Tumor-Educated Platelet Extracellular Vesicles: Proteomic Profiling and Crosstalk with Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Subjects
2.2. Preparation of Plasma and Platelet-Derived mEVs
2.3. Analysis of Plasma, Washed Platelets, and Platelet-Derived mEVs by Flow Cytometry
2.4. Cocultures of Cancer Cells with Platelet-Derived mEVs
2.5. mRNA Analysis
2.6. Assessment of Platelet-Derived mEV Proteins by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Individuals Enrolled in the Study
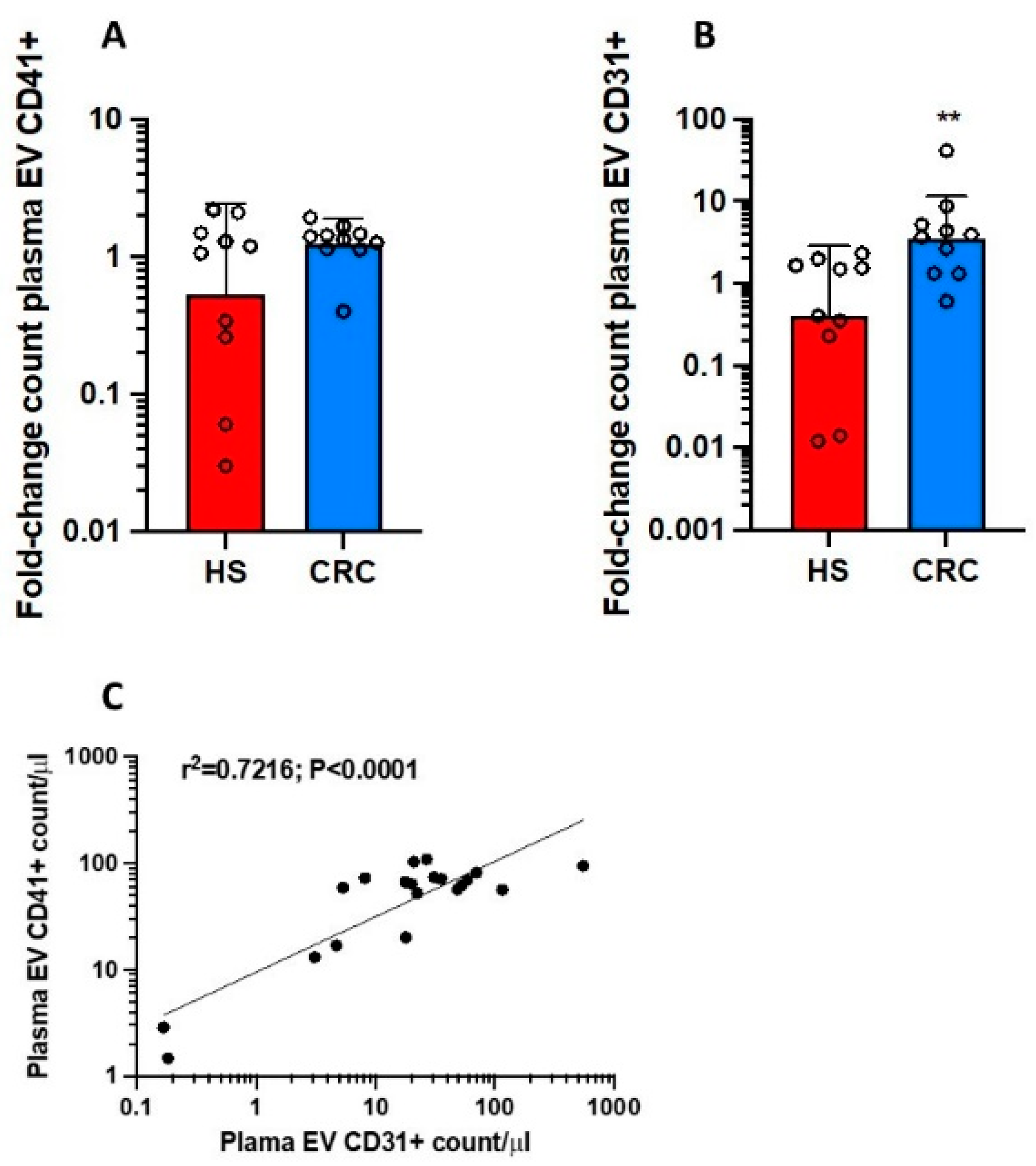
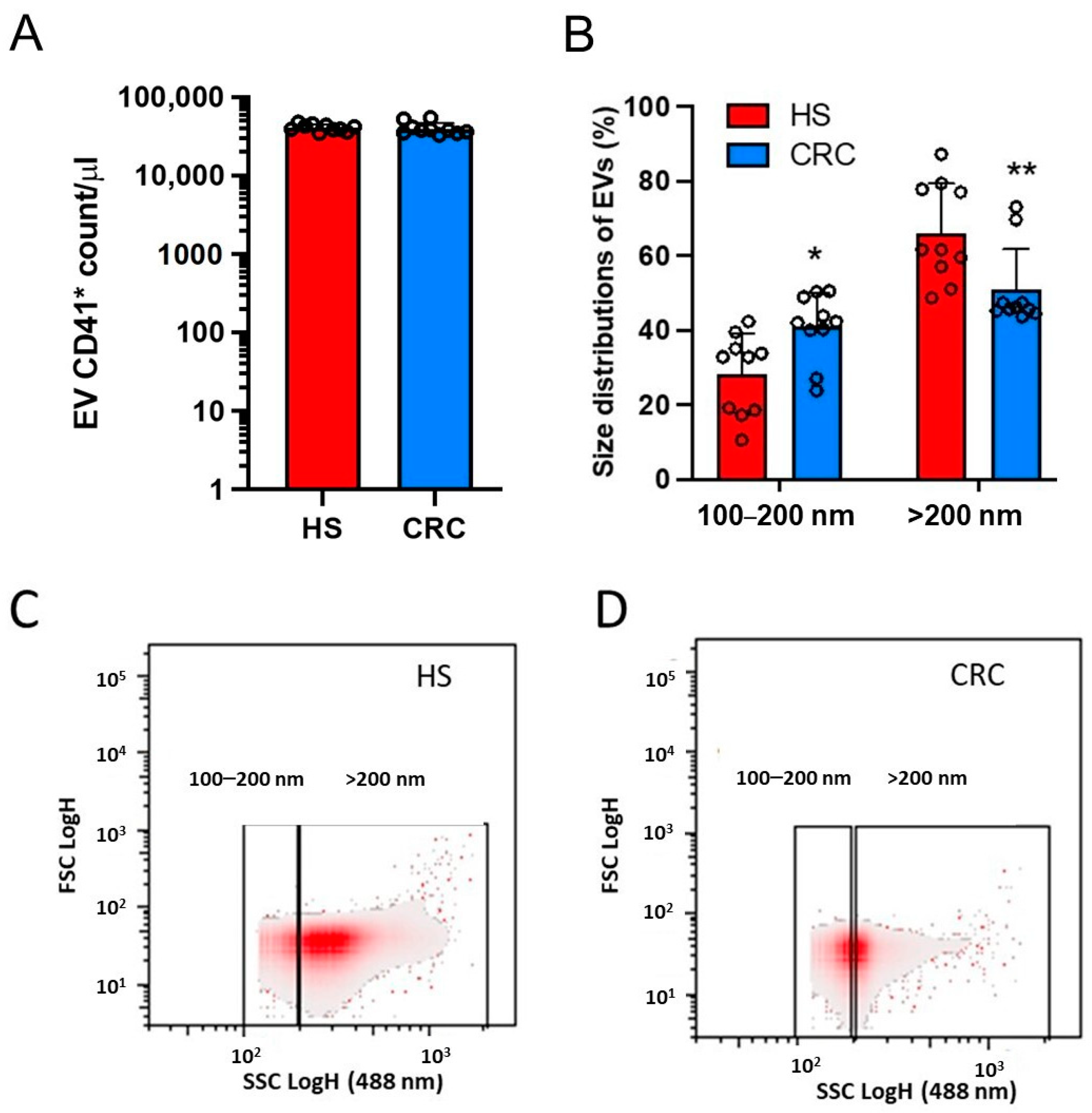
3.2. Count of Plasma mEVs and Generation of mEVs from Platelets of CRC Patients and HS
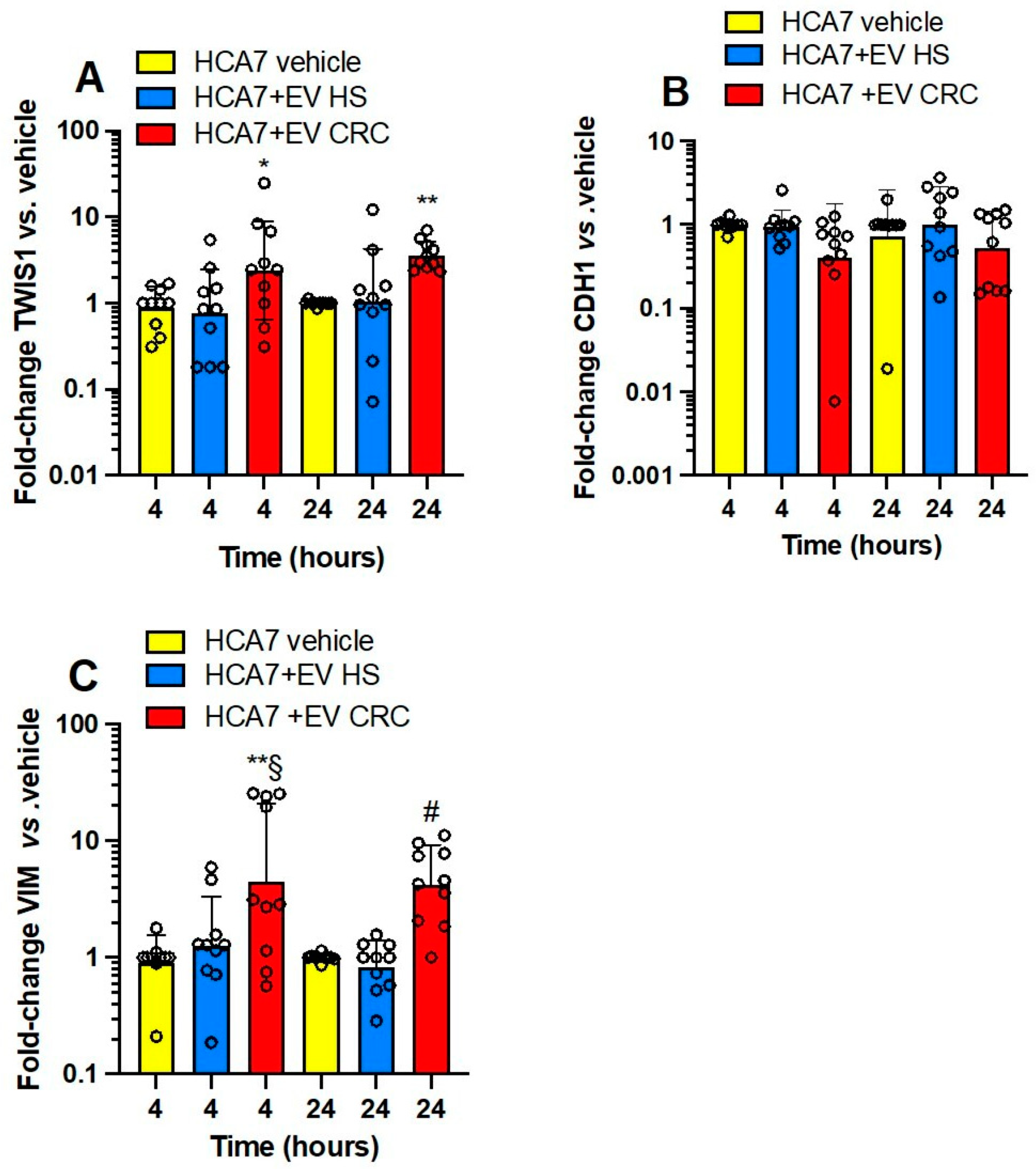
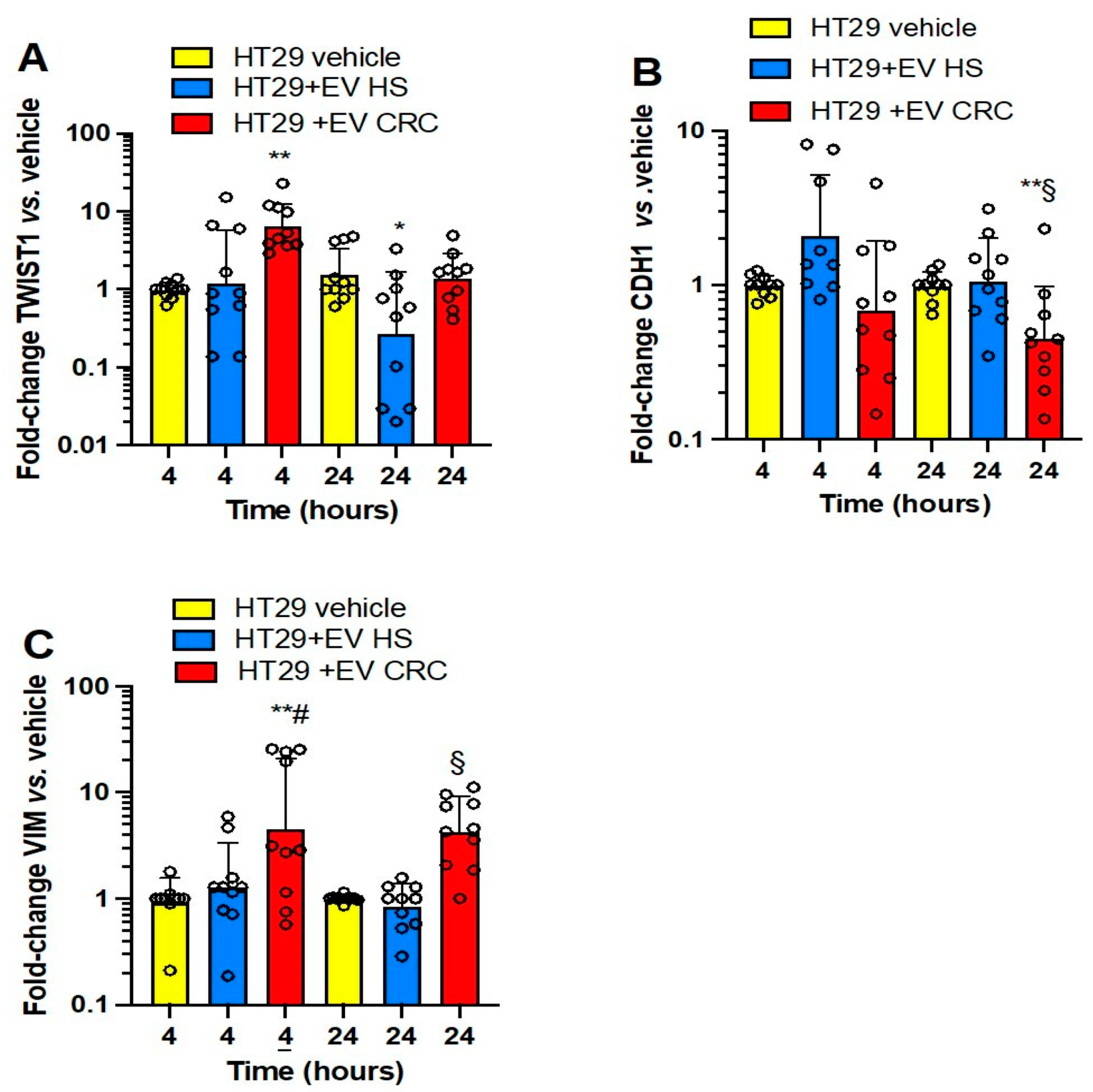
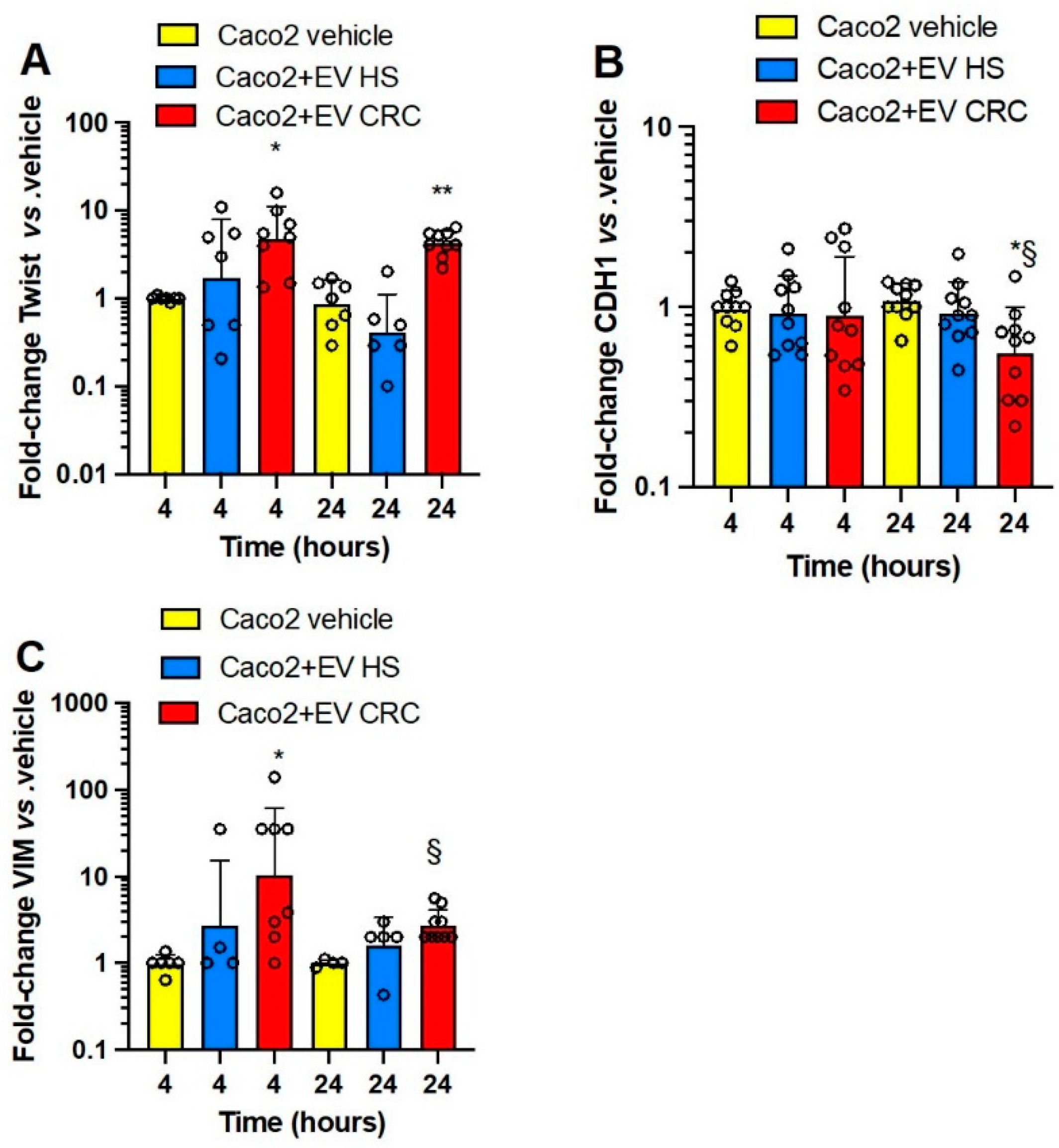
3.3. Effects of Platelet-Derived mEVs on Gene Expression Markers of EMT in Colorectal Cancer Cells
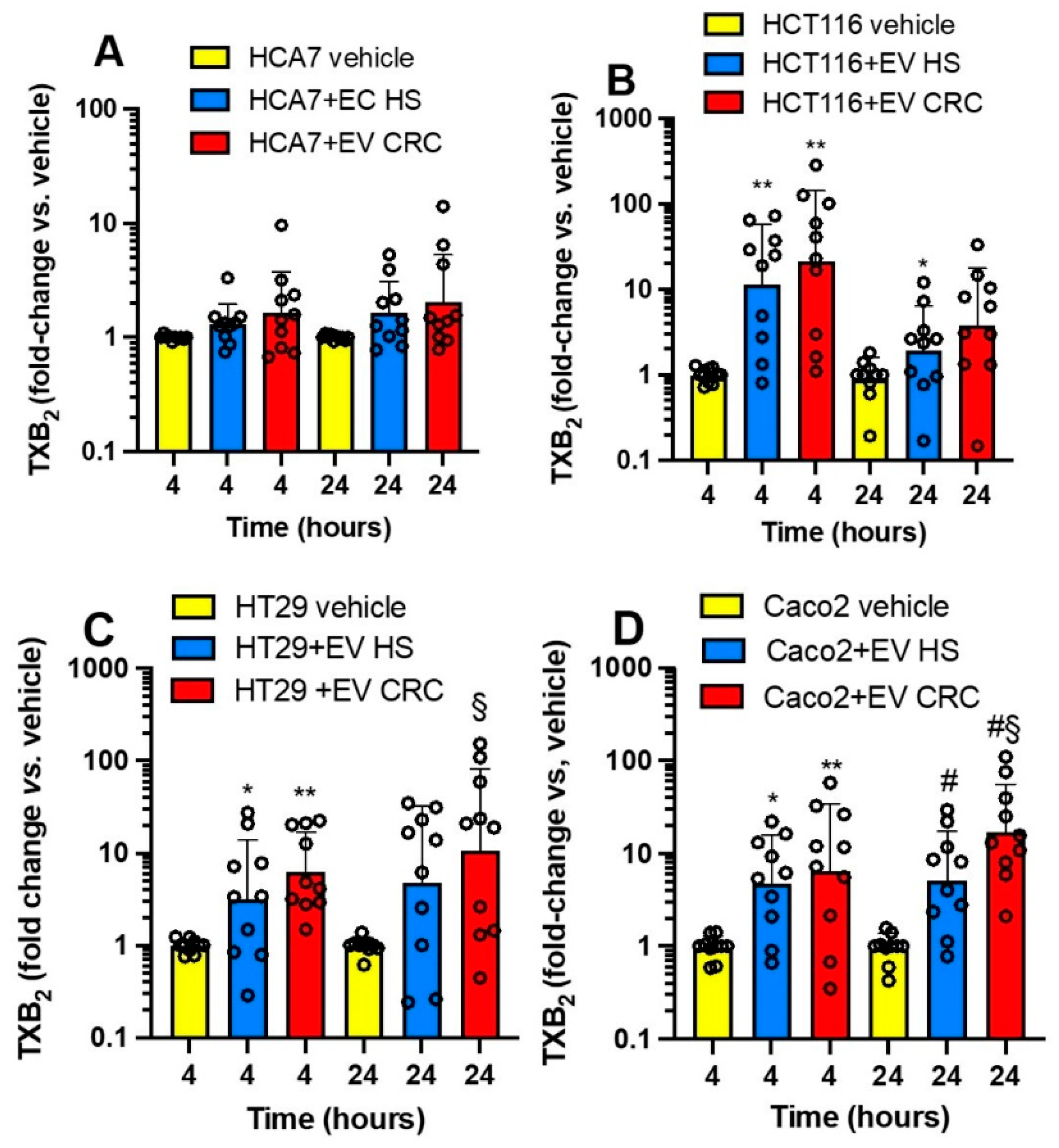
3.4. Effects of Platelet-Derived mEVs on the Expression of PTGS2 and TXB2 Generation by Colorectal Cancer Cells
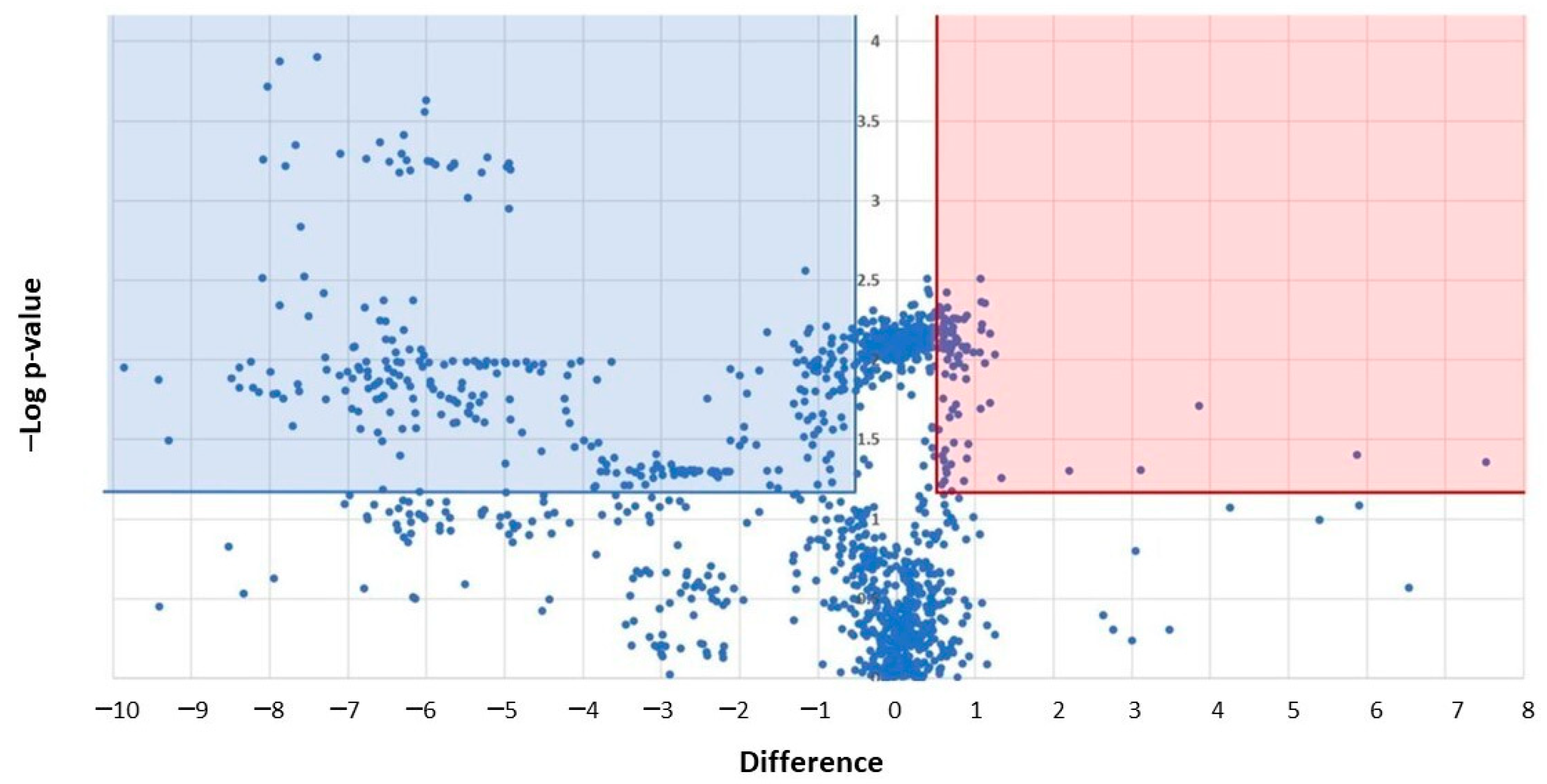
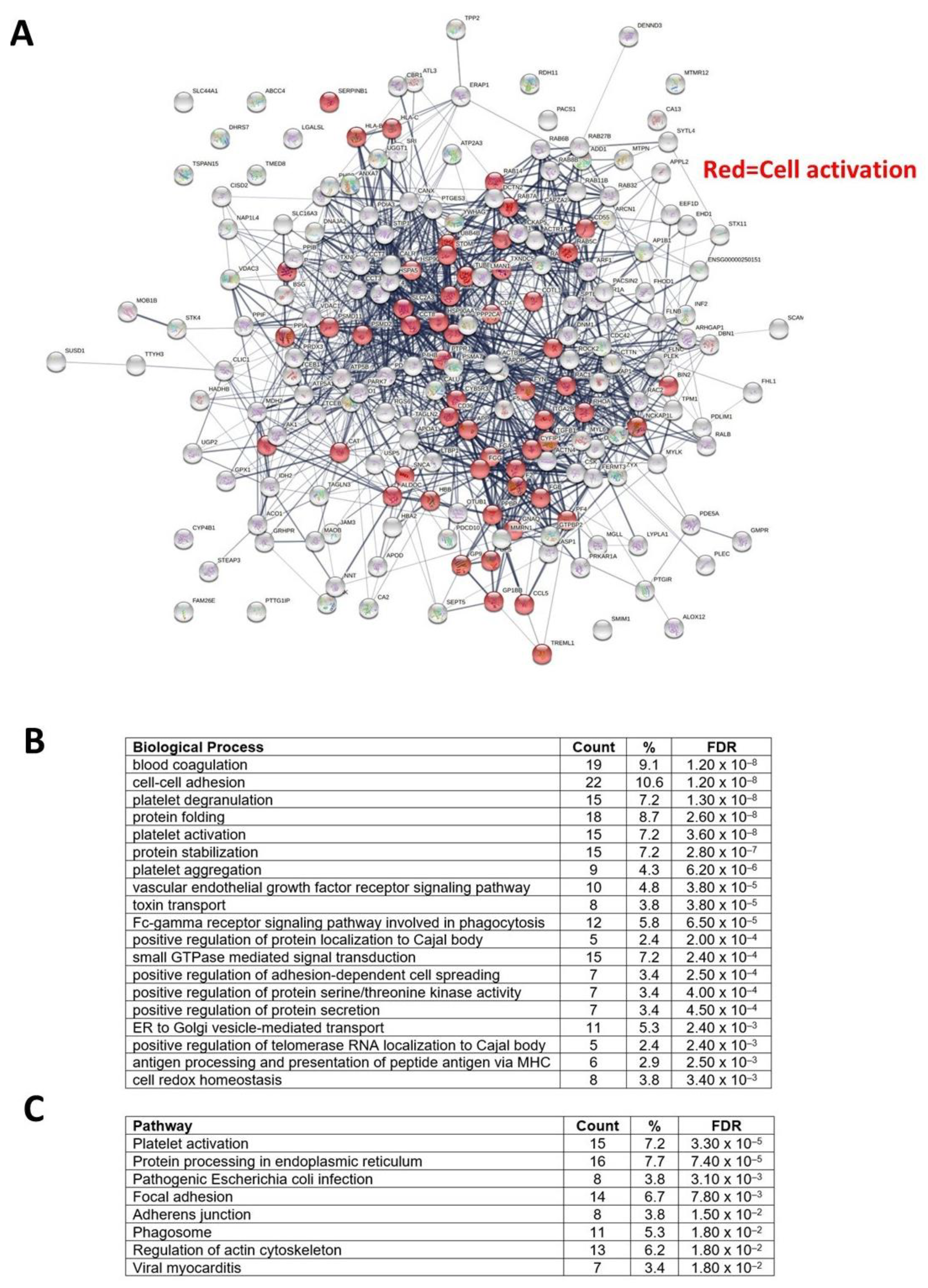
3.5. Proteomics Characterization of Platelet-Derived mEVs Obtained from CRC Patients and HS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Causes_of_death_statistics (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Patrono, C.; Patrignani, P.; García Rodríguez, L.A. Cyclooxygenase-selective inhibition of prostanoid formation: Transducing biochemical selectivity into clinical read-outs. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrignani, P.; Patrono, C. Aspirin and Cancer. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dovizio, M.; Sacco, A.; Patrignani, P. Curbing tumorigenesis and malignant progression through the pharmacological control of the wound healing process. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2017, 89, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labelle, M.; Begum, S.; Hynes, R.O. Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovizio, M.; Maier, T.J.; Alberti, S.; Di Francesco, L.; Marcantoni, E.; Münch, G.; John, C.M.; Suess, B.; Sgambato, A.; Steinhilber, D.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of platelet-tumor cell crosstalk prevents platelet-induced overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 in HT29 human colon carcinoma cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 84, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Dubois, R.N. Eicosanoids and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2010, 10, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Dubois, R.N. The role of COX-2 in intestinal inflammation and colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillem-Llobat, P.; Dovizio, M.; Bruno, A.; Ricciotti, E.; Cufino, V.; Sacco, A.; Grande, R.; Alberti, S.; Arena, V.; Cirillo, M.; et al. Aspirin prevents colorectal cancer metastasis in mice by splitting the crosstalk between platelets and tumor cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32462–32477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahata, N. Thromboxane A2: Physiology/pathophysiology, cellular signal transduction, and pharmacology. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 118, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, B.; Syed, F.; Khan, S.; Iqbal, A.; Ahmad, I. Characterization of extracellular vesicles by flow cytometry: Challenges and promises. Micron 2022, 161, 103341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, L.M.; Wang, M.Z. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, T.; Li, G. Plasma exosomes as novel biomarker for the early diagnosis of gastric cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 21, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Jiang, L.; Lin, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, K.; He, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, W. Platelet microparticle-mediated transfer of miR-939 to epithelial ovarian cancer cells promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 97464–97475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarà, M.; Guidetti, G.F.; Boselli, D.; Villa, C.; Canobbio, I.; Seppi, C.; Visconte, C.; Canino, J.; Torti, M. Release of Prometastatic Platelet-Derived Microparticles Induced by Breast Cancer Cells: A Novel Positive Feedback Mechanism for Metastasis. TH Open 2017, 1, e155–e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Tseng, C.C.; Chang, H.C.; Huang, K.T.; Fang, W.F.; Chen, Y.M.; Yang, C.T.; Hsiao, C.C.; Lin, M.C.; Ho, C.K.; et al. Circulating microparticles are prognostic biomarkers in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75952–75967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hron, G.; Kollars, M.; Weber, H.; Sagaster, V.; Quehenberger, P.; Eichinger, S.; Kyrle, P.A.; Weltermann, A. Tissue factor-positive microparticles: Cellular origin and association with coagulation activation in patients with colorectal cancer. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 97, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mege, D.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Ouaissi, M.; Robert, S.; Sielezneff, I.; Sastre, B.; Dignat-George, F.; Dubois, C. The origin and concentration of circulating microparticles differ according to cancer type and evolution: A prospective single-center study. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezouar, S.; Mege, D.; Darbousset, R.; Farge, D.; Debourdeau, P.; Dignat-George, F.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Dubois, C. Involvement of platelet-derived microparticles in tumor progression and thrombosis. Semin. Oncol. 2014, 41, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovizio, M.; Bruno, A.; Contursi, A.; Grande, R.; Patrignani, P. Platelets and extracellular vesicles in cancer: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italiano, J.E., Jr.; Mairuhu, A.T.; Flaumenhaft, R. Clinical relevance of microparticles from platelets and megakaryocytes. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2010, 17, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Janowska-Wieczorek, A.; Wysoczynski, M.; Kijowski, J.; Marquez-Curtis, L.; Machalinski, B.; Ratajczak, J.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Microvesicles derived from activated platelets induce metastasis and angiogenesis in lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 113, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, R.; Dovizio, M.; Marcone, S.; Szklanna, P.B.; Bruno, A.; Ebhardt, H.A.; Cassidy, H.; Ní Áinle, F.; Caprodossi, A.; Lanuti, P.; et al. Platelet-Derived Microparticles from Obese Individuals: Characterization of Number, Size, Proteomics, and Crosstalk with Cancer and Endothelial Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.H.; Stitham, J.; Gleim, S.; Di Febbo, C.; Porreca, E.; Fava, C.; Tacconelli, S.; Capone, M.; Evangelista, V.; Levantesi, G.; et al. Glucose and collagen regulate human platelet activity through aldose reductase induction of thromboxane. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4462–4476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marchisio, M.; Simeone, P.; Bologna, G.; Ercolino, E.; Pierdomenico, L.; Pieragostino, D.; Ventrella, A.; Antonini, F.; Del Zotto, G.; Vergara, D.; et al. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Circulating Extracellular Vesicle Subtypes from Fresh Peripheral Blood Samples. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, P.; Celia, C.; Bologna, G.; Ercolino, E.; Pierdomenico, L.; Cilurzo, F.; Grande, R.; Diomede, F.; Vespa, S.; Canonico, B.; et al. Diameters and Fluorescence Calibration for Extracellular Vesicle Analyses by Flow Cytometry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Pol, E.; Sturk, A.; van Leeuwen, T.; Nieuwland, R.; Coumans, F.; ISTH-SSC-VB Working group. Standardization of extracellular vesicle measurements by flow cytometry through vesicle diameter approximation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar]
- De Rond, L.; Coumans, F.A.W.; Nieuwland, R.; van Leeuwen, TG; van der Pol, E. Deriving Extracellular Vesicle Size From Scatter Intensities Measured by Flow Cytometry. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2018, 86, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, O.P.; Kazanietz, M.G.; Praticò, D.; FitzGerald, G.A. Arachidonic acid in platelet microparticles upregulates cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostaglandin formation via a protein kinase C/mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 7545–7556. [Google Scholar]
- Patrignani, P.; Tacconelli, S.; Piazuelo, E.; Di Francesco, L.; Dovizio, M.; Sostres, C.; Marcantoni, E.; Guillem-Llobat, P.; Del Boccio, P.; Zucchelli, M.; et al. Reappraisal of the clinical pharmacology of low-dose aspirin by comparing novel direct and traditional indirect biomarkers of drug action. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.E.M.; Szklanna, P.B.; Guerrero, J.A.; Wynne, K.; Dervin, F.; O’Connell, K.; Allen, S.; Egan, K.; Bennett, C.; McGuigan, C.; et al. Platelet Releasate Proteome Profiling Reveals a Core Set of Proteins with Low Variance between Healthy Adults. Proteomics 2018, 18, e1800219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contursi, A.; Schiavone, S.; Dovizio, M.; Hinz, C.; Fullone, R.; Tacconelli, S.; Tyrrell, V.J.; Grande, R.; Lanuti, P.; Marchisio, M.; et al. Platelets induce free and phospholipid-esterified 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid generation in colon cancer cells by delivering 12-lipoxygenase. J. Lipid Res. 2021, 62, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkland, S.C. Dome formation by a human colonic adenocarcinoma cell line (HCA-7). Cancer Res. 1985, 45, 3790–3795. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.; Ongchin, M.; Sharratt, E.; Dominguez, I.; Wang, J.; Brattain, M.G.; Rajput, A. Intra-tumoral heterogeneity in metastatic potential and survival signaling between iso-clonal HCT116 and HCT116b human colon carcinoma cell lines. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imesch, P.; Goerens, A.; Fink, D.; Fedier, A. MLH1-deficient HCT116 colon tumor cells exhibit resistance to the cytostatic and cytotoxic effect of the poly(A) polymerase inhibitor cordycepin (3’-deoxyadenosine) in vitro. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 3, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaumenhaft, R.; Dilks, J.R.; Richardson, J.; Alden, E.; Patel-Hett, S.R.; Battinelli, E.; Klement, G.L.; Sola-Visner, M.; Italiano, J.E., Jr. Megakaryocyte-derived microparticles: Direct visualization and distinction from platelet-derived microparticles. Blood 2009, 113, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taus, F.; Meneguzzi, A.; Castelli, M.; Minuz, P. Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Target of Antiplatelet Agents. What Is the Evidence? Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, G.L.; Yip, T.T.; Cassiola, F.; Kikuchi, L.; Cervi, D.; Podust, V.; Italiano, J.E.; Wheatley, E.; Abou-Slaybi, A.; Bender, E.; et al. Platelets actively sequester angiogenesis regulators. Blood 2009, 113, 2835–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, M.G.; Wesseling, P.; Wurdinger, T. Tumor-Educated Platelets as a Noninvasive Biomarker Source for Cancer Detection and Progression Monitoring. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3407–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszak, I.; Witkowska-Piłaszewicz, O.; Niewiadomska, Z.; Dworecka-Kaszak, B.; Ngosa Toka, F.; Jurka, P. Role of Cadherins in Cancer—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.Q.; Ma, C.; Wang, Q.; Song, Y.; Lv, T. The role of TWIST1 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancers. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Y.; Lin, H.H.; Tang, M.J.; Wang, Y.K. Vimentin contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition cancer cell mechanics by mediating cytoskeletal organization and focal adhesion maturation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15966–15983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Tilló, E.; de Barrios, O.; Siles, L.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Castells, A.; Postigo, A. β-catenin/TCF4 complex induces the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-activator ZEB1 to regulate tumor invasiveness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19204–19209. [Google Scholar]
- Zucchini-Pascal, N.; Peyre, L.; Rahmani, R. Crosstalk between beta-catenin and snail in the induction of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in hepatocarcinoma: Role of the ERK1/2 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20768–20792. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhou, B.P. Activation of β-catenin and Akt pathways by Twist are critical for the maintenance of EMT associated cancer stem cell-like characters. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas, M.; Tomlinson, I.P.; Rowan, A.; Pignatelli, M.; Bodmer, W.F. Beta-catenin mutations in cell lines established from human colorectal cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10330–10334. [Google Scholar]
- Dovizio, M.; Alberti, S.; Sacco, A.; Guillem-Llobat, P.; Schiavone, S.; Maier, T.J.; Steinhilber, D.; Patrignani, P. Novel insights into the regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by platelet-cancer cell crosstalk. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, B.M.; Harper, M.T.; Macaulay, I.C.; Morrell, C.N.; Perez-Tamayo, A.; Foy, M.; Habas, R.; Poole, A.W.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Maguire, P.B. Canonical Wnt signaling negatively regulates platelet function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19836–19841. [Google Scholar]
- Dervin, F.; Wynne, K.; Maguire, P. Human Platelet Exosome Proteomics Leads to the Identification of WNT Positive Exosomes Which Impact Canonical WNT Signalling in Target Cells Crossmark: Check for Updates. Blood 2014, 124, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, O.P.; Pratico, D.; Lawson, J.A.; FitzGerald, G.A. Transcellular activation of platelets and endothelial cells by bioactive lipids in platelet microparticles. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Brunson, A.; Adesina, O.; Keegan, T.H.M.; Wun, T. The incidence of cancer-associated thrombosis is increasing over time. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, S.L. Role of platelet microparticles in the production of thromboxane by rabbit pulmonary artery. Hypertension 2004, 43, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angénieux, C.; Dupuis, A.; Gachet, C.; de la Salle, H.; Maître, B. Cell surface expression of HLA I molecules as a marker of young platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthikonda, S.; Alviar, C.L.; Vaduganathan, M.; Arikan, M.; Tellez, A.; DeLao, T.; Granada, J.F.; Dong, J.F.; Kleiman, N.S.; Lev, E.I. Role of reticulated platelets and platelet size heterogeneity on platelet activity after dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel in patients with stable coronary artery disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colberg, L.; Cammann, C.; Greinacher, A.; Seifert, U. Structure and function of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Honn, K.V. 12(S)-HETE in cancer metastasis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1999, 447, 181–191. [Google Scholar]
- Gondek, T.; Szajewski, M.; Szefel, J.; Aleksandrowicz-Wrona, E.; Skrzypczak-Jankun, E.; Jankun, J.; Lysiak-Szydlowska, W. Evaluation of 12-lipoxygenase (12-LOX) and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) as prognostic markers in prostate cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 102478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, M.; Szefel, J.; Skrzypczak-Jankun, E.; Lysiak-Szydłowska, W.; Szajewski, M.; Aleksandrowicz-Wrona, E.; Jankun, J. The concentration of 12-lipoxygenase in platelet rich plasma as an indication of cancer of the prostate. Contemp. Oncol. 2013, 17, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, O.; Jesel, L.; Freyssinet, J.M.; Toti, F. Cellular mechanisms underlying the formation of circulating microparticles. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, W.L.; Lee, M.J.; Cummins, T.D.; Schultz, D.J.; Powell, D.W. Proteomic and functional characterisation of platelet microparticle size classes. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buecher, B.; Bouancheau, D.; Broquet, A.; Bezieau, S.; Denis, M.G.; Bonnet, C.; Heymann, M.F.; Jarry, A.; Galmiche, J.P.; Blottière, H.M. Growth inhibitory effect of celecoxib and rofecoxib on human colorectal carcinoma cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Peng, Y.; Fu, Y.; Cai, C.; Guo, C.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, E.; Long, K.; et al. MLH1 Deficiency Induces Cetuximab Resistance in Colon Cancer via Her-2/PI3K/AKT Signaling. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020, 7, 2000112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Bai, J.; Bandla, C.; Hewapathirana, S.; García-Seisdedos, D.; Kamatchinathan, S.; Kundu, D.; Prakash, A.; Frericks-Zipper, A.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database resources in 2022: A Hub for mass spectrometry-based proteomics evidences. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2022, 50, D543–D552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| HS | CRC | |
|---|---|---|
| Number, n | 16 | 16 |
| Sex, F, n | 9 | 9 |
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 60.38 ± 11.18 | 63.50 ± 12.29 |
| BMI, mean ± SD | 22.61 ± 3.00 | 24.29 ± 5.24 |
| Hypertension, n | 1 | 1 |
| Diagnosis | ||
| Adenocarcinoma ascending colon, n | - | 5 |
| Adenocarcinoma descending colon, n | - | 5 |
| Adenocarcinoma rectosigmoid junction, n | - | 1 |
| Adenocarcinoma rectum, n | - | 4 |
| Adenocarcinoma trasverse colon, n | - | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Contursi, A.; Fullone, R.; Szklanna-Koszalinska, P.; Marcone, S.; Lanuti, P.; Taus, F.; Meneguzzi, A.; Turri, G.; Dovizio, M.; Bruno, A.; et al. Tumor-Educated Platelet Extracellular Vesicles: Proteomic Profiling and Crosstalk with Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers 2023, 15, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020350
Contursi A, Fullone R, Szklanna-Koszalinska P, Marcone S, Lanuti P, Taus F, Meneguzzi A, Turri G, Dovizio M, Bruno A, et al. Tumor-Educated Platelet Extracellular Vesicles: Proteomic Profiling and Crosstalk with Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2023; 15(2):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020350
Chicago/Turabian StyleContursi, Annalisa, Rosa Fullone, Paulina Szklanna-Koszalinska, Simone Marcone, Paola Lanuti, Francesco Taus, Alessandra Meneguzzi, Giulia Turri, Melania Dovizio, Annalisa Bruno, and et al. 2023. "Tumor-Educated Platelet Extracellular Vesicles: Proteomic Profiling and Crosstalk with Colorectal Cancer Cells" Cancers 15, no. 2: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020350
APA StyleContursi, A., Fullone, R., Szklanna-Koszalinska, P., Marcone, S., Lanuti, P., Taus, F., Meneguzzi, A., Turri, G., Dovizio, M., Bruno, A., Pedrazzani, C., Tacconelli, S., Marchisio, M., Ballerini, P., Minuz, P., Maguire, P., & Patrignani, P. (2023). Tumor-Educated Platelet Extracellular Vesicles: Proteomic Profiling and Crosstalk with Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers, 15(2), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020350









