Progesterone Receptor Expression Level Predicts Prognosis of Estrogen Receptor-Positive/HER2-Negative Young Breast Cancer: A Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
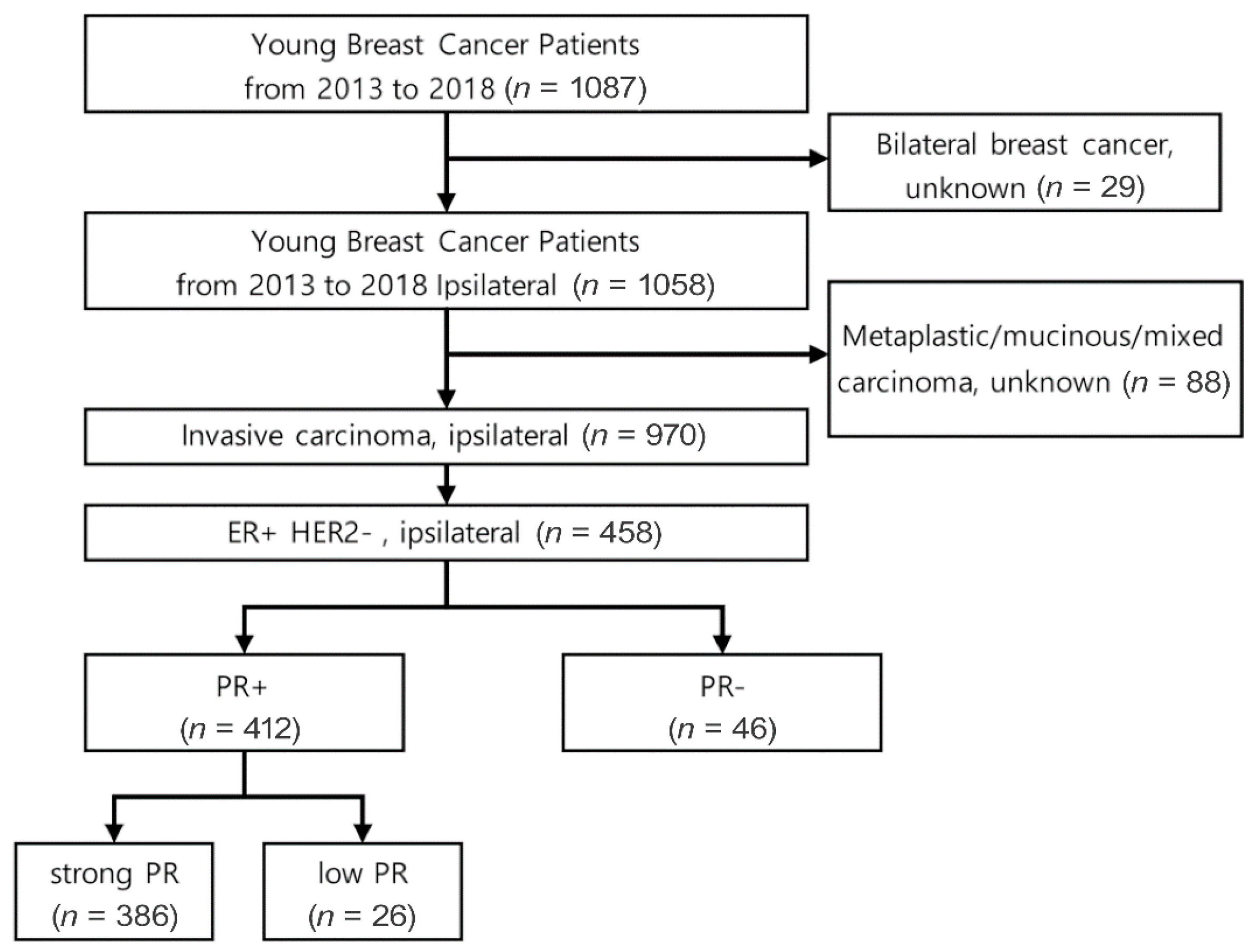
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. PR Stratification/Biologic Factors Definitions
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Clinicopathologic Characteristics
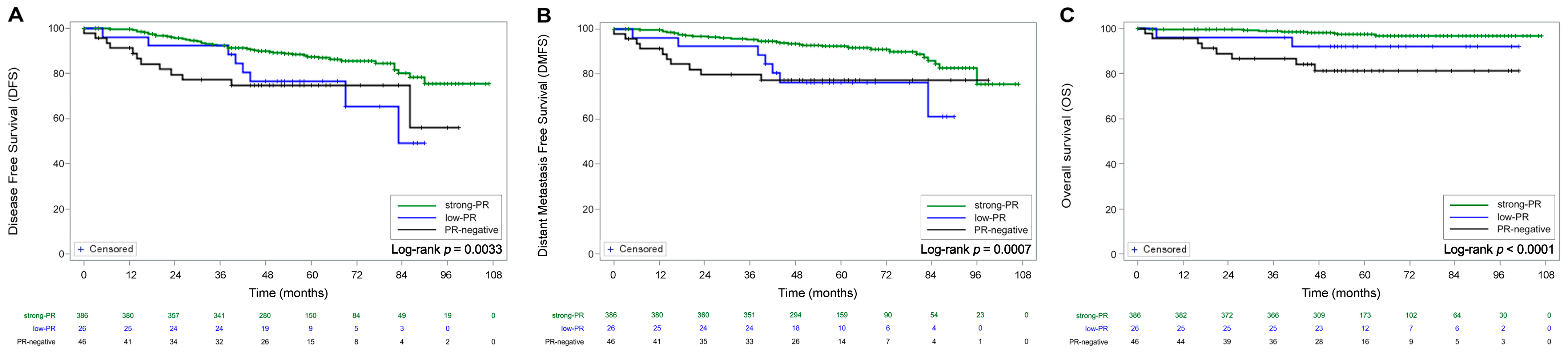
3.2. Oncologic Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bae, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, S.K.; Kil, W.H.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.E.; Nam, S.J. Poor prognosis of single hormone receptor- positive breast cancer: Similar outcome as triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabher, B.J. Breast Cancer: Evaluating Tumor Estrogen Receptor Status with Molecular Imaging to Increase Response to Therapy and Improve Patient Outcomes. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2020, 48, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Wang, J.; Hicks, D.G.; Wang, X.; Schiffhauer, L.; McMahon, L.; Yang, Q.; Shayne, M.; Huston, A.; Skinner, K.A.; et al. A lower Allred score for progesterone receptor is strongly associated with a higher recurrence score of 21-gene assay in breast cancer. Cancer Investig. 2010, 28, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFall, T.; McKnight, B.; Rosati, R.; Kim, S.; Huang, Y.; Viola-Villegas, N.; Ratnam, M. Progesterone receptor A promotes invasiveness and metastasis of luminal breast cancer by suppressing regulation of critical microRNAs by estrogen. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.S.; Mullins, M.; Cheang, M.C.; Leung, S.; Voduc, D.; Vickery, T.; Davies, S.; Fauron, C.; He, X.; Hu, Z.; et al. Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Yang, J. Treatment strategies for hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive (HR+/HER2+) metastatic breast cancer: A review. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 975463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart-Harris, R.; Shadbolt, B.; Palmqvist, C.; Chaudri Ross, H.A. The prognostic significance of single hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer: An analysis of three randomised phase III trials of aromatase inhibitors. Breast 2009, 18, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scabia, V.; Ayyanan, A.; De Martino, F.; Agnoletto, A.; Battista, L.; Laszlo, C.; Treboux, A.; Zaman, K.; Stravodimou, A.; Jallut, D.; et al. Estrogen receptor positive breast cancers have patient specific hormone sensitivities and rely on progesterone receptor. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardou, V.J.; Arpino, G.; Elledge, R.M.; Osborne, C.K.; Clark, G.M. Progesterone receptor status significantly improves outcome prediction over estrogen receptor status alone for adjuvant endocrine therapy in two large breast cancer databases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 1973–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Ingle, J.N.; Gelber, R.D.; Coates, A.S.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.J. Thresholds for therapies: Highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2009. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauphine, C.; Moazzez, A.; Neal, J.C.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Ozao-Choy, J. Single Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancers Have Distinct Characteristics and Survival. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 4687–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, J.S.; Korlimarla, A.; Desai, K.; Alexander, A.; Raghavan, R.; Anupama, C.; Dendukuri, N.; Manjunath, S.; Correa, M.; Raman, N.; et al. A Majority of Low (1–10%) ER Positive Breast Cancers Behave Like Hormone Receptor Negative Tumors. J. Cancer 2014, 5, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard-Fortier, A.; Provencher, L.; Blanchette, C.; Diorio, C. Prognostic and predictive value of low estrogen receptor expression in breast cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2017, 24, e106–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landmann, A.; Farrugia, D.J.; Zhu, L.; Diego, E.J.; Johnson, R.R.; Soran, A.; Dabbs, D.J.; Clark, B.Z.; Puhalla, S.L.; Jankowitz, R.C.; et al. Low Estrogen Receptor (ER)-Positive Breast Cancer and Neoadjuvant Systemic Chemotherapy: Is Response Similar to Typical ER-Positive or ER-Negative Disease? Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 150, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.C.; Park, M.H.; Choi, J.E.; Kang, S.H.; Bae, Y.K. Characteristics and Prognosis of Estrogen Receptor Low-Positive Breast Cancer. J. Breast Cancer 2022, 25, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunnwald, L.K.; Rossing, M.A.; Li, C.I. Hormone receptor status, tumor characteristics, and prognosis: A prospective cohort of breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9, R6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senel, F. The hormone receptor status in breast cancer and the relationship of subtypes with clinicopathological features. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2021, 64, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Yin, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yi, Z.; Li, H.; Li, H.; et al. Clinicopathological Characteristics and Breast Cancer-Specific Survival of Patients With Single Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e1918160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Choi, S.B.; Park, J.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, H.S.; Kim, S.I.; Park, B.W.; Park, S. Level of Combined Estrogen and Progesterone Receptor Expression Determines the Eligibility for Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy in Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.M.; Cameron, D.A.; Arthur, L.M.; Axelrod, D.M.; Renshaw, L.; Thomas, J.S.; Turnbull, A.; Young, O.; Loman, C.A.; Jakubowski, D.; et al. Accurate Estrogen Receptor Quantification in Patients with Negative and Low-Positive Estrogen-Receptor-Expressing Breast Tumors: Sub-Analyses of Data from Two Clinical Studies. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 828–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Wood, W.C.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.J. Strategies for subtypes--dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: Highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhirsch, A. Personalized adjuvant therapies: Lessons from the past: The opening address by the St. Gallen 2013 award recipient. Breast 2013, 22 (Suppl. 2), S3–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, A.S.; Winer, E.P.; Goldhirsch, A.; Gelber, R.D.; Gnant, M.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.J. Tailoring therapies—Improving the management of early breast cancer: St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2015. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, H.J.; Curigliano, G.; Loibl, S.; Dubsky, P.; Gnant, M.; Poortmans, P.; Colleoni, M.; Denkert, C.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.; Regan, M.; et al. Estimating the benefits of therapy for early-stage breast cancer: The St. Gallen International Consensus Guidelines for the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2019. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1541–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.H.; Bae, S.J.; Kim, K.; Chu, C.; Lee, K.A.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, J.; Ahn, S.G. Association between TP53 mutation and high 21-gene recurrence score in estrogen receptor-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.G.; Yoon, C.I.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Park, S.E.; Cha, Y.J.; Cha, C.; Bae, S.J.; Lee, K.A.; Jeong, J. Low PR in ER(+)/HER2(−) breast cancer: High rates of TP53 mutation and high SUV. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, S.; Shak, S.; Tang, G.; Kim, C.; Baker, J.; Cronin, M.; Baehner, F.L.; Walker, M.G.; Watson, D.; Park, T.; et al. A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, I.; Ben-Baruch, N.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Rizel, S.; Goldberg, H.; Yaal-Hahoshen, N.; Klein, B.; Geffen, D.B.; Kaufman, B. Association between standard clinical and pathologic characteristics and the 21-gene recurrence score in breast cancer patients: A population-based study. Cancer 2008, 112, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, M.B.; Dabbs, D.J.; Brufsky, A.M.; Beriwal, S.; Bhargava, R. Histopathologic variables predict Oncotype DX recurrence score. Mod. Pathol. 2008, 21, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erić, I.; Petek Erić, A.; Kristek, J.; Koprivčić, I.; Babić, M. Breast cancer in young women: Pathologic and immunohistochemical features. Acta Clin. Croat. 2018, 57, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadi, Z.; Lianos, G.D.; Ignatiadou, E.; Harissis, H.V.; Mitsis, M. Breast cancer in young women: An overview. Updates Surg. 2017, 69, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.W.; Ho, P. Hormonal receptor determination of 1,052 Chinese breast cancers. J. Surg. Oncol. 2000, 75, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ER+HER2− Characteristics | Strong PR (n = 386, 84.3%) | Low PR (n = 26, 5.7%) | PR-Negative (n = 46, 10.0%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (range) | 37 (20–43) | 35.5 (28–40) | 34.5 (25–40) | 0.0121 |
| Dx | 0.1889 | |||
| IDC | 362 (93.8) | 25 (96.2) | 46 (100) | |
| ILC | 24 (6.2) | 1 (3.8) | 0 (0) | |
| pT | 0.0566 | |||
| pCR | 4 (1.0) | 2 (7.7) | 3 (6.5) | |
| T1 | 210 (54.4) | 12 (46.2) | 26 (56.5) | |
| T2 | 142 (36.8) | 9 (34.6) | 15 (32.6) | |
| T3 | 30 (7.8) | 3 (11.5) | 2 (4.3) | |
| pN | 0.3810 | |||
| N0 | 219 (56.7) | 12 (46.2) | 31 (67.4) | |
| N1 | 113 (29.3) | 8 (30.8) | 11 (23.9) | |
| N2 | 40 (10.4) | 3 (11.5) | 3 (6.5) | |
| N3 | 14 (3.6) | 3 (11.5) | 1 (2.2) | |
| Stage | 0.0270 | |||
| pCR | 4 (1.0) | 2 (7.7) | 3 (6.5) | |
| I | 159 (41.2) | 7 (26.9) | 20 (43.5) | |
| II | 159 (41.2) | 10 (38.5) | 18 (39.1) | |
| III | 64 (16.6) | 7 (26.9) | 5 (10.9) | |
| Nuclear Grade | <0.0001 | |||
| low | 38 (9.8) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (10.9) | |
| intermediate | 298 (77.2) | 15 (57.7) | 12 (26.1) | |
| high | 50 (13.0) | 11 (42.3) | 29 (63.0) | |
| Ki-67 | <0.0001 | |||
| ≤20.0% | 283 (73.3) | 9 (34.6) | 10 (21.7) | |
| >20.0% | 103 (26.7) | 17 (65.4) | 36 (78.3) | |
| LVI | 0.0003 | |||
| yes | 181 (46.9) | 15 (57.7) | 8 (17.4) | |
| no | 205 (53.1) | 11 (42.3) | 38 (82.6) | |
| Multiplicity | 0.0137 | |||
| yes | 131 (33.9) | 7 (26.9) | 6 (13.0) | |
| no | 255 (66.1) | 19 (73.1) | 40 (87.0) | |
| BRCA1 Mutation | 0.0531 | |||
| not detected | 367 (95.1) | 24 (92.3) | 40 (87.0) | |
| equivocal | 17 (4.4) | 1 (3.8) | 5 (10.9) | |
| detected | 2 (0.5) | 1 (3.8) | 1 (2.2) | |
| BRCA2 Mutation | 0.3640 | |||
| not detected | 339 (87.8) | 23 (88.5) | 41 (89.1) | |
| equivocal | 29 (7.5) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (6.5) | |
| detected | 18 (4.7) | 3 (11.5) | 2 (4.3) | |
| Breast Surgery | 0.1609 | |||
| BCS | 216 (56.0) | 13 (50.0) | 32 (69.6) | |
| TM | 170 (44.0) | 13 (50.0) | 14 (30.4) | |
| Axillary Surgery | 0.1706 | |||
| SLNB | 253 (65.5) | 13 (50.0) | 33 (71.7) | |
| ALND | 133 (34.5) | 13 (50.0) | 13 (28.3) | |
| Adjuvant Radiation therapy | 0.2654 | |||
| Yes | 294 (76.2) | 20 (76.9) | 39 (84.8) | |
| No | 90 (23.3) | 6 (23.1) | 6 (13.0) | |
| unknown | 2 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.2) | |
| Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy | <0.0001 | |||
| Yes | 382 (99.0) | 26 (100) | 37 (80.4) | |
| No | 2 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (17.4) | |
| unknown | 2(0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.2) | |
| NAC | <0.0001 | |||
| Yes | 68 (17.6) | 13 (50.0) | 22 (47.8) | |
| No | 318 (82.4) | 13 (50.0) | 24 (52.2) | |
| Adjuvant Chemotherapy | 0.7450 | |||
| Yes | 160 (41.5) | 12 (46.2) | 22 (47.8) | |
| No | 224 (58.0) | 14 (53.8) | 24 (52.2) | |
| unknown | 2 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Chemotherapy | <0.0001 | |||
| Yes | 227 (58.8) | 25 (96.2) | 42 (91.3) | |
| No | 159 (41.2) | 1 (3.8) | 4 (8.7) |
| Hazard Ratio | p Value | Overall p Value | 95% CI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| DFS | univariable | strong PR vs. low PR | 2.321 | 0.0533 | 2.8870 | 0.991 | 5.439 |
| strong PR vs. PR-negative | 2.398 | 0.0127 | 1.170 | 4.918 | |||
| multivariable | strong PR vs. low PR | 1.017 | 1.0000 | 0.9832 | 0.381 | 2.353 | |
| strong PR vs. PR-negative | 0.933 | 1.0000 | 0.343 | 2.193 | |||
| DMFS | univariable | strong PR vs. low PR | 2.961 | 0.0174 | 0.0013 | 1.171 | 7.486 |
| strong PR vs. PR-negative | 2.887 | <0.0001 | 1.297 | 6.430 | |||
| multivariable | strong PR vs. low PR | 1.524 | 0.6480 | 0.4800 | 0.319 | 9.835 | |
| strong PR vs. PR-negative | 1.537 | 0.7465 | 1.818 | 21.479 | |||
| OS | univariable | strong PR vs. low PR | 2.905 | 0.3373 | <0.0001 | 0.512 | 16.49 |
| strong PR vs. PR-negative | 7.709 | <0.0001 | 2.660 | 22.342 | |||
| multivariable | strong PR vs. low PR | 2.270 | 0.5661 | 0.0051 | 0.319 | 9.835 | |
| strong PR vs. PR-negative | 6.257 | 0.0024 | 1.818 | 21.479 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwak, Y.; Jang, S.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, H.; Shin, D.S.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Ahn, J.-S.; Chae, B.J.; Yu, J.; et al. Progesterone Receptor Expression Level Predicts Prognosis of Estrogen Receptor-Positive/HER2-Negative Young Breast Cancer: A Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133435
Kwak Y, Jang SY, Choi JY, Lee H, Shin DS, Park YH, Kim J-Y, Ahn J-S, Chae BJ, Yu J, et al. Progesterone Receptor Expression Level Predicts Prognosis of Estrogen Receptor-Positive/HER2-Negative Young Breast Cancer: A Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(13):3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133435
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwak, Youngji, Sung Yoon Jang, Joon Young Choi, Hyunjun Lee, Dong Seung Shin, Yeon Hee Park, Ji-Yeon Kim, Jin-Seok Ahn, Byung Joo Chae, Jonghan Yu, and et al. 2023. "Progesterone Receptor Expression Level Predicts Prognosis of Estrogen Receptor-Positive/HER2-Negative Young Breast Cancer: A Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study" Cancers 15, no. 13: 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133435
APA StyleKwak, Y., Jang, S. Y., Choi, J. Y., Lee, H., Shin, D. S., Park, Y. H., Kim, J.-Y., Ahn, J.-S., Chae, B. J., Yu, J., Lee, J. E., Kim, S. W., Nam, S. J., & Ryu, J. M. (2023). Progesterone Receptor Expression Level Predicts Prognosis of Estrogen Receptor-Positive/HER2-Negative Young Breast Cancer: A Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study. Cancers, 15(13), 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133435






