Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Gynecologic Oligometastases: An Effective but Underutilized Approach
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
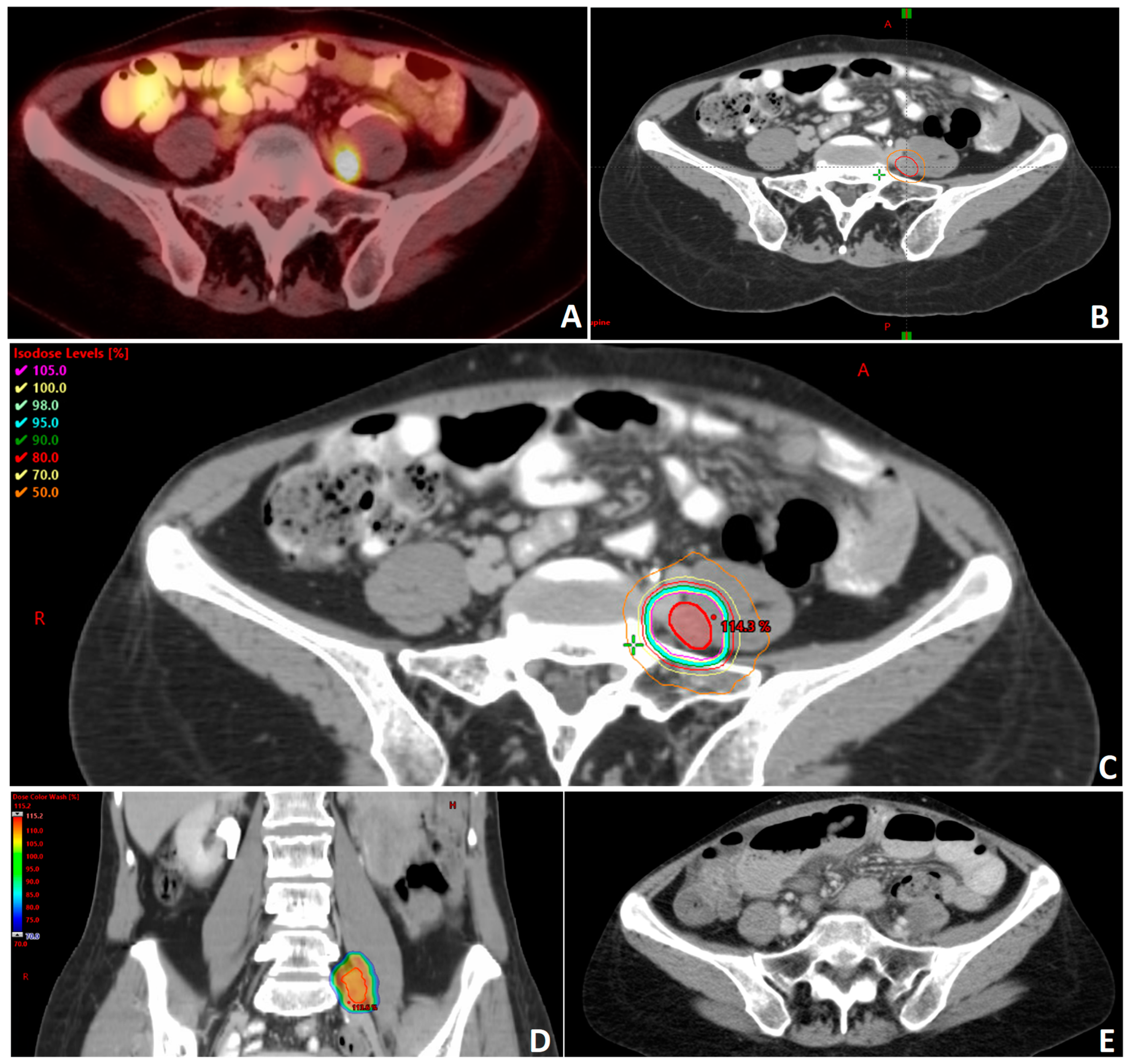
2. SBRT in Ovarian Primary Oligometastases
3. SBRT in Non-Ovarian Gynecologic Primary Oligometastases
| Year | Authors | Type of Study | # Patients (n) | # Lesions (n) | MFU (Months) | Outcomes | Toxicity | Progression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | Iftode et al. [14] | R | Ovarian n = 26 | 44 | 28.5 | 2yr LC 92.9% 2yr PFS 38% 2yr OS 92.7% | G2 = 11.3% No ≥ G3 | 7.7% L 3.8% LD 50% D |
| 2020 | Kowalchuk et al. [18] | R | Ovarian n = 35 | 98 | 33.67 | 2yr LC 80% 2yr PFS 12% 2yr OS 60% | 27 cases < G3 Single G5 duodenal ulcer | 17% L 32% LD 39% D |
| 2018 | Lazzari et al. [15] | R | Ovarian n = 82 | 156 | 17.4 | 2yr Local PFS 68% 2yr PFS 18% 2yr OS 71% | Acute G1 − G2 = 27% Late G1 − G2 = 28% No ≥ G3 | 3.5% L 5.5% LD 90% D |
| 2020 | Macchia et al. [13] | R | Ovarian n = 261 | 449 | 22 | 2yr LC 81.9% 2yr PFS 15.4% 2yr OS 73.6% | Acute G1 − G2 = 20.7% Late G1 − G2 = 6.1% 2yr late toxicity free survival = 95.1%. | 18.1% L 84.6% LD/D |
| 2022 | Macchia et al. [19] | R | Cervical n = 83 | 125 | 14.5 | 2yr LC 61.8% 2yr PFS 28.9% 2yr OS 59% | Acute G1 − G2 = 18.1% Late G1− G3 = 4.8% Single G3 pain toxicity | 38.2% L 71.1% LD/D |
| 2020 | Reddy et al. [20] | R | Uterine n = 27 | 61 | 16.9 | 1yr Local PFS 75.9% 1yr OS 65.4% | Total G1 − G2 = 29.6% of which acute = 93.3% & Late = 6.6% No ≥ G3 | 7.4% L 74.1% LD |
| 2020 | Onal et al. [17] | R | Ovarian n = 21 Cervical n = 8 Total = 29 | 35 | 15.3 | 2yr LC 84% 2yr PFS 18% 2yr OS 62% | G2 = 17% No ≥ G3 | 11% L 84% D |
| 2020 | Aghdam et al. [21] | R | Ovarian n = 10 Uterine n = 10 Total = 20 | 20 | 56 | 5yr LC 73% 5yr PFS 20% 5yr OS 56% | Single G3 MSK toxicity | NR |
| 2020 | Reshko et al. [20] | R | Ovarian n = 30 Cervical n = 20 Uterine n = 27 Vaginal n = 8 Vulva = 1 Total = 86 | 209 | 20 | 1yr LC 80% 1yr OS 70% | 4.3% ≥ G2 Single G3 GU toxicity | NR |
| 2020 | Yegya-Raman et al. [12] | SR | Ovarian n = 384 Cervical n = 181 Uterine n = 74 Vaginal n = 3 Vulvar n =2 Other/NS = 23 Total = 667 | 1071 | 22 (range 4.6-54.6) | 2yr LC 71–100% 2yr PFS 15.4–48.4% 2yr OS 57.5–85% | No ≥ G3 toxicity in 9/16 studies | Progression in 23.1–75% patients. 78.9–100% of progression including out-of-field component |
| 2021 | Cuccia et al. [22] | R | Ovarian n = 17 Cervical n = 4 Uterine n = 17 Vagina n = 2 Total = 40 | 63 | 27 | 2yr LC 100% 2yr PFS 23% 2yr OS 70% | No acute or late ≥ G2 toxicity | NR |
4. Radiation and the Impact of the Tumor Microenvironment
5. Immunotherapy in Gynecologic Malignancies
6. Novel Techniques, Dose Escalation and Safety in SBRT
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Gaede, S.; Louie, A.V.; Haasbeek, C.; Mulroy, L.; Lock, M.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Yaremko, B.P.; et al. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy versus Standard of Care Palliative Treatment in Patients with Oligometastatic Cancers (SABR-COMET): A Randomised, Phase 2, Open-Label Trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, D.R.; Blumenschein, G.R.; Lee, J.J.; Hernandez, M.; Ye, R.; Camidge, D.R.; Doebele, R.C.; Skoulidis, F.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gibbons, D.L.; et al. Local Consolidative Therapy versus Maintenance Therapy or Observation for Patients with Oligometastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer without Progression after First-Line Systemic Therapy: A Multicentre, Randomised, Controlled, Phase 2 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyengar, P.; Wardak, Z.; Gerber, D.E.; Tumati, V.; Ahn, C.; Hughes, R.S.; Dowell, J.E.; Cheedella, N.; Nedzi, L.; Westover, K.D.; et al. Consolidative Radiotherapy for Limited Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e173501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruers, T.; Punt, C.; Van Coevorden, F.; Pierie, J.P.E.N.; Borel-Rinkes, I.; Ledermann, J.A.; Poston, G.; Bechstein, W.; Lentz, M.A.; Mauer, M.; et al. Radiofrequency Ablation Combined with Systemic Treatment versus Systemic Treatment Alone in Patients with Non-Resectable Colorectal Liver Metastases: A Randomized EORTC Intergroup Phase II Study (EORTC 40004). Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2619–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, Y.; Guckenberger, M.; Gomez, D.; Hoyer, M.; Iyengar, P.; Kindts, I.; Méndez Romero, A.; Nevens, D.; Palma, D.; Park, C.; et al. Defining Oligometastatic Disease from a Radiation Oncology Perspective: An ESTRO-ASTRO Consensus Document. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 148, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelson, M.D.; Taylor Wharton, J.; Delclos, L.; Copeland, L.; Gershenson, D. Palliative Radiotherapy for Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1987, 13, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choan, E.; Quon, M.; Gallant, V.; Samant, R. Effective Palliative Radiotherapy for Symptomatic Recurrent or Residual Ovarian Cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2006, 102, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Balboni, T.; Taylor, A.; Liu, J.; Lee, L.J. Palliative Radiation Therapy for Recurrent Ovarian Cancer: Efficacy and Predictors of Clinical Response. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2018, 28, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, K.; Patel, M.; Liotta, M.; Harkenrider, M.; Guo, R.; Small, W.; Ronald, P. Long-Term Benefit of Tumor Volume-Directed Involved Field Radiation Therapy in the Management of Recurrent Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2016, 26, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.P.; Jhingran, A.; Klopp, A.H.; Schmeler, K.M.; Ramirez, P.T.; Eifel, P.J. Involved-Field Radiation Therapy for Locoregionally Recurrent Ovarian Cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 130, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chundury, A.; Apicelli, A.; Dewees, T.; Powell, M.; Mutch, D.; Thaker, P.; Robinson, C.; Grigsby, P.W.; Schwarz, J.K. Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy for Recurrent Ovarian Cancer Refractory to Chemotherapy. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 141, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yegya-Raman, N.; Cao, C.D.; Hathout, L.; Girda, E.; Richard, S.D.; Rosenblum, N.G.; Taunk, N.K.; Jabbour, S.K. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Oligometastatic Gynecologic Malignancies: A Systematic Review. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 159, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macchia, G.; Lazzari, R.; Colombo, N.; Laliscia, C.; Capelli, G.; D’Agostino, G.R.; Deodato, F.; Maranzano, E.; Ippolito, E.; Ronchi, S.; et al. A Large, Multicenter, Retrospective Study on Efficacy and Safety of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) in Oligometastatic Ovarian Cancer (MITO RT1 Study): A Collaboration of MITO, AIRO GYN, and MaNGO Groups. Oncologist 2020, 25, e311–e320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftode, C.; D’Agostino, G.R.; Tozzi, A.; Comito, T.; Franzese, C.; De Rose, F.; Franceschini, D.; Di Brina, L.; Tomatis, S.; Scorsetti, M. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Oligometastatic Ovarian Cancer: A Promising Therapeutic Approach. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2018, 28, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzari, R.; Ronchi, S.; Gandini, S.; Surgo, A.; Volpe, S.; Piperno, G.; Comi, S.; Pansini, F.; Fodor, C.; Orecchia, R.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Oligometastatic Ovarian Cancer: A Step Toward a Drug Holiday. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 101, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacChia, G.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A.; Lazzari, R.; Cerrotta, A.; Deodato, F.; Ippolito, E.; Aristei, C.; Gambacorta, M.A.; Scambia, G.; Valentini, V.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) in Oligometastatic/Persistent/Recurrent Ovarian Cancer: A Prospective, Multicenter Phase II Study (MITO-RT3/RAD). Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2022, 32, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onal, C.; Gultekin, M.; Oymak, E.; Guler, O.C.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Yuce Sari, S.; Akkus Yildirim, B.; Yildiz, F. Stereotactic Radiotherapy in Patients with Oligometastatic or Oligoprogressive Gynecological Malignancies: A Multi-Institutional Analysis. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2020, 30, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalchuk, R.O.; Waters, M.R.; Richardson, K.M.; Spencer, K.; Larner, J.M.; Irvin, W.P.; Kersh, C.R. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchia, G.; Nardangeli, A.; Laliscia, C.; Fodor, A.; Draghini, L.; Gentile, P.C.; D’Agostino, G.R.; Balcet, V.; Bonome, P.; Ferioli, M.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Oligometastatic Cervical Cancer (MITO-RT2/RAD Study): A Collaboration of MITO, AIRO GYN, and MaNGO Groups. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2022, 32, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.V.; Mills, M.N.; Reshko, L.B.; Martin Richardson, K.; Kersh, C.R. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Oligometastatic Uterine Cancer: Clinical Outcomes and Toxicity. Cancer Investig. 2020, 38, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, N.; Repka, M.C.; McGunigal, M.; Pepin, A.; Paydar, I.; Rudra, S.; Paudel, N.; Pernia Marin, M.; Suy, S.; Collins, S.P.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy: A Versatile, Well-Tolerated, and Effective Treatment Option for Extracranial Metastases From Primary Ovarian and Uterine Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 572564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuccia, F.; Pastorello, E.; Vitale, C.; Nicosia, L.; Mazzola, R.; Figlia, V.; Giaj-Levra, N.; Ricchetti, F.; Rigo, M.; Attinà, G.; et al. The Use of SBRT in the Management of Oligometastatic Gynecological Cancer: Report of Promising Results in Terms of Tolerability and Clinical Outcomes. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 3613–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.C.; Lee, K.B.; Shin, J.W.; Park, C.Y.; Sym, S.J.; Lee, J.-H. Radiation Therapy with Chemotherapy for Patients with Cervical Cancer and Supraclavicular Lymph Node Involvement. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 23, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, W.; Koh, H.K.; Kim, H.J.; Wu, H.-G.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, H.H. Salvage Radiotherapy for Lymph Node Recurrence after Radical Surgery in Cervical Cancer. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 23, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, M.S.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.S. Curative Chemoradiotherapy in Patients with Stage IVB Cervical Cancer Presenting with Paraortic and Left Supraclavicular Lymph Node Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, K.L.; Yoder, A.; De, B.; Lin, L.; Jhingran, A.; Joyner, M.M.; Eifel, P.J.; Colbert, L.E.; Lu, K.H.; Klopp, A.H. Long-Term Survival Following Definitive Radiation Therapy for Recurrence or Oligometastases in Gynecological Malignancies: A Landmark Analysis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2022, 164, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smile, T.; Reddy, C.A.; Qiao-Guan, G.; Amarnath, S.R.; Stephans, K.L.; Woody, N.M.; Balagamwala, E.H.; AlHilli, M.M.; Michener, C.; Mahdi, H.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for the Treatment of Oligometastatic Gynecological Malignancy in the Abdomen and Pelvis: A Single-Institution Experience. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 108, e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, T.; Naga, P.; Banerjee, S.; Gupta, D.; Narang, K.; Tayal, M.; Bisht, S.S. CyberKnife Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Recurrent or Oligometastatic Gynecological Cancers. South Asian J. Cancer 2021, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshko, L.B.; Baliga, S.; Crandley, E.F.; Harry Lomas, I.V.; Richardson, M.K.; Spencer, K.; Bennion, N.; Mikdachi, H.E.; Irvin, W.; Kersh, C.R. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) in Recurrent, Persistent or Oligometastatic Gynecological Cancers. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 159, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Kodaira, T.; Koide, Y.; Okuda, T.; Mizumatsu, S.; Oshima, Y.; Takeuchi, A.; Mori, T.; Abe, S.; Asai, A.; et al. Role of High-Dose Salvage Radiotherapy for Oligometastases of the Localised Abdominal/Pelvic Lymph Nodes: A Retrospective Study. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laliscia, C.; Fabrini, M.G.; Delishaj, D.; Morganti, R.; Greco, C.; Cantarella, M.; Tana, R.; Paiar, F.; Gadducci, A. Clinical Outcomes of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Oligometastatic Gynecological Cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2017, 27, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liang, C.; Chen, M.; Su, W. Association between Tumor-Stroma Ratio and Prognosis in Solid Tumor Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68954–68965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaupel, P.; Mayer, A. Hypoxia in Cancer: Significance and Impact on Clinical Outcome. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007, 26, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Physiology and Medicine. Cell 2012, 148, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Angiogenesis in Cancer and Other Diseases. Nature 2000, 407, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M.; Wilson, W.R. Exploiting Tumour Hypoxia in Cancer Treatment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.W.; Lee, Y.-J.; Griffin, R.J.; Park, I.; Koonce, N.A.; Hui, S.; Kim, M.-S.; Dusenbery, K.E.; Sperduto, P.W.; Cho, L.C. Indirect Tumor Cell Death After High-Dose Hypofractionated Irradiation: Implications for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy and Stereotactic Radiation Surgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 93, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.R.; Hay, M.P. Targeting Hypoxia in Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, H.E.; Paget, J.T.E.; Khan, A.A.; Harrington, K.J. The Tumour Microenvironment after Radiotherapy: Mechanisms of Resistance and Recurrence. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, E.B.; Chhabra, A.; Chachoua, A.; Adams, S.; Donach, M.; Fenton-Kerimian, M.; Friedman, K.; Ponzo, F.; Babb, J.S.; Goldberg, J.; et al. Local Radiotherapy and Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor to Generate Abscopal Responses in Patients with Metastatic Solid Tumours: A Proof-of-Principle Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Tao, Y.; He, L.; Guan, H.; Zhen, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, F. Clinical Application of Radiotherapy in Patients with Oligometastatic Ovarian Cancer: A Sharp Tool to Prolong the Interval of Systemic Treatment. Discov. Oncol. 2022, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Vanpouille-Box, C.; Melero, I.; Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Immunological Mechanisms Responsible for Radiation-Induced Abscopal Effect. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, D.J.; Nanavaty, N.S.; Devanaboyina, M.; Stanbery, L.; Hamouda, D.; Edelman, G.; Dworkin, L.; Nemunaitis, J.J. The Abscopal Effect of Radiation Therapy. Future Oncol. 2021, 17, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, F.G.; Bourhis, J.; Coukos, G. Radiotherapy Combination Opportunities Leveraging Immunity for the next Oncology Practice. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Farhood, B.; Eleojo Musa, A.; Taeb, S.; Rezaeyan, A.; Najafi, M. Abscopal Effect in Radioimmunotherapy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 85, 106663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, J.J.; Lemons, J.M.; Karrison, T.G.; Pitroda, S.P.; Melotek, J.M.; Zha, Y.; Al-Hallaq, H.A.; Arina, A.; Khodarev, N.N.; Janisch, L.; et al. Safety and Clinical Activity of Pembrolizumab and Multisite Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theelen, W.S.M.E.; Chen, D.; Verma, V.; Hobbs, B.P.; Peulen, H.M.U.; Aerts, J.G.J.V.; Bahce, I.; Niemeijer, A.L.N.; Chang, J.Y.; de Groot, P.M.; et al. Pembrolizumab with or without Radiotherapy for Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of Two Randomised Trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammers, H.J.; Vonmerveldt, D.; Ahn, C.; Nadal, R.M.; Drake, C.G.; Folkert, M.R.; Laine, A.M.; Courtney, K.D.; Brugarolas, J.; Song, D.Y.; et al. Combination of Dual Immune Checkpoint Inhibition (ICI) with Stereotactic Radiation (SBRT) in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (MRCC) (RADVAX RCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, K.S.; Sill, M.W.; Penson, R.T.; Huang, H.; Ramondetta, L.M.; Landrum, L.M.; Oaknin, A.; Reid, T.J.; Leitao, M.M.; Michael, H.E.; et al. Bevacizumab for Advanced Cervical Cancer: Final Overall Survival and Adverse Event Analysis of a Randomised, Controlled, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial (Gynecologic Oncology Group 240). Lancet 2017, 390, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, P.A.; Bang, Y.-J.; Berton-Rigaud, D.; Elez, E.; Pishvaian, M.J.; Rugo, H.S.; Puzanov, I.; Mehnert, J.M.; Aung, K.L.; Lopez, J.; et al. Safety and Antitumor Activity of Pembrolizumab in Advanced Programmed Death Ligand 1-Positive Endometrial Cancer: Results From the KEYNOTE-028 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2535–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marabelle, A.; Le, D.T.; Ascierto, P.A.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; De Jesus-Acosta, A.; Delord, J.-P.; Geva, R.; Gottfried, M.; Penel, N.; Hansen, A.R.; et al. Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in Patients with Noncolorectal High Microsatellite Instability/Mismatch Repair-Deficient Cancer: Results From the Phase II KEYNOTE-158 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, D.M.; Bariani, G.M.; Cassier, P.A.; Marabelle, A.; Hansen, A.R.; De Jesus Acosta, A.; Miller, W.H.; Safra, T.; Italiano, A.; Mileshkin, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Patients with Microsatellite Instability-High Advanced Endometrial Cancer: Results From the KEYNOTE-158 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, N.; Dubot, C.; Lorusso, D.; Caceres, M.V.; Hasegawa, K.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Tewari, K.S.; Salman, P.; Hoyos Usta, E.; Yañez, E.; et al. Pembrolizumab for Persistent, Recurrent, or Metastatic Cervical Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamarin, D.; Burger, R.A.; Sill, M.W.; Powell, D.J.; Lankes, H.A.; Feldman, M.D.; Zivanovic, O.; Gunderson, C.; Ko, E.; Mathews, C.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Nivolumab Versus Nivolumab and Ipilimumab for Recurrent or Persistent Ovarian Cancer: An NRG Oncology Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, R.W.; Hollebecque, A.; Meyer, T.; Devlin, M.-J.; Oaknin, A.; Kerger, J.; López-Picazo, J.M.; Machiels, J.-P.; Delord, J.-P.; Evans, T.R.J.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Nivolumab Monotherapy in Recurrent or Metastatic Cervical, Vaginal, or Vulvar Carcinoma: Results From the Phase I/II CheckMate 358 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2825–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jaeghere, E.A.; Tuyaerts, S.; Van Nuffel, A.M.T.; Belmans, A.; Bogaerts, K.; Baiden-Amissah, R.; Lippens, L.; Vuylsteke, P.; Henry, S.; Trinh, X.B.; et al. Pembrolizumab, Radiotherapy, and an Immunomodulatory Five-Drug Cocktail in Pretreated Patients with Persistent, Recurrent, or Metastatic Cervical or Endometrial Carcinoma: Results of the Phase II PRIMMO Study. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2023, 72, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, L.E.; Stanley, J.A.; Robinson, C.; Srivastava, A.; Contreras, J.A.; Curcuru, A.; Green, O.L.; Massad, L.S.; Kuroki, L.; Fuh, K.; et al. Phase I Trial of Stereotactic MRI-Guided Online Adaptive Radiation Therapy (SMART) for the Treatment of Oligometastatic Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 112, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, L.; Cuccia, F.; Mazzola, R.; Ricchetti, F.; Figlia, V.; Giaj-Levra, N.; Rigo, M.; Tomasini, D.; Pasinetti, N.; Corradini, S.; et al. Disease Course of Lung Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer Treated with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2020, 196, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sherwani, Z.; Parikh, S.; Yegya-Raman, N.; McKenna, K.; Deek, M.; Jabbour, S.; Hathout, L. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Gynecologic Oligometastases: An Effective but Underutilized Approach. Cancers 2023, 15, 3526. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133526
Sherwani Z, Parikh S, Yegya-Raman N, McKenna K, Deek M, Jabbour S, Hathout L. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Gynecologic Oligometastases: An Effective but Underutilized Approach. Cancers. 2023; 15(13):3526. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133526
Chicago/Turabian StyleSherwani, Zohaib, Shreel Parikh, Nikhil Yegya-Raman, Kelly McKenna, Matthew Deek, Salma Jabbour, and Lara Hathout. 2023. "Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Gynecologic Oligometastases: An Effective but Underutilized Approach" Cancers 15, no. 13: 3526. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133526
APA StyleSherwani, Z., Parikh, S., Yegya-Raman, N., McKenna, K., Deek, M., Jabbour, S., & Hathout, L. (2023). Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Gynecologic Oligometastases: An Effective but Underutilized Approach. Cancers, 15(13), 3526. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133526







