Fabrication of a Three-Dimensional Spheroid Culture System for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Using a Microfabricated Device
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Preparation of Microwell Device
2.3. Generation of Oral Cancer Cell Spheroids
2.4. Detection of Cell Viability in Spheroids
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (Real-Time RT-qPCR)
2.6. Immunohistochemistry for CSC Markers
2.7. Assessment of Sensitivity to Cisplatin
2.8. Assessment of Tumorigenicity in Mouse Xenograft Model
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
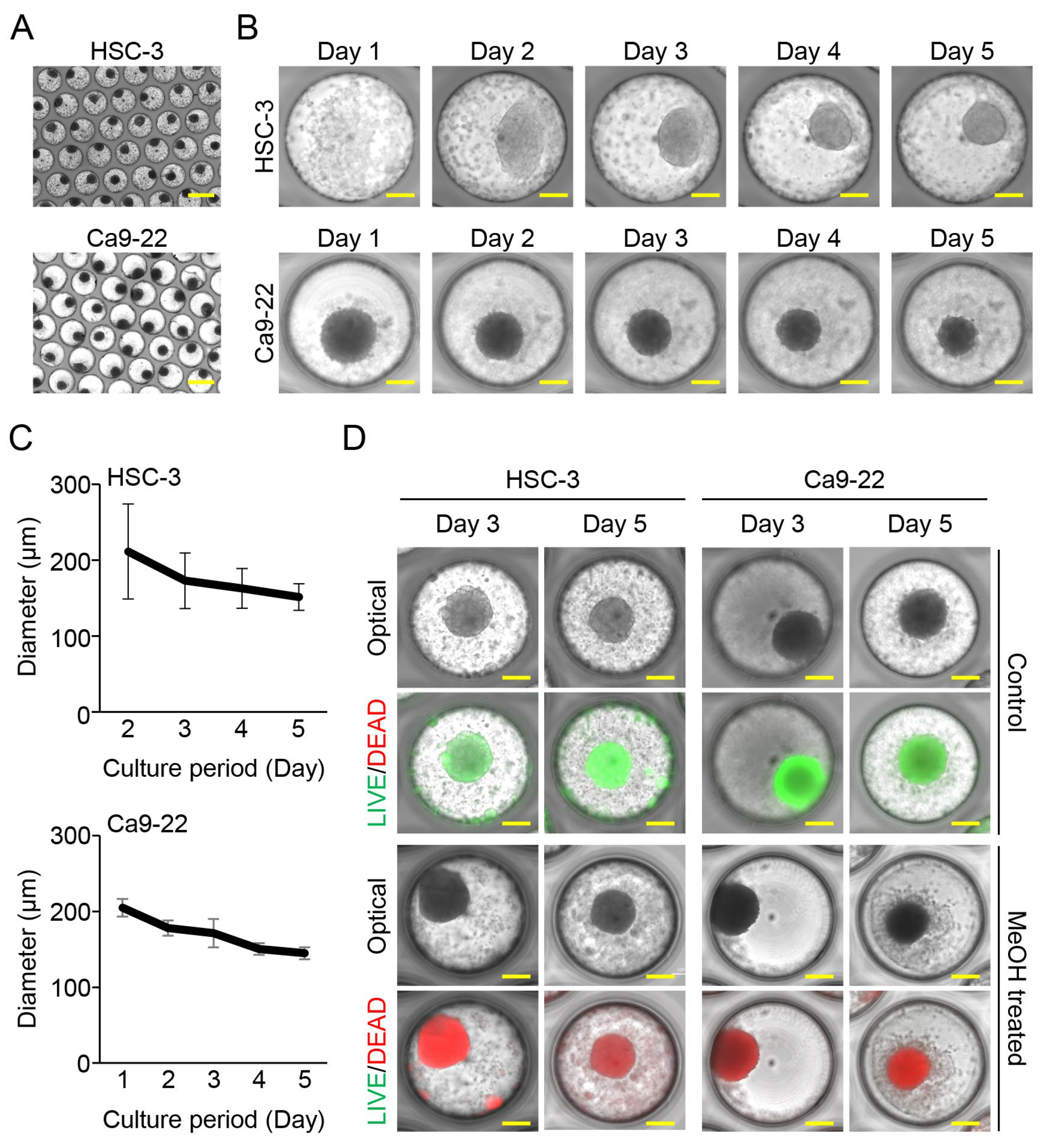
3.1. Oral Cancer Cells Aggregated and Formed Spheroids in Fabricated Microwell Device
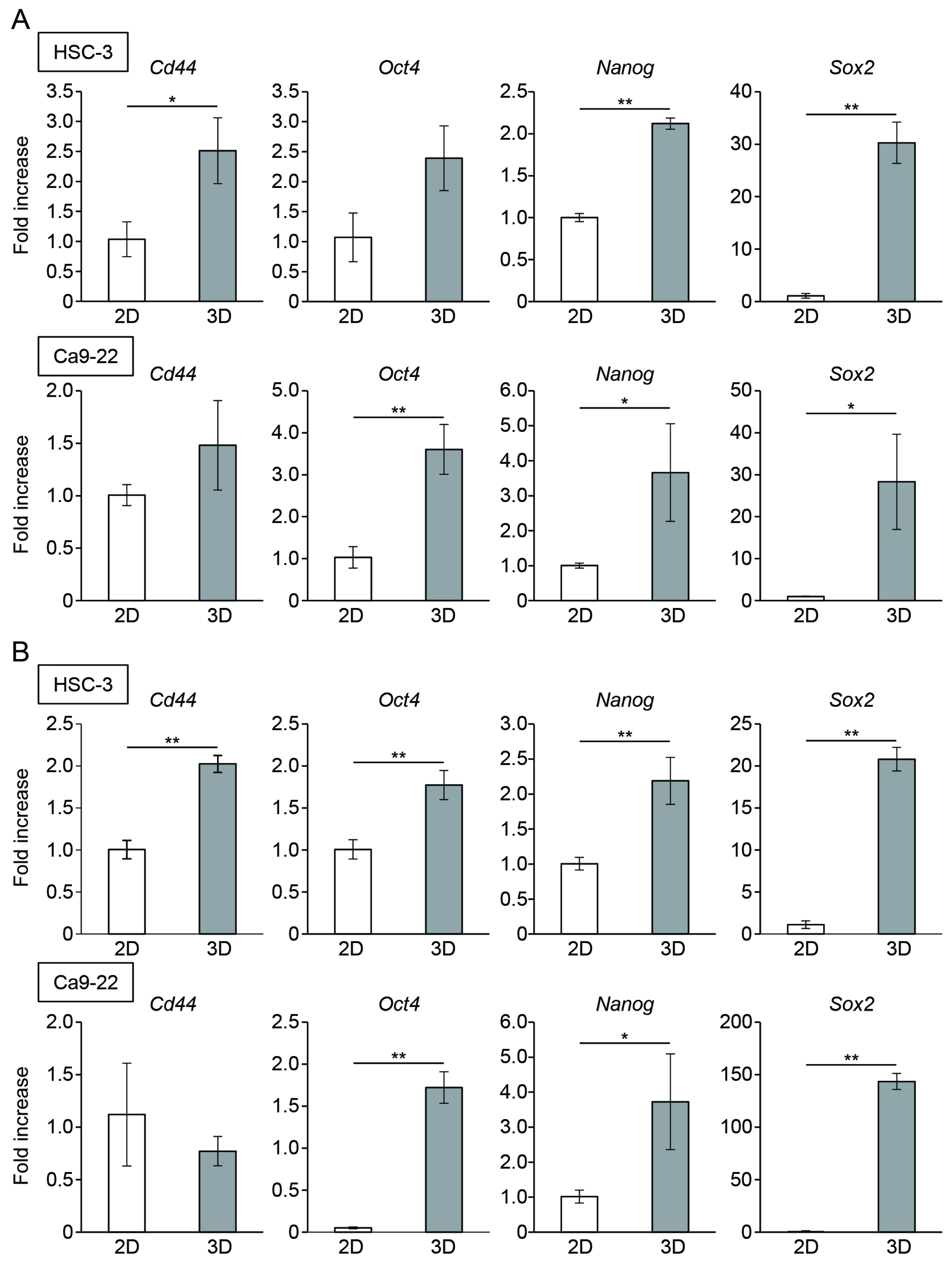
3.2. Oral Cancer Cells in Spheroids Enhanced the Expression of CSC Markers
3.3. Oral Cancer Cells in Spheroids Showed Increased Resistance to Anticancer Drugs
3.4. Stemness of Oral Cancer Cells Enhanced by Spheroid Culture Was Maintained under 2D-Culture Conditions
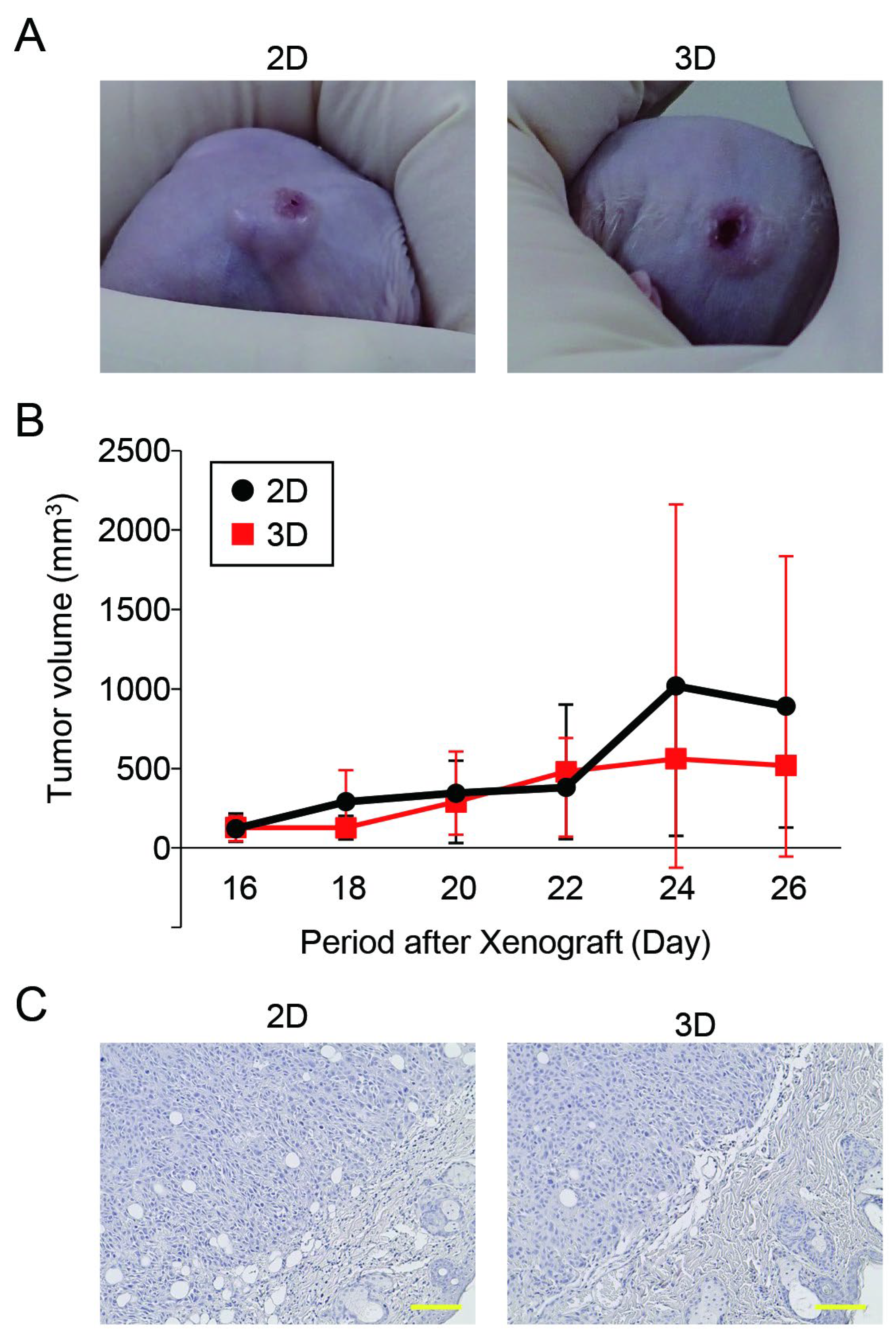
3.5. The Tumorigenic Potential of Oral Cancer Spheroids Generated in the Microwell Device Was Comparable to That of Monolayer Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattiuzzi, C.; Lippi, G. Current Cancer Epidemiology. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2019, 9, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, T.K.; Murphy, C.; Smith, A.B.; Kanatas, A.N.; Mitchell, D.A. Survival after surgery for oral cancer: A 30-year experience. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 55, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulte, D.; Brenner, H. Changes in survival in head and neck cancers in the late 20th and early 21st century: A period analysis. Oncologist 2010, 15, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemans, C.R.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Brakenhoff, R.H. The molecular landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, M.F. Clinical and Therapeutic Implications of Cancer Stem Cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, I.C. Stem cell properties and epithelial malignancies. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.M.; Zhang, J.G.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q. Targeting cancer stem cells for reversing therapy resistance: Mechanism, signaling, and prospective agents. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plemmenos, G.; Tzimogianni, V.; Fili, C.; Piperi, C. Contributing Role of High Mobility Group Box 1 Signaling in Oral Cancer Development and Therapy. Life 2023, 13, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.M.; Heguedusch, D.; Rodini, C.O.; Nunes, F.D.; Rodrigues, M. Mechanisms involved in cancer stem cell resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023, 6, 116–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguignon, L.Y.; Wong, G.; Shiina, M. Up-regulation of Histone Methyltransferase, DOT1L, by Matrix Hyaluronan Promotes MicroRNA-10 Expression Leading to Tumor Cell Invasion and Chemoresistance in Cancer Stem Cells from Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 10571–10585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorna, D.; Paluszczak, J. Targeting cancer stem cells as a strategy for reducing chemotherapy resistance in head and neck cancers. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 13417–13435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoni, D.; Burckel, H.; Josset, E.; Noel, G. Three-dimensional cell culture: A breakthrough in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 5517–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, M.A.G.; Xavier, C.P.R.; Pereira, R.F.; Petrikaitė, V.; Vasconcelos, M.H. 3D Cell Culture Models as Recapitulators of the Tumor Microenvironment for the Screening of Anti-Cancer Drugs. Cancers 2021, 14, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Hu, Z.; Lu, L.; Lu, H.; Xu, X. Three-dimensional cell culture: A powerful tool in tumor research and drug discovery. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 6999–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoarau-Véchot, J.; Rafii, A.; Touboul, C.; Pasquier, J. Halfway between 2D and Animal Models: Are 3D Cultures the Ideal Tool to Study Cancer-Microenvironment Interactions? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.C.; Moreira, A.F.; de Melo-Diogo, D.; Gaspar, V.M.; Carvalho, M.P.; Correia, I.J. 3D tumor spheroids: An overview on the tools and techniques used for their analysis. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1427–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, B.; Henriques, A.C.; Silva, P.M.A.; Bousbaa, H. Three-Dimensional Spheroids as In Vitro Preclinical Models for Cancer Research. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.Z.; Chang, H.Y. Recent advances in three-dimensional multicellular spheroid culture for biomedical research. Biotechnol. J. 2008, 3, 1172–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Yoshiura, Y.; Mori, R.; Tamura, T.; Yahiro, K.; Mori, H.; Kanemura, Y.; Yamasaki, M.; Nakazawa, K. Effect of microwell chip structure on cell microsphere production of various animal cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 110, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritani, Y.; Usui, M.; Sano, K.; Nakazawa, K.; Hanatani, T.; Nakatomi, M.; Iwata, T.; Sato, T.; Ariyoshi, W.; Nishihara, T.; et al. Spheroid culture enhances osteogenic potential of periodontal ligament mesenchymal stem cells. J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 870–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, K.; Usui, M.; Moritani, Y.; Nakazawa, K.; Hanatani, T.; Kondo, H.; Nakatomi, M.; Onizuka, S.; Iwata, T.; Sato, T.; et al. Co-cultured spheroids of human periodontal ligament mesenchymal stem cells and vascular endothelial cells enhance periodontal tissue regeneration. Regen. Ther. 2020, 14, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyoshi, W.; Usui, M.; Sano, K.; Kawano, A.; Okinaga, T.; Nakashima, K.; Nakazawa, K.; Nishihara, T. 3D spheroid culture models for chondrocytes using polyethylene glycol-coated microfabricated chip. Biomed. Res. 2020, 41, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, F.; Iwanaga, K.; Okinaga, T.; Takahashi, O.; Ariyoshi, W.; Suzuki, R.; Sugii, M.; Maruyama, K.; Tominaga, K.; Nishihara, T. Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted sonoporation with microbubbles enhances therapeutic efficacy in a squamous cell carcinoma model. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185293. [Google Scholar]
- Wanigasekara, J.; Carroll, L.J.; Cullen, P.J.; Tiwari, B.; Curtin, J.F. Three-Dimensional (3D) in vitro cell culture protocols to enhance glioblastoma research. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0276248. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallari, G.; Zuellig, R.A.; Lehmann, R.; Weber, M.; Moritz, W. Rat pancreatic islet size standardization by the “hanging drop” technique. Transplant. Proc. 2007, 39, 2018–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matak, D.; Brodaczewska, K.K.; Lipiec, M.; Szymanski, Ł.; Szczylik, C.; Czarnecka, A.M. Colony, hanging drop, and methylcellulose three dimensional hypoxic growth optimization of renal cell carcinoma cell lines. Cytotechnology 2017, 69, 565–578. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, R.; Aviles, D.; Krisulevicz, C.; Hunter, K.; Krill, L.; Warshal, D.; Ostrovsky, O. The Effects of Natural Epigenetic Therapies in 3D Ovarian Cancer and Patient-Derived Tumor Explants: New Avenues in Regulating the Cancer Secretome. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glicklis, R.; Merchuk, J.C.; Cohen, S. Modeling mass transfer in hepatocyte spheroids via cell viability, spheroid size, and hepatocellular functions. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 86, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouysségur, J.; Dayan, F.; Mazure, N.M. Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour regression. Nature. 2006, 441, 437–443. [Google Scholar]
- Al Tameemi, W.; Dale, T.P.; Al-Jumaily, R.M.K.; Forsyth, N.R. Hypoxia-Modified Cancer Cell Metabolism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, P.; Waghmare, S. Molecular signaling in cancer stem cells of tongue squamous cell carcinoma: Therapeutic implications and challenges. World J. Stem Cells 2023, 15, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmedo, I.; Martínez, D.; Carrasco-Rojas, J.; Jara, J.A. Mitochondria in oral cancer stem cells: Unraveling the potential drug targets for new and old drugs. Life Sci. 2023, 331, 122065. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rainho, M.A.; Mencalha, A.L.; Thole, A.A. Hypoxia effects on cancer stem cell phenotype in colorectal cancer: A mini-review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 7527–7535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Myszczyszyn, A.; Czarnecka, A.M.; Matak, D.; Szymanski, L.; Lian, F.; Kornakiewicz, A.; Bartnik, E.; Kukwa, W.; Kieda, C.; Szczylik, C. The Role of Hypoxia and Cancer Stem Cells in Renal Cell Carcinoma Pathogenesis. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2015, 11, 919–943. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karami Fath, M.; Garousi, S.; Mottahedi, M.; Ghasemzadeh, N.; Salmani, K.; Olfati, F.; Beit Saeed, M.; Sotoudeh, S.; Barati, G. The role of hypoxia-inducible factors in breast cancer stem cell specification. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 243, 154349. [Google Scholar]
- Ketkaew, Y.; Osathanon, T.; Pavasant, P.; Sooampon, S. Apigenin inhibited hypoxia induced stem cell marker expression in a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Arch. Oral Biol. 2017, 74, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Boretto, M.; Maenhoudt, N.; Luo, X.; Hennes, A.; Boeckx, B.; Bui, B.; Heremans, R.; Perneel, L.; Kobayashi, H.; Van Zundert, I.; et al. Patient-derived organoids from endometrial disease capture clinical heterogeneity and are amenable to drug screening. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Madoux, F.; Tanner, A.; Vessels, M.; Willetts, L.; Hou, S.; Scampavia, L.; Spicer, T.P. A 1536-Well 3D Viability Assay to Assess the Cytotoxic Effect of Drugs on Spheroids. SLAS Discov. 2017, 22, 516–524. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, P.; Bentivoglio, V.; Varani, M.; Signore, A. Three-Dimensional In Vitro Tumor Spheroid Models for Evaluation of Anticancer Therapy: Recent Updates. Cancers 2023, 15, 4846. [Google Scholar]
- Ponomarev, A.; Gilazieva, Z.; Solovyeva, V.; Allegrucci, C.; Rizvanov, A. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors Impacting Cancer Stemness and Tumor Progression. Cancers 2022, 14, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Song, X.; Xu, D.; Tiek, D.; Goenka, A.; Wu, B.; Sastry, N.; Hu, B.; Cheng, S.Y. Stem cell programs in cancer initiation, progression, and therapy resistance. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8721–8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Umemura, N.; Adachi, M.; Motoki, M.; Ohkoshi, E. ABCG2, CD44 and SOX9 are increased with the acquisition of drug resistance and involved in cancer stem cell activities in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 24, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Tan, Y.; Xu, M.; Xu, W.; Lu, H. New advances into cisplatin resistance in head and neck squamous carcinoma: Mechanisms and therapeutic aspects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114778. [Google Scholar]
- Dohle, E.; Bischoff, I.; Böse, T.; Marsano, A.; Banfi, A.; Unger, R.E.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. Macrophage-mediated angiogenic activation of outgrowth endothelial cells in co-culture with primary osteoblasts. Eur. Cell Mater. 2014, 27, 149–165, discussion 164–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolin, M.; Barbaro, V.; Breda, C.; Ferrari, S.; Marchini, G.; Pedrotti, E.; Ferrari, B.; Diego, P.; Fasolo, A. In vitro establishment, validation and characterisation of conjunctival epithelium outgrowth using tissue fragments and amniotic membrane. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 106, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amôr, N.G.; Buzo, R.F.; Ortiz, R.C.; Lopes, N.M.; Saito, L.M.; Mackenzie, I.C.; Rodini, C.O. In vitro and in vivo characterization of cancer stem cell subpopulations in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, Z.; Yoshida, T.; Okabe, M.; Koike, C.; Fathy, M.; Tsuno, H.; Tomihara, K.; Arai, N.; Noguchi, M.; Nikaido, T. CD44 and SSEA-4 positive cells in an oral cancer cell line HSC-4 possess cancer stem-like cell characteristics. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Kang, S.H.; Oh, S.Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Gum, S.; Kwon, T.G.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, S.T.; Hong, Y.J.; et al. Differential Angiogenic Potential of 3-Dimension Spheroid of HNSCC Cells in Mouse Xenograft. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Hong, S.; Jung, B.; Jeong, S.Y.; Byeon, J.H.; Jeong, G.S.; Choi, J.; Hwang, C. In vitro lung cancer multicellular tumor spheroid formation using a microfluidic device. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 116, 3041–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Ip, C.K.; Tang, M.Y.; Sy, S.K.; Yung, S.; Chan, T.M.; Yang, M.; Shum, H.C.; Wong, A.S. Modeling Ovarian Cancer Multicellular Spheroid Behavior in a Dynamic 3D Peritoneal Microdevice. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 120, 55337. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzari, G.; Nicolas, V.; Matsusaki, M.; Akashi, M.; Couvreur, P.; Mura, S. Multicellular spheroid based on a triple co-culture: A novel 3D model to mimic pancreatic tumor complexity. Acta Biomater. 2018, 78, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminska, A.; Wedzinska, A.; Kot, M.; Sarnowska, A. Effect of Long-Term 3D Spheroid Culture on WJ-MSC. Cells 2021, 10, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene | Primer Sequence (5’-3’) | |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | forward | 5′-GCG CGG CTA CAG CTT CA-3′ |
| reverse | 5′-CTT AAT GTC ACG CAC GAT TTC C-3′ | |
| Cd44 | forward | 5′-TGT GCA GCA AAC AAC ACA GG-3′ |
| reverse | 5′-TGG AGC TGA AGC ATT GAA GC-3′ | |
| Oct4 | forward | 5′-ACT CGA GCA ATT TGC CAA GC-3 |
| reverse | 5′-TTG AAG CAA GCT GCA GAG C-3′ | |
| Nanog | forward | 5′-GCA GAT GCA AGA ACT CTC CAA C-3′ |
| reverse | 5′-TCG GCC AGT TGT TTT TCT GC-3′ | |
| Sox2 | forward | 5′-TGA ATG CCT TCA TGG TGT GG-3′ |
| reverse | 5′-AGT TGT GCA TCT TGG GGT TC-3′ | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ikeda-Motonakano, R.; Hirabayashi-Nishimuta, F.; Yada, N.; Yamasaki, R.; Nagai-Yoshioka, Y.; Usui, M.; Nakazawa, K.; Yoshiga, D.; Yoshioka, I.; Ariyoshi, W. Fabrication of a Three-Dimensional Spheroid Culture System for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Using a Microfabricated Device. Cancers 2023, 15, 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215162
Ikeda-Motonakano R, Hirabayashi-Nishimuta F, Yada N, Yamasaki R, Nagai-Yoshioka Y, Usui M, Nakazawa K, Yoshiga D, Yoshioka I, Ariyoshi W. Fabrication of a Three-Dimensional Spheroid Culture System for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Using a Microfabricated Device. Cancers. 2023; 15(21):5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215162
Chicago/Turabian StyleIkeda-Motonakano, Reiko, Fumika Hirabayashi-Nishimuta, Naomi Yada, Ryota Yamasaki, Yoshie Nagai-Yoshioka, Michihiko Usui, Kohji Nakazawa, Daigo Yoshiga, Izumi Yoshioka, and Wataru Ariyoshi. 2023. "Fabrication of a Three-Dimensional Spheroid Culture System for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Using a Microfabricated Device" Cancers 15, no. 21: 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215162
APA StyleIkeda-Motonakano, R., Hirabayashi-Nishimuta, F., Yada, N., Yamasaki, R., Nagai-Yoshioka, Y., Usui, M., Nakazawa, K., Yoshiga, D., Yoshioka, I., & Ariyoshi, W. (2023). Fabrication of a Three-Dimensional Spheroid Culture System for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Using a Microfabricated Device. Cancers, 15(21), 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215162






