Non-Coding RNAs in Oral Cancer: Emerging Roles and Clinical Applications
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Oral Cancer: Current Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers
3. Diverse ncRNAs in OC
3.1. Role of miRNAs in Oral Cancer
3.2. Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Oral Cancer
| LncRNAs | Function on Up or Down Regulation | Targets/Associated Pathways | Study Model | Biomarker/Therapy | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| List of up-regulated lncRNAs | |||||
| lncRNA DANCR ↑ | Promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration, and suppresses apoptosis | miR-135a-5p/KLF8 axis, DANCR/miR-4707-3p/FOXC2 pathway | Patient samples and cell lines | Biomarker (prognostic and diagnostic), therapeutic target | [131] |
| lncRNA PCAT1 ↑ | Regulation of proliferation, and inhibits apoptosis | c-Myc-AKT1-p38 MAPK signaling pathways | Cell lines, patient tissue, and xenograft tumor model | Therapeutic target | [132] |
| lncRNA PVT1 ↑ | Increases metastasis, proliferation, and invasion, enhanced EMT and cancer cell stemness | Wnt/β-catenin signaling | Cell lines and xenograft tumor model | Therapeutic target | [133] |
| lncRNA MALAT1 ↑ | Associated with differentiation and clinical staging in TSCC. Correlated with tumor occurrence, development, and prognosis in HNSCC. Chemoresistance in LSCC and OSCC cells | Wnt/β-catenin in TSCC. G2/M in HNSCC. PI3K/AKT/mTORsignaling pathway in OSCC. | Cancer cell lines and tissue and plasma samples | Diagnostic biomarker | [122] |
| lncRNA-ROR ↑ | Regulates cellular differentiation, represses p53 | miR-145 | Clinical specimens | Prognostic biomarker | [134] |
| lncRNA NORAD ↑ | Causes cell proliferation, migration, decreasing apoptosis, sponges miR-577 to enhance TPM4. | miR-577/TPM4 axis | OC tissues and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [135] |
| lncRNA ELDR ↑ | Induces cell proliferation, and inhibits miR-7 to regulate EGFR. Regulates Cyclin E1 signaling through ILF3 | ILF3-cyclin E1 signaling, | Tissue samples, cell lines, and xenograft mouse model | Therapeutic target | [124] |
| lncRNA HOTAIR ↑ | Promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis, and represses E-cadherin in OSCC | EZH2 | Tissue, saliva samples and cell lines | Biomarker and therapeutic target | [136] |
| lncRNA HIFCAR ↑ | Modulates the hypoxia signal pathway and contributes to OSCC progression | hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α) | OC cell lines and xenograft mice model | Prognostic biomarker | [137] |
| lncRNA UCA1 ↑ | Promotes proliferation and cisplatin resistance, as well as suppressed apoptosis in OSCC cells | miR-184 | Tissue, saliva samples, cell lines, and xenograft mice model | Therapeutic target | [138] |
| lncRNA XIST ↑ | Regulates miR-29b expression, which induces cell apoptosis through the p53 pathway and promotes tumor growth in in vivo model | miR-29b | Xenograft model and OC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [139] |
| lncRNA ARNIL ↑ | Promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration | miR-125a | Tissues and serum, cell lines, and xenograft mouse model | Biomarker (prognostic) | [140] |
| lncRNA NEAT1 ↑ | Promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion | miR-365/RGS20 | OC cell lines, tissue, saliva samples, and mice model | Biomarkers and therapeutic target | [141,142] |
| lncRNA DLEU1 ↑ | Promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration | miR-149/CDK6 axis | OC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [143,144] |
| lncRNA AC007271.3 ↑ | Promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion, inhibits apoptosis, and induces tumor growth in vivo | Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, miR-125b-2-3p/Slug/E-cadherin axis | OC tissues, saliva, plasma, cell lines, and mice model | Therapeutic target | [145,146] |
| lncRNA LHFPL3-AS1 ↑ | Promotes OSCC growth and cisplatin resistance | LHFPL3-AS1/miR-362-5p/CHSY1 Pathway | OC tissues and cell lines | - | [147] |
| lncRNA 01296 ↑ | Promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration | SRSF1 protein | Tissue samples, cell lines, and xenograft mice model | Therapeutic target | [148] |
| lncRNA JPX ↑ | Promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration | miR-944/CDH2 axis | OC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [149] |
| lncRNA LINC00974 ↑ | Promotes invasion and migration | miR-122, RhoA | Tissue samples and cell lines | - | [150] |
| lncRNA PRNCR1 ↑ | Promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration | miR-326/FSCN1 axis | Cell lines, saliva, and plasma | - | [151] |
| lncRNA LOLA1 ↑ | Promotes migration, invasion, and EMT | AKT/GSK-3β pathway | Tissue samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [152] |
| lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 ↑ | Promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion | miR-204-5p/FOXC1 | Tissues and cells | - | [153] |
| lncRNA LINC00662 ↑ | Increased TNM stage and lymph node metastasis of the patients. Promotes cell growth and metastasis | miR-144-3p/EZH2 Axis | Tissues and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [154] |
| lncRNA HOTTIP ↑ | Causes lymph node metastasis. Regulates proliferation, migration, and invasion | HMGA2-Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway | Xenograft model, patient tissue and saliva, and cell lines | Biomarker (diagnosis) and therapeutic target | [155] |
| lncRNA MIR4435-2HG ↑ | Regulates cancer cell behavior. Involved in the promotion of cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion | TGF-β1 | Plasma samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [156] |
| lncRNA GACAT1 ↑ | Promotes tumor growth and migration | miR-149 | Tissue samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [157] |
| lncRNA TSPEAR-AS2 ↑ | Promotes tumor cell progression and is associated with advanced TNM staging | TSPEAR-AS2/miR-487a-3p/PPM1A axis | Tissues and cell lines | Biomarker and therapeutic strategy | [158] |
| lncRNA FTH1P3 ↑ | Induces cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion | PI3K/Akt/GSK3b/ Wnt/β-catenin | Tissues and cell lines | Biomarker | [159] |
| lncRNA PLAC2 ↑ | Promotes proliferation and invasion in OSCC cells as well as tumor growth and metastasis in vivo | Downstream Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway | Tissues cell lines, and xenograft mice model | Biomarker (prognosis and therapy) | [160] |
| lncRNA SNHG20 ↑ | Promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion | miRNA-19b-3p/RAB14 axis, miR-29a/DIXDC1/Wntsignaling pathway | Tissue samples and cell lines | Biomarker (diagnosis), and therapeutic target | [161,162] |
| lncRNA LINC01137 ↑ | Promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration | miR-22-3p | Cell lines | Therapeutic target | [163] |
| lncRNA PSMA3-AS1 ↑ | Promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration | miR-136-5p/FN1 axis | Patient samples | Prognostic marker | [164] |
| lncRNA DCST1-AS1 ↑ | Causes M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages, which thereby promotes tumor malignancy and metastasis | NF-κB pathway | OC cell lines and tumor xenograft model | Prognostic indicator | [165] |
| lncRNA TUG1 ↑ | Promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration, prevents apoptosis | TUG1/miR-593-3p/MAPK axis | OC cells, tissues, saliva and nude mice model | Therapeutic target and biomarker (diagnosis) | [166] |
| lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 ↑ | Associated with poor pathological grading and prognosis in patients. Promotes proliferation and colony formation as well as regulates the cell cycle signaling pathways | CDK2, CDK4, and P21 | OC cell lines | Therapeutic target and biomarker (prognosis) | [167] |
| lncRNA LINC01234 ↑ | Promotes growth, invasiveness, and metastasis | miR-637/NUPR1 axis, miR-433/PAK4 axis | Tissue samples, cell lines, and nude mice model | Therapeutic target | [168,169] |
| lncRNA LINC01207 ↑ | Promotes proliferation and migration, reduces apoptosis and autophagy of cells | miR-1301-3p/LDHA axis | Tissue samples and cell lines | Novel diagnostic and therapeutic target | [170] |
| lncRNA TTN-AS1 ↑ | Promotes cell growth, and migration and restricts apoptosis | miR-411-3p/NFAT5 axis | Tissue samples and cells, as well as mice model | Therapeutic target | [171] |
| lncRNA ZEB1-AS1 ↑ | Promotes EMT, cell invasion, and migration. Act as a tumor promoter | miR-23a | Patient samples, cell lines, and xenograft mice model | Therapeutic target | [172] |
| lncRNA H19↑ | Promotes proliferation, associated with the TNM staging and nodal invasion | H19/miR-138/EZH2 axis | Cell lines, tissue samples, and mice model | Therapeutic target | [173] |
| lncRNA HCP5 ↑ | Facilitates Cell Invasion And EMT | miR-140-5p/SOX4 axis | Patient samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [174] |
| lncRNA PTTG3P ↑ | Promotes proliferation and migration | PTTG3P/miR-142-5p/JAG1 axis | OC cell lines | - | [175] |
| lncRNA IGF2BP2-AS1 ↑ | Promotes cell growth, and migration and restricts apoptosis | Wnt/β-catenin pathway | Tissue samples, plasma, and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [176] |
| lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 ↑ | Promotes migration and invasion and facilitated metastasis in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma (SACC) | Binds with miR-143-3p and activates PI3K/Akt and MEK/Erksignaling | Tissue samples, cell lines, and xenograft mouse model | Therapeutic target | [177] |
| lncRNA LTSCCAT ↑ | Promotes EMT and promotes invasion and metastasis in both in vivo and in vitro | miR-103a-2-5p/SMYD3/TWIST1 axis | Tissue samples, cell lines and xenograft tumor model | Therapeutic target | [178] |
| lncRNA RP11-284F21.9 ↑ | Promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration | miR-383-5p/MAL2 axis | Tissue samples and cancer cell lines | Therapeutic target | [179] |
| lncRNA WWTR1-AS1 ↑ | Associated with larger tumor size, cervical node metastasis, and poor prognosis | WWTR1-AS1/WWTR1 axis | Cell lines | Biomarkers with prognostic significance | [180] |
| LINC00668 ↑ | Facilitate VEGFA expression, and promotes tumor growth | miR-297/VEGFA axis | OC cell lines and tissues | Biomarker (diagnosis) and therapeutic target | [181] |
| lncRNA HNF1A-AS1 ↑ | Promotes OSCC progression | Notch signaling pathway | Tissue samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [182] |
| lncRNA MINCR ↑ | Causes proliferation and migration | Wnt/β-catenin pathway | Tissue samples and cancer cell lines | Prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target | [183] |
| lncRNA LACAT1 ↑ | Promotes malignant progression | microRNA-4301 | Tissue samples and cancer cell lines | - | [184] |
| lncRNA CASC9 ↑ | Enhances tumor progression via suppression of autophagy-mediated cell apoptosis | AKT/mTOR pathway | Tissue samples, cell lines, and mice model | Biomarker (diagnosis and prognosis) | [185] |
| lncRNA SNHG26 ↑ | Promotes TSCC growth, metastasis, and cisplatin resistance | PGK1/Akt/mTOR | Tissue samples, cell lies, and xenograft mice model | Therapeutic target and biomarker (diagnosis) | [186] |
| lncRNA PART1 ↑ | Promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis | EZH2 | Tissue samples, cell lines, and mice model | Diagnosis biomarker and a novel therapeutic target | [187] |
| lncRNA LINC00152 ↑ | Induces tumor progression, and is associated with tumor size, invasion of muscles of the tongue, lymph node metastasis, and recurrence as well | - | Tissue samples | Biomarker (diagnosis and prognosis) | [188] |
| lncRNA HOXA-AS2 ↑ | Causes OC cell proliferation and promotes tumor growth in vivo | miR-567/CDK8 | Tissue and plasma samples, cell lines, and xenograft model | Biomarker (prognostic) and therapeutic target | [189] |
| lncRNA DNM3OS ↑ | Modulates cell viability and migration | DNM3OS/miR-204-5p/HIP1 axis | Clinical samples and OC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [190] |
| lncRNA SNHG1 ↑ | Leads to the proliferation of cancer cells | miR-421/HMGB2 axis | Cancer cell lines | Therapeutic target | [191] |
| lncRNA HOXA10-AS ↑ | Promotes OC growth, and metastasis. | TP63 mRNA | Xenograft model and cancer cell lines | Therapeutic target | [192] |
| lncRNA BBOX1 ↑ | Encourages proliferation and migration, and suppresses apoptosis | miR-3940-3p/laminin subunit gamma 2 axis | Tissue, saliva and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [193] |
| lncRNA IFITM4P ↑ | Induces cell proliferation and enhanced immune escape | PD-L1 | Tissue samples, cell lines, and xenografted tumors | Therapeutic target | [194] |
| lncRNA CACS15 ↑ | Promotes proliferation and reduces expression of lncRNA MEG3 | lncRNA MEG3 | Tissue and plasma samples | Diagnostic biomarker | [195] |
| lncRNA LINC00963 ↑ | Promotes cancer stemness, increases cancer aggressiveness, and reduces chemosensitivity | ABCB5 | Tissue samples, cancer cell lines, and xenograft nude mice model | Therapeutic target | [196] |
| lncRNA OIP5-AS1 ↑ | Enhances cancer stemness, and is associated with poor clinical outcome | - | Clinical specimens | - | [197] |
| lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 ↑ | Increases cisplatin resistance, regulates proliferation and metastasis of cisplatin-resistant TSCC | KCNQ1OT1/miR-124-3p/TRIM14 axis | Cisplatin-resistant TSCC samples and TSCC cell lines | - | [198] |
| lncRNA BLACAT1 ↑ | Regulates viability, and causes migration and invasion of cells | miR-142-5p | OC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [199] |
| lncRNA AFAP1-AS1 ↑ | Encourages tumor proliferation and indicates a poor prognosis | CCNA2 | OC cell lines, xenograft tumor model | Unfavorable biomarker, therapeutic target | [200] |
| lncRNA FAL1 ↑ | Causes proliferation and develops OSCC | microRNA-761/CRKL pathway | Tissues and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [201] |
| lncRNA HOXA11-AS ↑ | Promotes proliferation, and facilitates CDDP-resistance | miR-214-3p/PIM1 | Clinical tissue specimens, cell lines, and xenograft mice model | Therapeutic target | [202] |
| lncRNA FEZF1-AS1 ↑ | Promote the malignant progression of OSCC | miR-196a | Patient samples and OSCC cell lines | - | [203] |
| lncRNA SNHG6 ↑ | Improves cell viability, proliferation, and EMT. Inhibits apoptosis | β-catenin and E-cadherin | Tca1183 cells | - | [204] |
| lncRNA HOXC13-AS ↑ | Induces proliferation, migration, and EMT | miR-378g/HOXC13 axis | Patient samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [205] |
| lncRNA ORAOV1-B ↑ | Induces invasion, migration, and metastasis | Binds to Hsp90 and activates the NF-κB-TNFα loop. | OC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [206] |
| lncRNA LINC00319 ↑ | Induces proliferation, metastasis, EMT, invasion, and angiogenesis | miR-199a-5p/FZD4 axis | Cancer cells and tissues | Therapeutic target | [207] |
| lncRNA SLC16A1-AS1 ↑ | Promotes proliferation and accelerates cell cycle | SLC16A1-AS1/CCND1 (requires further elucidation) | OC cell lines and patient tissue and plasma samples | Therapeutic target and diagnostic indicator | [208] |
| lncRNA RP5-916L7.2 ↑ | Induces proliferation and represses apoptosis | miR-328 and miR-939 | Patient samples and OC cell lines | - | [209] |
| lncRNA LINC00284 ↑ | Causes cell proliferation and migration | miR-211-3p/MAFG axis | Patient samples and cell lines | Biomarker | [210] |
| lncRNA LINC00958 ↑ | Promotes proliferation, migration, EMT and retards apoptosis | miR-627-5p/YBX2 axis | Tissue, saliva, and cell lines | Therapeutic target and biomarker (prognostic) | [211] |
| lncRNA LEF1-AS1 ↑ | Increases cell survival, proliferation, and migration. Retards cell apoptosis | LATS1 | Plasma samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target and biomarker | [212] |
| lncRNA FOXC2-AS1 ↑ | Improves proliferation, invasion, migration, and EMT and regulates the cell cycle | miR-6868-5p/E2F3 axis | Patient samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [213] |
| lncRNA LINC01116 ↑ | Causes migration and invasion | LINC01116/miR-9/MMP1 axis | Patient samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [214] |
| List of down regulated lncRNAs | |||||
| lncRNA MORT ↓ | Low expression is associated with increased proliferation and poor survival | ROCK1 | Cell lines and patient samples | Therapeutic target | [215] |
| lncRNA AC012456.4 ↓ | Significantly associated with tumor staging and survival rates for patients | JAK-STAT and MAPK signaling pathways | Cell lines and patient samples | Diagnostic, therapeutic and prognostic biomarker | [216] |
| lncRNA MEG3 ↓ | Down-regulation alleviates the aggressiveness of cancer, and is associated with poor prognosis. Induces tumor growth by promotion of cell proliferation and metastasis, induced cell cycle and suppressed cell apoptosis | miR-421, Wnt/β-catenin pathway | OC cell lines and patient samples | - | [127] |
| lncRNA HCG11 ↓ | Enhances OSCC proliferation, increases G1/S transition and Ki67 levels | miR-455-5p | OC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [217] |
| lncRNA SCIRT ↓ | Inhibits cancer cell apoptosis | miR-221 | Patient samples | Biomarker | [218] |
| lncRNA C5orf66-AS1 ↓ | Induces proliferation, invasion, and migration and inhibits apoptosis | CYC1 | Clinical specimens and cell culture | Therapeutic target | [219] |
| lncRNA PTCSC3 ↓ | Promotes cancer cell proliferation and invasion | - | Tissues and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [220] |
| lncRNA GAS5 ↓ | Promotes proliferation, invasion, EMT, and migration | miR-21/PTEN axis | Tissue, serum, and cancer cell lines | Therapeutic target | [126] |
| lncRNA FENDRR ↓ | Fails to inhibit angiogenesis of OSCC | PI3K/AKT pathway | Cell lines and patient samples | Therapeutic target | [221] |
3.3. Role of Circular RNAs (circRNA) in Oral Cancer
3.4. Role of Small Nucleolar RNA (SnoRNA) in Oral Cancer
3.5. Role of piRNAs in Oral Cancer
4. NcRNAs in Oral Cancer Progression
5. NcRNAs in Body Fluid and Exosomes of Oral Cancer as Diagnostic Markers
6. Non-Coding RNA in Oral Cancer Clinical Trials
7. Future Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Nanavati, R.; Modi, T.G.; Dobariya, C. Oral cancer: Etiology and risk factors: A review. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.; Wiesenfeld, D. Oral Cancer. Aust. Dent. J. 2018, 63 (Suppl. S1), S91–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujir, N.; Ahmed, J.; Pai, K.; Denny, C.; Shenoy, N. Challenges in Early Diagnosis of Oral Cancer: Cases Series. Acta Stomatol. Croat. 2019, 53, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, L.; Chen, J.; Yan, H.; He, Q.; Luo, P.; Xu, Z.; Yang, X. Research Status and Outlook of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 3625–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharat, S.A.; Momin, M.; Bhavsar, C. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Current Treatment Strategies and Nanotechnology-Based Approaches for Prevention and Therapy. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2016, 33, 363–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamija, S.; Menon, M.B. Non-coding transcript variants of protein-coding genes—What are they good for? RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, P.; Romano, G.; Nana-Sinkam, P.; Acunzo, M. Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy: Focus on Lung Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, D.E.; Allinson, L.M.; Al Amri, W.S.; Poulter, J.A.; Pramanik, A.; Thorne, J.L.; Verghese, E.T.; Hughes, T.A. MiR-195 and Its Target SEMA6D Regulate Chemoresponse in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, A.; Alam, S.I.; Singh, N. Oral cancer diagnostics: An overview. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 12, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheeth, N.; Patil, N. Biomarkers in Head and Neck Cancer an Update. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 71, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Li, Y. Prospective applications of microRNAs in oral cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 3974–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.M.; Phillips, B.L.; Patel, R.S.; Cohen, D.M.; Jakymiw, A.; Kong, W.W.; Cheng, J.Q.; Chan, E.K. Keratinization-associated miR-7 and miR-21 regulate tumor suppressor reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (RECK) in oral cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29261–29272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakita, A.; Yanamoto, S.; Yamada, S.; Naruse, T.; Takahashi, H.; Kawasaki, G.; Umeda, M. MicroRNA-21 promotes oral cancer invasion via the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by targeting DKK2. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2014, 20, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Li, N.; Jia, X.; Peng, C.; Luo, L.; Deng, Y.; Yin, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, H.; Lu, M.; et al. MYCN-mediated miR-21 overexpression enhances chemo-resistance via targeting CADM1 in tongue cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.H.; Tsao, C.J. Emerging role of microRNA-21 in cancer. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukas, S.G.; Vageli, D.P.; Lazopoulos, G.; Spandidos, D.A.; Sasaki, C.T.; Tsatsakis, A. The Effect of NNK, A Tobacco Smoke Carcinogen, on the miRNA and Mismatch DNA Repair Expression Profiles in Lung and Head and Neck Squamous Cancer Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirave, P.; Gondaliya, P.; Kulkarni, B.; Rawal, R.; Garg, R.; Jain, A.; Kalia, K. Exosome mediated miR-155 delivery confers cisplatin chemoresistance in oral cancer cells via epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 1157–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.H.; Huang, X.F.; Wang, Z.Y.; Han, W.; Deng, R.Z.; Mou, Y.B.; Ding, L.; Hou, Y.Y.; Hu, Q.G. Upregulation of a potential prognostic biomarker, miR-155, enhances cell proliferation in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2014, 117, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yete, S.; Saranath, D. MicroRNAs in oral cancer: Biomarkers with clinical potential. Oral Oncol. 2020, 110, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.; Yang, H.; He, L.; Zhao, J.J.; Coppola, D.; Dalton, W.S.; Cheng, J.Q. MicroRNA-155 is regulated by the transforming growth factor beta/Smad pathway and contributes to epithelial cell plasticity by targeting RhoA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 6773–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Tang, Y.L.; Liang, X.H. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Insights into cellular responses. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 4799–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.L.; Chen, P.S.; Johansson, G.; Kuo, M.L. Function and regulation of let-7 family microRNAs. MicroRNA 2012, 1, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shen, N.; Wicha, M.S.; Luo, M. The Roles of the Let-7 Family of MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Cancer Stemness. Cells 2021, 10, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.J.; Hsu, C.C.; Chang, C.H.; Tsai, L.L.; Chang, Y.C.; Lu, S.W.; Yu, C.H.; Huang, H.S.; Wang, J.J.; Tsai, C.H.; et al. Let-7d functions as novel regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistant property in oral cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, S.; Jones, A.V.; Hinsley, E.E.; Whawell, S.A.; Lambert, D.W. MicroRNA-124 suppresses oral squamous cell carcinoma motility by targeting ITGB1. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, H.; Sun, L.; Yang, M.; Pan, C.; Chen, W.; Wu, D.; Lin, Z.; Zeng, C.; Yao, Y.; et al. MiR-21 indicates poor prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinomas as an apoptosis inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3998–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, C.; Roshan, V.G.D.; Khan, I.; Manasa, V.G.; Himal, I.; Kattoor, J.; Thomas, S.; Kondaiah, P.; Kannan, S. MiRNA expression profiling and emergence of new prognostic signature for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darda, L.; Hakami, F.; Morgan, R.; Murdoch, C.; Lambert, D.W.; Hunter, K.D. The role of HOXB9 and miR-196a in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.C.; Chang, J.T.; Liao, C.T.; Kang, C.J.; Huang, S.F.; Chen, I.H.; Huang, C.C.; Huang, Y.C.; Chen, W.H.; Tsai, C.Y.; et al. OncomiR-196 promotes an invasive phenotype in oral cancer through the NME4-JNK-TIMP1-MMP signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.Y.; Chou, C.H.; Yeh, L.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Chang, K.W.; Liu, C.J.; Fan Chiang, C.Y.; Lin, S.C. MicroRNA miR-31 targets SIRT3 to disrupt mitochondrial activity and increase oxidative stress in oral carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2019, 456, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.H.; Liu, H.; Chiang, W.F.; Chen, T.W.; Chu, L.J.; Yu, J.S.; Chen, S.J.; Chen, H.C.; Tan, B.C. MiR-31-5p-ACOX1 Axis Enhances Tumorigenic Fitness in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Via the Promigratory Prostaglandin E2. Theranostics 2018, 8, 486–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.J.; Tsai, M.M.; Hung, P.S.; Kao, S.Y.; Liu, T.Y.; Wu, K.J.; Chiou, S.H.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. miR-31 ablates expression of the HIF regulatory factor FIH to activate the HIF pathway in head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.C.; Liu, C.J.; Tu, H.F.; Chung, Y.T.; Yang, C.C.; Kao, S.Y.; Chang, K.W.; Lin, S.C. miR-31 targets ARID1A and enhances the oncogenicity and stemness of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57254–57267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, S.H.; Yang, C.C.; Yu, E.H.; Chang, C.; Lee, Y.S.; Liu, C.J.; Chang, K.W.; Lin, S.C. K14-EGFP-miR-31 transgenic mice have high susceptibility to chemical-induced squamous cell tumorigenesis that is associating with Ku80 repression. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.M.; Shiah, S.G.; Huang, C.C.; Hsiao, J.R.; Chang, J.Y. Up-regulation of miR-455-5p by the TGF-beta-SMAD signalling axis promotes the proliferation of oral squamous cancer cells by targeting UBE2B. J. Pathol. 2016, 240, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Hung, P.S.; Wang, P.W.; Liu, C.J.; Chu, T.H.; Cheng, H.W.; Lin, S.C. miR-181 as a putative biomarker for lymph-node metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2011, 40, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.S.; Liu, X.B.; Wong, B.Y.; Ng, R.W.; Yuen, A.P.; Wei, W.I. Mature miR-184 as Potential Oncogenic microRNA of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2588–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Shen, W.G.; Peng, S.Y.; Cheng, H.W.; Kao, S.Y.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. miR-134 induces oncogenicity and metastasis in head and neck carcinoma through targeting WWOX gene. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.Y.; Tu, H.F.; Yang, C.C.; Wu, C.H.; Liu, C.J.; Chang, K.W.; Lin, S.C. miR-134 targets PDCD7 to reduce E-cadherin expression and enhance oral cancer progression. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 2892–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, P.S.; Liu, C.J.; Chou, C.S.; Kao, S.Y.; Yang, C.C.; Chang, K.W.; Chiu, T.H.; Lin, S.C. miR-146a enhances the oncogenicity of oral carcinoma by concomitant targeting of the IRAK1, TRAF6 and NUMB genes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ren, S.; Su, Z.; Liu, C.; Deng, T.; Huang, D.; Tian, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, Y. Increased expression of miR-93 is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 3949–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.F.; Chang, K.W.; Lin, S.C.; Hung, W.W.; Ji, S.H.; Wu, H.L.; Liu, C.J. Aberrant miR-10b, miR-372, and miR-375 expression in the cytobrushed samples from oral potentially malignant disorders. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, L.Y.; Liu, C.J.; Wong, Y.K.; Chang, C.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. miR-372 inhibits p62 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6062–6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, L.Y.; Yang, C.C.; Wu, H.L.; Kao, S.Y.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, Y.F.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. The miR-372-ZBTB7A Oncogenic Axis Suppresses TRAIL-R2 Associated Drug Sensitivity in Oral Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Jin, Y.; Song, J.L.; Deng, F. MiR-373 promotes proliferation and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting SPOP. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 5270–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, S. Inhibition of miR-103a-3p suppresses the proliferation in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via targeting RCAN1. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Wang, Y.K.; Lv, B.; Jin, H. miR-454 performs tumor-promoting effects in oral squamous cell carcinoma via reducing NR3C2. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2020, 49, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, W.; Mao, C.; Wang, J. miR-654-5p Targets GRAP to Promote Proliferation, Metastasis, and Chemoresistance of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Through Ras/MAPK Signaling. DNA Cell Biol. 2018, 37, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Kim, S.A.; Ahn, S.G. HOXC6-Mediated miR-188-5p Expression Induces Cell Migration through the Inhibition of the Tumor Suppressor FOXN2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, C.; Shi, J.; Xu, Q. Exosomal miR-626 promotes the malignant behavior of oral cancer cells by targeting NFIB. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 4829–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; Sun, J.; Xiao, W.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Yue, J.; Xue, L.F.; Deng, J.; Zhi, K.Q.; Wang, Y.L. MiR-4513 mediates the proliferation and apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via targeting CXCL17. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 3821–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.Y.; Hsiao, J.R.; Chou, S.T.; Hsu, Y.M.; Wu, G.H.; Shieh, Y.S.; Shiah, S.G. MiR-944/CISH mediated inflammation via STAT3 is involved in oral cancer malignance by cigarette smoking. Neoplasia 2020, 22, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.W.; Liu, C.J.; Chu, T.H.; Cheng, H.W.; Hung, P.S.; Hu, W.Y.; Lin, S.C. Association between high miR-211 microRNA expression and the poor prognosis of oral carcinoma. J. Dent. Res. 2008, 87, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.F.; Yang, C.C.; Kao, S.Y.; Liu, C.J.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. MicroRNA-211 Enhances the Oncogenicity of Carcinogen-Induced Oral Carcinoma by Repressing TCF12 and Increasing Antioxidant Activity. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4872–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.H.; Yang, C.C.; Liu, C.J.; Lui, M.T.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. miR-211 promotes the progression of head and neck carcinomas by targeting TGFbetaRII. Cancer Lett. 2013, 337, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, J.; Jia, Y.; Liu, T.; Duan, Y.; Liang, X.; Liu, L. microRNA-211 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via targeting the bridging integrator 1 protein. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 4644–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lv, L.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X.; Yin, Q.; Hao, Y.; Xiao, L. MiR-223 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and migration by regulating FBXW7. Cancer Biomark. 2019, 24, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J.; Shen, W.G.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, Y.W.; Lu, H.H.; Tsai, M.M.; Lin, S.C. miR-221 and miR-222 expression increased the growth and tumorigenesis of oral carcinoma cells. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2011, 40, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Jiang, F.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yu, D. Downregulation of miR-221/222 by a microRNA sponge promotes apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells through upregulation of PTEN. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4419–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Yu, D. miR-222 regulates the cell biological behavior of oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting PUMA. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Ren, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, W.; He, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, A. Deregulation of the miR-222-ABCG2 regulatory module in tongue squamous cell carcinoma contributes to chemoresistance and enhanced migratory/invasive potential. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44538–44550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Lyu, B.; Hou, D.; Liu, X. Mir-5100 Mediates Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Via Targeting SCAI. J. Investig. Surg. 2021, 34, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.P.; Xu, K.; Cui, J.; Yuan, D.Y.; Zou, B.; Li, J.; Liu, J.L.; Li, K.Y.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, B. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal miR-382-5p promotes the migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wu, Q.; Liu, D.; Wang, X. miR-27b Suppresses Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Targeting ITGA5. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 11855–11867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, F.; Zhou, X. miR-204-5p regulates cell proliferation and metastasis through inhibiting CXCR4 expression in OSCC. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 82, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.C.; Chen, P.N.; Peng, C.Y.; Yu, C.H.; Chou, M.Y. Suppression of miR-204 enables oral squamous cell carcinomas to promote cancer stemness, EMT traits, and lymph node metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20180–20192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, B.J.; Bhattacharjee, S.; O’Dee, D.M.; Feingold, E.; Gollin, S.M. Decreased expression of miR-125b and miR-100 in oral cancer cells contributes to malignancy. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2009, 48, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Xue, X.; Lan, J.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W.; Song, W.; Zhi, Q. MicroRNA-29a upregulates MMP2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma to promote cancer invasion and anti-apoptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2014, 68, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Choi, D.W.; Kim, C.S.; Yu, S.K.; Kim, H.J.; Go, D.S.; Lee, S.A.; Moon, S.M.; Kim, S.G.; Chun, H.S.; et al. MicroRNA-203 Induces Apoptosis by Targeting Bmi-1 in YD-38 Oral Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 3477–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.A.; Kim, J.S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Yu, S.K.; Kim, C.S.; Chun, H.S.; Kim, J.; Park, J.T.; Go, D.; et al. miR-203 downregulates Yes-1 and suppresses oncogenic activity in human oral cancer cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 120, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, J.S.; Yu, S.K.; Go, D.S.; Lee, S.A.; Moon, S.M.; Chun, H.S.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, D.K. Suppression of Oral Carcinoma Oncogenic Activity by microRNA-203 via Down-regulation of SEMA6A. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 5425–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Lin, Y.; Fan, L.; Kuang, W.; Zheng, L.; Wu, J.; Shang, P.; Wang, Q.; Tan, J. miR-203 inhibits cell proliferation and promotes cisplatin induced cell death in tongue squamous cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, G.; Deva Magendhra Rao, A.K.; Manikandan, M.; Prasanna Srinivasa Rao, H.; Subbiah, S.; Ilangovan, R.; Murugan, A.K.; Munirajan, A.K. Dysregulation of miR-200 family microRNAs and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.S.; Liu, X.B.; Chung-Wai Ho, A.; Po-Wing Yuen, A.; Wai-Man Ng, R.; Ignace Wei, W. Identification of pyruvate kinase type M2 as potential oncoprotein in squamous cell carcinoma of tongue through microRNA profiling. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutallip, M.; Nohata, N.; Hanazawa, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Horiguchi, S.; Fujimura, L.; Kawakami, K.; Chiyomaru, T.; Enokida, H.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Glutathione S-transferase P1 (GSTP1) suppresses cell apoptosis and its regulation by miR-133alpha in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 27, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Dai, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, A.; Chen, Z.; Heidbreder, C.E.; Kolokythas, A.; Zhou, X. Identification and experimental validation of G protein alpha inhibiting activity polypeptide 2 (GNAI2) as a microRNA-138 target in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Hum. Genet. 2011, 129, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiiba, M.; Shinozuka, K.; Saito, K.; Fushimi, K.; Kasamatsu, A.; Ogawara, K.; Uzawa, K.; Ito, H.; Takiguchi, Y.; Tanzawa, H. MicroRNA-125b regulates proliferation and radioresistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1817–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Liu, K.; Wu, Y.; Fan, J.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Z. MicroRNA-9 inhibits the proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by suppressing expression of CXCR4 via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5017–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumoto, I.; Hanazawa, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Koshizuka, K.; Goto, Y.; Nishikawa, R.; Chiyomaru, T.; Enokida, H.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. MicroRNA expression signature of oral squamous cell carcinoma: Functional role of microRNA-26a/b in the modulation of novel cancer pathways. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.C.; Chan, S.H.; Jang, T.H.; Chang, J.W.; Ko, Y.C.; Yen, T.C.; Chiang, S.L.; Chiang, W.F.; Shieh, T.Y.; Liao, C.T.; et al. miRNA-491-5p and GIT1 serve as modulators and biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.H.; Cheng, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Bo, C.X.; Li, Y.L. MicroRNA-375 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma cell migration and invasion by targeting platelet-derived growth factor-A. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.M.; Patel, R.S.; Phillips, B.L.; Wang, H.; Cohen, D.M.; Reinhold, W.C.; Chang, L.J.; Yang, L.J.; Chan, E.K. Tumor suppressor miR-375 regulates MYC expression via repression of CIP2A coding sequence through multiple miRNA-mRNA interactions. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 1638–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, X.; Song, B.; Qiu, X.; Zhao, J. MiR-375/SLC7A11 axis regulates oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and invasion. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Jao, Y.C.; Hsieh, I.S.; Chang, K.C.; Hong, T.M. miR-320 regulates tumor angiogenesis driven by vascular endothelial cells in oral cancer by silencing neuropilin 1. Angiogenesis 2014, 17, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uesugi, A.; Kozaki, K.; Tsuruta, T.; Furuta, M.; Morita, K.; Imoto, I.; Omura, K.; Inazawa, J. The tumor suppressive microRNA miR-218 targets the mTOR component Rictor and inhibits AKT phosphorylation in oral cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5765–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.A.; Park, M.G.; Yu, S.K.; Lee, M.H.; Park, M.R.; Kim, S.G.; Oh, J.S.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. MicroRNA-205 suppresses the oral carcinoma oncogenic activity via down-regulation of Axin-2 in KB human oral cancer cell. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 387, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Hasegawa, S.; Uchida, F.; Terabe, T.; Ishibashi Kanno, N.; Kato, K.; Yamagata, K.; Sakai, S.; Kawashiri, S.; Sato, H.; et al. MicroRNA-205-5p suppresses the invasiveness of oral squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting TIMP-2 expression. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Hou, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, A. miR-181a-Twist1 pathway in the chemoresistance of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.H.; Bae, S.D.; Hong, H.S.; Kim, R.H.; Kang, M.K.; Park, N.H. miR-181a shows tumor suppressive effect against oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by downregulating K-ras. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 404, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Qu, Y.; Dang, S.; Yao, B.; Ji, M. MiR-145 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell growth by targeting c-Myc and Cdk6. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, Y.; Peng, W.; Ling, W.; Jiebing, H.; Zhuan, B. Reciprocal effects between microRNA-140-5p and ADAM10 suppress migration and invasion of human tongue cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 448, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.C.; Shiah, S.G.; Chu, H.C.; Hsu, Y.M.; Hsiao, J.R.; Chang, J.Y.; Hung, W.C.; Liao, C.T.; Cheng, A.J.; Lu, Y.C.; et al. Reciprocal regulation of microRNA-99a and insulin-like growth factor I receptor signaling in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Yadav, A.; Lang, J.; Teknos, T.N.; Kumar, P. Dysregulation of microRNA-34a expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma promotes tumor growth and tumor angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, S.T.; Lin, B.R.; Wu, T.S.; Lin, S.K.; Kuo, M.Y.; Tan, C.T. MicroRNA-17/20a functions to inhibit cell migration and can be used a prognostic marker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Li, J. Expression of MiRNA-137 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and its clinical significance. J. BUON 2018, 23, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, R.; Lu, Q.; Xu, B. hsa-miR-5580-3p inhibits oral cancer cell viability, proliferation and migration by suppressing LAMC2. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, Y.; Lv, H.; Zhou, S.; Sun, Z.; Wang, M. miR-98 suppresses tumor cell growth and metastasis by targeting IGF1R in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 12252–12259. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.Y.; Liao, Y.W.; Lu, M.Y.; Yu, C.H.; Yu, C.C.; Chou, M.Y. Downregulation of miR-1 enhances tumorigenicity and invasiveness in oral squamous cell carcinomas. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. = Taiwan Yi Zhi 2017, 116, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, B.; Kumar, A.; Raut, S.K.; Panda, N.K.; Rattan, V.; Joshi, N.; Khullar, M. Downregulation of miR-377 Promotes Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth and Migration by Targeting HDAC9. Cancer Investig. 2017, 35, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Qi, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, R. miR-23a-3p suppresses cell proliferation in oral squamous cell carcinomas by targeting FGF2 and correlates with a better prognosis: miR-23a-3p inhibits OSCC growth by targeting FGF2. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Luo, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F. MicroRNA-22 suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting NLRP3. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6705–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Jin, J.; Ma, T.; Zhai, H. MiR-139-5p inhibits the tumorigenesis and progression of oral squamous carcinoma cells by targeting HOXA9. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3730–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chang, K.; Gao, J.; Wei, J.; Xu, G.; Xiao, L.; Song, G. MicroRNA-504 functions as a tumor suppressor in oral squamous cell carcinoma through inhibiting cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting CDK6. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 119, 105663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Ma, C.; Liu, G.; Guo, Y. MiR-106a directly targets LIMK1 to inhibit proliferation and EMT of oral carcinoma cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.H. MicroRNA-16 functions as a tumor-suppressor gene in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting AKT3 and BCL2L2. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 9447–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ji, H. MicroRNA-495 targets Notch1 to prohibit cell proliferation and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiah, S.G.; Hsiao, J.R.; Chang, W.M.; Chen, Y.W.; Jin, Y.T.; Wong, T.Y.; Huang, J.S.; Tsai, S.T.; Hsu, Y.M.; Chou, S.T.; et al. Downregulated miR329 and miR410 promote the proliferation and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Wnt-7b. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7560–7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, L.; Liu, Y. MiR-132 inhibits migration and invasion and increases chemosensitivity of cisplatin-resistant oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via targeting TGF-beta1. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Jin, J.; Ma, T.; Zhai, H. MiR-376c-3p regulates the proliferation, invasion, migration, cell cycle and apoptosis of human oral squamous cancer cells by suppressing HOXB7. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.M.; Feng, Y. MiR-769-5p inhibits cancer progression in oral squamous cell carcinoma by directly targeting JAK1/STAT3 pathway. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.T.; Peng, H.Y.; Mo, K.C.; Hsu, Y.M.; Wu, G.H.; Hsiao, J.R.; Lin, S.F.; Wang, H.D.; Shiah, S.G. MicroRNA-486-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in oral cancer by targeting DDR1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sur, S.; Ray, R.B. Emerging role of lncRNA ELDR in development and cancer. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 3011–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Fan, T. Long Non-Coding RNAs: The Regulatory Mechanisms, Research Strategies, and Future Directions in Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 598817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, H.; Yu, Q.; Xiao, W.; Wang, D.O. LncRNA-mediated DNA methylation: An emerging mechanism in cancer and beyond. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2022, 41, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishteyaq Majeed, S.; Mashooq Ahmad, D.; Kaiser Ahmad, B.; Tashook Ahmad, D.; Fayaz, A.; Syed Mudasir, A. Long Non-Coding RNAs: Biogenesis, Mechanism of Action and Role in Different Biological and Pathological Processes. In Recent Advances in Noncoding RNAs; Lütfi, T., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2022; p. 118. [Google Scholar]
- Aznaourova, M.; Schmerer, N.; Schmeck, B.; Schulte, L.N. Disease-Causing Mutations and Rearrangements in Long Non-coding RNA Gene Loci. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 527484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahariya, S.; Paddibhatla, I.; Kumar, S.; Raghuwanshi, S.; Pallepati, A.; Gutti, R.K. Long non-coding RNA: Classification, biogenesis and functions in blood cells. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, E.; Shao, Z.; Shang, Z. Long Noncoding RNAs in the Metastasis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 616717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Deng, Y.; Shen, Z. The Role and Mechanism of MALAT1 Long Non-Coding RNA in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 4127–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q. Regulatory Networks of LncRNA MALAT-1 in Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 10181–10198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sur, S.; Nakanishi, H.; Steele, R.; Zhang, D.; Varvares, M.A.; Ray, R.B. Long non-coding RNA ELDR enhances oral cancer growth by promoting ILF3-cyclin E1 signaling. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e51042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sur, S.; Steele, R.; Ko, B.C.B.; Zhang, J.; Ray, R.B. Long noncoding RNA ELDR promotes cell cycle progression in normal oral keratinocytes through induction of a CTCF-FOXM1-AURKA signaling axis. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, B.; Li, Y.; Jiang, F.; Wei, C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, W.; Yu, D. LncRNA GAS5 suppresses proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the miR-21/PTEN axis. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 374, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Hsieh, P.L.; Peng, C.Y.; Liao, Y.W.; Yu, C.H.; Yu, C.C. LncRNA MEG3 inhibits self-renewal and invasion abilities of oral cancer stem cells by sponging miR-421. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. = Taiwan Yi Zhi 2021, 120, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, X.; Zhu, X.W.; Yang, D.C.; Chen, R.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, T. Long non-coding RNAs in Oral squamous cell carcinoma: Biologic function, mechanisms and clinical implications. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Klibanski, A. MEG3 noncoding RNA: A tumor suppressor. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 48, R45–R53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresini, O.; Ciotti, A.; Rossi, M.N.; Battistelli, C.; Carbone, M.; Maione, R. A cross-talk between DNA methylation and H3 lysine 9 dimethylation at the KvDMR1 region controls the induction of Cdkn1c in muscle cells. Epigenetics 2016, 11, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Fang, X. Long Non-coding RNA DANCR in Cancer: Roles, Mechanisms, and Implications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 753706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, S.; Nakanishi, H.; Steele, R.; Ray, R.B. Depletion of PCAT-1 in head and neck cancer cells inhibits tumor growth and induces apoptosis by modulating c-Myc-AKT1-p38 MAPK signalling pathways. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; She, L.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Z.; Cao, H.; Liu, Y. LncRNA PVT1 promotes malignant progression in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3593–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunkumar, G.; Deva Magendhra Rao, A.K.; Manikandan, M.; Arun, K.; Vinothkumar, V.; Revathidevi, S.; Rajkumar, K.S.; Rajaraman, R.; Munirajan, A.K. Expression profiling of long non-coding RNA identifies linc-RoR as a prognostic biomarker in oral cancer. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2017, 39, 1010428317698366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Liu, J.; Guo, P.; Xu, Y.; Hu, J.; Han, X. LncRNA NORAD facilitates oral squamous cell carcinoma progression by sponging miR-577 to enhance TPM4. Biol. Direct 2022, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Ren, X.; Wei, F.; Yu, W.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis by recruiting EZH2 and repressing E-cadherin in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 2586–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.W.; Chiang, W.F.; Wu, A.T.H.; Wu, M.H.; Wang, L.Y.; Yu, Y.L.; Hung, Y.W.; Wang, W.C.; Chu, C.Y.; Hung, C.L.; et al. Long noncoding RNA LncHIFCAR/MIR31HG is a HIF-1alpha co-activator driving oral cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Xie, W.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H.; Qiao, B. LncRNA UCA1 promotes proliferation and cisplatin resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma by sunppressing miR-184 expression. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, B.; Wang, D.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, Z.; Chang, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, W. Cucurbitacin B Inhibits Cell Proliferation by Regulating X-Inactive Specific Transcript Expression in Tongue Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 651648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y. The role of long non-coding RNA ANRIL in the carcinogenesis of oral cancer by targeting miR-125a. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; He, X.; Wei, X.L. lncRNA NEAT1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion by regulating miR-365/RGS20 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shang, W.; Zheng, F. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by sponging microRNA-365. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatanaka, Y.; Niinuma, T.; Kitajima, H.; Nishiyama, K.; Maruyama, R.; Ishiguro, K.; Toyota, M.; Yamamoto, E.; Kai, M.; Yorozu, A.; et al. DLEU1 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression by activating interferon-stimulated genes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Huang, W. Knockdown of lncRNA DLEU1 inhibits the tumorigenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma via regulation of miR-149-5p/CDK6 axis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, T.R.; Zheng, Z.N.; Chen, Y.C.; Wu, Q.Q.; Huang, G.Z.; Li, F.; Zeng, W.S.; Lv, X.Z. LncRNA AC007271.3 promotes cell proliferation, invasion, migration and inhibits cell apoptosis of OSCC via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 117087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.N.; Huang, G.Z.; Wu, Q.Q.; Ye, H.Y.; Zeng, W.S.; Lv, X.Z. NF-kappaB-mediated lncRNA AC007271.3 promotes carcinogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-125b-2-3p/Slug. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, D.; Lv, H.; Lei, X. LncRNA LHFPL3-AS1 Promotes Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth and Cisplatin Resistance Through Targeting miR-362-5p/CHSY1 Pathway. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 2293–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J. lncRNA LINC01296 Promotes Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Development by Binding with SRSF1. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6661520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, S.; Lu, N.; Yin, Y.; Liu, Z. LncRNA JPX overexpressed in oral squamous cell carcinoma drives malignancy via miR-944/CDH2 axis. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhong, L.; Gao, S.; Yu, Y.; Sun, D.; Liu, X.; Ji, J.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z. LncRNA LINC00974 Downregulates miR-122 to Upregulate RhoA in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2021, 36, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.K.; Li, Y.J.; Tian, B.; Sun, H.M.; Li, Q.Y.; Ren, B.F. LncRNA PRNCR1 aggravates the malignancy of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-326/FSCN1 axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 3226–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yao, Y.; Shi, L.; Tang, G.; Wu, L. A novel lncRNA LOLA1 may predict malignant progression and promote migration, invasion, and EMT of oral leukoplakia via the AKT/GSK-3beta pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 122, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Jiang, J. LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via regulating miR-204-5p/FOXC1. J. Investig. Med. Off. Publ. Am. Fed. Clin. Res. 2020, 68, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jin, F.; Meng, Z. LINC00662 Promotes Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Growth and Metastasis through miR-144-3p/EZH2 Axis. Yonsei Med. J. 2021, 62, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Tang, Y.; Tang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X. Downregulation of lncRNA HOTTIP Suppresses the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Regulation of HMGA2-Mediated Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020, 35, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Sun, B.; Yang, Y.; Cai, X.; Bi, L.; Deng, L.; Zhang, L. MIR4435-2HG regulates cancer cell behaviors in oral squamous cell carcinoma cell growth by upregulating TGF-beta1. Odontology 2020, 108, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gong, Z.; Ma, L.; Wang, Q. LncRNA GACAT1 induces tongue squamous cell carcinoma migration and proliferation via miR-149. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 8215–8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.C.; Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.S. lncRNA TSPEAR-AS2, a Novel Prognostic Biomarker, Promotes Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Upregulating PPM1A via Sponging miR-487a-3p. Dis. Mrk. 2021, 2021, 2217663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Gao, X.; Liu, C.L. Increased expression of lncRNA FTH1P3 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma cells migration and invasion by enhancing PI3K/Akt/GSK3b/ Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 8306–8314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Qi, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, R. lncRNA PLAC2 activated by H3K27 acetylation promotes cell proliferation and invasion via the activation of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J. Long noncoding RNA SNHG20 regulates cell migration, invasion, and proliferation via the microRNA-19b-3p/RAB14 axis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 3993–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.L.; Ding, S.Y.; Jinag, H. LncRNA SNHG20 enhances the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the miR-29a/DIXDC1/Wnt regulatory axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 5436–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, H.; Xing, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, X. Long non-coding RNA LINC01137 contributes to oral squamous cell carcinoma development and is negatively regulated by miR-22-3p. Cell. Oncol. 2021, 44, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Luan, K.; Yang, J.; Huang, Y. Targeting lncRNA PSMA3-AS1, a Prognostic Marker, Suppresses Malignant Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Dis. Mrk. 2021, 2021, 3138046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Liu, S.; Luo, H.; Wu, S.; Wei, H.; Tang, Z.; Li, X.; Zou, C. lncRNA DCST1-AS1 Facilitates Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization through Activating NF-kappaB Signaling. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 5524231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhou, B.; Fu, D.; Cheng, B. lncRNA TUG1 promotes the development of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the MAPK signaling pathway by sponging miR-593-3p. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 1856–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wu, G. FOXD2-AS1 Predicts Dismal Prognosis for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Regulates Cell Proliferation. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 963689720964411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Cao, J.; Peng, X. LINC01234 facilitates growth and invasiveness of oral squamous cell carcinoma through regulating the miR-637/NUPR1 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 120, 109507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Jian, X.; Xu, P.; Zhu, R.; Wang, Y. Linc01234 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-433/PAK4 axis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, R.; Meng, X.; Sun, F. Long non-coding RNA LINC01207 promotes cell proliferation and migration but suppresses apoptosis and autophagy in oral squamous cell carcinoma by the microRNA-1301-3p/lactate dehydrogenase isoform A axis. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 7780–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Shi, Z.Y.; Zhao, J.; He, Q.L. LncRNA TTN-AS1 promotes the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-411-3p/NFAT5 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Yan, G. Long Noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 Downregulates miR-23a, Promotes Tumor Progression, and Predicts the Survival of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 2699–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; He, H.; Sui, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, D. Long non-coding RNA H1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion by acting as a ceRNA of miR-138 and releasing EZH2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Bai, X.; Feng, C.; Shang, X.; Xi, Y. Long Non-Coding RNA HCP5 Facilitates Cell Invasion And Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition In Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma By miR-140-5p/SOX4 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 10455–10462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, X.; Su, K.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, P.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y. A novel mechanism of the lncRNA PTTG3P/miR-142-5p/JAG1 axis modulating tongue cancer cell phenotypes through the Notch1 signaling. Cells Dev. 2022, 169, 203762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Lu, Z. Knockdown of lncRNA IGF2BP2-AS1 inhibits proliferation and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2022, 51, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Fan, S.; Chen, W.; Pan, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; et al. Upregulation of lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 Promotes Salivary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Metastasis via PI3K/Akt and MEK/Erk Signaling. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 2766–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, Q.; Fan, S.; Su, F.; Jiang, C.; Cai, G.; Wang, Y.; Liao, G.; Lei, X.; Chen, W.; et al. LncRNA LTSCCAT promotes tongue squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via targeting the miR-103a-2-5p/SMYD3/TWIST1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Fu, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Gan, N. RP11-284F21.9 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma development via the miR-383-5p/MAL2 axis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2020, 49, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Diao, P.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Cheng, J. Overexpression of lncRNA WWTR1-AS1 associates with tumor aggressiveness and unfavorable survival in head-neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 18266–18277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Z. Long intergenic non-coding RNA 668 regulates VEGFA signaling through inhibition of miR-297 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 489, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Fan, S.; Lin, H.; Lian, W. STAT3-induced upregulation of long noncoding RNA HNF1A-AS1 promotes the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via activating Notch signaling pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Jin, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, F. LncRNA MINCR activates Wnt/beta-catenin signals to promote cell proliferation and migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huo, F.; Wang, X.R.; Xu, Y.Y. LncRNA LACAT1 promotes proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by inhibiting microRNA-4301. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 2427–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, H.; Yang, K. Increased expression of lncRNA CASC9 promotes tumor progression by suppressing autophagy-mediated cell apoptosis via the AKT/mTOR pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Qi, Q.; Li, J.; Xin, Y.; Qiu, J. lncRNA SNHG26 promoted the growth, metastasis, and cisplatin resistance of tongue squamous cell carcinoma through PGK1/Akt/mTOR signal pathway. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2022, 24, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Du, Y.; Wang, S.; Zheng, X. LncRNA PART1 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by blocking EZH2 degradation. J. Biochem. 2021, 169, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhang, S.; Gong, Z.; Tang, Y.; Yang, L.; He, Y.; Lian, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Upregulated long non-coding RNA LINC00152 expression is associated with progression and poor prognosis of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Zeng, Z. LncRNA HOXA-AS2 Promotes Tumor Progression by Suppressing miR-567 Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 5443–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Quan, H. Long non-coding RNA DNM3OS/miR-204-5p/HIP1 axis modulates oral cancer cell viability and migration. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2020, 49, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, C.; Yang, S.; Dong, C. LncRNA SNHG1 promotes the development of oral cavity cancer via regulating the miR-421/HMGB2 axis. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2020, 66, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Kan, C.H.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.H.; Wu, C.C.; Kuo, Y.P.; Chang, I.Y.; Chang, K.P.; Yu, J.S.; Tan, B.C. Modular scaffolding by lncRNA HOXA10-AS promotes oral cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Shi, W.; Chen, M. Long non-coding RNA BBOX1-antisense RNA 1 enhances cell proliferation and migration and suppresses apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-3940-3p/laminin subunit gamma 2 axis. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 11138–11153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, G.; Wu, L.; Yao, Y.; Shen, X.; Hou, Z.; et al. LncRNA IFITM4P promotes immune escape by up-regulating PD-L1 via dual mechanism in oral carcinogenesis. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 1564–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, B.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, W.; Ning, S.; Liu, L. Up-regulation of plasma lncRNA CACS15 distinguished early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma patient. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.P.; Hsieh, P.L.; Fang, C.Y.; Chu, P.M.; Liao, Y.W.; Yu, C.H.; Yu, C.C.; Tsai, L.L. LINC00963 Promotes Cancer Stemness, Metastasis, and Drug Resistance in Head and Neck Carcinomas via ABCB5 Regulation. Cancers 2020, 12, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, G.; Anand, S.; Raksha, P.; Dhamodharan, S.; Prasanna Srinivasa Rao, H.; Subbiah, S.; Murugan, A.K.; Munirajan, A.K. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 is overexpressed in undifferentiated oral tumors and integrated analysis identifies as a downstream effector of stemness-associated transcription factors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.Y.; Qiao, T.Y.; Jin, H.; Liu, L.L.; Zheng, M.D.; Wang, Z.L. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 contributes to the cisplatin resistance of tongue cancer through the KCNQ1OT1/miR-124-3p/TRIM14 axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Feng, X.D.; Zhu, W.Q.; Bao, Y.N. LncRNA BLACAT1 regulates the viability, migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting miR-142-5p. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 10313–10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, D.; Li, C.; Ru, L.; Wang, X. Silencing of LncRNA AFAP1-AS1 Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Oral Squamous Cancer by Suppressing CCNA2. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 7897–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Jiao, Y. LncRNA FAL1 promotes the development of oral squamous cell carcinoma through regulating the microRNA-761/CRKL pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 5779–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Shi, J. LncRNA HOXA11-AS Promotes Proliferation and Cisplatin Resistance of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Suppression of miR-214-3p Expression. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8645153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Hou, T.J.; Yang, P. Mechanism of lncRNA FEZF1-AS1 in promoting the occurrence and development of oral squamous cell carcinoma through targeting miR-196a. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 6505–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, K. [Knockdown of lncRNA SNHG6 inhibites the proliferation and epithelial mesenchymal transition in tongue cancer cells]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi = Chin. J. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 34, 806–811. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, D. HOXC13-AS accelerates cell proliferation and migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-378g/HOXC13 axis. Oral Oncol. 2020, 111, 104946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, F.; Wei, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, H.; Tian, G.; Gong, W.; Yuan, Y.; Feng, H.; et al. ORAOV1-B Promotes OSCC Metastasis via the NF-kappaB-TNFalpha Loop. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Jia, B.; Huang, Z.; Shen, J.; Luo, H.; Zhao, J. CCL18-induced LINC00319 promotes proliferation and metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-199a-5p/FZD4 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, X.; Lai, W.; Wang, J. Long non-coding RNA SLC16A1-AS1: Its multiple tumorigenesis features and regulatory role in cell cycle in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yan, W. lncRNA RP5-916L7.2 correlates with advanced tumor stage, and promotes cells proliferation while inhibits cells apoptosis through targeting miR-328 and miR-939 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 67, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Wu, F.; Peng, C.; Wang, M. Silencing of LINC00284 inhibits cell proliferation and migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma by the miR-211-3p/MAFG axis and FUS/KAZN axis. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2021, 22, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, M.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, X.; Tong, D. LINC00958 regulated miR-627-5p/YBX2 axis to facilitate cell proliferation and migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bao, C.; Zhang, X.; Lin, X.; Pan, D.; Chen, Y. Knockdown of lncRNA LEF1-AS1 inhibited the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) via Hippo signaling pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Q.; Wu, J.; Zou, H. H3K27ac-induced FOXC2-AS1 accelerates tongue squamous cell carcinoma by upregulating E2F3. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, X.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Z. LINC01116 Promotes Migration and Invasion of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Acting as a Competed Endogenous RNA in Regulation of MMP1 Expression. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 2857022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Jiang, S.; Jian, S.; Shang, Z. Long noncoding RNA MORT overexpression inhibits cancer cell proliferation in oral squamous cell carcinoma by downregulating ROCK1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 11702–11707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Qiu, Z.; Zeng, J.; Xiao, T.; Ke, Z.; Lyu, H. A novel long non-coding RNA, AC012456.4, as a valuable and independent prognostic biomarker of survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y. Down-regulation of lncRNA HCG11 promotes cell proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma through sponging miR-455-5p. J. Gene Med. 2021, 23, e3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yang, K.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J. LncRNA SCIRT absorbs miR-221 to advance the expression of lncRNA GAS5 in oral squamous cell carcinoma to inhibit cancer cell apoptosis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2022, 51, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Liu, H.; You, G. Long non-coding RNA C5orf66-AS1 prevents oral squamous cell carcinoma through inhibiting cell growth and metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 3291–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Xun, W.; Wang, J.; Song, W.; Wang, X. Long non-coding RNA PTCSC3 inhibits human oral cancer cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis and autophagy. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 17, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, E.; Shao, Z.; Shang, Z. LncRNA FENDRR in Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts Regulates the Angiogenesis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Through the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 616576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yu, F.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, W.; Ponnusamy, M.; Wang, K.; Li, P. Circular RNAs: A novel type of non-coding RNA and their potential implications in antiviral immunity. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sharpless, N.E. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, L.; Li, Q.; Zang, A.; Wang, H. Circular RNA: Biogenesis, degradation, functions and potential roles in mediating resistance to anticarcinogens. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Fang, N.; Wang, T.; Xu, T.; Shu, Y. CircRNAs in cancer metabolism: A review. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Zou, Y.; Gao, G.; Zheng, S.; Wu, S.; Xie, X.; Tang, H. The biogenesis, function and clinical significance of circular RNAs in breast cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 19, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, C.; Yuan, W.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Sun, Z. Roles of circRNAs in the tumour microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.Y.; Jiang, J.; Tang, Y.J.; Liang, X.H.; Tang, Y.L. CircRNAs: A New Chapter in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Biology. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 9071–9083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Tian, H.; Shan, Z.; Liu, W.; Pan, Z.; Ren, J. Circle RNA hsa_circRNA_100290 serves as a ceRNA for miR-378a to regulate oral squamous cell carcinoma cells growth via Glucose transporter-1 (GLUT1) and glycolysis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 19130–19140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Li, X.; Xie, D.; Tian, L. Overexpressed circPVT1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma promotes proliferation by serving as a miRNA sponge. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 3509–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Dou, Z.C.; Ren, W.H.; Li, S.M.; Liang, X.; Zhi, K.Q. CircCDR1as upregulates autophagy under hypoxia to promote tumor cell survival via AKT/ERK((1/2))/mTOR signaling pathways in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Y.; Yang, H. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0007059 indicates prognosis and influences malignant behavior via AKT/mTOR in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 15156–15166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Sun, S.; Li, M.; Shen, Y.; Yang, H. Hsa_circ_0005379 regulates malignant behavior of oral squamous cell carcinoma through the EGFR pathway. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatsirou, M.; Artemaki, P.I.; Karousi, P.; Scorilas, A.; Kontos, C.K. Circular RNAs: Emerging Regulators of the Major Signaling Pathways Involved in Cancer Progression. Cancers 2021, 13, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Zhao, C.; Li, S.; Dou, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Ren, W.; Zhi, K. circ-PKD2 inhibits carcinogenesis via the miR-204-3p/APC2 axis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 1783–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cui, Y.; Liu, L.; Qi, X.; Liu, J.; Ma, S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Splicing factor derived circular RNA circUHRF1 accelerates oral squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis via feedback loop. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.T.; Li, X.X.; Zeng, L.W. Circ_0001742 promotes tongue squamous cell carcinoma progression via miR-431-5p/ATF3 axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 10300–10312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zhou, C.; Liang, Y.; Lai, Y.F.; Liang, Y. Circ_0001971 regulates oral squamous cell carcinoma progression and chemosensitivity by targeting miR-194/miR-204 in vitro and in vivo. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2470–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zha, J.; Bo, P.; Tang, Y.; Guo, X.; et al. CircDOCK1 suppresses cell apoptosis via inhibition of miR-196a-5p by targeting BIRC3 in OSCC. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 951–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Liu, Y.; Jia, X.J.; Liu, S.X.; Dong, J.H.; Ren, X.M.; Xu, O.; Zhang, H.Z.; Duan, H.J.; Shan, C.G. Upregulation of circFLNA contributes to laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma migration by circFLNA-miR-486-3p-FLNA axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Li, X.; Wei, H.; Wu, S.; Song, J.; Tang, Z.; Luo, H.; Lv, X.; Ai, Y. Circular GOLPH3 RNA exerts oncogenic effects in vitro by regulating the miRNA-1299/LIF axis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 11012–11025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Yu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, D. Circular RNA circCLK3 promotes the progression of tongue squamous cell carcinoma via miR-455-5p/PARVA axis. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Fu, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, F. Circ_0014359 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression by sponging miR-149. Acta biochimica Polonica 2022, 69, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yin, Y.; Nan, F.; Ma, Z. Circ_LPAR3 promotes the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 589, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zou, C.; Wei, H.; Wu, S.; Huang, D. circ_SEPT9, a newly identified circular RNA, promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression through miR-1225/PKN2 axis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 13266–13277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, J.; Gui, R. Upregulation of circ_0000199 in circulating exosomes is associated with survival outcome in OSCC. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Knockdown of circ_0001883 may inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-125-5p/PI3K/AKT axis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Du, F.; Gong, X.; Xu, P. Circ_0005320 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis by sponging microRNA-486-3p and microRNA-637. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 440–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Y.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, S.B.; Huang, Z.K.; Liao, L. Salivary Circular RNAs Hsa_Circ_0001874 and Hsa_Circ_0001971 as Novel Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 2511–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Min, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jiao, J. Knockdown of circ_0011946 targets miR-216a-5p/BCL2L2 axis to regulate proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Song, J.; Wei, H.; Tang, Z.; Li, X.; Lv, X.; Luo, H.; Wu, S.; Zou, C. circ_0001461 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression through miR-145/TLR4/NF-kappaB axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 566, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; He, X.; Chen, S. Oncogenic circDHTKD1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo via upregulating miR-326-mediated GAB1. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. = Rev. Bras. De Pesqui. Med. E Biol. 2021, 54, e10837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, X.; Zou, A.; Mai, Z.; Huang, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhao, J. circIGHG-Induced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Promotes Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression via miR-142-5p/IGF2BP3 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ci, H.S.; Mao, Y.L.; Li, J.W.; Zuo, J.H. CircRNA_002178 promotes the proliferation and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by activating the Akt/mTOR pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 6122–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Qiu, X. circVAPA promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of oral cancer cells through the miR-132/HOXA7 axis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 3000605211013207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, C.; Ren, W.; Li, S.; Zheng, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhi, K.; Gao, L. Circ-LRP6 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and autophagy in oral squamous cell carcinomas. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.S.; Cheng, Y.N.; Zhang, W.B.; Fan, H.; Mao, Q.H.; Xu, P. circRNA_0000140 suppresses oral squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis by targeting miR-31 to inhibit Hippo signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Shen, Y.; Yang, H. Silencing circular RNA hsa_circ_0004491 promotes metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 116883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, Y. Circular RNA circSPATA6 Inhibits the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells by Regulating TRAF6 via miR-182. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 1817–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Z.T. Hsa_circ_0086414 Might Be a Diagnostic Biomarker of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2020, 26, e919383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Shen, Y.; Yang, H. Hsa_circ_0008309 May Be a Potential Biomarker for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Dis. Mrk. 2018, 2018, 7496890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. CircGDI2 Regulates the Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Apoptosis of OSCC via miR-454-3p/FOXF2 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Si, H. Circ-KIAA0907 inhibits the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the miR-96-5p/UNC13C axis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 19, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, H. circ_0004872 inhibits proliferation, invasion, and glycolysis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by sponged miR-424-5p. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, Q.B.; Zhi, Y.; Ren, W.H.; Li, S.M.; Zhao, C.Y.; Xing, X.M.; Dou, Z.C.; Liu, J.C.; Jiang, C.M.; et al. Down-regulation of hsa_circ_0092125 is related to the occurrence and development of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 49, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Kasamatsu, A.; Kawasaki, K.; Hiroshima, K.; Fukushima, R.; Iyoda, M.; Nakashima, D.; Endo-Sakamoto, Y.; Uzawa, K. Tumor Suppressive Circular RNA-102450: Development of a Novel Diagnostic Procedure for Lymph Node Metastasis from Oral Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Cheng, J.; Li, A. hsa_circ_0072387 Suppresses Proliferation, Metastasis, and Glycolysis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells by Downregulating miR-503-5p. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2021, 36, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragon, F.; Lemay, V.; Trahan, C. snoRNAs: Biogenesis, Structure and Function. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chamorro-Petronacci, C.; Perez-Sayans, M.; Padin-Iruegas, M.E.; Marichalar-Mendia, X.; Gallas-Torreira, M.; Garcia Garcia, A. Differential expression of snoRNAs in oral squamous cell carcinomas: New potential diagnostic markers. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Tong, D. Expression scoring of a small-nucleolar-RNA signature identified by machine learning serves as a prognostic predictor for head and neck cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 8071–8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tao, H. Small nucleolar RNA host gene 3 facilitates cell proliferation and migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma via targeting nuclear transcription factor Y subunit gamma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Yin, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, P. SNHG3/miR-2682-5p/HOXB8 promotes cell proliferation and migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Liang, D.; Yang, H. SNHG15 facilitated malignant behaviors of oral squamous cell carcinoma through targeting miR-188-5p/DAAM1. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, D.; Ma, S. SNHG1/miR-194-5p/MTFR1 Axis Promotes TGFbeta1-Induced EMT, Migration and Invasion of Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Biotechnol. 2022, 64, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. c-Myc induced upregulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG16 enhances progression and carcinogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2019, 26, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, F.; Guo, J.; Miao, Z.; Li, Z. LncRNA SNHG17 promotes the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by modulating miR-375/PAX6 axis. Cancer Biomark. 2021, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Dong, Y.; Gu, J.; Puthiyakunnon, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.G. Developmental piRNA profiles of the invasive vector mosquito Aedes albopictus. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, A.; Sachidanandam, R.; Hannon, G.J.; Carmell, M.A. A germline-specific class of small RNAs binds mammalian Piwi proteins. Nature 2006, 442, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.N.; Li, Y.; Xia, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zheng, J.H.; Li, W. PIWI Proteins and PIWI-Interacting RNA: Emerging Roles in Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Mai, D.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, J.; Bai, R.; Ye, Y.; Li, M.; Pan, L.; Su, J.; et al. PIWI-interacting RNA-36712 restrains breast cancer progression and chemoresistance by interaction with SEPW1 pseudogene SEPW1P RNA. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, M.E.; Firek, M.; Jliedi, A.; Amaar, Y.G. Identification and characterization of RASSF1C piRNA target genes in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 34268–34282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dou, M.; Song, X.; Dong, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Tao, J.; Li, W.; Yin, X.; Xu, W. The emerging role of the piRNA/piwi complex in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Li, H.; Cai, M.; Pathak, J.L.; Li, Z.; Huang, L.; Zeng, M.; Zheng, H.; et al. mRNA and P-element-induced wimpy testis-interacting RNA profile in chemical-induced oral squamous cell carcinoma mice model. Exp. Anim. 2020, 69, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, M.A.; Ku, J.; Kuo, S.Z.; Li, P.X.; Zheng, H.; Yu, M.A.; Wang-Rodriguez, J.; Ongkeko, W.M. Identification and characterization of dysregulated P-element induced wimpy testis-interacting RNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 2615–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmino, N.; Martinez, V.D.; Rowbotham, D.A.; Enfield, K.S.S.; Bennewith, K.L.; Lam, W.L. HPV status is associated with altered PIWI-interacting RNA expression pattern in head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 2016, 55, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.R.; Qu, Y.; Li, P.X.; Zou, A.E.; Califano, J.A.; Wang-Rodriguez, J.; Ongkeko, W.M. Computational methods reveal novel functionalities of PIWI-interacting RNAs in human papillomavirus-induced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 4614–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, T.; Gupta, P.; Nayak, R.; Mallick, B. Genome-wide profiling of dysregulated piRNAs and their target genes implicated in oncogenicity of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Gene 2023, 849, 146919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, A.R.; Korrapati, A.; Zou, A.E.; Qu, Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Califano, J.A.; Wang-Rodriguez, J.; Lippman, S.M.; Hovell, M.F.; Ongkeko, W.M. Smoking status regulates a novel panel of PIWI-interacting RNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2017, 65, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celetti, A.; Merolla, F.; Luise, C.; Siano, M.; Staibano, S. Novel Markers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Oral Intraepithelial Neoplasia; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay, E.; Singh, R.; Ray, A.; Roy, R.; De Sarkar, N.; Paul, R.R.; Pal, M.; Aich, R.; Roy, B. Expression deregulation of mir31 and CXCL12 in two types of oral precancers and cancer: Importance in progression of precancer and cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osan, C.; Chira, S.; Nutu, A.M.; Braicu, C.; Baciut, M.; Korban, S.S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The Connection between MicroRNAs and Oral Cancer Pathogenesis: Emerging Biomarkers in Oral Cancer Management. Genes 2021, 12, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubelnik, G.; Bostjancic, E.; Anicin, A.; Dovsak, T.; Zidar, N. MicroRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs as Regulators of NANOG Expression in the Development of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 579053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Qiu, W.; Wu, B.; Fang, F. Long non-coding RNAs are novel players in oral inflammatory disorders, potentially premalignant oral epithelial lesions and oral squamous cell carcinoma (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Exploring the long noncoding RNAs-based biomarkers and pathogenesis of malignant transformation from dysplasia to oral squamous cell carcinoma by bioinformatics method. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 29, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Song, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhou, H. Comprehensive analysis of circular RNA in oral leukoplakia: Upregulated circHLA-C as a potential biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.M.; Chu, T.H.; Chou, C.C.; Chien, C.Y.; Wang, J.S.; Huang, C.C. Exosome-derived microRNAs in oral squamous cell carcinomas impact disease prognosis. Oral Oncol. 2021, 120, 105402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momen-Heravi, F.; Bala, S. Extracellular vesicles in oral squamous carcinoma carry oncogenic miRNA profile and reprogram monocytes via NF-kappaB pathway. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 34838–34854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.; Pruthi, N.; Seers, C.; Belobrov, S.; McCullough, M.; Celentano, A. Extracellular Vesicles in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Blood-based circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for predicting the prognosis of head and neck cancer-a systematic review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 3833–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Patel, S.; Patel, P.; Mandlik, D.; Patel, K.; Tanavde, V. Salivary Exosomal miRNA-1307-5p Predicts Disease Aggressiveness and Poor Prognosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Jin, N.; Bu, W.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Tong, J.; Li, D. Long non-coding RNA TIRY promotes tumor metastasis by enhancing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in oral cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, H.; Xiong, J.; Feng, B.; Zhu, P.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, P.; Su, X.; Huang, X. Exosomal long noncoding RNAs MAGI2-AS3 and CCDC144NL-AS1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma development via the PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 240, 154219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Han, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Ji, X.; Wang, X.; Jin, J.; Wang, Q.; Guo, X.; Cheng, Z.; Lu, M.; et al. Oral mucosal mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: A potential therapeutic target in oral premalignant lesions. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J. Exosomal miR-200c suppresses chemoresistance of docetaxel in tongue squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing TUBB3 and PPP2R1B. Aging 2020, 12, 6756–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakubo-Yasukochi, T.; Morioka, M.; Hazekawa, M.; Yasukochi, A.; Nishinakagawa, T.; Ono, K.; Kawano, S.; Nakamura, S.; Nakashima, M. miR-200c-3p spreads invasive capacity in human oral squamous cell carcinoma microenvironment. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Liao, L.; Du, L. miR-144-3p inhibits tumor cell growth and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma through the downregulation of the oncogenic gene, EZH2. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husna, A.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Lai, Y.C.; Chen, H.W.; Hasan, M.N.; Nakagawa, T.; Miura, N. Identification of melanoma-specific exosomal miRNAs as the potential biomarker for canine oral melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021, 34, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chen, G.; Sun, D.; Lei, M.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, X.; Xue, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; et al. Exosomes containing miR-21 transfer the characteristic of cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN and PDCD4 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Biochim. Et Biophys. Sin. 2017, 49, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, M.; Jayachandran, D.; Aishwarya, S.Y.; Md Younus, P.; Venugopal, A.; Suresh Babu, H.W.; Ajay, E.; Sanjana, M.; Arul, N.; Balachandar, V. A new insight into the diverse facets of microRNA-31 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2022, 23, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Ping, F.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Deng, M.; Cheng, B.; Xia, J. Salivary exosomal miR-24-3p serves as a potential detective biomarker for oral squamous cell carcinoma screening. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Wang, H.M.; Tsai, C.Y.; Chen, W.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Fan, K.H.; Tsai, C.N.; Huang, S.F.; Kang, C.J.; et al. Oncogenic function and early detection potential of miRNA-10b in oral cancer as identified by microRNA profiling. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Bahrami, N.; Sayedyahossein, A.; Derakhshan, S. Evaluation of circulating serum 3 types of microRNA as biomarkers of oral squamous cell carcinoma; A pilot study. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2020, 49, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faur, C.I.; Roman, R.C.; Jurj, A.; Raduly, L.; Almasan, O.; Rotaru, H.; Chirila, M.; Moldovan, M.A.; Hedesiu, M.; Dinu, C. Salivary Exosomal MicroRNA-486-5p and MicroRNA-10b-5p in Oral and Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Medicina 2022, 58, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayyed, A.A.; Gondaliya, P.; Mali, M.; Pawar, A.; Bhat, P.; Khairnar, A.; Arya, N.; Kalia, K. MiR-155 Inhibitor-Laden Exosomes Reverse Resistance to Cisplatin in a 3D Tumor Spheroid and Xenograft Model of Oral Cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 3010–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickman, C.T.; Lawson, J.; Jabalee, J.; MacLellan, S.A.; LePard, N.E.; Bennewith, K.L.; Garnis, C. Selective extracellular vesicle exclusion of miR-142-3p by oral cancer cells promotes both internal and extracellular malignant phenotypes. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15252–15266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baber, S.; Bayat, M.; Mohamadnia, A.; Shamshiri, A.; Amini Shakib, P.; Bahrami, N. Role of miR153 and miR455-5p Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Isolated from Plasma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 22, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, J.; Vairaktaris, E.; Agaimy, A.; Kintopp, R.; Baran, C.; Neukam, F.W.; Nkenke, E. miR-186, miR-3651 and miR-494: Potential biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma extracted from whole blood. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclellan, S.A.; Lawson, J.; Baik, J.; Guillaud, M.; Poh, C.F.; Garnis, C. Differential expression of miRNAs in the serum of patients with high-risk oral lesions. Cancer Med. 2012, 1, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Tao, Y.W.; Gao, S.; Li, P.; Zheng, J.M.; Zhang, S.E.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Y. Cancer-associated fibroblasts contribute to oral cancer cells proliferation and metastasis via exosome-mediated paracrine miR-34a-5p. EBioMedicine 2018, 36, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, J.; Baran, C.; Wehrhan, F.; Weber, M.; Motel, C.; Kesting, M.; Nkenke, E. The altered expression levels of miR-186, miR-494 and miR-3651 in OSCC tissue vary from those of the whole blood of OSCC patients. Cancer Biomark. 2019, 24, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; He, Z.; Zhang, C. Exosome-derived long non-coding RNA ADAMTS9-AS2 suppresses progression of oral submucous fibrosis via AKT signalling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 2262–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Liang, J.; Liu, J.; Hao, J.; Wan, Q.; Liu, J.; Luo, C.; Lu, Z. CircRNA has_circ_0069313 induced OSCC immunity escape by miR-325-3p-Foxp3 axes in both OSCC cells and Treg cells. Aging 2022, 14, 4376–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Gong, M.; Deng, Y.; Fang, S.; Cao, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Shen, Z. Roles and clinical application of exosomal circRNAs in the diagnosis and treatment of malignant tumors. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, S.; Datta, S.; Ray, J.G.; Chaudhuri, K.; Chatterjee, R. Liquid biopsy: miRNA as a potential biomarker in oral cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019, 58, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkle, M.; El-Daly, S.M.; Fabbri, M.; Calin, G.A. Noncoding RNA therapeutics—Challenges and potential solutions. Nature reviews. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 629–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Shi, L.; Luo, Z. Long Non-coding RNAs in Cancer: Implications for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 612393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
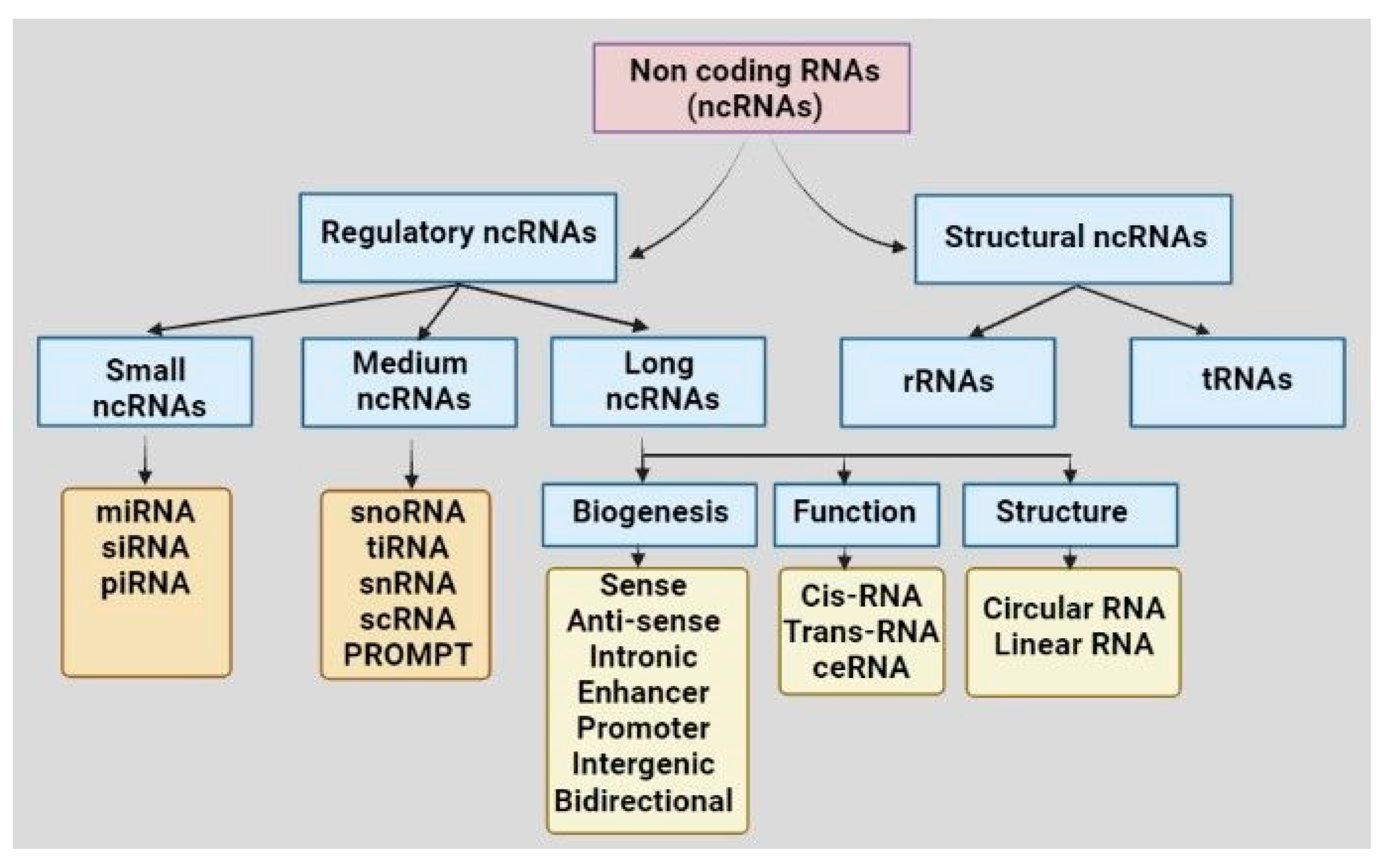
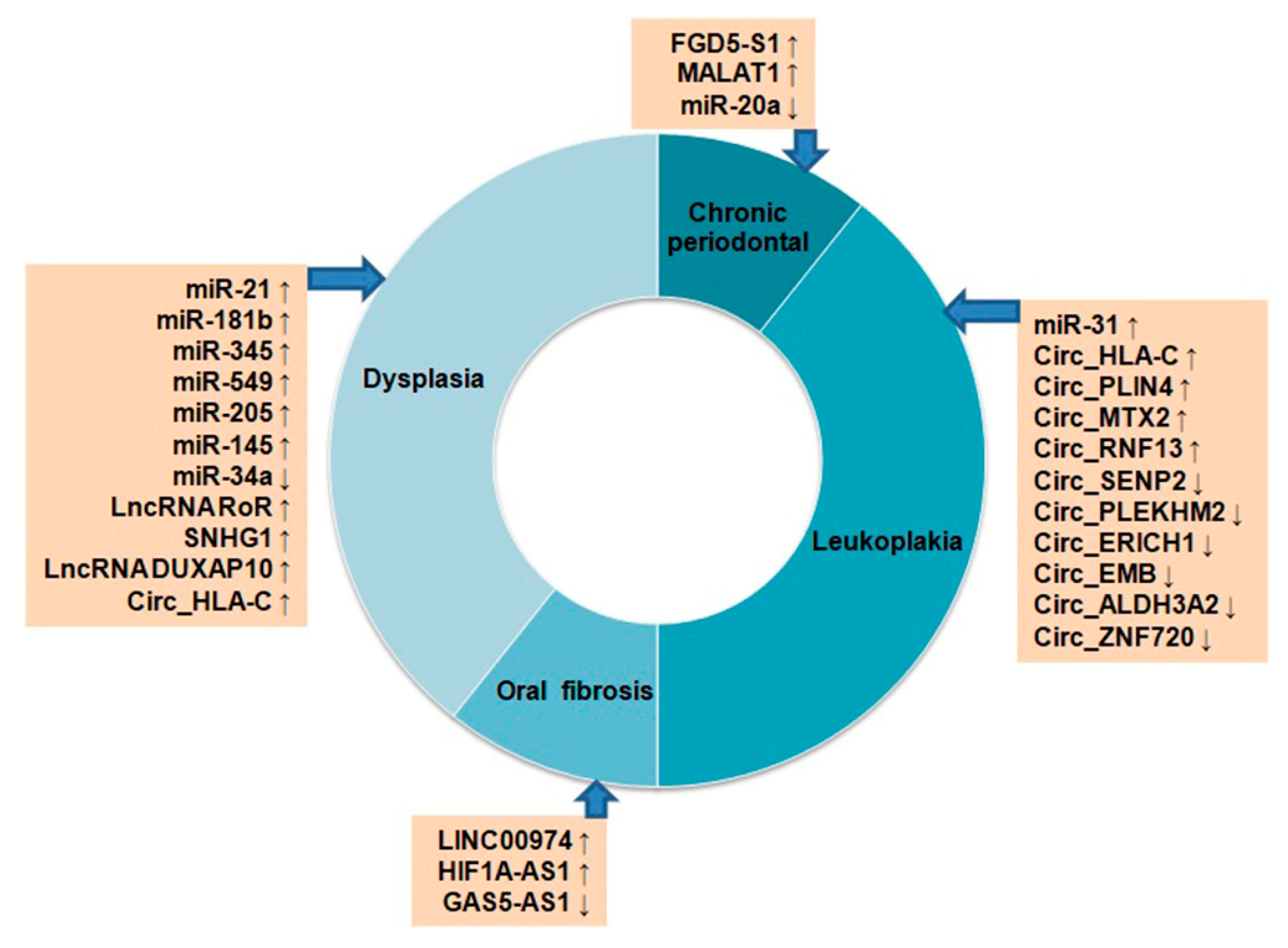
| miRNA Name | Function on Up or Down Regulation | Target Genes/Associated Pathways | Study Model | Bio-Marker/Therapy | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| List of Up-regulated miRNAs | |||||
| miR-21 ↑ | Associated with cell growth, cell proliferation, and cell cycle progression, as well as inhibits apoptosis | DKK2, PTEN, PDCD4, CADM1, RECK | Patient tissue, saliva, and plasma samples, cell lines | Biomarker (diagnosis and prognosis) and therapeutic target | [15,22,29,30] |
| miR-155 ↑ | Enhances cell proliferation in patients and confers cisplatin chemoresistance via EMT | FOXO3a | Patient tissue samples and blood exosome | Prognostic biomarker | [20,21,22] |
| miR-196a ↑ | Promotes cell migration, invasion, and lymph node metastasis | SPRR2C, ANXA1, S100A9, NME4-JNK-TIMP1-MMP signaling pathway, MAMDC2, | Patient tissue, saliva, plasma samples, and OC cell lines | Biomarker | [30,31,32] |
| miR-1237 ↑ | Causes cellular progression | FAM69C, PACS2, SPOP | Patient tissue and plasma samples | Biomarker (diagnosis and prognosis) | [30] |
| miR-31 ↑ | Increases oxidative stress in OSCC and enriches the oncogenicity and stemness of HNSCC. Regulates the reprogramming of lipid metabolism and enhances cell migration in OSCC | Ku80, FIH, ARID1A, SIRT3, ACOX1 | OC cell lines, tissue, plasma and saliva samples, and transgenic mice | Biomarker | [33,34,35,36,37] |
| miR-455 ↑ | Increases proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of OSCC cell | UBE2B | OC Cells, tissue and plasma samples, and xenograft mice model | Biomarker (prognosis) | [38] |
| miR-181 ↑ | Increases cell migration and invasion and may enhance lymph-node metastasis | - | Patient tissue sample and plasma | Biomarker | [39] |
| miR-184 ↑ | Increased cell proliferation rate and suppressed apoptosis | c-MYC | Tumor tissue, cell lines, and plasma | Biomarker (diagnosis) | [40] |
| miR-134 ↑ | Increases migration and reduces E-cadherin expression in OSCC cell lines. Enhances metastatic potential of OSCC xenografts | WWOX, PDCD7 | Tissue and plasma samples and OSCC cell lines | Biomarker | [41,42] |
| miR-146a ↑ | Increases the tumorigenicity and metastasis | IRAK1, TRAF6 and NUMB | Tissue, plasma and saliva samples, cell lines, and xenograft tumor model | Biomarker (diagnosis) and therapeutic target | [43] |
| miR-93 ↑ | Promotes metastasis, correlated with poor prognosis | -- | OC tissue, saliva samples and cell lines | Prognostic marker and therapeutic target | [44] |
| miR-10b ↑ | Role in cancer stemness and facilitates metastatic colonization | DIAPH2 | Patient tissue and saliva samples and cell lines | Diagnostic marker and therapeutic target | [45] |
| miR-372 ↑ | Enhanced drug resistance and migration. Also associated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis | p62, ZBTB7A | Cell lines, patient tissue and saliva samples, and xenograft tumor model | Diagnostic and prognostic marker | [45,46,47] |
| miR-373 ↑ | Enhances proliferation and metastasis | SPOP | OC samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [48] |
| miR-103a-3p ↑ | Induces proliferation and restricts cell apoptosis | RCAN1 | OC cell lines, tumor tissues, saliva, plasma, and xenograft tumor model | Diagnostic marker and therapeutic target | [49] |
| miR-454 ↑ | Involved in proliferation and colony formation, as well as inducing invasion and migration | NR3C2 | OC cell lines, tissues and saliva samples | Potential therapeutic direction for diagnosis and prognosis | [50] |
| miR-654-5p ↑ | Facilitates EMT, promotes cellular proliferation, tumor metastasis, and chemoresistance | GRAP, Ras/MAPK Signaling | OC cell lines, patient tissues, plasma, and xenograft tumor model | Biomarker for the clinical diagnosis and prognosis | [51] |
| miR-188-5p ↑ | Causes cell migration | FOXN2 | Cell lines | Potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target | [52] |
| miR-626 ↑ | Promotes cancer cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and G0/G1-to-S phase transition | NFIB | Patient tissue, plasma, cell lines, and xenograft tumor model | Therapeutic target | [53] |
| miR-4513 ↑ | Causes proliferation and apoptosis | CXCL17 | Saliva, plasma, and OC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [54] |
| miR-944 ↑ | Induces pro-inflammation cytokines secretion, migration, and invasion | CISH/STAT regulation | OC cell lines, tissue and saliva samples | -- | [55] |
| miR-211 ↑ | Causes proliferation, migration, invasion, and metastasis | BIN1, TCF12, TGFBRII, c-MYC | Tissue samples, cell lines, and xenograft tumor model | Therapeutic target and prognostic marker | [56,57,58,59] |
| miR-223 ↑ | Promotes OSCC proliferation and migration | FBXW7 | Tissue, saliva samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [60] |
| miR-221 ↑ | Regulates proliferation and invasion and inhibits apoptosis | PTEN | OC cell lines | Biomarker (diagnosis) | [61,62] |
| miR-222 ↑ | Causes proliferation, metastasis, and invasion and decreases apoptosis | PTEN, ABCG2, PUMA | Tumor tissue, saliva samples, and cell lines | Biomarker (diagnosis) and therapeutic target | [61,62,63,64] |
| Mir-5100 ↑ | Causes proliferation, migration, and invasion | SCAI | OC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [65] |
| miR-382-5p ↑ | Induced cell migration and invasion | - | Patients tissue and saliva samples, and TSCC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [66] |
| List of Down regulated miRNAs | |||||
| miR-27b ↓ | Causes proliferation, migration, and invasion. Induces tumor growth in vivo. Activates the EMT process and metastatic pathways | ITGA5 | TSCC cell lines, saliva, and xenograft tumor model | Therapeutic target | [67] |
| miR-204 ↓ | Regulates cancer stemness, cell proliferation, and metastasis | CXCR4, CDC42, RAB22A, EZR, Slug and Sox4 | OSCC cell lines, patient saliva, plasma samples, and nude mice model | Biomarker | [30,68,69] |
| miR-100 ↓ | Plays role in the development or progression of the disease, and may contribute to the loss of sensitivity to ionizing radiation | MMP13, ID1, FGFR3, EGR2 | OC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [70] |
| miR-29a ↓ | Promoted OSCC cell invasion and induced drug-resistance in vitro | MMP2 | OC cell lines and patient tissue and saliva samples | Therapeutic target | [71] |
| Let-7d ↓ | Induces chemoresistance to cisplatin and 5-FU | Snail and Twist | OC cell lines and saliva samples | Therapeutic target | [27] |
| miR-203 ↓ | Causes tumor proliferation and shows resistance to drugs. Also regulates apoptotic signaling | BMI-1, PI3KCA, YES-1, SEMA6A, | Plasma samples and cell lines | Biomarker (diagnosis and prognosis), anti-cancer therapeutics | [72,73,74,75] |
| miR-200 ↓ | Regulate EMT leading to OSCC progression | ZEB1, ZEB2 | Clinical specimens | - | [76] |
| miR-133a ↓ | Regulates tumor proliferation and differentiation, as well as showing antiapoptotic characteristics | PKM2, GSTP1 | Patient samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [77,78] |
| miR-133b ↓ | Regulates the proliferation rate of cancer cells as well as the number of apoptotic cells | PKM2 | Patient samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [77] |
| miR-138 ↓ | Causes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis | GNAI2 | TSCC cell lines and plasma | - | [79] |
| miR-125b ↓ | Regulates tumor proliferation and radioresistance mechanisms | ICAM2 signaling | Cell lines and tissue specimens | Prognostic markers | [80] |
| miR-9 ↓ | Cause proliferation of OSCC cells | CXCR4-Wnt/β-catenin | Patient plasma sample and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [81] |
| miR-26a/b ↓ | Promotes invasion and migration | TMEM184B | OC clinical specimens and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [82] |
| miR-491-5p ↓ | Responsible for poor overall survival of patients, invasion, and metastasis | GIT1 | OC tissues, plasma, cell lines, and mice model | Biomarker (prognosis) | [83] |
| miR-375 ↓ | Promotes tumor proliferation, migration, and invasion | CIP2A, SLC7A11, PDGF-A | Patient tissue and saliva samples and cell lines | Biomarker (diagnosis), therapeutic target | [84,85,86] |
| miR-320 ↓ | Regulates tumor angiogenesis | HIF-1α-NRP1-VEGF | Tissue, saliva, plasma samples, cell lines, and mice model | Therapeutic target | [87] |
| miR-218 ↓ | Contributes to oral carcinogenesis. | mTOR-Rictor-Akt | OC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [88] |
| miR-205 ↓ | Regulates cancer development by promoting migration, invasion, and inhibiting apoptosis | IL-24, caspase-3/-7, Axin-2, TIMP-2 | OC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [89,90] |
| miR-181a ↓ | Cause tumorigenesis via stimulating EMT, and enhances metastatic potential | K-ras, Twist1 | Cell lines | Therapeutic target | [91,92] |
| miR-145 ↓ | Causes cell proliferation and colony formation | c-Myc, Cdk6 | Cell lines and tissue samples | Potential biomarker for diagnosis and therapeutic target | [93] |
| miR-140-5p ↓ | Promotes invasion and migration | ADAM10, ERBB4, PAX6, and LAMC1 | TSCC cell lines | -- | [94] |
| miR-124 ↓ | Causes OSCC progression | ITGB1 | Cell lines | -- | [28] |
| miR-99a ↓ | Causes migration, invasion, and lung colonization in OSCC cells | IGF1R | Tissue samples | Therapeutic target | [95] |
| miR-34a ↓ | Promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis | E2F3 | Cell lines, plasma, and SCID mouse xenograft model | Therapeutic target | [96] |
| miR-17/20a ↓ | Causes tumor progression and migration. Expression is negatively correlated with TNM staging and lymphatic metastasis | ITGβ8 | Cell lines and tissue and saliva samples | Prognostic marker | [97] |
| miR-137 ↓ | Induces tumor differentiation | -- | OC tissues, plasma and cells | Potential marker for early diagnosis | [98] |
| miR-5580-3p ↓ | Possibly associated with cell viability, proliferation, and migration | LAMC2 | Tissue and cell lines | Therapeutic target and potential biomarker | [99] |
| miR-98 ↓ | Causes cell growth and metastasis | IGF1R | OC tissues and cell lines | Potential therapeutic target | [100] |
| miR-1 ↓ | Promotes migration and invasiveness in OSCC cells. | Slug | OC cell lines and tumor tissues | Therapeutic target | [101] |
| miR-377 ↓ | Promotes OSCC growth and migration | HDAC9 | Tissue samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [102] |
| miR-23a-3p ↓ | It is correlated with more advanced cancerous stage and poorer differentiation of OSCC cell | FGF2 | OC cell lines and tissue | Prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target | [103] |
| miR-22 ↓ | Increased cell viability, migration, and invasion | NLRP3 | OC tissues and plasma, cell lines, and nude mice xenograft models | Prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target | [104] |
| miR-139-5p ↓ | Causes tumorigenesis and progression | HOXA9 | Patients tissue and saliva samples, and cell lines | Therapeutic strategy for the treatment | [105] |
| miRNA-504 ↓ | Facilitates proliferation, causes migration and invasion | CDK6 | OC animal model and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [106] |
| miR-106a ↓ | Induces proliferation and EMT | LIMK1 | OC tissues and cell lines | Prognostic factor | [107] |
| miR-16 ↓ | Promotes proliferation and inhibited apoptosis | AKT3, BCL2L2 | OC patients and cancer cell lines | Therapeutic target | [108] |
| miR-495 ↓ | Induces cell proliferation and invasion | Notch1 | OC tissues and plasma and OC cells | Therapeutic target | [109] |
| miRNA-329 ↓, miRNA-410 ↓ | Promotes proliferation and invasion | Wnt-7b | OC cell lines and tissues | -- | [110] |
| miR-132 ↓ | Promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration, and confers OSCC cell resistance to CDDP-induced apoptosis in vitro | TGF-β1/Smad2/3 | Tissues and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [111] |
| miR-376c-3p ↓ | Associated with tumor progression, poorer differentiation, lymphoid metastasis, and lymphovascular invasion. | HOXB7 | Tissue specimens and OC cell lines | Biomarker (early diagnosis) | [112] |
| miR-769-5p ↓ | Causes cancer progression | JAK1/STAT3 pathway | OC tissues and cells | Therapeutic target | [113] |
| miR-486-3p ↓ | Promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis | DDR1 | Tissue, saliva, and plasma samples | Therapeutic target | [114] |
| circRNAs | Function on Up- or Down-Regulation | Targets/Associated Pathway | Study Model | Biomarker/Therapy | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| List of up-regulated circRNAs | |||||
| circ_0002185 ↑ | Promotes the proliferation, invasion, migration, EMT in vitro, and tumor growth in vivo | circUHRF1/miR-526-5p/c-Myc/TGFB1/ESRP1 feedback loop | OC tissues and cells | Therapeutic target | [237] |
| circPVT1 ↑ | Induces proliferation by serving as a miRNA sponge | circPVT1/miR-125b axis | Tissue samples and cell lines | Biomarker and therapeutic target | [231] |
| circ_100290 ↑ | Promotes glycolysis and cell proliferation in OSCC | circ_100290/miR-378a/GLUT1 | OC cell lines and tissues | -- | [230] |
| circ_0001742 ↑ | Encourages proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT, and resists apoptosis in TSCC cells | circ_0001742/miR-431-5p/ATF3 axis | TSCC tissues and cells | Therapeutic target | [238] |
| circ_0001971 ↑ | Regulates cell proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis, and chemosensitivity of OSCC | circ_0001971/miR-194/miR-204 | Tissues, saliva and cell lines | -- | [239] |
| circDOCK1 ↑ | Suppresses cell apoptosis | circDOCK1/miR-196-5p/BIRC3 | OC cell lines, tissue and saliva samples | Biomarker and therapeutic target | [240] |
| circFLNA ↑ | Contributes to laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) migration | circFLNA/miR-486-3p | LSCC tissues and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [241] |
| circGOLPH3 ↑ | Promotes the growth of OSCC in vitro and in vivo as well as up-regulating its cell migration and invasion | circGOLPH3/miR-1299/LIF axis | OC cell lines and plasma | Therapeutic target | [242] |
| circCLK3 ↑ | Promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and cell cycle in TSCC cells | miR-455-5p/PARVA axis | TSCC tissues and cell lines | -- | [243] |
| circCDR1 ↑ | Enhances OSCC cell viability, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and inhibits cell apoptosis under a hypoxic microenvironment | AKT/ERK½/mTORsignaling pathway | OSCC cell lines and mice model | Treatment strategy | [232] |
| circ_0014359 ↑ | Promotes cancer progression | circ_0014359/miR-149 pathway | Tissues, cell lines, and xenograft mouse model | Diagnosis and treatment | [244] |
| circ_LPAR3 ↑ | Causes tumor growth and angiogenesis | Circ_LPAR3/miR-513b-5p/VEGFC/AKT1 | OC cell lines and mice model | -- | [245] |
| circ_SEPT9 ↑ | Induced OSCC proliferation, migration, and invasion | circ_SEPT9/miR-1225/PKN2 | OC cell lines, tissues, and xenograft model | Therapeutic target | [246] |
| circ_0000199 ↑ | Associated with tumor size, lymphatic metastasis, and TNM staging in patients with OSCC | miR-145-5p and miR-29b-3p (in silico study) | Patient plasma samples and cell lines | Biomarker and potential therapeutic target | [247] |
| circ_0001883 ↑ | May be responsible for cell migration, invasion, and EMT of LSCC | miR-125-5p/PI3K/AKT axis | Patient samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target for LSCC treatment | [248] |
| circ_0005320 ↑ | Promotes tumorigenesis | circ_0005320-miR-486-3p/miR-637 axis | OC tissues, cells, and nude mice model | Biomarker and therapeutic target | [249] |
| circ_0001874 ↑, circ_0001971 ↑ | Associated with tumorigenesis (development and progression of OSCC) | miR-661, miR-662, miR-593-5p, miR-107, and miR-103a-3p (targets of circ_0001874), miR-152-5p, miR-103a-3p, miR-107, miR-505-3p, and miR-9-5p (targets of circ_0001971) | Patient sample (saliva) | Diagnostic, prognostic, biomarker and therapeutic target | [250] |
| circ_0011946 ↑ | Causes proliferation, migration, and invasion, as well as restricted apoptosis | miR-216a-5p/BCL2L2 axis | OC tissues and cell lines | -- | [251] |
| circ_0001461 ↑ | Promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Promotes resistance to TNF-α-induced apoptosis | miR-145/TLR4/NF-κB axis | OC cells and tissues | -- | [252] |
| Circ_DHTKD1 ↑ | Promotes tumor growth and metastasis of OSCC | miR-326/GAB1 axis | OC cell lines, tissues, and xenograft model | Therapeutic target for clinical diagnosis | [253] |
| Circ_IGHG ↑ | Induces EMT and promotes cancer progression | miR-142-5p/IGF2BP3 Signaling | OC cell lines | Diagnosis and treatment | [254] |
| circ_002178 ↑ | Promotes the proliferation and migration | Akt/mTOR pathway | OC tissues and cell lines | -- | [255] |
| Circ_VAPA ↑ | Promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion | miR-132/HOXA7 axis | OC tissues and cells | Prognosis | [256] |
| circ-LRP6 ↑ | Mediates EMT and autophagy | - | OC cells and tissues | -- | [257] |
| List of down regulated circRNAs | |||||
| circ_0000140 ↓ | Correlated negatively with poor prognostic outcomes in OSCC patients | miR-31/LATS2 axis of Hippo signaling pathway | Tissue, cell lines, and xenograft mouse model | Therapeutic target | [258] |
| circ-PKD2 ↓ | Reduced expression in OSCC patients is significantly correlated with aggressive tumor characteristics | circPDK2/miR-204-3p/APC2 | OC tissue samples and cell lines | Therapeutic target | [236] |
| circ_0005379 ↓ | Its expression is inversely correlated with tumor size and differentiation | EGFR pathway | OC patient samples, cell line, and xenograft mouse models | Therapeutic target | [234] |
| circ_0004491 ↓ | Reduced expression is associated with lymph node metastasis, and may facilitate OSCC cell invasion and migration | circ_0004491/miR-155-5p/SIRT1 | OC tissues and cells | Potential biomarker | [259] |
| circSPATA6 ↓ | Lower expression in OSCC cells fails to impede migration and invasion and facilitate cell cycle arrest and apoptosis | miR-182/TRAF6 axis | Cell lines and xenograft tumor model | Targeted therapy | [260] |
| circ_0086414 ↓ | Its lower expression promotes the processes of growth and metastasis in OSCC | AMPK and cAMPsignaling pathway | OC tissues and cells | Diagnostic biomarker and OSCC therapy | [261] |
| circ_0008309 ↓ | Associated with pathological differentiation of OSCC patients | hsa_circ_0008309-miR-136-5P/hsa-miR-382-5P-ATXN1 | OC cell lines | Therapeutic biomarker | [262] |
| circGDI2 ↓ | Fails to serve as a repressor to restrain OSCC malignancy and, thus, regulate OSCC progression | miR-454-3p/FOXF2 Axis | OC tissues, cells, and mice model | Biomarker for targeted OSCC therapy | [263] |
| circ-KIAA0907 ↓ | Fails to inhibit migration, invasion, glycolysis, and promote apoptosis, thereby leading to OSCC progression | miR-96-5p/UNC13C axis | OC tissues | Potential target for OSCC treatment | [264] |
| circ_0007059 ↓ | Determined to alter cell growth | AKT/mTORsignaling | SCC15 and CAL27 cells | Prognostic/therapeutic target | [233] |
| circ_0004872 ↓ | Reverse the promoting effect of miR-424-5p overexpression on the process of OSCC cells | sponges miR-424-5p | OC cell lines | Early diagnosis and targeted therapy of OSCC | [265] |
| circ_0092125 ↓ | Associated with clinicopathological factors in OSCC patients, including tumor size, TNM stage, and lymph node metastasis | -- | OC cells and tissues | Biomarker of the OSCC prognosis | [266] |
| circRNA-102450 ↓ | Low expression is associated with the tumor metastatic properties and act as a tumor suppressor | circRNA-102450/miR-1178 axis | Patient plasma samples | Biomarker | [267] |
| circ_0072387 ↓ | Associated with cell proliferation, migration, invasion, EMT, and glycolysis in OSCC | miR-503-5p | Patient sample, OSCC cells, and tissues | Therapeutic target | [268] |
| snoRNAs | Function | Targets | Study Model | Biomarker/Therapy | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNHG1 ↑ | Promotes TGFβ1-Induced EMT, migration, and invasion of TSCCs | SNHG1/miR-194-5p/MTFR1 Axis | TSCC cell lines | Therapeutic target | [275] |
| SNHG3 ↑ | Facilitates cell proliferation and migration in OSCC, and regulates HOXB8 | transcription factor Y subunit gamma, SNHG3/miR-2682-5p axis | OC cell lines | Biomarker | [272,273] |
| SNHG15 ↑ | Increases growth, and facilitates malignant behaviors, of OSCC cells | miR-188-5p/DAAM1 | OC cell lines | Treatment purpose | [274] |
| SNHG16 ↑ | Enhances progression and carcinogenesis | - | CAL-27 and TSCCA cells | -- | [276] |
| SNHG17 ↑ | Accelerates proliferation and metastasis of OSCC cells, while reducing apoptosis | miR-375/PAX6 axis | CAL-27 and Tca8113 cells | -- | [277] |
| SNHG20 ↑ | Enhances the progression of OSCC | miR-29a/DIXDC1/Wnt regulatory axis | SCC9 and SCC15 cells | A theoretical basis for the treatment | [162] |
| ncRNA Name | Sample | Expression Level in OC vs. Normal Cells | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-8485 | Chondrocyte-derived exosomes | Higher | [304] |
| miRNA-1307-5p | Salivary exosomes | Higher | [301] |
| miR-200c-3p | Serum exosomes | Higher | [305,306] |
| miR-143 and miR-221 | Plasma exosomes | Lower and higher, respectively | [307,308] |
| miR-21 | Plasma/seminal exosomes | Higher | [309] |
| miR-31-5p | Macrophage-derived exosomes | Higher | [310] |
| miR-24-3p | Salivary exosomes | Higher | [311] |
| miR-382-5p | Fibroblast-associated exosomes | Higher | [66] |
| miR-10b | Plasma | Higher | [312] |
| miR-29a-3p | Serum | Higher | [313] |
| miR-486-5p | Plasma, salivary exosomes | Higher (in Stage II) | [314] |
| miR-155 | Exosomes | Higher | [315] |
| miR-142-3p | Exosomes | Higher | [316] |
| miR 455-5p and miR153 | Blood plasma | Higher and lower, respectively | [317] |
| miR-200b-3p, miR-483-5p, miR-425-5p, miR-374b-5p, miR-191-5p, miR-let-7c, miR-29a, miR-103, miR-1234, miR-638, miR-572, miR-22, miR-29b, miR-24-3p, miR-223, miR-20a, miR-29c, miR-17, miR-196a | Blood | Higher | [300] |
| miR-187, miR-9, miR-223, and miR-29c | Lower | ||
| miR-494 | Whole blood | Higher | [318] |
| miR-16 and let-7b | Serum | Higher | [319] |
| miR-34a-5p | Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomes | Lower | [320] |
| miR-3651 | Whole blood | Lower | [321] |
| lncRNAs MAGI2-AS3 and CCDC144NL-AS1 | Serum exosomes | Higher | [303] |
| lncRNA TIRY | Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomes | Higher | [302] |
| lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 | Saliva, exosomes | Lower | [322] |
| circ_0069313 | Exosomes | Higher | [323] |
| circ_0000199 | Serum exosomes | Higher | [247] |
| circ_0026611 | Serum exosomes | Higher | [324] |
| circ_0001874 | Salivary exosomes | Higher | [250] |
| circ_0001971 | Salivary exosomes | Higher | [250] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dey, S.; Biswas, B.; Manoj Appadan, A.; Shah, J.; Pal, J.K.; Basu, S.; Sur, S. Non-Coding RNAs in Oral Cancer: Emerging Roles and Clinical Applications. Cancers 2023, 15, 3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153752
Dey S, Biswas B, Manoj Appadan A, Shah J, Pal JK, Basu S, Sur S. Non-Coding RNAs in Oral Cancer: Emerging Roles and Clinical Applications. Cancers. 2023; 15(15):3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153752
Chicago/Turabian StyleDey, Saurabh, Bini Biswas, Angela Manoj Appadan, Jaladhi Shah, Jayanta K. Pal, Soumya Basu, and Subhayan Sur. 2023. "Non-Coding RNAs in Oral Cancer: Emerging Roles and Clinical Applications" Cancers 15, no. 15: 3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153752
APA StyleDey, S., Biswas, B., Manoj Appadan, A., Shah, J., Pal, J. K., Basu, S., & Sur, S. (2023). Non-Coding RNAs in Oral Cancer: Emerging Roles and Clinical Applications. Cancers, 15(15), 3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153752







