Identification of Thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridine Derivatives as c-KIT Inhibitors for Overcoming Imatinib Resistance
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Cell Culture and Reagent
2.3. In Vitro Kinase Assay
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. Molecular Docking Study
2.6. Kinase Panel Profiling
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis Analysis
2.9. Migration Assay
2.10. Invasion Assay
2.11. Soft Agar Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridine Derivatives
3.2. Structure-Activity Relationships
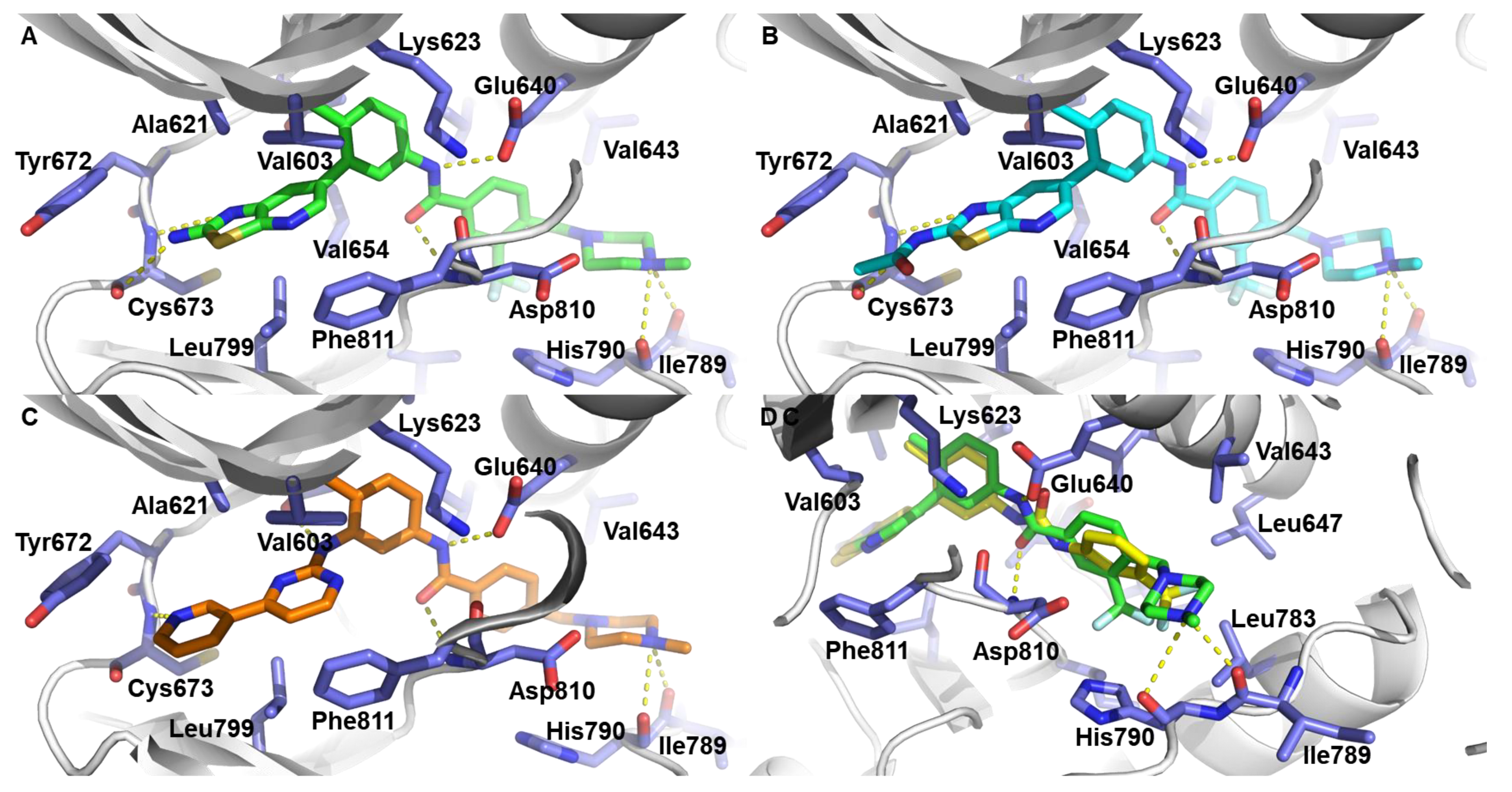
3.3. Molecular Docking Studies of 6j, 6r, and 7c with c-KIT
3.4. Kinase Panel Profiling of 6r
3.5. Inhibition of c-KIT Signaling in GIST-T1, HMC1.2, and c-KIT D816V Ba/F3 Cells
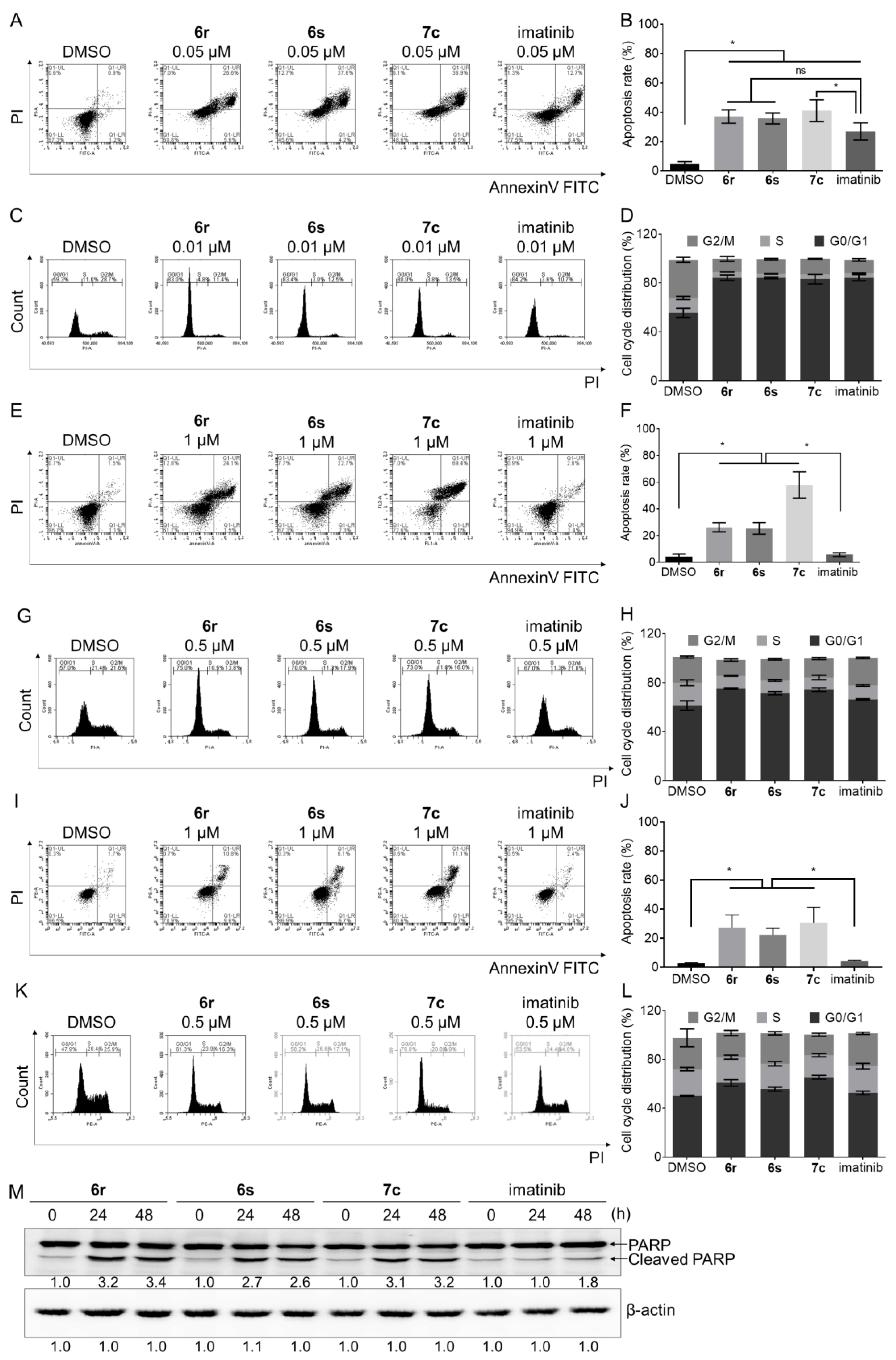
3.6. Induction of Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in GIST- T1 and HMC1.2 Cells
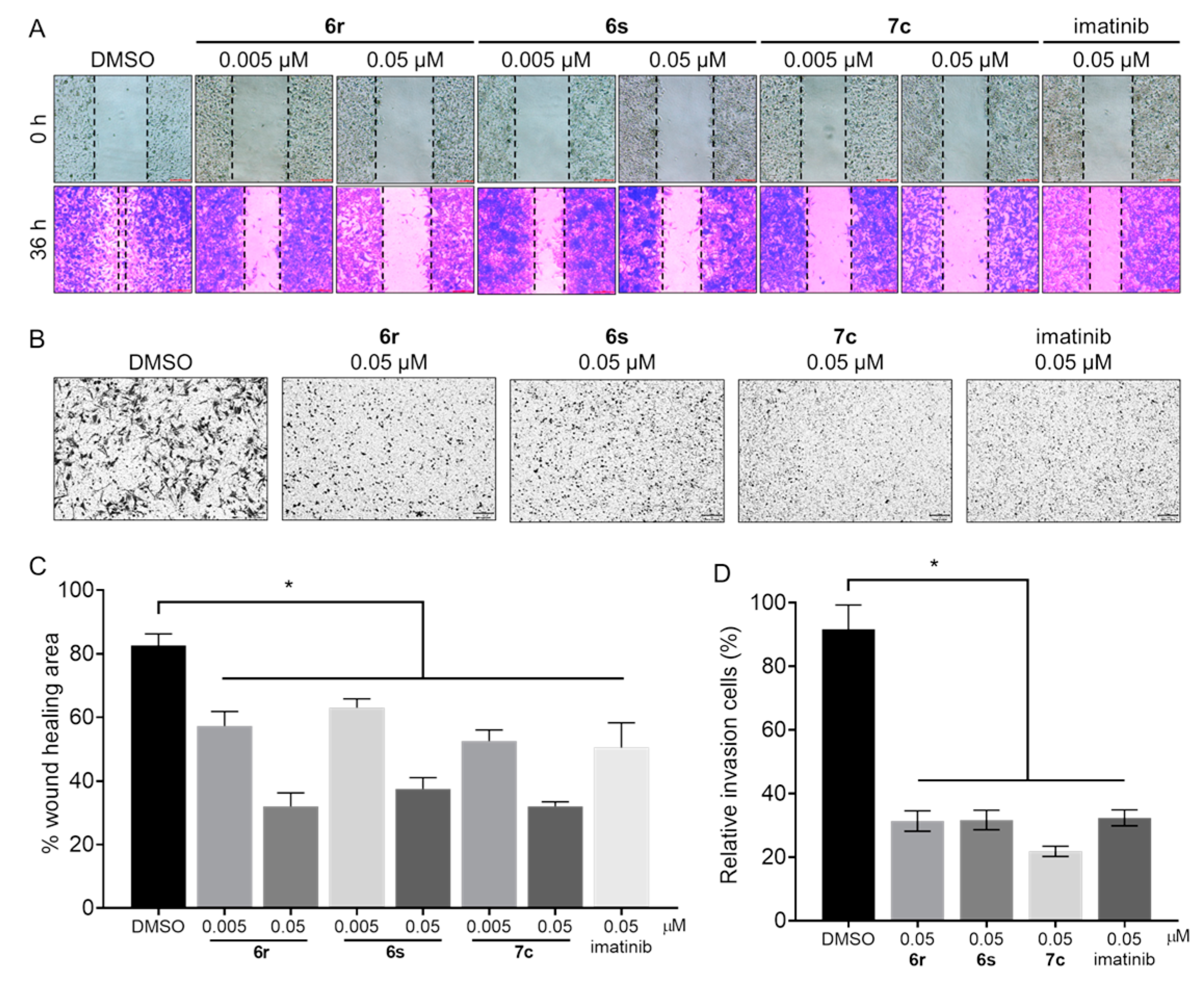
3.7. Suppression of Migration and Invasion in GIST-T1 Cells
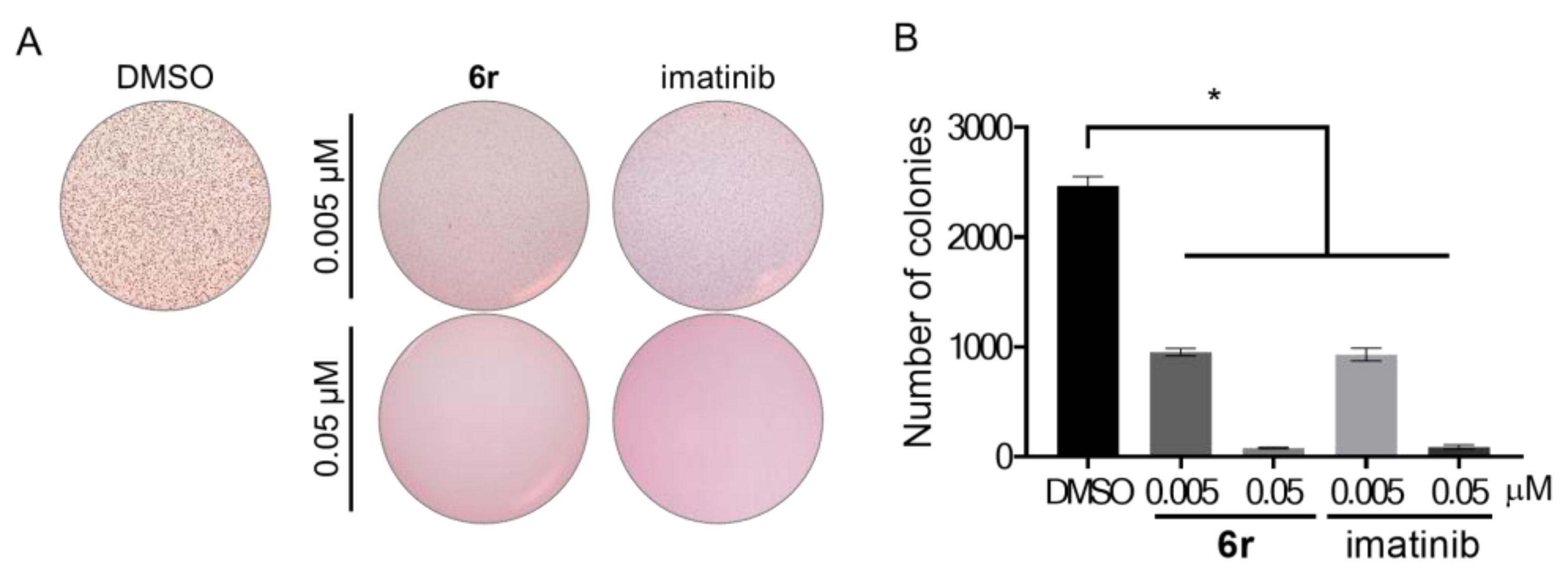
3.8. Suppression of Anchorage-Independent Growth in GIST-T1 Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Broudy, V.C.; Lin, N.L.; Sabath, D.F. The fifth immunoglobulin-like domain of the Kit receptor is required for proteolytic cleavage from the cell surface. Cytokine 2001, 15, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Silva, C.M.; Reid, R. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST): C-kit mutations, CD117 expression, differential diagnosis and targeted cancer therapy with Imatinib. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2003, 9, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittoni, P.; Piconese, S.; Tripodo, C.; Colombo, M.P. Tumor-intrinsic and-extrinsic roles of c-Kit: Mast cells as the primary off-target of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncogene 2011, 30, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.A.; Kamalidehghan, B.; Saleem, M.; Huri, H.Z.; Ahmadipour, F. Receptor tyrosine kinase (c-Kit) inhibitors: A potential therapeutic target in cancer cells. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 2443–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Ali, S. Role of c-kit/SCF in cause and treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST). Gene 2007, 401, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corless, C.L.; Fletcher, J.A.; Heinrich, M.C. Biology of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 3813–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigen, S.E.; Eide, T.J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs): A review. Apmis 2009, 117, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabone-Eglinger, S.; Subra, F.; El Sayadi, H.; Alberti, L.; Tabone, E.; Michot, J.-P.; Théou-Anton, N.; Lemoine, A.; Blay, J.-Y.; Emile, J.-F. KIT mutations induce intracellular retention and activation of an immature form of the KIT protein in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wu, Y.-L.; Chen, B.-J.; Zhang, W.; Tanaka, Y.; Sugiyama, H. The C-Kit receptor-mediated signal transduction and tumor-related diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corless, C.L.; Barnett, C.M.; Heinrich, M.C. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: Origin and molecular oncology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonescu, C.R.; Sommer, G.; Sarran, L.; Tschernyavsky, S.J.; Riedel, E.; Woodruff, J.M.; Robson, M.; Maki, R.; Brennan, M.F.; Ladanyi, M.; et al. Association of KIT exon 9 mutations with nongastric primary site and aggressive behavior: KIT mutation analysis and clinical correlates of 120 gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 3329–3337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vincenzi, B.; Napolitano, A.; Fiocco, M.; Mir, O.; Rutkowski, P.; Blay, J.-Y.; Reichardt, P.; Joensuu, H.; Fumagalli, E.; Gennatas, S.; et al. Adjuvant imatinib in patients with GIST harboring exon 9 KIT mutations: Results from a multi-institutional european retrospective study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, A.; Vincenzi, B. Secondary KIT mutations: The GIST of drug resistance and sensitivity. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, C.; Mariño-Enríquez, A.; Tao, D.L.; Ketzer, J.; Eilers, G.; Zhu, M.; Yu, C.; Mannan, A.M.; Rubin, B.P.; Demetri, G.D.; et al. Complementary activity of tyrosine kinase inhibitors against secondary kit mutations in imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Bosbach, B.; Loo, J.K.; Vitiello, G.A.; Zeng, S.; Seifert, A.M.; Medina, B.D.; Param, N.J.; Maltbaek, J.H.; Rossi, F.; et al. The V654A second-site KIT mutation increases tumor oncogenesis and STAT activation in a mouse model of gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Oncogene 2020, 39, 7153–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, A.; Liu, J.; Qi, Z.; Liu, X.; Yu, K.; Wu, H.; Chen, C.; Hu, C.; Wang, W.; et al. Discovery of N-((1-(4-(3-(3-((6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-3-yl)oxy)phenyl)ureido)-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)piperidin-4-yl)methyl)propionamide (CHMFL-KIT-8140) as a highly potent type II inhibitor capable of inhibiting the T670I “Gatekeeper” mutant of cKIT kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 8456–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, T.; Pavan, G.M.; Virdis, E.; Greco, A.; Fermeglia, M.; Sandri, M.; Pricl, S.; Pierotti, M.A.; Pilotti, S.; Tamborini, E. T670X KIT mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Making sense of missense. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajiwala, K.S.; Wu, J.C.; Christensen, J.; Deshmukh, G.D.; Diehl, W.; DiNitto, J.P.; English, J.M.; Greig, M.J.; He, Y.-A.; Jacques, S.L.; et al. KIT kinase mutants show unique mechanisms of drug resistance to imatinib and sunitinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumor patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1542–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zeng, S.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Akin, C.; Dimitrijevic, S.; Butterfield, J.H.; McMahon, G.; Longley, B.J. The c-KIT mutation causing human mastocytosis is resistant to STI571 and other KIT kinase inhibitors; kinases with enzymatic site mutations show different inhibitor sensitivity profiles than wild-type kinases and those with regulatory-type mutations. Blood 2002, 99, 1741–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; La Rosée, P. Imatinib therapy in chronic myelogenous leukemia: Strategies to avoid and overcome resistance. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.F.; Bacchi, C.E. Imatinib treatment for gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST). J. Cell Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetri, G.D.; Reichardt, P.; Kang, Y.-K.; Blay, J.-Y.; Rutkowski, P.; Gelderblom, H.; Hohenberger, P.; Leahy, M.; Von Mehren, M.; Joensuu, H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of regorafenib for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours after failure of imatinib and sunitinib (GRID): An international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.-N.; Chen, M.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Yen, C.-C.; Tzen, C.-Y.; Chen, L.-T.; Chen, J.-S. A phase II trial of regorafenib in patients with metastatic and/or a unresectable gastrointestinal stromal tumor harboring secondary mutations of exon 17. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44121–44130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lübke, J.; Naumann, N.; Kluger, S.; Schwaab, J.; Metzgeroth, G.; Evans, E.; Gardino, A.K.; Lengauer, C.; Hofmann, W.-K.; Fabarius, A.; et al. Inhibitory effects of midostaurin and avapritinib on myeloid progenitors derived from patients with KIT D816V positive advanced systemic mastocytosis. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunewald, S.; Klug, L.R.; Mühlenberg, T.; Lategahn, J.; Falkenhorst, J.; Town, A.; Ehrt, C.; Wardelmann, E.; Hartmann, W.; Schildhaus, H.-U.; et al. Resistance to avapritinib in PDGFRA-driven GIST is caused by secondary mutations in the PDGFRA kinase domain. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.D.; Kaufman, M.D.; Lu, W.-P.; Gupta, A.; Leary, C.B.; Wise, S.C.; Rutkoski, T.J.; Ahn, Y.M.; Al-Ani, G.; Bulfer, S.L.; et al. Ripretinib (DCC-2618) is a switch control kinase inhibitor of a broad spectrum of oncogenic and drug-resistant KIT and PDGFRA variants. Cancer cell 2019, 35, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, C.; George, S. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor: Challenges and opportunities for a new decade. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5078–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Mao, F.; Li, X.; Zheng, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Li, J. Discovery of potent, selective stem cell factor receptor/platelet derived growth factor receptor alpha (c-KIT/PDGFRα) dual inhibitor for the treatment of imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 5099–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-S.; Lin, W.-H.; Tsai, H.-J.; Hsueh, C.-C.; Hsu, T.; Wang, P.-C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Peng, Y.-H.; Lu, C.-T.; Lee, L.-C.; et al. Discovery of conformational control inhibitors switching off the activated c-KIT and targeting a broad range of clinically relevant c-KIT mutants. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 3940–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Zhang, K.; Tian, H.; Dong, Y.; Xu, H. Identification of novel thiazolo [5,4-b]pyridine derivatives as potent phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors. Molecules 2020, 25, 4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harling, J.D.; Deakin, A.M.; Campos, S.; Grimley, R.; Chaudry, L.; Nye, C.; Polyakova, O.; Bessant, C.M.; Barton, N.; Somers, D.; et al. Discovery of novel irreversible inhibitors of interleukin (IL)-2-inducible tyrosine kinase (Itk) by targeting cysteine 442 in the ATP pocket. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 28195–28206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.G.; Zhang, J.; Weisberg, E.; Griffin, J.D.; Sim, T.; Gray, N.S. Development of ‘DFG-out’ inhibitors of gatekeeper mutant kinases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 5297–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okaniwa, M.; Hirose, M.; Imada, T.; Ohashi, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Arita, T.; Yabuki, M.; Kakoi, K.; Kato, J.; et al. Design and synthesis of novel DFG-out RAF/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) inhibitors. 1. exploration of [5,6]-fused bicyclic scaffolds. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3452–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, M.; Okaniwa, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Imada, T.; Ohashi, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Arita, T.; Yabuki, M.; Kawamoto, T.; Tsutsumi, S.; et al. Design and synthesis of novel DFG-out RAF/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) inhibitors: 3. evaluation of 5-amino-linked thiazolo [5,4-d]pyrimidine and thiazolo [5,4-b]pyridine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 5600–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, A.P.; Gozgit, J.M.; Anjum, R.; Vodala, S.; Schrock, A.; Zhou, T.; Serrano, C.; Eilers, G.; Zhu, M.; Ketzer, J.; et al. Ponatinib inhibits polyclonal drug-resistant KIT oncoproteins and shows therapeutic potential in heavily pretreated gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5745–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Shin, I.; Ju, E.; Choi, S.; Hur, W.; Kim, H.; Hong, E.; Kim, N.D.; Choi, H.G.; Gray, N.S.; et al. First SAR study for overriding NRAS mutant driven acute myeloid leukemia. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 8353–8373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, T.; Sonobe, H.; Toyonaga, S.-I.; Yamasaki, I.; Shuin, T.; Takano, A.; Araki, K.; Akimaru, K.; Yuri, K. Conventional and molecular cytogenetic characterization of a new human cell line, GIST-T1, established from gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Lab. Investig. 2002, 82, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundström, M.; Vliagoftis, H.; Karlberg, P.; Butterfield, J.H.; Nilsson, K.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Nilsson, G. Functional and phenotypic studies of two variants of a human mast cell line with a distinct set of mutations in the c-kit proto-oncogene. Immunology 2003, 108, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furitsu, T.; Tsujimura, T.; Tono, T.; Ikeda, H.; Kitayama, H.; Koshimizu, U.; Sugahara, H.; Butterfield, J.H.; Ashman, L.K.; Kanayama, Y. Identification of mutations in the coding sequence of the proto-oncogene c-kit in a human mast cell leukemia cell line causing ligand-independent activation of c-kit product. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, C.D.; Dougen, D.R.; Schneider, T.R.; Skene, R.J.; Kraus, M.L.; Scheibe, D.N.; Snell, G.P.; Zou, H.; Sang, B.-C.; Wilson, K.P. Structural basis for the autoinhibition and STI-571 inhibition of c-Kit tyrosine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 31655–31663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, S.; Turk, S.; Volkamer, A.; Rippmann, F.; Fulle, S. KinMap: A web-based tool for interactive navigation through human kinome data. BMC Bioinf. 2017, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Sebastian, J.; Montiel-Cervantes, L.A.; Reyes-Maldonado, E.; Dominguez-Lopez, M.L.; Ortiz-Butron, R.; Castillo-Alvarez, A.; Lezama, R.A. Cell proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis are related to c-Kit activation in leukaemic lymphoblasts. Hematology 2018, 23, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.; Steelman, L.S.; Shelton, J.G.; Lee, J.T.; Navolanic, P.M.; Blalock, W.L.; Franklin, R.; McCubrey, J.A. Regulation of cell cycle progression and apoptosis by the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2003, 22, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Duensing, A.; Demetri, G.D.; Fletcher, J.A. KIT oncogenic signaling mechanisms in imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor: PI3-kinase/AKT is a crucial survival pathway. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7560–7568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosbach, B.; Rossi, F.; Yozgat, Y.; Loo, J.; Zhang, J.Q.; Berrozpe, G.; Warpinski, K.; Ehlers, I.; Veach, D.; Kwok, A.; et al. Direct engagement of the PI3K pathway by mutant KIT dominates oncogenic signaling in gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8448–E8457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juurikivi, A.; Sandler, C.; Lindstedt, K.A.; Kovanen, P.T.; Juutilainen, T.; Leskinen, M.J.; Mäki, T.; Eklund, K.K. Inhibition of c-kit tyrosine kinase by imatinib mesylate induces apoptosis in mast cells in rheumatoid synovia: A potential approach to the treatment of arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Weng, X.; Lin, G.; Huang, Z.; Shui, H. Establishment of a GIST-T1 gastrointestinal stromal tumour cell line resistant to imatinib mesylate. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 7589–7594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, X.; Xue, A.; Gao, X.; Shen, K. THZ1 targeting CDK7 suppresses c-KIT transcriptional activity in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | R1 | R2 | IC50 (μM) a | Entry | R1 | R2 | IC50 (μM) a |
| imatinib | - | - | 0.27 | 6p | 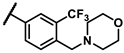 | - | 5.72 |
| sunitinib | - | - | 0.14 | 6q |  | - | 3.23 |
| 6a | 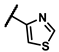 | - | inactiveb | 6r | 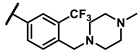 | - | 0.14 |
| 6b | 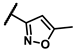 | - | inactiveb | 6s | 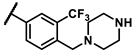 | - | 0.37 |
| 6c | 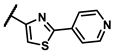 | - | inactiveb | 6t | 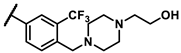 | - | 1.25 |
| 6d |  | - | inactiveb | 6u |  | - | 4.56 |
| 6e | 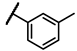 | - | inactiveb | 6v | 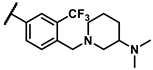 | - | 0.39 |
| 6f | 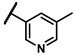 | - | inactiveb | 6w | 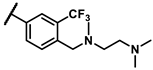 | - | 0.25 |
| 6g | 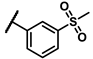 | - | inactiveb | 7a | 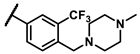 | cyclohexyl | 1.51 |
| 6h | 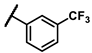 | - | 9.87 | 7b | 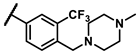 | phenyl | 0.74 |
| 6i |  | - | inactiveb | 7c | 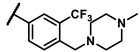 | methyl | 0.10 |
| 6j |  | - | inactiveb | 7d | 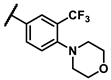 | cyclohexyl | inactiveb |
| 6k | 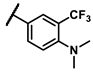 | - | 4.31 | 7e | 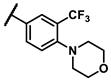 | methyl | 0.88 |
| 6l | 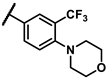 | - | 1.76 | 7f | 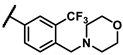 | methyl | 3.63 |
| 6m | 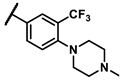 | - | 2.17 | 7g | 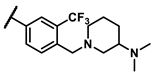 | methyl | 0.18 |
| 6n | 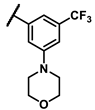 | - | Inactive b | 7h | 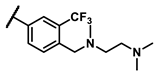 | methyl | 0.10 |
| 6o | 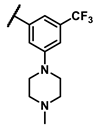 | - | 5.03 | ||||
| Entry | GI50 (μM) a | Entry | GI50 (μM) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GIST-T1 | HMC1.2 | GIST-T1 | HMC1.2 | ||
| imatinib | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 27.10 ± 3.36 | 6p | 0.66 ± 0.10 | 8.55 ± 2.40 |
| sunitinib | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 2.53 ± 0.35 | 6q | 0.42 ± 0.07 | 15.53 ± 3.97 |
| 6a | > 50 | Inactive b | 6r | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 1.15 ± 0.96 |
| 6b | 33.05 ± 7.09 | Inactive b | 6s | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 1.33 ± 0.43 |
| 6c | 33.69 ± 3.45 | Inactive b | 6t | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 6.62 ± 0.75 |
| 6d | 16.36 ± 2.73 | 25.18 ± 2.21 | 6u | 0.66 ± 0.08 | 11.31 ± 0.34 |
| 6e | 3.45 ± 0.41 | 11.53 ± 0.62 | 6v | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 6.81 ± 0.67 |
| 6f | 20.94 ± 2.00 | inactive b | 6w | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 4.99 ± 0.43 |
| 6g | 10.84 ± 1.06 | 36.77 ± 10.9 | 7a | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 4.58 ± 0.32 |
| 6h | 0.96 ± 0.10 | 7.26 ± 4.13 | 7b | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 5.22 ± 0.59 |
| 6i | 7.16 ± 0.87 | 9.65 ± 1.06 | 7c | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 1.52 ± 0.43 |
| 6j | 3.31 ± 0.73 | 6.35 ± 0.32 | 7d | 8.13 ± 1.81 | inactive b |
| 6k | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 2.27 ± 0.84 | 7e | 0.23 ± 0.07 | 14.04 ± 10.2 |
| 6l | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 4.34 ± 1.31 | 7f | 0.30 ± 0.06 | 28.39 ± 13.3 |
| 6m | 0.27 ± 0.17 | 3.41 ± 1.49 | 7g | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 4.88 ± 1.18 |
| 6n | 0.55 ± 0.09 | 7.00 ± 2.68 | 7h | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 4.98 ± 0.32 |
| 6o | 0.28 ± 0.08 | 2.36 ± 0.58 | |||
| Entry | IC50 (μM) a |
|---|---|
| c-KIT V560G/D816V | |
| imatinib | 37.93 ± 8.68 |
| sunitinib | 3.98 ± 1.18 |
| 6r | 4.77 ± 0.38 |
| 6s | 7.67 ± 2.64 |
| 7c | 5.07 ± 0.71 |
| Entry | Ba/F3 cells GI50 (μM) a | |
|---|---|---|
| c-KIT D816V | Parental | |
| imatinib | 12.25 ± 2.06 | 17.00 ± 0.20 |
| sunitinib | 0.58 ± 0.29 | 2.72 ± 0.30 |
| 6r | 1.11 ± 0.47 | 8.06 ± 0.57 |
| 6s | 1.06 ± 0.15 | 10.54 ± 3.59 |
| 7c | 0.53 ± 0.06 | 10.52 ± 3.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, Y.; Kim, C.; Han, J.; Ryu, S.; Cho, H.; Song, C.; Kim, N.D.; Kim, N.; Sim, T. Identification of Thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridine Derivatives as c-KIT Inhibitors for Overcoming Imatinib Resistance. Cancers 2023, 15, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010143
Nam Y, Kim C, Han J, Ryu S, Cho H, Song C, Kim ND, Kim N, Sim T. Identification of Thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridine Derivatives as c-KIT Inhibitors for Overcoming Imatinib Resistance. Cancers. 2023; 15(1):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010143
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Yunju, Chan Kim, Junghee Han, SeongShick Ryu, Hanna Cho, Chiman Song, Nam Doo Kim, Namkyoung Kim, and Taebo Sim. 2023. "Identification of Thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridine Derivatives as c-KIT Inhibitors for Overcoming Imatinib Resistance" Cancers 15, no. 1: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010143
APA StyleNam, Y., Kim, C., Han, J., Ryu, S., Cho, H., Song, C., Kim, N. D., Kim, N., & Sim, T. (2023). Identification of Thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridine Derivatives as c-KIT Inhibitors for Overcoming Imatinib Resistance. Cancers, 15(1), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010143





