Deep Learning for Automatic Diagnosis and Morphologic Characterization of Malignant Biliary Strictures Using Digital Cholangioscopy: A Multicentric Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population and Study Design
2.2. Digital-Single Operator Cholangioscopy Procedure and Definitions
2.3. Development of the Convolutional Neural Network
2.4. Model Performance and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
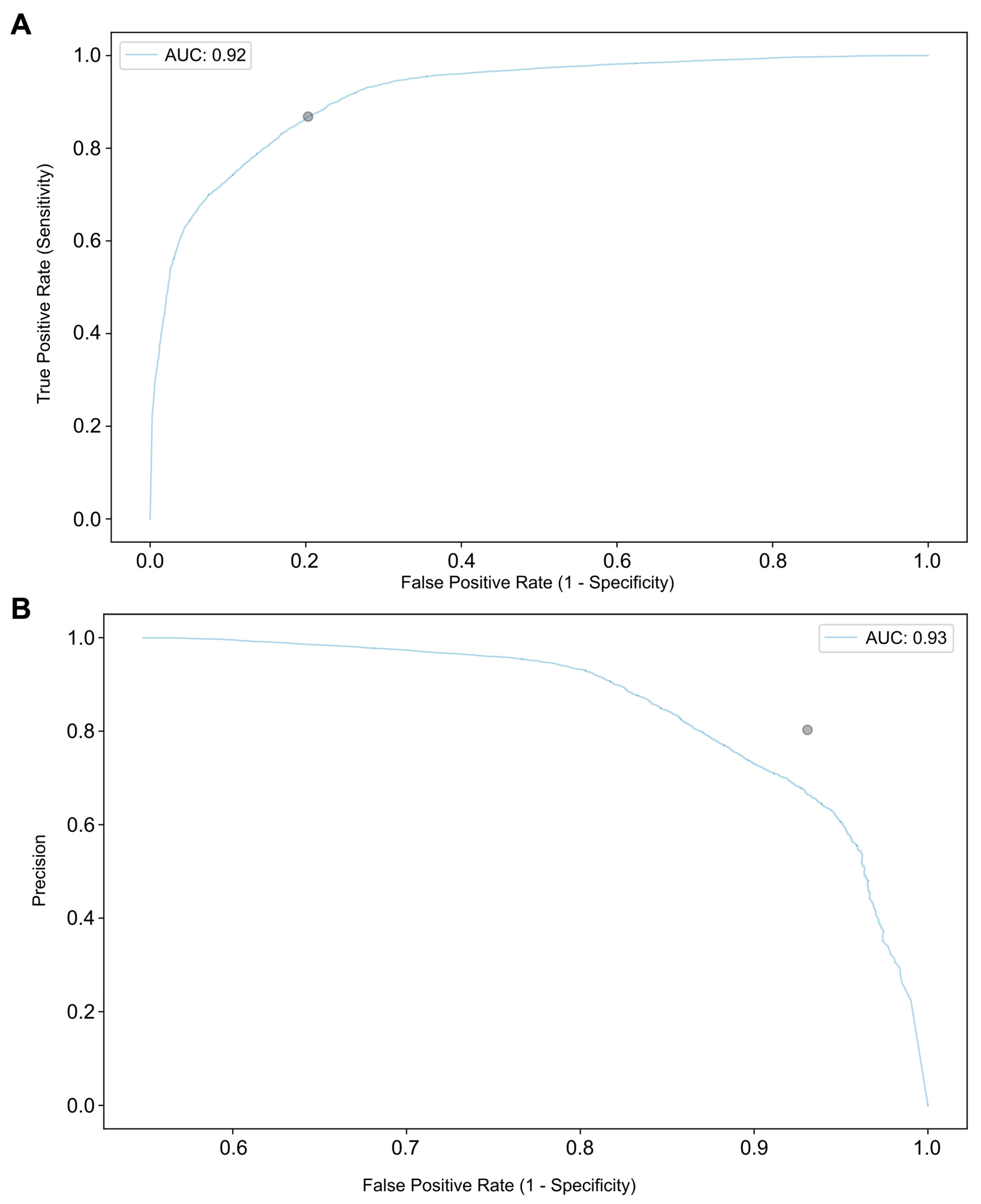
3.1. Performance of the Convolutional Neural Network
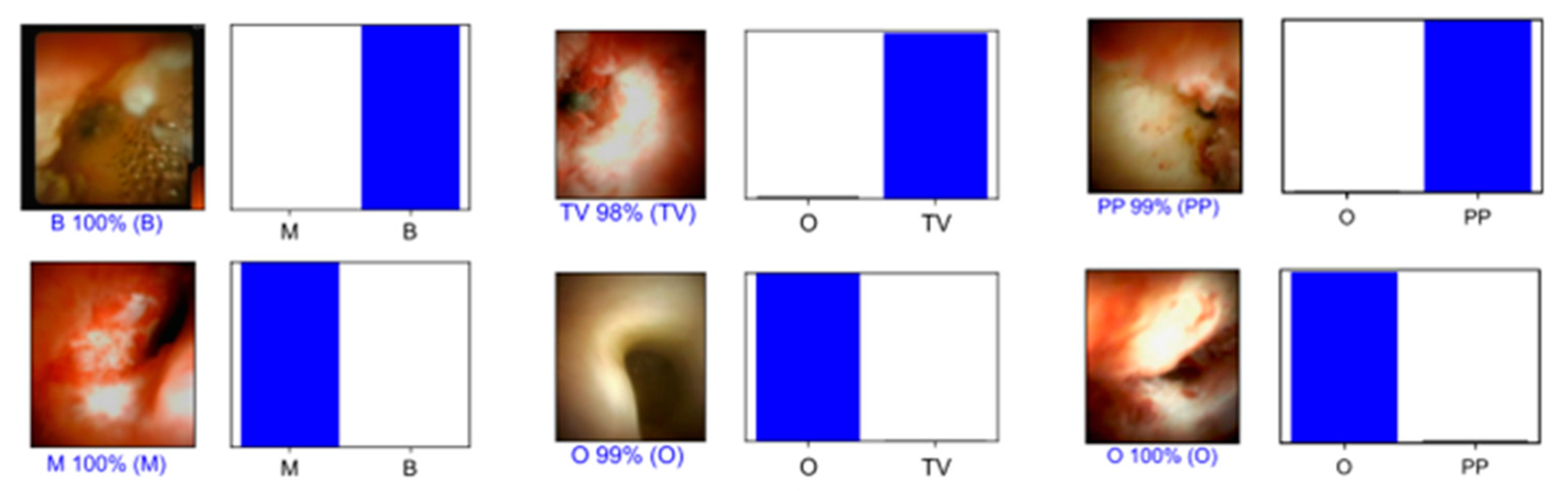
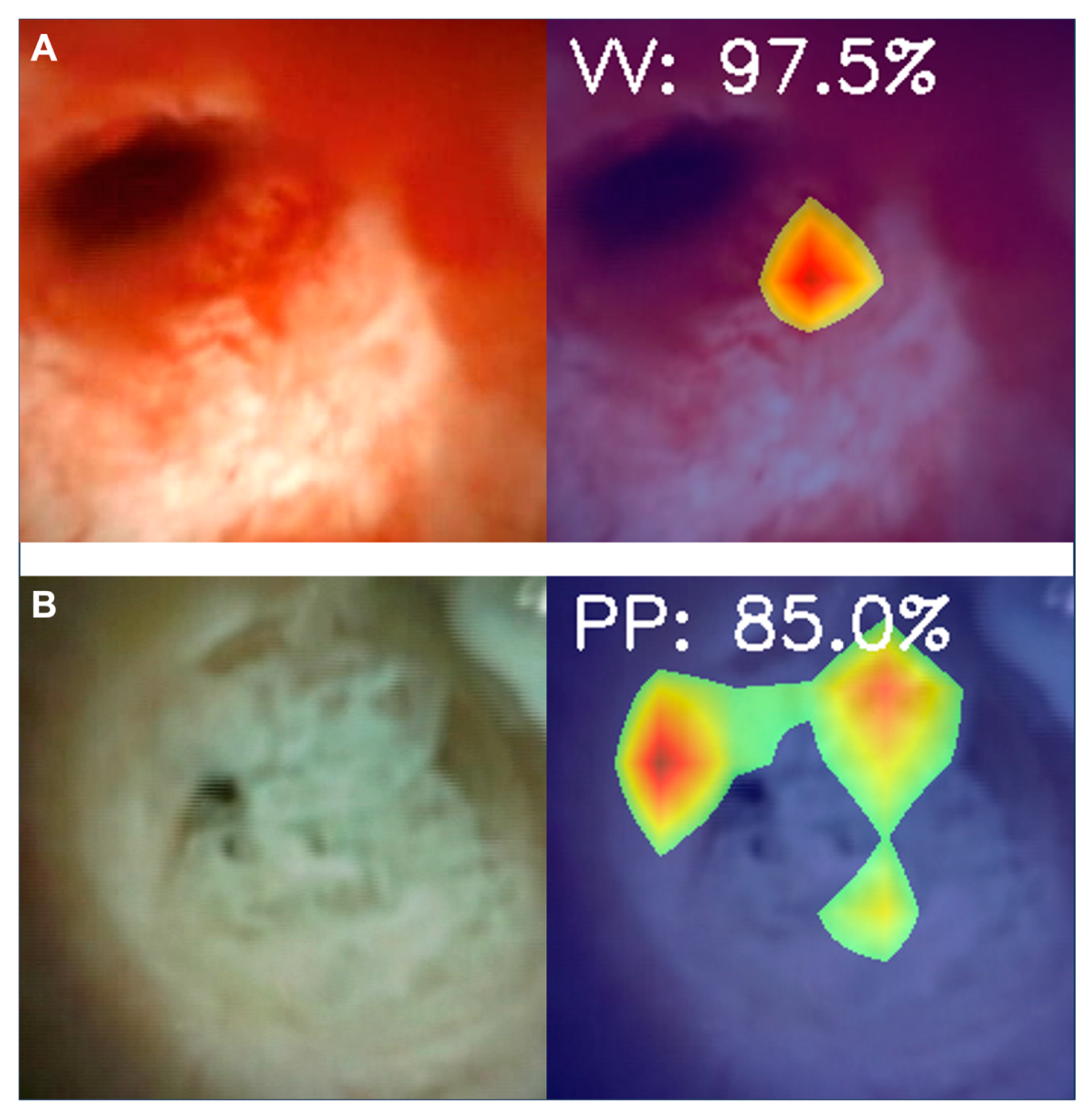
3.2. Detection of Morphological Characteristics Associated with Biliary Malignancy
3.3. Computational Performance of the CNN
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larghi, A.; Tringali, A.; Lecca, P.G.; Giordano, M.; Costamagna, G. Management of hilar biliary strictures. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 458–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimpinelli, M.; Makar, M.; Kahaleh, M. Endoscopic management of benign and malignant hilar stricture. Dig. Endosc. 2023, 35, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummala, P.; Munigala, S.; Eloubeidi, M.A.; Agarwal, B. Patients with obstructive jaundice and biliary stricture +/− mass lesion on imaging: Prevalence of malignancy and potential role of EUS-FNA. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranandi, B.; Oppong, K.W. Biliary strictures: Endoscopic assessment and management. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhi, A.D.; Slivka, A. Evaluation of indeterminate biliary strictures: Is there life on MARS? Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, A.S.; Calvert, T.J.; Chokshi, R.J. Sensitivity of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography standard cytology: 10-y review of the literature. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 184, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaneethan, U.; Njei, B.; Lourdusamy, V.; Konjeti, R.; Vargo, J.J.; Parsi, M.A. Comparative effectiveness of biliary brush cytology and intraductal biopsy for detection of malignant biliary strictures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Vilas-Boas, F.; Peixoto, A.; Andrade, P.; Lopes, J.; Macedo, G. How SpyGlass May Impact Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Practice and Patient Management. GE Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 25, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerges, C.; Beyna, T.; Tang, R.S.Y.; Bahin, F.; Lau, J.Y.W.; van Geenen, E.; Neuhaus, H.; Reddy, D.N.; Ramchandani, M. Digital single-operator peroral cholangioscopy-guided biopsy sampling versus ERCP-guided brushing for indeterminate biliary strictures: A prospective, randomized, multicenter trial (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 91, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Stevens, T.; Kou, L.; Vargo, J.J.; Parsi, M.A. Efficacy of digital single-operator cholangioscopy and factors affecting its accuracy in the evaluation of indeterminate biliary stricture. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 91, 385–393.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.K.; Pleskow, D.K. SpyGlass single-operator peroral cholangiopancreatoscopy system for the diagnosis and therapy of bile-duct disorders: A clinical feasibility study (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2007, 65, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Medranda, C.; Valero, M.; Soria-Alcivar, M.; Puga-Tejada, M.; Oleas, R.; Ospina-Arboleda, J.; Alvarado-Escobar, H.; Baquerizo-Burgos, J.; Robles-Jara, C.; Pitanga-Lukashok, H. Reliability and accuracy of a novel classification system using peroral cholangioscopy for the diagnosis of bile duct lesions. Endoscopy 2018, 50, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukasawa, Y.; Takano, S.; Fukasawa, M.; Maekawa, S.; Kadokura, M.; Shindo, H.; Takahashi, E.; Hirose, S.; Kawakami, S.; Hayakawa, H.; et al. Form-Vessel Classification of Cholangioscopy Findings to Diagnose Biliary Tract Carcinoma's Superficial Spread. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, A.; Tyberg, A.; Slivka, A.; Adler, D.; Desai, A.; Sejpal, D.; Pleskow, D.; Bertani, H.; Gan, S.-I.; Shah, R.; et al. Digital Single-operator Cholangioscopy (DSOC) Improves Interobserver Agreement (IOA) and Accuracy for Evaluation of Indeterminate Biliary Strictures: The Monaco Classification. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2022, 56, e94–e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Medranda, C.; Oleas, R.; Sánchez-Carriel, M.; Olmos, J.I.; Alcivar-Casquez, J.; Puga-Tejada, M.; Baquerizo-Burgos, J.; Icaza, I.; Pitanga-Lukashok, H. Vascularity can distinguish neoplastic from non-neoplastic bile duct lesions during digital single-operator cholangioscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahaleh, M.; Gaidhane, M.; Shahid, H.M.; Tyberg, A.; Sarkar, A.; Ardengh, J.C.; Kedia, P.; Andalib, I.; Gress, F.; Sethi, A.; et al. Digital single-operator cholangioscopy interobserver study using a new classification: The Mendoza Classification (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, A.; Doukides, T.; Sejpal, D.V.; Pleskow, D.K.; Slivka, A.; Adler, D.G.; Shah, R.J.; Edmundowics, S.A.; Itoi, T.; Petersen, B.T.; et al. Interobserver agreement for single operator choledochoscopy imaging: Can we do better? Diagn. Ther. Endosc. 2014, 2014, 730731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargeya, R.; Leng, T. Automated Identification of Diabetic Retinopathy Using Deep Learning. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.W.; Olgin, J.E.; Avram, R.; Abreau, S.A.; Sittler, T.; Radia, K.; Hsia, H.; Walters, T.; Lee, B.; Gonzalez, J.E.; et al. Performance of a Convolutional Neural Network and Explainability Technique for 12-Lead Electrocardiogram Interpretation. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Shi, H.; Zhang, H.; Meng, L.; Fan, M.; Han, C.; Zhang, K.; Ming, F.; Xie, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Gastroenterologist-Level Identification of Small-Bowel Diseases and Normal Variants by Capsule Endoscopy Using a Deep-Learning Model. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1044–1054.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, C.; Spadaccini, M.; Iannone, A.; Maselli, R.; Jovani, M.; Chandrasekar, V.T.; Antonelli, G.; Yu, H.; Areia, M.; Dinis-Riberio, M.; et al. Performance of artificial intelligence in colonoscopy for adenoma and polyp detection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 77–85.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Xia, T.; Pan, J.; Gao, F.; Wang, S.; Qian, Y.-Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, X.; Zou, W.-B.; et al. Use of artificial intelligence for detection of gastric lesions by magnetically controlled capsule endoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 133–139.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; Vanderplas, J.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn 2011, 12, 2825. [Google Scholar]
- Le Berre, C.; Sandborn, W.J.; Aridhi, S.; Devignes, M.-D.; Fournier, L.; Smail-Tabbone, M.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Application of Artificial Intelligence to Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 76–94.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.J.; Chen, J.H.; Xu, H.J.; Yu, Q.; Liu, R. Efficacy and Safety of Digital Single-Operator Cholangioscopy in the Diagnosis of Indeterminate Biliary Strictures by Targeted Biopsies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaneethan, U.; Hasan, M.K.; Kommaraju, K.; Zhu, X.; Hebert-Magee, S.; Hawes, R.H.; Vargo, J.J.; Varadarajulu, S.; Parsi, M.A. Digital, single-operator cholangiopancreatoscopy in the diagnosis and management of pancreatobiliary disorders: A multicenter clinical experience (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 84, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhou, Z.; Tian, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Fan, K.; Mao, Y.; Sun, G.; Yang, Y. Is single-operator peroral cholangioscopy a useful tool for the diagnosis of indeterminate biliary lesion? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 82, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njei, B.; McCarty, T.R.; Mohan, B.P.; Fozo, L.; Navaneethan, U. Artificial intelligence in endoscopic imaging for detection of malignant biliary strictures and cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2023, 36, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Medranda, C.; Baquerizo-Burgos, J.; Alcivar-Vasquez, J.; Kahaleh, M.; Raijman, I.; Kunda, R.; Puga-Tejada, M.; Egas-Izquierdo, M.; Arevalo-Mora, M.; Mendez, J.C.; et al. Artificial intelligence for diagnosing neoplasia on digital cholangioscopy: Development and multicenter validation of a convolutional neural network model. Endoscopy 2023, 55, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, D.; Zhou, J.D.; Ni, M.; Yan, P.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, T.; Zhan, Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, L.; et al. A real-time interpretable artificial intelligence model for the cholangioscopic diagnosis of malignant biliary stricture (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 98, 199–210.e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Ge, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, Q.; Luo, G.; Zheng, B.; Sha, M.; Shen, F.; Cheng, Q.; Sui, C.; et al. Latent Risk Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Susceptible to Adjuvant Treatment After Resection: A Clinical Deep Learning Approach. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, G.W.; Zhang, Y.D.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, F.-P.; Wang, K.; Xia, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Jiang, W.-J.; Li, X.-C.; Wang, X.-H. Biliary Tract Cancer at CT: A Radiomics-based Model to Predict Lymph Node Metastasis and Survival Outcomes. Radiology 2019, 290, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hao, X.; Gao, F.; Jiang, X. A Novel Prognostic Scoring System of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma With Machine Learning Basing on Real-World Data. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 576901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, F.; Huang, Q.; Wang, C.; Qiu, L.; Hu, Y.G.; Zha, S.Y. Artificial Neural Networking Model for the Prediction of Early Occlusion of Bilateral Plastic Stent Placement for Inoperable Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutan. Tech. 2018, 28, e54–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marya, N.B.; Powers, P.D.; Petersen, B.T.; Law, R.; Storm, A.; Abusaleh, R.R.; Rau, P.; Stead, C.; Levy, M.J.; Martin, J.; et al. Identification of patients with malignant biliary strictures using a cholangioscopy-based deep learning artificial intelligence (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 97, 268–278.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Mascarenhas, M.; Ribeiro, T.; Alfonso, J.; Ferreira, J.P.S.; Vilas-Boas, F.; Parente, M.P.L.; Jorge, R.N.; Macedo, G. Automatic detection of tumor vessels in indeterminate biliary strictures in digital single-operator cholangioscopy. Endosc. Int. Open 2022, 10, E262–E268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, Z. Non-iterative and Fast Deep Learning: Multilayer Extreme Learning Machines. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 8925–8955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Final Diagnosis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Malignant | Benign | ||
| CNN classification | Malignant | 6527 | 1673 |
| Benign | 1293 | 7823 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saraiva, M.M.; Ribeiro, T.; González-Haba, M.; Agudo Castillo, B.; Ferreira, J.P.S.; Vilas Boas, F.; Afonso, J.; Mendes, F.; Martins, M.; Cardoso, P.; et al. Deep Learning for Automatic Diagnosis and Morphologic Characterization of Malignant Biliary Strictures Using Digital Cholangioscopy: A Multicentric Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 4827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194827
Saraiva MM, Ribeiro T, González-Haba M, Agudo Castillo B, Ferreira JPS, Vilas Boas F, Afonso J, Mendes F, Martins M, Cardoso P, et al. Deep Learning for Automatic Diagnosis and Morphologic Characterization of Malignant Biliary Strictures Using Digital Cholangioscopy: A Multicentric Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(19):4827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194827
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaraiva, Miguel Mascarenhas, Tiago Ribeiro, Mariano González-Haba, Belén Agudo Castillo, João P. S. Ferreira, Filipe Vilas Boas, João Afonso, Francisco Mendes, Miguel Martins, Pedro Cardoso, and et al. 2023. "Deep Learning for Automatic Diagnosis and Morphologic Characterization of Malignant Biliary Strictures Using Digital Cholangioscopy: A Multicentric Study" Cancers 15, no. 19: 4827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194827
APA StyleSaraiva, M. M., Ribeiro, T., González-Haba, M., Agudo Castillo, B., Ferreira, J. P. S., Vilas Boas, F., Afonso, J., Mendes, F., Martins, M., Cardoso, P., Pereira, P., & Macedo, G. (2023). Deep Learning for Automatic Diagnosis and Morphologic Characterization of Malignant Biliary Strictures Using Digital Cholangioscopy: A Multicentric Study. Cancers, 15(19), 4827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194827








