Decoding Immune Signature to Detect the Risk for Early-Stage HCC Recurrence
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Immune Contexture of Liver: From Homeostasis to Carcinogenesis to Recurrence
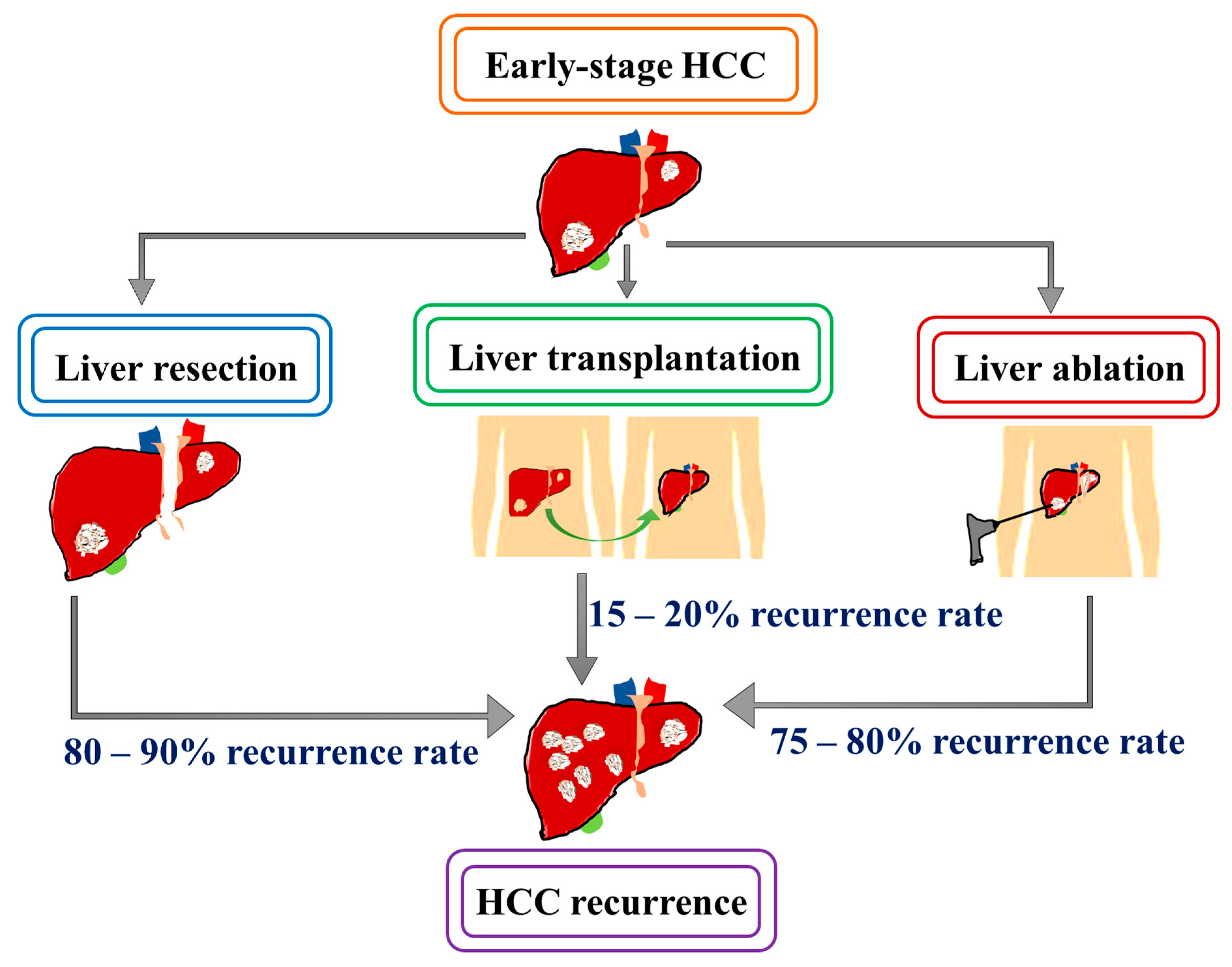
3. Recurrence Pattern after Curative Treatment in HCC
3.1. Surgical Resection
3.2. Orthotopic Liver Transplantation (OLT)
3.3. Local Ablative Therapy (LAT)
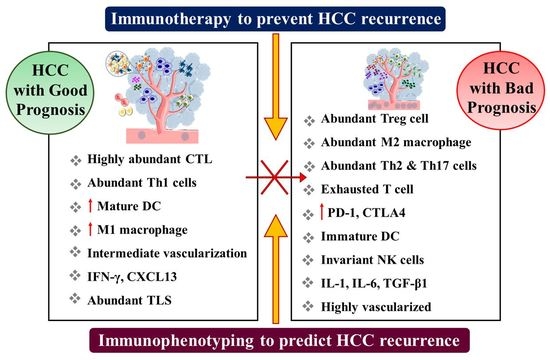
4. Immunological Factors as Predictive Biomarker for HCC Recurrence
4.1. T Lymphocyte
4.2. B Lymphocytes
4.3. Regulatory T Cells
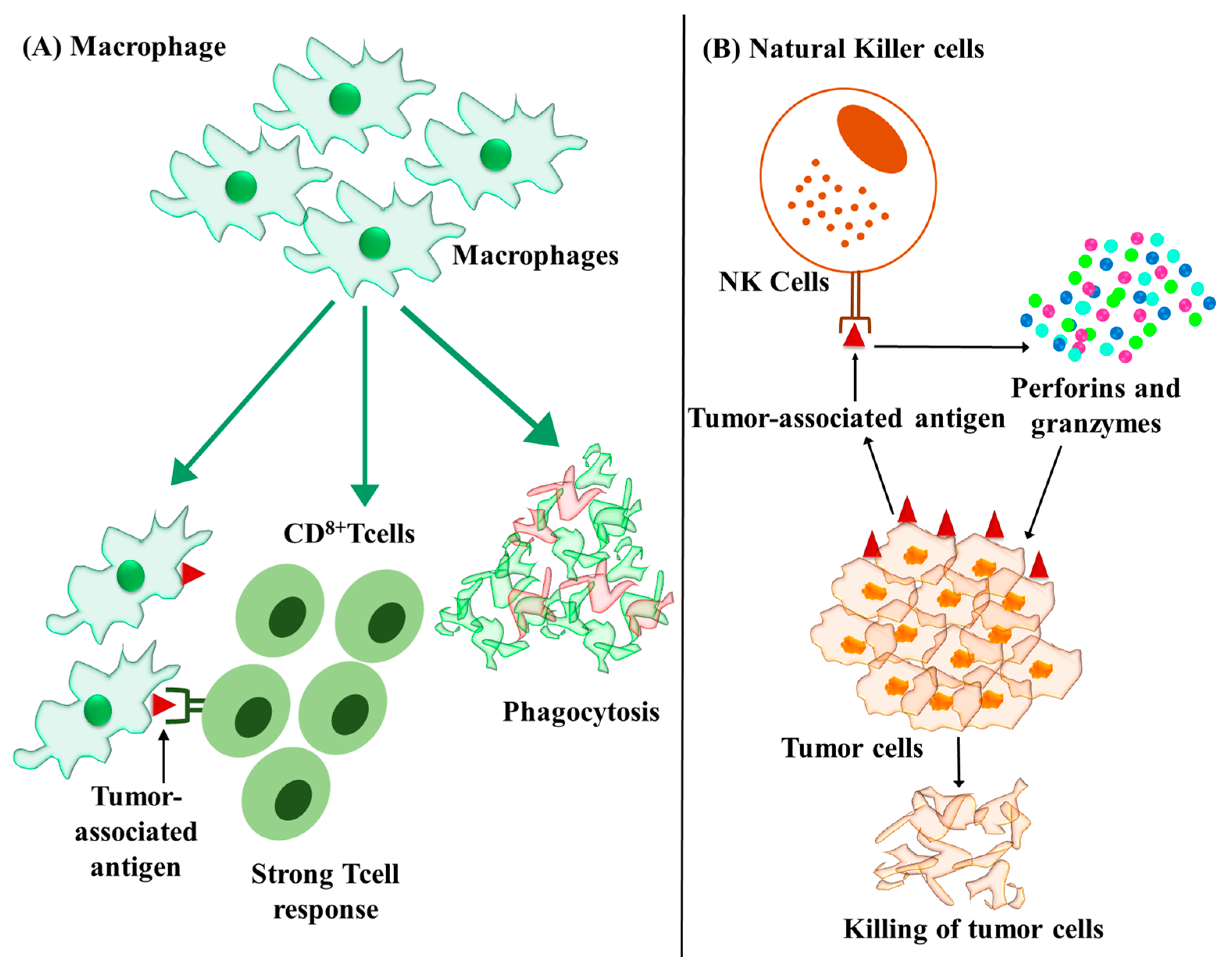
4.4. Macrophages
4.5. Natural Killer Cells
5. Immunotherapeutic Approaches to Prevent HCC Recurrence
| Trial Name/NCT Identifier | Curative Treatment | Neo-Adjuvant or Adjuvant Immunotherapy | Intervention Details | Primary Endpoints | Number of Participants | Phase and Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRIMER-1 NCT05185739 Intervention model: parallel assignment. Masking: open label. | Surgical resection. | Pembrolizumab (200 mg IV every 3 weeksfor two cycles) levantinib combination (8 or 12 mg PO once daily for 6 weeks). | Six-week pre-operative therapy of pembrolizumab–levantinib combination followed by up to 12 months’ treatment with permbrolizumab after resection. | Combination results in less than 10% viable cells at the time of resection. Relapse-free survival at 12 months from surgery. | 60 | Phase 2. Recruiting. |
| DYNAMIC/NCT04954339 Intervention model: single group assignment. Masking: open label. | Surgical resection. | Atezolizumab (1200 mg) plus bevacizumab (15 mg/kg). | Two cycles of pre-operative therapy of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab followed by four cycles of combination after surgery. | Rate of complete pathological response (absence of viable tumor cells in any nodule). Dynamic changes in the immune infiltrate following treatment. Recurrence-free survival. | 45 | Phase 2. Recruiting. |
| NCT03510871 Intervention model: single group assignment. Masking: open label. | Surgical resection. | Nivolumab plus ipilimumab. | Nivolumab 3 mg/kg plus ipilimumab 1 mg/kg intravenously on day 1 of each cycle (every 3 weeks). Eligible patients undergo surgery. | Percentage of patients with tumor shrinkage. Safety of nivolumab plus ipilimumab as adjuvant therapy. | 40 | Phase 2. Active. As of February 2021, the progression-free survival was 13.4 months [149]. |
| NCT03867370 Intervention model: sequential assignment. Masking: open label. | Surgical resection. | Arm A: Toripalimab (480 mg i.v single dose). Arm B: Toripalimab (480 mg i.v single dose) plus lenvatinib (12 or 8 mg daily orallybased on body weight). | Single dose pre-operative toripalimab, and after surgery, toripalimab for 48 weeks. | Pathological response rate. | 40 | Phase Ib/II Active. To September 2021, out of 18 enrolled patients, 16 were evaluable. Three patients achieved major pathologic response (MPR, residual tumor in <50% tumor bed) [150]. |
| MEDI4736 NCT05194293 Intervention model: single group assignment. Masking: open label. | Surgical resection. | Durvalumab–regorafenib. | Durvalumab–regorafenib combination every 28 days until surgery or up to 2 years post registration unless there is unacceptable toxicity. | Objective response rate, defined as a complete response or partial response. Recurrence-free survival. | 27 | Phase 2. Not yet recruiting. |
| NCT04224480 Intervention model: single group assignment. Masking: open label | Surgical resection. | Pembrolizumab 200 mg as intravenous infusion every 3 weeks. | Single dose of pembrolizumab prior to surgery. Adjuvant treatment with pembrolizumab will be administered 4 weeks after the surgery. | Number of subjects with recurrence. Number of CD8+ and Ki67+ T cells found in resected tumor from subjects. | 45 | Recruiting Phase 1. |
| NIVOLVE UMIN 00002664 Intervention model: single group assignment Masking: open label. | Resection or ablation. | Nivolumab. | Nivolumab (240 mg/body) every 2 weeks (eight cycles), followed by nivolumab (480 mg/body) every 4 weeks (eight cycles) within 6 weeks after SR or RFA. | One year recurrence-free survival rate of 78.6% and recurrence-free survival of 26.3 months [135]. | 55 | Completed. |
| CheckMate 9DX NCT03383458 Allocation: randomized. Intervention: parallel assignment. Masking: quadruple (participants, care providers, investigators and outcomes assessors). | Resection or ablation. | Arm A: Nivolumab. Arm B: Placebo comparator. | Nivolumab. Specified dose on specified days after resection or ablation. | Recurrence free survival. | 545 | Phase 3. Ongoing. |
| KEYNOTE-937 NCT03867084 Allocation: randomized. Intervention: parallel assignment. Masking: double (participants, investigators). | Resection or ablation. | Arm A: Pembrolizumab. Arm B: Placebo comparator (IV infusion of 0.9% NS). | Intravenous pembrolizumab at 200 mg on day 1 of each 21-day cycle for up to 17 cycles. | Recurrence-free survival. Overall survival. | 950 | Phase 3. Active. |
| EMERALD-2 NCT03847428 Allocation: randomized. Intervention: parallel assignment. Masking: quadruple (participants, care providers, investigators and outcomes assessors). | Hepatic resection or ablation. | Arm A: Durvalumab 1120 mg (Q3W) plus bevacizumab 15 mg/kg (Q3W). Arm B: Durvalumab 1120 mg (Q3W) plus bevacizumab placebo (Q3W). Arm C: Durvalumab placebo (Q3W) plus bevacizumab placebo (Q3W). | Durvalumab in combination with bevacizumab in high risk of recurrence HCC patients after curative treatment. | Recurrence-free survival. | 908 | Phase 3. Active. |
| IMbrave 050 NCT04102098 Allocation: randomized. Intervention: parallel assignment. Masking: open label. | Hepatic resection or ablation. | Arm A: Atezolizumab (1200 mg IV infusion on day 1 of each 21-day cycle) plus bevacizumab (IV infusion at a dose of 15 mg/kg on day 1 of each 21-day cycle). Arm B: Active surveillance comparator. Active surveillance of participants. | Participants will receive atezolizumab plus bevacizumab until unacceptable toxicity after resection or ablation. | Recurrence-free survival. | 668 | Phase 3. Active. |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A Global View of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Trends, Risk, Prevention and Management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refolo, M.G.; Messa, C.; Guerra, V.; Carr, B.I.; D’Alessandro, R. Inflammatory Mechanisms of HCC Development. Cancers 2020, 12, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Seki, E. Inflammation and Liver Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Semin. Liver Dis. 2019, 39, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Critelli, R.; Milosa, F.; Faillaci, F.; Condello, R.; Turola, E.; Marzi, L.; Lei, B.; Dituri, F.; Andreani, S.; Sighinolfi, P.; et al. Microenvironment Inflammatory Infiltrate Drives Growth Speed and Outcome of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Prospective Clinical Study. Cell. Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, J.; Iredale, J.P. The Inflammatory Microenvironment of HCC—The Plot Becomes Complex. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 853–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, N.E.; Yopp, A.C.; Singal, A.G. Medical Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Oncol. Pract. 2017, 13, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, D.; Ogura, T.; Akahoshi, K.; Tanabe, M. Current Topics in the Surgical Treatments for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2018, 2, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.W.H.; Zhong, J.; Berhane, S.; Toyoda, H.; Cucchetti, A.; Shi, K.; Tada, T.; Chong, C.C.N.; Xiang, B.-D.; Li, L.-Q.; et al. Development of Pre and Post-Operative Models to Predict Early Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Surgical Resection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova-Rusher, O.V.; Medina-Echeverz, J.; Duffy, A.G.; Greten, T.F. The Yin and Yang of Evasion and Immune Activation in HCC. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racanelli, V.; Rehermann, B. The Liver as an Immunological Organ. Hepatology 2006, 43, S54–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Green, M.D.; Huppert, L.A.; Chow, C.; Pierce, R.H.; Daud, A.I. The Liver-Immunity Nexus and Cancer Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horst, A.K.; Neumann, K.; Diehl, L.; Tiegs, G. Modulation of Liver Tolerance by Conventional and Nonconventional Antigen-Presenting Cells and Regulatory Immune Cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, E.R. In the Zone for Liver Proliferation. Science 2021, 371, 887–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Tian, Z. Liver-Mediated Adaptive Immune Tolerance. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.S.; Decaens, T. Liver Immunotolerance and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Patho-Physiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 87, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Mehal, W.; Nagy, L.E.; Rotman, Y. Immunological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets of Fatty Liver Diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassel, R.; Cruise, M.W.; Iezzoni, J.C.; Taylor, N.A.; Pruett, T.L.; Hahn, Y.S. Chronically Inflamed Livers Up-Regulate Expression of Inhibitory B7 Family Members. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Shi, M.; Zeng, Z.; Qi, R.-Z.; Liu, Z.-W.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Yang, Y.-P.; Tien, P.; Wang, F.-S. PD-1 and PD-L1 Upregulation Promotes CD8+ T-Cell Apoptosis and Postoperative Recurrence in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Mei, M.H.; Fei, R.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.H.; Liao, W.J.; Qin, L.L.; Wei, L.; Chen, H.S. Regulatory T Cells in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Affect the Immunopathogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Suppressing the Anti-Tumour Immune Responses. J. Viral Hepat. 2010, 17 (Suppl. S1), 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palucka, A.K.; Coussens, L.M. The Basis of Oncoimmunology. Cell 2016, 164, 1233–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, H.; Hagerling, C.; Werb, Z. Roles of the Immune System in Cancer: From Tumor Initiation to Metastatic Progression. Genes. Dev. 2018, 32, 1267–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.W.L.; Galon, J.; Fridman, W.-H.; Smyth, M.J. From Mice to Humans: Developments in Cancer Immunoediting. J. Clin. Invest. 2015, 125, 3338–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zeng, S.; Shen, H. From Bench to Bed: The Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Current Immunotherapeutic Strategies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Chen, D.; Cheng, C.; Li, Z.; Chi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Ang, B.; et al. Immunosuppressive Landscape in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Revealed by Single-Cell Sequencing. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 950536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Qin, L.; Liao, Z.; Song, J.; Yuan, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Pei, Y.; et al. Microenvironment Characterization and Multi-Omics Signatures Related to Prognosis and Immunotherapy Response of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oura, K.; Morishita, A.; Tani, J.; Masaki, T. Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Immunosuppressive Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Pan, C.; Yin, S.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S. Tumor Immune Microenvironment Characterization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Identifies Four Prognostic and Immunotherapeutically Relevant Subclasses. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 610513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devan, A.R.; Kumar, A.R.; Nair, B.; Anto, N.P.; Muraleedharan, A.; Mathew, B.; Kim, H.; Nath, L.R. Insights into an Immunotherapeutic Approach to Combat Multidrug Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.H.D.; Wasser, M.; Tan, C.T.; Lim, C.J.; Lai, H.L.H.; Seow, J.J.W.; DasGupta, R.; Phua, C.Z.J.; Ma, S.; Yang, J.; et al. Trajectory of Immune Evasion and Cancer Progression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.-Q.; Chen, Z.-L.; Feng, Z.-H.; Diao, Y.-K.; Li, C.; Sun, H.-Y.; Zhong, J.-H.; Chen, T.-H.; Gu, W.-M.; Zhou, Y.-H.; et al. Clinical Features of Recurrence After Hepatic Resection for Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Long-Term Survival Outcomes of Patients with Recurrence: A Multi-Institutional Analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 4291–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojiro, M. Pathomorphologic characteristics of small liver cancer in the early stage and the basic pathologic features of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gan Kagaku Ryoho 1989, 16, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Unitt, E.; Marshall, A.; Gelson, W.; Rushbrook, S.M.; Davies, S.; Vowler, S.L.; Morris, L.S.; Coleman, N.; Alexander, G.J.M. Tumour Lymphocytic Infiltrate and Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Following Liver Transplantation. J. Hepatol. 2006, 45, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Xu, D.; Liu, Z.; Shi, M.; Zhao, P.; Fu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.; et al. Increased Regulatory T Cells Correlate With CD8 T-Cell Impairment and Poor Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2328–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, A.; Bavetta, M.G.; Martinelli, E.; Bronte, F.; Giunta, E.F.; Manu, K.A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Therapeutic Algorithm for Localized and Advanced Disease. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 3817724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, G.; Ravaioli, F.; Vestito, A.; Rossini, B.; Dajti, E.; Colecchia, L.; Gjini, K.; Renzulli, M.; Golfieri, R.; Festi, D.; et al. Predictive Factors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence after Curative Treatments. Hepatoma Res. 2020, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Pagliaro, L. Natural History and Prognostic Indicators of Survival in Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review of 118 Studies. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portolani, N.; Coniglio, A.; Ghidoni, S.; Giovanelli, M.; Benetti, A.; Tiberio, G.A.M.; Giulini, S.M. Early and Late Recurrence after Liver Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications. Ann. Surg. 2006, 243, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris-Stiff, G.; Gomez, D.; de Liguori Carino, N.; Prasad, K.R. Surgical Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Is the Jury Still Out? Surg. Oncol. 2009, 18, 298–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariani, E.; Pilli, M.; Zerbini, A.; Rota, C.; Olivani, A.; Pelosi, G.; Schianchi, C.; Soliani, P.; Campanini, N.; Silini, E.M.; et al. Immunological and Molecular Correlates of Disease Recurrence after Liver Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Nakashima, O.; Kutami, R.; Yamamoto, O.; Kojiro, M. Clinicopathological Study on Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Lymphocytic Infiltration. Hepatology 1998, 27, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhu, A.; Forgues, M.; Ye, Q.-H.; Jia, H.-L.; He, P.; Zanetti, K.A.; Kammula, U.S.; Chen, Y.; Qin, L.-X.; Tang, Z.-Y.; et al. Prediction of Venous Metastases, Recurrence, and Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on a Unique Immune Response Signature of the Liver Microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2006, 10, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.-H.; Qin, L.-X.; Forgues, M.; He, P.; Kim, J.W.; Peng, A.C.; Simon, R.; Li, Y.; Robles, A.I.; Chen, Y.; et al. Predicting Hepatitis B Virus–Positive Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinomas Using Gene Expression Profiling and Supervised Machine Learning. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Regalia, E.; Doci, R.; Andreola, S.; Pulvirenti, A.; Bozzetti, F.; Montalto, F.; Ammatuna, M.; Morabito, A.; Gennari, L. Liver Transplantation for the Treatment of Small Hepatocellular Carcinomas in Patients with Cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodzin, A.S.; Lunsford, K.E.; Markovic, D.; Harlander-Locke, M.P.; Busuttil, R.W.; Agopian, V.G. Predicting Mortality in Patients Developing Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Liver Transplantation: Impact of Treatment Modality and Recurrence Characteristics. Ann. Surg. 2017, 266, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, S.; Mangus, R.S.; Kubal, C.A.; Ekser, B.; Fridell, J.A.; Klingler, K.R.; Maluccio, M.A.; Tector, A.J. Prognosis after Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Liver Transplantation: Predictors for Successful Treatment and Survival. Clin. Transpl. 2015, 29, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de’Angelis, N. Managements of Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Liver Transplantation: A Systematic Review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straś, W.A.; Wasiak, D.; Łągiewska, B.; Tronina, O.; Hreńczuk, M.; Gotlib, J.; Lisik, W.; Małkowski, P. Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Liver Transplantation: Risk Factors and Predictive Models. Ann. Transpl. 2022, 27, e934924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.Y.; Patt, C.H.; Geschwind, J.-F.; Thuluvath, P.J. The Outcome of Liver Transplantation in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the United States Between 1988 and 2001: 5-Year Survival Has Improved Significantly With Time. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 4329–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, A.; Te, H.S.; Verna, E.C.; Desai, A.P. A National Survey of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance Practices Following Liver Transplantation. Transplant. Direct 2020, 7, e638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueira, N.A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence after Liver Transplantation: Risk Factors, Screening and Clinical Presentation. World J. Hepatol. 2019, 11, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitzbauer, A.A.; Filmann, N.; Adam, R.; Bachellier, P.; Bechstein, W.O.; Becker, T.; Bhoori, S.; Bilbao, I.; Brockmann, J.; Burra, P.; et al. MTOR Inhibition Is Most Beneficial After Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Active Tumors. Ann. Surg. 2020, 272, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lo, C.M.; Man, K. Role of Intrahepatic Regional Immunity in Post-Transplant Cancer Recurrence. Engineering 2022, 10, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, K.; Fan, S.-T.; Lo, C.-M.; Liu, C.-L.; Fung, P.C.-W.; Liang, T.-B.; Lee, T.K.-W.; Tsui, S.H.-T.; Ng, I.O.-L.; Zhang, Z.-W.; et al. Graft Injury in Relation to Graft Size in Right Lobe Live Donor Liver Transplantation: A Study of Hepatic Sinusoidal Injury in Correlation with Portal Hemodynamics and Intragraft Gene Expression. Ann. Surg. 2003, 237, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhou, H.; Ni, M.; Wang, X.; Busuttil, R.; Kupiec-Weglinski, J.; Zhai, Y. Innate Immune Regulations and Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Transplantation 2016, 100, 2601–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devan, A.R.; Pavithran, K.; Nair, B.; Murali, M.; Nath, L.R. Deciphering the Role of Transforming Growth Factor-Beta 1 as a Diagnostic-Prognostic-Therapeutic Candidate against Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 5250–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, A.; Samstein, R.M.; Treuting, P.; Liang, Y.; Pils, M.C.; Heinrich, J.-M.; Jack, R.S.; Wunderlich, F.T.; Brüning, J.C.; Müller, W.; et al. Interleukin-10 Signaling in Regulatory T Cells Is Required for Suppression of Th17 Cell-Mediated Inflammation. Immunity 2011, 34, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovich, G.A.; Gabrilovich, D.; Sotomayor, E.M. Immunosuppressive Strategies That Are Mediated by Tumor Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 267–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, P.-Y.; Kuipers, H.; Boyman, O.; Rhyner, C.; Ouaked, N.; Rückert, B.; Karagiannidis, C.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Hendriks, R.W.; Crameri, R.; et al. GATA3-Driven Th2 Responses Inhibit TGF-Β1–Induced FOXP3 Expression and the Formation of Regulatory T Cells. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Hoffmann, K.; Schemmer, P. Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Liver Cancer 2012, 1, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, S.; Tateishi, R.; Arano, T.; Uchino, K.; Enooku, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Asaoka, Y.; Sato, T.; Masuzaki, R.; Kondo, Y.; et al. Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 10-Year Outcome and Prognostic Factors. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.K.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, M.Y.; Rhim, H.; Han, J.K. Systematic Review of Randomized Trials for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Percutaneous Ablation Therapies. Hepatology 2009, 49, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Long, J.; Wang, W.; Huang, T.; Xie, X.; Chen, S.; Huang, G.; Jiang, C.; Ye, J.; Long, H.; et al. Predictive Factors of Treatment Outcomes after Percutaneous Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Caudate Lobe: A Retrospective Study. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-Y.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, G.S.; Sohn, W.; Ahn, J.; Sinn, D.-H.; Gwak, G.-Y.; Paik, Y.-H.; Lee, J.H.; Koh, K.C.; et al. Clinical Significance and Predictive Factors of Early Massive Recurrence after Radiofrequency Ablation in Patients with a Single Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2016, 22, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizukoshi, E.; Yamashita, T.; Arai, K.; Sunagozaka, H.; Ueda, T.; Arihara, F.; Kagaya, T.; Yamashita, T.; Fushimi, K.; Kaneko, S. Enhancement of Tumor-Associated Antigen-Specific T Cell Responses by Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.Y.; Grimm, C.F.; Ritter, M.; Mohr, L.; Allgaier, H.-P.; Weth, R.; Bocher, W.O.; Endrulat, K.; Blum, H.E.; Geissler, M. Activation of Dendritic Cells by Local Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Du, F.; Liu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, X.; Wu, Z. Immunological Effect of Irreversible Electroporation on Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, N.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, X. Prognostic Significance of Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index-Based Nomogram for Early Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Radiofrequency Ablation. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 12, 735–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Z.; He, K.; Huang, R.Q.; Liu, L.W.; Ye, S.W.; Qian, J.L.; Peng, P.; Luo, Q.J.; Wang, Z.L.; Hu, Z.M. A Clinical Scoring System for Predicting Tumor Recurrence after Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation for 3 Cm or Less Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lei, K.; Liao, J.; Peng, Z.; Lin, M.; Liang, P.; Yu, J.; Peng, S.; Chen, S.; et al. Irreversible Electroporation Induces CD8+ T Cell Immune Response against Post-Ablation Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth. Cancer Lett. 2021, 503, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chen, L.; Wu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, B.; Zheng, X.; Sun, M.; Wen, W.; Dai, X.; Yang, M.; et al. PD-1 Blockade Boosts Radiofrequency Ablation–Elicited Adaptive Immune Responses against Tumor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Q.; Pan, Y.; Lin, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, X.; Hou, Z.; Yu, X.; Lin, X.; Lin, R.; Lu, F.; et al. High-Dimensional Single-Cell Analysis Delineates Radiofrequency Ablation Induced Immune Microenvironmental Remodeling in Pancreatic Cancer. Cell. Death Dis. 2020, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, N.M.; Dupuis, C.; Williams, M.; Dixon, K.; McWatters, A.; Avritscher, R.; Bouchard, R.; Kaseb, A.; Schachtschneider, K.M.; Rao, A.; et al. Molecularly Targeted Photothermal Ablation Improves Tumor Specificity and Immune Modulation in a Rat Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Shi, F.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, M.-N.; Chen, Y.; Chang, X.-J.; Lu, Y.-Y.; Bai, W.-L.; Qu, J.-H.; Wang, C.-P.; et al. Upregulation of Circulating PD-L1/PD-1 Is Associated with Poor Post-Cryoablation Prognosis in Patients with HBV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Zitvogel, L.; Palucka, A.K. Neutralizing Tumor-Promoting Chronic Inflammation: A Magic Bullet? Science 2013, 339, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Lee, S.W.; Jang, J.W.; Bae, S.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoon, S.K. Immunological Markers, Prognostic Factors and Challenges Following Curative Treatments for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon, J.; Costes, A.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Kirilovsky, A.; Mlecnik, B.; Lagorce-Pagès, C.; Tosolini, M.; Camus, M.; Berger, A.; Wind, P.; et al. Type, Density, and Location of Immune Cells Within Human Colorectal Tumors Predict Clinical Outcome. Science 2006, 313, 1960–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieu-Nosjean, M.-C.; Giraldo, N.A.; Kaplon, H.; Germain, C.; Fridman, W.H.; Sautès-Fridman, C. Tertiary Lymphoid Structures, Drivers of the Anti-Tumor Responses in Human Cancers. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 271, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffell, B.; Coussens, L.M. Macrophages and Therapeutic Resistance in Cancer. Cancer Cell. 2015, 27, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephs, D.H. Tumour-Associated Macrophage Polarisation and Re-Education with Immunotherapy. Front. Biosci. 2015, 7, 334–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becht, E.; Giraldo, N.A.; Germain, C.; de Reyniès, A.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Dieu-Nosjean, M.-C.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Fridman, W.H. Immune Contexture, Immunoscore, and Malignant Cell Molecular Subgroups for Prognostic and Theranostic Classifications of Cancers. In Advances in Immunology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 130, pp. 95–190. ISBN 978-0-12-805156-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.-C.; Wu, T.-J.; Chou, H.-S.; Yu, M.-C.; Hsu, P.-Y.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Wang, C.-C. The Impact of CD4+CD25+ T Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Surgery 2012, 151, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Galon, J. The Immune Contexture in Human Tumours: Impact on Clinical Outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Lin, J.; Long, J.; Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Lu, X.; Sang, X.; Zhao, H. T Lymphocytes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immune Microenvironment: Insights into Human Immunology and Immunotherapy. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 4585–4606. [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielson, A.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, J.; Kallakury, B.; Gatalica, Z.; Reddy, S.; Kleiner, D.; Fishbein, T.; Johnson, L.; et al. Intratumoral CD3 and CD8 T-Cell Densities Associated with Relapse-Free Survival in HCC. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, W.H.; Galon, J.; Pagès, F.; Tartour, E.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Kroemer, G. Prognostic and Predictive Impact of Intra- and Peritumoral Immune Infiltrates. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5601–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-P.; Yan, J.; Xu, J.; Pang, X.-H.; Chen, M.-S.; Li, L.; Wu, C.; Li, S.-P.; Zheng, L. Increased Intratumoral IL-17-Producing Cells Correlate with Poor Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhen, S.; Meng, F. T Cell Inflammation Profile after Surgical Resection May Predict Tumor Recurrence in HBV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 41, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.J.; Oh, J.-H.; Chun, S.-M.; Kim, D.; Ryu, Y.-M.; Hwang, H.S.; Kim, S.-Y.; An, J.; Cho, E.J.; Lee, H.; et al. Immunogenomic Landscape of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Immune Cell Stroma and EBV-Positive Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnelo, M.; Tan, A.; Her, Z.; Yeong, J.; Lim, C.J.; Chen, J.; Lim, K.H.; Weber, A.; Chow, P.; Chung, A.; et al. Interaction between Tumour-Infiltrating B Cells and T Cells Controls the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut 2017, 66, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-Y.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Z.-C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.-Y.; Min, Z.-H.; Shi, Y.-H.; Shi, G.-M.; Ding, Z.-B.; Ke, A.-W.; et al. Margin-Infiltrating CD20+ B Cells Display an Atypical Memory Phenotype and Correlate with Favorable Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5994–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, L.; Goswami, S.; Ma, J.; Zheng, B.; Duan, M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Dong, L.; et al. Landscape of Infiltrating B Cells and Their Clinical Significance in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. OncoImmunology 2019, 8, e1571388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharonov, G.V.; Serebrovskaya, E.O.; Yuzhakova, D.V.; Britanova, O.V.; Chudakov, D.M. B Cells, Plasma Cells and Antibody Repertoires in the Tumour Microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, G.J.; Demissie, E.; Pillai, S. B Lymphocytes and Cancer: A Love–Hate Relationship. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohue, Y.; Nishikawa, H. Regulatory T (Treg) Cells in Cancer: Can Treg Cells Be a New Therapeutic Target? Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Hiraoka, N.; Yamagami, W.; Ojima, H.; Kanai, Y.; Kosuge, T.; Nakajima, A.; Hirohashi, S. FOXP3+ Regulatory T Cells Affect the Development and Progression of Hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-H.; Jiang, C.-L.; Yan, W.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Yang, J.-T.; Zhang, C.; Yan, B.; Zhang, W.; Han, W.; Wang, J.-Z.; et al. FOXP3 Expression and Clinical Characteristics of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 5502–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, R.; Wang, F.; Gao, Y.; Wang, P.; Du, Z. Prognostic Value of Tumor-Infiltrating FoxP3+ T Cells in Gastrointestinal Cancers: A Meta Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Qiu, S.-J.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.-Y.; Xiao, Y.-S.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.-W.; Tang, Z.-Y. Intratumoral Balance of Regulatory and Cytotoxic T Cells Is Associated With Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Resection. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2586–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.X.; Ling, C.C.; Shao, Y.; Xu, A.; Li, X.C.; Ng, K.T.-P.; Liu, X.B.; Ma, Y.Y.; Qi, X.; Liu, H.; et al. CXCL10/CXCR3 Signaling Mobilized-Regulatory T Cells Promote Liver Tumor Recurrence after Transplantation. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Hou, X.; Liu, W.; Han, Z.; Wei, L. Macrophages and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell. Biosci. 2019, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango Duque, G.; Descoteaux, A. Macrophage Cytokines: Involvement in Immunity and Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.J.; Borregaard, N.; Wynn, T.A. Phenotypic and Functional Plasticity of Cells of Innate Immunity: Macrophages, Mast Cells and Neutrophils. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage Plasticity and Interaction with Lymphocyte Subsets: Cancer as a Paradigm. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, A.; Erreni, M.; Allavena, P.; Porta, C. Macrophage Polarization in Pathology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 4111–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, A.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage Plasticity and Polarization: In Vivo Veritas. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.; Plűddemann, A. Tissue Macrophage Heterogeneity: Issues and Prospects. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.O.; Gordon, S. The M1 and M2 Paradigm of Macrophage Activation: Time for Reassessment. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprinzl, M.F.; Reisinger, F.; Puschnik, A.; Ringelhan, M.; Ackermann, K.; Hartmann, D.; Schiemann, M.; Weinmann, A.; Galle, P.R.; Schuchmann, M.; et al. Sorafenib Perpetuates Cellular Anticancer Effector Functions by Modulating the Crosstalk between Macrophages and Natural Killer Cells. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2358–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.-X.; Ling, Y.; Wang, H.-Y. Role of Nonresolving Inflammation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development and Progression. Npj. Precis. Oncl. 2018, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, J.; Melero, I.; Sangro, B. Immunological Landscape and Immunotherapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 681–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, R.D.; Old, L.J.; Smyth, M.J. Cancer Immunoediting: Integrating Immunity’s Roles in Cancer Suppression and Promotion. Science 2011, 331, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, X.-D.; Sun, H.-C.; Xiong, Y.-Q.; Zhuang, P.-Y.; Xu, H.-X.; Kong, L.-Q.; Wang, L.; Wu, W.-Z.; Tang, Z.-Y. Depletion of Tumor-Associated Macrophages Enhances the Effect of Sorafenib in Metastatic Liver Cancer Models by Antimetastatic and Antiangiogenic Effects. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 3420–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsson, V.; Gibbs, D.L.; Brown, S.D.; Wolf, D.; Bortone, D.S.; Ou Yang, T.-H.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Gao, G.F.; Plaisier, C.L.; Eddy, J.A.; et al. The Immune Landscape of Cancer. Immunity 2018, 48, 812–830.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Ma, L.; Liu, L.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, S.; Dong, L.; Xue, R.; Chen, S. CD86+/CD206+, Diametrically Polarized Tumor-Associated Macrophages, Predict Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patient Prognosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zou, J.; Chen, R. An M0 Macrophage-Related Prognostic Model for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, C.; Gong, L.; Guo, Y.; Fu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y. Macrophage Polarization and Its Role in Liver Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 803037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossanen, J.C.; Tacke, F. Role of Lymphocytes in Liver Cancer. Oncoimmunology 2013, 2, e26468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, Z. Innate Lymphocytes: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Targets of Liver Diseases and Cancer. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, V.; Tow, C.; Teo, M.; Wong, H.L.; Chan, J.; Gehring, A.; Loh, M.; Bolze, A.; Quek, R.; Lee, V.K.M.; et al. Inflammatory Tumour Microenvironment Is Associated with Superior Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.A.; Goh, H.G.; Lee, Y.-S.; Jung, Y.K.; Kim, J.H.; Yim, H.J.; Lee, M.-G.; An, H.; Jeen, Y.T.; Yeon, J.E.; et al. Natural Killer Cell Activity Is a Risk Factor for the Recurrence Risk after Curative Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketomi, A.; Shimada, M.; Shirabe, K.; Kajiyama, K.; Gion, T.; Sugimachi, K. Natural Killer Cell Activity in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A New Prognostic Indicator after Hepatectomy. Cancer 1998, 83, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimine, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Tashiro, H.; Miki, D.; Imamura, M.; Aikata, H.; Tanaka, J.; Chayama, K.; Ohdan, H. Quantitative Effect of Natural Killer–Cell Licensing on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence after Curative Hepatectomy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.-S.; Gao, Q.; Xu, X.-N.; Li, Y.-W.; Ju, M.-J.; Cai, M.-Y.; Dai, C.-X.; Hu, J.; Qiu, S.-J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Combination of Intratumoral Invariant Natural Killer T Cells and Interferon-Gamma Is Associated with Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Resection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Wang, X.; Kirken, R.; He, L.; Zhang, J.-Y. Immunodiagnostic Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): The First Step in Detection and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-X.; Wu, L.-H.; Ai, L.; Pan, W.; Ren, J.-Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.-M. Construction of an HCC Recurrence Model Based on the Investigation of Immune-Related LncRNAs and Related Mechanisms. Mol. Ther.—Nucleic Acids 2021, 26, 1387–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Sun, B.; Peng, J.; Xu, Q. A New Risk Score Based on Eight Hepatocellular Carcinoma- Immune Gene Expression Can Predict the Prognosis of the Patients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 766072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Wu, L.; Zang, Y. A Prognostic Model of 15 Immune-Related Gene Pairs Associated With Tumor Mutation Burden for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 581354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-R.; Tian, M.-X.; Tang, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Song, S.-S.; Jiang, X.-F.; Wang, H.; Tao, C.-Y.; Zhou, P.-Y.; et al. Nine-Factor-Based Immunohistochemistry Classifier Predicts Recurrence for Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Resection. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oiseth, S.J.; Aziz, M.S. Cancer Immunotherapy: A Brief Review of the History, Possibilities, and Challenges Ahead. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2017, 3, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, K.; Hana, D.; Chou, J.T.-T.; Singh, C.; Mackiewicz, A.; Kaczmarek, M. Aspects of the Tumor Microenvironment Involved in Immune Resistance and Drug Resistance. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 656364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laschtowitz, A.; Roderburg, C.; Tacke, F.; Mohr, R. Preoperative Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current State of the Art. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2023, 10, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalabi, M.; Fanchi, L.F.; Dijkstra, K.K.; Van den Berg, J.G.; Aalbers, A.G.; Sikorska, K.; Lopez-Yurda, M.; Grootscholten, C.; Beets, G.L.; Snaebjornsson, P.; et al. Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy Leads to Pathological Responses in MMR-Proficient and MMR-Deficient Early-Stage Colon Cancers. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, C.U.; Rozeman, E.A.; Fanchi, L.F.; Sikorska, K.; van de Wiel, B.; Kvistborg, P.; Krijgsman, O.; van den Braber, M.; Philips, D.; Broeks, A.; et al. Neoadjuvant versus Adjuvant Ipilimumab plus Nivolumab in Macroscopic Stage III Melanoma. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Cortes, J.; Dent, R.; Pusztai, L.; McArthur, H.; Kümmel, S.; Bergh, J.; Denkert, C.; Park, Y.H.; Hui, R.; et al. VP7-2021: KEYNOTE-522: Phase III Study of Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab + Chemotherapy vs. Placebo + Chemotherapy, Followed by Adjuvant Pembrolizumab vs. Placebo for Early-Stage TNBC. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1198–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M. Combination Cancer Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2018, 7, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M. Adjuvant Immunotherapy after Curative Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2021, 10, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.J.; Zhu, Q.; Durham, J.; Popovic, A.; Xavier, S.; Leatherman, J.; Mohan, A.; Mo, G.; Zhang, S.; Gross, N.; et al. Neoadjuvant Cabozantinib and Nivolumab Convert Locally Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma into Resectable Disease with Enhanced Antitumor Immunity. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Tang, W.; Qian, X.; Li, X.; Cheng, F.; Wang, K.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, C.; Li, D.; Song, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Camrelizumab plus Apatinib during the Perioperative Period in Resectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Single-Arm, Open Label, Phase II Clinical Trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulgenzi, C.A.M.; D’Alessio, A.; Ogunbiyi, O.; Demirtas, C.O.; Gennari, A.; Cortellini, A.; Sharma, R.; Pinato, D.J. Novel Immunotherapy Combinations in Clinical Trials for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Will They Shape the Future Treatment Landscape? Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2022, 31, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Ueshima, K.; Nakahira, S.; Nishida, N.; Ida, H.; Minami, Y.; Nakai, T.; Wada, H.; Kubo, S.; Ohkawa, K.; et al. Final Results of Adjuvant Nivolumab for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) after Surgical Resection (SR) or Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) (NIVOLVE): A Phase 2 Prospective Multicenter Single-Arm Trial and Exploratory Biomarker Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, C.; Charalampakis, N.; Tsakatikas, S.; Vailas, M.; Moris, D.; Gkotsis, E.; Kykalos, S.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Schizas, D. Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A 2021 Update. Cancers 2020, 12, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.; Sofiya, L.; Sykiotis, G.P.; Lamine, F.; Maillard, M.; Fraga, M.; Shabafrouz, K.; Ribi, C.; Cairoli, A.; Guex-Crosier, Y.; et al. Adverse Effects of Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors: Epidemiology, Management and Surveillance. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, T.; Kang, Y.-K.; Kim, T.-Y.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Santoro, A.; Sangro, B.; Melero, I.; Kudo, M.; Hou, M.-M.; Matilla, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Previously Treated With Sorafenib: The CheckMate 040 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, e204564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Ikeda, M.; Sung, M.W.; Baron, A.D.; Kudo, M.; Okusaka, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Kumada, H.; Kaneko, S.; et al. A Phase Ib Study of Lenvatinib (LEN) plus Pembrolizumab (PEMBRO) in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma (UHCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; O’Donnell, J.S.; Yan, J.; Madore, J.; Allen, S.; Smyth, M.J.; Teng, M.W.L. Timing of Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy in Relation to Surgery Is Crucial for Outcome. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1581530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangro, B.; Sarobe, P.; Hervás-Stubbs, S.; Melero, I. Advances in Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 525–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Lin, Y.; Hsiao, C.; Ou, D.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Lee, W.; Lin, J.; Hsu, C.; Ho, M.; et al. P-124 Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab as Neoadjuvant Therapy for Potentially Resectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-H.; Ji, Y.; Liu, W.-R.; Pang, Y.-R.; Ding, Z.-B.; Fu, X.-T.; Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Sun, Y.-F.; Zhu, X.-D.; et al. Abstract 486: A Phase Ib/II, Open-Label Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Toripalimab Injection (JS001) or Combination with Lenvatinib as a Neoadjuvant Therapy for Patients with Resectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 denotes inhibition).
denotes inhibition).
 denotes inhibition).
denotes inhibition).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Devan, A.R.; Nair, B.; Aryan, M.K.; Liju, V.B.; Koshy, J.J.; Mathew, B.; Valsan, A.; Kim, H.; Nath, L.R. Decoding Immune Signature to Detect the Risk for Early-Stage HCC Recurrence. Cancers 2023, 15, 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102729
Devan AR, Nair B, Aryan MK, Liju VB, Koshy JJ, Mathew B, Valsan A, Kim H, Nath LR. Decoding Immune Signature to Detect the Risk for Early-Stage HCC Recurrence. Cancers. 2023; 15(10):2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102729
Chicago/Turabian StyleDevan, Aswathy R., Bhagyalakshmi Nair, Manu Kanjoormana Aryan, Vijayastelar B. Liju, Joel Joy Koshy, Bijo Mathew, Arun Valsan, Hoon Kim, and Lekshmi R. Nath. 2023. "Decoding Immune Signature to Detect the Risk for Early-Stage HCC Recurrence" Cancers 15, no. 10: 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102729
APA StyleDevan, A. R., Nair, B., Aryan, M. K., Liju, V. B., Koshy, J. J., Mathew, B., Valsan, A., Kim, H., & Nath, L. R. (2023). Decoding Immune Signature to Detect the Risk for Early-Stage HCC Recurrence. Cancers, 15(10), 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102729