Predicting Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Receiving Finite Periods of Antiviral Therapy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Clinical and Virological Variables
2.3. Antiviral Treatment Methods
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics of Treatment-Naïve Patients with CHB Infection Receiving NAs
3.2. Stepwise Selection for HCC after NAs
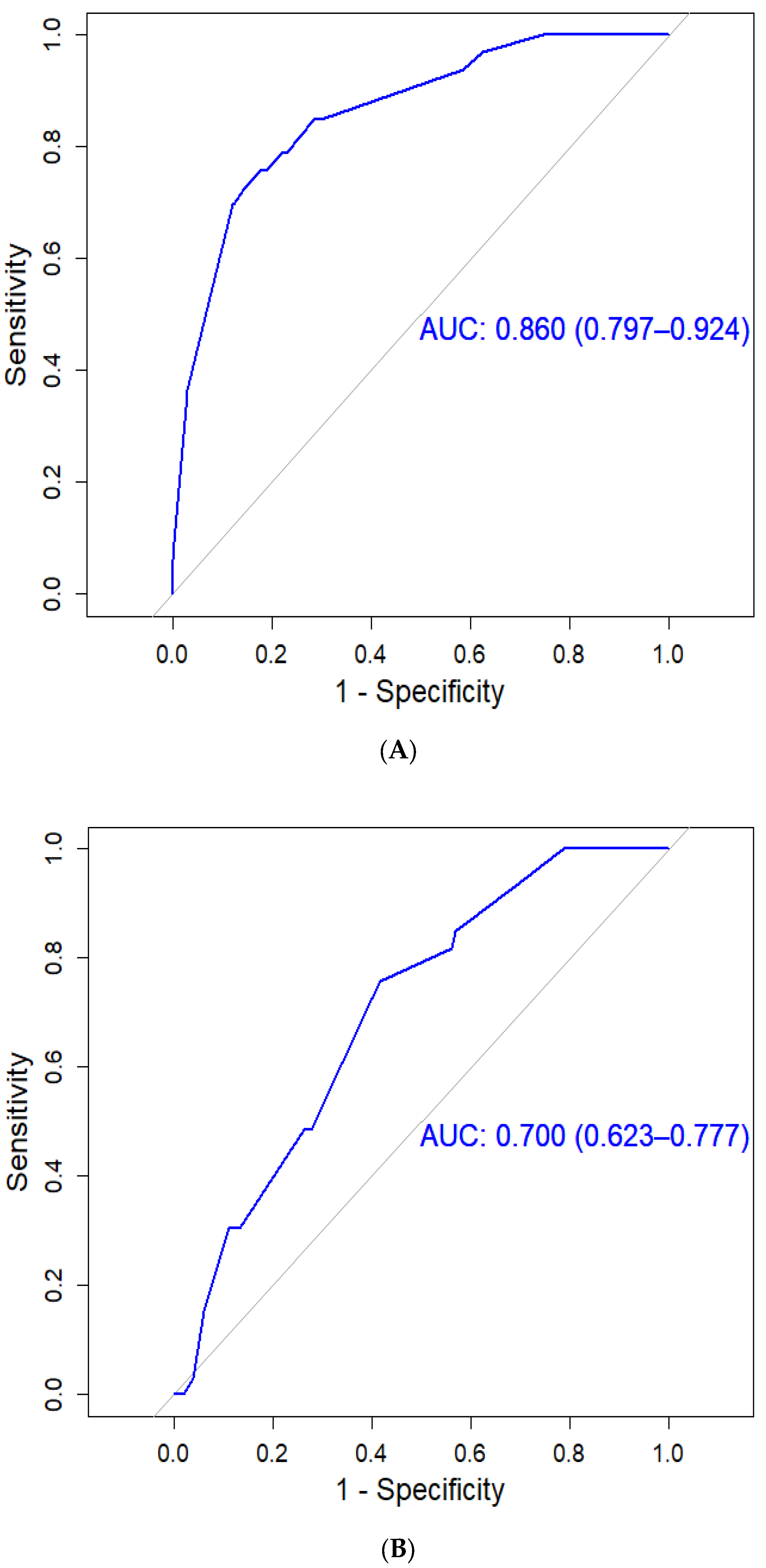
3.3. HCC Assessment Using the CGMH HCC Predictive Scoring System
3.4. HCC Assessment Using the PAGE-B Predictive Scoring System
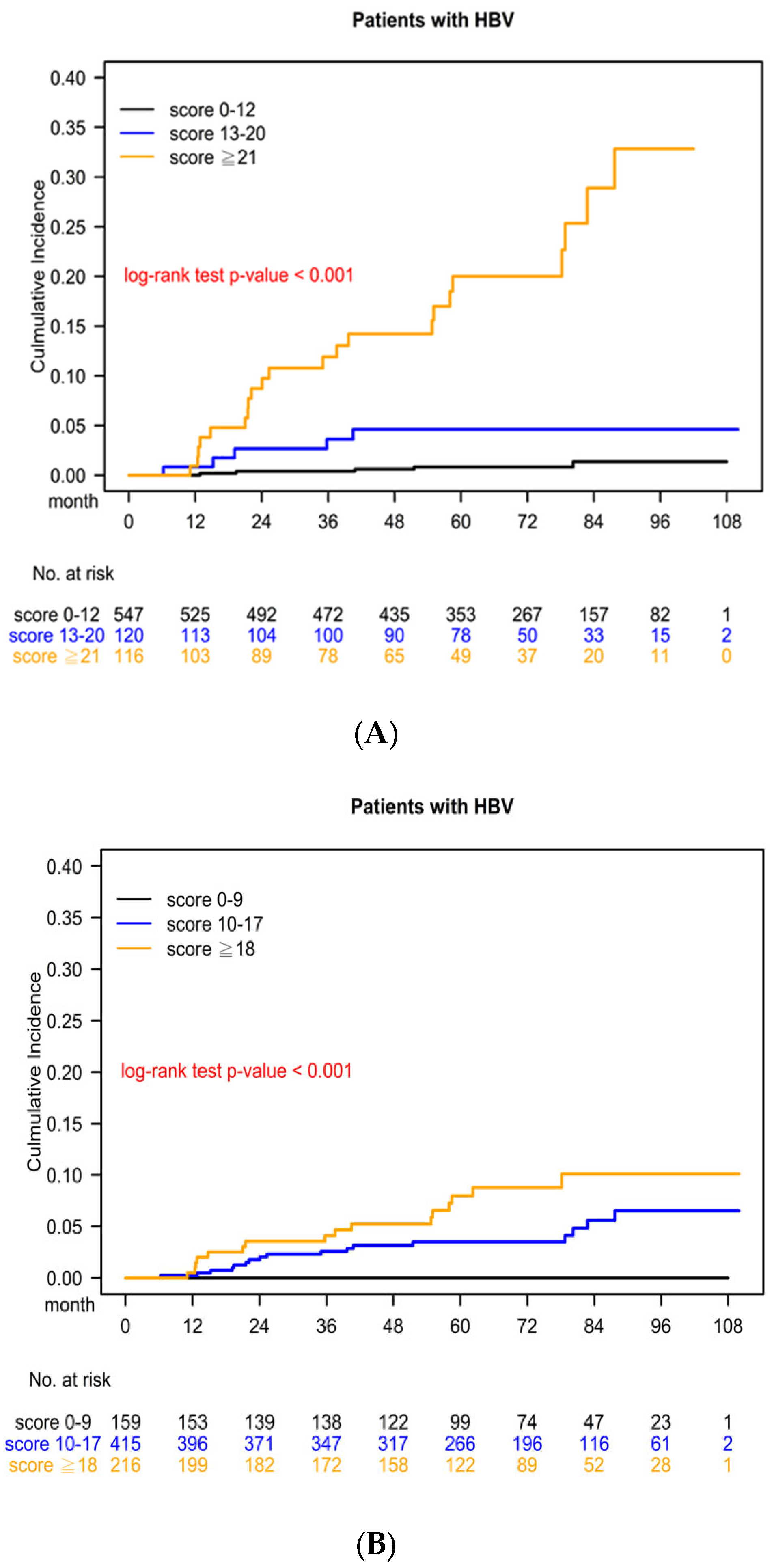
3.5. Kaplan–Meier Survival Curve for Cumulative HCC Risk Determined Using the CGMH HCC Predictive Scoring System
3.6. Kaplan–Meier Survival Curve for Cumulative HCC Risk Determined Using the PAGE-B Predictive Scoring System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Lin, C.L.; Kao, J.H. Perspectives and control of hepatitis B virus infection in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2015, 114, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Promotion Administration Ministry of Health and Welfare. Taiwan Cancer Registry Annual Report; Ministry of Health and Welfare: Taipei City, Taiwan, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffetti, E.; Fattovich, G.; Donato, F. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in untreated subjects with chronic hepatitis B: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, S.Y.; Jackson, P.E.; Wang, J.B.; Lu, P.X.; Munoz, A.; Qian, G.S.; Kensler, T.W.; Groopman, J.D. Specific mutations of hepatitis B virus in plasma predict liver cancer development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3575–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Han, Q.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J. The Mechanisms of HBV-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatocell Carcinoma 2021, 8, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varbobitis, I.; Papatheodoridis, G.V. The assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma risk in patients with chronic hepatitis B under antiviral therapy. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2016, 22, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levrero, M.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Mechanisms of HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S84–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.S.; Zhou, G.X. Significance of viral status on occurrence of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5999–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H.; Lu, G.Y.; Qiu, L.X.; Zhong, G.H.; Huang, Y.; Yao, X.M.; Liu, X.H.; Huang, S.J.; Wu, T.; Yuan, Q.; et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in antiviral treatment-naive chronic hepatitis B patients treated with entecavir or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: A network meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWitt, J.M.; Kessler, W.R.; Wo, J.M.; Stainko, S.; Perkins, A.; Dickason, D.; Al-Haddad, M.A.; Siwiec, R. Symptom Association for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease by pH Monitoring After Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 1316–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Yip, T.C.; Ho, H.J.; Wong, V.W.; Huang, Y.T.; El-Serag, H.B.; Lee, T.Y.; Wu, M.S.; Lin, J.T.; Wong, G.L.; et al. Development of a scoring system to predict hepatocellular carcinoma in Asians on antivirals for chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.I.; Yeh, M.L.; Wong, G.L.; Peng, C.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Trinh, H.N.; Cheung, K.S.; Xie, Q.; Su, T.H.; Kozuka, R.; et al. Real-World Effectiveness From the Asia Pacific Rim Liver Consortium for HBV Risk Score for the Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Treated With Oral Antiviral Therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrault, N.A.; Bzowej, N.H.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Murad, M.H.; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2016, 63, 261–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association For The Study of the Liver; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 908–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, M.; Cheng, A.L.; Kokudo, N.; Kudo, M.; Lee, J.M.; Jia, J.; Tateishi, R.; Han, K.H.; Chawla, Y.K.; Shiina, S.; et al. Asia-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A 2017 update. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 317–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialecki, E.S.; Di Bisceglie, A.M. Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB 2005, 7, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.L.; Lin, Y.L.; Liang, K.H.; Chen, L.W.; Chien, C.H.; Hu, C.C.; Huang, T.S.; Shyu, Y.C.; Yeh, C.T.; Chien, R.N. Prognosis Comparison Between Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Receiving a Finite Course of Tenofovir and Entecavir Treatment: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Taiwan. Clin. Ther. 2022, 44, 403–417.e406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batts, K.P.; Ludwig, J. Chronic hepatitis. An update on terminology and reporting. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1995, 19, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Chen, T.-M.; Kao, Y.-W.; Lin, K.-C.; Yuan, K.S.-P.; Wu, A.T.H.; Shia, B.-C.; Wu, S.-Y. Predicting 90-Day Mortality in Locoregionally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma after Curative Surgery. Cancers 2018, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodoridis, G.; Dalekos, G.; Sypsa, V.; Yurdaydin, C.; Buti, M.; Goulis, J.; Calleja, J.L.; Chi, H.; Manolakopoulos, S.; Mangia, G.; et al. PAGE-B predicts the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in Caucasians with chronic hepatitis B on 5-year antiviral therapy. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, M.F.; Tanaka, Y.; Fong, D.Y.; Fung, J.; Wong, D.K.; Yuen, J.C.; But, D.Y.; Chan, A.O.; Wong, B.C.; Mizokami, M.; et al. Independent risk factors and predictive score for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.; Chan, S.L.; Mo, F.; Chan, T.C.; Loong, H.H.; Wong, G.L.; Lui, Y.Y.; Chan, A.T.; Sung, J.J.; Yeo, W.; et al. Clinical scoring system to predict hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B carriers. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1660–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.I.; Yuen, M.F.; Chan, H.L.; Han, K.H.; Chen, P.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Chen, C.J.; Wong, V.W.; Seto, W.K.; et al. Risk estimation for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B (REACH-B): Development and validation of a predictive score. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.C.; Yeh, C.C.; Chen, R.Y.; Su, C.T.; Wang, W.C.; Bai, C.H.; Chan, C.F.; Su, F.H. Seroprevalence of hepatitis B virus in Taiwan 30 years after the commencement of the national vaccination program. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.C.; Su, T.H.; Tseng, T.C.; Chen, C.L.; Hsu, S.J.; Liao, S.H.; Hong, C.M.; Liu, C.H.; Lan, T.Y.; Yang, H.C.; et al. Distinct effects of hepatic steatosis and metabolic dysfunction on the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol. Int. 2023. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Tran, A.; Yeh, M.L.; Yasuda, S.; Tsai, P.C.; Huang, C.F.; Dai, C.Y.; Ogawa, E.; Ishigami, M.; Ito, T.; et al. Antiviral therapy substantially reduces hepatocellular carcinoma risk in chronic Hepatitis B patients in the indeterminate phase. Hepatology 2023. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Lampertico, P.; Manolakopoulos, S.; Lok, A. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients receiving nucleos(t)ide therapy: A systematic review. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunaka, T.; Ikeda, F.; Wada, N.; Morimoto, Y.; Fujioka, S.; Toshimori, J.; Kobashi, H.; Kariyama, K.; Morimoto, Y.; Takayama, H.; et al. Entecavir Reduces Hepatocarcinogenesis in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Acta Med. Okayama 2016, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.Y.; Paik, Y.H.; Sohn, W.; Cho, H.C.; Gwak, G.Y.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Koh, K.C.; Paik, S.W.; Yoo, B.C. Patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with oral antiviral therapy retain a higher risk for HCC compared with patients with inactive stage disease. Gut 2014, 63, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.S.; Park, J.Y.; Chon, Y.E.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, W.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, D.Y.; Han, K.H.; Ahn, S.H. Clinical outcomes and predictors for relapse after cessation of oral antiviral treatment in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yao, Z.; Hu, K.; Zhong, Y.; Li, M.; Xiong, Z.; Deng, M. Hepatitis B Virus Core Promoter A1762T/G1764A (TA)/T1753A/T1768A Mutations Contribute to Hepatocarcinogenesis by Deregulating Skp2 and P53. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, Y.F.; Sung, J.J.; Chow, W.C.; Farrell, G.; Lee, C.Z.; Yuen, H.; Tanwandee, T.; Tao, Q.M.; Shue, K.; Keene, O.N.; et al. Lamivudine for patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced liver disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Lau, G.K.; Abbas, Z.; Chan, H.L.; Chen, C.J.; Chen, D.S.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, P.J.; Chien, R.N.; et al. Asian-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B: A 2015 update. Hepatol. Int. 2016, 10, 1–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.L.; Chan, H.L.; Chan, H.Y.; Tse, P.C.; Tse, Y.K.; Mak, C.W.; Lee, S.K.; Ip, Z.M.; Lam, A.T.; Iu, H.W.; et al. Accuracy of risk scores for patients with chronic hepatitis B receiving entecavir treatment. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Dalekos, G.N.; Yurdaydin, C.; Buti, M.; Goulis, J.; Arends, P.; Sypsa, V.; Manolakopoulos, S.; Mangia, G.; Gatselis, N.; et al. Incidence and predictors of hepatocellular carcinoma in Caucasian chronic hepatitis B patients receiving entecavir or tenofovir. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, P.; Sonneveld, M.J.; Zoutendijk, R.; Carey, I.; Brown, A.; Fasano, M.; Mutimer, D.; Deterding, K.; Reijnders, J.G.; Oo, Y.; et al. Entecavir treatment does not eliminate the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B: Limited role for risk scores in Caucasians. Gut 2015, 64, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Patients with CHB Receiving NAs without HCC | Patients with CHB Receiving NAs with HCC | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 757 | N = 33 | ||||
| N | % | N | % | ||
| Age | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 48.40 ± 12.84 | 53.46 ± 8.34 | 0.025 | ||
| Median (IQR) | 48.94 (39.38, 57.03) | 53.61 (45.79, 58.36) | 0.015 | ||
| Gender | 0.028 | ||||
| Female | 226 | 29.9% | 4 | 12.1% | |
| Male | 531 | 70.2% | 29 | 87.9% | |
| Laboratory data | |||||
| Alpha-fetoprotein (ng/mL) | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 24.15 ± 83.76 | 11.14 ± 18.26 | 0.373 | ||
| Median (IQR) | 4.30 (3.00, 9.20) | 4.00 (3.00, 7.00) | 0.966 | ||
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 175.51 ± 306.87 | 74.36 ± 68.01 | 0.059 | ||
| Median (IQR) | 72.00 (44.00, 148.00) | 49.00 (39.00, 80.00) | 0.016 | ||
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 245.98 ± 393.09 | 81.45 ± 76.87 | 0.017 | ||
| Median (IQR) | 115.00 (60.00, 232.00) | 50.00 (37.00, 103.00) | <.0001 | ||
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 1.50 ± 2.98 | 1.22 ± 2.12 | 0.593 | ||
| Median (IQR) | 0.80 (0.50, 1.10) | 0.70 (0.50, 1.20) | 0.603 | ||
| International normalized ratio | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 1.18 ± 0.81 | 1.14 ± 0.15 | 0.761 | ||
| Median (IQR) | 1.00 (1.00, 1.10) | 1.10 (1.00, 1.20) | 0.059 | ||
| Platelet (103/μL) | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 178.16 ± 72.86 | 141.64 ± 50.73 | 0.005 | ||
| Median (IQR) | 174.00 (140.00, 210.0) | 144.00 (117.00, 165.0) | 0.001 | ||
| HBV DNA titer | |||||
| HBV DNA (copies/mL) | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 917.82 ± 5672.48 | 166.67 ± 799.77 | 0.448 | ||
| Median (IQR) | 25.30 (1.51, 640.20) | 4.09 (1.24, 23.63) | 0.018 | ||
| logHBV DNA | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 7.30 ± 1.61 | 6.77 ± 1.00 | 0.058 | ||
| Median (IQR) | 7.40 (6.18, 8.81) | 6.61 (6.09, 7.37) | 0.018 | ||
| Relapse after NA withdraw | 0.002 | ||||
| No | 233 | 30.8% | 2 | 6.1% | |
| Yes | 524 | 69.2% | 31 | 93.9% | |
| Courses of NA treatment | 0.655 | ||||
| 1 | 575 | 76.0% | 27 | 81.8% | |
| 2 | 149 | 19.7% | 6 | 18.2% | |
| 3 | 27 | 3.6% | 0 | 0.0% | |
| 4 | 6 | 0.8% | 0 | 0.0% | |
| Antiviral treatment strategies | |||||
| Peginterferon in combination with entecavir | 0.240 | ||||
| No | 722 | 95.4% | 30 | 90.9% | |
| Yes | 35 | 4.6% | 3 | 9.1% | |
| Entecavir monotherapy followed by NA switching or addition | 0.065 | ||||
| No | 353 | 46.6% | 10 | 30.3% | |
| Yes | 404 | 53.4% | 23 | 69.7% | |
| Entecavir monotherapy | 0.018 | ||||
| No | 318 | 42.0% | 7 | 21.2% | |
| Yes | 439 | 58.0% | 26 | 78.8% | |
| Tenofovir monotherapy switching to or addition of other NAs | 0.856 | ||||
| No | 657 | 86.8% | 29 | 87.9% | |
| Yes | 100 | 13.2% | 4 | 12.1% | |
| Initial lamivudine or telbivudine therapy | 0.042 | ||||
| No | 602 | 79.5% | 31 | 93.9% | |
| Yes | 155 | 20.5% | 2 | 6.1% | |
| Peginterferon monotherapy | 0.275 | ||||
| No | 694 | 91.7% | 32 | 97.0% | |
| Yes | 63 | 8.3% | 1 | 3.0% | |
| HBeAg | 0.418 | ||||
| Negative | 499 | 65.9% | 24 | 72.7% | |
| Positive | 258 | 34.1% | 9 | 27.3% | |
| Anti-HBe | 0.044 | ||||
| Negative | 240 | 31.7% | 5 | 15.2% | |
| Positive | 517 | 68.3% | 28 | 84.9% | |
| Liver Cirrhosis | <.0001 | ||||
| No | 591 | 78.1% | 7 | 21.2% | |
| Yes | 166 | 21.9% | 26 | 78.8% | |
| HBV Genotype | |||||
| Genotype B | 0.004 | ||||
| No | 177 | 23.4% | 15 | 45.5% | |
| Yes | 580 | 76.6% | 18 | 54.6% | |
| Genotype C | 0.008 | ||||
| No | 586 | 77.4% | 19 | 57.6% | |
| Yes | 171 | 22.6% | 14 | 42.4% | |
| HBV viral point mutation | |||||
| G1719T | 0.034 | ||||
| No | 712 | 94.1% | 28 | 84.9% | |
| Yes | 45 | 5.9% | 5 | 15.2% | |
| G172A/C | 0.506 | ||||
| No | 747 | 98.7% | 33 | 100.0% | |
| Yes | 10 | 1.3% | 0 | 0.0% | |
| C1730G | 0.005 | ||||
| No | 575 | 76.0% | 18 | 54.6% | |
| Yes | 182 | 24.0% | 15 | 45.5% | |
| A1752G | 0.519 | ||||
| No | 486 | 64.2% | 23 | 69.7% | |
| Yes | 271 | 35.8% | 10 | 30.3% | |
| T1753C/A | 0.713 | ||||
| No | 659 | 87.1% | 28 | 84.9% | |
| Yes | 98 | 13.0% | 5 | 15.2% | |
| A1762T | 0.003 | ||||
| No | 428 | 56.5% | 10 | 30.3% | |
| Yes | 329 | 43.5% | 23 | 69.7% | |
| G1764A | 0.001 | ||||
| No | 413 | 54.6% | 8 | 24.2% | |
| Yes | 344 | 45.4% | 25 | 75.8% | |
| C1766T | 0.038 | ||||
| No | 711 | 93.9% | 28 | 84.9% | |
| Yes | 46 | 6.1% | 5 | 15.2% | |
| T1768A | 0.022 | ||||
| No | 715 | 94.5% | 28 | 84.9% | |
| Yes | 42 | 5.6% | 5 | 15.2% | |
| C1799G | 0.012 | ||||
| No | 176 | 23.3% | 14 | 42.4% | |
| Yes | 581 | 76.8% | 19 | 57.6% | |
| G1896A | 0.829 | ||||
| No | 243 | 32.1% | 10 | 30.3% | |
| Yes | 514 | 67.9% | 23 | 69.7% | |
| G1899A | 0.574 | ||||
| No | 604 | 79.8% | 25 | 75.8% | |
| Yes | 153 | 20.2% | 8 | 24.2% | |
| Factor | aHR * | 95% CI | p Value | Assigned Points | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype C | 2.23 | 1.09 | 4.55 | 0.029 | 2 |
| Relapse after NA withdraw | 6.96 | 1.64 | 29.62 | 0.009 | 7 |
| Male | 4.19 | 1.43 | 12.33 | 0.009 | 4 |
| Liver Cirrhosis | 11.14 | 4.79 | 25.92 | <0.0001 | 11 |
| T1768A | 3.21 | 1.19 | 8.69 | 0.022 | 3 |
| CGMH Predictive Scoring System | Number of Patients without HCC | Number of Patients with HCC | HCC Incidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 36 | 0 | 0.00% |
| 2 | 13 | 0 | 0.00% |
| 3 | 5 | 0 | 0.00% |
| 4 | 104 | 0 | 0.00% |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 0.00% |
| 6 | 32 | 0 | 0.00% |
| 7 | 93 | 1 | 1.06% |
| 9 | 29 | 1 | 3.33% |
| 11 | 227 | 3 | 1.30% |
| 12 | 7 | 0 | 0.00% |
| 13 | 39 | 2 | 4.88% |
| 14 | 4 | 0 | 0.00% |
| 15 | 19 | 1 | 5.00% |
| 16 | 8 | 0 | 0.00% |
| 17 | 7 | 0 | 0.00% |
| 18 | 23 | 1 | 4.17% |
| 20 | 16 | 1 | 5.88% |
| 21 | 3 | 0 | 0.00% |
| 22 | 70 | 12 | 14.63% |
| 23 | 2 | 1 | 33.33% |
| 24 | 16 | 7 | 30.43% |
| 25 | 2 | 1 | 33.33% |
| 27 | 1 | 2 | 66.67% |
| Total | 757 | 33 | 4.17% |
| CGMH Predictive Scoring | Group | HCC Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Score | No HCC, N (%) | HCC, N (%) | |
| 0–12 | Low risk | 547 (99.09%) | 5 (0.91%) |
| 13–20 | Moderate risk | 116 (95.87%) | 5 (4.13%) |
| ≥21 | High risk | 94 (80.34%) | 23 (19.66%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-L.; Wu, S.-Y.; Lai, M.-W.; Hsu, C.-W.; Chen, W.-M.; Jao, A.-T.; Chien, C.-H.; Hu, C.-C.; Chien, R.-N.; Yeh, C.-T. Predicting Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Receiving Finite Periods of Antiviral Therapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 3343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133343
Lin C-L, Wu S-Y, Lai M-W, Hsu C-W, Chen W-M, Jao A-T, Chien C-H, Hu C-C, Chien R-N, Yeh C-T. Predicting Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Receiving Finite Periods of Antiviral Therapy. Cancers. 2023; 15(13):3343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133343
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chih-Lang, Szu-Yuan Wu, Ming-Wei Lai, Chao-Wei Hsu, Wan-Ming Chen, An-Tzu Jao, Cheng-Hung Chien, Ching-Chih Hu, Rong-Nan Chien, and Chau-Ting Yeh. 2023. "Predicting Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Receiving Finite Periods of Antiviral Therapy" Cancers 15, no. 13: 3343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133343
APA StyleLin, C.-L., Wu, S.-Y., Lai, M.-W., Hsu, C.-W., Chen, W.-M., Jao, A.-T., Chien, C.-H., Hu, C.-C., Chien, R.-N., & Yeh, C.-T. (2023). Predicting Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Receiving Finite Periods of Antiviral Therapy. Cancers, 15(13), 3343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133343







