Quality of Life, Clinical, and Patient-Reported Outcomes after Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy Delivered for Intracranial Grade WHO 1–2 Meningioma in Children and Adolescents
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Treatment Characteristics
3.3. Clinical and Patient-Reported Outcomes
4. Discussion
| Author Year Reference n. | n | FU (m) | Mean Age (y) (Range) M:F Ratio | Location/NF Status/ Resection (%)/WHO Grade | Radiation Therapy N (%)/Indication/Dose, Technique | Outcomes R Recurrence (%)/† Mortality (%)/ ° RT Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amirjamshidi 2000 [66] | 24 | 130.2 | 9.47 (2–17) 11:13 | 20 IC, 1 IO 5 NF (excluded) 21 GTR (87.5%) - | 1 (4.2%) Irresectable recurrence - | R: 6 (25%) † 1 (16.6%) - |
| Lund-Johansen 2001 [67] | 27 | - | 14.8 (0–20) 16:11 | 20 IC 5 NF 19 GTR (70.4%) 27 G1 (100%) | 3 (11.1%) Residual tumor, recurrence 2 GK, cRT | R: 8 (29.6%), 2 after GTR † 3 (11 %), 1 surgery-related - |
| Im 2001 [46] | 11 | 108 | 8 (0.5–14) 5:6 | 10 IC, 1 IO 1 NF 8 GTR (72.7%) - | 4 (36%) 2 residual and 2 recurrences GK, cRT | R: 3 (27.2%) † 1 (9%) °3 SD, 1 death not tumor-related. |
| Zwerdling 2002 [68] | 18 | 11 (1.6–17) 8:10 | 13 IC, 4 IO - 11 GTR (61%) 4 G3 (22%) | 4 (22.2%) 2 postoperative, 2 definitive - | R: 3 (16.6%) † 2 (11%) °2/4 died, after 4 and 16 m survival | |
| Rochat 2004 [44] | 22 | 192 | 5 (M),11.5 (F) (0–14) 8:14 | All IC 3 NF 15 GTR (68.2%) 20 G1 (90%) | 8 (36%) - - | R: 9 (40.9%) † 13/22 tumor-related (59%). OS rate 38%. - |
| Rushing 2005 [69] | 87 | 68.5 | 14 (0.42–20) 52:35 | 81 IC 9 NF2 53 GTR (62%) 62 G1 (71.3%), 21 G2, 4 G3 (4.6%) | 4 postoperative (4.6%) Residual tumor, recurrence - | R: 12 † 7/62 (11.3 %) ° 2/4 died |
| Tufan 2005 [47] | 11 | 72 | 12.7 (1.2–17) 6:5 | All IC 1 NF 8 GTR (73%) 6 G1 (54.5%), 2 G2, 3 G3 (4.6%) | 1 postoperative (9.1%) Recurrence - | R: 3 (27.2 %) † 3, (2 perioperative) - |
| Caroli 2006 [42] | 27 | 108 | 11.3 (0.5–16) 2.8:1 | - - 21 GTR (77.8%) 3 G3 (11.1%) | - | R: 13% † 1, preoperative - |
| Greene 2008 [70] | 20 | 20 | 13 (3–20) 11:9 | 15 IC, 2 IO 5 NF2 - 2 G3 (10%) | 4 (20%) - Median 59.4Gy (range 52.2–59.4) | R: 4 (20 %) † 3 (15 %), 1 tumor-related - |
| Arivazhagan 2008 [45] | 33 | 23.4 | 14.7 (5–18) 19:14 | 32 IC, 1 IO 3NF 22 GTR or near (66.7%) 29 G1 (87.9%), 2 G2, 2 G3 (6%) | 4 adjuvant (12%) Atypical incomplete resection and anaplastic - | R: 6 recurrences/regrowth (18.1%) † 3 (9%) - |
| Liu 2008 [7] | 12 | - | 9.9 (0.5–15) 1.4:1 | 12 IC 0 NF - 0 G3 | - | - † 3.3% (Including patients from 8 series reported in the literature) - |
| Harold Lee 2008 [19] | 14 | 150 | 13.8 (6–18) 8:6 | All ONS 4NF2 4 GTR (28.6%), 7 STR, 2 Bx, 1 none - | 3 (25%) 2 only biopsied, 1 after re-resection of recurrence Conformal RT | R: 7 (50%) alive with disease, 7 (50%) alive without disease † 0 ° 1 alive without disease (after 31y FU), 2 alive with disease (after 3m FU) |
| Gao 2009 [16] | 54 | 62.7 | 13.1 (2.8–18) 29:25 | 52 IC, 1 IO 5 NF2 39 GTR (72.2%) 18.5% G2–3 | 7 adjuvant (13%) Incomplete resection, anaplastic - | R: 10 (30.3 %) † 9 (16.6 %), 2 perioperative (3.7%) ° 3 recurrences (42.8%) |
| Li 2009 [71] | 34 | 48 | Med 10 (2–17) 29:30 | 34 IC - 20 GTR, 11 STR 6 (17.6%) G2–3 | 15 (44.1%) Residual, malignant, and recurrent tumors | R: 7 (20.5 %) † 6 (17.6 %) ° 3 recurrences (20%) |
| Menon 2009 [72] | 38 | 56.9 | 15.53 (2.5–<20) 20:18 | 31 IC, 2 IO 11 NF (28.9%), 2NF2 20 GTR (48.8%) 30 (73.2%) G1, 9 G2, 2 G3 (4.9%) | - Adjuvant therapy in G 2 and 3 variants - | R: 7 (18.4%). † 1 (2.6%). - |
| Mehta 2009 [41] | 18 | 73.2 | 12.81 (0.75–18) 1.57:1 | 18 IC 2 NF2 18 GTR (100%) 1 G3 (5.6%) | 4 postoperative (22.2%) Aggressive pathology - | R: 2 after 2 and 5 years (14.2%). † 1 perioperative (0.1%) - |
| Lakhdar 2010 [22] | 21 | 33 | 10.3 (2–16) 13:8 | 21 IC 1 NF 13 GTR (61.9%), 8 STR 6 G3 (28.6%) | 5 (23.8%) postoperative 4 Residual tumor, 1 after recurrence 50–60 Gy | R: 7 (33.3%) † 2 (9.5%) - |
| Thuijs 2012 [9] | 72 | 57.6 | 13 (0–18) 39:33 | 51 IC, 4 IO 13 NF2 (18%) 35 GTR (48.6%), 29 STR 53 G1 (73.6%), 13 G2, 6 G3 (8.3%) | 15 (20.8%) postoperative Recurrence, atypical, or malignant Mean dose 42.75 Gy (13–60) | R: 26 (36%) 12/46 (GTR) recurrences, 14/43 (STR) re-growths † 16.1% 1y OS 96% (n = 50) 5 y OS 83.9% (n = 31) 1y PFS 84.3% (n = 51) 5 y PFS 55.6% (n = 36) |
| Santos 2012 [73] | 15 | 60 | 12 (4–18) 9:6 | 14 IC 3 NF2 (20%) 14 GTR (93.3%) 11 G1 (73.3%), 4 G2 | 1 (6.6%) Recurrence SRS | R: 5 recurrences (33.3%), 4 re-operated - - |
| Wang 2012 [49] | 23 | 70 | 12.1 (2–18) 18:5 | 20 IC, 3 SP 3 NF2 (13%) 11 GTR, 11 STR, 1 missing 15 G2 (65%), 8 G3 (35%) | 9 (39.1%) - - | R: 10/20 (50%) in a mean time of 22.4m † 1 postoperatively, 2 lost FU 10y-PFS rate 54.5% 10 y-OS rate 63.3% ° 4/9 recurred (44.4%) |
| Ravindranath 2013 [43] | 31 | 46.2 | 14.15 (0.7–<18) 22:9 1:2.4 | All IC 2 NF2 (6%) 26 (83%) GTR, STR 5 20 G1 (64.5%), 11 G2–3 | 9 (29%) Higher grade and recurrence 45–50 Gy | R: 20 recurrences (64%), 15 after GTR. † 1 death (3%), 3 lost - |
| Grossbach 2017 [12] | 39 | - | 14.1±4.57 (1–20) 15:24 | 28 IC, 3 IO, 8 SP 8 NF (20.5%), 4 NF2 27 G1 (69.2%), 10 G2, 2 G3 (5.1%) | 13 (33.3%) Recurrences, aggressive pathology, multiplicity, STR and inoperability. Fractionated RT, 52.7–64.8Gy. 1 SRS. | R: 15/36 who underwent resection (42%) - - |
| Huntoon 2017 [13] | 15 | - | 12.8 (1–18) 6:9 | 14 IC, 1 SP - (excluded) - 8 G1 (53.3%), 5G2, 2 G3 (13.3%) | 2 (13.3%) G3 1 cRT, 1GK | - - ° 1 alive, 1 died. |
| Liu 2017 [23] | 19 | 40.9 | 14.7 (7–18) 9:10 | Infra-tentorial 2 NF2 GTR 14 (73.7%), 5 STR G2–3 (26.3%) | 8 (42%) 4 GK, 2 as primary treatment, 2 for recurrent/STR 4 cRT G2,3 | R: 5 (26.3%) - ° 2 cRT had quick recurrence |
| Wu 2017 [17] | 14 | 66.1 | 11.1 (4–16) 9:5 | 14 SP - (excluded) 11 GTR (78.6%), 2 STR, 1 PR 5 G2 | 3 (21.4%) Recurrences, following re-resection Dose not specified | R: 4 (28.6%). 1 after GTR, 3 in STR and PR. 4 in G1, 5 in G3. - °2 recurrences after re-resection + RT |
| Fan 2017 [74] | 32 | 48 | 13.7 (2–18) 17:15 1.13:1 | All IC - 19 GTR (48.7), 13 STR 16 G1 (50%), 5 G2, 11 G3 (34.4%) | 1 (3%) Recurrence Focal salvage RT | R: 9 (28.1%), 4 after GTR, 5 after STR † 1, 9 m after the diagnosis of recurrence - |
| Dudley 2018 [39] | 381 7464 51,303 | 35 | 0–21, 22–45, >45 | 328 IC (86.1%), 50 SP - 163 GTR (43.4%), 24 STR, 67 Bx, 122 any | 55 (14.6%) 883 (12.0%) 4313 (8.5%) | † 4.5% all-cause mortality 4.5% 24.6% |
| El Beltagy 2019 [11] | 39 | 38.5 | 8.19 21:18 | 36 IC, 3 SP 4 NF2 (10.2%) 28 GTR (71.8%), 8 STR, 3 Bx 16 G1 (41%), 11 G2, 12 G3 (30.8%) | 19 (48.7%) Higher grade (14 after GTR, 5 STR) - | R: 5-year EFS (event FS) 85.6% † 5 (12.8%, tumor-related) 5-year OS 87.8% ° 1 R 4m after GTR+RT |
| He 2020 [6] | 39 | 54.4 | Med 13 (1–18) 1.3:1 | 36 IC, 1 ONS, 2 IO 3NF, 1NF2 28 GTR (71.8%), 11 STR 26 G1 (66.7%), 10 G2, 3 G3 (7.9%) | 8 (20.5%) Residual tumor, high grade, recurrence GK | R: rate 41.9% mean time to R 20.2m (median 12m) 5 years EFS 55.1% - |
| Isikai 2020 [48] | 23 | 123.6 | 13.1 (-sd ±4.4) 12:11 | 19 IC, 4 SP 6 NF (26.1%), 5 NF2, 1 NF1 19 GTR (70.4%), 8 STR 15 G1 (56%), 9 G2, 3 G3 (13%) | 5 (21.7%) STR after recurrence | R: 10 (43.5%), 4 after GTR, 6 after STR † 3 (13%) 1y OS 91% 10y OS 86% - |
| Jain 2020 [75] | 37 | 24 | 14 (2.5–20) 20:17 | 31 IC, 6 SP 16% NF >50% GTR >50% G1 | 4 (10.8%) Residual tumor, high grade, recurrence | R: 8 (33.3%; re-surgery) - - |
| Thevandiran 2020 [14] | 10 | 60 | 10.5 (1–18) 4:6 | 9 IC, 1 SP 1 NF2, 1 NF1 7 GTR (70%), 3 STR 6 G1 (60%); 4 G2. | No RT | R: 1 (11.1%), after 12m - - |
| Liu 2021 [18] | 40 | 82.1 | 10.8 (0–15) 1:1.11 | 38 (95.2 %) IC, 1 ONS, 1 SP (2.4%) 0 NF (excluded) 35 GTR (83.3%), 7 STR (17.5%) 28 G1 (66.7%), 9 G2, 5 G3 (11.9%) | 2 (5%) G3 - | R: 9 (22.5%) † 5 (12.5%) - |
| Mishra 2022 [54] | 20/61 neoplasms in 40 children | 15 | 6–18 | - 14 NF2 - - | GK (12.55 Gy mean marginal dose) 6 primaries, 14 secondaries (after surgery/cRT) - | ° 6 reduced sizes, 14 SD - |
| Opoku 2022 [10] | 10 | 24 | 9.3 (4–16) 6:4 | 9 IC, 1 foramen magnum 0 NF (excluded) 10 (100%) GTR 3 G1 (12.5%), 4 G2, 3 G3 (12.5%) | No RT | R: 0 † 1 postoperative |
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Gittleman, H.; Patil, N.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2012–2016. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, V1–V100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; De Blank, P.M.; Kruchko, C.; Petersen, C.M.; Liao, P.; Finlay, J.L.; Stearns, D.S.; Wolff, J.E.; Wolinsky, Y.; Letterio, J.J.; et al. Alex’s Lemonade Stand Foundation Infant and Childhood Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2007–2011. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, x1–x35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; De Blank, P.M.; Finlay, J.L.; Gurney, J.G.; McKean-Cowdin, R.; Stearns, D.S.; Wolff, J.E.; Liu, M.; Wolinsky, Y.; et al. American Brain Tumor Association Adolescent and Young Adult Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2008–2012. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 18, i1–i50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toland, A.; McNulty, S.N.; Pekmezci, M.; Evenson, M.; Huntoon, K.; Pierson, C.R.; Boue, D.R.; Perry, A.; Dahiya, S. Pediatric Meningioma: A Clinicopathologic and Molecular Study with Potential Grading Implications. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirches, E.; Sahm, F.; Korshunov, A.; Bluecher, C.; Waldt, N.; Kropf, S.; Schrimpf, D.; Sievers, P.; Stichel, D.; Schüller, U.; et al. Molecular Profiling of Pediatric Meningiomas Shows Tumor Characteristics Distinct from Adult Meningiomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 142, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Liu, Z.; Teng, H.; Tang, L.; Jie, D.; Duan, Z.; Yu, H.; Xu, J. Pediatric Meningiomas: 10-Year Experience with 39 Patients. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 149, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Zhu, S.; Liu, M.; Wu, C. Clinical Features and Treatment of Meningiomas in Children: Report of 12 Cases and Literature Review. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2008, 44, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotecha, R.S.; Pascoe, E.M.; Rushing, E.J.; Rorke-Adams, L.B.; Zwerdling, T.; Gao, X.; Li, X.; Greene, S.; Amirjamshidi, A.; Kim, S.-K.; et al. Meningiomas in Children and Adolescents: A Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuijs, N.B.; Uitdehaag, B.M.J.; Van Ouwerkerk, W.J.R.; Van Der Valk, P.; Vandertop, W.P.; Peerdeman, S.M. Pediatric Meningiomas in the Netherlands 1974–2010: A Descriptive Epidemiological Case Study. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2012, 28, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, I.; Yang, L.; Sun, P.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Ren, J.; Du, J.; Feng, L.; Zeng, G. Pediatric Cerebral Meningioma: A Single-Center Study with 10 Children Not Associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 2 and Literature Review. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2023, 57, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Beltagy, M.A.; Enayet, A.E.; Atteya, M.M.E.; Reda, M.; Refaat, A.; Taha, H.; Ahmed, S.; Abdelaziz, A. Management of Pediatric CNS Meningiomas: CCHE-57357 Experience in 39 Cases. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2019, 35, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossbach, A.J.; Mahaney, K.B.; Menezes, A.H. Pediatric Meningiomas: 65-Year Experience at a Single Institution. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 20, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntoon, K.; Pluto, C.P.; Ruess, L.; Boué, D.R.; Pierson, C.R.; Rusin, J.A.; Leonard, J. Sporadic Pediatric Meningiomas: A Neuroradiological and Neuropathological Study of 15 Cases. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 20, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevandiran, D.; Nga, V.; Chang, K.T.E.; Ng, L.P.; Seow, W.T.; Low, D.C.Y.; Yeo, T.T.; Low, S.Y.Y. Paediatric Meningiomas in Singapore—Case Series of a Rare Entity. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 73, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdiçler, P.; Lena, G.; Sanoglu, A.C.; Kuday, C.; Choux, M. Intracranial Meningiomas in Children: Review Of 29 Cases. Surg. Neurol. 1998, 49, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, R.; Mao, Y.; Wang, Y. Childhood and Juvenile Meningiomas. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2009, 25, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Yang, C.; Liu, T.; Fang, J.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y. Clinical Features and Long-Term Outcomes of Pediatric Spinal Meningiomas. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, K.; Wang, J.; Shu, K. Clinical Features and Long-Term Outcomes of Pediatric Meningiomas. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2021, 37, 3041–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harold Lee, H.B.; Garrity, J.A.; Cameron, J.D.; Strianese, D.; Bonavolontà, G.; Patrinely, J.R. Primary Optic Nerve Sheath Meningioma in Children. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2008, 53, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traunecker, H.; Mallucci, C.; Grundy, R.; Pizer, B.; Saran, F. Children’s Cancer and Leukaemia Group (CCLG): Guidelines for the Management of Intracranial Meningioma in Children and Young People. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 22, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szychot, E.; Goodden, J.; Whitfield, G.; Curry, S. Children’s Cancer and Leukaemia Group (CCLG): Review and Guidelines for the Management of Meningioma in Children, Teenagers and Young Adults. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 34, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhdar, F.; Arkha, Y.; El Ouahabi, A.; Melhaoui, A.; Rifi, L.; Derraz, S.; El Khamlichi, A. Intracranial Meningioma in Children: Different from Adult Forms? A Series of 21 Cases. Neurochirurgie 2010, 56, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Luo, W.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y. Pediatric Infratentorial Meningiomas: A Series of 19 Cases and Review of the Literature. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2017, 33, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombi, B.; Ruggi, A.; Sardi, I.; Zucchelli, M.; Scagnet, M.; Toni, F.; Cammelli, S.; Giulietti, G.; Fabbri, V.P.; Gianno, F.; et al. Proton Therapy: A Therapeutic Opportunity for Aggressive Pediatric Meningioma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e28919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, P.S.; Tran, S.; Kroeze, S.G.C.; Pica, A.; Hrbacek, J.; Bachtiary, B.; Walser, M.; Leiser, D.; Lomax, A.J.; Weber, D.C. Outcomes of Adolescents and Young Adults Treated for Brain and Skull Base Tumors with Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, B.R.; Esiashvili, N.; Kim, S.; Weyman, E.A.; Thornton, L.T.; Mazewski, C.; MacDonald, T.; Ebb, D.; MacDonald, S.M.; Tarbell, N.J.; et al. Clinical Outcomes among Children with Standard-Risk Medulloblastoma Treated with Proton and Photon Radiation Therapy: A Comparison of Disease Control and Overall Survival the Study Was Presented in Oral Form at the Annual Meeting of International Society of Paediatric Oncology 2014 in Toronto, ON, Canada. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 94, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, L.M.; Grieco, J.A.; Evans, C.L.; Kuhlthau, K.A.; MacDonald, S.M.; Tarbell, N.J.; Yock, T.I.; Pulsifer, M.B. Executive Functioning, Academic Skills, and Quality of Life in Pediatric Patients with Brain Tumors Post-Proton Radiation Therapy. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 137, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, J.P.; Powell, S.; Zelko, F.; Hartsell, W.; Goldman, S.; Fangusaro, J.; Lulla, R.R.; Smiley, N.P.; Chang, J.H.C.; Gondi, V. Improved Neuropsychological Outcomes Following Proton Therapy Relative to X-Ray Therapy for Pediatric Brain Tumor Patients. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D. The Recurrence of Intracranial Meningiomas after Surgical Treatment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1957, 20, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Frei, M.; Buehrer, S.; Feurer, R.; Goitein, G.; Timmermann, B. Deep Propofol Sedation for Vacuum-Assisted Bite-Block Immobilization in Children Undergoing Proton Radiation Therapy of Cranial Tumors. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2007, 17, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torp, S.H.; Solheim, O.; Skjulsvik, A.J. The WHO 2021 Classification of Central Nervous System Tumours: A Practical Update on What Neurosurgeons Need to Know—A Minireview. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 2453–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.Y.; Bi, W.L.; Griffith, B.; Kaufmann, T.J.; La Fougère, C.; Schmidt, N.O.; Tonn, J.C.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Wen, P.Y.; Aldape, K.; et al. Imaging and Diagnostic Advances for Intracranial Meningiomas. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, I44–I61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganetti, H.; Niemierko, A.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Gerweck, L.E.; Goitein, M.; Loeffler, J.S.; Suit, H.D. Relative Biological Effectiveness (RBE) Values for Proton Beam Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 53, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, S.E.; Baumert, B.G.; Bendszus, M.; Bozzao, A.; Brada, M.; Fariselli, L.; Fiorentino, A.; Ganswindt, U.; Grosu, A.L.; Lagerwaard, F.L.; et al. ESTRO ACROP Guideline for Target Volume Delineation of Skull Base Tumors. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 156, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldbrunner, R.; Minniti, G.; Preusser, M.; Jenkinson, M.D.; Sallabanda, K.; Houdart, E.; von Deimling, A.; Stavrinou, P.; Lefranc, F.; Lund-Johansen, M.; et al. EANO Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Meningiomas. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e383–e391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Cancer Institute. Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program. Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_5x7.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours: Revised RECIST Guideline (Version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varni, J.W.; Seid, M.; Kurtin, P.S. PedsQLTM 4.0: Reliability and Validity of the Pediatric Quality of Life InventoryTM Version 4.0 Generic Core Scales in Healthy and Patient Populations. Med. Care 2001, 39, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, R.W.R.; Torok, M.R.; Randall, S.; Béland, B.; Handler, M.H.; Mulcahy-Levy, J.M.; Liu, A.K.; Hankinson, T.C. Pediatric versus Adult Meningioma: Comparison of Epidemiology, Treatments, and Outcomes Using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 137, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaeboe, L.; Lonn, S.; Scheie, D.; Auvinen, A.; Christensen, H.C.; Feychting, M.; Johansen, C.; Salminen, T.; Tynes, T. Incidence of Intracranial Meningiomas in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden, 1968–1997. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 117, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Bhagwati, S.; Parulekar, G. Meningiomas in Children: A Study of 18 Cases. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2009, 4, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroli, E.; Russillo, M.; Ferrante, L. Intracranial Meningiomas in Children: Report of 27 New Cases and Critical Analysis of 440 Cases Reported in the Literature. J. Child. Neurol. 2006, 21, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindranath, K.; Vasudevan, M.C.; Pande, A.; Symss, N. Management of Pediatric Intracranial Meningiomas: An Analysis of 31 Cases and Review of Literature. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2013, 29, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochat, P.; Hjorth Johannesen, H.; Gjerris, F. Long-Term Follow up of Children with Meningiomas in Denmark: 1935 to 1984. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2004, 100, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arivazhagan, A.; Devi, B.I.; Kolluri, S.V.R.; Abraham, R.G.; Sampath, S.; Chandramouli, B.A. Pediatric Intracranial Meningiomas—Do They Differ from Their Counterparts in Adults? Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2007, 44, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, S.H.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, S.K.; Oh, C.W.; Kim, D.G.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, N.R.; Chi, J.G.; Cho, B.K. Childhood Meningioma: Unusual Location, Atypical Radiological Findings, and Favorable Treatment Outcome. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2001, 17, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufan, K.; Dogulu, F.; Kurt, G.; Emmez, H.; Ceviker, N.; Baykaner, M.K. Intracranial Meningiomas of Childhood and Adolescence. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2005, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isikay, I.; Hanalioglu, S.; Narin, F.; Basar, I.; Bilginer, B. Long-Term Outcomes of Pediatric Meningioma Surgery: Single Center Experience with 23 Patients. Turk. Neurosurg. 2020, 30, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Jiang, C.C.; Zhao, L.; Gong, Y.; Hu, J.; Chen, H. Clinical Features and Treatment of World Health Organization Grade II and III Meningiomas in Childhood: Report of 23 Cases. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2012, 10, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, M.C.; Tsao-Wei, D.D.; Groshen, S. Temozolomide for Treatment-Resistant Recurrent Meningioma. Neurology 2004, 62, 1210–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, K.; Ung, T.H.; Damek, D.; Lillehei, K.O.; Ormond, D.R. Concomitant Temozolomide plus Radiotherapy for High-Grade and Recurrent Meningioma: A Retrospective Chart Review. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioka, C.; Kyritsis, A.P. Chemotherapy, Hormonal Therapy, and Immunotherapy for Recurrent Meningiomas. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 92, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Usami, K.; Hirokawa, D.; Ogiwara, H. Pediatric Meningiomas: A Report of 5 Cases and Review of Literature. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2019, 35, 2219–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, H.; Pahwa, B.; Agrawal, D.; Ch, M.S.M.; Ch, S.S.K.M. Gamma Knife Radiosurgery as an Efficacious Treatment for Paediatric Central Nervous System Tumours: A Retrospective Study of 61 Neoplasms. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2022, 38, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, D.C.; Bizzocchi, N.; Bolsi, A.; Jenkinson, M.D. Proton Therapy for Intracranial Meningioma for the Treatment of Primary/Recurrent Disease Including Re-Irradiation. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 558845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt Nabors, L.; Portnow, J.; Baehring, J.; Bhatia, A.; Bloch, O.; Brem, S.; Butowski, N.; Cannon, D.M.; Chao, S.; Chheda, M.G.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Version 1. 2023 Central Nervous System Cancers Continue NCCN Guidelines Panel Disclosures; National Comprehensive Cancer Network: Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Merchant, T.E.; Hua, C.H.; Shukla, H.; Ying, X.; Nill, S.; Oelfke, U. Proton versus Photon Radiotherapy for Common Pediatric Brain Tumors: Comparison of Models of Dose Characteristics and Their Relationship to Cognitive Function. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2008, 51, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulino, A.C.; Ludmir, E.B.; Grosshans, D.R.; Su, J.M.; McGovern, S.L.; Okcu, M.F.; McAleer, M.F.; Baxter, P.A.; Mahajan, A.; Chintagumpala, M.M. Overall Survival and Secondary Malignant Neoplasms in Children Receiving Passively Scattered Proton or Photon Craniospinal Irradiation for Medulloblastoma. Cancer 2021, 127, 3865–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatner, R.E.; Niemierko, A.; Misra, M.; Weyman, E.A.; Goebel, C.P.; Ebb, D.H.; Jones, R.M.; Huang, M.S.; Mahajan, A.; Grosshans, D.R.; et al. Endocrine Deficiency as a Function of Radiation Dose to the Hypothalamus and Pituitary in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients with Brain Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2854–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanathan, V.; Pradhan, K.; Eugster, E. Pituitary Hormone Dysfunction after Proton Beam Radiation Therapy in Children with Brain Tumors. Endocr. Pract. 2011, 17, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentieri, S.C.; Meyer, E.A.; Delaney, B.L.; Victoria, M.L.; Gannon, B.K.; Doyle, J.M.; Kieran, M.W. Psychosocial and Behavioral Functioning among Pediatric Brain Tumor Survivors. J. Neurooncol. 2003, 63, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.A.; Steele, R.G.; Herrera, E.A.; Phipps, S. Parent and Child Reporting of Negative Life Events: Discrepancy and Agreement across Pediatric Samples. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2003, 28, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kroeze, S.G.C.; Mackeprang, P.-H.; De Angelis, C.; Pica, A.; Bachtiary, B.; Kliebsch, U.L.; Weber, D.C.; Korevaar, E.; Van Der Schaaf, A.; Conti, A. A Prospective Study on Health-Related Quality of Life and Patient-Reported Outcomes in Adult Brain Tumor Patients Treated with Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, H.; Fukushima, T.; Suzuki, R.; Iwabuchi, A.; Hidaka, K.; Shinkai, T.; Masumoto, K.; Muroi, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Nakao, T.; et al. Comorbidity and Quality of Life in Childhood Cancer Survivors Treated with Proton Beam Therapy. Pediatr. Int. 2017, 59, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlthau, K.A.; Pulsifer, M.B.; Yeap, B.Y.; Morales, D.R.; Delahaye, J.; Hill, K.S.; Ebb, D.; Abrams, A.N.; MacDonald, S.M.; Tarbell, N.J.; et al. Prospective Study of Health-Related Quality of Life for Children with Brain Tumors Treated with Proton Radiotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirjamshidi, A.; Mehrazin, M.; Abbassioun, K. Meningiomas of the Central Nervous System below the Age of 17: Report of 24 Cases Not associated with Neurofibromatosis and Review of Literature. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2000, 16, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund-Johansen, M.; Scheie, D.; Muller, T.; Lundar, T.; Helseth, E. Neurosurgical Treatment of Meningiomas in Children and Young Adults. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2001, 17, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwerdling, T.; Dothage, J. Meningiomas in Children and Adolescents. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2002, 24, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushing, E.J.; Olsen, C.; Mena, H.; Rueda, M.-E.; Lee, Y.-S.; Keating, R.F.; Packer, R.J.; Santi, M. Central Nervous System Meningiomas in the First Two Decades of Life: A Clinicopathological Analysis of 87 Patients. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 103, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, S.; Nair, N.; Ojemann, J.G.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; Avellino, A.M. Meningiomas in Children. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2007, 44, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, J. Intracranial Meningiomas of Childhood and Adolescence: Report of 34 Cases with Follow-Up. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2009, 25, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, G.; Nair, S.; Sudhir, J.; Rao, B.R.M.; Mathew, A.; Bahuleyan, B. Childhood and Adolescent Meningiomas: A Report of 38 Cases and Review of Literature. Acta Neurochir. 2009, 151, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.V.; Furlanetti, L.; Valera, E.T.; Brassesco, M.S.; Tone, L.G.; De Oliveira, R.S. Pediatric Meningiomas: A Single-Center Experience with 15 Consecutive Cases and Review of the Literature. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2012, 28, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.C.; Fang, W.; Liu, K.; Wang, C.; Deng, W.S.; Sun, P.; Tang, W.Z. Paediatric Intracranial Meningiomas: Eight-Year Experience with 32 Cases. Chin. Neurosurg. J. 2017, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Muzumdar, D.; Shah, A.; Goel, A. A Treatise on Pediatric Meningiomas: Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Experience and Review of Literature. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2020, 15, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Case ID | Symptoms | Main Cause | Irradiated Tumor Site |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Behavior changes | Tumor-related | Right clinoid process |
| 2 | Decline in school performance Left-sided exophthalmos Left-sided severe hearing loss * Right-sided distal radial paresis * Right-sided visual impairment ~ | Tumor-related | Left retro-bulbar/pterygoid |
| 3 | Left-sided exophthalmos and ptosis Left-sided trigeminal palsy with secondary left corneal dystrophy | Both tumor- and surgery-related | Left cavernous sinus, cerebellopontine angle and left temporal region |
| 4 | Seizures Left-sided hemiparesis with the need of orthopedic cast for walking and wheelchair for long distances Right-sided VI and VII cranial nerves palsy Communication skills impaired | Surgery-related | Right posterior fossa and cerebellopontine angle |
| 5 | Left-sided limited gaze elevation in adduction Left-sided temporal visual field defect Right-sided amaurosis | Tumor-related | Suprasellar |
| 6 | Right-sided VII palsy Right-sided postoperative deafness Right-sided hemiplegia with the need for a lower limb cast for long distances * | Both tumor- and surgery-related | Right cerebellopontine angle |
| 7 | Left-sided visual impairment Left-sided exophthalmos and ptosis Diplopia Left-sided mild neurosensory hearing loss * | Tumor-related | Left optic nerve sheath |
| 8 | Hearing impairment Decreased sensitivity in the right territory of V3 | Tumor-related | Right cavum Meckel, petrous bone, prepontine cistern |
| 9 | Left-sided hearing loss | Tumor-related | Left carotid space, jugular foramen, middle ear, and auditory canal |
| 10 | None | - | Right parietal |
| ID | Sex | Age (Y) | Location | NF2 | WHO Grade | Simpson Resection | T Intent | Dose (GyRBE) fr (n) | GTV (cc) | PTV (cc) | FU Time (m) | Acute Tox, Grade | Late Tox, Grade | Time to LF (m) | LF (Type) | Salvage Therapy | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 7 | Skull base | No | 2 | IV | Postop. | 64.0 32 | 32.2 | 81.4 | 249.7 | Alopecia, 1 Dermatitis, 1 | Hypopituitarism, 1 Endocrinol other, 1 | 55.4 | Yes (in-field) | Hydroxyurea (Litalir) | Alive |
| 2 | M | 13 | Optic nerve sheath | Yes | 2 | IV | Postop. | 54.0 30 | 46.2 | 101.0 | 175.3 | Dermatitis, 2 Conjunctivitis, 1 | Cataract, 3 Hypopituitarism, 2 | 51.8 | Yes (marginal) | Four debulking surgeries 45 Gy in 25 fractions of 1.8 Gy Bevacizumab (Avastin) | Alive |
| 3 | F | 3 | Skull base | No | 1 | IV | Postop. | 59.4 33 | 9.7 | 36.7 | 132.7 | Alopecia, 1 Appetite loss, 1 | Hypopituitarism, 2 | 32.4 | Yes (in-field) | Surgery | Alive |
| 4 | M | 6 | Skull base | No | 2 | IV | Postop. | 57.6 32 | 24.5 | 58.2 | 127.1 | Alopecia, 1 Dermatitis, 1 | Hearing loss, 1 Hypopituitarism, 2 | No | Death * | ||
| 5 | M | 4 | Skull base | No | 2 | IV | Postop. | 61.2 34 | 30.5 | 70.9 | 104.4 | No | Hypopituitarism, 2 Vascular, 2 | 28.4 | Yes (in-field) | Avastin/Irinotecan Sandostatin Sunitinib Temodal Embolization + surgery TTF/Optune | Alive |
| 6 | M | 14 | Skull base | Yes | 2 | IV | Savage | 59.4 33 | 34.4 | 170.2 | 37.8 | Alopecia, 1 Fatigue, 1 Nausea, 2 | No | No | Alive | ||
| 7 | M | 17 | Optic nerve sheath | Yes | NA | NA | Definitive | 50.4 28 | 9.6 | 27.5 | 26.0 | Conjunctivitis, 1 | Alopecia, 1 | No | Alive | ||
| 8 | F | 15 | Skull base | No | 2 | IV | Savage | 60.0 30 | 5.8 | 64.7 | 17.7 | Alopecia, 1 | Alopecia, 1 | 17.7 | Yes (in-field) | GK, 16 Gy to 53% isodose | Alive |
| 9 | M | 16 | Skull base | No | 1 | V | Definitive | 50.4 28 | 241.7 | 528.2 | 5.8 | Dermatitis, 2 Oral mucositis, 2 | No | No | Alive | ||
| 10 | M | 14 | Convexity | No | 2 | IV | Postop. | 59.4 33 | 142.3 | 454.0 | 2.5 | Alopecia, 2 Dermatitis, 1 Fatigue, 1 | No | Alive |
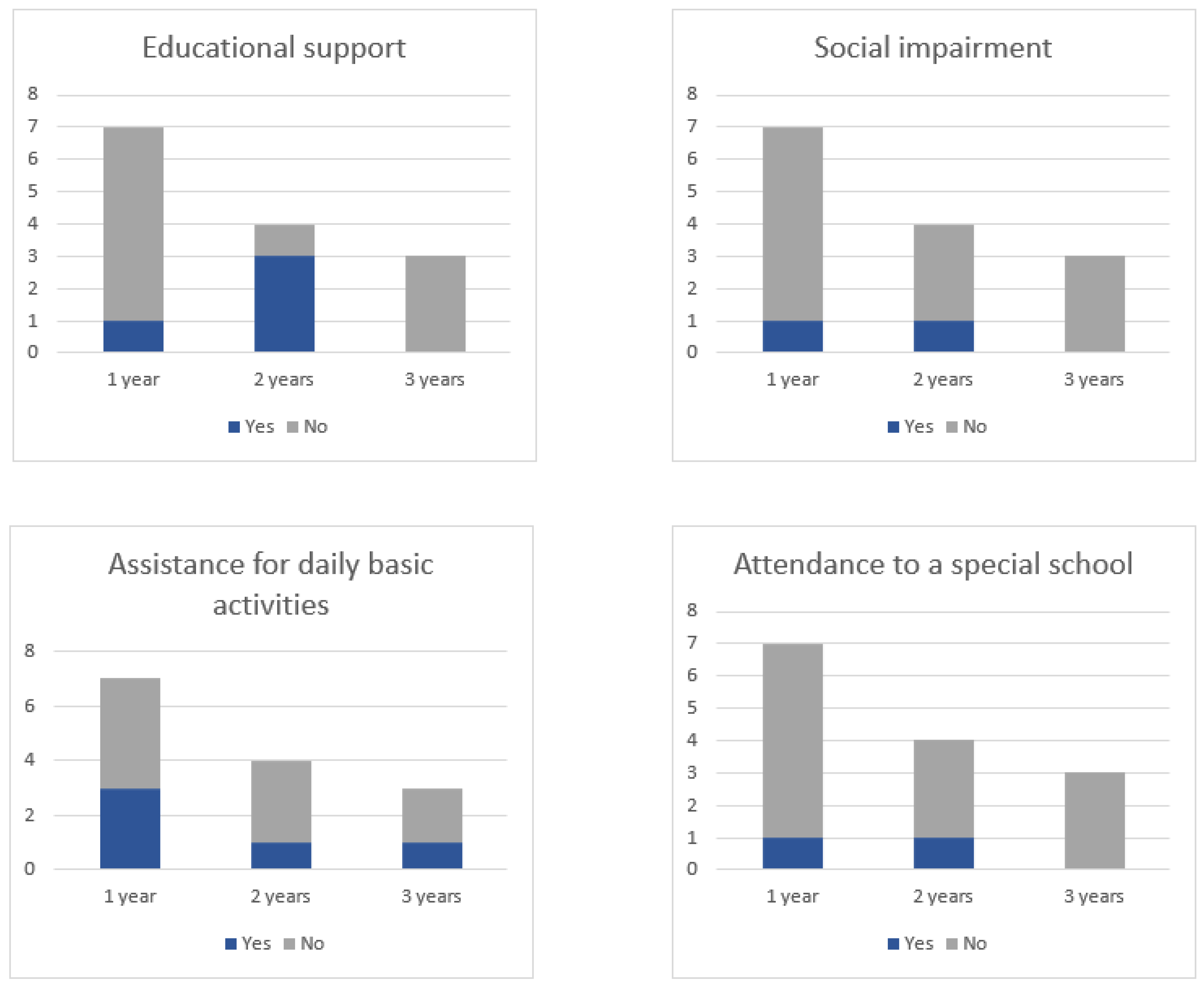
| ID | Educational Support | Special School | Social Impairment | Assistance for DBA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No | No | Yes | No |
| 2 | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| 3 | Yes | No | No | No |
| 4 | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| 5 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 6 | No | No | No | No |
| 7 | No | No | No | No |
| 8 | No | No | No | No |
| 9 | No | No | No | Yes |
| 10 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Marqueta, M.; Vázquez, M.; Krcek, R.; Kliebsch, U.L.; Baust, K.; Leiser, D.; van Heerden, M.; Pica, A.; Calaminus, G.; Weber, D.C. Quality of Life, Clinical, and Patient-Reported Outcomes after Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy Delivered for Intracranial Grade WHO 1–2 Meningioma in Children and Adolescents. Cancers 2023, 15, 4447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184447
García-Marqueta M, Vázquez M, Krcek R, Kliebsch UL, Baust K, Leiser D, van Heerden M, Pica A, Calaminus G, Weber DC. Quality of Life, Clinical, and Patient-Reported Outcomes after Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy Delivered for Intracranial Grade WHO 1–2 Meningioma in Children and Adolescents. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184447
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Marqueta, Marta, Miriam Vázquez, Reinhardt Krcek, Ulrike L. Kliebsch, Katja Baust, Dominic Leiser, Michelle van Heerden, Alessia Pica, Gabriele Calaminus, and Damien C. Weber. 2023. "Quality of Life, Clinical, and Patient-Reported Outcomes after Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy Delivered for Intracranial Grade WHO 1–2 Meningioma in Children and Adolescents" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184447
APA StyleGarcía-Marqueta, M., Vázquez, M., Krcek, R., Kliebsch, U. L., Baust, K., Leiser, D., van Heerden, M., Pica, A., Calaminus, G., & Weber, D. C. (2023). Quality of Life, Clinical, and Patient-Reported Outcomes after Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy Delivered for Intracranial Grade WHO 1–2 Meningioma in Children and Adolescents. Cancers, 15(18), 4447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184447







