Framework for Implementing Individualised Dosing of Anti-Cancer Drugs in Routine Care: Overcoming the Logistical Challenges
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
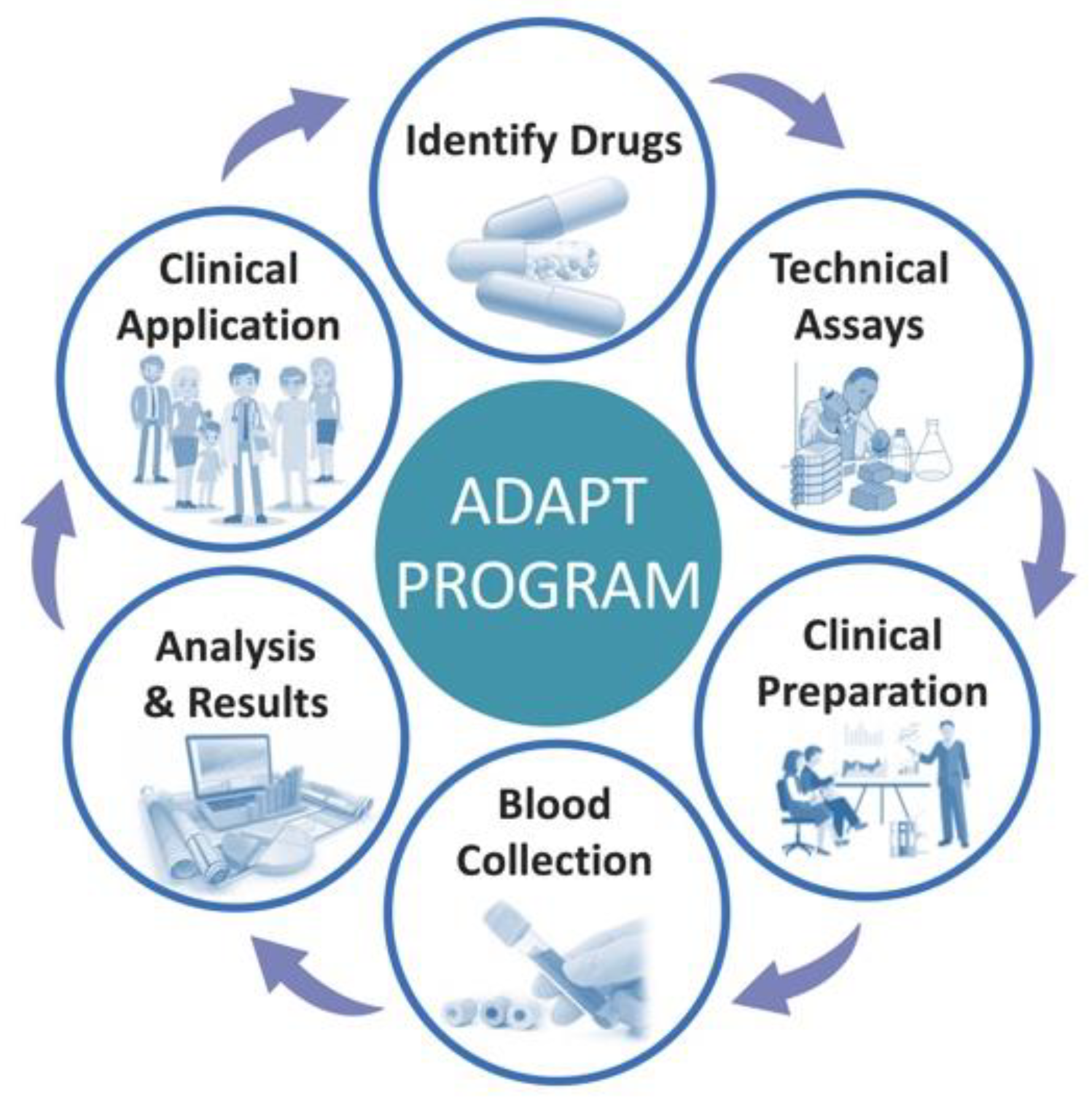
2. General Framework and Six-Step Process for Establishing Individualised Dosing Programs
2.1. Step 1: Evaluate the Evidence and Identify the Cancer Drugs
2.2. Step 2: Establishment of Analytical Equipment for Drug Assays for Clinical Purpose
2.3. Step 3: Clinical Preparation and Education
2.4. Step 4: Blood Collection, Sample Preparation and Analyses
2.5. Step 5: Interpret and Release Results with Recommendations
2.6. Step 6: Clinical Application
3. Continuous Evaluation: Identification of Facilitators and Barriers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Wit, D.; Guchelaar, H.J.; den Hartigh, J.; Gelderblom, H.; van Erp, N.P. Individualized dosing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Are we there yet? Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumpen, H.J.; Samer, C.F.; Mathijssen, R.H.; Schellens, J.H.; Gurney, H. Moving towards dose individualization of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2011, 37, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Schoell, A.; Groenland, S.L.; Scherf-Clavel, O.; van Dyk, M.; Huisinga, W.; Michelet, R.; Jaehde, U.; Steeghs, N.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Kloft, C. Therapeutic drug monitoring of oral targeted antineoplastic drugs. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 77, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, S.; Lopez-Cortes, A.; Indacochea, A.; Garcia-Cardenas, J.M.; Zambrano, A.K.; Cabrera-Andrade, A.; Guevara-Ramirez, P.; Gonzalez, D.A.; Leone, P.E.; Paz, Y.M.C. Analysis of Racial/Ethnic Representation in Select Basic and Applied Cancer Research Studies. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerdijk, K.; Desar, I.M.E.; Steeghs, N.; van der Graaf, W.T.A.; van Erp, N.P.; Dutch, P.; Oncology, G. Imatinib, sunitinib and pazopanib: From flat-fixed dosing towards a pharmacokinetically guided personalized dose. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankheet, N.A.; Knapen, L.M.; Schellens, J.H.; Beijnen, J.H.; Steeghs, N.; Huitema, A.D. Plasma concentrations of tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib, erlotinib, and sunitinib in routine clinical outpatient cancer care. Ther. Drug Monit. 2014, 36, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Steeghs, N.; Nijenhuis, C.M.; Schellens, J.H.; Beijnen, J.H.; Huitema, A.D. Practical guidelines for therapeutic drug monitoring of anticancer tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Focus on the pharmacokinetic targets. Clin. Pharm. 2014, 53, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, R.J.; Park, C.C.; Powell, J.R.; Patterson, J.H.; Weiner, D.; Watkins, P.B.; Gonzalez, D. Precision Dosing Priority Criteria: Drug, Disease, and Patient Population Variables. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Project Optimus: Reforming the Dose Optimization and Dose Selection Paradigm in Oncology. 2022. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/oncology-center-excellence/project-optimus (accessed on 22 October 2022).
- Groenland, S.L.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; Beijnen, J.H.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Steeghs, N. Individualized dosing of oral targeted therapies in oncology is crucial in the era of precision medicine. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 75, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, R.B.; Yu, H.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H.; Steeghs, N.; Huitema, A.D.R. Practical Recommendations for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Kinase Inhibitors in Oncology. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenland, S.L.; van Eerden, R.A.G.; Verheijen, R.B.; Koolen, S.L.W.; Moes, D.; Desar, I.M.E.; Reyners, A.K.L.; Gelderblom, H.J.; van Erp, N.P.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; et al. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Oral Anticancer Drugs: The Dutch Pharmacology Oncology Group-Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Protocol for a Prospective Study. Ther. Drug Monit. 2019, 41, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaud, A.; Urva, S.R.; Grosch, K.; Cheung, W.K.; Anak, O.; Sellami, D.B. Relationship between everolimus exposure and safety and efficacy: Meta-analysis of clinical trials in oncology. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, R.B.; Atrafi, F.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; Steeghs, N. Pharmacokinetic Optimization of Everolimus Dosing in Oncology: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Clin. Pharm. 2018, 57, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, D.A.; Care, M.M.; Holland, K.; Agricola, K.; Tudor, C.; Mangeshkar, P.; Wilson, K.A.; Byars, A.; Sahmoud, T.; Franz, D.N. Everolimus for subependymal giant-cell astrocytomas in tuberous sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1801–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shipkova, M.; Hesselink, D.A.; Holt, D.W.; Billaud, E.M.; van Gelder, T.; Kunicki, P.K.; Brunet, M.; Budde, K.; Barten, M.J.; De Simone, P.; et al. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Everolimus: A Consensus Report. Ther. Drug Monit. 2016, 38, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetri, G.D.; Wang, Y.; Wehrle, E.; Racine, A.; Nikolova, Z.; Blanke, C.D.; Joensuu, H.; von Mehren, M. Imatinib plasma levels are correlated with clinical benefit in patients with unresectable/metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3141–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, R.A.; Druker, B.J.; Guilhot, F.; O’Brien, S.G.; Riviere, G.J.; Krahnke, T.; Gathmann, I.; Wang, Y.; Group, I.S. Imatinib pharmacokinetics and its correlation with response and safety in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: A subanalysis of the IRIS study. Blood 2008, 111, 4022–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilhot, F.; Hughes, T.P.; Cortes, J.; Druker, B.J.; Baccarani, M.; Gathmann, I.; Hayes, M.; Granvil, C.; Wang, Y. Plasma exposure of imatinib and its correlation with clinical response in the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Optimization and Selectivity Trial. Haematologica 2012, 97, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, S.; Titier, K.; Etienne, G.; Teilhet, E.; Ducint, D.; Bernard, M.A.; Lassalle, R.; Marit, G.; Reiffers, J.; Begaud, B.; et al. Trough imatinib plasma levels are associated with both cytogenetic and molecular responses to standard-dose imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2007, 109, 3496–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankheet, N.A.G.; Desar, I.M.E.; Mulder, S.F.; Burger, D.M.; Kweekel, D.M.; van Herpen, C.M.L.; van der Graaf, W.T.A.; van Erp, N.P. Optimizing the dose in cancer patients treated with imatinib, sunitinib and pazopanib. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 2195–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotta, V.; Widmer, N.; Decosterd, L.A.; Chalandon, Y.; Heim, D.; Gregor, M.; Benz, R.; Leoncini-Franscini, L.; Baerlocher, G.M.; Duchosal, M.A.; et al. Clinical usefulness of therapeutic concentration monitoring for imatinib dosage individualization: Results from a randomized controlled trial. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 74, 1307–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchet, S.; Poulette, S.; Titier, K.; Moore, N.; Lassalle, R.; Abouelfath, A.; Italiano, A.; Chevreau, C.; Bompas, E.; Collard, O.; et al. Relationship between imatinib trough concentration and outcomes in the treatment of advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours in a real-life setting. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 57, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houk, B.E.; Bello, C.L.; Poland, B.; Rosen, L.S.; Demetri, G.D.; Motzer, R.J. Relationship between exposure to sunitinib and efficacy and tolerability endpoints in patients with cancer: Results of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic meta-analysis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 66, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankheet, N.A.; Kloth, J.S.; Gadellaa-van Hooijdonk, C.G.; Cirkel, G.A.; Mathijssen, R.H.; Lolkema, M.P.; Schellens, J.H.; Voest, E.E.; Sleijfer, S.; de Jonge, M.J.; et al. Pharmacokinetically guided sunitinib dosing: A feasibility study in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttle, A.B.; Ball, H.A.; Molimard, M.; Hutson, T.E.; Carpenter, C.; Rajagopalan, D.; Lin, Y.; Swann, S.; Amado, R.; Pandite, L. Relationships between pazopanib exposure and clinical safety and efficacy in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, C.N.; Donskov, F.; Haas, N.B.; Doehn, C.; Russo, P.; Elmeliegy, M.; Baneyx, G.; Banerjee, H.; Aimone, P.; Motzer, R.J. Pazopanib Exposure Relationship with Clinical Efficacy and Safety in the Adjuvant Treatment of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3005–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, R.B.; Swart, L.E.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Steeghs, N. Exposure-survival analyses of pazopanib in renal cell carcinoma and soft tissue sarcoma patients: Opportunities for dose optimization. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, R.B.; Bins, S.; Mathijssen, R.H.; Lolkema, M.P.; van Doorn, L.; Schellens, J.H.; Beijnen, J.H.; Langenberg, M.H.; Huitema, A.D.; Steeghs, N.; et al. Individualized Pazopanib Dosing: A Prospective Feasibility Study in Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5738–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenland, S.L.; van Eerden, R.A.G.; Verheijen, R.B.; de Vries, N.; Thijssen, B.; Rosing, H.; Beijnen, J.H.; Koolen, S.L.W.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; Huitema, A.D.R.; et al. Cost-Neutral Optimization of Pazopanib Exposure by Splitting Intake Moments: A Prospective Pharmacokinetic Study in Cancer Patients. Clin. Pharm. 2020, 59, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubberman, F.J.; Gelderblom, H.; Hamberg, P.; Vervenne, W.L.; Mulder, S.F.; Jansman, F.G.; Colbers, A.; van der Graaf, W.T.; Burger, D.M.; Luelmo, S. The effect of using pazopanib with food vs. fasted on pharmacokinetics, patient safety, and preference (DIET study). Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 106, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, E.I.; Chiorean, E.G.; Sweeney, C.J.; Hodge, J.P.; Lager, J.J.; Forman, K.; Malburg, L.; Arumugham, T.; Dar, M.M.; Suttle, A.B.; et al. A phase I study of the pharmacokinetic and safety profiles of oral pazopanib with a high-fat or low-fat meal in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 88, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porritt, K.; McArthur, A.; Lockwood, C.; Munn, Z. JBI Handbook for Evidence Implementation; JBI: Adelaide, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bleijenberg, N.; de Man-van Ginkel, J.M.; Trappenburg, J.C.A.; Ettema, R.G.A.; Sino, C.G.; Heim, N.; Hafsteindottir, T.B.; Richards, D.A.; Schuurmans, M.J. Increasing value and reducing waste by optimizing the development of complex interventions: Enriching the development phase of the Medical Research Council (MRC) Framework. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2018, 79, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, P.; Dieppe, P.; Macintyre, S.; Michie, S.; Nazareth, I.; Petticrew, M.; Medical Research Council, G. Developing and evaluating complex interventions: The new Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ 2008, 337, a1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skivington, K.; Matthews, L.; Simpson, S.A.; Craig, P.; Baird, J.; Blazeby, J.M.; Boyd, K.A.; Craig, N.; French, D.P.; McIntosh, E.; et al. A new framework for developing and evaluating complex interventions: Update of Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ 2021, 374, n2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, P.; Dieppe, P.; Macintyre, S.; Michie, S.; Nazareth, I.; Petticrew, M. Developing and Evaluating Complex Interventions; Medical Research Council: Swindon, UK, 2011.
- Campbell, M.; Fitzpatrick, R.; Haines, A.; Kinmonth, A.L.; Sandercock, P.; Spiegelhalter, D.; Tyrer, P. Framework for design and evaluation of complex interventions to improve health. BMJ 2000, 321, 694–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, B.J.; Fernandez, M.E.; Williams, N.J.; Aarons, G.A.; Beidas, R.S.; Lewis, C.C.; McHugh, S.M.; Weiner, B.J. Enhancing the Impact of Implementation Strategies in Healthcare: A Research Agenda. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltz, T.J.; Powell, B.J.; Matthieu, M.M.; Damschroder, L.J.; Chinman, M.J.; Smith, J.L.; Proctor, E.K.; Kirchner, J.E. Use of concept mapping to characterize relationships among implementation strategies and assess their feasibility and importance: Results from the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) study. Implement. Sci. 2015, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenland, S.L.; Verheijen, R.B.; Joerger, M.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; Sparreboom, A.; Beijnen, J.H.; Beumer, J.H.; Steeghs, N.; Huitema, A.D.R. Precision Dosing of Targeted Therapies Is Ready for Prime Time. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 6644–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebe, S.K.; Singh, R.J. LC-MS/MS in the Clinical Laboratory—Where to From Here? Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2011, 32, 5–31. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation. 2001. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Bioanalytical-Method-Validation-Guidance-for-Industry.pdf (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Chambers, D.A.; Feero, W.G.; Khoury, M.J. Convergence of Implementation Science, Precision Medicine, and the Learning Health Care System: A New Model for Biomedical Research. JAMA 2016, 315, 1941–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, L.; Francis, J.; Islam, R.; O’Connor, D.; Patey, A.; Ivers, N.; Foy, R.; Duncan, E.M.; Colquhoun, H.; Grimshaw, J.M.; et al. A guide to using the Theoretical Domains Framework of behaviour change to investigate implementation problems. Implement. Sci. 2017, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K. Organizational unlearning: Time to expand our horizons? Learn. Organ. 2018, 25, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaic, M.; Kapp, S.; Hudson, P.; Chapman, W.; Denehy, L.; Story, D.; Francis, J.J. Implementability of healthcare interventions: An overview of reviews and development of a conceptual framework. Implement. Sci. 2022, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchester, J.; Gray-Miceli, D.L.; Metcalf, J.A.; Paolini, C.A.; Napier, A.H.; Coogle, C.L.; Owens, M.G. Facilitating Lewin’s change model with collaborative evaluation in promoting evidence based practices of health professionals. Eval. Program Plann. 2014, 47, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michie, S.; van Stralen, M.M.; West, R. The behaviour change wheel: A new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implement. Sci. 2011, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, E.R.; Hart, J.K.; Swift, J.; Baxter, K.; McLauchlan, N.; Joseph, S.; Byrne-Davis, L.M.T. An organisational participatory research study of the feasibility of the behaviour change wheel to support clinical teams implementing new models of care. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2019, 19, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.M.; Boland, R.J., Jr.; Aron, D.C. The physician’s experience of changing clinical practice: A struggle to unlearn. Implement. Sci. 2017, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensing, M. Implementation science in healthcare: Introduction and perspective. Z. Evidenz Fortbild. Qual. Gesundh. 2015, 109, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.S.; Damschroder, L.; Hagedorn, H.; Smith, J.; Kilbourne, A.M. An introduction to implementation science for the non-specialist. BMC Psychol. 2015, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.S.; Kirchner, J. Implementation science: What is it and why should I care? Psychiatry Res. 2020, 283, 112376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, M.A.; Gorukanti, A.; Cattamanchi, A. Strategies for implementing implementation science: A methodological overview. Emerg. Med. J. 2016, 33, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, D.C.; Katz, J.; Chien, V.; Wandersman, A.; Scaccia, J.P.; Wright, A. Practical implementation science: Developing and piloting the quality implementation tool. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2012, 50, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, C.G.; Jarrett, B.A.; Kwon, C.-S.; Song, L.; Jetté, N.; Sapag, J.C.; Bass, J.; Murray, L.; Rao, D.; Baral, S. Implementation science and stigma reduction interventions in low-and middle-income countries: A systematic review. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moullin, J.C.; Dickson, K.S.; Stadnick, N.A.; Rabin, B.; Aarons, G.A. Systematic review of the exploration, preparation, implementation, sustainment (EPIS) framework. Implement. Sci. 2019, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, A.; van Dyk, M.; Mangoni, A.A.; Miners, J.O.; McKinnon, R.A.; Wiese, M.D.; Rowland, A.; Kichenadasse, G.; Gurney, H.; Sorich, M.J. Kinase inhibitor pharmacokinetics: Comprehensive summary and roadmap for addressing inter-individual variability in exposure. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alffenaar, J.W.; Märtson, A.G.; Heysell, S.K.; Cho, J.G.; Patanwala, A.; Burch, G.; Kim, H.Y.; Sturkenboom, M.G.G.; Byrne, A.; Marriott, D.; et al. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in Non-Tuberculosis Mycobacteria Infections. Clin. Pharm. 2021, 60, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.W.; Wagner, D.P.; Krane, N.K.; Rougas, S.C.; Lowitt, N.R.; Offodile, R.S.; Easdown, L.J.; Andrews, M.A.; Kodner, C.M.; Lypson, M.; et al. What are the implications of implementation science for medical education? Med. Educ. Online 2015, 20, 27003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, C.R.; Sherbino, J. How does an “opinion leader” influence my practice? CJEM 2010, 12, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, T.W.; Pumpuang, P. Identifying opinion leaders to promote behavior change. Health Educ. Behav. 2007, 34, 881–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimshaw, J.M.; Eccles, M.P.; Greener, J.; Maclennan, G.; Ibbotson, T.; Kahan, J.P.; Sullivan, F. Is the involvement of opinion leaders in the implementation of research findings a feasible strategy? Implement. Sci. 2006, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-Oliveira, G.; Lippi, G.; Salvagno, G.L.; Picheth, G.; Guidi, G.C. Laboratory Diagnostics and Quality of Blood Collection. J. Med. Biochem. 2015, 34, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van Leuven, J.; Evans, S.; Kichenadasse, G.; Steeghs, N.; Bonevski, B.; Mikus, G.; van Dyk, M. Framework for Implementing Individualised Dosing of Anti-Cancer Drugs in Routine Care: Overcoming the Logistical Challenges. Cancers 2023, 15, 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133293
van Leuven J, Evans S, Kichenadasse G, Steeghs N, Bonevski B, Mikus G, van Dyk M. Framework for Implementing Individualised Dosing of Anti-Cancer Drugs in Routine Care: Overcoming the Logistical Challenges. Cancers. 2023; 15(13):3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133293
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan Leuven, Jason, Simon Evans, Ganessan Kichenadasse, Neeltje Steeghs, Billie Bonevski, Gerd Mikus, and Madelé van Dyk. 2023. "Framework for Implementing Individualised Dosing of Anti-Cancer Drugs in Routine Care: Overcoming the Logistical Challenges" Cancers 15, no. 13: 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133293
APA Stylevan Leuven, J., Evans, S., Kichenadasse, G., Steeghs, N., Bonevski, B., Mikus, G., & van Dyk, M. (2023). Framework for Implementing Individualised Dosing of Anti-Cancer Drugs in Routine Care: Overcoming the Logistical Challenges. Cancers, 15(13), 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133293






