Prognostic Significance of Cyclin D1 Expression in Small Intestinal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
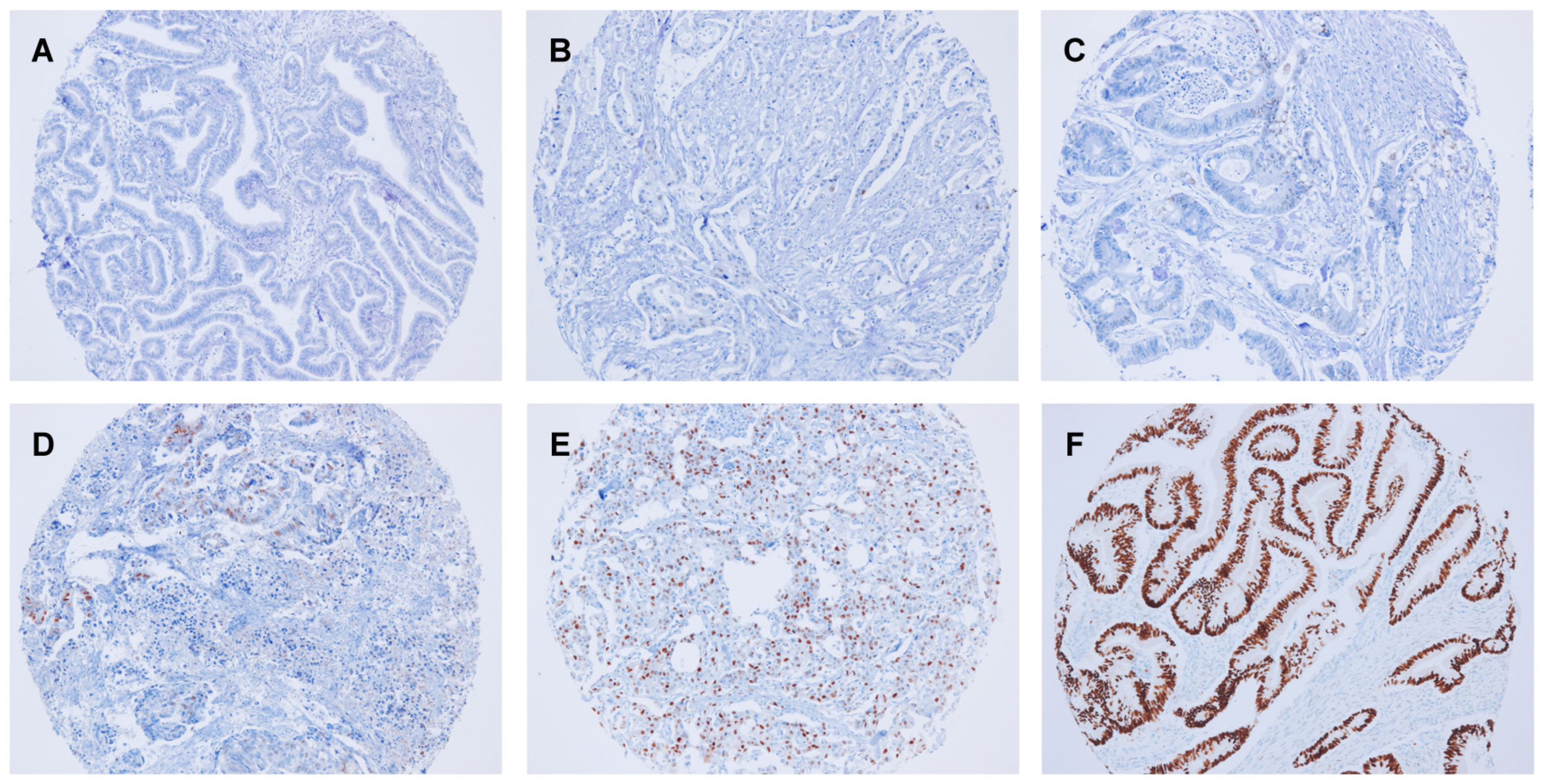
2.2. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.3. Molecular Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinicopathological Characteristics
3.2. Cyclin D1 Expression
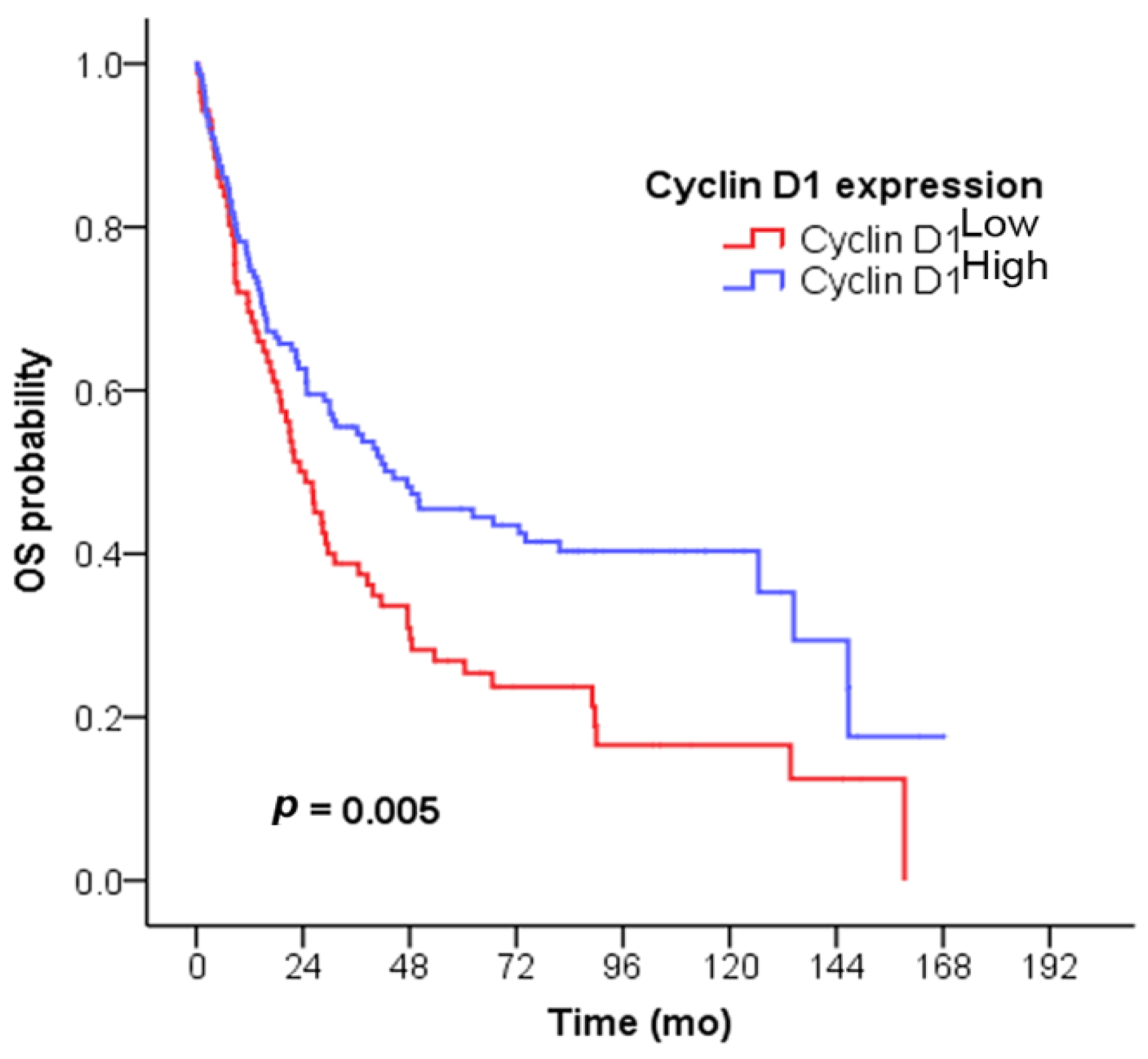
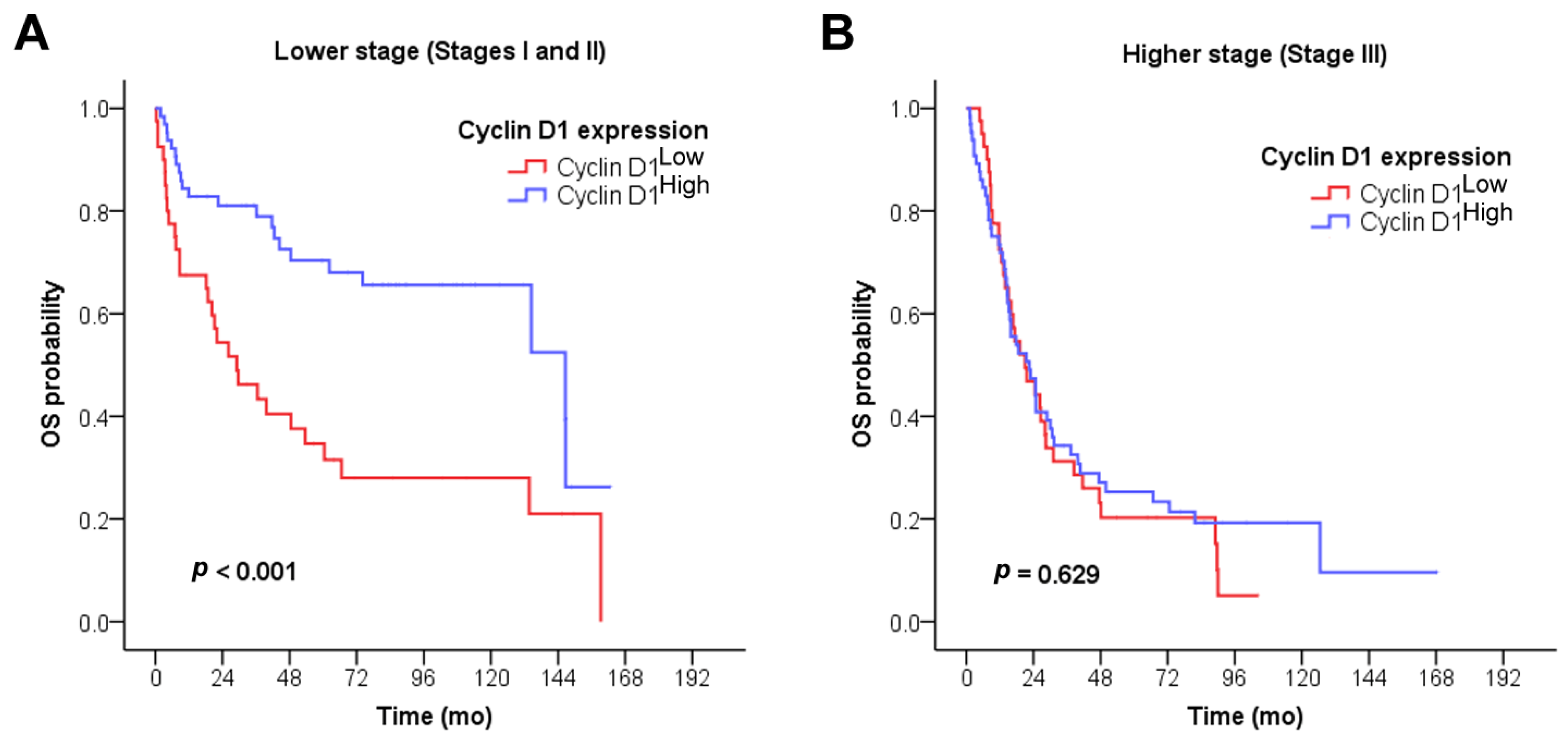
3.3. Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Fang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, L.; Tang, Y.; Fan, Y. Prognostic significance of cyclin D1 expression in renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi Binabaj, M.; Bahrami, A.; Khazaei, M.; Ryzhikov, M.; Ferns, G.A.; Avan, A.; Mahdi Hassanian, S. The prognostic value of cyclin D1 expression in the survival of cancer patients: A meta-analysis. Gene 2020, 728, 144283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlin, C.; Lundgren, C.; Embretsén-Varro, E.; Jirström, K.; Blomqvist, C.; Fjällskog, M.L. High expression of cyclin D1 is associated to high proliferation rate and increased risk of mortality in women with ER-positive but not in ER-negative breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 164, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levidou, G.; Saetta, A.A.; Karlou, M.; Thymara, I.; Pratsinis, H.; Pavlopoulos, P.; Isaiadis, D.; Diamantopoulou, K.; Patsouris, E.; Korkolopoulou, P. D-type cyclins in superficial and muscle-invasive bladder urothelial carcinoma: Correlation with clinicopathological data and prognostic significance. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 136, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luangdilok, S.; Wanchaijiraboon, P.; Chantranuwatana, P.; Teerapakpinyo, C.; Shuangshoti, S.; Sriuranpong, V. Cyclin D1 expression as a potential prognostic factor in advanced KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, Y.; Pirkmaier, A.; Alvarez, J.V.; Frank, D.A.; Keselman, I.; Logothetis, D.; Mandeli, J.; O’Connell, M.J.; Waxman, S.; Germain, D. Cyclin D1 overexpression and response to bortezomib treatment in a breast cancer model. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cancer Stat Facts: Small Intestine Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/smint.html (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Annual Report of Cancer Statistics in Korea in 2020. Available online: http://ncc.re.kr/cancerStatsList.ncc?searchKey=total&searchValue=&pageNum=1 (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Klimstra, D.; Nagteggal, I.; Rugge, M.; Salto-Tellez, M. Tumours of the small intestine and ampulla. In WHO Classification of Tumours: Digestive System Tumours, 5th ed.; Carneiro, F., Ochiai, A., Chan, J., Oliva, E., Cheung, N.-Y., Rous, B., Cree, I., Singh, R., Eds.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2019; pp. 111–134. [Google Scholar]
- Symons, R.; Daly, D.; Gandy, R.; Goldstein, D.; Aghmesheh, M. Progress in the treatment of small intestine cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2023, 24, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.I.; Mongoue-Tchokote, S.; Wieghard, N.; Mori, M.; Vaccaro, G.M.; Sheppard, B.C.; Tsikitis, V.L. Treatment and survival of small-bowel adenocarcinoma in the United States: A comparison with colon cancer. Dis. Colon Rectum 2016, 59, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.Y.; Park, E.S.; Lee, J.J.; Chang, H.K.; Jung, E.S.; Oh, Y.H.; Hong, S.M. Prognostic significance of stromal and intraepithelial tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in small intestinal adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 153, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.Y.; Lee, E.J.; Hong, S.M.; Jung, E.S.; Chung, J.Y. Tumor microenvironmental prognostic risk in primary operable small intestinal adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2021, 45, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.Y.; Kim, M.; Gu, M.J.; Bae, Y.K.; Chang, H.K.; Jung, E.S.; Jang, K.T.; Kim, J.; Yu, E.; Eom, D.W.; et al. Clinicopathologic and prognostic associations of KRAS and BRAF mutations in small intestinal adenocarcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, A.B.; Venook, A.P.; Al-Hawary, M.M.; Arain, M.A.; Chen, Y.J.; Ciombor, K.K.; Cohen, S.A.; Cooper, H.S.; Deming, D.A.; Garrido-Laguna, I.; et al. Small bowel adenocarcinoma, version 1.2020, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2019, 17, 1109–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wei, J.; Xu, C.; Zhao, Z.; You, T. Prognostic significance of cyclin D1 expression in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Yoon, N.; Maeng, L.S.; Byun, J.H. Prognostic potential of cyclin D1 expression in colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoma, O.M.; Neurath, M.F.; Waldner, M.J. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and their therapeutic potential in colorectal cancer treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 757120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Helms, T.L.; Feng, N.; Gay, J.; Chang, Q.E.; Tian, F.; Wu, J.Y.; Toniatti, C.; Heffernan, T.P.; Powis, G.; et al. Efficacy of the combination of MEK and CDK4/6 inhibitors in vitro and in vivo in KRAS mutant colorectal cancer models. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 39595–39608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Gong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Van Horn, R.D.; Yin, T.; Huber, L.; Burke, T.F.; Manro, J.; Iversen, P.W.; Wu, W.; et al. RAF inhibitor LY3009120 sensitizes RAS or BRAF mutant cancer to CDK4/6 inhibition by abemaciclib via superior inhibition of phospho-RB and suppression of cyclin D1. Oncogene 2018, 37, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, N.; Hibshoosh, H.; Yasui, W.; Neugut, A.I.; Hibshoosh, A.; Yao, Y.; Sgambato, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Shapira, I.; Rosenman, D.; et al. Abnormalities in the expression of cell cycle-related proteins in tumors of the small bowel. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark. Prev. 1999, 8, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, S.Y.; Chung, J.Y.; Yoon, N.; Jung, E.S.; Oh, Y.H.; Hong, S.M. Tumor budding and poorly differentiated clusters in small intestinal adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, S.B.; Greene, F.L.; Schilsky, R.L.; Gaspar, L.E.; Washington, M.K.; Sullivan, D.C.; Brookland, R.K.; Brierley, J.D.; Balch, C.M.; Campton, C.C.; et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cheuk, W.; Wong, K.O.; Wong, C.S.; Chan, J.K. Consistent immunostaining for cyclin D1 can be achieved on a routine basis using a newly available rabbit monoclonal antibody. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2004, 28, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruneri, G.; Valentini, S.; Bertolini, F.; Del Curto, B.; Maiorano, E.; Viale, G. SP4, a novel anti-cyclin D1 rabbit monoclonal antibody, is a highly sensitive probe for identifying mantle cell lymphomas bearing the t(11;14)(q13;q32) translocation. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2005, 13, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torlakovic, E.; Nielsen, S.; Vyberg, M. Antibody selection in immunohistochemical detection of cyclin D1 in mantle cell lymphoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 124, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, K.Y.; Kim, Y.N.; Bae, J.S.; Chung, M.J.; Moon, W.S.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, D.G.; Park, H.S. Expression of cyclin D1 is associated with β-catenin expression and correlates with good prognosis in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2012, 5, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, S.; Nosho, K.; Irahara, N.; Kure, S.; Shima, K.; Baba, Y.; Toyoda, S.; Chen, L.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; et al. A cohort study of cyclin D1 expression and prognosis in 602 colon cancer cases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4431–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seicean, R.; Crisan, D.; Boers, J.E.; Mocan, T.; Seicean, A.; Funariu, G.; Ciuce, C. The prognostic role of apoptosis mediators in rectal adenocarcinoma. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2011, 58, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stor, Z.; Frković, G.S.; Bracko, M.; Repse, S. Prognostic value of clinical, pathological and immunohistochemical markers in stage II colon cancer patients. Acta Chir. Lugosl. 2008, 55, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilska, M.; Collan, Y.U.; Laine, J.V.O.; Kossi, J.; Hirsimaki, P.; Laato, M.; Roberts, P.J. The significance of tumor markers for proliferation and apoptosis in predicting survival in colorectal cancer. Dis. Colon Rectum 2005, 48, 2197–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, J.A.; Douglas, J.J.; Ross, V.G.; Curran, S.; Loane, J.F.; Ahmed, F.Y.; Cassidy, J.; McLeod, H.L.; Murray, G.I. Analysis of key cell-cycle checkpoint proteins in colorectal tumours. J. Pathol. 2002, 196, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Stockmar-Von Wangenheim, C.A.; Monig, S.P.; Schneider, P.M.; Landsberg, S.; Drebber, U.; Holscher, A.H.; Dienes, H.P.; Baldus, S.E. p16, cyclin D1 and Rb expression in colorectal carcinomas: Correlations with clinico-pathological parameters and prognosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2008, 1, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lyall, M.S.; Dundas, S.R.; Curran, S.; Murray, G.I. Profiling markers of prognosis in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, J.A.; Douglas, J.J.; Ross, V.G.; Curran, S.; Murray, G.I.; Cassidy, J.; McLeod, H.L. Cyclin D1 protein expression and gene polymorphism in colorectal cancer. Aberdeen Colorectal Initiative. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 88, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatavdekar, J.M.; Patel, D.D.; Chikhlikar, P.R.; Shah, N.G.; Vora, H.H.; Ghosh, N.; Trivedi, T.I. Molecular markers are predictors of recurrence and survival in patients with Dukes B and Dukes C colorectal adenocarcinoma. Dis. Colon Rectum 2001, 44, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahnassy, A.A.; Zekri, A.R.; El-Houssini, S.; El-Shehaby, A.M.; Mahmoud, M.R.; Abdallah, S.; El-Serafi, M. Cyclin A and cyclin D1 as significant prognostic markers in colorectal cancer patients. BMC Gastroentero. 2004, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, H.G.; Shia, J.; Klimstra, D.S.; Ruo, L.; Mazumdar, M.; Schwartz, G.K.; Minsky, B.D.; Saltz, L.; Guillem, J.G. Expression of p27 in residual rectal cancer after preoperative chemoradiation predicts long-term outcome. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2004, 11, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, T.A.; Elder, J.; McCloud, J.M.; Hall, C.; Deakin, M.; Fryer, A.A.; Elder, J.B.; Hoban, P.R. Subcellular localisation of cyclin D1 protein in colorectal tumours is associated with p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression and correlates with patient survival. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 95, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Chung, Y.; Kang, S.; Ogawa, M.; Onoda, N.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Ikehara, T.; Nakata, B.; Okuno, M.; Sowa, M. Cyclin D1 overexpression and prognosis in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Oncology 1998, 55, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Chung, Y.S.; Kang, S.M.; Ogawa, M.; Onoda, N.; Nakata, B.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Ikehara, T.; Okuno, M.; Sowa, M. Overexpression of cyclin D1 and p53 associated with disease recurrence in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 74, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.L.; Yeh, Y.S.; Chang, Y.T.; Yang, I.P.; Lin, C.H.; Kuo, C.H.; Juo, S.H.; Wang, J.Y. Co-existence of cyclin D1 and vascular endothelial growth factor protein expression is a poor prognostic factor for UICC stage I-III colorectal cancer patients after curative resection. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 107, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belt, E.J.; Brosens, R.P.; Delis-van Diemen, P.M.; Bril, H.; Tijssen, M.; van Essen, D.F.; Heymans, M.W.; Belien, J.A.; Stockmann, H.B.; Meijer, S.; et al. Cell cycle proteins predict recurrence in stage II and III colon cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19 (Suppl. 3), S682–S692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mao, Y.; Li, Z.; Lou, C.; Zhang, Y. Expression of phosphorylated Stat5 predicts expression of cyclin D1 and correlates with poor prognosis of colonic adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2011, 26, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.J.; Lu, Z.H.; Wang, G.Q.; Pan, Z.Z.; Zhou, Z.W.; Yun, J.P.; Zhang, M.F.; Wan, D.S. Elevated expressions of MMP7, TROP2, and survivin are associated with survival, disease recurrence, and liver metastasis of colon cancer. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2009, 24, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouraklis, G.; Theocharis, S.; Vamvakas, P.; Vagianos, C.; Glinavou, A.; Giaginis, C.; Sioka, C. Cyclin D1 and Rb protein expression and their correlation with prognosis in patients with colon cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bondi, J.; Husdal, A.; Bukholm, G.; Nesland, J.M.; Bakka, A.; Bukholm, I.R. Expression and gene amplification of primary (A, B1, D1, D3, and E) and secondary (C and H) cyclins in colon adenocarcinomas and correlation with patient outcome. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondi, J.; Bukholm, G.; Nesland, J.M.; Bukholm, I.R. Expression of non-membranous beta-catenin and gamma-catenin, c-Myc and cyclin D1 in relation to patient outcome in human colon adenocarcinomas. APMIS 2004, 112, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.; Sachan, R.; Maurya, M.; Patel, M.L.; Sankhwar, P. ROC-analysis derived immunohistochemical p53 cut-off scores as an adjunct to routine histopathology for better diagnostic compartmentalisation of cervical lesions. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2022, 12, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Filho, J.S.; Savage, K.; Lambros, M.B.; James, M.; Steele, D.; Jones, R.L.; Dowsett, M. Cyclin D1 protein overexpression and CCND1 amplification in breast carcinomas: An immunohistochemical and chromogenic in situ hybridisation analysis. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, E.K.; Sgambato, A.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Santella, R.M.; Doki, Y.; Cacace, A.M.; Schieren, I.; Weinstein, I.B. Stable overexpression of cyclin D1 in a human mammary epithelial cell line prolongs the S-phase and inhibits growth. Oncogene 1995, 10, 953–961. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, R.S.; Estus, S.; Johnson, E.M., Jr. Analysis of cell cycle-related gene expression in postmitotic neurons: Selective induction of cyclin D1 during programmed cell death. Neuron 1994, 12, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atadja, P.; Wong, H.; Veillete, C.; Riabowol, K. Overexpression of cyclin D1 blocks proliferation of normal diploid fibroblasts. Exp. Cell Res. 1995, 217, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musgrove, E.A.; Caldon, C.E.; Barraclough, J.; Stone, A.; Sutherland, R.L. Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoj, M.; Milosevic, Z.; Bankovic, J.; Dinic, J.; Pesic, M.; Tanic, N.; Stankovic, T. Association of CCND1 overexpression with KRAS and PTEN alterations in specific subtypes of non-small cell lung carcinoma and its influence on patients’ outcome. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 8773–8780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragnev, K.H.; Ma, T.; Cyrus, J.; Galimberti, F.; Memoli, V.; Busch, A.M.; Tsongalis, G.J.; Seltzer, M.; Johnstone, D.; Erkmen, C.P.; et al. Bexarotene plus erlotinib suppress lung carcinogenesis independent of KRAS mutations in two clinical trials and transgenic models. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemke, E.K.; Dosch, J.S.; Maust, J.D.; Shettigar, A.; Sen, A.; Welling, T.H.; Hardiman, K.M.; Sebolt-Leopold, J.S. Sensitivity of KRAS-mutant colorectal cancers to combination therapy that cotargets MEK and CDK4/6. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimura, T.; Kakuda, S.; Ochiai, Y.; Nakagawa, H.; Kuwahara, Y.; Takai, Y.; Kobayashi, J.; Komatsu, K.; Fukumoto, M. Acquired radioresistance of human tumor cells by DNA-PK/AKT/GSK3beta-mediated cyclin D1 overexpression. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4826–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biliran, H., Jr.; Wang, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Xu, H.; Heng, H.; Thakur, A.; Bollig, A.; Sarkar, F.H.; Liao, J.D. Overexpression of cyclin D1 promotes tumor cell growth and confers resistance to cisplatin-mediated apoptosis in an elastase-myc transgene-expressing pancreatic tumor cell line. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 6075–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musgrove, E.A.; Sutherland, R.L. Biological determinants of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalish, L.H.; Kwong, R.A.; Cole, I.E.; Gallagher, R.M.; Sutherland, R.L.; Musgrove, E.A. Deregulated cyclin D1 expression is associated with decreased efficacy of the selective epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7764–7774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley, K.S.; Lioni, M.; Dalla Palma, M.; Xiao, M.; Desai, B.; Egyhazi, S.; Hansson, J.; Wu, H.; King, A.J.; Van Belle, P.; et al. Increased cyclin D1 expression can mediate BRAF inhibitor resistance in BRAF V600E-mutated melanomas. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2876–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudas, M.; Lehnert, M.; Huynh, A.; Jakesz, R.; Singer, C.; Lax, S.; Schippinger, W.; Dietze, O.; Greil, R.; Stiglbauer, W.; et al. Cyclin D1 expression in breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant tamoxifen-based therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics, n (%) | Total | Cyclin D1Low | Cyclin D1High | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients | 87 (37.5) | 145 (62.5) | |||
| Age (y) | ≤50 | 52 (22.4) | 25 (48.1) | 27 (51.9) | 0.074 |
| >50 | 180 (77.6) | 62 (34.4) | 118 (65.6) | ||
| Sex | Male | 148 (63.8) | 58 (39.2) | 90 (60.8) | 0.481 |
| Female | 84 (36.2) | 29 (34.5) | 55 (65.5) | ||
| Tumor size (cm, mean ± SD) | 4.3 ± 2.4 | 4.4 ± 2.6 | 0.200 | ||
| Growth pattern (n = 224) a | Polypoid | 40 (17.9) | 11 (27.5) | 29 (72.5) | 0.164 |
| Nodular | 17 (7.6) | 9 (52.9) | 8 (47.1) | ||
| Infiltrative | 167 (74.5) | 66 (39.5) | 101 (60.5) | ||
| Tumor location | Duodenum | 140 (60.3) | 55 (39.3) | 85 (60.7) | 0.289 |
| Jejunum | 58 (25.0) | 17 (29.3) | 41 (70.7) | ||
| Ileum | 34 (14.7) | 15 (44.1) | 19 (55.9) | ||
| Histologic type | Tubular | 205 (88.4) | 74 (36.1) | 131 (63.9) | 0.489 |
| Mucinous | 12 (5.2) | 6 (50.0) | 6 (50.0) | ||
| Signet ring cell | 4 (1.7) | 3 (75.0) | 1 (25.0) | ||
| Medullary | 6 (2.6) | 2 (33.3) | 4 (66.7) | ||
| Undifferentiated | 5 (2.1) | 2 (40.0) | 3 (60.0) | ||
| Differentiation | Low grade | 184 (79.3) | 64 (34.8) | 120 (65.2) | 0.094 |
| High grade | 48 (20.7) | 23 (47.9) | 25 (52.1) | ||
| Pancreatic invasion | Present | 87 (37.5) | 37 (42.5) | 50 (57.5) | 0.220 |
| Other loop invasion | Present | 6 (2.6) | 2 (33.3) | 4 (66.7) | 1.000 |
| Retroperitoneal seeding | Present | 16 (6.9) | 9 (56.2) | 7 (43.8) | 0.108 |
| Lymphovascular invasion (n = 231) a | Absent | 118 (51.1) | 38 (32.2) | 80 (67.8) | 0.106 |
| Present | 113 (48.9) | 48 (42.5) | 65 (57.5) | ||
| Perineural invasion (n = 231) a | Absent | 155 (67.1) | 53 (34.2) | 102 (65.8) | 0.173 |
| Present | 76 (32.9) | 33 (43.4) | 43 (56.6) | ||
| Margin status (n = 218) a | No involvement | 209 (95.9) | 78 (37.3) | 131 (62.7) | 0.491 |
| Involved by cancer | 9 (4.1) | 2 (22.2) | 7 (77.8) | ||
| Chemotherapy (n = 227) a | Absent | 145 (63.9) | 49 (33.8) | 96 (66.2) | 0.183 |
| Present | 82 (36.1) | 35 (42.7) | 47 (57.3) | ||
| Radiotherapy (n = 226) a | Absent | 200 (88.5) | 71 (35.5) | 129 (64.5) | 0.150 |
| Present | 26 (11.5) | 13 (50.0) | 13 (50.0) | ||
| Nodal metastasis (n = 215) a | Absent | 109 (50.7) | 40 (36.7) | 69 (53.3) | 0.764 |
| Present | 106 (49.3) | 41 (38.7) | 65 (61.3) | ||
| T category | Tis | 4 (1.7) | 0 | 4 (100) | 0.046 b |
| T1 | 13 (5.6) | 1 (7.7) | 12 (92.3) | ||
| T2 | 14 (6.1) | 4 (28.6) | 10 (71.4) | ||
| T3 | 68 (29.3) | 25 (36.8) | 43 (63.2) | ||
| T4 | 133 (57.3) | 57 (42.9) | 76 (57.1) | ||
| N category (n = 215) a | N0 | 109 (50.7) | 40 (36.7) | 69 (63.3) | 0.865 |
| N1 | 54 (25.1) | 22 (40.7) | 32 (59.3) | ||
| N2 | 52 (24.2) | 19 (36.5) | 33 (63.5) | ||
| Stage grouping (n = 215) a | Stage 0 | 4 (1.9) | 0 | 4 (100) | 0.003 b |
| Stage I | 22 (10.2) | 2 (9.1) | 20 (90.9) | ||
| Stage II | 83 (38.6) | 38 (45.8) | 45 (54.2) | ||
| Stage III | 106 (49.3) | 41 (38.7) | 65 (61.3) | ||
| KRAS (n = 186) a | Absent | 126 (67.7) | 55 (43.7) | 71 (56.3) | 0.026 b |
| Present | 60 (32.3) | 16 (26.7) | 44 (73.3) | ||
| BRAF (n = 176) a | Absent | 174 (98.9) | 66 (37.9) | 108 (62.1) | |
| Present | 2 (1.1) | 1 (50.0) | 1 (50.0) | ||
| Characteristics | Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (mo) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | ||
| Cyclin D1 expression | Cyclin D1Low | 24.5 | 0.005 a | 0.68 (0.47–0.96) | 0.031 a |
| Cyclin D1High | 44.4 | ||||
| Age (y) | ≤50 | 39.9 | 0.143 | ||
| >50 | 30.0 | ||||
| Sex | Male | 30.0 | 0.873 | ||
| Female | 31.4 | ||||
| Tumor size (cm) | 1.00 (0.94–1.07) b | 0.970 | |||
| Growth pattern (n = 224) c | Polypoid | 48.5 | 0.408 | ||
| Nodular | 36.2 | ||||
| Infiltrative | 26.6 | ||||
| Tumor location | Proximal (duodenum) | 41.7 | 0.007 a | 1.34 (0.92–1.94) | 0.125 |
| Distal (jejunum and ileum) | 22.5 | ||||
| Histologic type | Tubular | 36.2 | 0.578 | ||
| Nontubular | 28.2 | ||||
| Differentiation | Low grade | 36.2 | 0.397 | ||
| High grade | 29.1 | ||||
| Pancreatic invasion | Absent | 36.2 | 0.931 | ||
| Present | 31.1 | ||||
| Other loop invasion | Absent | 36.2 | 0.044 a | 0.98 (0.22–4.27) | 0.976 |
| Present | 5.1 | ||||
| Retroperitoneal seeding | Absent | 37.4 | <0.001 a | 2.53 (1.28–4.98) | 0.007 a |
| Present | 14.0 | ||||
| Lymphovascular invasion (n = 231) c | Absent | 66.6 | <0.001 a | 1.68 (1.33–2.50) | 0.010 a |
| Present | 17.8 | ||||
| Perineural invasion (n = 231) c | Absent | 47.6 | 0.004 a | 0.329 | |
| Present | 18.7 | ||||
| Margin status (n = 218) c | No involvement | 36.2 | 0.636 | ||
| Involved by cancer | 15.9 | ||||
| Chemotherapy (n = 227) c | Absent | 37.4 | 0.314 | ||
| Present | 29.1 | ||||
| Radiotherapy (n = 226) c | Absent | 39.7 | 0.005 a | 1.34 (0.82–2.21) | 0.247 |
| Present | 22.0 | ||||
| Nodal metastasis (n = 215) c | Absent | 133.7 | <0.001 a | ||
| Present | 21.6 | ||||
| T category (n = 228) c | T1-T2 | – d | <0.001 a | 1.30 (0.57–2.96) | 0.528 |
| T3-T4 | 26.3 | ||||
| N category (n = 215) c | N0 | 133.7 | <0.001 a | 0.001 a | |
| N1 | 28.2 | 1.68 (1.07–2.63) | 0.024 a | ||
| N2 | 17.8 | 2.41 (1.51–3.83) | <0.001 a | ||
| Stage grouping (n = 211) c | Stage I | – d | <0.001 a | ||
| Stage II | 60.4 | ||||
| Stage III | 21.6 | ||||
| KRAS (n = 186) c | Absent | 39.7 | 0.098 | ||
| Present | 21.0 | ||||
| BRAF (n = 176) c | Absent | 30.0 | 0.682 | ||
| Present | 22.6 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jun, S.-Y.; Hong, S.-M.; Jang, K.-T. Prognostic Significance of Cyclin D1 Expression in Small Intestinal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 5032. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15205032
Jun S-Y, Hong S-M, Jang K-T. Prognostic Significance of Cyclin D1 Expression in Small Intestinal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(20):5032. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15205032
Chicago/Turabian StyleJun, Sun-Young, Seung-Mo Hong, and Kee-Taek Jang. 2023. "Prognostic Significance of Cyclin D1 Expression in Small Intestinal Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 15, no. 20: 5032. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15205032
APA StyleJun, S.-Y., Hong, S.-M., & Jang, K.-T. (2023). Prognostic Significance of Cyclin D1 Expression in Small Intestinal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 15(20), 5032. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15205032







