Simple Summary
In this study, 17 acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients were identified to pose a pericentric inv(3) aberration with breakpoints at 3p23 (n = 11), 3p25 (n = 3), 3p21 (n = 2) and 3p13 (n = 1) on 3p and 3q26.2 on 3q, leading to MECOM rearrangement (MECOM-R). These pericentric inv(3)s were overlooked by karyotyping initially in 16 of 17 cases and later detected by metaphase FISH analysis. Compared to AML patients with classic/paracentric inv(3)(q21q26.2), our patients with pericentric inv(3)s also exhibited frequent cytopenia, morphological dysplasia (especially megakaryocytes), −7/del(7q) and dismal outcomes (median overall survival: 14 months). However, the patients in this cohort also exhibited certain unique features: high frequencies of thrombocytopenia (n = 15, 88%) and monocytosis in peripheral blood (n = 15, 88%) and decreased megakaryocytes (n = 11, 65%). In summary, the pericentric inv(3)s are often subtle/cryptic by chromosomal analysis. A reflex FISH analysis for MECOM-R is recommended in myeloid neoplasms showing −7/del(7q).
Abstract
MECOM rearrangement (MECOM-R) resulting from 3q26.2 aberrations is often associated with myeloid neoplasms and inferior prognosis in affected patients. Uncommonly, certain 3q26.2/MECOM-R can be subtle/cryptic and consequently overlooked by karyotyping. We identified 17 acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients (male/female: 13/4 with a median age of 67 years, range 42 to 85 years) with a pericentric inv(3) leading to MECOM-R, with breakpoints at 3p23 (n = 11), 3p25 (n = 3), 3p21 (n = 2) and 3p13 (n = 1) on 3p and 3q26.2 on 3q. These pericentric inv(3)s were overlooked by karyotyping initially in 16 of 17 cases and later detected by metaphase FISH analysis. Similar to the patients with classic/paracentric inv(3)(q21q26.2), patients with pericentric inv(3) exhibited frequent cytopenia, morphological dysplasia (especially megakaryocytes), −7/del(7q), frequent NRAS (n = 6), RUNX1 (n = 5) and FLT-3 (n = 4) mutations and dismal outcomes (median overall survival: 14 months). However, patients with pericentric inv(3) more frequently had AML with thrombocytopenia (n = 15, 88%), relative monocytosis in peripheral blood (n = 15, 88%), decreased megakaryocytes (n = 11, 65%), and lower SF3B1 mutation. We conclude that AML with pericentric inv(3) shares some similarities with AML associated with classic/paracentric inv(3)/GATA2::MECOM but also shows certain unique features. Pericentric inv(3)s are often subtle/cryptic by chromosomal analysis. A reflex FISH analysis for MECOM-R is recommended in myeloid neoplasms showing −7/del(7q).
1. Introduction
Approximately 4% of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have neoplasms associated with rearrangements of the myelodysplasia syndrome 1 (MDS1) and ecotropic viral integration site 1 (EVI1) complex locus (MECOM). MECOM rearrangement (MECOM-R) is a biomarker for disease progression and inferior prognosis in AML patients [1,2,3,4,5] and is considered as a defining genetic abnormality for AML regardless of blasts count under the 5th World Health Organization Classification for hematologic malignancies [6]. In 30–50% of these cases, MECOM-R is derived from the classic inv(3)(q21q26.2)/t(3;3)(q21;q26.2) or inv(3)/t(3;3), in which the super-enhancer of GATA binding protein 2 (GATA2) located at 3q21 has been hijacked by MECOM located at 3q26.2, resulting in a cascade of transcriptional dysregulation including the inhibition of GATA2 expression and the overexpression of MECOM [1,7,8]. In the remaining AML cases, MECOM-R can be caused by a wide spectrum (over 120 types) of chromosomal aberrations involving 3q26.2 [9,10]. The term “atypical 3q26.2/MECOM-R” has been used to describe this subgroup of cases [11]. In some cases with atypical 3q26.2/MECOM-R, chimeric transcripts have been identified, such as t(2;3)(p21;q26.2) with THADA::MECOM fusion [12,13], t(3;7)(q26.2;q21) with CDK6::MECOM fusion [11,14,15,16,17], t(3;12)(q26.2;p13) with ETV6::MECOM fusion [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34], t(3;21)(q26.2;q11.2) with NRIP1::MECOM fusion [16,35,36], t(3;21)(q26.2;q22) with RUNX1::MECOM fusion [37,38,39,40] and so on. However, no chimeric transcript has been isolated in most AML cases with atypical 3q26.2/MECOM-R; therefore, the underlying mechanism of dysregulation of MECOM in these cases very likely mimics cases with typical 3q26.2/MECOM-R, as mentioned above. For example, in a group of AML cases with t(3;8)(q26.2;q24.2)/MECOM-R [41,42,43,44], MECOM and MYC are not re-joined to each other. Instead, a super-enhancer-located downstream of MYC (MYCSE) has been translocated upstream of the promotor of MECOM, which consequently upregulates MECOM expression, as demonstrated in both clinical cases and engineered cell models [44].
Up to 15% of AML cases have high MECOM expression, as detected by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), almost triple the percentage of AML cases with 3q26.2/MECOM-R detected by conventional cytogenetics [2,3,45,46,47]. There are multiple factors associated with this phenomenon. First, certain AML cases may have MECOM overexpression but without 3q26.2/MECOM-R. For example, in a study of transcriptome profiles in pediatric AML by Shiba et al. [30], 30% (9/30) of AML cases with t(9;11)(p21;q23)/KMT2A::MLLT3, representing 50% of all KMT2A (MLL) rearrangement (KMT2A-R) AML cases in their cohort, and over 50% of cases with acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AML with FAB-M7) overexpress MECOM but without 3q26.2/MECOM-R. The mechanisms related to MECOM overexpression remain unknown in these cases. Second, some chromosomal aberrations related to MECOM-R may be complex and are often categorized as unidentifiable marker chromosome(s). An assessment by a fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) assay is often necessary and beneficial for identifying the MECOM-R status in these cases [9,10]. Third, some AML cases may possess MECOM amplification instead of MECOM-R as a cause of MECOM overexpression. A segmental duplication/amplification involving 3q26.2/MECOM manifesting as an intra-chromosomal homogenous staining region (HSR) or extra-chromosomal double minutes (dm) may occur in these cases [48,49,50]. Lastly, certain chromosomal aberrations related to MECOM-R can be subtle or even cryptic when studied by conventional cytogenetics. For example, t(3;21)(q26.2;q11)/NRIP1::MECOM, t(3;7)(q26.2;q21)/CDK6::MECOM and inv(3)(p24q26)/MECOM-R have been considered as cryptic for chromosomal analysis. They could be easily overlooked by chromosomal analysis only. FISH testing, especially metaphase FISH or, ideally, mapback FISH testing performing on previously G-banding analyzed metaphase(s), is usually required to identify/confirm MECOM-R and the underlying subtle/cryptic aberrations [16].
In this study, we reported a cohort of 17 myeloid neoplasms associated with MECOM-R via pericentric inv(3)s at various band levels of 3p. These abnormalities were mostly overlooked by chromosomal analyses initially. This subset of 3q26.2/MECOM-R cases arising via pericentric inv(3) is associated with some characterized pathological features when compared with MECOM-R cases that arise through the classic inv(3)(q21q26.2)/t(3;3)(q21;q26.2).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Selection
We searched the cytogenetics database at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDACC) for cases with pericentric inv(3) involving 3q26.2/MECOM-R, as confirmed by FISH results from 1 May 2009 to 30 September 2022. The clinicopathologic and other laboratory information of selected cases was collected through electronic medical record review. This study was approved by the MDACC Institutional Review Board (IRB) and conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. Conventional Karyotype Analysis
Conventional cytogenetic analysis (G-banded chromosomal analysis or karyotyping) was performed on unstimulated 24 h and 48 h bone marrow aspirate cultures using standard techniques. A total of 20 metaphases were routinely analyzed by two technologists, and the results were reported following the 2020 International System for Human Cytogenetics Nomenclature (ISCN 2020) guidelines [10,43]. A complex karyotype is defined as ≥3 clonal chromosomal abnormalities, of which at least one structural chromosomal abnormality is present.
2.3. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Analysis
The commercial MECOM (EVI1) dual color, breakapart (BAP) DNA probe (#KI-10204) from Leica Biosystems/Kreatech (Buffalo Grove, IL, USA) and a home-brew tri-color MECOM probe were employed. The commercial probe is used routinely as a diagnostic test for all cases [10,43], whereas the home-brew probe is applied only in the cases with an atypical signal pattern obtained using the commercial probe to further confirm a positive status of MECOM-R in this study [51]. At least one metaphase MECOM FISH image with a decisive signal pattern and locations of all signals was captured in each case. In certain cases, mapback FISH was performed on a previously G-banded slide to better locate all FISH signals on the chromosome(s) involved. In addition, the Vysis LSI 5p15.1/EGR1 probe set, CEP7/7S522 probe set, KMT2A(MLL) BAP probe and TP53/CEP17 probe set were applied in certain cases, as requested by clinicians.
2.4. Morphological Examination
Peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM) aspirate smears were stained with Wright–Giemsa stain, and bone marrow core biopsy sections were stained with hematoxylin-eosin. The initial diagnostic BM biopsy carried out at the referral hospitals was sent to us for review (cases #1, 2, 5, 12, Table 1). The bone marrow core biopsy specimens were also stained with reticulin and trichrome for access to myelofibrosis, which was graded following the European Consensus on the grading of BM fibrosis [52].

Table 1.
Demographic and Clinical Information.
2.5. Immunophenotyping by Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometric immunophenotypic analysis (PharmLyseTM, BD Biosciences, San Diego, CA, USA) was performed routinely on fresh bone marrow aspirate specimens as a part of the clinical work-up by following the standard procedures. All samples in this cohort were examined with antibody panels designed to assess leukemic cells, as reported previously [43], and the CD markers assessed include the following: CD2, surface and cytoplasmic CD3, CD4, CD5, CD7, CD13, CD14, CD15, CD19, CD25, CD33, CD34, CD36, CD38, CD41, CD45, CD56, CD64, CD117, CD123, HLA-DR, MPO and TdT. However, not all CD markers are assessed in all cases in this cohort.
2.6. Gene Mutation Profiling
A next-generation sequencing (NGS)-based analysis for the detection of somatic mutations in the coding sequences of 81 genes (81-gene panel) was routinely performed as part of the clinical work-up for all patients, as reported previously [53].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Kaplan–Meier curves were employed to estimate the unadjusted overall survival (OS) duration. In this study, overall survival (OS) was calculated from the date of the first detection of pericentric inv(3) or the date of the initial diagnosis of the disease to death or the last follow-up. A student t-test was applied to perform all univariate analyses, and a chi-square (X2) test was utilized to compare the frequencies of different groups. All statistical analyses were conducted in GraphPad Prism 8, and statistical significance was considered if p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. General Information and Clinicopathologic Characteristics
From 1 May 2009 to 30 September 2022, 283 myeloid neoplasm cases with MECOM-R, as confirmed by a FISH study, were identified in our institute; less than 50% of all cases exhibited a classic, paracentric inv(3)(q21q26.2) (n = 117, 41.3%) or t(3;3)(q21;q26.2) (n = 19, 6.7%), while the rest (n = 147, 51.9%) presented an atypical 3q26.2 aberration/MECOM-R through various mechanisms reported previously [10]. Out of this 3q26.2 aberration/MECOM-R cohort, we identified 17 cases (6%) with a pericentric inv(3), including 13 men and 4 women with a diagnosis of AML (n = 15), MDS (n = 1) or chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML, n = 1) (Table 1) according to the 4th World Health Organization Classification [1]. Five patients had a prior history of other types of cancer and had been treated, including non-small cell lung cancer (case #11); prostate cancer (case #12), ovary cancer (case #13), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (case #14) and Burkitt lymphoma (case #17). These five patients had been treated with chemotherapy and developed therapy-related AML (t-AML) or therapy-related MDS (t-MDS). Patient #10 had a history of CMML. Patients #3, #9 and #17 had a preceding history of MDS and transformed to AML. The median age was 67 years (range, 42 to 85) at the first detection of pericentric inv(3). All patients were treated with various chemotherapy regimens, as well as immunotherapy and targeted therapy in certain cases, such as nivolumab and ipilimumab in case #1; gemtuzumab in case #5; tegavivint (beta-catenin inhibitor) in case #6; PLX51107 (BRD4 inhibitor) in case #7; quizartinib in case #8; and gilteritinib in case #15. Two patients (cases #1 & #6) received a stem cell transplant (SCT); patient # 1 also received chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) NK cell therapy. By the endpoint of this study, 14 patients died and 3 were alive (1 partial remission and 2 progressive disease) (Table 1). The median overall survival was 4–5 months (range, 0 to 30 months) after the initial detection of pericentric inv(3) (Figure 1A and Table 1) or 14 months (range, 1 to 62 months) after the initial diagnosis of their myeloid neoplasm (Figure 1B and Table 1).
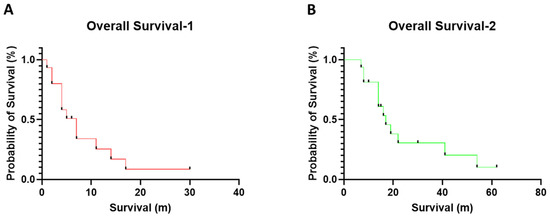
Figure 1.
The overall survivals in this cohort with 3q26 aberration/MECOM-R myeloid neoplasms. (A) The overall survival was calculated from the time of the initial detection of pericentric inv(3)s; (B) the median overall survival was calculated from the initial diagnosis of myeloid neoplasm.
The PB and BM findings at the time of pericentric inv(3) detection are summarized in Table 2. All patients (100%) showed anemia, 15 patients showed thrombocytopenia and 11 (64.7%) patients showed pancytopenia. The median white blood cell (WBC) count was 6.9 × 109/L (range, 0.5–96.5); the median hemoglobin level was 8.4 g/dL (range, 6.5–13.1); and the median platelet count was 29 × 109/L (range, 7–225). The percentage of monocytes (normal: 2–7%) was increased in 15/17 patients (median 15%, range 0–52%). The median blast percentage was 8% (range, 0–76) in PB. BM cellularity was variable; the number of megakaryocytes was decreased in 11 (65%) cases, increased in 5 (29%) cases and adequate in 1 case. Monocytes were increased (normal <4%) in 11 (65%) cases. Morphologic dysplasia was found in all 15 cases who had enough cells to evaluate, 8 (53%) cases exhibited trilineage dysplasia. The most characteristic finding was megakaryocytes, which frequently were small and hypolobated (Figure 2A,B). Seven of the thirteen cases evaluated had bone marrow fibrosis, and seven showed mild reticulin fibrosis (MF-1).

Table 2.
Peripheral blood and bone marrow findings.
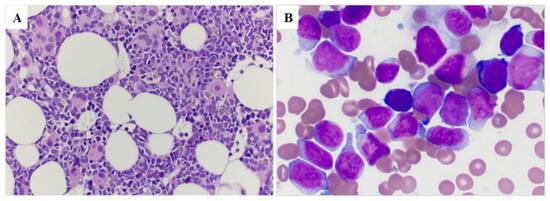
Figure 2.
Bone marrow morphology in a representative case (case #8). (A) Bone marrow core biopsy shows a hypercellular marrow with increased immature cells as well as many dysplastic megakaryocytes with small hypolobated or separated nuclear lobes (100×); (B) Bone marrow smear shows increased blasts that are large with dispersed chromatin and distinct nucleoli (500×).
3.2. Immunophenotypic Features
All cases in this cohort showed a myeloid immunophenotype, CD13+/CD33+/CD34+/CD117+. All cases expressed CD123+, and all cases except for one were positive for HLA-DR. CD7 was positive in 12 of 17 cases, myeloperoxidase was positive in 6 of 14 cases assessed, CD64 was positive in 3 of 17, CD19 was positive in 2/17 and CD5 was positive in 1/17 cases. All cases were negative for CD14. The numbers of tested and positive cases for each marker/antigen are summarized in Supplementary Table S1.
We also compared the antigen expression between cases with −7/7q abnormalities (n = 12) and cases without −7/7q abnormalities (n = 5); no statistically significant differences were observed (see Supplementary Table S1).
3.3. Cytogenetic Characteristics
The involved band levels at 3p were determined as follows: 1 at 3p13 (case #1), 2 at 3p21 (cases #2–3), 11 at 3p23 (cases #4–14) and 3 at 3p25 (cases #15–17), (Table 3). The inv(3)(p23q26.2) and inv(3)(p25q26.2) are considered as subtle or even cryptic abnormalities by conventional cytogenetics (Figure 3). Nine (53%) neoplasms had a complex karyotype, six (35.3%) cases had additional chromosomal aberration and two had pericentric inv(3)s as the sole chromosomal aberration. Twelve (70.6%) cases simultaneously exhibited 7q aberrations including monosomy 7 (−7, n = 10), 7q deletion (7q-, n = 1) or ring chromosome 7 or r(7) (n = 1).

Table 3.
Cytogenetic features of cases with pericentric inv(3)/MECOM-R in this cohort.
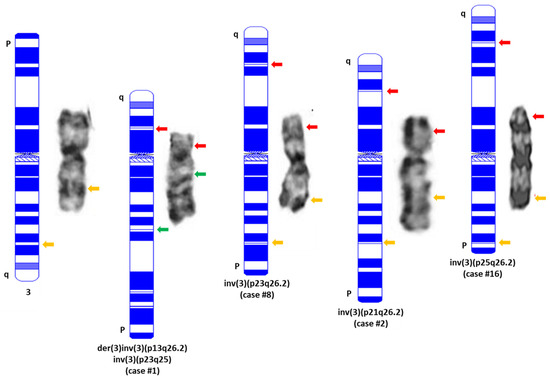
Figure 3.
Representative images of normal chromosome 3 and pericentric inv(3)s detected in this study. A karyogram drawn using online software (CyDAS, http://www.cydas.org/OnlineAnalysis/ accessed on 10 November 2022) is placed on the left side of each chromosome with an indication of the sites and colors of MECOM BAP FISH using the two-color commercial probe in this study. Yellow: intact MECOM signal; Red: 5′MECOM; Green: 3′MECOM. It is necessary to point out that all the pericentric inv(3)s listed in this figure are intentionally exhibited in a direction from q (top) to p (bottom) after inversion so that their centromeres remain as the normal chromosome 3.
Sixteen patients had karyotyping and/or MECOM FISH information at other hospitals before they were referred to our cancer center, but pericentric inv(3) was identified in only one case (case #2) at a referral hospital. MECOM-R was reported by referral hospitals in three cases (cases #1, #2 and #12), and the status of pericentric inv(3)/MECOM-R was missed in the remaining 12 cases at the referral hospitals. We retrospectively checked the count sheet used by our technologists for chromosomal analyses, though an abnormal chromosome 3 or der(3) was identified by our technologists in 7 cases, and a pericentric inv(3) abnormality was initially missed in 13 cases. The median interval between the detection of pericentric inv(3)s/MECOM-R and the initial diagnosis of diseases was 7 months (range, 0 to 50) in this cohort (Table 3).
All cases were MECOM BAP FISH-positive, and a split signal pattern with 3ʹMECOM signal (green) locating on 3p and 5ʹMECOM signal (red) locating on 3q of the affected chromosome 3 documented by metaphase FISH and/or mapback FISH was observed in 13 cases. Four cases (cases #2, #8, #14 and #16) showed an atypical split signal pattern [10] with a fusion signal (yellow) located on 3p and 5ʹMECOM signal (red) located on 3q of the affected chromosome 3 (e.g., cases #2 and #16 in Figure 3). The latter four cases were further confirmed with a home-brew, tri-color MECOM BAP FISH for their MECOM-R status (Supplementary Figure S1) [51].
3.4. Gene Mutation Profiles
A total of 52 mutation events affecting 23 genes were identified in this cohort, with an average of 3 mutations per case. All cases exhibit mutation(s) affecting one to eight genes simultaneously (one gene, n = 3; two genes, n = 7; three genes, n = 1; four genes, n = 3; five genes, n = 1; seven genes, n = 1 and eight genes, n = 1) (Figure 4). NRAS showed the highest frequency of mutation (n = 6), followed by RUNX1 (n = 5), FLT3 (n = 4), ASXL1, PTPN11, SF3B1 and TP53 (n = 3). These 7 genes accounted for 27 of the 52 (53%) mutation events. Sixteen other genes were mutated at a low frequency (n = 2 or n = 1) (Figure 4).
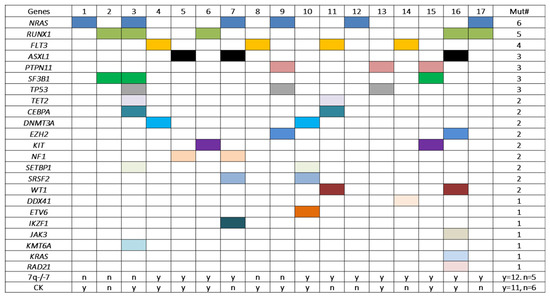
Figure 4.
Gene mutations detected in patients with pericentric inv(3)s in this cohort. Each colored square represents a mutation event. All cases carried mutation(s) affecting at least one gene. Cases #16 and #3 had mutations involving seven and eight genes simultaneously. The first six genes (NRAS, RUNX1, FLT3, ASXL1, PTPN11, SF3B1 and TP53) from the top showed frequencies of mutation of 3/17 to 6/17. However, no statistically significant association was found between the mutation frequencies and the status of −7/7q- and/or complex karyotype. Mut: mutation; CK: complex karyotype; n: no; y: yes.
4. Discussion
The first myeloid neoplasm associated with a pericentric inv(3) was reported by Grigg et al. in 1993 [54]. The patient presented with inv(3)(p25q27) and was categorized as one of the miscellaneous 3q abnormalities in a cohort of 24 cases with various 3q abnormalities, mostly classic inv(3)/t(3;3)(q21;q26.2). Three additional cases were reported by Heimann et al. [55], Shi et al. [56] and Smith et al. [57], respectively. However, the status of MECOM rearrangement was not clarified and remained unknown in all of these four cases. Poppe et al. reported the first pericentric inv(3) case with MECOM-R, as confirmed by FISH [58]. The patient was reported to have an inv(3)(p12q26), an apparent abnormality of chromosome 3. Since then, several groups reported various forms of pericentric inv(3), and most of these cases had MECOM-R, as confirmed by FISH (Table 4) [3,16,59,60,61,62,63]. Therefore, to the best of our knowledge, a total of 26 cases with pericentric inv(3) have been reported, including an inv(3)(p21.3q26.2) case reported by Dias et al. [62], which is considered a constitutional abnormality transmitted from donor to recipient but without causing any diseases.

Table 4.
A summary of cases with pericentric inv(3)s reported in the literature.
Here, we add 17 cases for a total of 33 cases with pericentric inv(3)/MECOM-R [3,16,58,61,63]. However, the band levels of 3p involvement varied very much among these cases, e.g., p25 (n = 5), p24 (n = 11), p23 (n = 12), p21 (n = 3) and p13 (n = 2) (Table 3 and Table 4). Locus 3p24 and 3p23 involvement account for over two-thirds of these cases, and these two adjacent bands can barely be distinguished from each other if the resolution of a metaphase cell is <400-band levels. Interestingly, most cases with 3p25, 3p24 and 3p23 are considered as subtle or even cryptic by chromosome analysis, as described by others [16,61]. Without MECOM BAP FISH testing with split signals located on both the p and q arms of the affected chromosome 3 simultaneously (Figure 3), the pericentric inv(3)s would not have been recognized/confirmed in these cases. In fact, as mentioned previously, almost all of these pericentric inv(3) abnormalities were missed initially by chromosomal analyses in this cohort, and some of these abnormalities were missed multiple times. The add-on MECOM FISH by clinicians and/or the reflex FISH test due to the presence of −7/7q- helped to discover the MECOM-R as well as the pericentric inv(3)s in this study. A further analysis of the karyotype results of all cases with subtle/cryptic pericentric inv(3), including 13 cases in this study and 15 cases in the literature, revealed a high frequency of −7 and 7q- which was about 75%, higher than that in cases with classic inv(3)/t(3;3) or other 3q26.2/MECOM-R abnormalities (<22%) [3,9,10,11]. More interestingly, −7 or 7q- was the only additional chromosomal aberration in 14 cases. Therefore, −7 and 7q- including r(7) can be considered as an indicator for performing MECOM FISH to confirm/exclude a pericentric inv(3)/MECOM-R status in these cases.
The recognition of pericentric inv(3) with MECOM-R is clinically important for neoplasm classification and risk stratification in affected patients [1,3,9,11]. The detection of pericentric inv(3) may cause the cytogenetics risk group to change from intermediate-risk to high-risk in cases #2 and #8 and change the diagnosis from MDS to AML in cases #10 and #14 under the 5th edition of the WHO Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms, where AML with MECOM-R is a subentity of AML regardless of blast counts [6,27]. Lastly, although there is no targeted therapy specifically against MECOM-R currently, several studies have shown that certain targets and/or existing therapeutical drugs may be promising for an effective treatment of MECOM-R AML. For example, Fenouille et al. [64] reported that an ATP-buffering mitochondrial creatine kinase (CKMT1A) is tightly associated with MECOM/EVI1 expression in AML, and the administration of cyclocreatine, a CKMT1A inhibitor, can dramatically reduce the viability of MECOM/EVI1-expressing AML cells. Recently, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) inhibitors have also been identified as a potential new therapy for MECOM-R AML patients [40]. Since there are several FDA-approved PARP inhibitors available as well as ongoing clinical trials involving treating AML/MDS with PARP inhibitors [65,66], clinical trials involving treating MECOM-R AML patients with PARP inhibitors may be available soon. Therefore, the immediate identification of cryptic MECOM-R-associated chromosomal abnormalities is crucial for the recruitment of qualified patients for clinical trials once targeted therapies become fully available. FISH testing, especially that which utilizes a breakapart (BAP) FISH probe, is currently the main method applied clinically for the exclusion/confirmation of MECOM-R. However, a BAP FISH test will not provide information on the partner gene for MECOM-R, if any exists, and one BAP FISH test may not always provide a definite conclusion in some cases due to the complexities of 3q26.2 abnormalities and the wide range of breakpoints involving MECOM as well as its flanking regions [9,10,51]. NGS-based whole genome structural variant (SV) profiling methods, such as optical genome mapping (OGM) [67], whole exome sequencing (WES) [36,68,69], whole genome sequencing (WGS) [7,30,36,69] and/or whole transcriptome sequencing (WTS) [30,36], have been successfully applied in the diagnosis of AML/MDS cases with MECOM-R through cryptic 3q26.2 aberrations for chromosomal analysis. Fusion genes involving MECOM have been identified in all these cases. We would like to point out that we have not investigated any of these cases with pericentric inv(3)/MECOM-R with one of these NGS-based whole genome structural variant (SV) profiling methods yet, but they are all worthy of being further explored.
Patients with pericentric inv(3) shared similar clinicopathologic features with the classic inv(3)(q21q26.2): anemia, morphologic dysplasia (including characteristic dysmorphic megakaryocytes) and inferior outcomes. On the other hand, patients with pericentric inv(3) more frequently showed increased monocytes in PB and BM, thrombocytopenia and decreased megakaryocytes compared to patients with classic inv(3)/t(3;3), which could largely be due to the difference in the partner genes on 3p other than GATA1 on 3q21. An average of three mutation events per case has been observed in our cohort with pericentric inv(3)/MECOM-R, which is slightly higher than the average of two mutation events per case observed in AML with classic inv(3)/t(3;3) [11,61,63,68]. NRAS mutations showed the highest frequency, about 35%, followed by RUNX1 and FLT3 mutations, similar to the mutation profiles of the pericentric inv(3) cases reported by other groups [61,63]. It is relevant to point out that SF3B1 mutations are common in classic inv(3)/t(3;3) cases [61,67]. In contrast, only three cases with pericentric inv(3) in this cohort had an SF3B1 mutation.
In summary, we report 17 patients with pericentric inv(3)/MECOM-R with different breakpoints on 3p. Along with the cases reported in the literature, inv(3)(p25q26.2), inv(3)(p24q26.2) and inv(3)(p23q26.2) can be subtle or even cryptic and thus be easily overlooked by conventional chromosomal analysis. About 75% of the cases in this study have monosomy 7 or deletions of 7q that can serve as an indicator to reflex MECOM FISH to further exclude/confirm the subtle/cryptic aberrations. The immediate recognition of pericentric inv(3)/MECOM-R is associated with the diagnosis and risk stratification of certain patients.
5. Conclusions
The chromosomal aberrations associated with MECOM-R can be subtle or even cryptic and thus be easily overlooked by karyotyping only, including the majority of cases with pericentric inv(3)s in this study. The early detection and confirmation of 3q26.2 aberrations/MECOM-R are relevant for the diagnosis, risk stratification and clinical management of the affected patients. Our study indicates that cases with 7q-/−7 are worthy of being further investigated for a potential 3q26.2 aberration/MECOM-R—for example, performing a reflex MECOM FISH test.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cancers15020458/s1, Figure S1: MECOM FISH tests using two breakapart probe sets in Case #10. (A) Commercial two-color breakapart probe; (B) home-brew tri-color breakapart probe [51]; Table S1: Immunophenotypical features of cases with pericentric inv(3)/MECOM-R in this study.
Author Contributions
Z.T., W.W., S.Y. and G.T.: conceptualization; Z.T., W.W., S.Y., G.A.T. and H.F.: methodology; Z.T., W.W., S.Y. and G.T.: data generation and data curation; Z.T., W.W., S.Y., G.T., G.A.T. and C.C.Y.: validation; Z.T. and W.W.: original draft preparation; H.E.A., H.F., K.A.N., J.X., B.T., E.A., G.C.I., C.C.Y., M.J.Y., R.N.M., J.D.K., L.J.M. and G.T.: review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (PA 2022-0218; Date of approval: 30 March 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article (and supplementary material).
Acknowledgments
All authors acknowledge all of our staff in the Clinical Cytogenetic Laboratory for their dedication in the chromosomal and FISH analyses of all the difficult cases presented in this study. All authors acknowledge Xinyan Lu and Medina Sukhanova at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine for sharing their interesting cases.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Arber, D.A.; Brunning, R.D.; Le Beau, M.M.; Falini, B.; Vardiman, J.W. Acute myeloid leukemia with recurrent genetic abnormalities. In WHO Classification of Tumors of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; Swerdlow, S.H., Ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2016; pp. 140–155. [Google Scholar]
- Lugthart, S.; van Drunen, E.; van Norden, Y.; van Hoven, A.; Erpelinck, C.A.; Valk, P.J.; Beverloo, H.B.; Löwenberg, B.; Delwel, R. High EVI1 levels predict adverse outcome in acute myeloid leukemia: Prevalence of EVI1 overexpression and chromosome 3q26 abnormalities underestimated. Blood 2008, 111, 4329–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugthart, S.; Gröschel, S.; Beverloo, H.B.; Kayser, S.; Valk, P.J.; van Zelderen-Bhola, S.L.; Jan Ossenkoppele, G.; Vellenga, E.; van den Berg-de Ruiter, E.; Schanz, U.; et al. Clinical, molecular, and prognostic significance of WHO type inv(3)(q21q26.2)/t(3;3)(q21;q26.2) and various other 3q abnormalities in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3890–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Sun, J.; Cotta, C.V.; Medeiros, L.J.; Lin, P. Myelodysplastic syndrome with inv(3)(q21q26.2) or t(3;3)(q21;q26.2) has a high risk for progression to acute myeloid leukemia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 136, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Konoplev, S.N.; Wang, X.; Cui, W.; Chen, S.S.; Medeiros, L.J.; Lin, P. De novo acute myeloid leukemia with inv(3)(q21q26.2) or t(3;3)(q21;q26.2): A clinicopathologic and cytogenetic study of an entity recently added to the WHO classification. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gröschel, S.; Sanders, M.A.; Hoogenboezem, R.; de Wit, E.; Bouwman, B.A.M.; Erpelinck, C.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Havermans, M.; Avellino, R.; van Lom, K.; et al. A single oncogenic enhancer rearrangement causes concomitant EVI1 and GATA2 deregulation in leukemia. Cell 2014, 157, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Suzuki, M.; Otsuki, A.; Shimizu, R.; Bresnick, E.H.; Engel, J.D.; Yamamoto, M. A remote GATA2 hematopoietic enhancer drives leukemogenesis in inv(3)(q21;q26) by activating EVI1 expression. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Braekeleer, M.; Le Bris, M.J.; De Braekeleer, E.; Basinko, A.; Morel, F.; Douet-Guilbert, N. 3q26/EVI1 rearrangements in myeloid hemopathies: A cytogenetic review. Future Oncol. 2015, 11, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Tang, G.; Hu, S.; Patel, K.P.; Yin, C.C.; Wang, W.; Lin, P.; Toruner, G.A.; Ok, C.Y.; Gu, J.; et al. Deciphering the complexities of MECOM rearrangement-driven chromosomal aberrations. Cancer Genet. 2019, 233–234, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottema, S.; Mulet-Lazaro, R.; Beverloo, H.B.; Erpelinck, C.; van Herk, S.; van der Helm, R.; Havermans, M.; Grob, T.; Valk, P.J.M.; Bindels, E.; et al. Atypical 3q26/MECOM rearrangements genocopy inv(3)/t(3;3) in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2020, 136, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubia, M.; Albano, F.; Cavazzini, F.; Cambrin, G.R.; Quarta, G.; Fabbiano, F.; Ciambelli, F.; Magro, D.; Hernandezo, J.M.; Mancini, M.; et al. Characterization of a recurrent translocation t(2;3)(p15-22;q26) occurring in acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia 2006, 20, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Braekeleer, M.; Guéganic, N.; Tous, C.; Le Bris, M.J.; Basinko, A.; Morel, F.; Douet-Guilbert, N. Breakpoint heterogeneity in (2;3)(p15-23;q26) translocations involving EVI1 in myeloid hemopathies. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2015, 54, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henzan, H.; Yoshimoto, G.; Okeda, A.; Nagasaki, Y.; Hirano, G.; Takase, K.; Tanimoto, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Fukuda, T.; Nagafuji, K.; et al. Myeloid/natural killer cell blast crisis representing an additional translocation, t(3;7)(q26;q21) in Philadelphia-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 2004, 83, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storlazzi, C.T.; Anelli, L.; Albano, F.; Zagaria, A.; Ventura, M.; Rocchi, M.; Panagopoulos, I.; Pannunzio, A.; Ottaviani, E.; Liso, V.; et al. A novel chromosomal translocation t(3;7)(q26;q21) in myeloid leukemia resulting in overexpression of EVI1. Ann. Hematol. 2004, 83, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haferlach, C.; Bacher, U.; Grossmann, V.; Schindela, S.; Zenger, M.; Kohlmann, A.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; Schnittger, S. Three novel cytogenetically cryptic EVI1 rearrangements associated with increased EVI1 expression and poor prognosis identified in 27 acute myeloid leukemia cases. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012, 51, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capela de Matos, R.R.; Othman, M.A.K.; Ferreira, G.M.; Costa, E.S.; Melo, J.B.; Carreira, I.M.; de Souza, M.T.; Lopes, B.A.; Emerenciano, M.; Land, M.G.P.; et al. Molecular approaches identify a cryptic MECOM rearrangement in a child with a rapidly progressive myeloid neoplasm. Cancer Genet. 2018, 221, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, S.D.; Baens, M.; Grosgeorge, J.; Rodgers, K.; Reid, C.D.; Dainton, M.; Dyer, M.; Fuzibet, J.G.; Gratecos, N.; Taillan, B.; et al. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of t(3; 12)(q26; p13): A recurring chromosomal abnormality involving the TEL gene (ETV6) in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1996, 88, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, P.; Wlodarska, I.; Baens, M.; Criel, A.; Selleslag, D.; Hagemeijer, A.; Van den Berghe, H.; Marynen, P. Fusion of ETV6 to MDS1/EVI1 as a result of t(3;12)(q26;p13) in myeloproliferative disorders. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 564–569. [Google Scholar]
- Pekarsky, Y.; Rynditch, A.; Wieser, R.; Fonatsch, C.; Gardiner, K. Activation of a novel gene in 3q21 and identification of intergenic fusion transcripts with ecotropic viral insertion site I in leukemia. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 3914–3919. [Google Scholar]
- Roulston, D.; Espinosa, R., III; Nucifora, G.; Larson, R.A.; Le Beau, M.M.; Rowley, J.D. CBFA2(AML1) translocations with novel partner chromosomes in myeloid leukemias: Association with prior therapy. Blood 1998, 92, 2879–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlander, S.K. Fusion genes in leukemia: An emerging network. Fusion genes in leukemia: An emerging network. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 2000, 91, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, Y.; Ito, T.; Oikawa, T.; Eguchi, M.; Eguchi-Ishimae, M.; Kamada, N.; Kishi, K.; Asano, S.; Sakaki, Y.; Sato, Y. A new ETV6/TEL partner gene, ARG (ABL-related gene or ABL2), identified in an AML-M3 cell line with a t(1;12)(q25;p13) translocation. Blood 2000, 95, 2126–2131. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, Y.; Nakazato, H.; Sato, Y.; Furusawa, S.; Mitani, K. Expression of the TEL/EVI1 fusion transcript in a patient with chronic myelogenous leukemia with t(3;12)(q26;p13). Am. J. Hematol. 2002, 69, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristóbal, I.; Blanco, F.J.; Garcia-Orti, L.; Marcotegui, N.; Vicente, C.; Rifon, J.; Novo, F.J.; Bandres, E.; Calasanz, M.J.; Bernabeu, C.; et al. SETBP1 overexpression is a novel leukemogenic mechanism that predicts adverse outcome in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2010, 115, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duhoux, F.P.; Ameye, G.; Montano-Almendras, C.P.; Bahloula, K.; Mozziconacci, M.J.; Laibe, S.; Wlodarska, I.; Michaux, L.; Talmant, P.; Richebourg, S.; et al. PRDM16 (1p36) translocations define a distinct entity of myeloid malignancies with poor prognosis but may also occur in lymphoid malignancies. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 156, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achkar, W.A.; Aljapawe, A.; Liehr, T.; Wafa, A. De novo acute myeloid leukemia subtype-M4 with initial trisomy 8 and later acquired t(3;12)(q26;p12) leading to ETV6/MDS1/EVI1 fusion transcript expression: A case report. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 7, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Yang, J.J.; Han, Y.; Kim, S.; Yang, H.S.; Yoon, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, W.I.; Park, T.S. A Rare Case of ETV6/MECOM Rearrangement in Therapy-Related Acute Myeloid Leukemia with t(3;12) and Monosomy 7. Clin. Lab. 2017, 63, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noris, P.; Pecci, A. Hereditary thrombocytopenias: A growing list of disorders. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2017, 2017, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, N.; Yoshida, K.; Hara, Y.; Yamato, G.; Shiraishi, Y.; Matsuo, H.; Okuno, Y.; Chiba, K.; Tanaka, H.; Kaburagi, T.; et al. Transcriptome analysis offers a comprehensive illustration of the genetic background of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3157–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Yakushijin, K.; Ichikawa, H.; Okamura, A.; Nagao, S.; Kakiuchi, S.; Kurata, K.; Kawamoto, S.; Matsui, K.; Nakamachi, Y.; et al. Coexpression of ETV6/MDS1/EVI1 and ETV6/EVI1 fusion transcripts in acute myeloid leukemia with t(3;12)(q26.2;p13) and thrombocytosis. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aypar, U.; Yao, J.; Londono, D.M.; Khoobyar, R.; Scalise, A.; Arcila, M.E.; Roshal, M.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, Y. Rare and novel RUNX1 fusions in myeloid neoplasms: A single-institute experience. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2021, 60, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, S.; Pommerenke, C.; Meyer, C.; Drexler, H.G. NKL Homeobox Gene VENTX Is Part of a Regulatory Network in Human Conventional Dendritic Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronaghy, A.; Hu, S.; Tang, Z.; Wang, W.; Tang, G.; Loghavi, S.; Medeiros, L.J.; Muzzafar, T. Myeloid neoplasms associated with t(3;12)(q26.2;p13) are clinically aggressive, show myelodysplasia, and frequently harbor chromosome 7 abnormalities. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angiò, M.; Fazio, G.; Grioni, A.; Palamini, S.; Sala, S.; Galbiati, M.; Biondi, A.; Balduzzi, A.; Rizzari, C.; Cazzaniga, G. High EVI1 Expression due to NRIP1/EVI1 Fusion in Therapy-related Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Description of the First Pediatric Case. Hemasphere 2020, 4, e471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, A.; Shahswar, R.; Haferlach, T.; Walter, W.; Hutter, S.; Meggendorfer, M.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, C. Whole transcriptome sequencing detects a large number of novel fusion transcripts in patients with AML and MDS. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5393–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senyuk, V.; Sinha, K.K.; Li, D.; Rinaldi, C.R.; Yanamandra, S.; Nucifora, G. Repression of RUNX1 activity by EVI1: A new role of EVI1 in leukemogenesis. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5658–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokita, K.; Maki, K.; Mitani, K. RUNX1/EVI1, which blocks myeloid differentiation, inhibits CCAAT-enhancer binding protein alpha function. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1752–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellaway, S.G.; Keane, P.; Kennett, E.; Bonifer, C. RUNX1-EVI1 disrupts lineage determination and the cell cycle by interfering with RUNX1 and EVI1 driven gene regulatory networks. Haematologica 2021, 106, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiehlmeier, S.; Rafiee, M.R.; Bakr, A.; Mika, J.; Kruse, S.; Müller, J.; Schweiggert, S.; Herrmann, C.; Sigismondo, G.; Schmezer, P.; et al. Identification of therapeutic targets of the hijacked super-enhancer complex in EVI1-rearranged leukemia. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3127–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, P.A.; Abruzzo, L.V.; Medeiros, L.J.; Cromwell, C.; Zhang, X.; Yin, C.C.; Kornblau, S.M.; Konopieva, M.; Lin, P. Aberrant EVI1 expression in acute myeloid leukemias associated with the t(3;8)(q26;q24). Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2007, 177, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Su, M.; Levy, N.B.; Mohtashamian, A.; Monaghan, S.; Kaur, P.; Zaremba, C.; Garcia, R.; Broome, H.E.; Dell’Aquila, M.L.; et al. Myeloid neoplasm with t(3;8)(q26;q24): Report of six cases and review of the literature. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 55, 2532–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Hu, S.; Wang, S.A.; Xie, W.; Lin, P.; Xu, J.; Toruner, G.; Zhao, M.; Gu, J.; Doty, M.; et al. t(3;8)(q26.2;q24) Often Leads to MECOM/MYC Rearrangement and Is Commonly Associated with Therapy-Related Myeloid Neoplasms and/or Disease Progression. J. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 21, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottema, S.; Mulet-Lazaro, R.; Erpelinck-Verschueren, C.; van Herk, S.; Havermans, M.; Arricibita Varea, A.; Vermeulen, M.; Beverloo, H.B.; Gröschel, S.; Haferlach, T.; et al. The leukemic oncogene EVI1 hijacks a MYC super-enhancer by CTCF-facilitated loops. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinai, A.A.; Valk, P.J. Review: Aberrant EVI1 expression in acute myeloid leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 172, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gröschel, S.; Lugthart, S.; Schlenk, R.F.; Valk, P.J.; Eiwen, K.; Goudswaard, C.; van Putten, W.J.; Kayser, S.; Verdonck, L.F.; Lübbert, M.; et al. High EVI1 expression predicts outcome in younger adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia and is associated with distinct cytogenetic abnormalities. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2101–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, E.; Wilson, M.P.; McGrath, K.E.; Li, A.J.; Frisch, B.J.; Palis, J.; Calvi, L.M.; Zhang, Y.; Perkins, A.S. EVI1 overexpression reprograms hematopoiesis via upregulation of Spi1 transcription. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.; Fergusson, W.D.; Whetton, A.D.; Moreira-Leite, F.; Pepper, S.D.; Miller, C.; Saunders, E.K.; White, D.J.; Will, A.M.; Eden, T.; et al. Amplification and translocation of 3q26 with overexpression of EVI1 in Fanconi anemia-derived childhood acute myeloid leukemia with biallelic FANCD1/BRCA2 disruption. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2007, 46, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygalewicz, B.; Woroniecka, R.; Pastwińska, A.; Rygier, J.; Krawczyk, P.; Borg, K.; Makuch-Łasica, H.; Patkowska, E.; Pieńkowska-Grela, B. Acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis with EVI1 amplification. Cancer Genet. 2012, 205, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkert, S.; Schnittger, S.; Zenger, M.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; Haferlach, C. Amplification of EVI1 on cytogenetically cryptic double minutes as new mechanism for increased expression of EVI1. Cancer Genet. 2014, 207, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Medeiros, L.J.; Wang, W.; Tang, G.; Jung, H.S.; Sfamenos, S.M.; Fang, H.; Toruner, G.A.; Hu, S.; Yin, C.C.; et al. Newly designed breakapart FISH probe helps to identify cases with true MECOM rearrangement in myeloid malignancies. Cancer Genet. 2022, 262–263, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianelli, U.; Vener, C.; Bossi, A.; Cortinovis, I.; Iurlo, A.; Fracchiolla, N.S.; Savi, F.; Moro, A.; Grifoni, F.; De Philippis, C.; et al. The European Consensus on grading of bone marrow fibrosis allows a better prognostication of patients with primary myelofibrosis. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakori, M.; Kadia, T.; Loghavi, S.; Daver, N.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Pierce, S.; Sui, D.; Wei, P.; Khodakarami, F.; Tang, Z.; et al. TP53 copy number and protein expression inform mutation status across risk categories in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2022, 140, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, A.P.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Phillips, G.L.; Horsman, D.E. Clinical, haematological and cytogenetic features in 24 patients with structural rearrangements of the Q arm of chromosome 3. Br. J. Haematol. 1993, 83, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, P.; Vamos, E.; Ferster, A.; Sariban, E. Granulocytic sarcoma showing chromosomal changes other than the t(8;21). Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1994, 74, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Weh, H.J.; Martensen, S.; Seeger, D.; Hossfeld, D.K. 3p21 is a recurrent treatment-related breakpoint in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1996, 74, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Heaps, L.S.; Sharma, P.; Jarvis, A.; Forsyth, C. Abnormal dicentric chromosome with co-amplification of sequences from chromosomes 11 and 19: A novel rearrangement in a patient with myelodysplastic syndrome transforming to acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2001, 130, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, B.; Dastugue, N.; Vandesompele, J.; Cauwelier, B.; De Smet, B.; Yigit, N.; De Paepe, A.; Cervera, J.; Recher, C.; De Mas, V.; et al. EVI1 is consistently expressed as principal transcript in common and rare recurrent 3q26 rearrangements. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2006, 45, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najfeld, V.; Cozza, A.; Berkofsy-Fessler, W.; Prchal, J.; Scalise, A. Numerical gain and structural rearrangements of JAK2, identified by FISH, characterize both JAK2617V>F-positive and -negative patients with Ph-negative MPD, myelodysplasia, and B-lymphoid neoplasms. Exp. Hematol. 2007, 35, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, N.; Shimada, A.; Taketani, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Kojima, S.; Kato, K. Childhood acute myeloid leukemia with bone marrow eosinophilia caused by t(16;21)(q24;q22). Int. J. Hematol. 2012, 95, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerer, I.; Haferlach, C.; Meggendorfer, M.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; Stengel, A. Prognosis of MECOM (EVI1)-rearranged MDS and AML patients rather depends on accompanying molecular mutations than on blast count. Leuk. Lymphoma 2020, 61, 1756–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.; Al-Kali, A.; Van Dyke, D.; Niederwieser, D.; Vucinic, V.; Lemke, J.; Muller, C.; Schwind, S.; Teichmann, A.C.; Bakken, R.; et al. Inversion 3 Cytogenetic Abnormality in an Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipient Representative of a Donor-Derived Constitutional Abnormality. Biol. Blood Marrow. Transplant. 2017, 23, 1582–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Gurbuxani, S.; Zak, T.; Kocherginsky, M.; Ji, P.; Wehbe, F.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.H.; Lu, X.; Jennings, L.; et al. Comparison of myeloid neoplasms with nonclassic 3q26.2/MECOM versus classic inv(3)/t(3;3) rearrangements reveals diverse clinicopathologic features, genetic profiles, and molecular mechanisms of MECOM activation. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2022, 61, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenouille, N.; Bassil, C.F.; Ben-Sahra, I.; Benajiba, L.; Alexe, G.; Ramos, A.; Pikman, Y.; Conway, A.S.; Burgess, M.R.; Li, Q.; et al. The creatine kinase pathway is a metabolic vulnerability in EVI1-positive acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbyli, R.; Song, Y.; Liu, W.; Gao, Y.; Biancon, G.; Chandhok, N.S.; Wang, X.; Fu, X.; Patel, A.; Sundaram, R.; et al. In vivo anti-tumor effect of PARP inhibition in IDH1/2 mutant MDS/AML resistant to targeted inhibitors of mutant IDH1/2. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, C.; Portwood, S.M.; Przespolewski, A.; Wang, E.S. PARP goes the weasel! Emerging role of PARP inhibitors in acute leukemias. Blood Rev. 2021, 45, 100696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Sasaki, K.; Montalban-Bravo, G.; Tang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Kadia, T.; Chien, K.; Rush, D.; Nguyen, H.; et al. High-resolution structural variant profiling of myelodysplastic syndromes by optical genome mapping uncovers cryptic ab-errations of prognostic and therapeutic significance. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröschel, S.; Sanders, M.A.; Hoogenboezem, R.; Zeilemaker, A.; Havermans, M.; Erpelinck, C.; Bindels, E.M.; Beverloo, H.B.; Döhner, H.; Löwenberg, B.; et al. Mutational spectrum of myeloid malignancies with inv(3)/t(3;3) reveals a predominant involvement of RAS/RTK signaling pathways. Blood 2015, 125, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.R.; Ma, J.; Kamens, J.; Westover, T.; Walsh, M.P.; Brady, S.W.; Robert Michael, J.; Chen, X.; Montefiori, L.; Song, G.; et al. The acquisition of molecular drivers in pediatric therapy-related myeloid neoplasms. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).