The Risk of Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke in Head and Neck Cancer: A Longitudinal Cohort Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
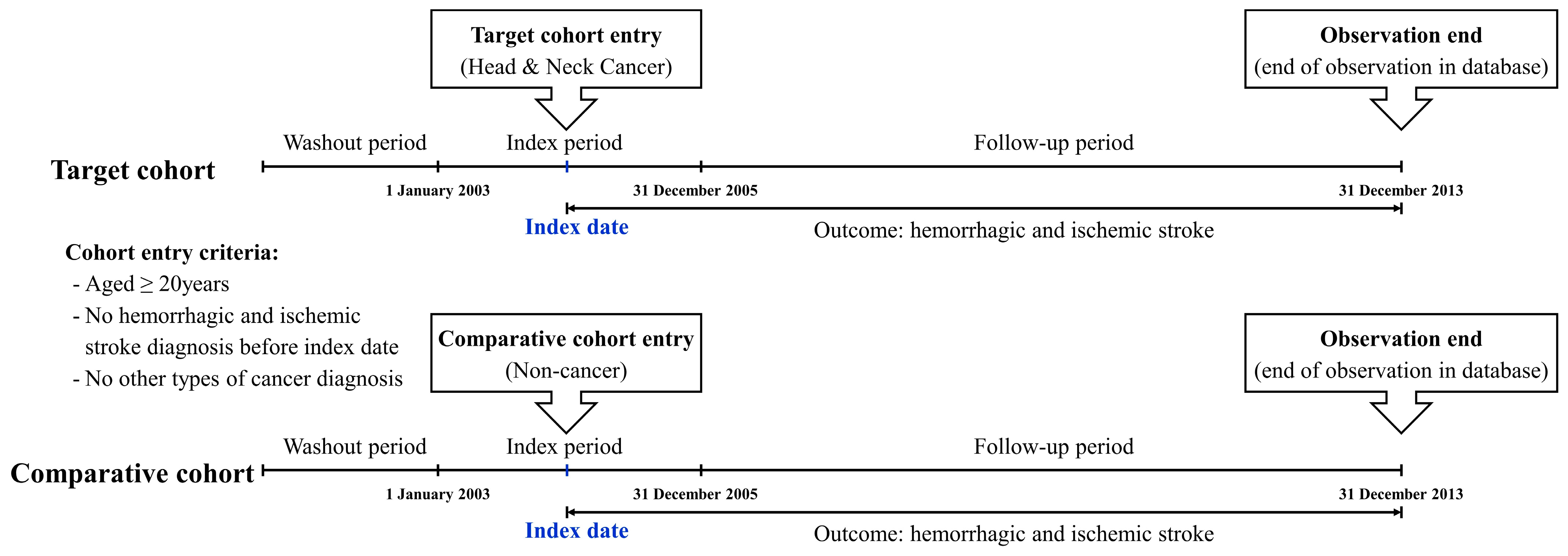
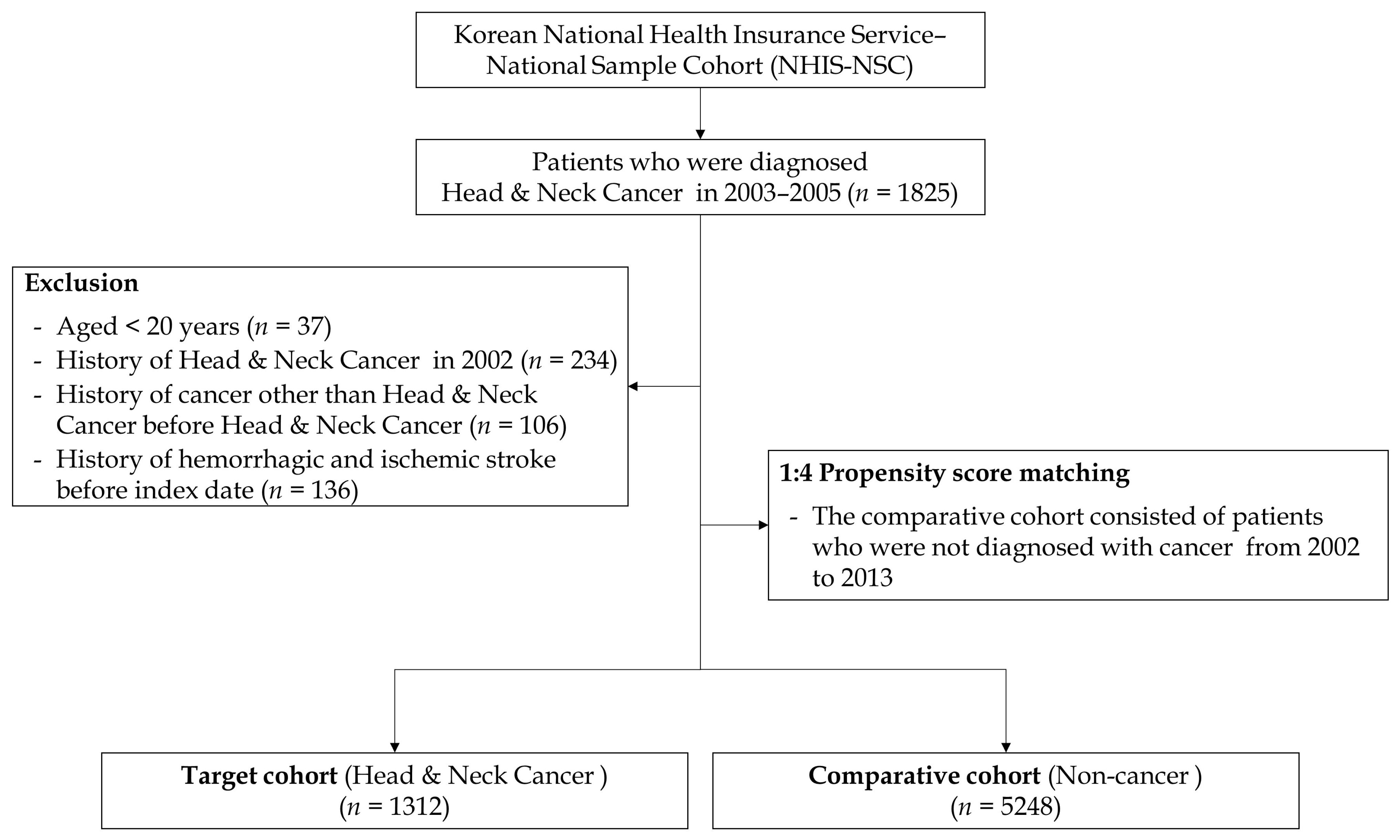
2.1. Study Dataset
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Matching/Descriptive Portion of the Analysis
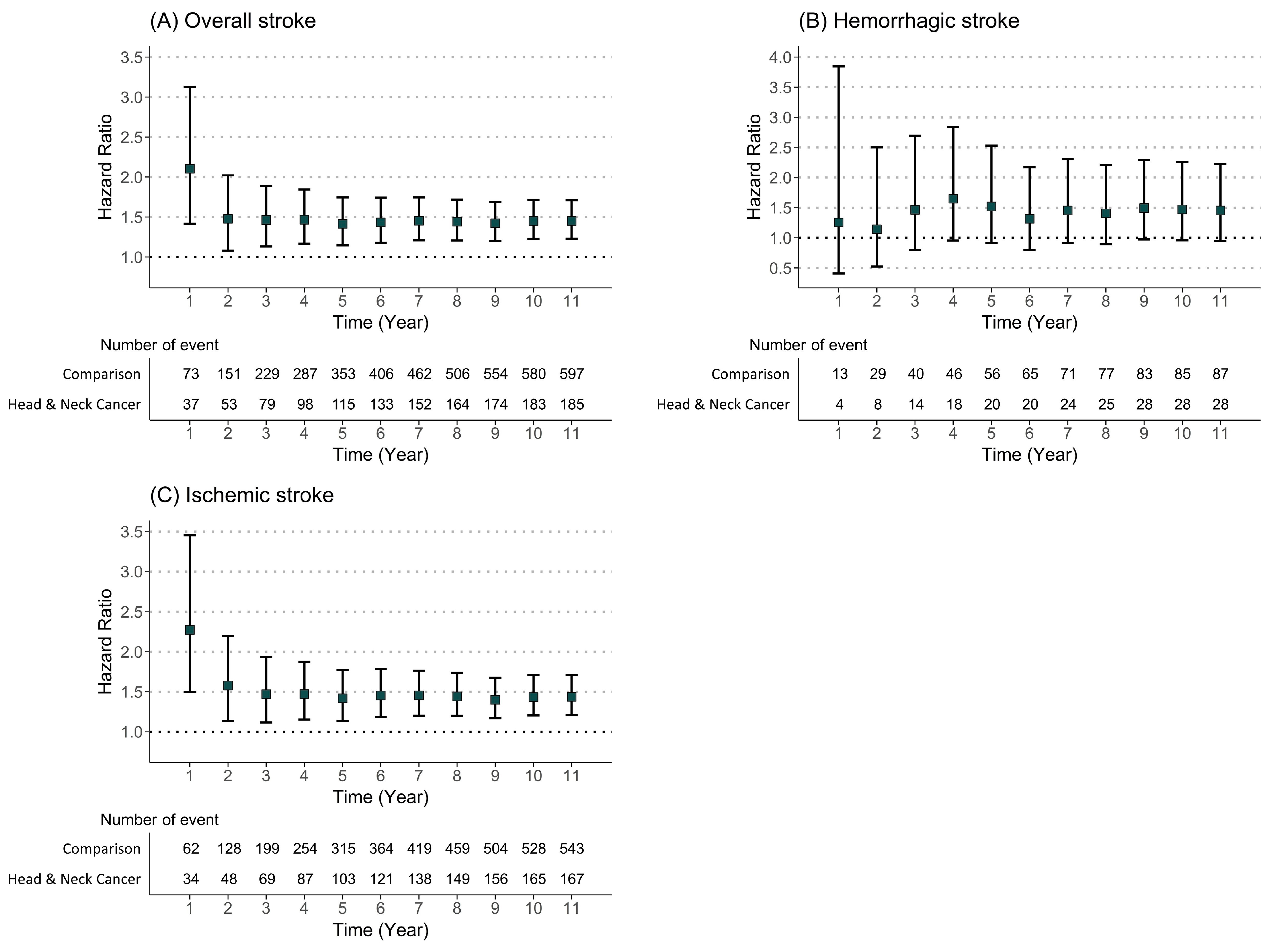
3.2. Incidence Analysis
3.3. Risk Analysis
3.4. Subtype of Head and Neck Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zöller, B.; Ji, J.; Sundquist, J.; Sundquist, K. Risk of haemorrhagic and ischaemic stroke in patients with cancer: A nationwide follow-up study from Sweden. Eur. J. Cancer. 2012, 48, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, J.M.; Segal, A.Z. Incidence and etiology of cerebrovascular disease in patients with malignancy. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2005, 7, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaorsky, N.G.; Zhang, Y.; Tchelebi, L.T.; Mackley, H.B.; Chinchilli, V.M.; Zacharia, B.E. Stroke among cancer patients. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun, R.; Roy, D.C.; Hao, Y.; Deka, R.; Huang, W.K.; Navi, B.B.; Siegal, D.M.; Ramsay, T.; Fergusson, D.; Shorr, R.; et al. Incidence of stroke in the first year after diagnosis of cancer—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 966190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, O.; Vera, N.; Otto, B.; Heinz, L.; Wolfgang, G. Stroke in cancer patients: A risk factor analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 94, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navi, B.B.; Reiner, A.S.; Kamel, H.; Iadecola, C.; Elkind, M.S.; Panageas, K.S.; DeAngelis, L.M. Association between incident cancer and subsequent stroke. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 77, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dearborn, J.L.; Urrutia, V.C.; Zeiler, S.R. Stroke and cancer- A complicated relationship. J. Neurol. Transl. Neurosci. 2014, 2, 1039. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Xu, J.; Ward, E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2010, 60, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillison, M.L. Current topics in the epidemiology of oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers. Head. Neck. 2007, 29, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Kuan, F.C.; Huang, S.F.; Lu, C.H.; Chen, P.T.; Huang, C.E.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Lee, K.D. Accelerated risk of premature ischemic stroke in 5-year survivors of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncologist 2019, 24, e891–e897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Chen, C.Y.; Lai, W.T.; Kuo, C.C.; Huang, Y.B. Increasing risks of ischemic stroke in oral cancer patients treated with radiotherapy or chemotherapy: A nationwide cohort study. Int. J. Neurosci. 2015, 125, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Su, Y.C.; Ho, H.C.; Hung, S.K.; Lee, M.S.; Chiou, W.Y.; Chou, P.; Huang, Y.S. Increased risk of ischemic stroke in young nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, e833–e838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuan, F.C.; Lee, K.D.; Huang, S.F.; Chen, P.T.; Huang, C.E.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, M.C. Radiotherapy is associated with an accelerated risk of ischemic stroke in oral cavity cancer survivors after primary surgery. Cancers 2020, 12, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.S.; Lee, C.C.; Chang, T.S.; Ho, H.C.; Su, Y.C.; Hung, S.K.; Lee, M.S.; Chou, P.; Chang, Y.H.; Lee, C.C. Increased risk of stroke in young head and neck cancer patients treated with radiotherapy or chemotherapy. Oral. Oncol. 2011, 47, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.N.; Chen, P.C.; Bai, L.Y.; Muo, C.H.; Sung, F.C.; Chen, S.W. Young nasopharyngeal cancer patients with radiotherapy and chemotherapy are most prone to ischaemic risk of stroke: A national database, controlled cohort study. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2013, 38, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.N.; Chen, S.W.; Bai, L.Y.; Mou, C.H.; Hsu, C.Y.; Sung, F.C. Increase in stroke risk in patients with head and neck cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Br. J. Cancer. 2011, 105, 1419–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, S.C.; Kim, Y.Y.; Park, S.K.; Khang, Y.H.; Kim, H.C.; Park, J.H.; Kang, H.J.; Do, C.H.; Song, J.S.; Lee, E.J.; et al. Cohort profile: The National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) in Korea. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Shin, S.A.; Kim, K. Cohort profile: The National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC), South Korea. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, C.; Yu, H.; Kim, D.K. Relationship of depression, anxiety, and bipolar disease with burning mouth syndrome: A nationwide cohort study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, C.; Yu, H.; Kim, D.K. Analysis of the incidence of Type 2 diabetes, requirement of insulin treatment, and diabetes-related complications among patients with cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Yu, H.; Kim, D.K. Glaucoma is associated with the risk of obstructive sleep apnea: A population-based nationwide cohort study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Lee, S.Y. Could mid- to late-onset glaucoma be associated with an increased risk of incident dementia? A nationwide retrospective cohort study. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, S.; Ren, G.; Cui, F.; Zhou, P.K. Radiotherapy exposure in cancer patients and subsequent risk of stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthurs, E.; Hanna, T.P.; Zaza, K.; Peng, Y.; Hall, S.F. Stroke after radiation therapy for head and neck cancer: What is the risk? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 96, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, T.L.; Hsieh, C.T.; Hsu, H.Y.; Tsai, M.C.; Wang, C.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Hsiao, B.Y.; Jhuang, J.R.; Chiang, C.J.; Lee, W.C.; et al. The risk of ischemic stroke in head and neck cancer patients and those who were treated with radiotherapy: A population-based cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2022, 31, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardiotis, E.; Aloizou, A.M.; Markoula, S.; Siokas, V.; Tsarouhas, K.; Tzanakakis, G.; Libra, M.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Brotis, A.G.; Aschner, M.; et al. Cancer-associated stroke: Pathophysiology, detection and management. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navi, B.B.; Iadecola, C. Ischemic stroke in cancer patients: A review of an underappreciated pathology. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.Y.; Bhaskar, S.M.M. Bridging the gap in cancer-related stroke management: Update on therapeutic and preventive approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, K.; Du, P.; Yang, W.; He, Y.; Li, T.; Mei, Z. Risk of stroke in cancer survivors: A meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies. Neurology 2021, 96, e513–e526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.; Murchie, P.; Derby, S.; Ong, A.Y.; Walji, L.; McLernon, D.; Macleod, M.J.; Adam, R. Is stroke incidence increased in survivors of adult cancers? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cancer Surviv. 2022, 16, 1414–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
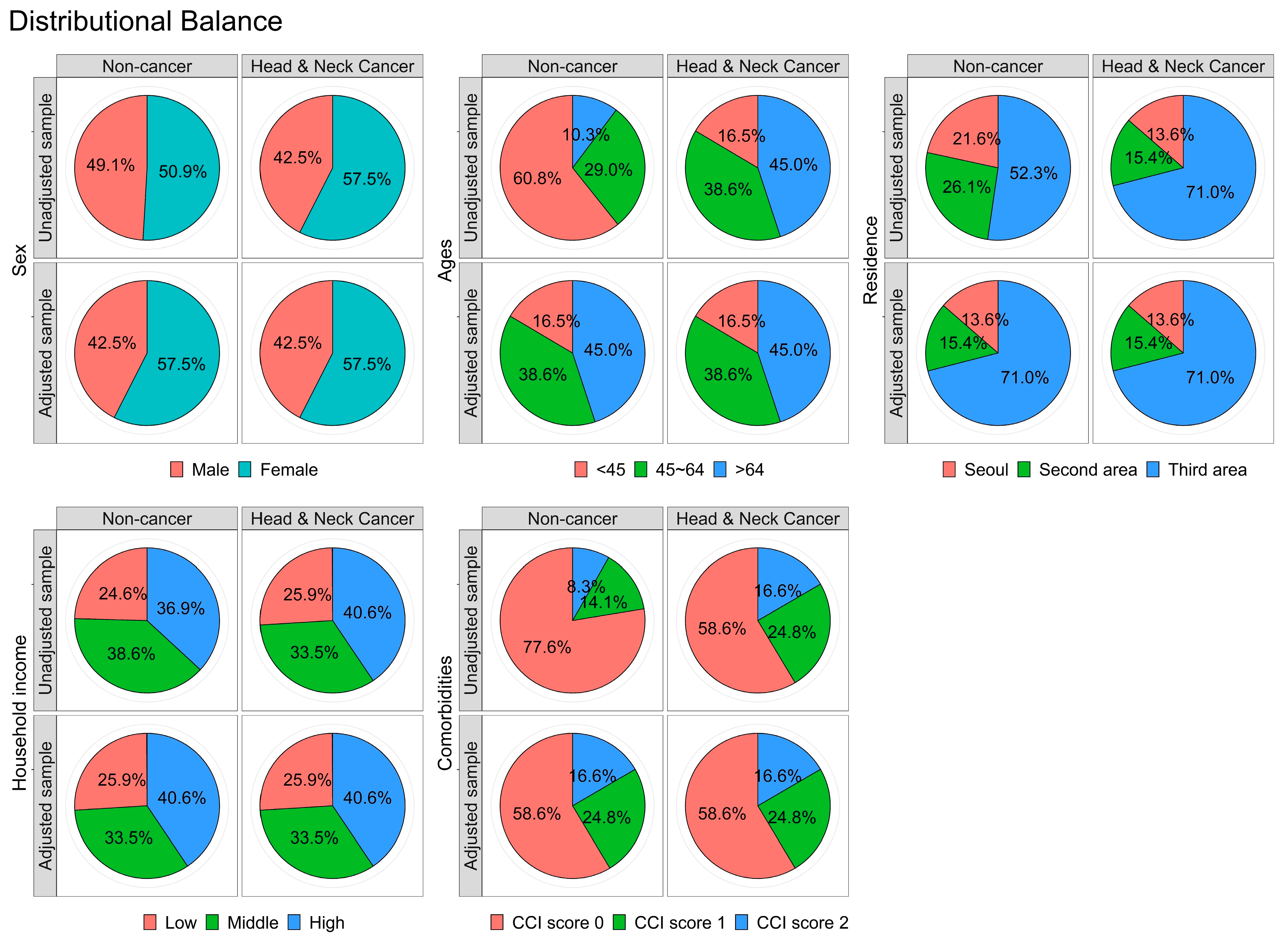
| Variables | Comparison (n = 5248) | Head and Neck Cancer (n = 1312) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 1.000 | ||
| Male | 2228 (42.5%) | 557 (42.5%) | |
| Female | 3020 (57.5%) | 755 (57.5%) | |
| Ages (years) | 1.000 | ||
| <45 | 864 (16.5%) | 216 (16.5%) | |
| 45–64 | 2024 (38.6%) | 506 (38.6%) | |
| >64 | 2360 (45.0%) | 590 (45.0%) | |
| Residence | 1.000 | ||
| Largest metropolitan | 712 (13.6%) | 178 (13.6%) | |
| Other metropolitan | 808 (15.4%) | 202 (15.4%) | |
| Other cities | 3728 (71.0%) | 932 (71.0%) | |
| Household income | 1.000 | ||
| Low (0–30%) | 1360 (25.9%) | 340 (25.9%) | |
| Middle (30–70%) | 1756 (33.5%) | 439 (33.5%) | |
| High (70–100%) | 2132 (40.6%) | 533 (40.6%) | |
| Charlson comorbidity index | 1.000 | ||
| 0 | 3076 (58.6%) | 769 (58.6%) | |
| 1 | 1300 (24.8%) | 325 (24.8%) | |
| ≥2 | 872 (16.6%) | 218 (16.6%) |
| Hazard Ratio | Comparison | Head and Neck Cancer |
|---|---|---|
| Stroke | ||
| Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.43 (1.21–1.68) *** |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.45 (1.23–1.71) *** |
| Hemorrhagic stroke | ||
| Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.44 (0.94–2.20) |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.45 (0.95–2.23) |
| Ischemic stroke | ||
| Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.42 (1.19–1.68) *** |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.44 (1.21–1.71) *** |
| Sex | Male | Female | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison | Head and Neck Cancer | Comparison | Head and Neck Cancer | |
| Stroke | ||||
| Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.49 (1.15–1.92) ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.38 (1.12–1.72) ** |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.52 (1.17–1.97) ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.40 (1.13–1.74) ** |
| Hemorrhagic stroke | ||||
| Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.59 (0.83–3.06) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.34 (0.76–2.35) |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.58 (0.82–3.05) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.34 (0.76–2.36) |
| Ischemic stroke | ||||
| Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.44 (1.09–1.89) * | 1.00 (ref) | 1.40 (1.12–1.75) ** |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.47 (1.11–1.93) ** | 1.00 (ref) | 1.41 (1.13–1.77) ** |
| Variables | N | Case | Person Year | Incidence Rate | Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer type | ||||||
| Comparison | 5248 | 543 | 44,749.9 | 12.13 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.00 (ref) |
| Oral cavity | 949 | 140 | 7034.0 | 19.90 | 1.62 (1.35–1.96) *** | 1.53 (1.27–1.85) *** |
| Salivary gland | 45 | 2 | 338.8 | 5.90 | 0.48 (0.12–1.92) | 0.89 (0.22–3.56) |
| Oropharynx | 51 | 5 | 400.7 | 12.48 | 1.03 (0.43–2.48) | 1.14 (0.47–2.76) |
| Nasopharynx | 59 | 5 | 399.8 | 12.51 | 1.02 (0.42–2.46) | 1.42 (0.59–3.44) |
| Hypopharynx | 30 | 2 | 218.8 | 9.14 | 0.75 (0.19–3.00) | 0.84 (0.21–3.38) |
| Sinonasal tract | 45 | 2 | 356.8 | 5.61 | 0.46 (0.12–1.85) | 0.96 (0.24–3.87) |
| Larynx | 133 | 11 | 890.8 | 12.35 | 1.01 (0.55–1.83) | 1.07 (0.58–1.95) |
| Variables | N | Case | Person Year | Incidence Rate | Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer type | ||||||
| Comparison | 5248 | 87 | 46,713.5 | 1.86 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.00 (ref) |
| Oral cavity | 949 | 26 | 7532.5 | 3.45 | 1.81 (1.17–2.81) ** | 1.76 (1.13–2.74) * |
| Salivary gland | 45 | 0 | 341.4 | - | 0.00 (0–Inf) | 0.00 (0–Inf) |
| Oropharynx | 51 | 1 | 410.2 | 2.44 | 1.29 (0.18–9.26) | 1.36 (0.19–9.77) |
| Nasopharynx | 59 | 1 | 406.4 | 2.46 | 1.29 (0.18–9.26) | 1.65 (0.23–11.87) |
| Hypopharynx | 30 | 0 | 231.5 | - | 0.00 (0–Inf) | 0.00 (0–Inf) |
| Sinonasal tract | 45 | 0 | 358.4 | - | 0.00 (0–Inf) | 0.00 (0–Inf) |
| Larynx | 133 | 0 | 922.6 | - | 0.00 (0-Inf) | 0.00 (0–Inf) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, C.; Yu, H.; Kim, D.-K. The Risk of Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke in Head and Neck Cancer: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 3503. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133503
Kim C, Yu H, Kim D-K. The Risk of Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke in Head and Neck Cancer: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(13):3503. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133503
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Chulho, Hyunjae Yu, and Dong-Kyu Kim. 2023. "The Risk of Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke in Head and Neck Cancer: A Longitudinal Cohort Study" Cancers 15, no. 13: 3503. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133503
APA StyleKim, C., Yu, H., & Kim, D.-K. (2023). The Risk of Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke in Head and Neck Cancer: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. Cancers, 15(13), 3503. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133503






