Cancer 1984, 50, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre-Garau, X.; Jouve, M.; Asselain, B.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Beuzeboc, P.; Dorval, T.; Durand, J.C.; Fourquet, A.; Pouillart, P. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: Clinicopathologic analysis of 975 cases with reference to data on conservative therapy and metastatic patterns. Cancer Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 1996, 77, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwast, A.B.; Groothuis-Oudshoorn, K.C.; Grandjean, I.; Ho, V.K.; Voogd, A.C.; Menke-Pluymers, M.B.; van der Sangen, M.J.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C.; Kiemeney, L.A.; Siesling, S. Histological type is not an independent prognostic factor for the risk pattern of breast cancer recurrences. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 135, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, T.; Kuukasjärvi, T.; Huhtala, H.; Alarmo, E.-L.; Holli, K.; Kallioniemi, A.; Pylkkänen, L. The impact of lobular and ductal breast cancer histology on the metastatic behavior and long term survival of breast cancer patients. Breast 2013, 22, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, F.W., Jr.; Stewart, F.W. Lobular carcinoma in situ: A rare form of mammary cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 1941, 17, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechner, R.E. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma without lobular carcinoma in situ. Cancer 1972, 29, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, J.S.; Ratze, M.A.; van Amersfoort, M.; Eisemann, T.; Vlug, E.J.; Niklaas, M.T.; Chin, S.F.; Caldas, C.; van Diest, P.J.; Jonkers, J. αE-catenin is a candidate tumor suppressor for the development of E-cadherin-expressing lobular-type breast cancer. J. Pathol. 2018, 245, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, V.; Azzopardi, J. Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: Incidence and variants. Histopathology 1979, 3, 467–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fechner, R.E. Histologic variants of infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast. Hum. Pathol. 1975, 6, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christgen, M.; Bartels, S.; van Luttikhuizen, J.L.; Schieck, M.; Pertschy, S.; Kundu, S.; Lehmann, U.; Sander, B.; Pelz, E.; Länger, F. Subclonal analysis in a lobular breast cancer with classical and solid growth pattern mimicking a solid-papillary carcinoma. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2017, 3, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakha, E.A.; Abbas, A.; Sheeran, R. Invasive lobular carcinoma mimicking papillary carcinoma: A report of three cases. Pathobiology 2016, 83, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motanagh, S.A.; Muller, K.E. Invasive lobular carcinoma with papillary features: A newly described variant that poses a difficult histologic differential diagnosis. Breast J. 2020, 26, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monhollen, L.; Morrison, C.; Ademuyiwa, F.O.; Chandrasekhar, R.; Khoury, T. Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma: A distinctive clinical and molecular breast cancer type. Histopathology 2012, 61, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakha, E.A.; Van Deurzen, C.H.; Paish, E.C.; Macmillan, R.D.; Ellis, I.O.; Lee, A.H. Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the breast: Is it a prognostically significant pathological subtype independent of histological grade? Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelt, B.; Geyer, F.C.; Natrajan, R.; Lopez-Garcia, M.A.; Ahmad, A.S.; Savage, K.; Kreike, B.; Reis-Filho, J.S. The molecular underpinning of lobular histological growth pattern: A genome-wide transcriptomic analysis of invasive lobular carcinomas and grade-and molecular subtype-matched invasive ductal carcinomas of no special type. J. Pathol. J. Pathol. Soc. Great Br. Irel. 2010, 220, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, L.; Palacios, D.; Bryant, B.; Krebs, P.; Otis, C.; Merino, M. Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma: Morphology, immunohistochemistry, and molecular analysis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2000, 24, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhi, J. Immunohistochemical analysis of pleomorphic lobular carcinoma: Higher expression of p53 and chromogranin and lower expression of ER and PgR. Histopathology 2000, 36, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolik, D.; Caduff, R.; Varga, Z. Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the breast: Its cell kinetics, expression of oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes compared with invasive ductal carcinomas and classical infiltrating lobular carcinomas. Histopathology 2001, 39, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sneige, N.; Wang, J.; Baker, B.A.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Middleton, L.P. Clinical, histopathologic, and biologic features of pleomorphic lobular (ductal-lobular) carcinoma in situ of the breast: A report of 24 cases. Mod. Pathol. 2002, 15, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, J.; Sarrió, D.; García-Macias, M.C.; Bryant, B.; Sobel, M.E.; Merino, M.J. Frequent E-cadherin gene inactivation by loss of heterozygosity in pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the breast. Mod. Pathol. 2003, 16, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, I.R.; Djordjevic, N.P.; Randjelovic, P.J.; Stojanovic, N.M.; Radulovic, N.S.; Ilic, R.S. Seven-year survey of classical and pleomorphic invasive lobular breast carcinomas in women from southeastern Serbia: Differences in clinicopathological and immunohistochemical features. J. BUON 2016, 21, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.L.; Choi, C.; Lee, S.M.; Zhong, X.; Hibshoosh, H.; Kalinsky, K.; Connolly, E.P. Invasive lobular breast carcinoma: Pleomorphic versus classical subtype, associations and prognosis. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa-Rosa, J.M.; Caniego-Casas, T.; Leskela, S.; Cristobal, E.; González-Martínez, S.; Moreno-Moreno, E.; López-Miranda, E.; Holgado, E.; Pérez-Mies, B.; Garrido, P. High frequency of ERBB2 activating mutations in invasive lobular breast carcinoma with pleomorphic features. Cancers 2019, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedlinger, G.M.; Joshi, S.; Hirshfield, K.M.; Barnard, N.; Ganesan, S. Targetable alterations in invasive pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ward, B.M.; Yu, J.; Matthew-Onabanjo, A.N.; Janusis, J.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Tomaszewicz, K.; Hutchinson, L.; Zhu, L.J.; Kandil, D. IRS2 mutations linked to invasion in pleomorphic invasive lobular carcinoma. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e97398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christgen, M.; Bartels, S.; Radner, M.; Raap, M.; Rieger, L.; Christgen, H.; Gluz, O.; Nitz, U.; Harbeck, N.; Lehmann, U. ERBB2 mutation frequency in lobular breast cancer with pleomorphic histology or high-risk characteristics by molecular expression profiling. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2019, 58, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eusebi, V.; Magalhaes, F.; Azzopardi, J.G. Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the breast: An aggressive tumor showing apocrine differentiation. Hum. Pathol. 1992, 23, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, N.; Semple, J.P. Pleomorphic variant of invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Hum. Pathol. 1992, 23, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentz, J.S.; Yassa, N.; Clayton, F. Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the breast: Clinicopathologic features of 12 cases. Mod. Pathol. 1998, 11, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christgen, M.; Gluz, O.; Harbeck, N.; Kates, R.E.; Raap, M.; Christgen, H.; Clemens, M.; Malter, W.; Nuding, B.; Aktas, B. Differential impact of prognostic parameters in hormone receptor–positive lobular breast cancer. Cancer 2020, 126, 4847–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, W.; Arms, A.; Verma, V.; Hatch, S.; Butler, E.B.; Teh, B.S. Outcomes of pleomorphic lobular carcinoma versus invasive lobular carcinoma. Breast 2019, 43, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, C.I.; Font, R.L.; Zimmerman, L.E. Metastatic mammary carcinoma in the eyelid with histiocytoid appearance. Cancer 1973, 31, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Filho, J.S.; Fulford, L.G.; Freeman, A.; Lakhani, S.R. Pathologic quiz case: A 93-year-old woman with an enlarged and tender left breast. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2003, 127, 1626–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasashima, S.; Kawashima, A.; Zen, Y.; Ozaki, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Tsujibata, A.; Minato, H. Expression of aberrant mucins in lobular carcinoma with histiocytoid feature of the breast. Virchows Arch. 2007, 450, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.H.; Harada, O.; Thike, A.A.; Tse, G.M.-K. Histiocytoid breast carcinoma: An enigmatic lobular entity. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 64, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrecher, J.S.; Silverberg, S.G. Signet-ring cell carcinoma of the breast. The mucinous variant of infiltrating lobular carcinoma? Cancer 1976, 37, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslow, A.; Brancaccio, M. Intracellular mucin production by lobular breast carcinoma cells. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1976, 100, 620–621. [Google Scholar]
- Eusebi, V.; Pich, A.; Macchiorlatti, E.; Bussolati, G. Morpho-functional differentiation in lobular carcinoma of the breast. Histopathology 1977, 1, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Schepper, M.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Christgen, M.; Van Baelen, K.; Richard, F.; Tsuda, H.; Kurozumi, S.; Brito, M.J.; Cserni, G.; Schnitt, S. Results of a worldwide survey on the currently used histopathological diagnostic criteria for invasive lobular breast cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christgen, M.; Kandt, L.D.; Antonopoulos, W.; Bartels, S.; Van Bockstal, M.R.; Bredt, M.; Brito, M.J.; Christgen, H.; Colpaert, C.; Cserni, B. Inter-observer agreement for the histological diagnosis of invasive lobular breast carcinoma. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2022, 8, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabbs, D.J.; Bhargava, R.; Chivukula, M. Lobular versus ductal breast neoplasms: The diagnostic utility of p120 catenin. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørlie, T. Molecular portraits of breast cancer: Tumour subtypes as distinct disease entities. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 2667–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelt, B.; Horlings, H.; Kreike, B.; Hayes, M.; Hauptmann, M.; Wessels, L.; De Jong, D.; Van de Vijver, M.; Veer, L.V.t.; Peterse, J. Refinement of breast cancer classification by molecular characterization of histological special types. J. Pathol. J. Pathol. Soc. Great Br. Irel. 2008, 216, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christgen, M.; Steinemann, D.; Kühnle, E.; Länger, F.; Gluz, O.; Harbeck, N.; Kreipe, H. Lobular breast cancer: Clinical, molecular and morphological characteristics. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2016, 212, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.H.; Ellis, I.; Allison, K.; Brogi, E.; Fox, S.B.; Lakhani, S.; Lazar, A.J.; Morris, E.A.; Sahin, A.; Salgado, R. The 2019 WHO classification of tumours of the breast. Histopathology 2020, 77, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christgen, M.; Cserni, G.; Floris, G.; Marchio, C.; Djerroudi, L.; Kreipe, H.; Derksen, P.W.; Vincent-Salomon, A. Lobular breast cancer: Histomorphology and different concepts of a special spectrum of tumors. Cancers 2021, 13, 3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.; Rosa, M. Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the breast: A morphologically and clinically distinct variant of lobular carcinoma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2013, 137, 1688–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, P.; Hamilton, E.; Tolaney, S.M.; Cortes, J.; Morganti, S.; Ferraro, E.; Marra, A.; Viale, G.; Trapani, D.; Cardoso, F. HER2-low breast cancer: Pathological and clinical landscape. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douganiotis, G.; Kontovinis, L.; Markopoulou, E.; Ainali, A.; Zarampoukas, T.; Natsiopoulos, I.; Papazisis, K. Prognostic significance of low HER2 expression in patients with early hormone receptor positive breast cancer. Cancer Diagn. Progn. 2022, 2, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, H.T.; Clelland, E.; Patterson, A.; Molina-Vega, J.; Kaur, M.; Symmans, W.F.; Schwartz, C.J.; Chien, A.J.; Mukhtar, R.A. HER-2 low status in early-stage invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: Associated factors and outcomes in an institutional series. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 199, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Baelen, K.; Geukens, T.; Maetens, M.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.; Lord, C.J.; Linn, S.; Bidard, F.C.; Richard, F.; Yang, W.W.; Steele, R.E.; et al. Current and future diagnostic and treatment strategies for patients with invasive lobular breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 769–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmedt, C.; Zoppoli, G.; Gundem, G.; Pruneri, G.; Larsimont, D.; Fornili, M.; Fumagalli, D.; Brown, D.; Rothé, F.; Vincent, D. Genomic characterization of primary invasive lobular breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1872–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaut, M.; Chin, S.-F.; Majewski, I.; Severson, T.M.; Bismeijer, T.; De Koning, L.; Peeters, J.K.; Schouten, P.C.; Rueda, O.M.; Bosma, A.J. Integration of genomic, transcriptomic and proteomic data identifies two biologically distinct subtypes of invasive lobular breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A.E.M.; Kutasovic, J.R.; Lakhani, S.R.; Simpson, P.T. Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: Morphology, biomarkers and’omics. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareja, F.; Ferrando, L.; Lee, S.S.; Beca, F.; Selenica, P.; Brown, D.N.; Farmanbar, A.; Da Cruz Paula, A.; Vahdatinia, M.; Zhang, H. The genomic landscape of metastatic histologic special types of invasive breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2020, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrio, D.; Perez-Mies, B.; Hardisson, D.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Suarez, A.; Cano, A.; Martin-Perez, J.; Gamallo, C.; Palacios, J. Cytoplasmic localization of p120ctn and E-cadherin loss characterize lobular breast carcinoma from preinvasive to metastatic lesions. Oncogene 2004, 23, 3272–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtidis, A.; Ngok, S.P.; Anastasiadis, P.Z. p120 catenin: An essential regulator of cadherin stability, adhesion-induced signaling, and cancer progression. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2013, 116, 409–432. [Google Scholar]
- Bajrami, I.; Marlow, R.; van de Ven, M.; Brough, R.; Pemberton, H.N.; Frankum, J.; Song, F.; Rafiq, R.; Konde, A.; Krastev, D.B. E-cadherin/ROS1 inhibitor synthetic lethality in breast cancer. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 498–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neoadjuvant Study of Targeting ROS1 in Combination with Endocrine Therapy in Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast (ROSALINE). Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04551495 (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Crizotinib in Lobular Breast, Diffuse Gastric and Triple Negative Lobular Breast Cancer or CDH1-Mutated Solid Tumours. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03620643 (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Sanchez, C.G.; Ma, C.X.; Crowder, R.J.; Guintoli, T.; Phommaly, C.; Gao, F.; Lin, L.; Ellis, M.J. Preclinical modeling of combined phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibition with endocrine therapy for estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, R21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.W.; Hennessy, B.T.; González-Angulo, A.M.; Fox, E.M.; Mills, G.B.; Chen, H.; Higham, C.; García-Echeverría, C.; Shyr, Y.; Arteaga, C.L. Hyperactivation of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase promotes escape from hormone dependence in estrogen receptor–positive human breast cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2406–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeGraffenried, L.A.; Friedrichs, W.E.; Russell, D.H.; Donzis, E.J.; Middleton, A.K.; Silva, J.M.; Roth, R.A.; Hidalgo, M. Inhibition of mTOR activity restores tamoxifen response in breast cancer cells with aberrant Akt Activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8059–8067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J.; Campone, M.; Piccart, M.; Burris, H.A., III; Rugo, H.S.; Sahmoud, T.; Noguchi, S.; Gnant, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Lebrun, F. Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor–positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortobagyi, G.N. Everolimus plus exemestane for the treatment of advanced breast cancer: A review of subanalyses from BOLERO-2. Neoplasia 2015, 17, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachelot, T.; Bourgier, C.; Cropet, C.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Ferrero, J.-M.; Freyer, G.; Abadie-Lacourtoisie, S.; Eymard, J.-C.; Debled, M.; Spaëth, D. Randomized phase II trial of everolimus in combination with tamoxifen in patients with hormone receptor–positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative metastatic breast cancer with prior exposure to aromatase inhibitors: A GINECO study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2718–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.C.; Oliveira, M.; Howell, S.J.; Dalenc, F.; Cortes, J.; Gomez Moreno, H.L.; Hu, X.; Jhaveri, K.; Krivorotko, P.; Loibl, S. Capivasertib in Hormone Receptor–Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagle, A.M.; Levine, K.M.; Tasdemir, N.; Scott, J.A.; Burlbaugh, K.; Kehm, J.; Katz, T.A.; Boone, D.N.; Jacobsen, B.M.; Atkinson, J.M. Loss of E-cadherin Enhances IGF1–IGF1R pathway activation and sensitizes breast cancers to anti-IGF1R/InsR inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5165–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangovan, A.; Hooda, J.; Savariau, L.; Puthanmadhomnarayanan, S.; Yates, M.E.; Chen, J.; Brown, D.D.; McAuliffe, P.F.; Oesterreich, S.; Atkinson, J.M. Loss of E-cadherin Induces IGF1R Activation and Reveals a Targetable Pathway in Invasive Lobular Breast Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2022, 20, 1405–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Basudan, A.; Sikora, M.J.; Bahreini, A.; Tasdemir, N.; Levine, K.M.; Jankowitz, R.C.; McAuliffe, P.F.; Dabbs, D.; Haupt, S. Frequent amplifications of ESR1, ERBB2 and MDM4 in primary invasive lobular breast carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2019, 461, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.S.; Wang, K.; Sheehan, C.E.; Boguniewicz, A.B.; Otto, G.; Downing, S.R.; Sun, J.; He, J.; Curran, J.A.; Ali, S. Relapsed Classic E-Cadherin (CDH1)–Mutated Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer Shows a High Frequency of HER2 (ERBB2) Gene Mutations. ERBB2 Mutations in Lobular Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2668–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, R.; Kavuri, S.M.; Searleman, A.C.; Shen, W.; Shen, D.; Koboldt, D.C.; Monsey, J.; Goel, N.; Aronson, A.B.; Li, S. Activating HER2 mutations in HER2 gene amplification negative breast cancer. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurozumi, S.; Alsaleem, M.; Monteiro, C.J.; Bhardwaj, K.; Joosten, S.E.; Fujii, T.; Shirabe, K.; Green, A.R.; Ellis, I.O.; Rakha, E.A. Targetable ERBB2 mutation status is an independent marker of adverse prognosis in estrogen receptor positive, ERBB2 non-amplified primary lobular breast carcinoma: A retrospective in silico analysis of public datasets. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.S.; Gay, L.M.; Wang, K.; Ali, S.M.; Chumsri, S.; Elvin, J.A.; Bose, R.; Vergilio, J.A.; Suh, J.; Yelensky, R. Nonamplification ERBB2 genomic alterations in 5605 cases of recurrent and metastatic breast cancer: An emerging opportunity for anti-HER2 targeted therapies. Cancer 2016, 122, 2654–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.X.; Luo, J.; Freedman, R.A.; Pluard, T.J.; Nangia, J.R.; Lu, J.; Valdez-Albini, F.; Cobleigh, M.; Jones, J.M.; Lin, N.U. The phase II MutHER study of neratinib alone and in combination with fulvestrant in HER2-mutated, non-amplified metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaveri, K.; Eli, L.; Wildiers, H.; Hurvitz, S.; Guerrero-Zotano, A.; Unni, N.; Brufsky, A.; Park, H.; Waisman, J.; Yang, E.; et al. Neratinib + fulvestrant + trastuzumab for HR-positive, HER2-negative, HER2-mutant metastatic breast cancer: Outcomes and biomarker analysis from the SUMMIT trial. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Filho, J.S.; Simpson, P.T.; Turner, N.C.; Lambros, M.B.; Jones, C.; Mackay, A.; Grigoriadis, A.; Sarrio, D.; Savage, K.; Dexter, T. FGFR1 emerges as a potential therapeutic target for lobular breast carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6652–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidemann, E.R.; Shajahan-Haq, A.N. Resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulvestrant, Palbociclib and Erdafitinib in ER+/HER2-/FGFR-Amplified Metastatic Breast Cancer. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03238196 (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Fu, X.; Jeselsohn, R.; Pereira, R.; Hollingsworth, E.F.; Creighton, C.J.; Li, F.; Shea, M.; Nardone, A.; De Angelis, C.; Heiser, L.M. FOXA1 overexpression mediates endocrine resistance by altering the ER transcriptome and IL-8 expression in ER-positive breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6600–E6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruabarrena-Aristorena, A.; Maag, J.L.; Kittane, S.; Cai, Y.; Karthaus, W.R.; Ladewig, E.; Park, J.; Kannan, S.; Ferrando, L.; Cocco, E. FOXA1 mutations reveal distinct chromatin profiles and influence therapeutic response in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 534–550.e539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, A.; Qiu, X.; Spisak, S.; Nagy, Z.; Feiglin, A.; Feit, A.; Cohen Feit, G.; Xie, Y.; Font-Tello, A.; Guarducci, C. A distinct chromatin state drives therapeutic resistance in invasive lobular breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 3673–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, S.W.; Mayne, C.G.; Dharmarajan, V.; Carlson, K.E.; Martin, T.A.; Novick, S.J.; Toy, W.; Green, B.; Panchamukhi, S.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Estrogen receptor alpha somatic mutations Y537S and D538G confer breast cancer endocrine resistance by stabilizing the activating function-2 binding conformation. eLife 2016, 5, e12792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeselsohn, R.; Bergholz, J.S.; Pun, M.; Cornwell, M.; Liu, W.; Nardone, A.; Xiao, T.; Li, W.; Qiu, X.; Buchwalter, G. Allele-specific chromatin recruitment and therapeutic vulnerabilities of ESR1 activating mutations. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 173–186.e175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, G.; Tian, L.; Gao, M.; Rechoum, Y.; Gelsomino, L.; Dustin, D.; Corona-Rodriguez, A.; Beyer, A.R.; Tsimelzon, A.; Zhang, X. The Y537S ESR1 mutation is a dominant driver of distant ER-positive breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toy, W.; Shen, Y.; Won, H.; Green, B.; Sakr, R.A.; Will, M.; Li, Z.; Gala, K.; Fanning, S.; King, T.A. ESR1 ligand-binding domain mutations in hormone-resistant breast cancer. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehir, A.; Benayed, R.; Shah, R.H.; Syed, A.; Middha, S.; Kim, H.R.; Srinivasan, P.; Gao, J.; Chakravarty, D.; Devlin, S.M. Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fribbens, C.; O’Leary, B.; Kilburn, L.; Hrebien, S.; Garcia-Murillas, I.; Beaney, M.; Cristofanilli, M.; Andre, F.; Loi, S.; Loibl, S. Plasma ESR1 mutations and the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2961–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmedt, C.; Pingitore, J.; Rothé, F.; Marchio, C.; Clatot, F.; Rouas, G.; Richard, F.; Bertucci, F.; Mariani, O.; Galant, C. ESR1 mutations in metastatic lobular breast cancer patients. NPJ Breast Cancer 2019, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidard, F.-C.; Kaklamani, V.G.; Neven, P.; Streich, G.; Montero, A.J.; Forget, F.; Mouret-Reynier, M.-A.; Sohn, J.H.; Taylor, D.; Harnden, K.K. Elacestrant (oral selective estrogen receptor degrader) versus standard endocrine therapy for estrogen receptor–positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative advanced breast cancer: Results from the randomized phase III EMERALD trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vile, R.G.; Melcher, A.; Pandha, H.; Harrington, K.J.; Pulido, J.S. APOBEC and cancer viroimmunotherapy: Thinking the unthinkable. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3280–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.S.; Liddament, M.T. Retroviral restriction by APOBEC proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammons, S.; Elliott, A.; Force, J.M.; DeVito, N.C.; Marcom, P.K.; Swain, S.M.; Tan, A.R.; Torres, E.T.R.; Zeng, J.; Khasraw, M. Genomic evaluation of tumor mutational burden-high (TMB-H) versus TMB-low (TMB-L) metastatic breast cancer to reveal unique mutational features. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso-Sousa, R.; Jain, E.; Cohen, O.; Kim, D.; Buendia-Buendia, J.; Winer, E.; Lin, N.; Tolaney, S.; Wagle, N. Prevalence and mutational determinants of high tumor mutation burden in breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumsri, S.; Raskina, K.; Sammons, S.; Alder, L.; Danziger, N.; Schrock, A.B.; McGregor, K.; Sokol, E. Abstract PD14-09: APOBEC signature, clinical characteristics, and outcome in hormone receptor-positive (HR+) HER2-negative (HER2-) breast cancer (BC) patients (pts) in real-world data (RWD). Cancer Res. 2022, 82, PD14-09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corso, G.; Intra, M.; Trentin, C.; Veronesi, P.; Galimberti, V. CDH1 germline mutations and hereditary lobular breast cancer. Fam. Cancer 2016, 15, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petridis, C.; Arora, I.; Shah, V.; Moss, C.L.; Mera, A.; Clifford, A.; Gillett, C.; Pinder, S.E.; Tomlinson, I.; Roylance, R. Frequency of pathogenic germline variants in CDH1, BRCA2, CHEK2, PALB2, BRCA1, and TP53 in sporadic lobular breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Hu, C.; Nathanson, K.L.; Weitzel, J.N.; Goldgar, D.E.; Kraft, P.; Gnanaolivu, R.D.; Na, J.; Huang, H.; Boddicker, N.J. Germline pathogenic variants in cancer predisposition genes among women with invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3918–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LobularCard Trial: Searching for Novel Germline Mutations in Lobular Breast Cancer Patients. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT05410951 (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Győrffy, B.; Hatzis, C.; Sanft, T.; Hofstatter, E.; Aktas, B.; Pusztai, L. Multigene prognostic tests in breast cancer: Past, present, future. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.C.; Chagpar, A.B.; Cicek, A.F.; Bossuyt, V.; Buza, N.; Mougalian, S.; Killelea, B.K.; Patel, N.; Harigopal, M. Breast cancer histopathology is predictive of low-risk Oncotype Dx recurrence score. Breast J. 2018, 24, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makower, D.; Qin, J.; Lin, J.; Xue, X.; Sparano, J.A. The 21-gene recurrence score in early non-ductal breast cancer: A National Cancer Database analysis. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomeisl, P.E.; Thompson, C.L.; Harris, L.N.; Gilmore, H.L. Comparison of Oncotype DX Recurrence Score by Histologic Types of Breast Carcinoma; The College of American Pathologists: Northfield, IL, USA, 2015; Volume 139, pp. 1546–1549. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, M.L.; Lillemoe, T.J.; Finkelstein, M.J.; Money, J.E.; Susnik, B.; Grimm, E.; Kang, S.-H.L.; Swenson, K.K. Utility of Oncotype DX risk assessment in patients with invasive lobular carcinoma. Clin. Breast Cancer 2016, 16, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, N.; Ross, D.S.; Howard, J.; Catalano, J.P.; Dickler, M.N.; Tan, L.K. Is there a role for oncotype Dx testing in invasive lobular carcinoma? Breast J. 2015, 21, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizy, S.; Huang, J.L.; Marmor, S.; Tuttle, T.M.; Hui, J.Y.C. Impact of the 21-gene recurrence score on outcome in patients with invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 165, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, A.B.; Wen, H.Y.; Morrow, M. Breast cancers of special histologic subtypes are biologically diverse. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 3158–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, Z.-Y.; Dong, Y.; Sun, J.-Y.; Zhang, W.-W.; Wu, S.-G. The distribution and outcomes of the 21-gene recurrence score in T1-T2N0 estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer with different histologic subtypes. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felts, J.L.; Zhu, J.; Han, B.; Smith, S.J.; Truica, C.I. An analysis of Oncotype DX recurrence scores and clinicopathologic characteristics in invasive lobular breast cancer. Breast J. 2017, 23, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.M.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Bianchini, G.; Litton, J.K.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Pusztai, L. Utility of oncotype DX risk estimates in clinically intermediate risk hormone receptor-positive, HER2-normal, grade II, lymph node-negative breast cancers. Cancer 2010, 116, 5161–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, M.K.; Shui, A.M.; Chien, A.J.; Rugo, H.S.; Melisko, M.; Baehner, F.; Mukhtar, R.A. The 21-gene recurrence score in clinically high-risk lobular and ductal breast cancer: A National Cancer Database study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7739–7747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van’t Veer, L.J.; Dai, H.; Van De Vijver, M.J.; He, Y.D.; Hart, A.A.; Mao, M.; Peterse, H.L.; Van Der Kooy, K.; Marton, M.J.; Witteveen, A.T. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 2002, 415, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van’t Veer, L.J.; Dai, H.; van de Vijver, M.J.; He, Y.D.; Hart, A.A.; Bernards, R.; Friend, S.H. Expression profiling predicts outcome in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2002, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glas, A.M.; Floore, A.; Delahaye, L.J.; Witteveen, A.T.; Pover, R.C.; Bakx, N.; Lahti-Domenici, J.S.; Bruinsma, T.J.; Warmoes, M.O.; Bernards, R. Converting a breast cancer microarray signature into a high-throughput diagnostic test. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delahaye, L.J.; Wehkamp, D.; Floore, A.N.; Bernards, R.; van’t Veer, L.J.; Glas, A.M. Performance characteristics of the MammaPrint® breast cancer diagnostic gene signature. Pers. Med. 2013, 10, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beumer, I.J.; Persoon, M.; Witteveen, A.; Dreezen, C.; Chin, S.-F.; Sammut, S.-J.; Snel, M.; Caldas, C.; Linn, S.; van’t Veer, L.J. Prognostic value of MammaPrint® in invasive lobular breast cancer. Biomark. Insights 2016, 11, BMI-S38435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, O.; Cardoso, F.; Poncet, C.; Desmedt, C.; Linn, S.; Wesseling, J.; Hilbers, F.; Aalders, K.; Delorenzi, M.; Delaloge, S. Clinical utility of MammaPrint testing in invasive lobular carcinoma: Results from the MINDACT phase III trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 138, S5–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.A.; Marmor, S.; Hui, J.Y.C.; Beckwith, H.; Blaes, A.H.; Potter, D.; Tuttle, T.M. The 70-gene signature test as a prognostic and predictive biomarker in patients with invasive lobular breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 191, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, M.K.; Shui, A.M.; Melisko, M.; Chien, A.J.; Yoshida, E.J.; Lancaster, E.M.; Van’t Veer, L.; Esserman, L.J.; Mukhtar, R.A. The incidence of discordant clinical and genomic risk in patients with invasive lobular or ductal carcinoma of the breast: A National Cancer Database Study. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestak, I.; Filipits, M.; Buus, R.; Rudas, M.; Balic, M.; Knauer, M.; Kronenwett, R.; Fitzal, F.; Cuzick, J.; Gnant, M. Prognostic Value of EndoPredict in Women with Hormone Receptor–Positive, HER2-Negative Invasive Lobular Breast CancerRisk Prediction by EndoPredict for ILC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4682–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.S.; Mullins, M.; Cheang, M.C.; Leung, S.; Voduc, D.; Vickery, T.; Davies, S.; Fauron, C.; He, X.; Hu, Z. Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lænkholm, A.-V.; Jensen, M.-B.; Eriksen, J.O.; Roslind, A.; Buckingham, W.; Ferree, S.; Nielsen, T.; Ejlertsen, B. Population-based study of Prosigna-PAM50 and outcome among postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive and HER2-negative operable invasive lobular or ductal breast cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2020, 20, e423–e432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerevall, P.-L.; Ma, X.-J.; Li, H.; Salunga, R.; Kesty, N.C.; Erlander, M.G.; Sgroi, D.; Holmlund, B.; Skoog, L.; Fornander, T. Prognostic utility of HOXB13: IL17BR and molecular grade index in early-stage breast cancer patients from the Stockholm trial. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1762–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, R.; Sella, T.; Treuner, K.; Atkinson, J.M.; Wong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Exman, P.; Dabbs, D.; Richardson, A.L.; Schnabel, C.A. Prognostic utility of breast cancer index to stratify distant recurrence risk in invasive lobular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5688–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, C.; Wirapati, P.; Loi, S.; Harris, A.; Fox, S.; Smeds, J.; Nordgren, H.; Farmer, P.; Praz, V.; Haibe-Kains, B. Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: Understanding the molecular basis of histologic grade to improve prognosis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger-Filho, O.; Michiels, S.; Bertucci, F.; Catteau, A.; Salgado, R.; Galant, C.; Fumagalli, D.; Singhal, S.; Desmedt, C.; Ignatiadis, M. Genomic grade adds prognostic value in invasive lobular carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCart Reed, A.E.; Lal, S.; Kutasovic, J.R.; Wockner, L.; Robertson, A.; de Luca, X.M.; Kalita-de Croft, P.; Dalley, A.J.; Coorey, C.P.; Kuo, L. LobSig is a multigene predictor of outcome in invasive lobular carcinoma. NPJ Breast Cancer 2019, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 Interactions for Cancer Immunotherapy; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 1223–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Tille, J.-C.; Vieira, A.F.; Saint-Martin, C.; Djerroudi, L.; Furhmann, L.; Bidard, F.-C.; Kirova, Y.; Tardivon, A.; Reyal, F.; Carton, M. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are associated with poor prognosis in invasive lobular breast carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2198–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmedt, C.; Salgado, R.; Fornili, M.; Pruneri, G.; Van den Eynden, G.; Zoppoli, G.; Rothe, F.; Buisseret, L.; Garaud, S.; Willard-Gallo, K. Immune infiltration in invasive lobular breast cancer. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, E.D.; Taube, J.M.; Asch-Kendrick, R.J.; Ogurtsova, A.; Xu, H.; Sharma, R.; Meeker, A.; Argani, P.; Emens, L.A.; Cimino-Mathews, A. PD-L1 expression and the immune microenvironment in primary invasive lobular carcinomas of the breast. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorwerk, L.; Isaeva, O.I.; Horlings, H.M.; Balduzzi, S.; Chelushkin, M.; Bakker, N.A.; Champanhet, E.; Garner, H.; Sikorska, K.; Loo, C.E. PD-L1 blockade in combination with carboplatin as immune induction in metastatic lobular breast cancer: The GELATO trial. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassetta, L.; Pollard, J.W. Targeting macrophages: Therapeutic approaches in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 887–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutilier, A.J.; Elsawa, S.F. Macrophage polarization states in the tumor microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onkar, S.; Cui, J.; Zou, J.; Cardello, C.; Cillo, A.R.; Uddin, M.R.; Sagan, A.; Joy, M.; Osmanbeyoglu, H.U.; Pogue-Geile, K.L. Immune landscape in invasive ductal and lobular breast cancer reveals a divergent macrophage-driven microenvironment. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 516–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Li, Z.; Gao, R.; Xing, B.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qin, S.; Zhang, L.; Ouyang, H.; Du, P. A pan-cancer single-cell transcriptional atlas of tumor infiltrating myeloid cells. Cell 2021, 184, 792–809.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deligne, C.; Midwood, K.S. Macrophages and extracellular matrix in breast cancer: Partners in crime or protective allies? Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 620773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Kieffer, Y.; Scholer-Dahirel, A.; Pelon, F.; Bourachot, B.; Cardon, M.; Sirven, P.; Magagna, I.; Fuhrmann, L.; Bernard, C. Fibroblast heterogeneity and immunosuppressive environment in human breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 463–479.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelon, F.; Bourachot, B.; Kieffer, Y.; Magagna, I.; Mermet-Meillon, F.; Bonnet, I.; Costa, A.; Givel, A.-M.; Attieh, Y.; Barbazan, J. Cancer-associated fibroblast heterogeneity in axillary lymph nodes drives metastases in breast cancer through complementary mechanisms. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraman, M.; Bambrough, P.J.; Arnold, J.N.; Roberts, E.W.; Magiera, L.; Jones, J.O.; Gopinathan, A.; Tuveson, D.A.; Fearon, D.T. Suppression of antitumor immunity by stromal cells expressing fibroblast activation protein–α. Science 2010, 330, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lin, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, W.; Yin, W.; Dang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Fan, J.; He, R. FAP promotes immunosuppression by cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment via STAT3–CCL2 SignalingFAP via STAT3–CCL2 promote tumor immunosuppression. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4124–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ertl, H.C. Depletion of FAP+ cells reduces immunosuppressive cells and improves metabolism and functions CD8+ T cells within tumors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 23282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.K.; Jung, W.H.; Koo, J.S. Expression of cancer-associated fibroblast-related proteins differs between invasive lobular carcinoma and invasive ductal carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 159, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Cuadrado, L.; Bullock, E.; Mabruk, Z.; Zhao, H.; Souleimanova, M.; Noer, P.R.; Turnbull, A.K.; Oxvig, C.; Bertos, N.; Byron, A. Characterisation of the stromal microenvironment in lobular breast cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batra, H.; Pandurengan, R.K.; Ibarguen, H.P.; McAllen, S.A.; Ding, Q.; Sahin, A.; Wistuba, I.; Parra, E.R.; Raso, M.G. Abstract P2-21-07: Exploring spatial correlations in Breast invasive Lobular Carcinoma subtypes using a novel CAF multiplex immunofluorescence panel. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, P2-21-07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, H.; Ding, Q.; Pandurengan, R.; Ibarguen, H.; Rabassedas, N.B.; Sahin, A.; Wistuba, I.; Parra, E.R.; Raso, M.G. Exploration of cancer associated fibroblasts phenotypes in the tumor microenvironment of classical and pleomorphic Invasive Lobular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1281650. [Google Scholar]
- Karagiannis, T.; Boura, P.; Tsapas, A. Safety of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors: A perspective review. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2014, 5, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, R.B.; Albert, M. Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 Inhibition Enhances Lymphocyte Trafficking, Improving Both Naturally Occurring Tumor Immunity and Immunotherapy. U.S. Patent No. 11,000,521, 11 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Cha, Y.J.; Koo, J.S. Adipocyte biology in breast cancer: From silent bystander to active facilitator. Prog. Lipid Res. 2018, 69, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybinska, I.; Agresti, R.; Trapani, A.; Tagliabue, E.; Triulzi, T. Adipocytes in breast cancer, the thick and the thin. Cells 2020, 9, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, J.N. Cancer stem cells in radiation resistance. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8980–8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Langerød, A.; Ji, Y.; Nowels, K.W.; Nesland, J.M.; Tibshirani, R.; Bukholm, I.K.; Kåresen, R.; Botstein, D.; Børresen-Dale, A.-L. Different gene expression patterns in invasive lobular and ductal carcinomas of the breast. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 2523–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Jung, W.H.; Koo, J.S. Expression of metabolism-related proteins in invasive lobular carcinoma: Comparison to invasive ductal carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 10381–10393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.J.; Kim, H.M.; Koo, J.S. Expression of lipid metabolism-related proteins differs between invasive lobular carcinoma and invasive ductal carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isnaldi, E.; Richard, F.; De Schepper, M.; Leduc, S.; Maetens, M.; Geukens, T.; Van Baelen, K.; Nguyen, H.-L.; Rouas, G.; Zoppoli, G. The association between adiposity and anti-proliferative response to neoadjuvant endocrine therapy with letrozole in post-menopausal patients with estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, M.; Collet, L.; Rediti, M.; Lifrange, F.; Venet, D.; Occelli, N.; Vincent, D.; Rouas, G.; Larsimont, D.; Craciun, L. 1726P Investigating adipocytes-tumor cells interaction and its effect on disease progression in lobular breast cancer with spatial transcriptomics. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouabbi, J.A.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Khorkova, S.; Turova, P.; Kotlov, N.; Chernyshov, K.; Kushnarev, V.; Love, A.; Clayton, P.; Nomie, K. Differential Genomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of Invasive Lobular and Ductal Carcinomas; American Society of Clinical Oncology: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, O.; Yang, W. Imaging of breast cancers with predilection for nonmass pattern of growth: Invasive lobular carcinoma and DCIS—Does imaging capture it all? Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helvie, M.A.; Paramagul, C.; Oberman, H.A.; Adler, D.D. Invasive lobular carcinoma imaging features and clinical detection. Investig. Radiol. 1993, 28, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilleren, D.J.; Andersson, I.T.; Lindholm, K.; Linnell, F. Invasive lobular carcinoma: Mammographic findings in a 10-year experience. Radiology 1991, 178, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelson, M.T.; Oestreicher, N.; Porter, P.L.; White, D.; Finder, C.A.; Taplin, S.H.; White, E. Breast density as a predictor of mammographic detection: Comparison of interval-and screen-detected cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R.; Venta, L.A.; Wiley, E.; Ellis, R.; Dempsey, P.; Rubin, E. Sonographic evaluation of infiltrating lobular carcinoma. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1999, 172, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selinko, V.L.; Middleton, L.P.; Dempsey, P.J. Role of sonography in diagnosing and staging invasive lobular carcinoma. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2004, 32, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phalak, K.A.; Milton, D.R.; Yang, W.T.; Bevers, T.B.; Dogan, B.E. Supplemental ultrasound screening in patients with a history of lobular neoplasia. Breast J. 2019, 25, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.M.; Hoogeveen, Y.L.; Blickman, J.G.; Boetes, C. MRI compared to conventional diagnostic work-up in the detection and evaluation of invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: A review of existing literature. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 107, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, R.M. The effectiveness of MR imaging in the assessment of invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. 2010, 18, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, S.J.; Anderson, E.; Mullen, R. Magnetic resonance imaging for invasive lobular carcinoma: Is it worth it? Gland Surg. 2019, 8, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvi, V.; Nori, J.; Meattini, I.; Francolini, G.; Morelli, N.; Di Benedetto, D.; Bicchierai, G.; Di Naro, F.; Gill, M.K.; Orzalesi, L. Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the preoperative staging and work-up of patients affected by invasive lobular carcinoma or invasive ductolobular carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1569060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schacht, D.V.; Yamaguchi, K.; Lai, J.; Kulkarni, K.; Sennett, C.A.; Abe, H. Importance of a personal history of breast cancer as a risk factor for the development of subsequent breast cancer: Results from screening breast MRI. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Senkus, E.; Curigliano, G.; Aapro, M.; André, F.; Barrios, C.; Bergh, J.; Bhattacharyya, G.; Biganzoli, L. 5th ESO-ESMO international consensus guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC 5). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1623–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, M.P.; Goldman, D.A.; Dashevsky, B.; Riedl, C.C.; Gönen, M.; Osborne, J.R.; Jochelson, M.; Hudis, C.; Morrow, M.; Ulaner, G.A. Comparison of 18F-FDG PET/CT for systemic staging of newly diagnosed invasive lobular carcinoma versus invasive ductal carcinoma. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1674–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tade, F.I.; Cohen, M.A.; Styblo, T.M.; Odewole, O.A.; Holbrook, A.I.; Newell, M.S.; Savir-Baruch, B.; Li, X.; Goodman, M.M.; Nye, J.A. Anti-3-18F-FACBC (18F-Fluciclovine) PET/CT of breast cancer: An exploratory study. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaner, G.A.; Jhaveri, K.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Hatzoglou, V.; Riedl, C.C.; Lewis, J.S.; Mauguen, A. Head-to-head evaluation of 18F-FES and 18F-FDG PET/CT in metastatic invasive lobular breast cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaner, G.A.; Mankoff, D.A.; Clark, A.S.; Fowler, A.M.; Linden, H.M.; Peterson, L.M.; Dehdashti, F.; Kurland, B.F.; Mortimer, J.; Mouabbi, J. Summary: Appropriate Use Criteria for Estrogen Receptor–Targeted PET Imaging with 16α-18F-Fluoro-17β-Fluoroestradiol. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 64, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluciclovine and PSMA PET/CT for the Classification and Improved Staging of Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04750473 (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- 18F-Fluoroestradiol (FES) PET/CT for Breast Cancer. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04883814 (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Shenoy, H.; Peter, M.; Masannat, Y.; Dall, B.; Dodwell, D.; Horgan, K. Practical advice on clinical decision making during neoadjuvant chemotherapy for primary breast cancer. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 18, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, D.J.; Davey, M.G.; Barkley, L.R.; Kerin, M.J. Differences in sensitivity to neoadjuvant chemotherapy among invasive lobular and ductal carcinoma of the breast and implications on surgery—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast 2022, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babiera, G.V.; Lowy, A.M.; Davidson, B.S.; Singletary, S.E. The role of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy in invasive lobular carcinoma. Breast J. 1997, 3, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhu, G.-Q.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.-Y. Long-term survival differences between T1-2 invasive lobular breast cancer and corresponding ductal carcinoma after breast-conserving surgery: A propensity-scored matched longitudinal cohort study. Clin. Breast Cancer 2019, 19, e101–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, A.E.; Ballman, K.V.; McCall, L.; Beitsch, P.D.; Brennan, M.B.; Kelemen, P.R.; Ollila, D.W.; Hansen, N.M.; Whitworth, P.W.; Blumencranz, P.W. Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: The ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, A.E.; Hunt, K.K.; Ballman, K.V.; Beitsch, P.D.; Whitworth, P.W.; Blumencranz, P.W.; Leitch, A.M.; Saha, S.; McCall, L.M.; Morrow, M. Axillary dissection vs. no axillary dissection in women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2011, 305, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, S.; Bortul, M.; Scomersi, S.; Bigal, C.; Bottin, C.; Zanconati, F.; Fox, S.; Giudici, F.; Generali, D. Management of the axilla in breast cancer: Outcome analysis in a series of ductal versus lobular invasive cancers. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 180, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Sahin, A.A.; Yi, M.; Caudle, A.; Hunt, K.K.; Wu, Y. Outcomes of sentinel lymph node dissection alone vs. axillary lymph node dissection in early stage invasive lobular carcinoma: A retrospective study of the surveillance, epidemiology and end results (SEER) database. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamtani, A.; Zabor, E.C.; Stempel, M.; Morrow, M. Lobular histology does not predict the need for axillary dissection among ACOSOG Z0011-eligible breast cancers. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 3269–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.N.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Yi, M.; Buchholz, T.A.; Ames, F.C.; Kuerer, H.M.; Bedrosian, I.; Hunt, K.K. Outcomes of breast-conservation therapy for invasive lobular carcinoma are equivalent to those for invasive ductal carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. 2006, 192, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.; Kyriakides, S.; Ohno, S.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Poortmans, P.; Rubio, I.; Zackrisson, S.; Senkus, E. Early breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1194–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sledge, G.W.; Chagpar, A.; Perou, C. Collective wisdom: Lobular carcinoma of the breast. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2016, 36, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luveta, J.; Parks, R.M.; Heery, D.M.; Cheung, K.-L.; Johnston, S.J. Invasive lobular breast cancer as a distinct disease: Implications for therapeutic strategy. Oncol. Ther. 2020, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.M.; Renshaw, L.; Dixon, J.; Thomas, J. Invasive lobular carcinoma: Response to neoadjuvant letrozole therapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 130, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger Filho, O.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Mallon, E.; Gusterson, B.; Viale, G.; Winer, E.P.; Thürlimann, B.; Gelber, R.D.; Colleoni, M.; Ejlertsen, B. Relative effectiveness of letrozole compared with tamoxifen for patients with lobular carcinoma in the BIG 1-98 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knauer, M.; Gruber, C.; Dietze, O.; Greil, R.; Stöger, H.; Rudas, M.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Mlineritsch, B.; Kwasny, W.; Singer, C. Abstract S2-06: Survival advantage of anastrozol compared to tamoxifen for lobular breast cancer in the ABCSG-8 study. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, S2-06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palbociclib and Endocrine Therapy for LObular Breast Cancer Preoperative Study (PELOPS). Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02764541 (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Finn, R.S.; Martin, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Jones, S.; Im, S.-A.; Gelmon, K.; Harbeck, N.; Lipatov, O.N.; Walshe, J.M.; Moulder, S. Palbociclib and letrozole in advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.J.; Cheng, J.; Bloomquist, E.; Sanchez, J.; Wedam, S.B.; Singh, H.; Amiri-Kordestani, L.; Ibrahim, A.; Sridhara, R.; Goldberg, K.B. CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment for patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced or metastatic breast cancer: A US Food and Drug Administration pooled analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.J.; Cheng, J.; Prowell, T.M.; Bloomquist, E.; Tang, S.; Wedam, S.B.; Royce, M.; Krol, D.; Osgood, C.; Ison, G. Overall survival in patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced or metastatic breast cancer treated with a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor plus fulvestrant: A US Food and Drug Administration pooled analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouabbi, J.A.; Raghavendra, A.S.; Bassett, R.L., Jr.; Hassan, A.; Tripathy, D.; Layman, R.M. Histology-based survival outcomes in hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer treated with targeted therapies. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toi, M.; Inoue, K.; Masuda, N.; Iwata, H.; Sohn, J.; Hae Park, I.; Im, S.A.; Chen, S.C.; Enatsu, S.; Turner, P.K. Abemaciclib in combination with endocrine therapy for East Asian patients with HR+, HER2− advanced breast cancer: MONARCH 2 & 3 trials. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 2381–2392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yardley, D.A. MONALEESA clinical program: A review of ribociclib use in different clinical settings. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 2673–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.-S.; Sonke, G.S.; Hart, L.; Campone, M.; Petrakova, K.; Winer, E.P.; Janni, W. Overall survival with ribociclib plus letrozole in advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafner, M.; Mills, C.E.; Subramanian, K.; Chen, C.; Chung, M.; Boswell, S.A.; Everley, R.A.; Liu, C.; Walmsley, C.S.; Juric, D. Multiomics profiling establishes the polypharmacology of FDA-approved CDK4/6 inhibitors and the potential for differential clinical activity. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 1067–1080.e1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Water, W.; Fontein, D.B.; van Nes, J.G.; Bartlett, J.M.; Hille, E.T.; Putter, H.; Robson, T.; Liefers, G.-J.; Roumen, R.M.; Seynaeve, C. Influence of semi-quantitative oestrogen receptor expression on adjuvant endocrine therapy efficacy in ductal and lobular breast cancer–a TEAM study analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Metzger, O.; Parimi, N.; Siuliukina, N.; Zhang, Y.; Treuner, K.; Liefers, G.-J. Abstract P2-03-13: Breast Cancer Index (BCI) identifies fewer patients with high risk of late recurrence and high likelihood of benefit from extended endocrine therapy with invasive lobular compared to invasive ductal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, P2-03-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradishar, W.J.; Moran, M.S.; Abraham, J.; Aft, R.; Agnese, D.; Allison, K.H.; Anderson, B.; Burstein, H.J.; Chew, H.; Dang, C. Breast cancer, version 3.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 691–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ETOP IBCSG Partners Foundation; National Cancer Institute; Breast International Group. Triptorelin with Either Exemestane or Tamoxifen in Treating Premenopausal Women with Hormone-Responsive Breast Cancer. 2003. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00066703 (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- ETOP IBCSG Partners Foundation; Breast International Group; Cancer and Leukemia Group B; National Cancer Institute (NCI); NSABP Foundation Inc.; NCIC Clinical Trials Group; North Central Cancer Treatment Group; SWOG Cancer Research Network. Suppression of Ovarian Function with Either Tamoxifen or Exemestane Compared with Tamoxifen Alone in Treating Premenopausal Women with Hormone-Responsive Breast Cancer. 2003. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00066690 (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Pagani, O.; Regan, M.M.; Walley, B.A.; Fleming, G.F.; Colleoni, M.; Láng, I.; Gomez, H.L.; Tondini, C.; Burstein, H.J.; Perez, E.A. Adjuvant exemestane with ovarian suppression in premenopausal breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, P.A.; Fleming, G.F.; Láng, I.; Ciruelos, E.M.; Bonnefoi, H.R.; Bellet, M.; Bernardo, A.; Climent, M.A.; Martino, S.; Bermejo, B. Adjuvant endocrine therapy in premenopausal breast cancer: 12-Year results from SOFT. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Record, H.; Clelland, E.; Rothschild, H.T.; Kaur, M.; Chien, A.J.; Melisko, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Mujir, F.; Huppert, L.; Mukhtar, R.A. Tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors with ovarian function suppression in pre-menopausal stage I-III lobular breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2023, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, A.H.; Niman, S.M.; Ruggeri, M.; Peccatori, F.A.; Azim, H.A., Jr.; Colleoni, M.; Saura, C.; Shimizu, C.; Sætersdal, A.B.; Kroep, J.R. Interrupting endocrine therapy to attempt pregnancy after breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocquyt, V.; Blondeel, P.; Depypere, H.; Praet, M.; Schelfhout, V.; Silva, O.; Hurley, J.; Serreyn, R.; Daems, K.; Van Belle, S. Different responses to preoperative chemotherapy for invasive lobular and invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2003, 29, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.; Sneige, N.; Kau, S.-W.; Broglio, K.; Theriault, R.L.; Valero, V.; Buzdar, A.U.; Kuerer, H.; Buccholz, T.A. Invasive lobular carcinoma classic type: Response to primary chemotherapy and survival outcomes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpech, Y.; Coutant, C.; Hsu, L.; Barranger, E.; Iwamoto, T.; Barcenas, C.; Hortobagyi, G.; Rouzier, R.; Esteva, F.; Pusztai, L. Clinical benefit from neoadjuvant chemotherapy in oestrogen receptor-positive invasive ductal and lobular carcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loibl, S.; Volz, C.; Mau, C.; Blohmer, J.-U.; Costa, S.D.; Eidtmann, H.; Fasching, P.A.; Gerber, B.; Hanusch, C.; Jackisch, C. Response and prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in 1,051 patients with infiltrating lobular breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 144, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lips, E.H.; Mukhtar, R.A.; Yau, C.; De Ronde, J.J.; Livasy, C.; Carey, L.A.; Loo, C.E.; Vrancken-Peeters, M.-J.T.; Sonke, G.S.; Berry, D.A. Lobular histology and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, F.; Barni, S. Response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in ductal compared to lobular carcinoma of the breast: A meta-analysis of published trials including 1,764 lobular breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 142, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapani, D.; Gandini, S.; Corti, C.; Crimini, E.; Bellerba, F.; Minchella, I.; Criscitiello, C.; Tarantino, P.; Curigliano, G. Benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with lobular breast cancer: A systematic review of the literature and metanalysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 97, 102205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, R.; Bradley, R.; Braybrooke, J.; Liu, Z.; Peto, R.; Davies, L.; Dodwell, D.; McGale, P.; Pan, H.; Taylor, C. Increasing the dose intensity of chemotherapy by more frequent administration or sequential scheduling: A patient-level meta-analysis of 37 298 women with early breast cancer in 26 randomised trials. Lancet 2019, 393, 1440–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Nonneville, A.; Jauffret, C.; Gonçalves, A.; Classe, J.-M.; Cohen, M.; Reyal, F.; Mazouni, C.; Chauvet, M.-P.; Chopin, N.; Colombo, P.-E. Adjuvant chemotherapy in lobular carcinoma of the breast: A clinicopathological score identifies high-risk patient with survival benefit. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 175, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gregorio, A.; Janni, W.; Friedl, T.W.; Nitz, U.; Rack, B.; Schneeweiss, A.; Kates, R.; Fehm, T.; Kreipe, H.; Christgen, M. The impact of anthracyclines in intermediate and high-risk HER2-negative early breast cancer—A pooled analysis of the randomised clinical trials PlanB and SUCCESS C. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Dabbs, D.J.; Shuai, Y.; Niemeier, L.A.; Bhargava, R. Classical-type invasive lobular carcinoma with HER2 overexpression: Clinical, histologic, and hormone receptor characteristics. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 136, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, F.; Majjaj, S.; Venet, D.; Rothé, F.; Pingitore, J.; Boeckx, B.; Marchio, C.; Clatot, F.; Bertucci, F.; Mariani, O. Characterization of Stromal Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes and Genomic Alterations in Metastatic Lobular Breast CancerGenomic Characterization of Metastatic Lobular Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 6254–6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger-Filho, O.; Procter, M.; de Azambuja, E.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Gelber, R.D.; Dowsett, M.; Loi, S.; Saini, K.S.; Cameron, D.; Untch, M. Magnitude of trastuzumab benefit in patients with HER2-positive, invasive lobular breast carcinoma: Results from the HERA trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumsri, S.; Li, Z.; Shachner, T.; Advani, P.; Sideras, K.; Moreno-Aspitia, A.; Colon-Otero, G.; Knutson, K.L.; Nassar, A.; Perez, E.A. Outcome and Immune Landscape of HER2-Positive Invasive Lobular Carcinoma in the North Central Cancer Treatment Group (NCCTG) N9831 (Alliance) Trial; Wolters Kluwer Health: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jhaveri, K.; Park, H.; Waisman, J.; Goldman, J.W.; Guerrero-Zotano, A.; Boni, V.; Haley, B.; Mayer, I.A.; Brufsky, A.; Yang, E. Neratinib+ fulvestrant+ trastuzumab for hormone receptor-positive, HER2-mutant metastatic breast cancer and neratinib+ trastuzumab for triple-negative disease: Latest updates from the SUMMIT trial. In Proceedings of the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, San Antonio, TX, USA, 7–10 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dirix, L.Y.; Takacs, I.; Jerusalem, G.; Nikolinakos, P.; Arkenau, H.-T.; Forero-Torres, A.; Boccia, R.; Lippman, M.E.; Somer, R.; Smakal, M. Avelumab, an anti-PD-L1 antibody, in patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer: A phase 1b JAVELIN Solid Tumor study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 167, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugo, H.S.; Delord, J.-P.; Im, S.-A.; Ott, P.A.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Bedard, P.L.; Sachdev, J.; Tourneau, C.L.; van Brummelen, E.M.; Varga, A. Safety and Antitumor Activity of Pembrolizumab in Patients with Estrogen Receptor–Positive/Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Negative Advanced Breast Cancer. Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in ER+/HER2− Advanced Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2804–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonke, G.S.; Van Ommen-Nijhof, A.; Wortelboer, N.; van der Noort, V.; Swinkels, A.C.; Blommestein, H.M.; Beeker, A.; Beelen, K.; Hamming, L.C.; Heijns, J.B. Primary Outcome Analysis of the Phase 3 SONIA Trial (BOOG 2017-03) on Selecting the Optimal Position of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) Inhibitors for Patients with Hormone Receptor-Positive (HR+), HER2-Negative (HER2-) Advanced Breast Cancer (ABC); American Society of Clinical Oncology: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- European Institute of Oncology. CDH1 Germline Mutations in Lobular Breast Cancer. 2018. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT04206891 (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- McAuliffe, P. Endocrine Response in Women with Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer. 2015. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02206984 (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Walsh, L.; Haley, K.E.; Moran, B.; Mooney, B.; Tarrant, F.; Madden, S.F.; Di Grande, A.; Fan, Y.; Das, S.; Rueda, O.M. BET inhibition as a rational therapeutic strategy for invasive lobular breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 7139–7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
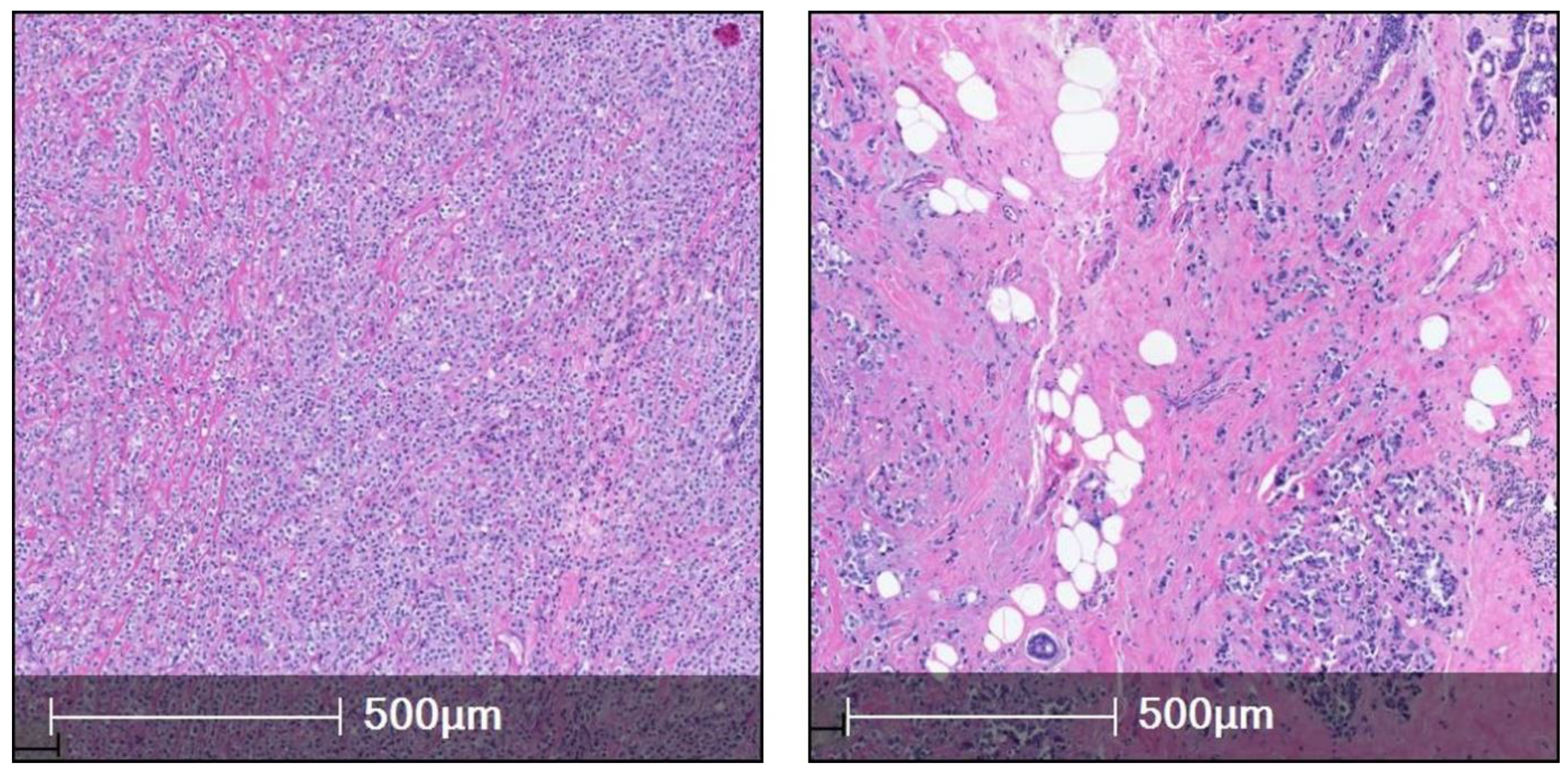

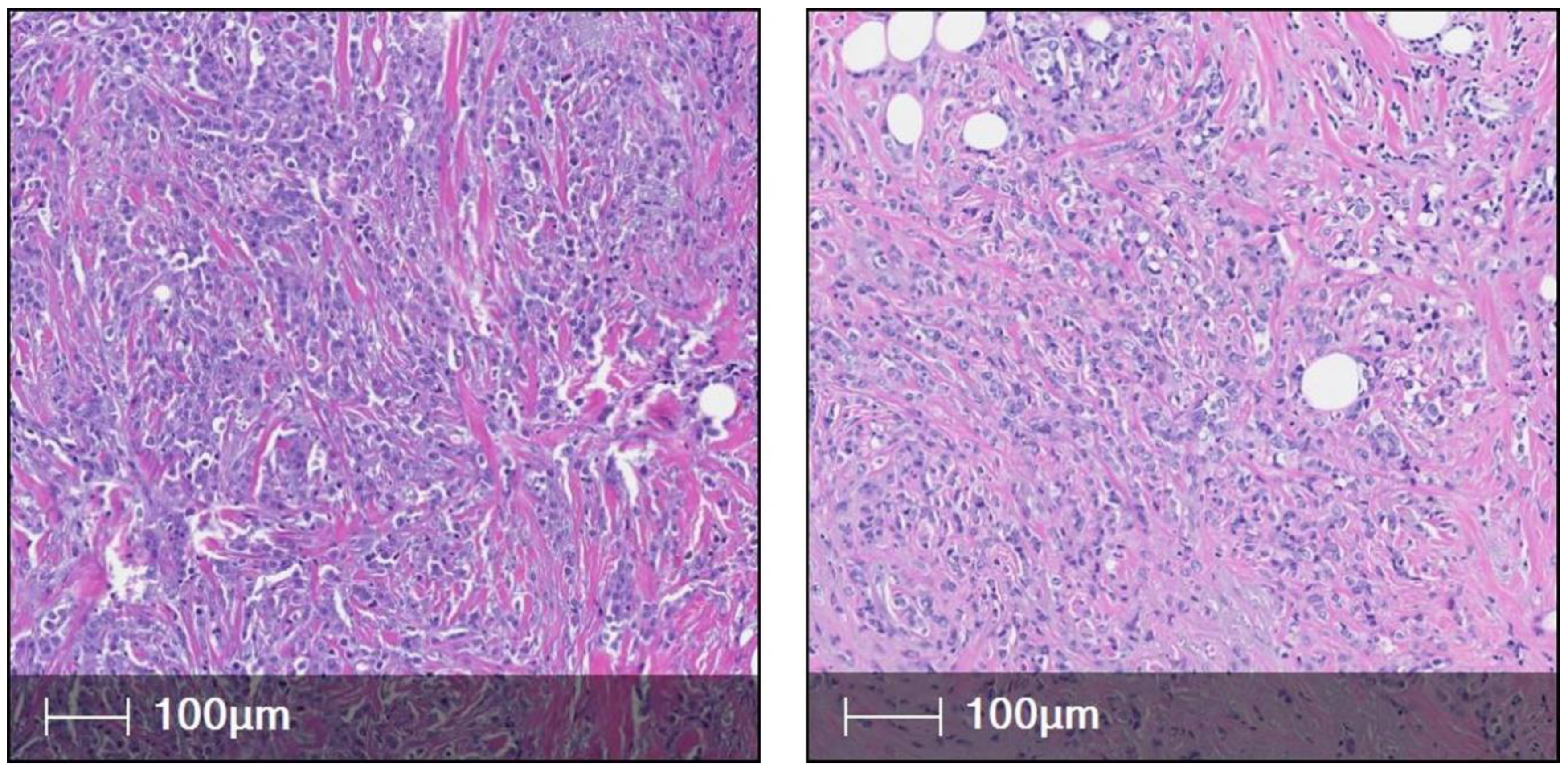

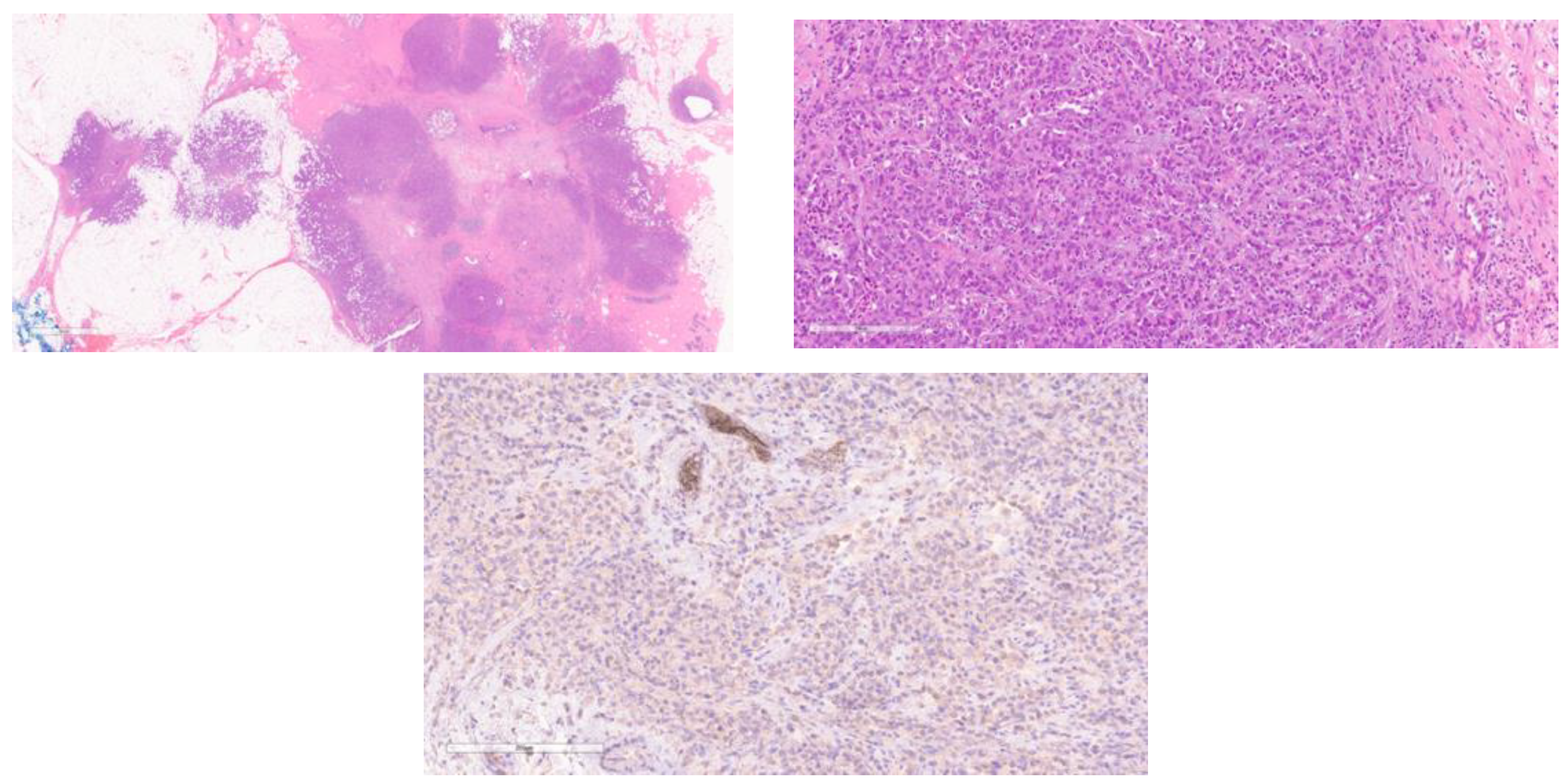

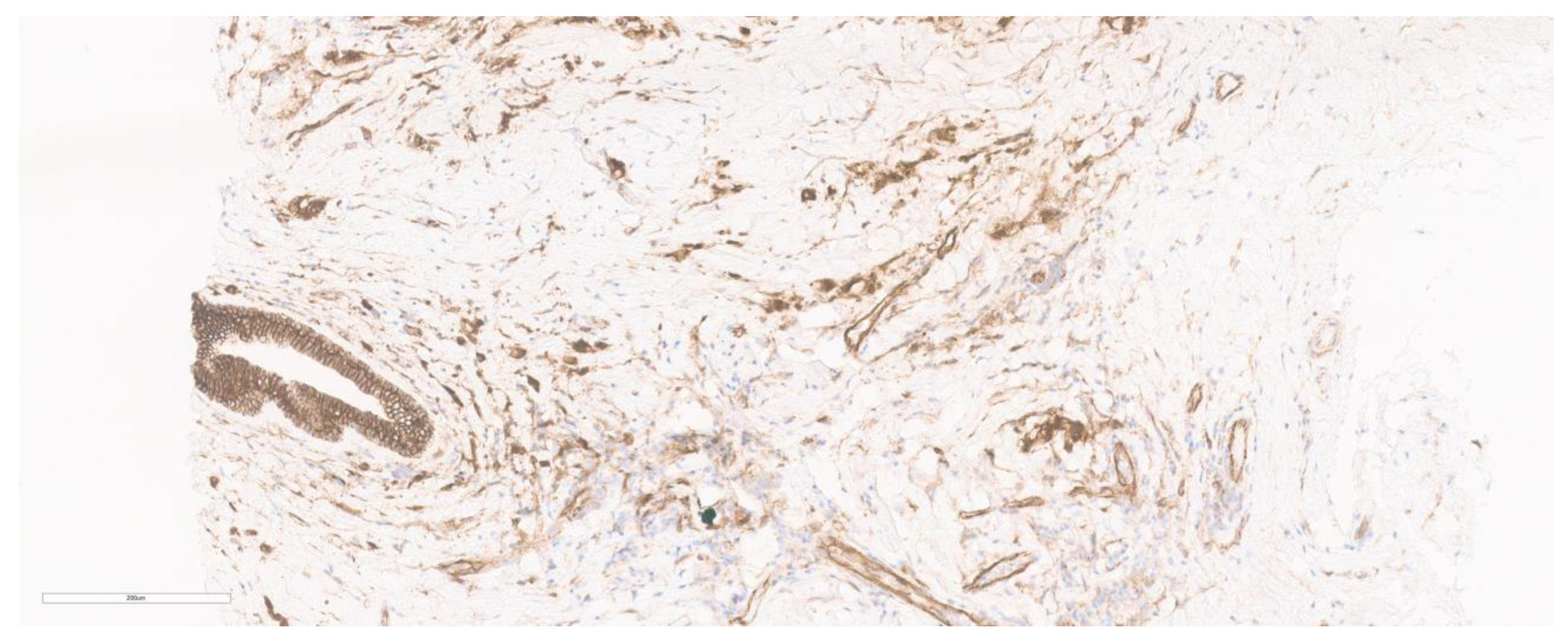
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batra, H.; Mouabbi, J.A.; Ding, Q.; Sahin, A.A.; Raso, M.G. Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast: A Comprehensive Review with Translational Insights. Cancers 2023, 15, 5491. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225491
Batra H, Mouabbi JA, Ding Q, Sahin AA, Raso MG. Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast: A Comprehensive Review with Translational Insights. Cancers. 2023; 15(22):5491. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225491
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatra, Harsh, Jason Aboudi Mouabbi, Qingqing Ding, Aysegul A. Sahin, and Maria Gabriela Raso. 2023. "Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast: A Comprehensive Review with Translational Insights" Cancers 15, no. 22: 5491. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225491
APA StyleBatra, H., Mouabbi, J. A., Ding, Q., Sahin, A. A., & Raso, M. G. (2023). Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast: A Comprehensive Review with Translational Insights. Cancers, 15(22), 5491. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225491






