The Role of Age and Comorbidities in Esophagogastric Cancer Chemoradiation of the Frail Elderly (>70 Years): An Analysis from a Tertiary High Volume-Center
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patient Cohort
2.2. Radiotherapy
2.3. Chemotherapy
2.4. Monitoring under Chemoradiation and Associated Supportive Measures
2.5. Aftercare
2.6. Evidence-Based Definitions, Statistical Analysis, and Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Chemotherapy
3.2. Toxicities
3.2.1. Acute
3.2.2. Late
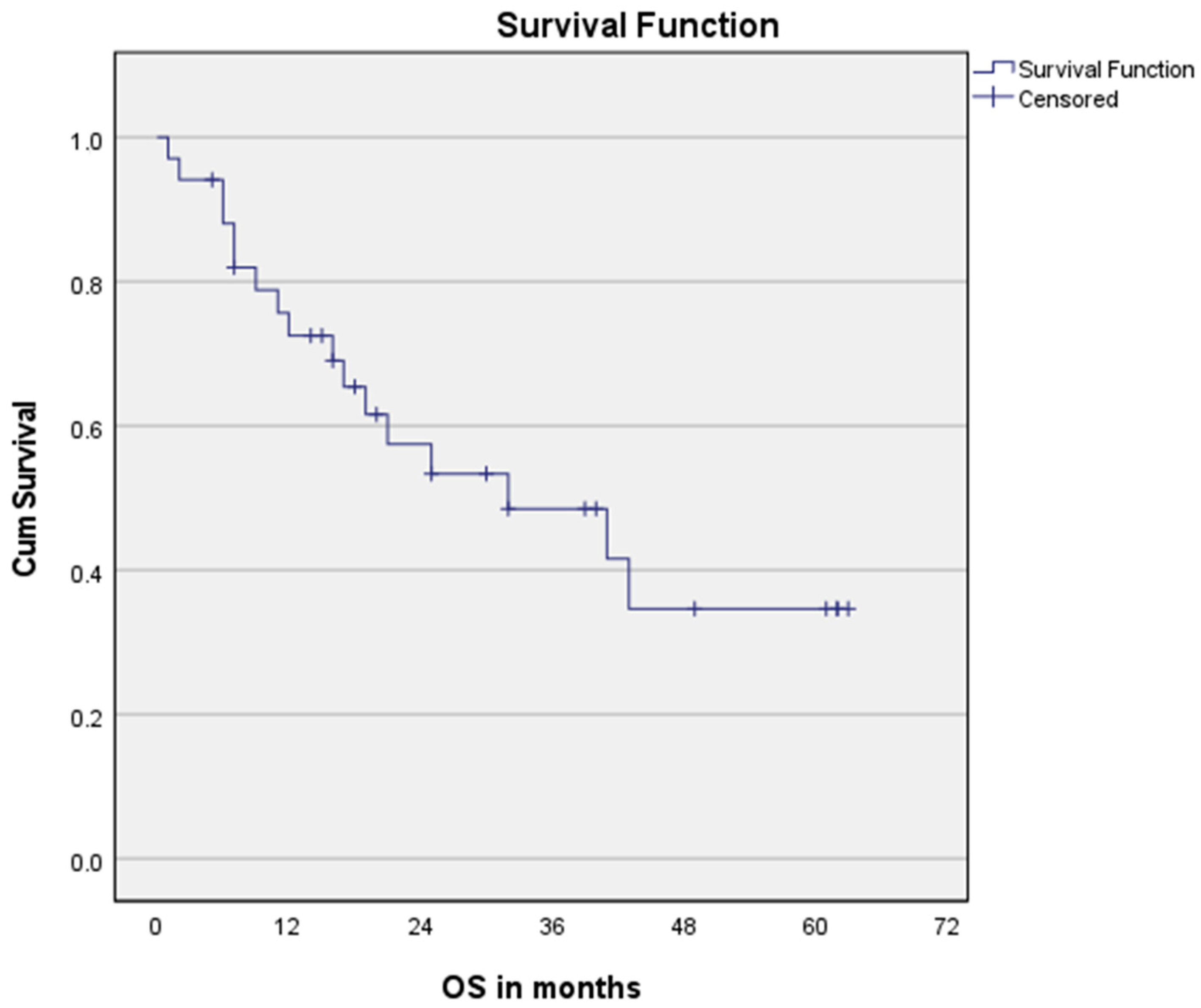
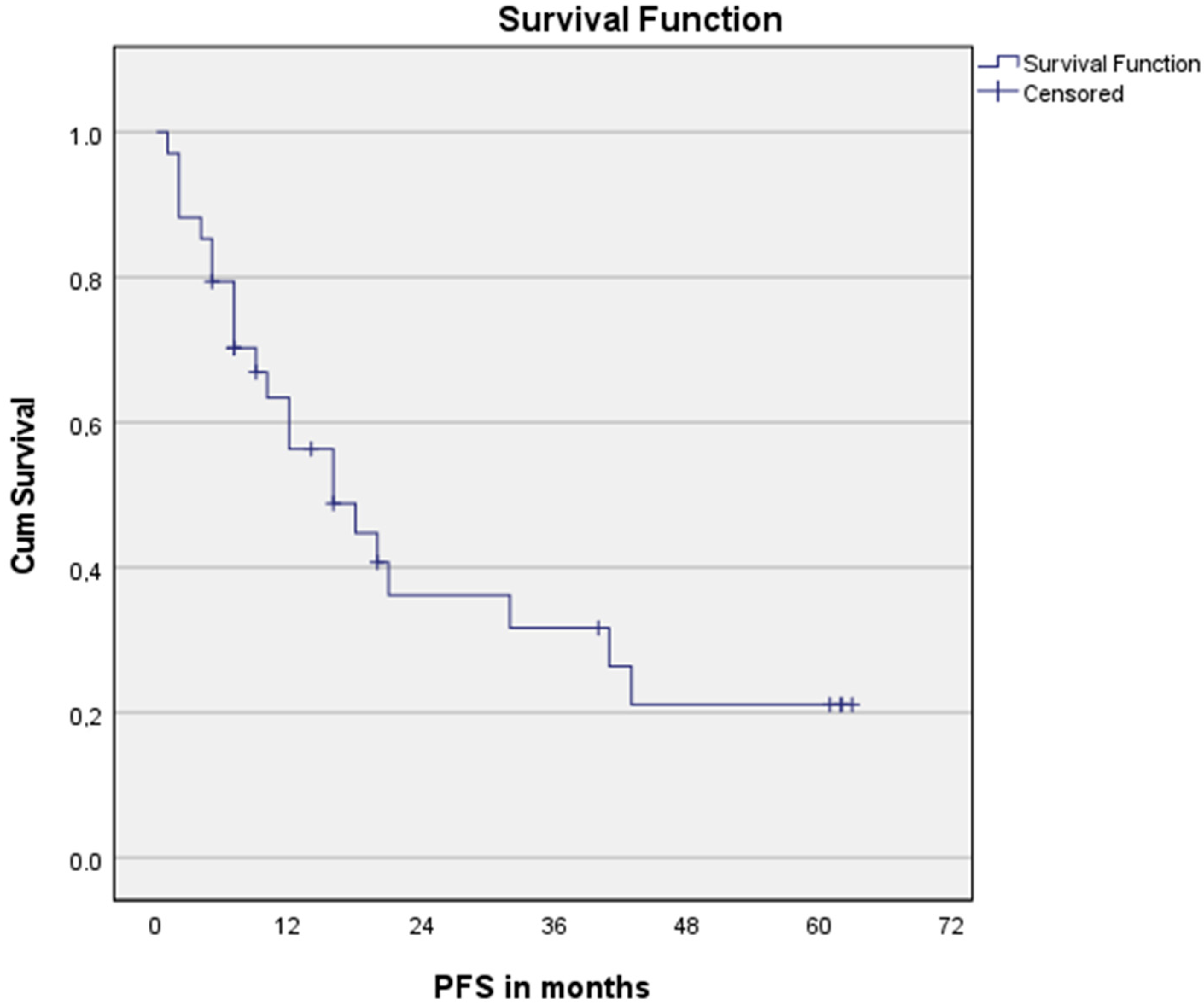
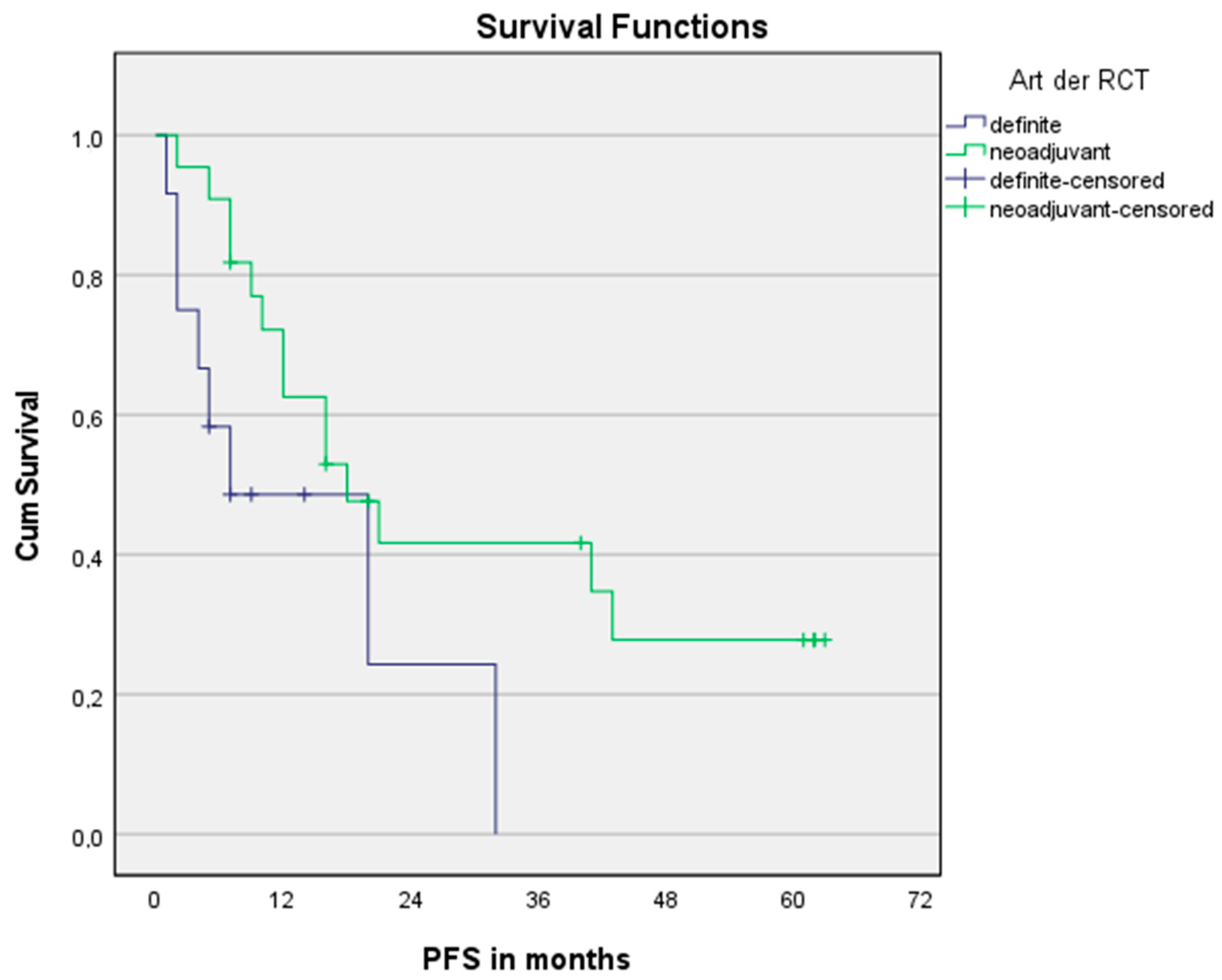
3.3. Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D-CRT | 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy |
| AC | Adenocarcinoma |
| Carb/TAX | Carboplatin and paclitaxel |
| dCRT | Definite chemoradiation therapy |
| EC | Esophageal cancer |
| GTV | Gross target volume |
| Gy | Gray |
| IMRT | Intensity-modulated radiotherapy |
| nCRT | Neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PET/CT | Positron emission tomography/computed tomography |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| PTV | Planning target volume |
| SCC | Squamous cell carcinoma |
| QOL | Quality of life |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajani, J.A.; D’Amico, T.A.; Bentrem, D.J.; Chao, J.; Corvera, C.; Das, P.; Denlinger, C.S.; Enzinger, P.C.; Fanta, P.; Farjah, F.; et al. Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Cancers, Version 2.2019, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 855–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnal, M.J.D.; Arenas, Á.F.; Arbeloa, Á.L. Esophageal cancer: Risk factors, screening and endoscopic treatment in Western and Eastern countries. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 7933–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Various: Bevölkerungsvorausberechnung–Annahmen zur künftigen Entwicklung der Lebenserwartung, Statistisches Bundesamt (Destatis). 2021. Available online: https://www.destatis.de/DE/Themen/Gesellschaft-Umwelt/Bevoelkerung/Bevoelkerungsvorausberechnung/Methoden/Erlaeuterungen/Sterblichkeit.html (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- OECD. Elderly Population (Indicator). Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/social-issues-migration-health/elderly-population/indicator/english_8d805ea1-en (accessed on 3 September 2022).
- Orimo, H.; Ito, H.; Suzuki, T.; Araki, A.; Hosoi, T.; Sawabe, M. Reviewing the definition of “elderly”. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2006, 6, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.C.; Royce, T.J.; Extermann, M.; Reeve, B.B. Impact of age and comorbidity on treatment and outcomes in elderly cancer patients. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 22, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Kanapuru, B.; Smith, C.; Fashoyin-Aje, L.A.; Myers, A.; Kim, G.; Pazdur, R. FDA analysis of enrollment of older adults in clinical trials for cancer drug registration: A 10-year experience by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35 (Suppl. 15), 10009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daste, A.; Chakiba, C.; Domblides, C.; Gross-Goupil, M.; Quivy, A.; Ravaud, A.; Soubeyran, P. Targeted therapy and elderly people: A review. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 69, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, S.M.; Kate, F.J.W.T.; Reitsma, J.B.; Busch, O.R.C.; Van Lanschot, J.J.B. Prognostic factors in adenocarcinoma of the esophagus or gastroesophageal junction. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4347–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloubeidi, M.A.; Desmond, R.; Arguedas, M.R.; Reed, C.E.; Wilcox, C.M. Prognostic factors for the survival of patients with esophageal carcinoma in the U.S.: The importance of tumor length and lymph node status. Cancer 2002, 95, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semrau, R.; Herzog, S.; Vallböhmer, D.; Kocher, M.; Hölscher, A.; Müller, R.-P. Radiotherapy in elderly patients with inoperable esophageal cancer. Is there a benefit? Strahlenther. Onkol. 2012, 188, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, S.; Ohtsu, A.; Doi, T.; Kojima, T.; Minashi, K.; Mera, K.; Yano, T.; Tahara, M.; Muto, M.; Nihei, K. A retrospective study of definitive chemoradiotherapy for elderly patients with esophageal cancer. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 30, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hagen, P.; Hulshof, M.C.; van Lanschot, J.J.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Henegouwen, M.V.B.; Wijnhoven, B.P.L. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Haque, W.; Zheng, D.; Osayande, F.; Lin, C. Patterns of Care and Outcomes of Elderly Esophageal Cancer Patients Not Meeting Age-based Criteria of the CROSS Trial. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 42, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefner, M.F.; Lang, K.; Verma, V.; Koerber, S.A.; Uhlmann, L.; Debus, J.; Sterzing, F. Neoadjuvant versus definitive chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced esophageal cancer: Outcomes and patterns of failure. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2018, 194, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tougeron, D.; Hamidou, H.; Scotte, M.; Di Fiore, F.; Antonietti, M.; Paillot, B.; Michel, P. Esophageal cancer in the elderly: An analysis of the factors associated with treatment decisions and outcomes. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, S.-I.; Lee, W.S.; Kang, M.H.; Song, H.-N.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, H.-G.; Lee, G.W.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, J.-H.; et al. Response to concurrent chemoradiotherapy as a prognostic marker in elderly patients with locally advanced esophageal cancer. Tumori J. 2012, 98, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, E.; Ilson, D.H. Management of localized esophageal cancer in the older patient. Oncologist 2014, 19, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molena, D.; Stem, M.; Blackford, A.L.; Lidor, A.O. Esophageal cancer treatment is underutilized among elderly patients in the USA. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2017, 21, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Wang, J.; Allen, P.K.; Correa, A.M.; Maru, D.M.; Swisher, S.G.; Hofstetter, W.L.; Liao, Z.; Ajani, J.A. A nomogram that predicts pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation also predicts survival outcomes after definitive chemoradiation for esophageal cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2014, 6, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, P.; Constine, L.S.; Fajardo, L.F.; Phillips, T.L.; Wasserman, T.H. Late effects of normal tissues (LENT) scoring system. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1995, 31, 1041–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Version 5; National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2009.
- Oken, M.M.; Creech, R.H.; Tormey, D.C.; Horton, J.; Davis, T.E.; McFadden, E.T.; Carbone, P.P. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1982, 5, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson, M.; Szatrowski, T.P.; Peterson, J.; Gold, J. Validation of a combined comorbidity index. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1994, 47, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T.; Tracy, R.; Kop, W.J.; Burke, G.; et al. Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M146–M157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, G.F.; Šaltytė Benth, J.; Grønberg, B.H.; Rostoft, S.; Kirkhus, L.; Kirkevold, Ø. Geriatric impairments are prevalent and predictive of survival in older patients with cancer receiving radiotherapy: A prospective observational study. Acta Oncol. 2022, 61, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, L.Z.; Harker, J.O.; Salvà, A.; Guigoz, Y.; Vellas, B. Screening for Undernutrition in Geriatric Practice: Developing the Short-Form Mini-Nutritional Assessment (MNA-SF). J. Gerontol. 2001, 56, M366–M377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, A.; Fidanza, F.; Karvonen, M.J.; Kimura, N.; Taylor, H.L. Indices of relative weight and obesity. J. Chronic Dis. 1972, 25, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borda, F.; Borda, A.; Jimenez, J.; Zozaya, J.M.; Prieto, C.; Gomez, M. Predictive value of pre-treatment hypoalbuminemia in prognosis of resected colorectal cancer. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 37, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crumley, A.B.; Stuart, R.C.; McKernan, M.; McMillan, D.C. Is hypoalbuminemia an independent prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer? World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 2393–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, H.; Chen, L. Prognostic role of pre-treatment C-reactive protein/albumin ratio in esophageal cancer: A meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velissaris, D.; Pantzaris, N.; Koniari, I.; Koutsogiannis, N.; Karamouzos, V.; Kotroni, I.; Skroumpelou, A.; Ellul, J. C-Reactive Protein and Frailty in the Elderly: A Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2017, 9, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Chung, K.S.; Song, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, E.Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Kang, Y.A.; Park, M.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Chang, J.; et al. The C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio as a Predictor of Mortality in Critically Ill Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, E.L.; Meier, P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1958, 53, 457–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.R.; Oakes, D. Analysis of Survival Data; Chapman Hall: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Xi, M.; Zhao, L.; Shen, J.-X.; Li, Q.-Q.; He, L.-R.; Liu, S.-L.; Liu, M.-Z. Is there a benefit in receiving concurrent chemoradiotherapy for elderly patients with inoperable thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jingu, K.; Takahashi, N.; Murakami, Y.; Ishikawa, K.; Itasaka, S.; Takahashi, T.; Isohashi, F.; Sakayauchi, T.; Ogawa, K. Is Concurrent Chemotherapy with Radiotherapy for Esophageal Cancer Beneficial in Patients Aged 80 Years or Older? Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 4279–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustgi, A.K.; El-Serag, H.B. Esophageal carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2499–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantziari, S.; Farinha, H.T.; Bouygues, V.; Vignal, J.-C.; Deswysen, Y.; Demartines, N.; Schäfer, M.; Piessen, G. Esophageal Cancer in Elderly Patients, Current Treatment Options and Outcomes; A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herskovic, A.; Martz, K.; Al-Sarraf, M.; Leichman, L.; Brindle, J.; Vaitkevicius, V.; Cooper, J.; Byhardt, R.; Davis, L.; Emami, B. Combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy compared with radiotherapy alone in patients with cancer of the esophagus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Du, X.; Zhu, W.; Yang, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, L. Efficacy of Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy With S-1 vs Radiotherapy Alone for Older Patients with Esophageal Cancer: A Multicenter Randomized Phase 3 Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakui, R.; Yamashita, H.; Okuma, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Shiraishi, K.; Terahara, A.; Sasano, N.; Ohtomo, K.; Nakagawa, K. Esophageal cancer: Definitive chemoradiotherapy for elderly patients. Dis. Esophagus 2010, 23, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlacich, G.; Samson, P.P.; Perkins, S.M.; Roach, M.C.; Parikh, P.J.; Bradley, J.D.; Lockhart, A.C.; Puri, V.; Meyers, B.F.; Kozower, B.; et al. Treatment utilization and outcomes in elderly patients with locally advanced esophageal carcinoma: A review of the National Cancer Database. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2886–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Han, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Pang, Q.; Sun, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, K.; Li, L.; et al. Does chemoradiotherapy benefit elderly patients with esophageal squamous cell cancer? A propensity-score matched analysis on multicenter data (3JECROG R-03A). BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Internullo, E.; Moons, J.; Nafteux, P.; Coosemans, W.; Decker, G.; De Leyn, P.; Van Raemdonck, D.; Lerut, T. Outcome after esophagectomy for cancer of the esophagus and GEJ in patients aged over 75 years. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2008, 33, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, M.; Egashira, A.; Yoshida, R.; Ikeda, K.; Ohgaki, K.; Shibahara, K.; Oki, E.; Sadanaga, N.; Kakeji, Y.; Maehara, Y. Esophagectomy in patients 80 years of age and older with carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexiou, C.; Beggs, D.; Salama, F.; Brackenbury, E.; Morgan, W. Surgery for esophageal cancer in elderly patients: The view from Nottingham. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1998, 116, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Kimura, K.; Zhou, Q.; Sasaki, K.; Saiki, T.; Moriyama, M.; Saijo, Y. Treatments and outcomes of older patients with esophageal cancer: Comparison with younger patients. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 11, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.M.; Biagi, J.J.; Hopman, W.M.; Mahmud, A. Shifting practice in definitive chemoradiation for localized esophageal cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2017, 24, e379–e387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honing, J.; Smit, J.K.; Muijs, C.T.; Burgerhof, J.G.M.; de Groot, J.W.; Paardekooper, G.; Muller, K.; Woutersen, D.; Legdeur, M.J.C.; Fiets, W.E.; et al. A comparison of carboplatin and paclitaxel with cisplatinum and 5-fluorouracil in definitive chemoradiation in esophageal cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, R.L.G.M.; Sosef, M.N.; Nap, M.; Lammering, G.; Berkmortel, F.V.D.; Hulshof, M.C.; Meijer, S.; Wilmink, H.W.; Henegouwen, M.I.V.B. Comparison of two neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy regimens in patients with potentially curable esophageal carcinoma. Dis. Esophagus 2013, 27, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münch, S.; Pigorsch, S.U.; Feith, M.; Slotta-Huspenina, J.; Weichert, W.; Friess, H.; Combs, S.E.; Habermehl, D. Comparison of neoadjuvant chemoradiation with carboplatin/paclitaxel or cisplatin/5-fluoruracil in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munch, S.; Pigorsch, S.U.; Devečka, M.; Dapper, H.; Weichert, W.; Friess, H. Comparison of definite chemoradiation therapy with carboplatin/paclitaxel or cisplatin/5-fluoruracil in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyerberg, E.W.; Neville, B.; Weeks, J.C.; Earle, C.C. Referral patterns, treatment choices, and outcomes in locoregional esophageal cancer: A population-based analysis of elderly patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2389–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchardy, C.; Rapiti, E.; Blagojevic, S.; Vlastos, A.-T.; Vlastos, G. Older female cancer patients: Importance, causes, and consequences of undertreatment. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1858–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, D.C. Poor prognosis in elderly patients with cancer: The role of bias and undertreatment. J. Support. Oncol. 2004, 1 (Suppl. 2), 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Chen, W.T.-L.; Kung, P.-T.; Chiu, C.-F.; Wang, Y.-H.; Shieh, S.-H.; Tsai, W.-C. Characteristics, survival, and related factors of newly diagnosed colorectal cancer patients refusing cancer treatments under a universal health insurance program. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, E.-M.; Pavic, M.; Stark, L.S.; Hertler, C.; Guckenberger, M. Radiotherapy of the oldest old–feasibility and institutional analysis. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2020, 196, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kooten, R.T.; Voeten, D.M.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Hartgrink, H.H.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; van Hillegersberg, R. Patient-Related Prognostic Factors for Anastomotic Leakage, Major Complications, and Short-Term Mortality Following Esophagectomy for Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 1358–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirpara, D.H.; Kidane, B.; Rogalla, P.; Cypel, M.; de Perrot, M.; Keshavjee, S.; Pierre, A.; Waddell, T.; Yasufuku, K.; Darling, G.E. Frailty assessment prior to thoracic surgery for lung or esophageal cancer: A feasibility study. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 1535–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaker, M.E.; Jonker, J.M.; de Rooij, S.E.; Vos, A.G.; Smorenburg, C.H.; van Munster, B.C. Frailty screening methods for predicting outcome of a comprehensive geriatric assessment in elderly patients with cancer: A systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, e437–e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prytherch, D.R.; Whiteley, M.S.; Higgins, B.; Weaver, P.C.; Prout, W.G.; Powell, S.J. POSSUM and Portsmouth POSSUM for predicting mortality. Physiological and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity. Br. J. Surg. 1998, 85, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekkis, P.P.; McCulloch, P.; Poloniecki, J.D.; Prytherch, D.R.; Kessaris, N.; Steger, A.C. Risk-adjusted prediction of operative mortality in oesophagogastric surgery with O-POSSUM. Br. J. Surg. 2004, 91, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyerberg, E.W.; Neville, B.A.; Koppert, L.B.; Lemmens, V.E.; Tilanus, H.W.; Coebergh, J.W.W. Surgical mortality in patients with esophageal cancer: Development and validation of a simple risk score. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4277–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Journo, X.B.; Boulate, D.; Fourdrain, A.; Loundou, A.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Gisbertz, S.S. Risk Prediction Model of 90-Day Mortality After Esophagectomy for Cancer. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wei, C.; Tucker, S.L.; Myles, B.; Palmer, M.; Hofstetter, W.L.; Swisher, S.G.; Ajani, J.A.; Cox, J.D.; Komaki, R.; et al. Predictors of postoperative complications after trimodality therapy for esophageal cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 86, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimy, E.; Koong, A.; Toesca, D.; White, M.N.; Panjwani, N.; Fisher, G.; Chang, D.; Pollom, E. Outcomes and Tolerability of Definitive and Preoperative Chemoradiation in Elderly Patients with Esophageal Cancer: A Retrospective Institutional Review. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 5, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.; Minnella, E.M.; Awasthi, R.; Gamsa, A.; Ferri, L.; Mulder, D.; Sirois, C.; Spicer, J.; Schmid, S.; Carli, F. Multimodal Prehabilitation for Lung Cancer Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 112, 1600–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausys, A.; Mazeikaite, M.; Bickaite, K.; Bausys, B.; Bausys, R.; Strupas, K. The Role of Prehabilitation in Modern Esophagogastric Cancer Surgery: A Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnella, E.M.; Awasthi, R.; Loiselle, S.; Agnihotram, R.V.; Ferri, L.E.; Carli, F. Effect of Exercise and Nutrition Prehabilitation on Functional Capacity in Esophagogastric Cancer Surgery: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, Y.; Sasaki, A.; Fujii, Y.; Fujisawa, R.; Sasaki, N.; Nikai, H.; Endo, F.; Baba, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kimura, T.; et al. Efficacy of enhanced prehabilitation for patients with esophageal cancer undergoing esophagectomy. Esophagus 2021, 18, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, C.; Nichols, F.C., 3rd; Cassivi, S.D.; Allen, M.S.; Pairolero, P.C. Long-term function and quality of life after esophageal resection for cancer and Barrett’s. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 85, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.E.; Sherbourne, C.D. The MOS 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36): I. Conceptual Framework and Item Selection. Med. Care 1992, 30, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; He, B.; Li, W.; Wen, Q.; Wang, S.; Sun, X.; Meng, X.; Yu, J. Development and validation of a risk prediction model for radiotherapy-related esophageal fistula in esophageal cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muro, K.; Lordick, F.; Tsushima, T.; Pentheroudakis, G.; Baba, E.; Lu, Z.; Cho, B.C.; Nor, I.M.; Ng, M.; Chen, L.-T.; et al. Pan-Asian adapted ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic oesophageal cancer: A JSMO-ESMO initiative endorsed by CSCO, KSMO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulshof, M.C.C.M.; Geijsen, E.D.; Rozema, T.; Oppedijk, V.; Buijsen, J.; Neelis, K.J.; Nuyttens, J.J.M.E.; van der Sangen, M.J.C.; Jeene, P.M.; Reinders, J.G.; et al. Randomized Study on Dose Escalation in Definitive Chemoradiation for Patients With Locally Advanced Esophageal Cancer (ARTDECO Study). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2816–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollschweiler, E.; Plum, P.S.; Mönig, S.P.; Hölscher, A.H. Current and future treatment options for esophageal cancer in the elderly. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2017, 18, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Metastasis Patterns and Prognosis of Elderly Patients With Esophageal Adenocarcinoma in Stage IVB: A Population-Based Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 625720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münch, S.; Aichmeier, S.; Hapfelmeier, A.; Duma, M.-N.; Oechsner, M.; Feith, M.; Combs, S.E.; Habermehl, D. Comparison of dosimetric parameters and toxicity in esophageal cancer patients undergoing 3D conformal radiotherapy or VMAT. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2016, 192, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cijs, T.M.; Verhoef, C.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Koppert, L.B.; Tran, T.K.; Wijnhoven, B.P.; Tilanus, H.W.; de Jonge, J. Outcome of esophagectomy for cancer in elderly patients. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 90, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, D.J.; Craig, S.R.; Sang, C.T.; Cameron, E.W.; Walker, W.S. Esophagectomy for carcinoma in the octogenarian. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1996, 61, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahamim, J.; Murphy, G.; Awan, Y.; Junemann-Ramirez, M. The effect of age on the outcome of surgical treatment for carcinoma of the oesophagus and gastric cardia. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2003, 23, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabel, M.S.; Smith, J.L.; Nava, H.R.; Mollen, K.; Douglass, H.O.; Gibbs, J.F. Esophageal resection for carcinoma in patients older than 70 years. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2002, 9, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, E.; Ripat, C.; Koshenkov, V.; Prescott, A.T.; Sethi, K.; Stuart, H.; Tiesi, G.; Livingstone, A.S.; Yakoub, D. Esophagectomy for cancer in octogenarians: Should we do it? Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2017, 402, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranov, N.S.; Slootmans, C.; van Workum, F.; Klarenbeek, B.R.; Schoon, Y.; Rosman, C. Outcomes of curative esophageal cancer surgery in elderly: A meta-analysis. World. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repetto, L. Greater risks of chemotherapy toxicity in elderly patients with cancer. J. Support. Oncol. 2004, 1 (Suppl. 2), 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wasil, T.; Lichtman, S.M. Clinical pharmacology issues relevant to the dosing and toxicity of chemotherapy drugs in the elderly. Oncologist 2005, 10, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.J.; Ajani, J.A.; Kuzdzal, J.; Zander, T.; Van Cutsem, E.; Piessen, G.; Mendez, G.; Feliciano, J.; Motoyama, S.; Lièvre, A.; et al. Adjuvant Nivolumab in Resected Esophageal or Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sex | Grading | ||
| Female | 10 (29.4%) | 1 | 1 (2.9%) |
| Male | 24 (70.6%) | 2 | 16 (47.0%) |
| Age | 3 | 11 (32.3%) | |
| Median | 75 y | Gx/Unknown | 6 (17.6%) |
| Mean | 75.4 y | T-stage | |
| Range | 71–82 y | 2 | 7 (20.5%) |
| ECOG | 3 | 25 (73.5%) | |
| 0 | 18 (52.9%) | 4 | 1 (2.9%) |
| 1 | 12 (35.3%) | Tx/Unknown | 1 (2.9%) |
| 3 | 4 (11.8%) | N-stage | |
| Tumor site | 0 | 1 (2.9%) | |
| Cervical | 1 (2.9%) | 1 | 28 (82.3%) |
| Upper thoracic | 2 (5.9%) | 2 | 1 (2.9%) |
| Middle thoracic | 11 (32.4%) | 3 | 1 (2.9%) |
| Lower thoracic | 20 (58.8) | Nx/Unknown | 3 (8.8%) |
| Histology | M-stage | ||
| Adeno | 19 (55.9%) | 0 | 31 (91.1%) |
| SCC | 15 (44.1%) | 1 | 2 (5.8%) |
| Mx/Unknown | 1 (2.9%) | ||
| AJCC/UICC stage I | SCC | Adeno | |
| II | 1 (2.9%) | None | |
| III | 12 (35.3%) | 13 (38.2%) | |
| IVA | 2 (5.8%) | None | |
| IVB | None | 2 (5.8%) | |
| Unknown | None | 4 (11.8%) | |
| Chemotherapy | RT technique | ||
| Neoadjuvant | 22 (64.7%) | APPA (two-field) | 6 (17.6%) |
| Definite | 12 (35.2%) | 3D-CRT (multi-field) | 17 (50.0%) |
| Agents | IMRT | 10 (29.4%) | |
| Carb/TAX | 29 (85.2%) | Unknown | 1 (2.9%) |
| Others | 3 (8.8%) | ||
| None | 2 (5.8%) | ||
| Charlson Score I | SCC | Adeno | |
| ≤3 | 6 (17.6%) | 5 (14.7%) | |
| ≥3 | 9 (26.4%) | 14 (41.1%) | |
| Age adjusted Charlson score | Active smoking | ||
| ≥5 | 34 (100%) | Yes | 12 (35.2%), (5 SCC (14.7%)) |
| Frail scale | Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form | ||
| Median | 1 pt | Median | 8.5 pt |
| Mean | 1.2 pt | Mean | 8.1 pt |
| Range | 0–3 pt | Range | 3–12 pt |
| Fit and agile (0 pt) | 7 (20.6%) | Normal nutritional state (12–14 pt) | 2 (5.9%) |
| Prefrail (1–2 pt) | 26 (76.5%) | Risk for malnutrition (8–11 pt) | 17 (50%) |
| Frail (≥3 pt) | 1 (2.9%) | Malnutrition (0–7 pt) | 15 (44.1%) |
| BMI (weight (kg)/[height(m)]2) | Weight (kg) | ||
| Median | 24.6 | Median | 76 |
| Mean | 24.5 | Mean | 75.1 |
| Range | 15.2–37.2 | Range | 35–120 |
| Obesity (30 pt or higher) | 4 (11.8%) | C-reactive/albumin ratio | |
| Overweight (25.0 to 29.9 pt) | 10 (29.4%) | Median | 0.1 |
| Healthy Weight (18.5 to 24.9 pt) | 15 (44.1%) | Mean | 0.5 |
| Underweight (below 18.5 pt) | 5 (14.7%) | Range | 0.1–7.0 |
| CTC Grade | 0 | % | 1 | % | 2 | % | 3 | % | 4 | % | 5 | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hematological | 7 | 20.6 | 10 | 29.4 | 13 | 38.2 | 2 | 5.9 | 1 | 2.9 | 1 | 2.9 |
| Odynodysphagia | 19 | 55.9 | 10 | 29.4 | 2 | 5.9 | 3 | 8.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nausea | 28 | 82.4 | 6 | 17.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Skin toxicity | 22 | 64.7 | 11 | 32.4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fatigue | 24 | 70.6 | 7 | 20.6 | 2 | 5.9 | 1 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cardiopulmonary | 34 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Inappetence/loss of weight | 32 | 94.1 | 1 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other 1 | 30 | 88.2 | 3 | 8.8 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| All Grades | Grade 1–2 | Grade 3–5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Odynodysphagia | 30 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 9.9 |
| Nausea | 30 | 100 | 3 | 10.0 | 0 | 0 |
| Skin toxicity | 30 | 100 | 4 | 13.3 | 0 | 0 |
| Fatigue | 30 | 100 | 1 | 3.3 | 0 | 0 |
| Cardiopulmonary | 30 | 100 | 1 | 3.3 | 0 | 0 |
| Inappetence/loss of weight | 30 | 100 | 1 | 3.3 | 0 | 0 |
| Other 1 | 30 | 100 | 3 | 10.0 | 0 | 0 |
| Parameter | OS HR [95% CI] | p-Value | PFS HR [95% CI] | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment regimen (nCRT vs. dCRT) | 0.381 [0.146; 0.998] | 0.049 | 0.411 [0.164; 1.028] | 0.057 |
| Age | ||||
| 70–74 y (nCRT vs. dCRT) | 0.067 [0.007; 0.674] | 0.022 | 0.233 [0.050; 1.077] | 0.062 |
| ECOG (2–3 vs. 0–1) | 17.808 [3.903; 81.258] | <0.001 | 11.391 [3.079; 42.138] | <0.001 |
| BMI | ||||
| Healthy Weight (nCRT vs. dCRT) | 0.159 [0.029; 0.878] | 0.035 | 0.500 [0.140; 1.789] | 0.286 |
| T-stage | ||||
| T3 (nCRT vs. dCRT) | 0.095 [0.022; 0.407] | 0.002 | 0.205 [0.062; 0.678] | 0.009 |
| Grading | ||||
| G3 (nCRT vs. dCRT) | 0.309 [0.072; 1.326] | 0.114 | 0.233 [0.053; 1.033] | 0.055 |
| Histology | ||||
| SCC (nCRT vs. dCRT) | 0.161 [0.018; 1.445] | 0.103 | 0.142 [0.016; 1.290] | 0.083 |
| AC (nCRT vs. dCRT) | 0.284 [0.073; 1.112] | 0.071 | 0.469 [0.128; 1.713] | 0.252 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Linde, P.; Mallmann, M.; Adams, A.; Wegen, S.; Fan, J.; Rosenbrock, J.; Trommer, M.; Marnitz, S.; Baues, C.; Celik, E. The Role of Age and Comorbidities in Esophagogastric Cancer Chemoradiation of the Frail Elderly (>70 Years): An Analysis from a Tertiary High Volume-Center. Cancers 2023, 15, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010106
Linde P, Mallmann M, Adams A, Wegen S, Fan J, Rosenbrock J, Trommer M, Marnitz S, Baues C, Celik E. The Role of Age and Comorbidities in Esophagogastric Cancer Chemoradiation of the Frail Elderly (>70 Years): An Analysis from a Tertiary High Volume-Center. Cancers. 2023; 15(1):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010106
Chicago/Turabian StyleLinde, Philipp, Markus Mallmann, Anne Adams, Simone Wegen, Jiaqi Fan, Johannes Rosenbrock, Maike Trommer, Simone Marnitz, Christian Baues, and Eren Celik. 2023. "The Role of Age and Comorbidities in Esophagogastric Cancer Chemoradiation of the Frail Elderly (>70 Years): An Analysis from a Tertiary High Volume-Center" Cancers 15, no. 1: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010106
APA StyleLinde, P., Mallmann, M., Adams, A., Wegen, S., Fan, J., Rosenbrock, J., Trommer, M., Marnitz, S., Baues, C., & Celik, E. (2023). The Role of Age and Comorbidities in Esophagogastric Cancer Chemoradiation of the Frail Elderly (>70 Years): An Analysis from a Tertiary High Volume-Center. Cancers, 15(1), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010106





