Association of Metabolic Syndrome with the Risk of Head and Neck Cancer: A 10-Year Follow-Up Study of 10 Million Initially Healthy Individuals
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Data
2.2. Patient Selection
2.3. Definition of Metabolic Syndrome
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characteristics
3.2. Associations between Metabolic Syndrome and Head and Neck Cancer
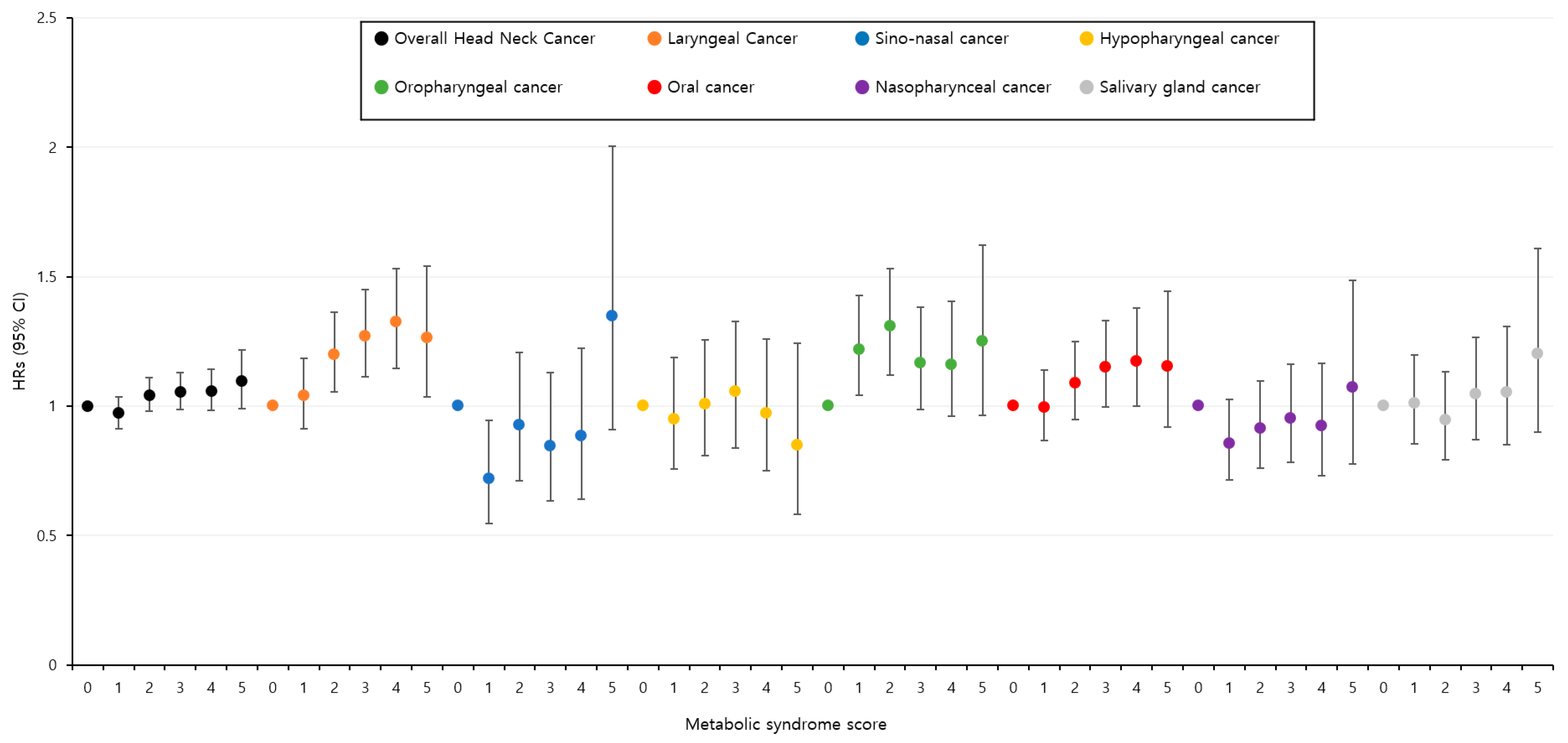
3.3. Association between Individual Components of Metabolic Syndrome and Head and Neck Cancer
3.4. Associations between Other Risk Factors and Head and Neck Cancer
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellastella, G.; Scappaticcio, L.; Esposito, K.; Giugliano, D.; Maiorino, M.I. Metabolic syndrome and cancer: “the common soil hypothesis”. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 143, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Reynolds, K.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Duan, X.; Reynolds, R.F.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. InterASIA Collaborative Group. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome and overweight among adults in China. Lancet 2005, 365, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Chiodini, P.; Colao, A.; Lenzi, A.; Giugliano, D. Metabolic syndrome and risk of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2402–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashibe, M.; Brennan, P.; Benhamou, S.; Castellsague, X.; Chen, C.; Curado, M.P.; Dal Maso, L.; Daudt, A.W.; Fabianova, E.; Fernandez, L.; et al. Alcohol drinking in never users of tobacco, cigarette smoking in never drinkers, and the risk of head and neck cancer: Pooled analysis in the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology Consortium. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 16, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubin, J.H.; Gaudet, M.M.; Olshan, A.F.; Kelsey, K.; Boffetta, P.; Brennan, P.; Castellsague, X.; Chen, C.; Curado, M.P.; Maso, L.D.; et al. Body mass index, cigarette smoking, and alcohol consumption and cancers of the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx: Modeling odds ratios in pooled case-control data. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 171, 1250–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudet, M.M.; Olshan, A.F.; Chuang, S.C.; Berthiller, J.; Zhang, Z.F.; Lissowska, J.; Zaridze, D.; Winn, D.M.; Wei, Q.; Talamini, R.; et al. Body mass index and risk of head and neck cancer in a pooled analysis of case-control studies in the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology (INHANCE) Consortium. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maasland, D.H.E.; Brandt, P.A.V.D.; Kremer, B.; Schouten, L.J. Body mass index and risk of subtypes of head-neck cancer: The Netherlands Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudet, M.M.; Patel, A.V.; Sun, J.; Hildebrand, J.S.; McCullough, M.L.; Chen, A.Y.; Gapstur, S.M. Prospective studies of body mass index with head and neck cancer incidence and mortality. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2012, 21, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, F.; Cortellini, A.; Indini, A.; Tomasello, G.; Ghidini, M.; Nigro, O.; Salati, M.; Dottorini, L.; Iaculli, A.; Varricchio, A.; et al. Association of Obesity with Survival Outcomes in Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e213520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J.; Chang, Y.C.; Cheng, T.Y.; Lo, K.; Liu, S.J.; Yeh, T.L. The association between metabolically healthy obesity and risk of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e13049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, H.M.; Lin, J.T.; Shun, C.T.; Liang, J.T.; Lee, Y.C.; Huang, S.P.; Wu, M.S. Association of metabolic syndrome with proximal and synchronous colorectal neoplasm. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laukkanen, J.A.; Laaksonen, D.E.; Niskanen, L.; Pukkala, E.; Hakkarainen, A.; Salonen, J.T. Metabolic syndrome and the risk of prostate cancer in Finnish men: A population-based study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2004, 13, 1646–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund Håheim, L.; Wisløff, T.F.; Holme, I.; Nafstad, P. Metabolic syndrome predicts prostate cancer in a cohort of middle-aged Norwegian men followed for 27 years. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 164, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasanisi, P.; Berrino, F.; De Petris, M.; Venturelli, E.; Mastroianni, A.; Panico, S. Metabolic syndrome as a prognostic factor for breast cancer recurrences. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.T.; He, H.; Yu, K.; Xie, J.; Lei, M.; Ma, R.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z. The association between thyroid cancer and insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and its components: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 57, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, X.; Han, Y.; Teng, W.; Shan, Z. Correlation Between Thyroid Nodules and Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 730279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça, F.M.; de Sousa, F.R.; Barbosa, A.L.; Martins, S.C.; Araújo, R.L.; Soares, R.; Abreu, C. Metabolic syndrome and risk of cancer: Which link? Metabolism 2015, 64, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S. Introduction: Health of the health care system in Korea. Soc. Work Public Health 2010, 25, 127–141. [Google Scholar]
- Yhim, H.Y.; Jang, M.J.; Bang, S.M.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Nam, S.H.; Bae, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Mun, Y.C.; Kim, I.; et al. Incidence of venous thromboembolism following major surgery in Korea: From the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service database. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J. Metabolic syndrome--a new world-wide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renehan, A.G.; Frystyk, J.; Flyvbjerg, A. Obesity and cancer risk: The role of the insulin-IGF axis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 17, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Choi, M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Han, K.; Kim, B.; Kim, D.H.; Park, Y.G. Metabolic Syndrome and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Thyroid 2020, 30, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berstein, L.M. Modern approach to metabolic rehabilitation of cancer patients: Biguanides (phenformin and metformin) and beyond. Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, P.P.; Fan, S.H.; Say, Y.H. Screening of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) alpha, gamma and alpha Gene Polymorphisms for Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome Association in the Multi-Ethnic Malaysian Population. Ethn. Dis. 2015, 25, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunusova, N.V.; Spirina, L.V.; Frolova, A.E.; Afanas’ev, S.G.; Kolegova, E.S.; Kondakova, I.V. Association of IGFBP-6 expression with metabolic syndrome and adiponectin and IGF-IR receptor levels in colorectal cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 3963–3969. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Teng, F.; Tian, W.; Yang, W.; Yan, Y.; Xue, F. Visfatin stimulates endometrial cancer cell proliferation via activation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK1/2 signalling pathways. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 143, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Tian, J.; Lv, Y.; Shi, F.; Kong, F.; Shi, H.; Zhao, L. Leptin induces functional activation of cyclooxygenase-2 through JAK2/STAT3, MAPK/ERK, and PI3K/AKT pathways in human endometrial cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott-Miller, M.; Chen, C.; Chuang, S.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Boccia, S.; Brenner, H.; Cadoni, G.; Dal Maso, L.; La Vecchia, C.; Lazarus, P.; et al. History of diabetes and risk of head and neck cancer: A pooled analysis from the international head and neck cancer epidemiology consortium. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2012, 21, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wideroff, L.; Gridley, G.; Mellemkjaer, L.; Chow, W.H.; Linet, M.; Keehn, S.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Olsen, J.H. Cancer incidence in a population-based cohort of patients hospitalized with diabetes mellitus in Denmark. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1997, 89, 1360–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suba, Z. Gender-related hormonal risk factors for oral cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2007, 13, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, E.; Messerli, F.H.; Boyko, V.; Goldbourt, U. Is there an association between hypertension and cancer mortality? Am. J. Med. 2002, 112, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weikert, S.; Boeing, H.; Pischon, T.; Weikert, C.; Olsen, A.; Tjonneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Becker, N.; Linseisen, J.; Trichopoulou, A.; et al. Blood pressure and risk of renal cell carcinoma in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 167, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidayat, K.; Du, X.; Zou, S.Y.; Shi, B.M. Blood pressure and kidney cancer risk: Meta-analysis of prospective studies. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, Q.N.; Drummond, G.R.; Sobey, C.G.; Chrissobolis, S. Roles of inflammation, oxidative stress, and vascular dysfunction in hypertension. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 406960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radoï, L.; Paget-Bailly, S.; Cyr, D.; Papadopoulos, A.; Guida, F.; Tarnaud, C.; Menvielle, G.; Schmaus, A.; Cénée, S.; Carton, M.; et al. Body mass index, body mass change, and risk of oral cavity cancer: Results of a large population-based case-control study, the ICARE study. Cancer Causes Control 2013, 24, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.S.; Park, J.O.; Nam, I.C.; Park, S.J.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.B.; Han, K.D.; Joo, Y.H. Associations of Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference with the Risk of Head and Neck Cancer: A National Population-Based Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Overall Head and Neck Cancer, No. (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Yes (n = 10,732) | No (n = 9,587,353) | p-Value |
| Age (years) | <0.001 | ||
| <40 | 744 (6.9) | 3,029,454 (31.6) | |
| 40–64 | 6547 (61) | 5,336,521 (55.7) | |
| ≥65 | 3441 (32.1) | 1,221,378 (12.7) | |
| Gender | <0.001 | ||
| Male | 8500 (79.2) | 5,212,301 (54.4) | |
| Female | 2232 (20.8) | 4,375,052 (45.6) | |
| Smoking status | <0.001 | ||
| Non-smoker | 4273 (39.8) | 5,768,089 (60.2) | |
| Ex-smoker | 2239 (20.9) | 1,323,213 (13.8) | |
| Current smoker | 4220 (39.3) | 2,496,051 (26) | |
| Drinking status | <0.001 | ||
| Non-drinker | 4726 (44) | 4,934,585 (51.5) | |
| Mild drinker | 4441 (41.4) | 3,888,132 (40.5) | |
| Heavy drinker | 1565 (14.6) | 764,636 (8) | |
| Regular exercise | 2263 (21.1) | 1,706,149 (17.8) | <0.001 |
| Low income | 2199 (20.5) | 1,875,717 (19.6) | 0.016 |
| Diabetes | 1728 (16.1) | 828,911 (8.7) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 4618 (43) | 2,462,226 (25.7) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia | 2491 (23.2) | 1,733,875 (18.1) | <0.001 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.69 | 23.7 | 0.812 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 83.16 | 80.2 | <0.001 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 127.13 | 122.42 | <0.001 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 78.43 | 76.31 | <0.001 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 102.69 | 97.23 | <0.001 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 55.49 | 56.5 | 0.002 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 126.8 (125.45–128.17) | 112.66 (112.62–112.7) | <0.001 |
| Metabolic syndrome score | <0.001 | ||
| 0 | 1617 (15.1) | 2,604,250 (27.2) | |
| 1 | 2519 (23.5) | 2,592,085 (27) | |
| 2 | 2684 (25) | 1,999,486 (20.9) | |
| 3 | 2107 (19.6) | 1,362,223 (14.2) | |
| 4 | 1317 (12.2) | 769,221 (8) | |
| 5 | 488 (4.6) | 260,088 (2.7) | |
| Cancer | Metabolic Syndrome | No. of Patients | Person- Years | Incidence Rates | Hazard Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||||
| Head and neck cancer | |||||||
| Yes | 3912 | 19,527,470 | 0.2 | 1.75 (1.68–1.82) | 1.07 (1.03–1.11) | 1.06 (1.01–1.10) | |
| No | 6820 | 59,435,425 | 0.115 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | |
| Oral cavity cancer | |||||||
| Yes | 825 | 19,536,667 | 0.018 | 1.80 (1.65–1.96) | 1.13 (1.04–1.24) | 1.12 (1.03–1.23) | |
| No | 1400 | 59,451,603 | 0.023 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | |
| Salivary gland cancer | |||||||
| Yes | 434 | 19,537,796 | 0.022 | 1.58 (1.40–1.77) | 1.10 (0.97–1.24) | 1.09 (0.96–1.23) | |
| No | 839 | 59,453,425 | 0.014 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | |
| Nasopharyngeal cancer | |||||||
| Yes | 357 | 19,538,140 | 0.018 | 1.46 (1.28–1.65) | 1.05 (0.92–1.20) | 1.05 (0.92–1.19) | |
| No | 744 | 59,453,685 | 0.012 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | |
| Oropharyngeal cancer | |||||||
| Yes | 615 | 19,537,376 | 0.031 | 1.56 (1.42–1.72) | 0.98 (0.89–1.09) | 0.97 (0.88–1.08) | |
| No | 1199 | 59,452,193 | 0.02 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | |
| Hypopharyngeal cancer | |||||||
| Yes | 348 | 19,538,399 | 0.017 | 1.82 (1.59–2.08) | 1.02 (0.89–1.17) | 1.02 (0.89–1.17) | |
| No | 581 | 59,454,974 | 0.01 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | |
| Sinonasal cancer | |||||||
| Yes | 194 | 19,538,730 | 0.01 | 1.71 (1.43–2.04) | 1.08 (0.90–1.29) | 1.06 (0.89–1.27) | |
| No | 345 | 59,455,278 | 0.006 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | |
| Laryngeal cancer | |||||||
| Yes | 1190 | 19,535,161 | 0.061 | 2.03 (1.89–2.19) | 1.18 (1.09–1.27) | 1.18 (1.09–1.27) | |
| No | 1782 | 59,450,381 | 0.03 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | |
| No. of Patients | Person-Years | Incidence Rates | Hazard Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||
| High waist circumference | ||||||
| Yes | 2718 | 15,436,055 | 0.176 | 1.40 (1.34–1.46) | 1.01 (0.97–1.06) | 1.01 (0.97–1.06) |
| No | 8014 | 63,526,839 | 0.126 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| High fasting glucose | ||||||
| Yes | 4590 | 24,537,413 | 0.187 | 1.66 (1.60–1.72) | 1.05 (1.01–1.09) | 1.04 (1.00–1.08) |
| No | 6142 | 54,425,482 | 0.113 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| High blood pressure | ||||||
| Yes | 6568 | 34,137,709 | 0.192 | 2.07 (1.99–2.15) | 1.09 (1.05–1.14) | 1.08 (1.04–1.13) |
| No | 4164 | 44,825,185 | 0.093 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| High triglycerides | ||||||
| Yes | 4756 | 27,591,045 | 0.172 | 1.48 (1.43–1.54) | 1.07 (1.03–1.11) | 1.02 (0.99–1.06) |
| No | 5976 | 51,371,849 | 0.116 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| Low HDL cholesterol | ||||||
| Yes | 3284 | 21,603,446 | 0.152 | 1.17 (1.12–1.22) | 1.02 (0.97–1.06) | 1.03 (0.99–1.08) |
| No | 7448 | 57,359,448 | 0.13 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| Parameter | Metabolic Syndrome | Number | Event | Person-Years | Incidence Rates | Hazard Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ||||||
| <40 | Yes | 342,900 | 116 | 2,836,339 | 0.041 | 1.13 (0.92–1.38) |
| No | 2,687,298 | 628 | 22,312,742 | 0.028 | 1 (reference) | |
| 40–64 | Yes | 1,465,717 | 2297 | 12,109,039 | 0.19 | 1.05 (0.10–1.10) |
| No | 3,877,351 | 4250 | 32,159,366 | 0.132 | 1 (reference) | |
| ≥65 | Yes | 586,827 | 1499 | 4,582,091 | 0.327 | 1.05 (0.98–1.12) |
| No | 637,992 | 1942 | 4,963,316 | 0.391 | 1 (reference) | |
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | Yes | 1,393,195 | 3094 | 11,302,299 | 0.274 | 1.08 (1.03–1.13) |
| No | 3,827,606 | 5406 | 31,429,032 | 0.172 | 1 (reference) | |
| Female | Yes | 1,002,249 | 818 | 8,225,170 | 0.099 | 1.17 (1.06–1.28) |
| No | 3,375,035 | 1414 | 28,006,392 | 0.051 | 1 (reference) | |
| Never- or ex-smoker | ||||||
| Yes | Yes | 1,770,124 | 2474 | 14,454,066 | 0.171 | 1.09 (1.04–1.15) |
| No | 5,327,690 | 4038 | 44,049,312 | 0.092 | 1 (reference) | |
| No | Yes | 625,320 | 1438 | 5,073,403 | 0.283 | 1.05 (0.99–1.12) |
| No | 1,874,951 | 2782 | 15,386,112 | 0.181 | 1 (reference) | |
| Non- or mild drinker | ||||||
| Yes | Yes | 2,154,161 | 3309 | 17,562,691 | 0.188 | 1.07 (1.02–1.12) |
| No | 6,677,723 | 5858 | 55,128,638 | 0.106 | 1 (reference) | |
| No | Yes | 241,283 | 603 | 1,964,778 | 0.307 | 1.03 (0.93–1.14) |
| No | 524,918 | 962 | 4,306,786 | 0.223 | 1 (reference) | |
| Regular exercise | ||||||
| Yes | Yes | 454,650 | 846 | 3,725,877 | 0.227 | 1.07 (0.98–1.17) |
| No | 1,253,762 | 1417 | 10,369,431 | 0.137 | 1 (reference) | |
| No | Yes | 1,940,794 | 3066 | 15,801,592 | 0.194 | 1.05 (1.00–1.10) |
| No | 5,948,879 | 5403 | 49,065,993 | 0.11 | 1 (reference) | |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | ||||||
| <25 | Yes | 943,413 | 1905 | 7,612,933 | 0.25 | 1.13 (1.07–1.19) |
| No | 5,523,085 | 5342 | 45,536,885 | 0.117 | 1 (reference) | |
| ≥25 | Yes | 1,452,031 | 2007 | 11,914,537 | 0.17 | 1.09 (1.01–1.16) |
| No | 1,679,556 | 1478 | 13,898,539 | 0.106 | 1 (reference) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, G.-J.; Han, K.-D.; Joo, Y.-H. Association of Metabolic Syndrome with the Risk of Head and Neck Cancer: A 10-Year Follow-Up Study of 10 Million Initially Healthy Individuals. Cancers 2023, 15, 4118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164118
Kim G-J, Han K-D, Joo Y-H. Association of Metabolic Syndrome with the Risk of Head and Neck Cancer: A 10-Year Follow-Up Study of 10 Million Initially Healthy Individuals. Cancers. 2023; 15(16):4118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164118
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Geun-Jeon, Kyung-Do Han, and Young-Hoon Joo. 2023. "Association of Metabolic Syndrome with the Risk of Head and Neck Cancer: A 10-Year Follow-Up Study of 10 Million Initially Healthy Individuals" Cancers 15, no. 16: 4118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164118
APA StyleKim, G.-J., Han, K.-D., & Joo, Y.-H. (2023). Association of Metabolic Syndrome with the Risk of Head and Neck Cancer: A 10-Year Follow-Up Study of 10 Million Initially Healthy Individuals. Cancers, 15(16), 4118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164118






