Optimisation of Sample Preparation from Primary Mouse Tissue to Maintain RNA Integrity for Methods Examining Translational Control
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Models
2.2. Tissue Preparation
2.3. Cell Lysis
2.4. Total RNA Extraction from TRIzol
2.5. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
2.6. Sucrose Gradients
2.7. RNA Extraction of Sucrose Gradient Fractions
2.8. RNA Integrity Value Calculations
2.9. RNase Expression Level Data
3. Results
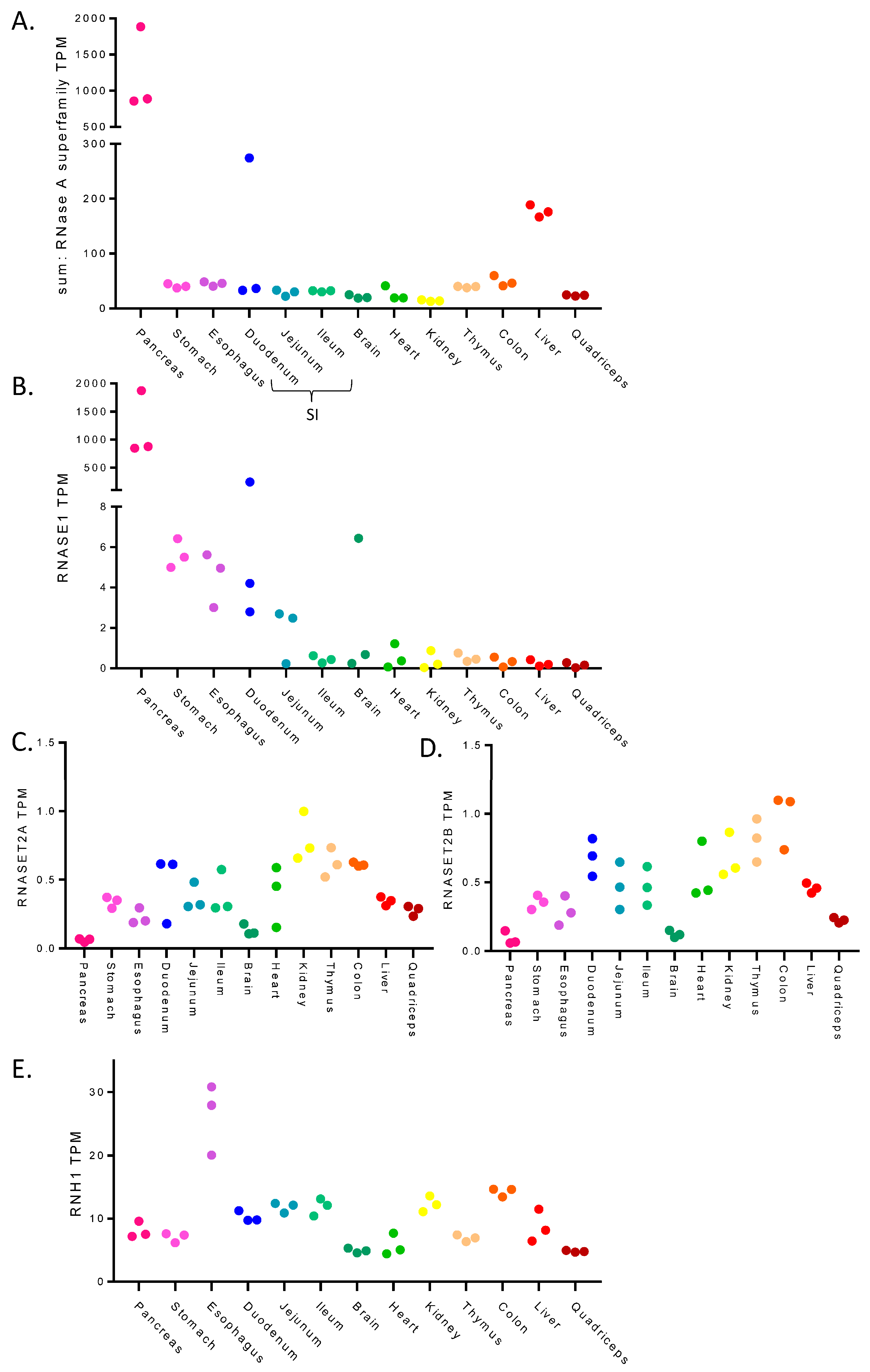
3.1. RNase Expression across Tissues
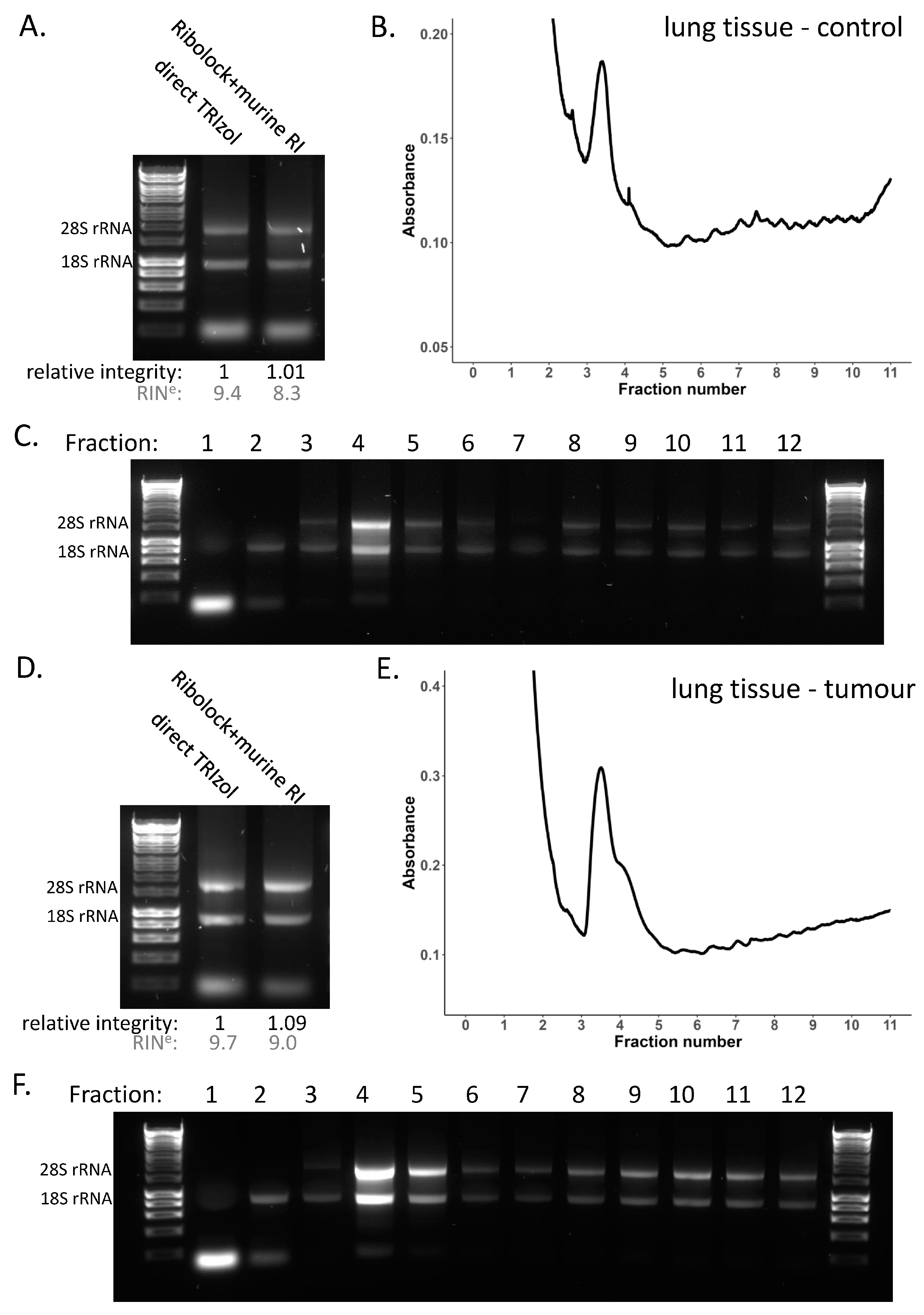
3.2. Retaining RNA Integrity in Non-Denaturing Conditions
3.3. The Complexity of the Pancreas
3.4. Polysome Profiling in Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwanhäusser, B.; Busse, D.; Li, N.; Dittmar, G.; Schuchhardt, J.; Wolf, J.; Chen, W.; Selbach, M. Global Quantification of Mammalian Gene Expression Control. Nature 2011, 473, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Vera, M.; Gandin, V.; Singer, R.H.; Tutucci, E. Intracellular mRNA Transport and Localized Translation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 483–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, S.; Verhagen, B.M.P.; Tanenbaum, M.E. Heterogeneity in mRNA Translation. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, D.W.; Nicchitta, C.V. Diversity and Selectivity in mRNA Translation on the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupinacci, F.C.S.; Kuasne, H.; Roffé, M.; Vassalakis, J.A.; da Silva, F.F.; Santos, T.G.; Andrade, V.P.; Sanematsu, P.; Martins, V.R.; Rogatto, S.R.; et al. Polysome Profiling of a Human Glioblastoma Reveals Intratumoral Heterogeneity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doroudgar, S.; Hofmann, C.; Boileau, E.; Malone, B.; Riechert, E.; Gorska, A.A.; Jakobi, T.; Sandmann, C.; Jürgensen, L.; Kmietczyk, V.; et al. Monitoring Cell-Type–Specific Gene Expression Using Ribosome Profiling In Vivo During Cardiac Hemodynamic Stress. Circ. Res. 2019, 125, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernabò, P.; Tebaldi, T.; Groen, E.J.N.; Lane, F.M.; Perenthaler, E.; Mattedi, F.; Newbery, H.J.; Zhou, H.; Zuccotti, P.; Potrich, V.; et al. In Vivo Translatome Profiling in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Reveals a Role for SMN Protein in Ribosome Biology. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hien, A.; Molinaro, G.; Liu, B.; Huber, K.M.; Richter, J.D. Ribosome Profiling in Mouse Hippocampus: Plasticity-Induced Regulation and Bidirectional Control by TSC2 and FMRP. Mol. Autism 2020, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans, M.D.; Crozier, S.J.; Vogel, N.L.; D’Alecy, L.G.; Williams, J.A. Dietary Protein and Amino Acid Deficiency Inhibit Pancreatic Digestive Enzyme Translation by Multiple Mechanisms. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labno, A.; Tomecki, R.; Dziembowski, A. Cytoplasmic RNA Decay Pathways—Enzymes and Mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 3125–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuichi, Y.; LaFiandra, A.; Shatkin, A.J. 5′-Terminal Structure and mRNA Stability. Nature 1977, 266, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.M.; Barnes, T.; Lee, C.H. Endoribonucleases—Enzymes Gaining Spotlight in mRNA Metabolism. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, W. The Action of Boiled Pancreas Extract on Yeast Nucleic Acid. Am. J. Physiol.-Leg. Content 1920, 52, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beintema, J.J.; Wietzes, P.; Weickmann, J.L.; Glitz, D.G. The Amino Acid Sequence of Human Pancreatic Ribonuclease. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 136, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raines, R.T. Ribonuclease A. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1045–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, P.M.; Scragg, I.G.; Coghill, E.; Dwek, R.A. Separation and Analysis of the Glycoform Populations of Ribonuclease B Using Capillary Electrophoresis. Glycoconj. J. 1992, 9, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joao, H.C.; Scragg, I.G.; Dwek, R.A. Effects of Glycosylation on Protein Conformation and Amide Proton Exchange Rates in RNase B. FEBS Lett. 1992, 307, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorrentino, S. The Eight Human “Canonical” Ribonucleases: Molecular Diversity, Catalytic Properties, and Special Biological Actions of the Enzyme Proteins. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koczera, P.; Martin, L.; Marx, G.; Schuerholz, T. The Ribonuclease A Superfamily in Humans: Canonical RNases as the Buttress of Innate Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Dyer, K.D.; Rosenberg, H.F. RNase 8, a Novel RNase A Superfamily Ribonuclease Expressed Uniquely in Placenta. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, S.; Beintema, J.J.; Zhang, J. The Ribonuclease A Superfamily of Mammals and Birds: Identifying New Members and Tracing Evolutionary Histories. Genomics 2005, 85, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Li, J.; Moussaoui, M.; Boix, E. Immune Modulation by Human Secreted RNases at the Extracellular Space. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.K.; Haigh, B.J.; Wheeler, T.T. Abundance of RNase4 and RNase5 mRNA and Protein in Host Defence Related Tissues and Secretions in Cattle. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 8, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyons, S.M.; Fay, M.M.; Akiyama, Y.; Anderson, P.J.; Ivanov, P. RNA Biology of Angiogenin: Current State and Perspectives. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.-H.; Wang, Y.-N.; Hung, M.-C. Functional Roles of the Human Ribonuclease A Superfamily in RNA Metabolism and Membrane Receptor Biology. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 70, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, R.A.; Shankar, V. Ribonucleases from T2 Family. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 28, 79–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greulich, W.; Wagner, M.; Gaidt, M.M.; Stafford, C.; Cheng, Y.; Linder, A.; Carell, T.; Hornung, V. TLR8 Is a Sensor of RNase T2 Degradation Products. Cell 2019, 179, 1264–1275.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotte, G.; Menegazzi, M. Biological Activities of Secretory RNases: Focus on Their Oligomerization to Design Antitumor Drugs. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lomax, J.E.; Bianchetti, C.M.; Chang, A.; Phillips, G.N.; Fox, B.G.; Raines, R.T. Functional Evolution of Ribonuclease Inhibitor: Insights from Birds and Reptiles. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 3041–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickson, K.A.; Haigis, M.C.; Raines, R.T. Ribonuclease Inhibitor: Structure and Function. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 2005, 80, 349–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, F.S.; Vallee, B.L. Structure and Action of Mammalian Ribonuclease (Angiogenin) Inhibitor. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1993, 44, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.P.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.-S.; Raines, R.T. Knockout of the Ribonuclease Inhibitor Gene Leaves Human Cells Vulnerable to Secretory Ribonucleases. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 6359–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, S.P.; Hoang, T.T.; Ressler, V.T.; Raines, R.T. Human Angiogenin Is a Potent Cytotoxin in the Absence of Ribonuclease Inhibitor. RNA 2018, 24, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furia, A.; Moscato, M.; Calì, G.; Pizzo, E.; Confalone, E.; Amoroso, M.R.; Esposito, F.; Nitsch, L.; D’Alessio, G. The Ribonuclease/Angiogenin Inhibitor Is Also Present in Mitochondria and Nuclei. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Söllner, J.F.; Leparc, G.; Hildebrandt, T.; Klein, H.; Thomas, L.; Stupka, E.; Simon, E. An RNA-Seq Atlas of Gene Expression in Mouse and Rat Normal Tissues. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dastgheib, S.; Irajie, C.; Assaei, R.; Koohpeima, F.; Mokarram, P. Optimization of RNA Extraction from Rat Pancreatic Tissue. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 39, 282–288. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, M.; Abu-El-Haija, M.; Abu-El-Haija, M.; Rokhlina, T.; Uc, A. Simplified and Versatile Method for Isolation of High-Quality RNA from Pancreas. BioTechniques 2012, 52, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azevedo-Pouly, A.C.P.; Elgamal, O.A.; Schmittgen, T.D. RNA Isolation from Mouse Pancreas: A Ribonuclease-Rich Tissue. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2014, 51779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, D.; Ven Murthy, M.R. Polysomes during Early Postnatal Development of Brain in the Rat. Neurochem. Res. 1986, 11, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lamirande, G.; Weber, G.; Cantero, A. In Vivo Effect of Heparin on Acid and Alkaline Ribonuclease Activities of Mouse Liver. Am. J. Physiol. 1956, 184, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berger, S.L. Isolation of Cytoplasmic RNA: Ribonucleoside-Vanadyl Complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1987, 152, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, S.L.; Birkenmeier, C.S. Inhibition of Intractable Nucleases with Ribonucleoside—Vanadyl Complexes: Isolation of Messenger Ribonucleic Acid from Resting Lymphocytes. Biochemistry 1979, 18, 5143–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auer, H.; Lyianarachchi, S.; Newsom, D.; Klisovic, M.I.; Marcucci, U.; Kornacker, K. Chipping Away at the Chip Bias: RNA Degradation in Microarray Analysis. Nat. Genet. 2003, 35, 292–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, A.; Mueller, O.; Stocker, S.; Salowsky, R.; Leiber, M.; Gassmann, M.; Lightfoot, S.; Menzel, W.; Granzow, M.; Ragg, T. The RIN: An RNA Integrity Number for Assigning Integrity Values to RNA Measurements. BMC Mol. Biol. 2006, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imbeaud, S.; Graudens, E.; Boulanger, V.; Barlet, X.; Zaborski, P.; Eveno, E.; Mueller, O.; Schroeder, A.; Auffray, C. Towards Standardization of RNA Quality Assessment Using User-Independent Classifiers of Microcapillary Electrophoresis Traces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mašek, T.; Valášek, L.; Pospíšek, M. Polysome Analysis and RNA Purification from Sucrose Gradients. In RNA: Methods and Protocols; Nielsen, H., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 293–309. ISBN 978-1-59745-248-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia, N.T.; Brar, G.A.; Rouskin, S.; McGeachy, A.M.; Weissman, J.S. The Ribosome Profiling Strategy for Monitoring Translation in Vivo by Deep Sequencing of Ribosome-Protected mRNA Fragments. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1534–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider-Poetsch, T.; Ju, J.; Eyler, D.E.; Dang, Y.; Bhat, S.; Merrick, W.C.; Green, R.; Shen, B.; Liu, J.O. Inhibition of Eukaryotic Translation Elongation by Cycloheximide and Lactimidomycin. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collart, M.A.; Weiss, B. Ribosome Pausing, a Dangerous Necessity for Co-Translational Events. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riba, A.; Di Nanni, N.; Mittal, N.; Arhné, E.; Schmidt, A.; Zavolan, M. Protein Synthesis Rates and Ribosome Occupancies Reveal Determinants of Translation Elongation Rates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 15023–15032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arava, Y.; Wang, Y.; Storey, J.D.; Liu, C.L.; Brown, P.O.; Herschlag, D. Genome-Wide Analysis of mRNA Translation Profiles in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3889–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Nunez, R.T.; Sanford, J.R. Studying Isoform-Specific mRNA Recruitment to Polyribosomes with Frac-Seq. In Post-Transcriptional Gene Regulation; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1358, pp. 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangenberg, L.; Shigunov, P.; Abud, A.P.R.; Cofré, A.R.; Stimamiglio, M.A.; Kuligovski, C.; Zych, J.; Schittini, A.V.; Costa, A.D.T.; Rebelatto, C.K.; et al. Polysome Profiling Shows Extensive Posttranscriptional Regulation during Human Adipocyte Stem Cell Differentiation into Adipocytes. Stem Cell Res. 2013, 11, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, D.J.; Junttila, M.R.; Pouyet, L.; Karnezis, A.; Shchors, K.; Bui, D.A.; Brown-Swigart, L.; Johnson, L.; Evan, G.I. Distinct Thresholds Govern Myc’s Biological Output in Vivo. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, E.L.; Willis, N.; Mercer, K.; Bronson, R.T.; Crowley, D.; Montoya, R.; Jacks, T.; Tuveson, D.A. Analysis of Lung Tumor Initiation and Progression Using Conditional Expression of Oncogenic K-Ras. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 3243–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prete, M.J.D.; Vernal, R.; Dolznig, H.; Müllner, E.W.; Garcia-Sanz, J.A. Isolation of Polysome-Bound mRNA from Solid Tissues Amenable for RT-PCR and Profiling Experiments. RNA 2007, 13, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Augereau, C.; Lemaigre, F.P.; Jacquemin, P. Extraction of High-Quality RNA from Pancreatic Tissues for Gene Expression Studies. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 500, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adsani, A.M.; Barhoush, S.A.; Bastaki, N.K.; Al-Bustan, S.A.; Al-Qattan, K.K. Comparing and Optimizing RNA Extraction from the Pancreas of Diabetic and Healthy Rats for Gene Expression Analyses. Genes 2022, 13, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerashchenko, M.V.; Gladyshev, V.N. Ribonuclease Selection for Ribosome Profiling. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelemen, B.R.; Schultz, L.W.; Sweeney, R.Y.; Raines, R.T. Excavating an Active Site: The Nucleobase Specificity of Ribonuclease A. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 14487–14494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Inhibitor | Supplier | Cost | Working Concentration | Targets | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RiboLock | Thermo Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA) | £19.52/1000 U | 1000 U/mL | RNase A, B & C | Limited targeting |
| SUPERase.In | Invitrogen (Waltham, MA, USA) | £68/1000 U | 1000 U/mL | RNase A, B & C RNase T1 RNase I | Inhibition of RNases used in ribosome profiling (e.g., RNase I) limits its application |
| Heparin | Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) | £0.77/mg | 1 mg/mL | broad spectrum | Can block downstream applications—requires LiCl precipitation to remove Inhibition of RNases used in ribosome profiling (e.g., RNase I) limits its application |
| murine RNase inhibitor | New England Biolabs (Ipswich, MA, USA) | £25.60/1000 U | 1000 U/mL | RNase A, B & C | Limited targeting |
| Ibonucleoside Vanadyl Complex | New England Biolabs (Ipswich, MA, USA) | £4.10/10 mM | 10 mM | broad spectrum | Need to add EGTA to remove after use Inhibition of RNases used in ribosome profiling (e.g., RNase I) limits its application |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munro, J.; Gillen, S.L.; Mitchell, L.; Laing, S.; Karim, S.A.; Rink, C.J.; Waldron, J.A.; Bushell, M. Optimisation of Sample Preparation from Primary Mouse Tissue to Maintain RNA Integrity for Methods Examining Translational Control. Cancers 2023, 15, 3985. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153985
Munro J, Gillen SL, Mitchell L, Laing S, Karim SA, Rink CJ, Waldron JA, Bushell M. Optimisation of Sample Preparation from Primary Mouse Tissue to Maintain RNA Integrity for Methods Examining Translational Control. Cancers. 2023; 15(15):3985. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153985
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunro, June, Sarah L. Gillen, Louise Mitchell, Sarah Laing, Saadia A. Karim, Curtis J. Rink, Joseph A. Waldron, and Martin Bushell. 2023. "Optimisation of Sample Preparation from Primary Mouse Tissue to Maintain RNA Integrity for Methods Examining Translational Control" Cancers 15, no. 15: 3985. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153985
APA StyleMunro, J., Gillen, S. L., Mitchell, L., Laing, S., Karim, S. A., Rink, C. J., Waldron, J. A., & Bushell, M. (2023). Optimisation of Sample Preparation from Primary Mouse Tissue to Maintain RNA Integrity for Methods Examining Translational Control. Cancers, 15(15), 3985. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153985





