Centrosome Amplification Is a Potential Molecular Target in Paediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primary Human Patient Samples
2.2. Immortal Cell-Lines
2.3. In Vitro Drug Profiling of Primary B-ALL Cells
2.4. Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. Generation of 289 Cells Resistant to CCIs
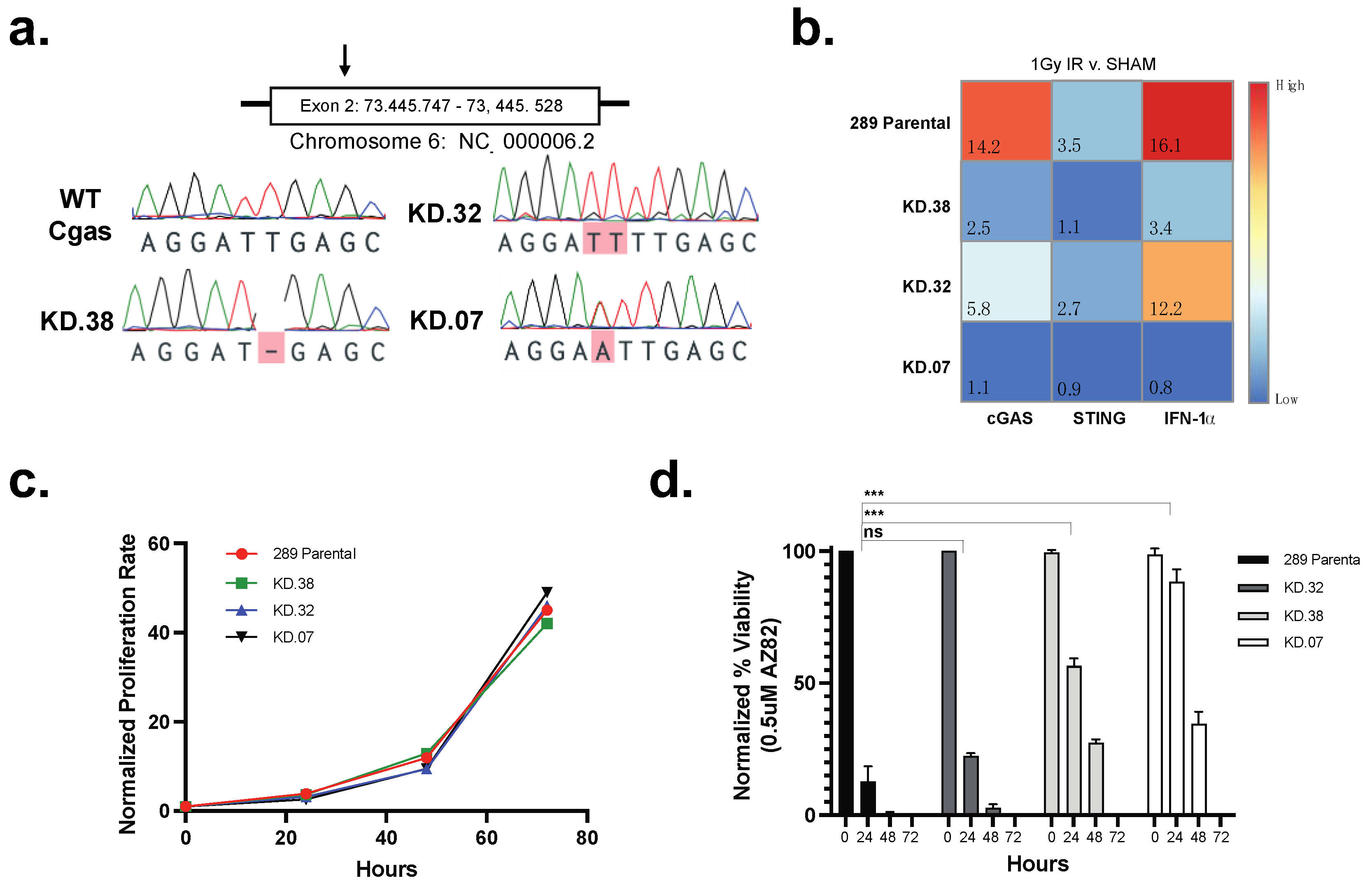
2.6. Generation of 289 cGAS Knock-Down Clones Using CRISPR-Cas9
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Confocal Microscopy and Image Acquisition
2.9. High-Content Imaging
2.10. TaqMan Mouse Immune Array
2.11. qPCR Analysis of cGAS Knock-Down Clones
2.12. Statistics
3. Results
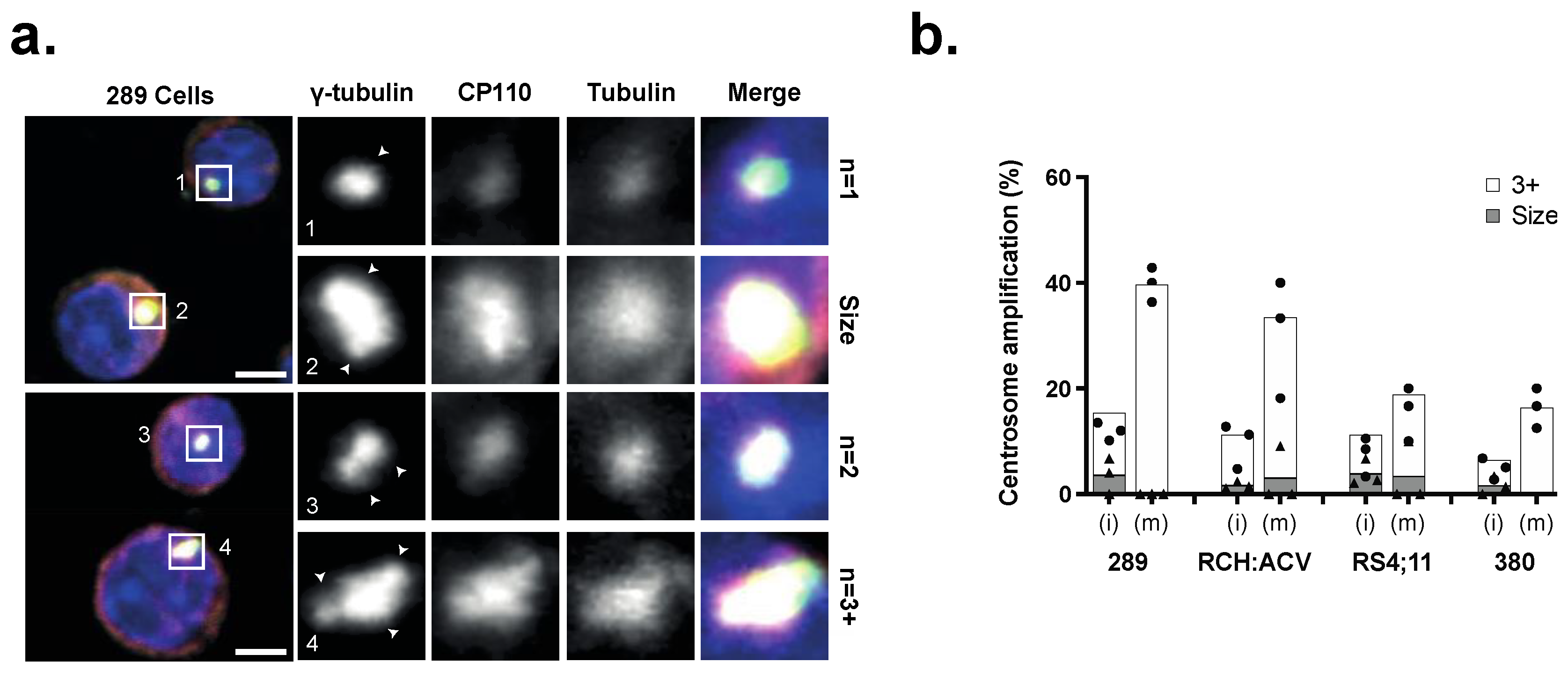
3.1. Centrosome Clustering Is Required for the Viability of B-ALL Cell Lines
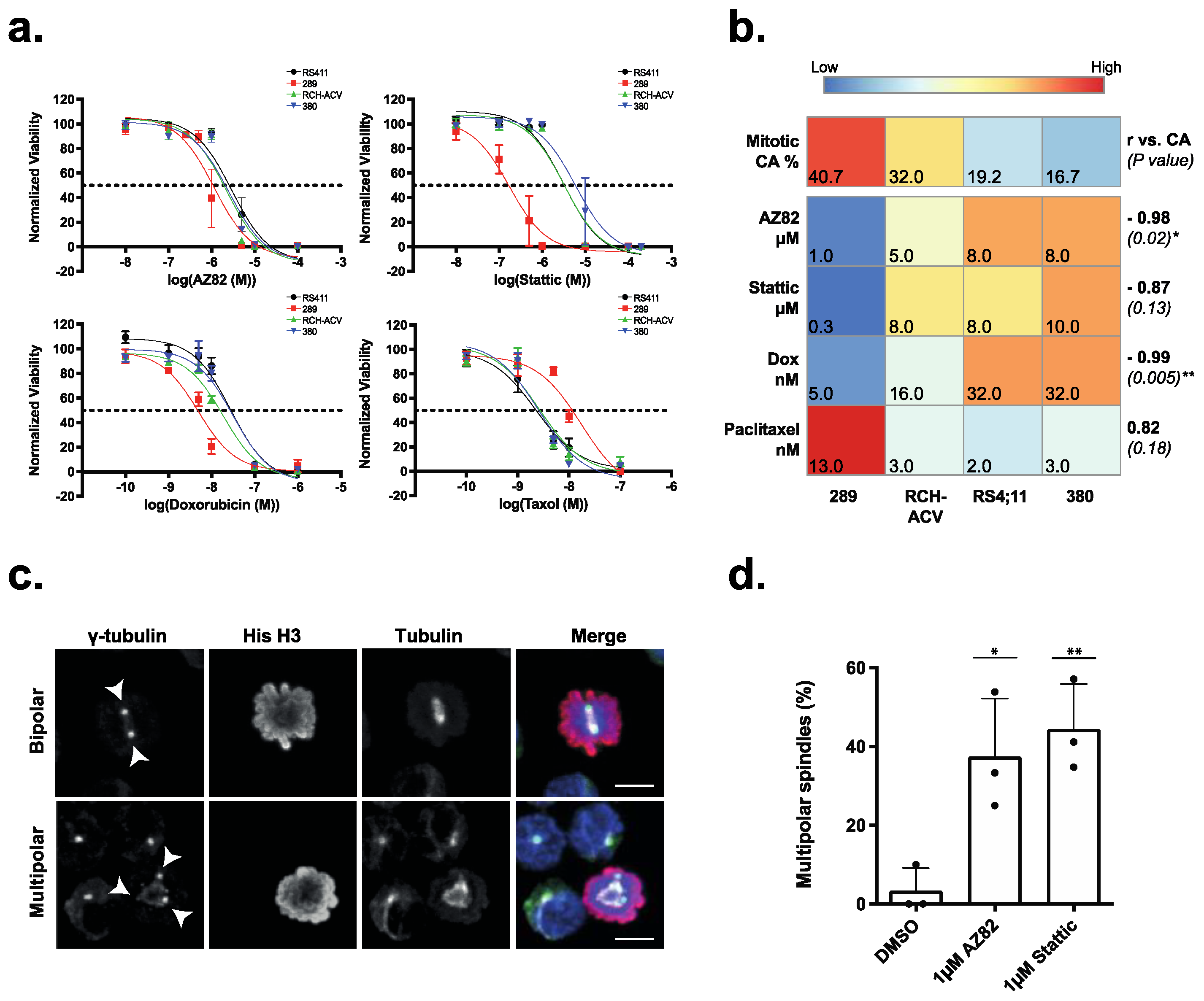
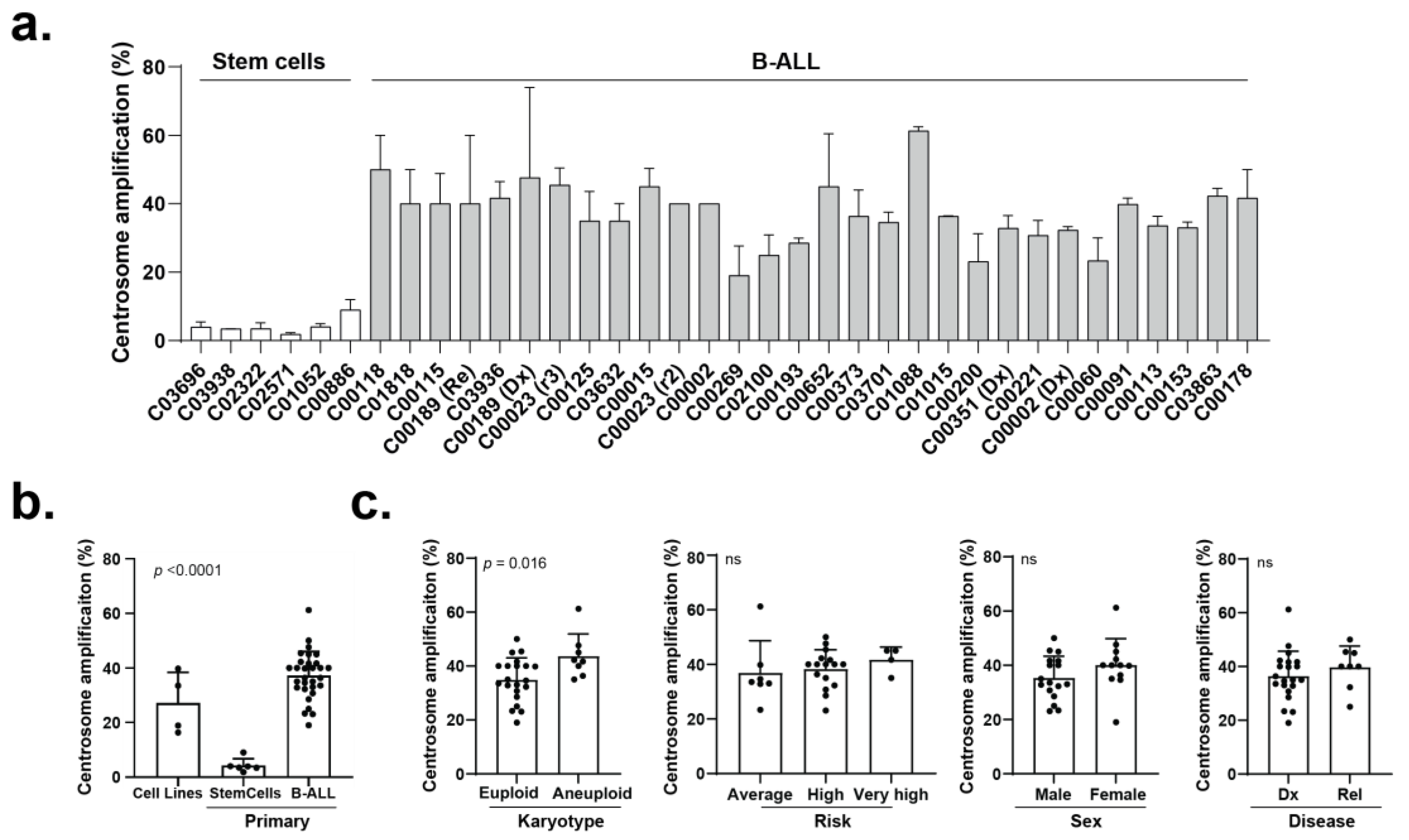
3.2. The Efficacy of CCIs Correlates with the Levels of CA Measured in Primary B-ALL Patient Samples
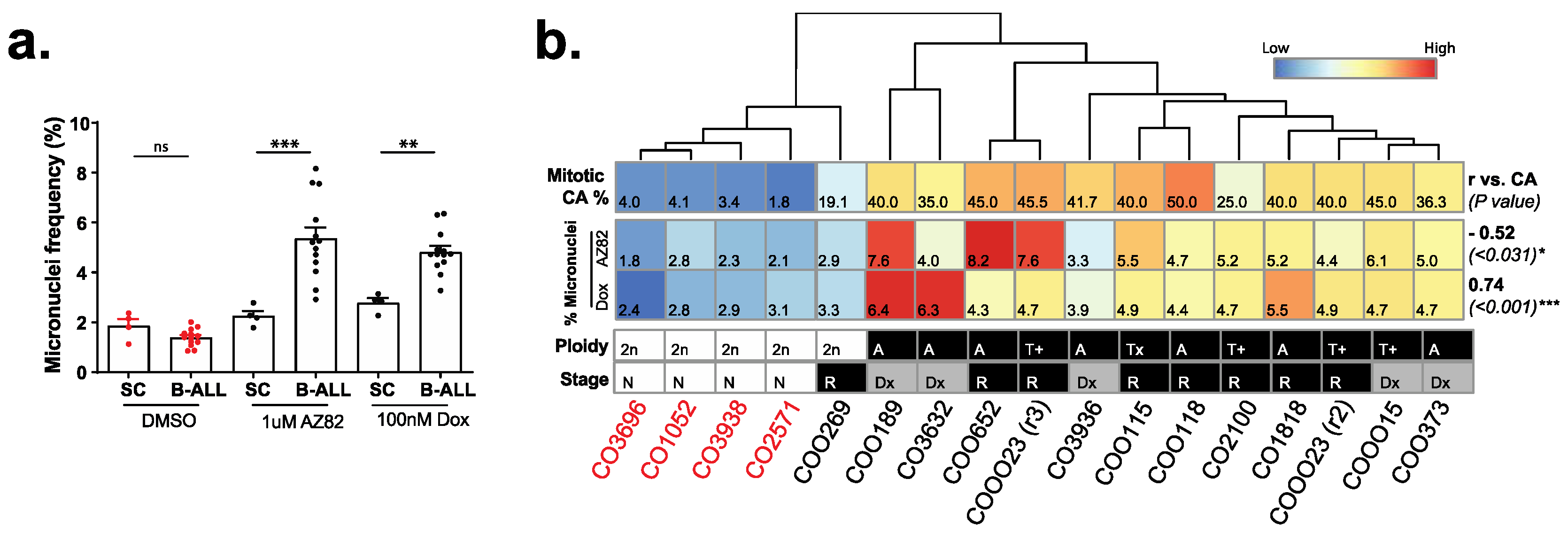
3.3. B-ALL Cells Refractory to CCIs Display Markers for Genome Instability and Activate cGAS-NF κB Proinflammatory Signaling
3.4. cGAS Is Necessary for 289 B-ALL Cell Responses to CCI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ward, E.; DeSantis, C.; Robbins, A.; Kohler, B.; Jemal, A. Childhood and adolescent cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.A.; Seibel, N.L.; Altekruse, S.F.; Ries, L.A.; Melbert, D.L.; O’Leary, M.; Smith, F.O.; Reaman, G.H. Outcomes for children and adolescents with cancer: Challenges for the twenty-first century. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2625–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouvarine, P.; Antić, Ž.; Lentes, J.; Schröder, C.; Alten, J.; Brüggemann, M.; Carrillo-de Santa Pau, E.; Illig, T.; Laguna, T.; Schewe, D.; et al. Transcriptional and mutational profiling of b-other acute lymphoblastic leukemia for improved diagnostics. Cancers 2021, 13, 5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Boer, M.L.; van Slegtenhorst, M.; De Menezes, R.X.; Cheok, M.H.; Buijs-Gladdines, J.G.; Peters, S.T.; Van Zutven, L.J.; Beverloo, H.B.; Van der Spek, P.J.; Escherich, G.; et al. A subtype of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with poor treatment outcome: A genome-wide classification study. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-F.; Dai, Y.-T.; Lilljebjörn, H.; Shen, S.-H.; Cui, B.-W.; Bai, L.; Liu, Y.-F.; Qian, M.-X.; Kubota, Y.; Kiyoi, H.; et al. Transcriptional landscape of B cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia based on an international study of 1,223 cases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11711–E11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lühmann, J.L.; Stelter, M.; Wolter, M.; Kater, J.; Lentes, J.; Bergmann, A.K.; Schieck, M.; Göhring, G.; Möricke, A.; Cario, G.; et al. The clinical utility of optical genome mapping for the assessment of genomic aberrations in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsson, K.; Johansson, B. High hyperdiploid childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2009, 48, 637–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, A.V.; Richards, S.M.; Martineau, M.; Cheung, K.L.; Robinson, H.M.; Jalali, G.R.; Broadfield, Z.J.; Harris, R.L.; E Taylor, K.; Gibson, B.E.S.; et al. Outcome heterogeneity in childhood high-hyperdiploid acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2003, 102, 2756–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, M.M.; Seif, A.E.; Hunger, S.P. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 4939–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, H.; Fan, H.; Su, B.; Zhang, G.; Dong, L. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of pediatric patients with B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia relapse. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, R.; Li, S.; Dover, D.C.; Sallan, S.; Leisenring, W.; Oeffinger, K.C.; Yasui, Y.; Robison, L.L.; Neglia, J.P. Twenty-five–year follow-up among survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Blood 2008, 111, 5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mahayri, Z.N.; AlAhmad, M.M.; Ali, B.R. Long-Term Effects of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Chemotherapy: Can Recent Findings Inform Old Strategies? Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godinho, S.A.; Pellman, D. Causes and consequences of centrosome abnormalities in cancer. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marthiens, V.; Piel, M.; Basto, R. Never tear us apart—The importance of centrosome clustering. J. Cell. Sci. 2012, 125, 3281–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalkan, B.M.; Ozcan, S.C.; Quintyne, N.J.; Reed, S.L.; Acilan, C. Keep Calm and Carry on with Extra Centrosomes. Cancers 2022, 14, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Z.Y.; Yang, W.X. Molecular mechanisms of kinesin-14 motors in spindle assembly and chromosome segregation. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 2097–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleylein-Sohn, J.; Pöllinger, B.; Ohmer, M.; Nigg, E.A.; Hemmings, B.A.; Wartmann, M. Acentrosomal spindle organization renders cancer cells dependent on the kinesin HSET. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5391–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavali, P.L.; Chandrasekaran, G.; Barr, A.R.; Tátrai, P.; Taylor, C.; Papachristou, E.K.; Woods, C.G.; Chavali, S.; Gergely, F. A CEP215-HSET complex links centrosomes with spindle poles and drives centrosome clustering in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Godinho, S.A.; Chandhok, N.S.; Ganem, N.J.; Azioune, A.; Thery, M.; Pellman, D. Mechanisms to suppress multipolar divisions in cancer cells with extra centrosomes. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 2189–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Mikule, K.; Wang, W.; Su, N.; Petteruti, P.; Gharahdaghi, F.; Code, E.; Zhu, X.; Jacques, K.; Lai, Z.; et al. Discovery and mechanistic study of a small molecule inhibitor for motor protein KIFC1. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2201–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johmura, Y.; Soung, N.-K.; Park, J.-E.; Yu, L.-R.; Zhou, M.; Bang, J.K.; Kim, B.-Y.; Veenstra, T.D.; Erikson, R.L.; Lee, K.S. Regulation of microtubule-based microtubule nucleation by mammalian polo-like kinase 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11446–11451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schust, J.; Sperl, B.; Hollis, A.; Mayer, T.U.; Berg, T. Stattic: A Small-Molecule Inhibitor of STAT3 Activation and Dimerization. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.J.; Kawamura, E.; Gillespie, J.A.; Balgi, A.; Kannan, N.; Muller, W.J.; Roberge, M.; Dedhar, S. Stat3 regulates centrosome clustering in cancer cells via Stathmin/PLK1. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, M. A causal mechanism for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, O.; Vinyoles, M.; Granada, I.; Roca-Ho, H.; Gutierrez-Agüera, F.; Valledor, L.; López-López, C.M.; Rodríguez-González, P.; Trincado, J.L.; Tirados-Menéndez, S.; et al. Impaired condensin complex and Aurora B kinase underlie mitotic and chromosomal defects in hyperdiploid B-cell ALL. Blood 2020, 136, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerketta, L.S.; Ghosh, K.; Nadkarni, A.; Madkaikar, M.; Vundinti, B.R. Centrosome Aberration Frequency and Disease Association in B-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. In Vivo 2017, 31, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wasserman, R.; Zeng, X.X.; Hardy, R.R. The Evolution of B Precursor Leukemia in the Eμ-ret Mouse. Blood 1998, 92, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.X.; Zhang, H.; Hardy, R.R.; Wasserman, R. The Fetal Origin of B-Precursor Leukemia in the Eμ-ret Mouse. Blood 1998, 92, 3529–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frismantas, V.; Dobay, M.P.; Rinaldi, A.; Tchinda, J.; Dunn, S.H.; Kunz, J.; Richter-Pechanska, P.; Marovca, B.; Pail, O.; Jenni, S.; et al. Ex vivo drug response profiling detects recurrent sensitivity patterns in drug-resistant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, e26–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Chai, S.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Si, J.; Huang, F.; et al. KIF5B-RET fusion kinase promotes cell growth by multilevel activation of STAT3 in lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Suh, J.M.; Kim, H.; Song, J.H.; Hwang, E.S.; Park, K.C.; Chung, H.K.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, T.-H.; et al. Activation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 by Oncogenic RET/PTC (Rearranged in Transformation/Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma) Tyrosine Kinase: Roles in Specific Gene Regulation and Cellular Transformation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godinho, S.A.; Picone, R.; Burute, M.; Dagher, R.; Su, Y.; Leung, C.T.; Polyak, K.; Brugge, J.S.; Théry, M.; Pellman, D. Oncogene-like induction of cellular invasion from centrosome amplification. Nature 2014, 510, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, K.; Kaur, J.; Jaczko, M.; Wei, G.; Toss, M.S.; Rakha, E.A.; Janssen, E.A.M.; Søiland, H.; Kucuk, O.; Reid, M.D.; et al. Centrosome amplification: A quantifiable cancer cell trait with prognostic value in solid malignancies. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 40, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.Y. A Clinical Overview of Centrosome Amplification in Human Cancers. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, C.A.; Keats, J.J.; Belch, A.R.; Pilarski, L.M.; Reiman, T. Receptor for Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility Correlates with Centrosome Abnormalities in Multiple Myeloma and Maintains Mitotic Integrity. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Mei, L.; Connell, M.; Maxwell, C.A. Hyaluronan Mediated Motility Receptor (HMMR) Encodes an Evolutionarily Conserved Homeostasis, Mitosis, and Meiosis Regulator Rather than a Hyaluronan Receptor. Cells 2020, 9, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chng, W.J.; Ahmann, G.J.; Henderson, K.; Santana-Davila, R.; Greipp, P.R.; Gertz, M.A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Dispenzieri, A.; Kumar, S.; Rajkumar, S.V.; et al. Clinical implication of centrosome amplification in plasma cell neoplasm. Blood 2006, 107, 3669–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cells 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, P.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Ye, L.; He, Y.; et al. CGAS-STING, an important pathway in cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, M.; Rever, J.; Nguyen, P.N.U.; Akella, N.M.; Reid, G.S.D.; Maxwell, C.A. Centrosome Amplification Is a Potential Molecular Target in Paediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2023, 15, 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010154
Guo M, Rever J, Nguyen PNU, Akella NM, Reid GSD, Maxwell CA. Centrosome Amplification Is a Potential Molecular Target in Paediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers. 2023; 15(1):154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010154
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Meiyun, Jenna Rever, Phuong N. U. Nguyen, Neha M. Akella, Gregor S. D. Reid, and Christopher A. Maxwell. 2023. "Centrosome Amplification Is a Potential Molecular Target in Paediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia" Cancers 15, no. 1: 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010154
APA StyleGuo, M., Rever, J., Nguyen, P. N. U., Akella, N. M., Reid, G. S. D., & Maxwell, C. A. (2023). Centrosome Amplification Is a Potential Molecular Target in Paediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers, 15(1), 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010154





