Evaluation of Potential Targets for Fluorescence-Guided Surgery in Pediatric Ewing Sarcoma: A Preclinical Proof-of-Concept Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Selection
2.2. Biomarkers
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
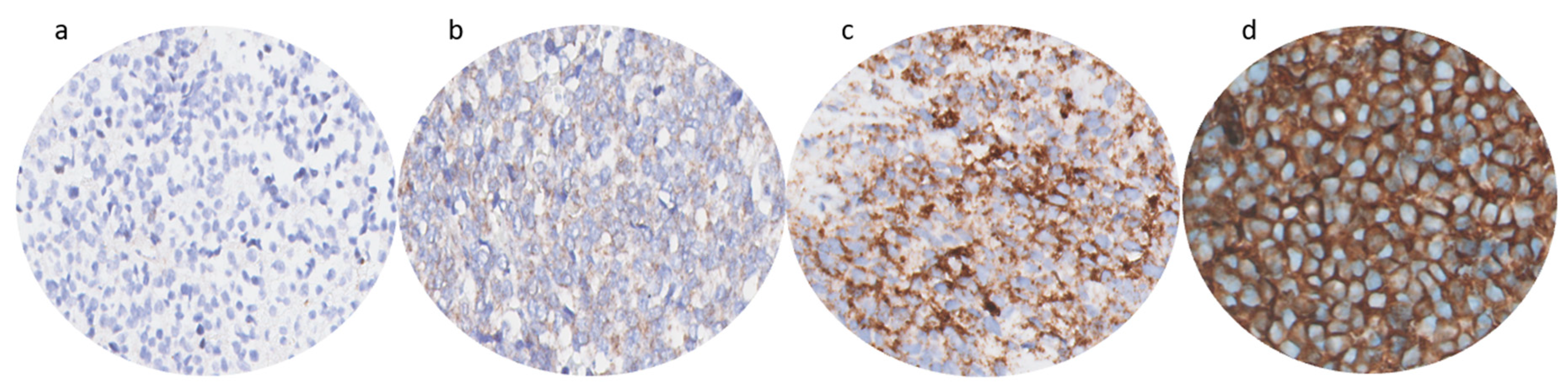
2.4. Immunohistochemistry Scoring Method
2.5. Human Cancer Lines
2.6. Antibodies Used for Flow Cytometry and Immunofluorescence Microscopy
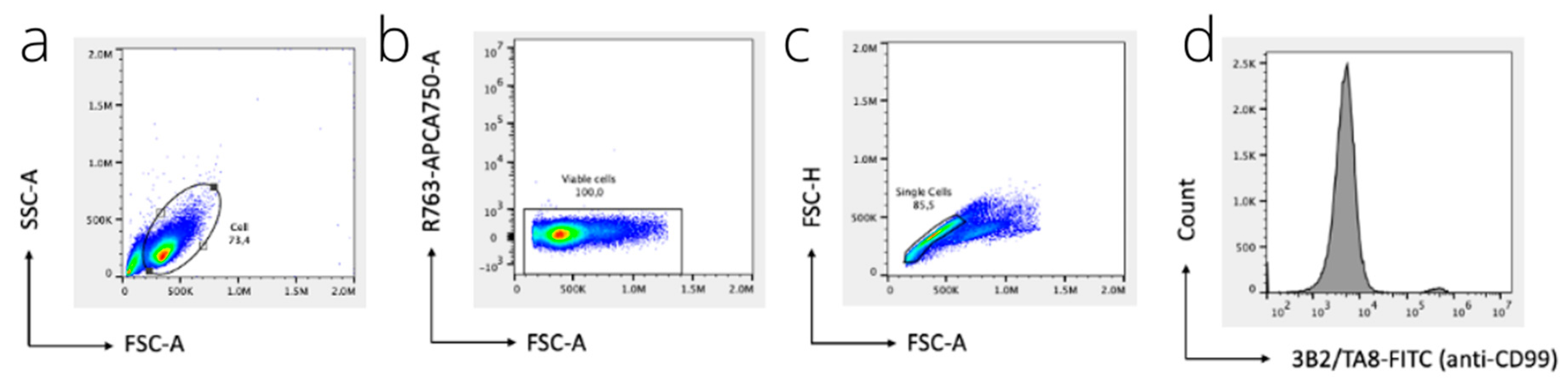
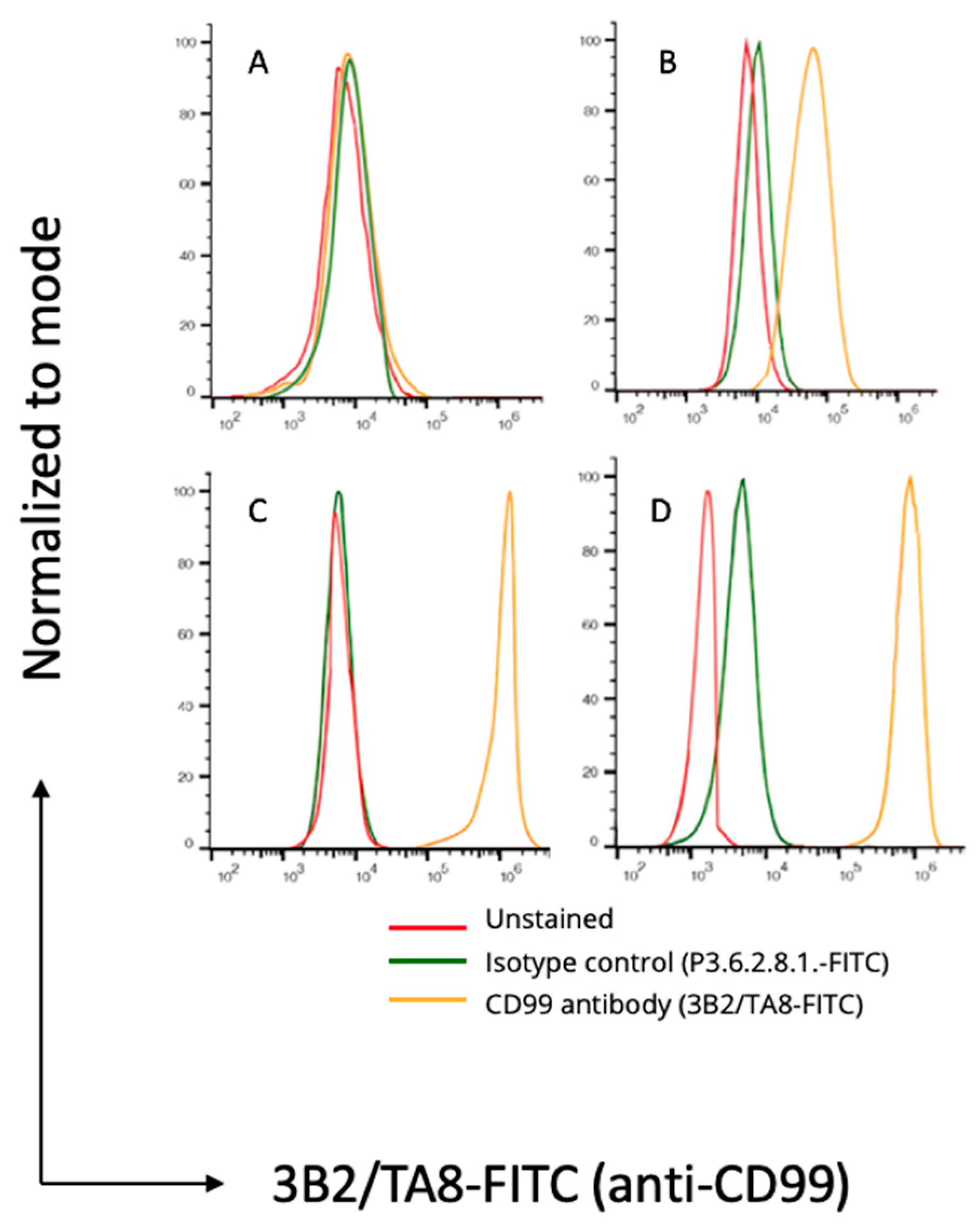
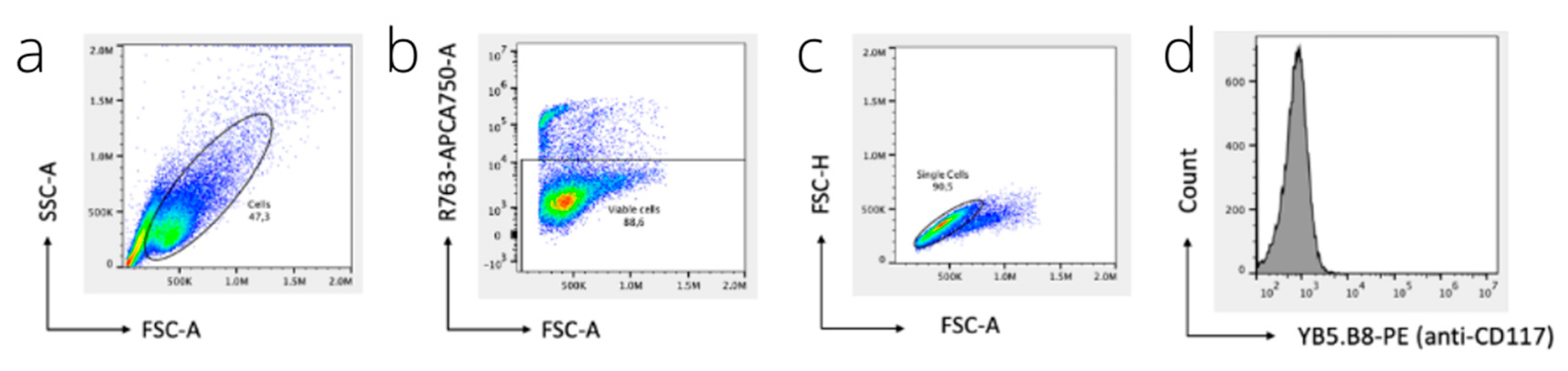
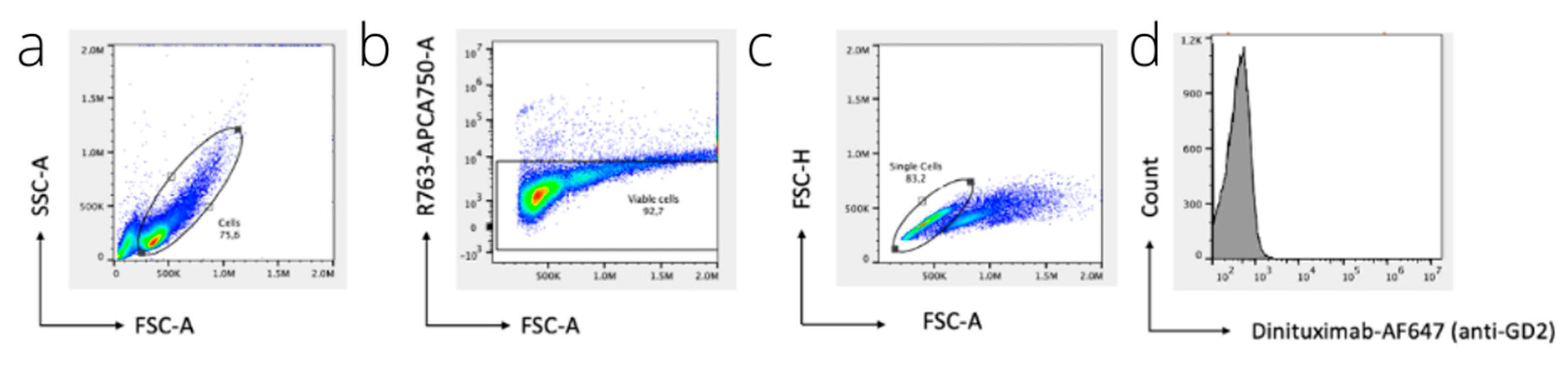
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
2.9. Topical Application and Imaging
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
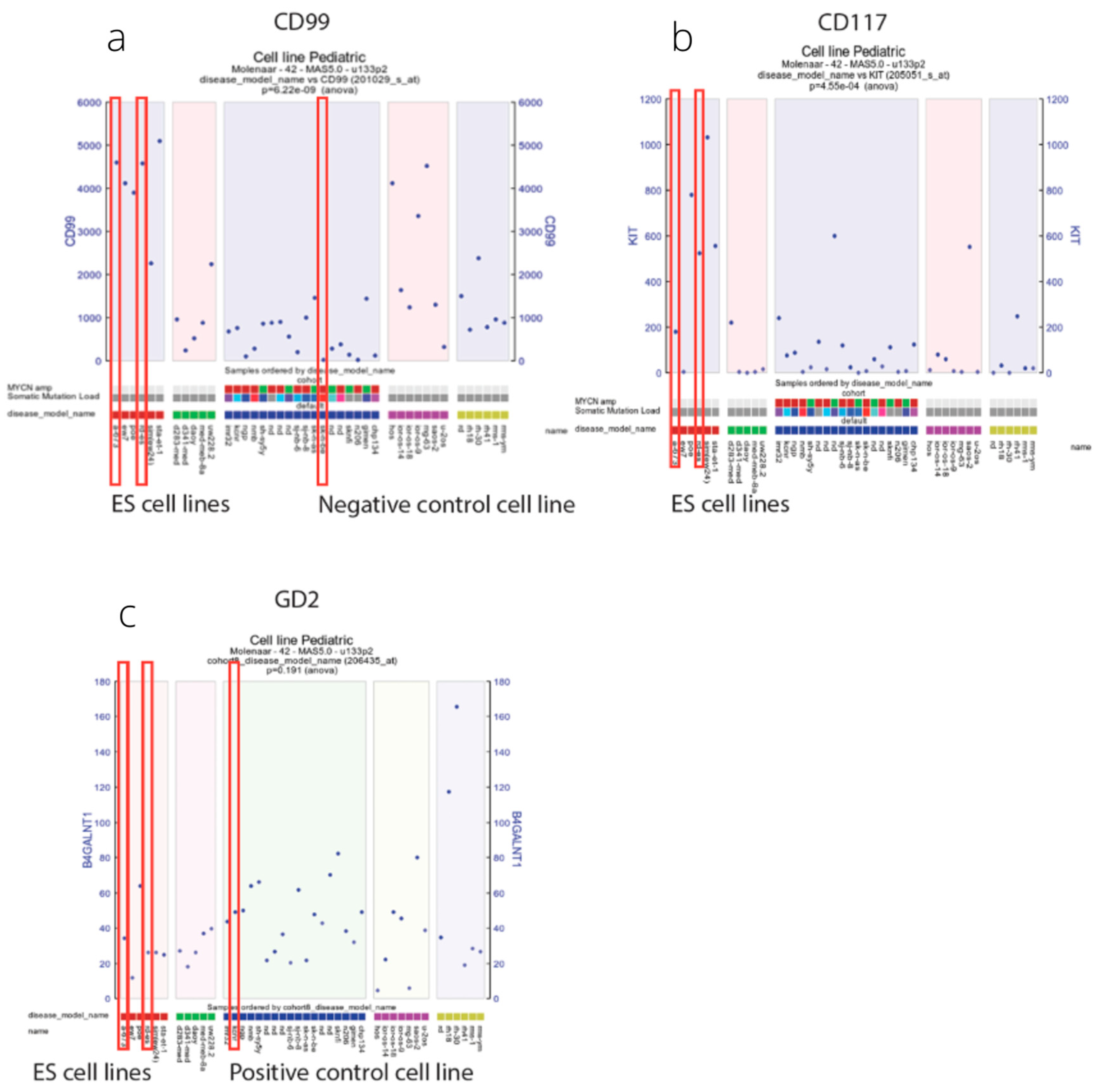
3.1. Immunohistochemistry
3.2. Flow Cytometry and Immunofluorescence Microscopy
3.3. Topical Application
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Antigen | Source | Clone | Manufacturer | Positive Control | Negative Control | Dilution | Retrieval Buffer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD99 | Rabbit monoclonal | CB1 | Leica | Pancreas, tonsil, liver, and colon | None | 1:40 | pH high (Tris/EDTA) |
| CD117 | Rabbit monoclonal | EP10 | Leica | GIST, colon, skin | Liver | Ready to use | pH high (Tris/EDTA) |
| CXCR4 | Mouse monoclonal | EP394 | Cell Marque | Thymus, Hodgkin lymphoma, bone marrow, tonsil, spleen | Liver | 1:60 | pH high (Tris/EDTA) |
| NPY-R-Y1 | Rabbit polyclonal | AB183108 | Abcam | Brain and breast carcinoma | Liver | 1:80 | pH high (Tris/EDTA) |
| LINGO-1 | Rabbit polyclonal | HPA074653 | Sigma | Brain | Liver | 1:80 | pH high (Tris/EDTA) |
| IGF-1R | Rabbit monoclonal | D38B1XP | Cell signaling technology | Placenta | Skin | 1:300 | pH low (citrate) |
| GD2 | Mouse monoclonal | 14.G2a and H3F8 | BD Pharmingen and Creative Biolabs | Brain and neuroblastoma | Kidney and liver | 1:100 and 1:1000 | Various antigen retrieval buffers were tested |
Appendix B
| BC27T | BC62T | |
|---|---|---|
| CD99 | 2245 | 3463 |
| CD117 | 1 | 5301 |
| GD2 | 1 | 993 |
Appendix C
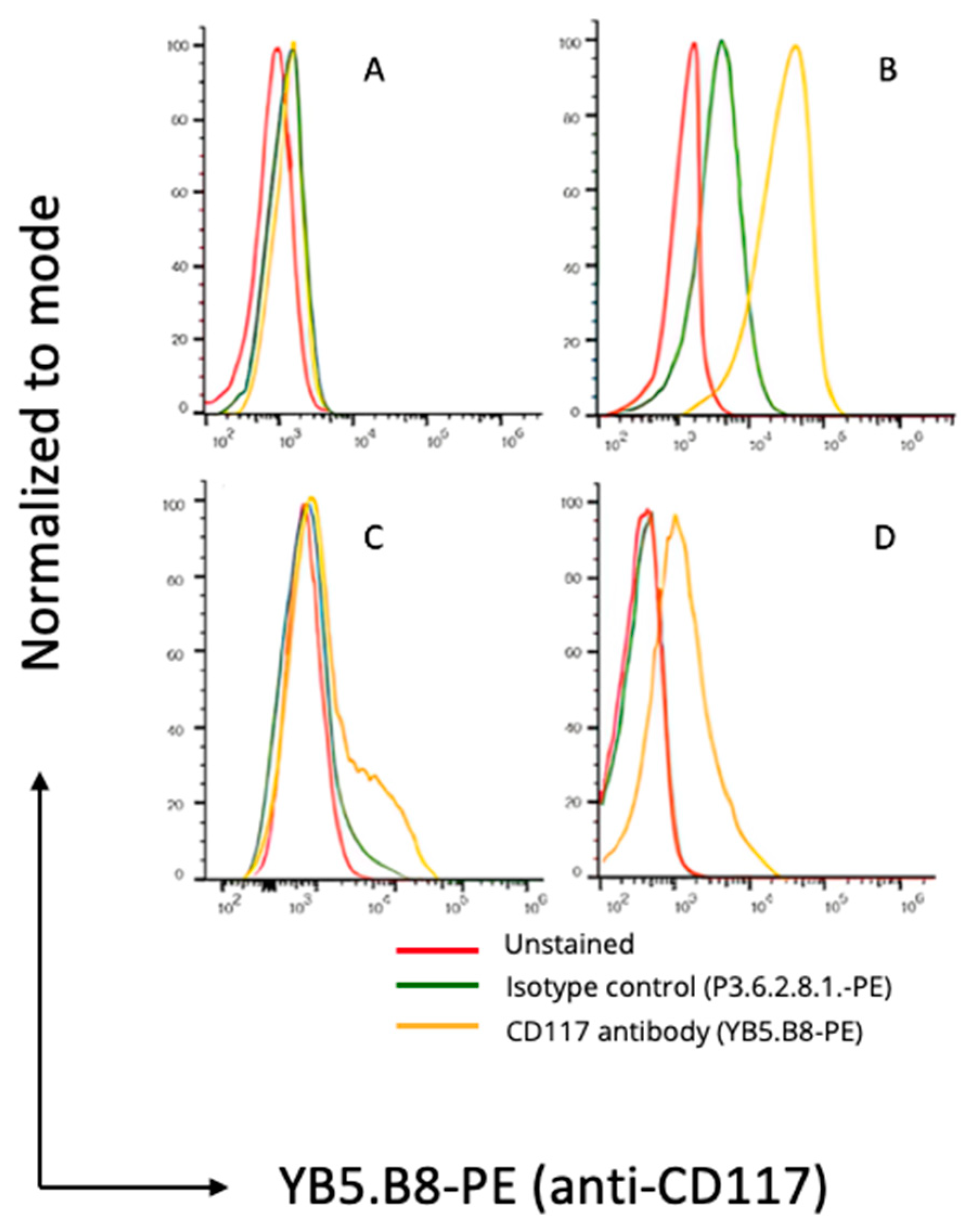
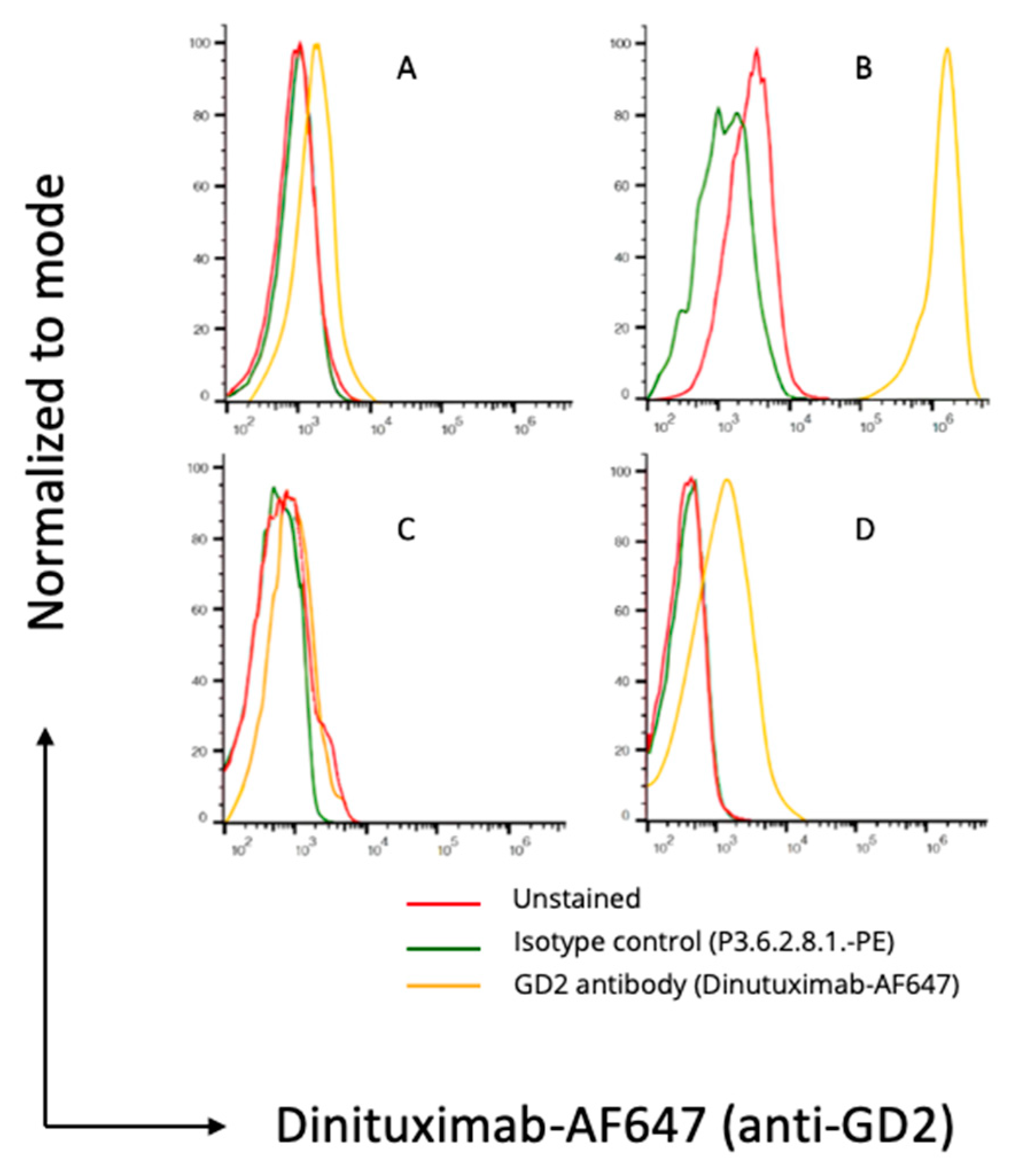
References
- Zöllner, S.K.; Amatruda, J.F.; Bauer, S.; Collaud, S.; de Álava, E.; DuBois, S.G.; Hardes, J.; Hartmann, W.; Kovar, H.; Metzler, M.; et al. Ewing Sarcoma-Diagnosis, Treatment, Clinical Challenges and Future Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1685. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Esiashvili, N.; Goodman, M.; Marcus, R.B., Jr. Changes in incidence and survival of Ewing sarcoma patients over the past 3 decades: Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results data. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2008, 30, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damron, T.A.; Ward, W.G.; Stewart, A. Osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and Ewing’s sarcoma: National Cancer Data Base Report. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2007, 459, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, A., Jr.; Ullah, E.; Wahab, S.; Kumar, V., Jr. Relevance of MRI in prediction of malignancy of musculoskeletal system--a prospective evaluation. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2009, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulaner, G.; Hwang, S.; Lefkowitz, R.A.; Landa, J.; Panicek, D.M. Musculoskeletal tumors and tumor-like conditions: Common and avoidable pitfalls at imaging in patients with known or suspected cancer: Part A: Benign conditions that may mimic malignancy. Int. Orthop. 2013, 37, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderton, J.; Moroz, V.; Marec-Bérard, P.; Gaspar, N.; Laurence, V.; Martín-Broto, J.; Sastre, A.; Gelderblom, H.; Owens, C.; Kaiser, S.; et al. International randomised controlled trial for the treatment of newly diagnosed EWING sarcoma family of tumours—EURO EWING 2012 Protocol. Trials 2020, 21, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kreyer, J.; Ranft, A.; Timmermann, B.; Juergens, H.; Jung, S.; Wiebe, K.; Boelling, T.; Schuck, A.; Vieth, V.; Streitbuerger, A.; et al. Impact of the Interdisciplinary Tumor Board of the Cooperative Ewing Sarcoma Study Group on local therapy and overall survival of Ewing sarcoma patients after induction therapy. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e27384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacci, G.; Longhi, A.; Briccoli, A.; Bertoni, F.; Versari, M.; Picci, P. The role of surgical margins in treatment of Ewing’s sarcoma family tumors: Experience of a single institution with 512 patients treated with adjuvant and neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 65, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, T.; Hillmann, A.; Hoffmann, C.; Rübe, C.; Blasius, S.; Dunst, J.; Jürgens, H.; Winkelmann, W. Significance of surgical margin on the prognosis of patients with Ewing’s sarcoma. A report from the Cooperative Ewing’s Sarcoma Study. Cancer 1996, 78, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluga, M.; Windhager, R.; Lang, S.; Heinzl, H.; Krepler, P.; Mittermayer, F.; Dominkus, M.; Zoubek, A.; Kotz, R. The role of surgery and resection margins in the treatment of Ewing’s sarcoma. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2001, 392, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunst, J.; Schuck, A. Role of radiotherapy in Ewing tumors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2004, 42, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.N.; Carlson, R.; Hasan, H.; Rassekh, S.R.; Goddard, K. Long-term Outcomes and Complications in Pediatric Ewing Sarcoma. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 40, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, A.C. Late effects of radiotherapy for pediatric extremity sarcomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 60, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulon, S.; Brennan, B.; Gaspar, N.; Dirksen, U.; Jeys, L.; Cassoni, A.; Claude, L.; Seddon, B.; Marec-Berard, P.; Whelan, J.; et al. Can postoperative radiotherapy be omitted in localised standard-risk Ewing sarcoma? An observational study of the Euro-E.W.I.N.G group. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 61, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahrmeijer, A.L.; Hutteman, M.; van der Vorst, J.R.; van de Velde, C.J.; Frangioni, J.V. Image-guided cancer surgery using near-infrared fluorescence. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rijs, Z.; Jeremiasse, B.; Shifai, N.; Gelderblom, H.; Sier, C.F.M.; Vahrmeijer, A.L.; van Leeuwen, F.W.B.; van der Steeg, A.F.W.; van de Sande, M.A.J. Introducing Fluorescence-Guided Surgery for Pediatric Ewing, Osteo-, and Rhabdomyosarcomas: A Literature Review. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernot, S.; van Manen, L.; Debie, P.; Mieog, J.S.D.; Vahrmeijer, A.L. Latest developments in molecular tracers for fluorescence image-guided cancer surgery. Lancet. Oncol. 2019, 20, e354–e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Valk, K.S.; Deken, M.M.; Schaap, D.P.; Meijer, R.P.; Boogerd, L.S.; Hoogstins, C.E.; van der Valk, M.J.; Kamerling, I.M.; Bhairosingh, S.S.; Framery, B.; et al. Dose-Finding Study of a CEA-Targeting Agent, SGM-101, for Intraoperative Fluorescence Imaging of Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 1832–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogstins, C.E.; Tummers, Q.R.; Gaarenstroom, K.N.; de Kroon, C.D.; Trimbos, J.B.; Bosse, T.; Smit, V.T.; Vuyk, J.; van de Velde, C.J.; Cohen, A.F.; et al. A Novel Tumor-Specific Agent for Intraoperative Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging: A Translational Study in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2929–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meijer, R.P.J.; de Valk, K.S.; Deken, M.M.; Boogerd, L.S.F.; Hoogstins, C.E.S.; Bhairosingh, S.S.; Swijnenburg, R.J.; Bonsing, B.A.; Framery, B.; Fariña Sarasqueta, A.; et al. Intraoperative detection of colorectal and pancreatic liver metastases using SGM-101, a fluorescent antibody targeting CEA. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinkamp, P.J.; Pranger, B.K.; Li, M.F.; Linssen, M.D.; Voskuil, F.J.; Been, L.B.; van Leeuwen, B.L.; Suurmeijer, A.J.H.; Nagengast, W.B.; Kruijff, S.; et al. Fluorescence-Guided Visualization of Soft-Tissue Sarcomas by Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A: A Phase 1 Single-Center Clinical Trial. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, C.W.; Gibbs, S.L. Fluorescence Image-Guided Surgery—A Perspective on Contrast Agent Development. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2020, 11222, 2545292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosma, S.E.; van Driel, P.B.; Hogendoorn, P.C.; Dijkstra, P.S.; Sier, C.F. Introducing fluorescence guided surgery into orthopedic oncology: A systematic review of candidate protein targets for Ewing sarcoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 118, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kailayangiri, S.; Altvater, B.; Meltzer, J.; Pscherer, S.; Luecke, A.; Dierkes, C.; Titze, U.; Leuchte, K.; Landmeier, S.; Hotfilder, M.; et al. The ganglioside antigen G(D2) is surface-expressed in Ewing sarcoma and allows for MHC-independent immune targeting. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wellens, L.M.; Deken, M.M.; Sier, C.F.M.; Johnson, H.R.; de la Jara Ortiz, F.; Bhairosingh, S.S.; Houvast, R.D.; Kholosy, W.M.; Baart, V.M.; Pieters, A.; et al. Anti-GD2-IRDye800CW as a targeted probe for fluorescence-guided surgery in neuroblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasov, N.J.; Dombrowski, F.; Lode, H.N.; Spasova, M.; Ivanova, L.; Mumdjiev, I.; Burnusuzov, H.; Siebert, N. First-line Anti-GD2 Therapy Combined With Consolidation Chemotherapy in 3 Patients With Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Ewing Sarcoma or Ewing-like Sarcoma. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 44, e948–e953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingerter, A.; El Malki, K.; Sandhoff, R.; Seidmann, L.; Wagner, D.C.; Lehmann, N.; Vewinger, N.; Frauenknecht, K.B.M.; Sommer, C.J.; Traub, F.; et al. Exploiting Gangliosides for the Therapy of Ewing’s Sarcoma and H3K27M-Mutant Diffuse Midline Glioma. Cancers 2021, 13, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Protein Atlas. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- Dekkers, J.F.; van Vliet, E.J.; Sachs, N.; Rosenbluth, J.M.; Kopper, O.; Rebel, H.G.; Wehrens, E.J.; Piani, C.; Visvader, J.E.; Verissimo, C.S.; et al. Long-term culture, genetic manipulation and xenotransplantation of human normal and breast cancer organoids. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 1936–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, N.; de Ligt, J.; Kopper, O.; Gogola, E.; Bounova, G.; Weeber, F.; Balgobind, A.V.; Wind, K.; Gracanin, A.; Begthel, H.; et al. A Living Biobank of Breast Cancer Organoids Captures Disease Heterogeneity. Cell 2018, 172, 373–386.e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rijpkema, M.; Bos, D.L.; Cornelissen, A.S.; Franssen, G.M.; Goldenberg, D.M.; Oyen, W.J.; Boerman, O.C. Optimization of Dual-Labeled Antibodies for Targeted Intraoperative Imaging of Tumors. Mol. Imaging 2015, 14, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Town, J.; Pais, H.; Harrison, S.; Stead, L.F.; Bataille, C.; Bunjobpol, W.; Zhang, J.; Rabbitts, T.H. Exploring the surfaceome of Ewing sarcoma identifies a new and unique therapeutic target. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3603–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sariola, H.; Terävä, H.; Rapola, J.; Saarinen, U.M. Cell-surface ganglioside GD2 in the immunohistochemical detection and differential diagnosis of neuroblastoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1991, 96, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poon, V.I.; Roth, M.; Piperdi, S.; Geller, D.; Gill, J.; Rudzinski, E.R.; Hawkins, D.S.; Gorlick, R. Ganglioside GD2 expression is maintained upon recurrence in patients with osteosarcoma. Clin. Sarcoma. Res. 2015, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vries, H.M.; Bekers, E.; van Oosterom, M.N.; Karakullukcu, M.B.; van, H.G.; Poel, D.; van Leeuwen, F.W.B.; Buckle, T.; Brouwer, O.R. c-MET Receptor-Targeted Fluorescence on the Road to Image-Guided Surgery in Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, L.A.; Hattori, T.; Ali, M.A.E.; Ketavarapu, G.; Koide, A.; Park, C.Y.; Koide, S. High-valency Anti-CD99 Antibodies Toward the Treatment of T Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersting, C.; Packeisen, J.; Leidinger, B.; Brandt, B.; von Wasielewski, R.; Winkelmann, W.; van Diest, P.J.; Gosheger, G.; Buerger, H. Pitfalls in immunohistochemical assessment of EGFR expression in soft tissue sarcomas. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 59, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, E.J.; Green, J.A.; Clark, A.H.; Youngson, J.H. Comparison of different scoring systems for immunohistochemical staining. J. Clin. Pathol. 1999, 52, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rijs, Z.; Belt, E.; Kalisvaart, G.M.; Sier, C.F.M.; Kuppen, P.J.K.; Cleven, A.H.G.; Vahrmeijer, A.L.; van de Sande, M.A.J.; van Driel, P. Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Candidate Biomarkers for Fluorescence-Guided Surgery of Myxofibrosarcoma Using an Objective Scoring Method. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernández, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, L.; Ding, Y.; Niu, X.; Liu, W. Accuracy of bony resection under computer-assisted navigation for bone sarcomas around the knee. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 21, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
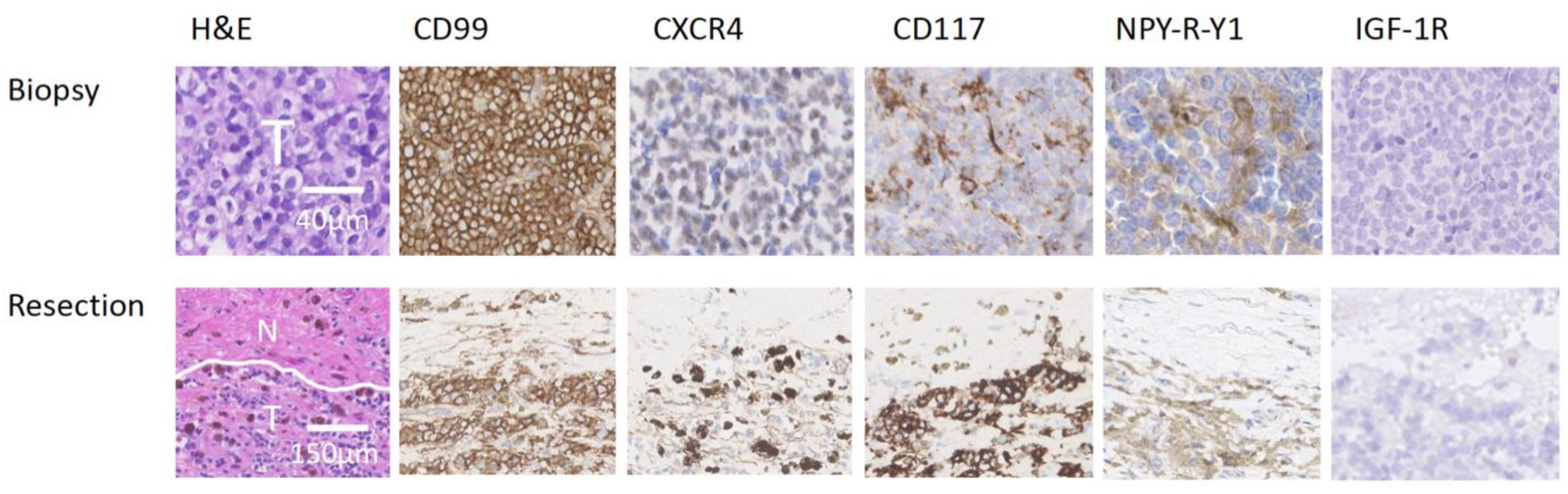

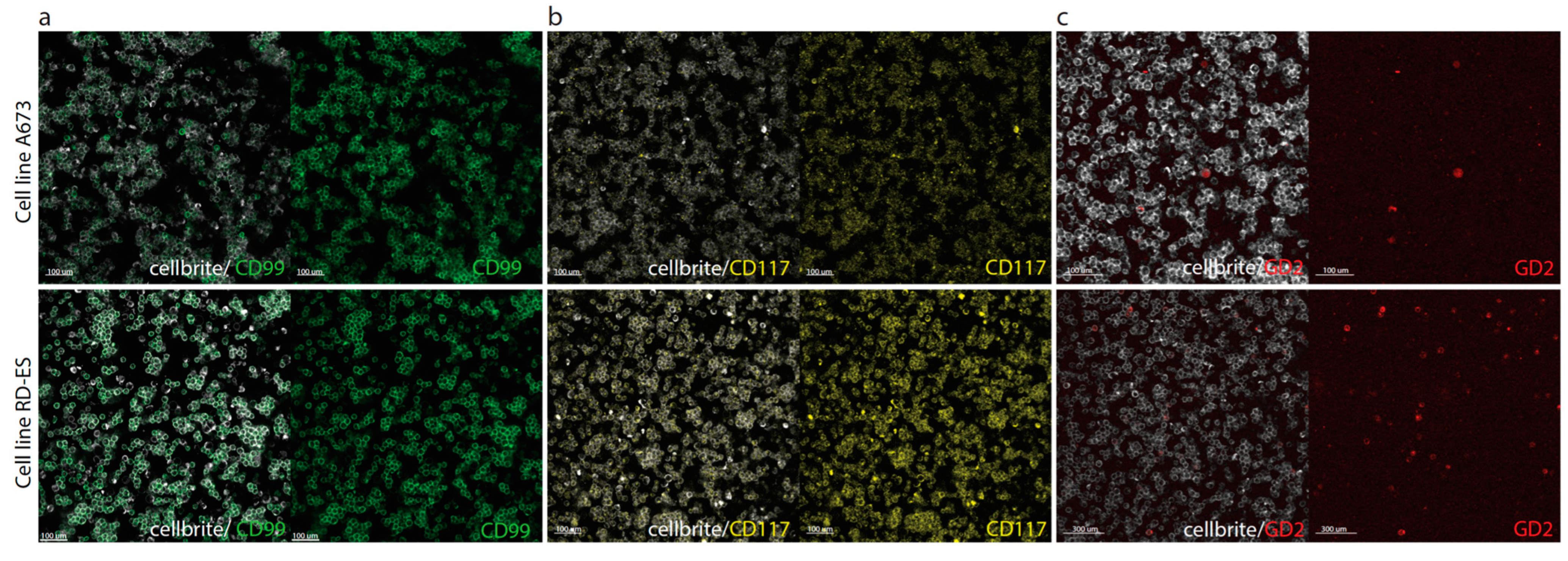
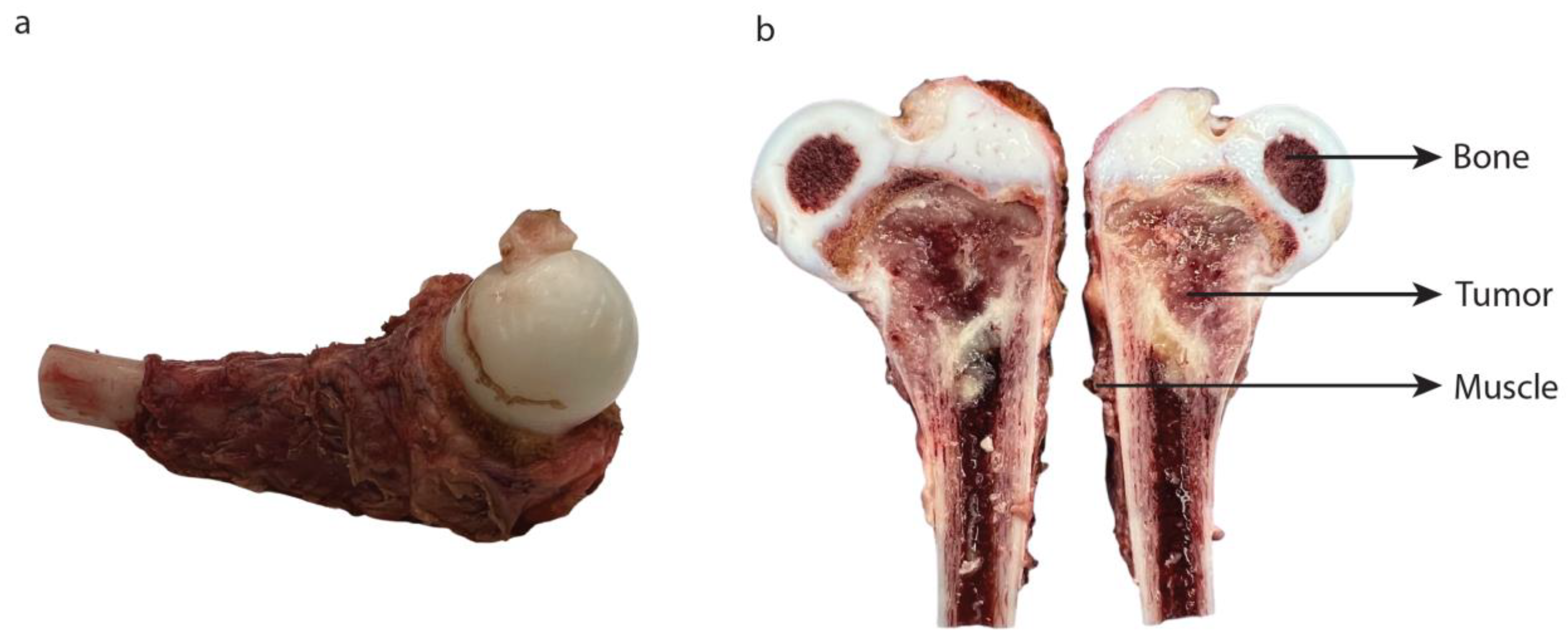

| Patient | Gender | Age * | Preoperative Therapy | % Vital Tumor in Resection Specimen | cTNM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Female | 13 | VIDE | 30% | cT1N0M0 | |
| 2 | Female | 16 | VIDE, Melphalan/Treosulfan, Irinotecan/Temozolomide | N.A. | cTxN0M0 | |
| 3 | Male | 14 | VIDE, Dactinomycin, Melphalan/Treosulfan | 40% | cT2N1M1 | |
| 4 | Female | 2 | VIDE, VAI | N.A. | cT1N0M1 | |
| 5 | Male | 5 | VIDE, VAI | 40% | cT1N0M0 | |
| 6 | Male | 14 | VIDE, VAC, Melphalan/Treosulfan | 40% | cT2N1M0 | |
| 7 | Male | 6 | VIDE, VAI, Busulfan/Melphalan | 80% | cT1N0M0 | |
| 8 | Male | 5 | Cyclofosfamide/Topotecan, Tremozolamide/Irinotecan, Treosulfan/Melphalan, VIDE, VAI, Vinorelbine | N.A. | cT2N0M1 | |
| 9 | Male | 6 | VIDE, VAI | N.A. | cT2N0M0 | |
| 10 | Female | 8 | VIDE, Treosulfan/Melphalan | 40% | cT2N1M0 | |
| 11 | Female | 18 | VIDE | N.A. | cT2N0M0 | |
| 12 | Male | 16 | VIDE, VAI, Treosulfan/Melphalan | 50% | cT2N0M0 | |
| 13 | Male | 14 | VIDE, Treosulfan/Melphalan, VAC, Cyclofosfamide/topotecan | 40% | cT2N0M1 | |
| Target | Tested Ewing Sarcoma Cell Lines | Positive Control | Negative Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD99 | A673 and RD-ES | BC62T | SK-N-BE |
| CD117 | A673 and RD-ES | BC62T | BC27T |
| GD2 | A673 and RD-ES | KCNR | BC27T |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeremiasse, B.; Rijs, Z.; Angoelal, K.R.; Hiemcke-Jiwa, L.S.; de Boed, E.A.; Kuppen, P.J.K.; Sier, C.F.M.; van Driel, P.B.A.A.; van de Sande, M.A.J.; Wijnen, M.H.W.A.; et al. Evaluation of Potential Targets for Fluorescence-Guided Surgery in Pediatric Ewing Sarcoma: A Preclinical Proof-of-Concept Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 3896. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153896
Jeremiasse B, Rijs Z, Angoelal KR, Hiemcke-Jiwa LS, de Boed EA, Kuppen PJK, Sier CFM, van Driel PBAA, van de Sande MAJ, Wijnen MHWA, et al. Evaluation of Potential Targets for Fluorescence-Guided Surgery in Pediatric Ewing Sarcoma: A Preclinical Proof-of-Concept Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(15):3896. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153896
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeremiasse, Bernadette, Zeger Rijs, Karieshma R. Angoelal, Laura S. Hiemcke-Jiwa, Ella A. de Boed, Peter J. K. Kuppen, Cornelis F. M. Sier, Pieter B. A. A. van Driel, Michiel A. J. van de Sande, Marc H. W. A. Wijnen, and et al. 2023. "Evaluation of Potential Targets for Fluorescence-Guided Surgery in Pediatric Ewing Sarcoma: A Preclinical Proof-of-Concept Study" Cancers 15, no. 15: 3896. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153896
APA StyleJeremiasse, B., Rijs, Z., Angoelal, K. R., Hiemcke-Jiwa, L. S., de Boed, E. A., Kuppen, P. J. K., Sier, C. F. M., van Driel, P. B. A. A., van de Sande, M. A. J., Wijnen, M. H. W. A., Rios, A. C., & van der Steeg, A. F. W. (2023). Evaluation of Potential Targets for Fluorescence-Guided Surgery in Pediatric Ewing Sarcoma: A Preclinical Proof-of-Concept Study. Cancers, 15(15), 3896. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153896









