Plexins as Regulators of Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasivity
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
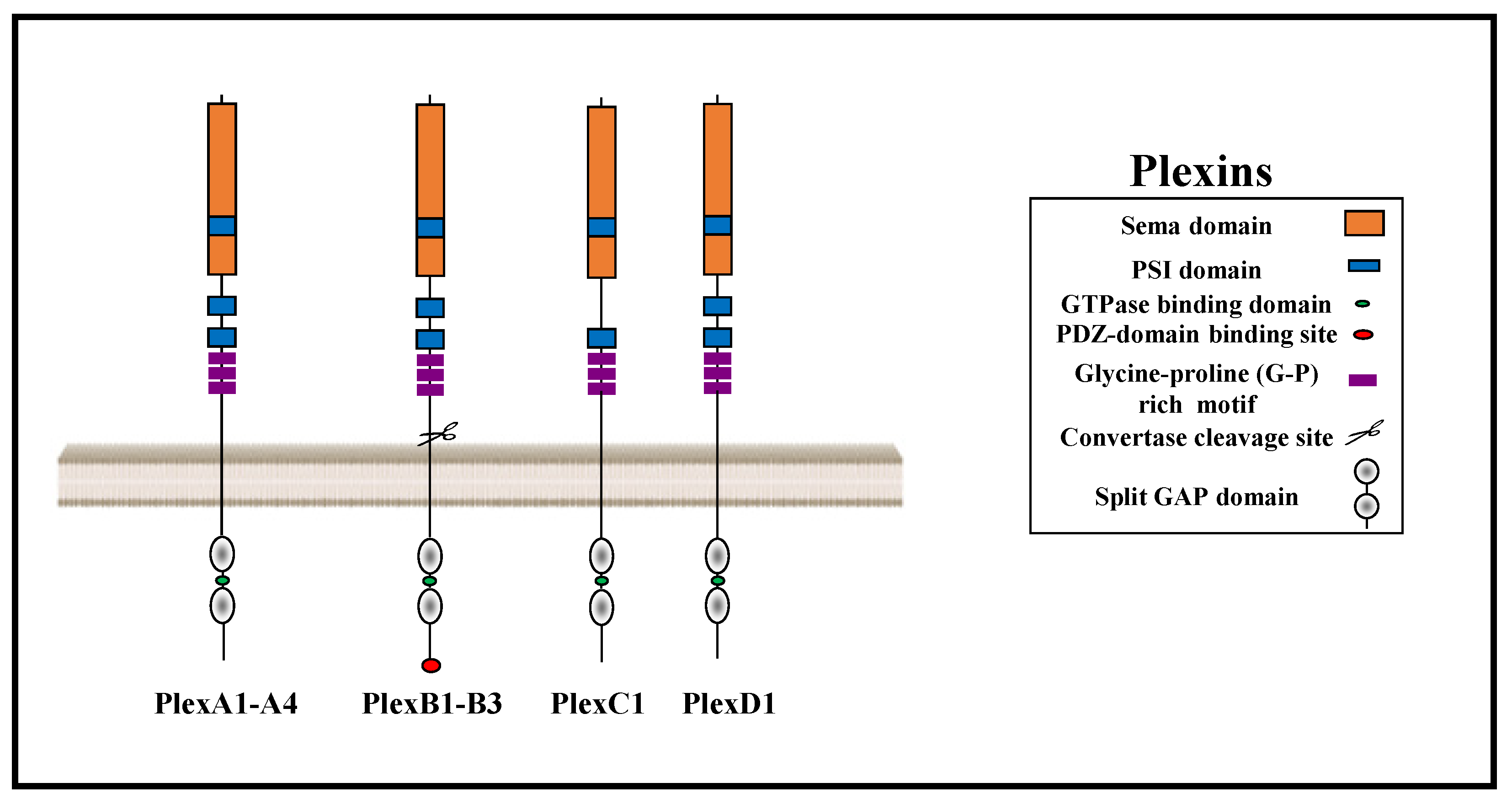
1. The Plexin Receptor Family
2. The Role of the Different Plexins in Tumor Progression
2.1. Type-A Plexins
2.1.1. Plexin-A1
| Plexin | Modulators of Plexin-Mediated Signal Transduction | Role | Cancer Type | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plexin-A1 | Sema3A | Inhibition of proliferation | Malignant mesothelial cells | [45] |
| Sema3A, NRP-1, Perlecan | Promotion of metastatic dissemination | Prostate cancer cells | [46] | |
| Sema6D, VEGFR-2 | Promotion of survival and tumor growth | Malignant mesothelioma cells | [32] | |
| Sema3A | Promotion of proliferation and glycolytic activity | Lung cancer cells | [48] | |
| Sema3A, NRP-1 | Inhibition of proliferation | Brain tumor stem cells | [49] | |
| Plexin-A2 | Enhancement of migration and invasion | Prostate cancer cells | [50] | |
| Sema3C, NRP-1, MAOA, MET | Promotion of perineural invasion | Prostate cancer cells | [51] | |
| Sema3A, KIAA1199 | Inhibition of apoptosis | Cervical cancer cells | [52] | |
| Enabling cell proliferation and the development of tumors | Glioblastoma derived cells | [53] | ||
| Plexin-A3 | Inhibition of cell invasion | Epithelial ovarian cancer cells | [54] | |
| Plexin-A4 | Sema6B | Promotion of pro- proliferative signals | Glioblastoma-derived cells, lung-cancer-derived cells, malignant-melanoma-derived cells | [26] |
| miR-564 | Promotion of cell proliferation and migration | Non-small cell lung carcinoma cells | [55] | |
| Plexin-B1 | Sema4D | Promotion of EMT and tumor cell metastasis | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | [56] |
| Sema4D | Promotion of cell invasion, proliferation, and migration | Osteosarcoma cells | [57] | |
| Sema3C, NRP-1/2, EGFR, ErbB2, MET | Promotion of cancer growth | Castration-resistant prostate cancer cells | [31] | |
| TMPRSS2-ERG | Promotion of cell migration and invasion | Prostate cancer cells | [58] | |
| Promotion of cell migration and invasion | Ovarian cancer derived cells | [59] | ||
| Inhibition of breast cancer cell motility | Breast cancer cells | [60] | ||
| Suppression of tumorigenesis | Primary melanoma cells | [61] | ||
| Inhibition of cell proliferation | Basal cell carcinoma cells | [62] | ||
| Plexin-B2 | Inhibition of cell proliferation | Basal cell carcinoma cells | [62] | |
| Sema4C, ErbB2 | Promotion of proliferation and development of tumor metastasis | Breast cancer derived cells | [63] | |
| Sema4C, MET | Promotion of glioma and glioblastoma cell invasion | Glioma and Glioblastoma cells | [64] | |
| Angiogenin | Inhibition of tumor cell proliferation and inhibition of tumor development | Glioblastoma cells, breast cancer cells, and myelogenous leukemia cells | [65] | |
| Angiogenin | Enhancement of CSC stemness and resistance to chemotherapy | Prostate cancer stem cells | [66] | |
| Angiogenin | Promotion of proliferation, invasion, and tumor growth | Glioblastoma cells | [67] | |
| Circular RNA, Circ_0013958 | Promotion of proliferation, migration, invasion, and tumor growth | Ovarian cancer cells | [68] | |
| EGFR | Promotion of proliferation, invasiveness and tumor-forming ability by constitutively active plexin-B2 | Stem cells from cancers from unknown primary tumors | [69] | |
| Plexin-B3 | Sema5A | Inhibition of migration and invasion | Glioma cells | [70] |
| Inhibition of migration, invasion, and tumor metastasis | Pancreatic cancer cells | [71] | ||
| Promotion of cancer cell growth, cell migration, cell invasion, and tumor progression | Triple-negative breast cancer cells | [72] | ||
| Plexin-C1 | Sema7A | Inhibition of tumor progression | Melanoma cells | [73] |
| Inhibition of tumor progression | Glioma cells | [74] | ||
| Sema7A, β1 integrin receptors | Promotion of metastasis | Melanoma and breast cancer cells | [75] | |
| Promotion of migration and proliferation | Gastric cancer cells | [76] | ||
| Plexin-D1 | P61-sema3E, ErbB2 | Promotion of tumor cell invasiveness and tumor cell metastasis | Melanoma cells, lung carcinoma cells, colon carcinoma cells | [34,35] |
| NR4A1 | Promotion of apoptosis | Breast cancer cells | [77] | |
| Sema3C, plexin-A2, NRP-1 | Promotion of cell survival | Glioma stem cells | [78] |
2.1.2. Plexin-A2
2.1.3. Plexin-A3
2.1.4. Plexin-A4
2.2. Type-B Plexins
2.2.1. Plexin-B1
2.2.2. Plexin-B2
2.2.3. Plexin-B3
2.3. Plexin-C1
2.4. Plexin-D1
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hota, P.K.; Buck, M. Plexin structures are coming: Opportunities for multilevel investigations of semaphorin guidance receptors, their cell signaling mechanisms, and functions. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 3765–3805. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Raible, D.; Raper, J.A. Collapsin: A protein in brain that induces the collapse and paralysis of neuronal growth cones. Cell 1993, 75, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, T.; Strittmatter, S.M. PlexinA1 Autoinhibition by the Plexin Sema Domain. Neuron 2001, 29, 429–439. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, B.J.; Robinson, R.A.; Perez-Branguli, F.; Bell, C.H.; Mitchell, K.J.; Siebold, C.; Jones, E.Y. Structural basis of semaphorin-plexin signalling. Nature 2010, 467, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Nogi, T.; Yasui, N.; Mihara, E.; Matsunaga, Y.; Noda, M.; Yamashita, N.; Toyofuku, T.; Uchiyama, S.; Goshima, Y.; Kumanogoh, A.; et al. Structural basis for semaphorin signalling through the plexin receptor. Nature 2010, 467, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artigiani, S.; Barberis, D.; Fazzari, P.; Longati, P.; Angelini, P.; van de Loo, J.W.; Comoglio, P.M.; Tamagnone, L. Functional regulation of semaphorin receptors by proprotein convertases. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 10094–10101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siebold, C.; Jones, E.Y. Structural insights into semaphorins and their receptors. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 24, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oinuma, I.; Ishikawa, Y.; Katoh, H.; Negishi, M. The Semaphorin 4D receptor Plexin-B1 is a GTPase activating protein for R-Ras. Science 2004, 305, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oinuma, I.; Katoh, H.; Negishi, M. Molecular dissection of the semaphorin 4D receptor plexin-B1-stimulated R-Ras GTPase-activating protein activity and neurite remodeling in hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 11473–11480. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, Y.; Oinuma, I.; Fujimoto, S.; Negishi, M. Plexin-B1 is a GTPase activating protein for M-Ras, remodelling dendrite morphology. EMBO Rep. 2009, 10, 614–621. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; He, H.; Srivastava, N.; Vikarunnessa, S.; Chen, Y.B.; Jiang, J.; Cowan, C.W.; Zhang, X. Plexins Are GTPase-Activating Proteins for Rap and Are Activated by Induced Dimerization. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uesugi, K.; Oinuma, I.; Katoh, H.; Negishi, M. Different requirement for Rnd GTPases of R-Ras GAP activity of plexin-C1 and plexin-D1. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6743–6751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamagnone, L.; Artigiani, S.; Chen, H.; He, Z.; Ming, G.I.; Song, H.; Chedotal, A.; Winberg, M.L.; Goodman, C.S.; Poo, M.; et al. Plexins are a large family of receptors for transmembrane, secreted, and GPI-anchored semaphorins in vertebrates. Cell 1999, 99, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Tamagnone, L.; Comoglio, P.M. Signalling by semaphorin receptors: Cell guidance and beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2000, 10, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rohm, B.; Ottemeyer, A.; Lohrum, M.; Puschel, A.W. Plexin/neuropilin complexes mediate repulsion by the axonal guidance signal semaphorin 3A. Mech. Dev. 2000, 93, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; Nakashima, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Kodama, T.; Kumanogoh, A.; Takayanagi, H. Osteoprotection by semaphorin 3A. Nature 2012, 485, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puschel, A.W. GTPases in semaphorin signaling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 600, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zanata, S.M.; Hovatta, I.; Rohm, B.; Puschel, A.W. Antagonistic effects of Rnd1 and RhoD GTPases regulate receptor activity in Semaphorin 3A-induced cytoskeletal collapse. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 471–477. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, S.; Terman, J.R.; Reisler, E. MICAL-mediated oxidation of actin and its effects on cytoskeletal and cellular dynamics. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1124202. [Google Scholar]
- Perrot, V.; Vazquez-Prado, J.; Gutkind, J.S. Plexin B regulates Rho through the guanine nucleotide exchange factors Leukemia-associated RhoGEF (LARG) and PDZ-RhoGEF. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 278, 26111–26119. [Google Scholar]
- Oinuma, I.; Katoh, H.; Harada, A.; Negishi, M. Direct interaction of Rnd1 with Plexin-B1 regulates PDZ-RhoGEF-mediated Rho activation by Plexin-B1 and induces cell contraction in COS-7 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 25671–25677. [Google Scholar]
- Swiercz, J.M.; Worzfeld, T.; Offermanns, S. Semaphorin 4D signaling requires the recruitment of phospholipase C gamma into the plexin-B1 receptor complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 6321–6334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Driessens, M.H.; Olivo, C.; Nagata, K.; Inagaki, M.; Collard, J.G. B plexins activate Rho through PDZ-RhoGEF. FEBS Lett. 2002, 529, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Worzfeld, T.; Swiercz, J.M.; Senturk, A.; Genz, B.; Korostylev, A.; Deng, S.; Xia, J.; Hoshino, M.; Epstein, J.A.; Chan, A.M.; et al. Genetic dissection of plexin signaling in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2194–2199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shalaby, M.A.; Hampson, L.; Oliver, A.; Hampson, I. Identification of PlexinD1 and AHDC1 as a putative interactors for Tip-1 protein. Genes Genom. 2011, 33, 399–405. [Google Scholar]
- Kigel, B.; Rabinowicz, N.; Varshavsky, A.; Kessler, O.; Neufeld, G. Plexin-A4 promotes tumor progression and tumor angiogenesis by enhancement of VEGF and bFGF signaling. Blood 2011, 118, 4285–4296. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, T.; Fournier, A.; Nakamura, F.; Wang, L.H.; Murakami, Y.; Kalb, R.G.; Fujisawa, H.; Strittmatter, S.M. Plexin-neuropilin-1 complexes form functional semaphorin-3A receptors. Cell 1999, 99, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, S.; Corso, S.; Conrotto, P.; Artigiani, S.; Gilestro, G.; Barberis, D.; Tamagnone, L.; Comoglio, P.M. The Semaphorin 4D receptor controls invasive growth by coupling with Met. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 720–724. [Google Scholar]
- Conrotto, P.; Corso, S.; Gamberini, S.; Comoglio, P.M.; Giordano, S. Interplay between scatter factor receptors and B plexins controls invasive growth. Oncogene 2004, 23, 5131–5137. [Google Scholar]
- Conrotto, P.; Valdembri, D.; Corso, S.; Serini, G.; Tamagnone, L.; Comoglio, P.M.; Bussolino, F.; Giordano, S. Sema4D induces angiogenesis through Met recruitment by Plexin B1. Blood 2005, 105, 4321–4329. [Google Scholar]
- Peacock, J.W.; Takeuchi, A.; Hayashi, N.; Liu, L.; Tam, K.J.; Al, N.N.; Khazamipour, N.; Tombe, T.; Dejima, T.; Lee, K.C.; et al. SEMA3C drives cancer growth by transactivating multiple receptor tyrosine kinases via Plexin B1. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Catalano, A.; Lazzarini, R.; Di, N.S.; Orciari, S.; Procopio, A. The Plexin-A1 Receptor Activates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Receptor 2 and Nuclear Factor-kappaB to Mediate Survival and Anchorage-Independent Growth of Malignant Mesothelioma Cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiercz, J.M.; Kuner, R.; Offermanns, S. Plexin-B1/RhoGEF-mediated RhoA activation involves the receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB-2. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 165, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Casazza, A.; Finisguerra, V.; Capparuccia, L.; Camperi, A.; Swiercz, J.M.; Rizzolio, S.; Rolny, C.; Christensen, C.; Bertotti, A.; Sarotto, I.; et al. Sema3E-Plexin D1 signaling drives human cancer cell invasiveness and metastatic spreading in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2684–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casazza, A.; Kigel, B.; Maione, F.; Capparuccia, L.; Kessler, O.; Giraudo, E.; Mazzone, M.; Neufeld, G.; Tamagnone, L. Tumour growth inhibition and anti-metastatic activity of a mutated furin-resistant Semaphorin 3E isoform. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.; Tamagnone, L. Tyrosine phosphorylation in semaphorin signalling: Shifting into overdrive. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 865–871. [Google Scholar]
- Toledano, S.; Nir-Zvi, I.; Engelman, R.; Kessler, O.; Neufeld, G. Class-3 Semaphorins and Their Receptors: Potent Multifunctional Modulators of Tumor Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 556. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Li, H.; Tamagnone, L.; You, H. Semaphorins and Their Receptors in Hematological Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 382. [Google Scholar]
- Bica, C.; Tirpe, A.; Nutu, A.; Ciocan, C.; Chira, S.; Gurzau, E.S.; Braicu, C.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Emerging roles and mechanisms of semaphorins activity in cancer. Life Sci. 2023, 318, 121499. [Google Scholar]
- Kanth, S.M.; Gairhe, S.; Torabi-Parizi, P. The Role of Semaphorins and Their Receptors in Innate Immune Responses and Clinical Diseases of Acute Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 672441. [Google Scholar]
- Kolodkin, A.L.; Levengood, D.V.; Rowe, E.G.; Tai, Y.T.; Giger, R.J.; Ginty, D.D. Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell 1997, 90, 753–762. [Google Scholar]
- Sabag, A.D.; Smolkin, T.; Mumblat, Y.; Ueffing, M.; Kessler, O.; Gloeckner, C.J.; Neufeld, G. The role of the plexin-A2 receptor in Sema3A and Sema3B signal transduction. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 5240–5252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guttmann-Raviv, N.; Shraga-Heled, N.; Varshavsky, A.; Guimaraes-Sternberg, C.; Kessler, O.; Neufeld, G. Semaphorin-3A and Semaphorin-3F Work Together to Repel Endothelial Cells and to Inhibit Their Survival by Induction of Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 26294–26305. [Google Scholar]
- Casazza, A.; Laoui, D.; Wenes, M.; Rizzolio, S.; Bassani, N.; Mambretti, M.; Deschoemaeker, S.; Van Ginderachter, J.A.; Tamagnone, L.; Mazzone, M. Impeding Macrophage Entry into Hypoxic Tumor Areas by Sema3A/Nrp1 Signaling Blockade Inhibits Angiogenesis and Restores Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 695–709. [Google Scholar]
- Catalano, A.; Caprari, P.; Rodilossi, S.; Betta, P.; Castellucci, M.; Casazza, A.; Tamagnone, L.; Procopio, A. Cross-talk between vascular endothelial growth factor and semaphorin-3A pathway in the regulation of normal and malignant mesothelial cell proliferation. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tellman, T.V.; Cruz, L.A.; Grindel, B.J.; Farach-Carson, M.C. Cleavage of the Perlecan-Semaphorin 3A-Plexin A1-Neuropilin-1 (PSPN) Complex by Matrix Metalloproteinase 7/Matrilysin Triggers Prostate Cancer Cell Dyscohesion and Migration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Staton, C.A.; Shaw, L.A.; Valluru, M.; Hoh, L.; Koay, I.; Cross, S.S.; Reed, M.W.; Brown, N.J. Expression of class 3 semaphorins and their receptors in human breast neoplasia. Histopathology 2011, 59, 274–282. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, D.; Watanabe, S.; Kawahara, K.; Maeda, T. Plexin A1 signaling confers malignant phenotypes in lung cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 480, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, D.M.O.; Caliva, M.; Schroeder, M.; Carlson, B.; Upadhyayula, P.S.; Milligan, B.D.; Cheshier, S.H.; Weissman, I.L.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Meyer, F.B.; et al. Semaphorin 3A mediated brain tumor stem cell proliferation and invasion in EGFRviii mutant gliomas. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1213. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, T.V.; Tomavo, N.; Huot, L.; Flourens, A.; Bonnelye, E.; Flajollet, S.; Hot, D.; Leroy, X.; de Launoit, Y.; Duterque-Coquillaud, M. Identification of novel TMPRSS2:ERG mechanisms in prostate cancer metastasis: Involvement of MMP9 and PLXNA2. Oncogene 2013, 33, 2204–2214. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Pu, T.; Wei, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, B.J. MAOA promotes prostate cancer cell perineural invasion through SEMA3C/PlexinA2/NRP1-cMET signaling. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shostak, K.; Zhang, X.; Hubert, P.; Goktuna, S.I.; Jiang, Z.; Klevernic, I.; Hildebrand, J.; Roncarati, P.; Hennuy, B.; Ladang, A.; et al. NF-kappaB-induced KIAA1199 promotes survival through EGFR signalling. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toledano, S.; Sabag, A.D.; Ilan, N.; Liburkin-Dan, T.; Kessler, O.; Neufeld, G. Plexin-A2 enables the proliferation and the development of tumors from glioblastoma derived cells. Cell Death. Dis. 2023, 14, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Syed, V.; Zhang, X.; Lau, K.M.; Cheng, R.; Mukherjee, K.; Ho, S.M. Profiling estrogen-regulated gene expression changes in normal and malignant human ovarian surface epithelial cells. Oncogene 2005, 24, 8128–8143. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Li, L.; Gu, B.; Ni, Y.; Chen, S. MicroRNA-564 inhibits the progression of non-small cell lung cancer via targeting plexin A4. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Qiao, H.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Jin, B.; Fu, M.; Wang, G.; Li, W. CD100-Plexin-B1 induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and promotes metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2019, 455, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wan, L.; Wang, P.; Guan, X.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Sema4D/Plexin-B1 promotes the progression of osteosarcoma cells by activating Pyk2-PI3K-AKT pathway. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2021, 21, 577–583. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Gu, X.; Huang, T.; Luan, Y.; Ding, X. Identification of TMPRSS2-ERG mechanisms in prostate cancer invasiveness: Involvement of MMP-9 and plexin B1. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.; Hao, X.; Zhou, T.; Wu, M.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, X.; Ji, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Plexin-B1 silencing inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration and invasion. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 611. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, M.F.A.; Riaz, S.K.; Waqar, S.H.; Haq, F.; Ye, L.; Jiang, W.G. Role of Plexin B1 in a Breast Cancer Cohort of Pakistani Patients and its Contribution Towards Cancer Metastasis as Indicated by an In Vitro Model. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 4483–4488. [Google Scholar]
- Argast, G.M.; Croy, C.H.; Couts, K.L.; Zhang, Z.; Litman, E.; Chan, D.C.; Ahn, N.G. Plexin B1 is repressed by oncogenic B-Raf signaling and functions as a tumor suppressor in melanoma cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2697–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Javed, A.; Kaiser, L.; Nava, M.M.; Xu, R.; Brandt, D.T.; Zhao, D.; Mayer, B.; Fernández-Baldovinos, J.; Zhou, L.; et al. Mechanochemical control of epidermal stem cell divisions by B-plexins. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrapu, S.; Pupo, E.; Franzolin, G.; Lanzetti, L.; Tamagnone, L. Sema4C/PlexinB2 signaling controls breast cancer cell growth, hormonal dependence and tumorigenic potential. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1259–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.P.; Huang, Y.; Pingle, S.C.; Kesari, S.; Wang, H.; Yong, R.L.; Zou, H.; Friedel, R.H. Plexin-B2 promotes invasive growth of malignant glioma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7293–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Goncalves, K.A.; Li, S.; Kishikawa, H.; Sun, G.; Yang, H.; Vanli, N.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, M.G.; et al. Plexin-B2 Mediates Physiologic and Pathologic Functions of Angiogenin. Cell 2017, 171, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Goncalves, K.A.; Lyu, B.; Yuan, L.; Hu, G.F. Chemosensitization of prostate cancer stem cells in mice by angiogenin and plexin-B2 inhibitors. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 26–0750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yuan, L.; Ibaragi, S.; Li, S.; Shapiro, R.; Vanli, N.; Goncalves, K.A.; Yu, W.; Kishikawa, H.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Angiogenin and plexin-B2 axis promotes glioblastoma progression by enhancing invasion, vascular association, proliferation and survival. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Meng, K.; Qiu, R. Circular RNA Circ_0013958 Functions as a Tumor Promoter in Ovarian Cancer by Regulating miR-637/PLXNB2 Axis. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 644451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundu, S.; Napolitano, V.; Franzolin, G.; Lo, C.E.; Mastrantonio, R.; Sardo, G.; Cascardi, E.; Verginelli, F.; Sarnataro, S.; Gambardella, G.; et al. Mutated axon guidance gene PLXNB2 sustains growth and invasiveness of stem cells isolated from cancers of unknown primary. EMBO Mol. Med. 2023, 15, e16104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Law, J.W.; Lee, A.Y. Semaphorin 5A and plexin-B3 regulate human glioma cell motility and morphology through Rac1 and the actin cytoskeleton. Oncogene 2011, 31, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saxena, S.; Prajapati, D.R.; Goel, P.; Tomar, B.; Hayashi, Y.; Atri, P.; Rachagani, S.; Grandgenett, P.M.; Hollingsworth, M.A.; Batra, S.K.; et al. Plexin-B3 Regulates Cellular Motility, Invasiveness, and Metastasis in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, L.; Govindarajan, M.; Mejia-Guerrero, S.; Ignatchenko, V.; Liu, L.Y.; Grünwald, B.T.; Cruickshank, J.; Berman, H.; Khokha, R.; Kislinger, T. Glycoproteomics Identifies Plexin-B3 as a Targetable Cell Surface Protein Required for the Growth and Invasion of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 2224–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, G.A.; McClelland, L.A.; Fricke, A.F.; Fender, A. Plexin C1, A Receptor for Semaphorin 7A, Inactivates Cofilin and Is a Potential Tumor Suppressor for Melanoma Progression. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Zheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Xue, Y. Gas5 Exerts Tumor-suppressive Functions in Human Glioma Cells by Targeting miR-222. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Herzog, E.L.; Lee, C.G.; Peng, X.; Lee, C.M.; Chen, X.; Rockwell, S.; Koo, J.S.; Kluger, H.; Herbst, R.S.; et al. Role of Chitinase 3-like-1 and Semaphorin 7A in Pulmonary Melanoma Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2014, 75, 487–496. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Sun, B.; Wu, J.; Du, C. PLXNC1 Enhances Carcinogenesis Through Transcriptional Activation of IL6ST in Gastric Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchino, J.; Hocine, M.; Amoureux, M.C.; Gibert, B.; Bernet, A.; Royet, A.; Treilleux, I.; Lecine, P.; Borg, J.P.; Mehlen, P.; et al. Semaphorin 3E Suppresses Tumor Cell Death Triggered by the Plexin D1 Dependence Receptor in Metastatic Breast Cancers. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Man, J.; Shoemake, J.; Zhou, W.; Fang, X.; Wu, Q.; Rizzo, A.; Prayson, R.; Bao, S.; Rich, J.N.; Yu, J.S. Sema3C promotes the survival and tumorigenicity of glioma stem cells through Rac1 activation. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1812–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maione, F.; Molla, F.; Meda, C.; Latini, R.; Zentilin, L.; Giacca, M.; Seano, G.; Serini, G.; Bussolino, F.; Giraudo, E. Semaphorin 3A is an endogenous angiogenesis inhibitor that blocks tumor growth and normalizes tumor vasculature in transgenic mouse models. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3356–3372. [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan, D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature 1985, 315, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, Y.; Sekido, Y.; Kondo, M.; Gao, B.; Yokota, J.; Roche, J.; Drabkin, H.; Lerman, M.I.; Gazdar, A.F.; Minna, J.D. Inhibition of lung cancer cell growth and induction of apoptosis after reexpression of 3p21.3 candidate tumor suppressor gene SEMA3B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13954–13959. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tischoff, I.; Markwarth, A.; Witzigmann, H.; Uhlmann, D.; Hauss, J.; Mirmohammadsadegh, A.; Wittekind, C.; Hengge, U.R.; Tannapfel, A. Allele loss and epigenetic inactivation of 3p21.3 in malignant liver tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 115, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, P.N.; McArdle, L.; Cornell, J.; Cohn, S.L.; Stallings, R.L. High-resolution analysis of 3p deletion in neuroblastoma and differential methylation of the SEMA3B tumor suppressor gene. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2007, 174, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pyatnitskiy, M.; Karpov, D.; Poverennaya, E.; Lisitsa, A.; Moshkovskii, S. Bringing Down Cancer Aircraft: Searching for Essential Hypomutated Proteins in Skin Melanoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142819. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.L. Plexin A3 is involved in semaphorin 3F-mediated oligodendrocyte precursor cell migration. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 530, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotan, L.D.; Ternier, G.; Cakir, A.D.; Emeksiz, H.C.; Turan, I.; Delpouve, G.; Kardelen, A.D.; Ozcabi, B.; Isik, E.; Mengen, E.; et al. Loss-of-function variants in SEMA3F and PLXNA3 encoding semaphorin-3F and its receptor plexin-A3 respectively cause idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.J.; Bagri, A.; Yaron, A.; Stein, E.; Pleasure, S.J.; Tessier-Lavigne, M. Plexin-a3 mediates semaphorin signaling and regulates the development of hippocampal axonal projections. Neuron 2001, 32, 249–263. [Google Scholar]
- Doci, C.L.; Mikelis, C.M.; Lionakis, M.S.; Molinolo, A.A.; Gutkind, J.S. Genetic identification of SEMA3F as an anti-lymphangiogenic metastasis suppressor gene in head and neck squamous carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2937–2948. [Google Scholar]
- Bielenberg, D.R.; Hida, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Kaipainen, A.; Kreuter, M.; Kim, C.C.; Klagsbrun, M. Semaphorin 3F, a chemorepulsant for endothelial cells, induces a poorly vascularized, encapsulated, nonmetastatic tumor phenotype. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, O.; Shraga-Heled, N.; Lange, T.; Gutmann-Raviv, N.; Sabo, E.; Baruch, L.; Machluf, M.; Neufeld, G. Semaphorin-3F Is an Inhibitor of Tumor Angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suto, F.; Tsuboi, M.; Kamiya, H.; Mizuno, H.; Kiyama, Y.; Komai, S.; Shimizu, M.; Sanbo, M.; Yagi, T.; Hiromi, Y.; et al. Interactions between Plexin-A2, Plexin-A4, and Semaphorin 6A Control Lamina-Restricted Projection of Hippocampal Mossy Fibers. Neuron 2007, 53, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haklai-Topper, L.; Mlechkovich, G.; Savariego, D.; Gokhman, I.; Yaron, A. Cis interaction between Semaphorin6A and Plexin-A4 modulates the repulsive response to Sema6A. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2635–2645. [Google Scholar]
- Celus, W.; Oliveira, A.I.; Rivis, S.; Van Acker, H.H.; Landeloos, E.; Serneels, J.; Cafarello, S.T.; Van, H.Y.; Mastrantonio, R.; Köhler, A.; et al. Plexin-A4 Mediates Cytotoxic T-cell Trafficking and Exclusion in Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2022, 10, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tejero, R.; Lee, V.K.; Brusco, C.; Hannah, T.; Bertucci, T.B.; Junqueira, A.C.; Katsyv, I.; Kluge, M.; Foty, R.; et al. Plexin-B2 facilitates glioblastoma infiltration by modulating cell biomechanics. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Fett, J.W.; Strydom, D.J.; Lobb, R.R.; Alderman, E.M.; Bethune, J.L.; Riordan, J.F.; Vallee, B.L. Isolation and characterization of angiogenin, an angiogenic protein from human carcinoma cells. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 5480–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wen, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; He, Q.; Feng, D. Loss of plexin-B3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Juo, Z.S.; Shim, A.H.; Focia, P.J.; Chen, X.; Garcia, K.C.; He, X. Structural Basis of Semaphorin-Plexin Recognition and Viral Mimicry from Sema7A and A39R Complexes with PlexinC1. Cell 2010, 142, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabas, G.; Cetin, M.; Turhal, S.; Baloglu, H.; Sayan, A.E.; Yagci, T. Plexin C1 Marks Liver Cancer Cells with Epithelial Phenotype and Is Overexpressed in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 4040787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NazimTurhal, S.; Dogan, M.; Esendagli, G.; Artac, M.; Korkmaz, L.; Coskun, H.S.; Goker, E.; PerranYumuk, F.; Bilgetekin, I.; Kose, F.; et al. The Relationship Between Plexin C1 Overexpression and Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Turkish Oncology Group (TOG) Study. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2021, 53, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ni, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, J.; Hu, M.; Chen, Q.; Ge, B.; Huang, Q. PLXNC1: A Novel Potential Immune-Related Target for Stomach Adenocarcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 662707. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, F.O.; Gordon, S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Roodink, I.; Raats, J.; Van Der, Z.B.; Verrijp, K.; Kusters, B.; Van Bokhoven, H.; Linkels, M.; de Waal, R.M.; Leenders, W.P. Plexin d1 expression is induced on tumor vasculature and tumor cells: A novel target for diagnosis and therapy? Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 8317–8323. [Google Scholar]
- Vivekanandhan, S.; Mukhopadhyay, D. Divergent roles of Plexin D1 in Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2019, 1872, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Yoshida, Y.; Livet, J.; Reimert, D.V.; Mann, F.; Merte, J.; Henderson, C.E.; Jessell, T.M.; Kolodkin, A.L.; Ginty, D.D. Semaphorin 3E and plexin-D1 control vascular pattern independently of neuropilins. Science 2005, 307, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.J.; Hu, J.; Uemura, A.; Tetzlaff, F.; Augustin, H.G.; Fischer, A. Semaphorin-3C signals through Neuropilin-1 and PlexinD1 receptors to inhibit pathological angiogenesis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 20, 1267–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Smolkin, T.; Nir-Zvi, I.; Duvshani, N.; Mumblat, Y.; Kessler, O.; Neufeld, G. Complexes of plexin-A4 and plexin-D1 convey semaphorin-3C signals to induce cytoskeletal collapse in the absence of neuropilins. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs208298. [Google Scholar]
- Mumblat, Y.; Kessler, O.; Ilan, N.; Neufeld, G. Full length semaphorin-3C functions as an inhibitor of tumor lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar]
- Bassi, D.E.; Fu, J.; de Lopez, C.R.; Klein-Szanto, A.J. Proprotein convertases: “master switches” in the regulation of tumor growth and progression. Mol. Carcinog. 2005, 44, 151–161. [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby, M.A.; Hampson, L.; Oliver, A.; Hampson, I. Plexin d1: New potential biomarker for cervical cancer. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2012, 33, 223–233. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toledano, S.; Neufeld, G. Plexins as Regulators of Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasivity. Cancers 2023, 15, 4046. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164046
Toledano S, Neufeld G. Plexins as Regulators of Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasivity. Cancers. 2023; 15(16):4046. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164046
Chicago/Turabian StyleToledano, Shira, and Gera Neufeld. 2023. "Plexins as Regulators of Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasivity" Cancers 15, no. 16: 4046. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164046
APA StyleToledano, S., & Neufeld, G. (2023). Plexins as Regulators of Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasivity. Cancers, 15(16), 4046. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164046






