Current Status of Research on Small Extracellular Vesicles for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Urological Tumors
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Background
2. Overview of Small Extracellular Vesicles
2.1. Composition of Small Extracellular Vesicles
2.2. Formation of Small Extracellular Vesicles
2.3. Isolation Techniques for Small Extracellular Vesicles
3. General Function of Small Extracellular Vesicles in Urological Tumors
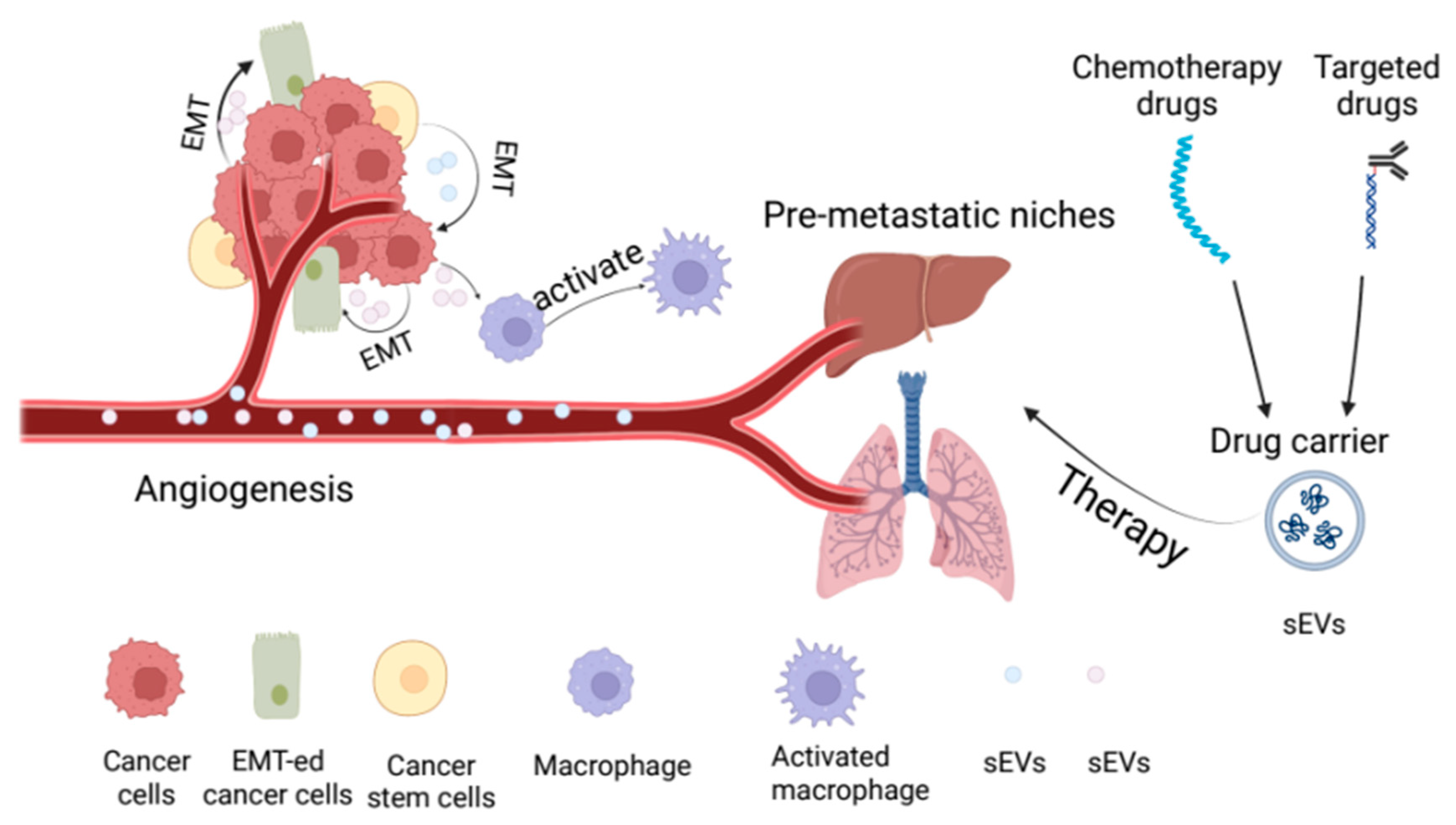
3.1. sEVs Promotes Angiogenesis in Urological Tumors
3.2. sEVs Promotes Epithelial—Mesenchymal Transformation in Urological Tumors
3.3. Involvement in the Occurrence of Pre-Metastatic Niches in Urological Tumors
3.4. sEVs Regulates the Tumor Microenvironment
3.5. Antitumor Effects of sEVs in Urological Tumors
4. Application of Small Extracellular Vesicles in the Diagnosis of Urinary Tumors
4.1. miRNAs in Small Extracellular Vesicles
4.2. lncRNA in Small Extracellular Vesicles
4.3. CircRNAs in Small Extracellular Vesicles
4.4. Proteins in Small Extracellular Vesicles
5. Investigations of Small Extracellular Vesicles in the Treatment of Urological Tumors
5.1. Small Extracellular Vesicles and Tumor Drug Resistance
5.2. Small Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Carriers
5.3. Small Extracellular Vesicles and Tumor Vaccines
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.A.; Naghavi, M.; Global Burden of Disease Bladder Cancer Collaborators. Global, regional and national burden of bladder cancer and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study 2019. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e004128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, M.Y.; Rathkopf, D.E.; Kantoff, P. Treatment of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 2019, 70, 479–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, R.E.; Harris, G.T. Renal Cell Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Management. Am. Fam. Phys. 2019, 99, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Zebrowska, A.; Widlak, P.; Whiteside, T.; Pietrowska, M. Signaling of Tumor-Derived sEV Impacts Melanoma Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.T.; Lai, R.C.; Padmanabhan, J.; Sim, W.K.; Choo, A.B.H.; Lim, S.K. Assessment of Tumorigenic Potential in Mesenchymal-Stem/Stromal-Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles (MSC-sEV). Pharmaceutics 2021, 14, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Hurley, J.; Roberts, D.; Chakrabortty, S.K.; Enderle, D.; Noerholm, M.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J.K. Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: Opportunities and challenges. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2021, 32, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, M.; Yabuta, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Takakura, Y. Interleukin-4-carrying small extracellular vesicles with a high potential as anti-inflammatory therapeutics based on modulation of macrophage function. Biomaterials 2021, 278, 121160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Takakura, Y. Intercellular delivery of NF-κB inhibitor peptide utilizing small extracellular vesicles for the application of anti-inflammatory therapy. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2020, 328, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urabe, F.; Kosaka, N.; Ito, K.; Kimura, T.; Egawa, S.; Ochiya, T. Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C29–C39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bi, J.; Huang, J.; Tang, Y.; Du, S.; Li, P. Exosome: A Review of Its Classification, Isolation Techniques, Storage, Diagnostic and Targeted Therapy Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 6917–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, L.M.; Wang, M.Z. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Chen, J.; Hu, D.; Xie, F.; Yang, T.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhong, J.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Advances in Biological Function and Clinical Application of Small Extracellular Vesicle Membrane Proteins. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 675940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, D.; Feng, Q.; Liu, Z. Diabetic Nephropathy: Perspective on Extracellular Vesicles. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javeed, N. Shedding Perspective on Extracellular Vesicle Biology in Diabetes and Associated Metabolic Syndromes. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberro, A.; Iparraguirre, L.; Fernandes, A.; Otaegui, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Blood: Sources, Effects, and Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso Bavisotto, C.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Campanella, C.; Bucchieri, F.; Cappello, F. Extracellular heat shock proteins in cancer: From early diagnosis to new therapeutic approach. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 86, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, M.; Névo, N.; Jouve, M.; Valenzuela, J.I.; Maurin, M.; Verweij, F.J.; Palmulli, R.; Lankar, D.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; et al. Specificities of exosome versus small ectosome secretion revealed by live intracellular tracking of CD63 and CD9. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrowska, M.; Zebrowska, A.; Gawin, M.; Marczak, L.; Sharma, P.; Mondal, S.; Mika, J.; Polańska, J.; Ferrone, S.; Kirkwood, J.M.; et al. Proteomic profile of melanoma cell-derived small extracellular vesicles in patients’ plasma: A potential correlate of melanoma progression. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, D.; Nakao, Y.; Mauer, A.S.; Thompson, J.M.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Liao, C.Y.; Krishnan, A.; Lucien, F.; Guo, Q.; Liu, M.; et al. IRE1A Stimulates Hepatocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles That Promote Inflammation in Mice with Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1487–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McVey, M.J.; Weidenfeld, S.; Maishan, M.; Spring, C.; Kim, M.; Tabuchi, A.; Srbely, V.; Takabe-French, A.; Simmons, S.; Arenz, C.; et al. Platelet extracellular vesicles mediate transfusion-related acute lung injury by imbalancing the sphingolipid rheostat. Blood 2021, 137, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzanowska, J.; Semira, C.; Costa-Silva, B. DNA in extracellular vesicles: Biological and clinical aspects. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yu, S.; Wang, Z.; He, X.; Su, Y.; Guo, T.; Sheng, H.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Long RNA Sequencing Reveals Abundant mRNA, circRNA, and lncRNA in Human Blood as Potential Biomarkers for Cancer Diagnosis. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Zhan, W.; Gao, Y.; Huang, L.; Gong, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Gao, S.; Kang, T. RAB31 marks and controls an ESCRT-independent exosome pathway. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. Research progress of extracellular vesicles in type 2 diabetes and its complications. Diabet. Med. J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2022, 39, e14865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Approach for Kidney Disease Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 3603–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, W.; Cai, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, S. Extracellular vesicles in urologic malignancies-Implementations for future cancer care. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitorino, R.; Ferreira, R.; Guedes, S.; Amado, F.; Thongboonkerd, V. What can urinary exosomes tell us? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 3265–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkova, E.E.; Sedykh, S.E.; Nevinsky, G.A. Human Placenta Exosomes: Biogenesis, Isolation, Composition, and Prospects for Use in Diagnostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, N.; Cvjetkovic, A.; Jang, S.C.; Crescitelli, R.; Hosseinpour Feizi, M.A.; Nieuwland, R.; Lötvall, J.; Lässer, C. Detailed analysis of the plasma extracellular vesicle proteome after separation from lipoproteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2018, 75, 2873–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.H.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, J.; Kwon, H.H.; Park, G.H.; Yang, S.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Choi, H.; Lee, J.H.; Sung, S.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell-Derived Exosomes for Immunomodulatory Therapeutics and Skin Regeneration. Cells 2020, 9, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, S.; Goldfinger, L.E. Platelets and extracellular vesicles and their cross talk with cancer. Blood 2021, 137, 3192–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wan, M.; Liu, F.; Gong, M.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Mitochondrial Damage and Inflammation by Stabilizing Mitochondrial DNA. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1519–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Xu, Y.; Lv, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, K.; Ni, C.; Wang, K.; Kong, M.; et al. Small extracellular vesicles containing miR-486-5p promote angiogenesis after myocardial infarction in mice and nonhuman primates. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabb0202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Dou, R.; Wei, C.; Liu, K.; Shi, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Xiong, B. Tumor-derived exosomal microRNA-106b-5p activates EMT-cancer cell and M2-subtype TAM interaction to facilitate CRC metastasis. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2021, 29, 2088–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yin, T.; Yang, C.; Yang, J. Extracellular vesicles derived from M1 macrophages deliver miR-146a-5p and miR-146b-5p to suppress trophoblast migration and invasion by targeting TRAF6 in recurrent spontaneous abortion. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5813–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Wang, W.; Lan, X.L.; Zeng, Z.C.; Liang, Y.S.; Yan, Y.R.; Song, F.Y.; Zhu, X.H.; Liao, W.J.; Liao, W.T.; et al. CAFs secreted exosomes promote metastasis and chemotherapy resistance by enhancing cell stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Lei, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Chung, C.; Wang, M.; Hu, M.; Deng, L. New Insights Into the Regulatory Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in Tumor Angiogenesis and Their Clinical Implications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 791882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Hou, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Lu, C. Extracellular vesicles secreted by hypoxia pre-challenged mesenchymal stem cells promote non-small cell lung cancer cell growth and mobility as well as macrophage M2 polarization via miR-21-5p delivery. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, B.; Katari, V.; Adapala, R.; Bhavnani, N.; Dougherty, J.; Khan, M.; Paruchuri, S.; Thodeti, C. Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Induce Abnormal Angiogenesis via TRPV4 Downregulation and Subsequent Activation of YAP and VEGFR2. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 790489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangadaran, P.; Rajendran, R.L.; Lee, H.W.; Kalimuthu, S.; Hong, C.M.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, J.; Ahn, B.-C. Extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells activates VEGF receptors and accelerates recovery of hindlimb ischemia. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2017, 264, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Xun, C.; Li, W.; Jin, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhuo, Y.; Duan, D.; Hu, Z.; Chen, P.; Lu, M. Extracellular vesicles derived from hypoxia-preconditioned olfactory mucosa mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenesis via miR-612. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Fan, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Zang, J.; Ye, J.; Xiao, M.; et al. Exosome-mediated targeted delivery of miR-210 for angiogenic therapy after cerebral ischemia in mice. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Cheng, J.; Li, B.; Nie, D.; Li, C.; Gui, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Up-regulation of the expressions of MiR-149-5p and MiR-99a-3p in exosome inhibits the progress of pituitary adenomas. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2021, 37, 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yan, T.; Huang, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, E.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, K.; Shao, Z.; et al. Melanoma cell-secreted exosomal miR-155-5p induce proangiogenic switch of cancer-associated fibroblasts via SOCS1/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wei, K.; Yang, F.; Guo, Z.; Pan, C.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-3157-3p promotes angiogenesis, vascular permeability and metastasis by targeting TIMP/KLF2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zheng, X.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Lan, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, A.; Huang, H.; Chen, W. Renal cell carcinoma-derived exosomes deliver lncARSR to induce macrophage polarization and promote tumor progression via STAT3 pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 3209–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishn, S.R.; Salem, I.; Quaglia, F.; Naranjo, N.M.; Agarwal, E.; Liu, Q.; Sarker, S.; Kopenhaver, J.; McCue, P.A.; Weinreb, P.H.; et al. The αvβ6 integrin in cancer cell-derived small extracellular vesicles enhances angiogenesis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1763594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigol, A.N.; Rode, M.P.; Silva, A.H.; Cisilotto, J.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B. Pro-angiogenic effect of PC-3 exosomes in endothelial cells in vitro. Cell. Signal. 2021, 87, 110126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wei, Z.; Yu, H.; Xu, Y.; He, W.; Zhou, X.; Gou, X. Secretory autophagy-induced bladder tumour-derived extracellular vesicle secretion promotes angiogenesis by activating the TPX2-mediated phosphorylation of the AURKA-PI3K-AKT axis. Cancer Lett. 2021, 523, 10–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Peng, X.; Zhang, C.; Bai, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Guo, H.; He, W.; Zhou, X.; Gou, X. Bladder Cancer-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Tumor Angiogenesis by Inducing HBP-Related Metabolic Reprogramming and SerRS O-GlcNAcylation in Endothelial Cells. Adv. Sci. Weinh. Baden-Wurtt. Ger. 2022, 9, e2202993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sai, B.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, G.; Tang, J.; Xiang, J. Hypoxic BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs promote metastasis of lung cancer cells via STAT3-induced EMT. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Avellán-Llaguno, R.D.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q. DEHP-elicited small extracellular vesicles miR-26a-5p promoted metastasis in nearby normal A549 cells. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 116005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Si, M.; Yang, J.; Sun, S.; Wu, H.; Cui, S.; Qu, X.; Yu, X. Exosome-encapsulated miRNAs contribute to CXCL12/CXCR4-induced liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by enhancing M2 polarization of macrophages. Cancer Lett. 2020, 474, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, D.; Xie, M. Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Activation of Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts and Facilitate Invasion and Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer by Carrying miR-630. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 652322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Orta, E.; Ramirez-Ricardo, J.; Garcia-Hernandez, A.; Cortes-Reynosa, P.; Salazar, E.P. Extracellular vesicles from MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells stimulated with insulin-like growth factor 1 mediate an epithelial-mesenchymal transition process in MCF10A mammary epithelial cells. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 16, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, R.; Tan, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, L.; et al. High TSPAN8 expression in epithelial cancer cell-derived small extracellular vesicles promote confined diffusion and pronounced uptake. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, G.; Zhao, D.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Peng, Q.; Wang, H.; Fang, R.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; et al. CD103-positive CSC exosome promotes EMT of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Role of remote MiR-19b-3p. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, D.; Gu, J.; Qian, D.; Qin, X.; Chen, Y. Exosome carrying PSGR promotes stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of low aggressive prostate cancer cells. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulet, C.R.; Champagne, A.; Bernard, G.; Vandal, D.; Chabaud, S.; Pouliot, F.; Bolduc, S. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition of bladder cancer cells through paracrine IL-6 signalling. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Yu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Han, J.; Li, K.; Zhuang, J.; Lv, Q.; Yang, X.; Yang, H. Bladder cancer-derived exosomal KRT6B promotes invasion and metastasis by inducing EMT and regulating the immune microenvironment. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, P.; He, T.C.; Han, J.H.; Zhang, R.; Lin, J.; Fan, J.; Lu, L.; Zhu, W.W.; et al. Cancer-derived exosomal HSPC111 promotes colorectal cancer liver metastasis by reprogramming lipid metabolism in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wortzel, I.; Dror, S.; Kenific, C.M.; Lyden, D. Exosome-Mediated Metastasis: Communication from a Distance. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Li, Q.; Shi, J.; Wei, J.; Li, P.; Chang, C.H.; Shultz, L.D.; Ren, G. Lung fibroblasts facilitate pre-metastatic niche formation by remodeling the local immune microenvironment. Immunity 2022, 55, 1483–1500.e1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Zhou, L.; Sui, H.; Yang, L.; Wu, X.; Song, Q.; Jia, R.; Li, R.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Primary tumors release ITGBL1-rich extracellular vesicles to promote distal metastatic tumor growth through fibroblast-niche formation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Qian, N.; Ling, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, J.; Du, R.; Zhong, G.; Liu, C.; Yu, G.; et al. Breast cancer exosomes contribute to pre-metastatic niche formation and promote bone metastasis of tumor cells. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1429–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, X.; Wang, X.; Xiao, H.; Jing, N.; Xue, W.; Dong, B.; Gao, W.Q.; Fang, Y.-X. Tumor-derived miR-378a-3p-containing extracellular vesicles promote osteolysis by activating the Dyrk1a/Nfatc1/Angptl2 axis for bone metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2022, 526, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvers, C.R.; Messing, E.M.; Miyamoto, H.; Lee, Y.-F. Tenascin-C expression in the lymph node pre-metastatic niche in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.Z.; Jin, W.-L. The updated landscape of tumor microenvironment and drug repurposing. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.M.; Simon, M.C. The tumor microenvironment. Curr. Biol. CB 2020, 30, R921–R925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, B.; Cao, Y.; Yao, S.; Liu, Y.; Jin, G.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cui, K.; Zhou, L.; et al. Colorectal Cancer-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Tumor Immune Evasion by Upregulating PD-L1 Expression in Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Adv. Sci. Weinh. Baden-Wurtt. Ger. 2022, 9, 2102620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yan, Y.; Ang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Sun, B.; Lin, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Extracellular vesicles-derived OncomiRs mediate communication between cancer cells and cancer-associated hepatic stellate cells in hepatocellular carcinoma microenvironment. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannandrea, D.; Platonova, N.; Colombo, M.; Mazzola, M.; Citro, V.; Adami, R.; Maltoni, F.; Ancona, S.; Dolo, V.; Giusti, I.; et al. Extracellular vesicles mediate the communication between multiple myeloma and bone marrow microenvironment in a NOTCH dependent way. Haematologica 2022, 107, 2183–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brossa, A.; Tapparo, M.; Fonsato, V.; Papadimitriou, E.; Delena, M.; Camussi, G.; Bussolati, B. Coincubation as miR-Loading Strategy to Improve the Anti-Tumor Effect of Stem Cell-Derived EVs. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatina, T.; Grange, C.; Fonsato, V.; Tapparo, M.; Brossa, A.; Fallo, S.; Pitino, A.; Herrera-Sanchez, M.B.; Kholia, S.; Camussi, G.; et al. Extracellular vesicles from human liver stem cells inhibit tumor angiogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, D.; Bresolin, N.; Comi, G.P.; Corti, S. Extracellular vesicles and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: From misfolded protein vehicles to promising clinical biomarkers. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, J.B.; Hou, L.K.; Yu, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Tang, X.M.; Sun, F.; Lu, H.M.; Deng, J.; et al. Liquid biopsy in lung cancer: Significance in diagnostics, prediction, and treatment monitoring. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu-Maekawa, Y.; Kawakami, K.; Fujita, Y.; Takai, M.; Kato, D.; Nakane, K.; Kato, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Koie, T.; Miura, Y.; et al. Profiling of Serum Extracellular Vesicles Reveals miRNA-4525 as a Potential Biomarker for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2021, 18, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Xing, Z.; Guo, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, Z. Hypoxia-induced microRNA-155 overexpression in extracellular vesicles promotes renal cell carcinoma progression by targeting FOXO3. Aging 2021, 13, 9613–9626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, F.; Teixeira, A.L.; Nogueira, I.; Morais, M.; Maia, J.; Bodo, C.; Ferreira, M.; Silva, A.; Vilhena, M.; Lobo, J.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Enriched in hsa-miR-301a-3p and hsa-miR-1293 Dynamics in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients: Potential Biomarkers of Metastatic Disease. Cancers 2020, 12, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.T.; Lai, W.J.; Zhu, W.A.; Wang, H. MicroRNA Derived from Circulating Exosomes as Noninvasive Biomarkers for Diagnosing Renal Cell Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 10765–10774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Hu, H.; Sun, W.; Chen, L.; Jin, S.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Zeng, S. miR-224-5p Contained in Urinary Extracellular Vesicles Regulates PD-L1 Expression by Inhibiting Cyclin D1 in Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurahashi, R.; Kadomatsu, T.; Baba, M.; Hara, C.; Itoh, H.; Miyata, K.; Endo, M.; Morinaga, J.; Terada, K.; Araki, K.; et al. MicroRNA-204-5p: A novel candidate urinary biomarker of Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1897–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Long, M.; Yu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; et al. Urinary exosome miR-30c-5p as a biomarker of clear cell renal cell carcinoma that inhibits progression by targeting HSPA5. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 6755–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iinuma, K.; Kawakami, K.; Mizutani, K.; Fujita, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ito, M.; Kumano, T.; Matsuo, M.; Nakano, M.; Koie, T.; et al. miRNA-93 in Serum Extracellular Vesicles Before and After Low Dose Rate Prostate Brachytherapy. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 2411–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.X.; Dong, B.; Du, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Gao, W.Q.; Xue, W. Discovery of extracellular vesicles derived miR-181a-5p in patient’s serum as an indicator for bone-metastatic prostate cancer. Theranostics 2021, 11, 878–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabegina, L.; Nazarova, I.; Nikiforova, N.; Slyusarenko, M.; Sidina, E.; Knyazeva, M.; Tsyrlina, E.; Novikov, S.; Reva, S.; Malek, A. A New Approach for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis by miRNA Profiling of Prostate-Derived Plasma Small Extracellular Vesicles. Cells 2021, 10, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cho, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, J. Evaluation of micro-RNA in extracellular vesicles from blood of patients with prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0262017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, M.; Benzina, S.; Savoie, M.; Breault, G.; Ghosh, A.; Ouellette, R.J. Affinity Captured Urinary Extracellular Vesicles Provide mRNA and miRNA Biomarkers for Improved Accuracy of Prostate Cancer Detection: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Fujita, K.; Tomiyama, E.; Hatano, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Wang, C.; Ishizuya, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Kato, T.; et al. MiR-30b-3p and miR-126-3p of urinary extracellular vesicles could be new biomarkers for prostate cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2021, 10, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabo, A.A.; Birolo, G.; Naccarati, A.; Dragomir, M.P.; Aneli, S.; Allione, A.; Oderda, M.; Allasia, M.; Gontero, P.; Sacerdote, C.; et al. Small Non-Coding RNA Profiling in Plasma Extracellular Vesicles of Bladder Cancer Patients by Next-Generation Sequencing: Expression Levels of miR-126-3p and piR-5936 Increase with Higher Histologic Grades. Cancers 2020, 12, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shal, A.S.; Shalaby, S.M.; Abouhashem, S.E.; Elbary, E.H.A.; Azazy, S.; Rashad, N.M.; Sarhan, W. Urinary exosomal microRNA-96-5p and microRNA-183-5p expression as potential biomarkers of bladder cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 4361–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ji, J.; Lyu, J.; Jin, X.; He, X.; Mo, S.; Xu, H.; He, J.; Cao, Z.; Chen, X.; et al. A Novel Urine Exosomal lncRNA Assay to Improve the Detection of Prostate Cancer at Initial Biopsy: A Retrospective Multicenter Diagnostic Feasibility Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Işın, M.; Uysaler, E.; Özgür, E.; Köseoğlu, H.; Şanlı, Ö.; Yücel, Ö.B.; Gezer, U.; Dalay, N. Exosomal lncRNA-p21 levels may help to distinguish prostate cancer from benign disease. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, K.; Li, T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; Guo, C.; Qing, L.; Shen, J.; et al. Exosomal long noncoding RNA HOXD-AS1 promotes prostate cancer metastasis via miR-361-5p/FOXM1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Du, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Liang, J.; Wang, W.; Lv, Q.; Qin, C.; Chu, H.; Wang, M.; et al. Exosome-transmitted long non-coding RNA PTENP1 suppresses bladder cancer progression. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbastabar, M.; Sarfi, M.; Golestani, A.; Karimi, A.; Pourmand, G.; Khalili, E. Tumor-derived urinary exosomal long non-coding RNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for bladder cancer. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Shi, J. Exosomal circular RNA_400068 promotes the development of renal cell carcinoma via the miR-210-5p/SOCS1 axis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 4810–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Sun, X.; Chen, L. Exosome circ_0044516 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation and metastasis as a potential biomarker. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 2118–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruda, M.; Yoshino, H.; Okamura, S.; Kuroshima, K.; Osako, Y.; Sakaguchi, T.; Sugita, S.; Tatarano, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Enokida, H. Oncogenic effects of RAB27B through exosome independent function in renal cell carcinoma including sunitinib-resistant. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliuk, A.; Wu, X.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; Hadisurya, M.; Boris, R.S.; Tao, W.A. Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Phosphoproteomics through Chemical Affinity Purification. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 2563–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, E.; Tan, Y.; Geng, B.; Kang, C.; Li, X. PTRF/CAVIN1, regulated by SHC1 through the EGFR pathway, is found in urine exosomes as a potential biomarker of ccRCC. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logozzi, M.; Mizzoni, D.; Capasso, C.; Del Prete, S.; Di Raimo, R.; Falchi, M.; Angelini, D.F.; Sciarra, A.; Maggi, M.; Supuran, C.T.; et al. Plasmatic exosomes from prostate cancer patients show increased carbonic anhydrase IX expression and activity and low pH. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomiyama, E.; Matsuzaki, K.; Fujita, K.; Shiromizu, T.; Narumi, R.; Jingushi, K.; Koh, Y.; Matsushita, M.; Nakano, K.; Hayashi, Y.; et al. Proteomic analysis of urinary and tissue-exudative extracellular vesicles to discover novel bladder cancer biomarkers. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 2033–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, K.; Zeng, Q.; Dong, W. The clinical significance of microRNA-409 in pancreatic carcinoma and associated tumor cellular functions. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ren, L.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Fu, W.; Yi, J.; Wang, J.; Du, G. The biology, function, and applications of exosomes in cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2783–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, K.; Chen, L.; Liu, D.; Dong, S.; Xia, J.; Long, Q.; Yue, Y.; Zhao, P.; et al. Identification of a distinct luminal subgroup diagnosing and stratifying early stage prostate cancer by tissue-based single-cell RNA sequencing. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igami, K.; Uchiumi, T.; Shiota, M.; Ueda, S.; Tsukahara, S.; Akimoto, M.; Eto, M.; Kang, D. Extracellular vesicles expressing CEACAM proteins in the urine of bladder cancer patients. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 3120–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; He, J.; Min, L.; He, Y.; Guan, H.; Wang, J.; Peng, X. Extracellular vesicles transmitted miR-31-5p promotes sorafenib resistance by targeting MLH1 in renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, J.W.; Kim, H.; Moustafa, A.A.; Datta, A.; Barata, P.C.; Boulares, A.H.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Krane, L.S. Repurposing ketoconazole as an exosome directed adjunct to sunitinib in treating renal cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, G.; Gu, J.; Zhou, D.; Li, L.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Tang, T.; Wang, X. Cancer-associated fibroblast-secreted exosomal miR-423-5p promotes chemotherapy resistance in prostate cancer by targeting GREM2 through the TGF-β signaling pathway. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1809–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhao, S. Exosome-derived miR-27a produced by PSC-27 cells contributes to prostate cancer chemoresistance through p53. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 515, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.; Zhou, X.; Gu, J.; Zhou, D.; Cheng, W.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Tang, T.; Wang, X. Downregulated exosomal microRNA-148b-3p in cancer associated fibroblasts enhance chemosensitivity of bladder cancer cells by downregulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and upregulating PTEN. Cell. Oncol. Dordr. 2021, 44, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Liang, X.; Peng, Y.; Wu, C.; Lu, R.; Pan, Y.; et al. A Biomimetic Drug Delivery System by Integrating Grapefruit Extracellular Vesicles and Doxorubicin-Loaded Heparin-Based Nanoparticles for Glioma Therapy. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayamajhi, S.; Nguyen, T.D.T.; Marasini, R.; Aryal, S. Macrophage-derived exosome-mimetic hybrid vesicles for tumor targeted drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2019, 94, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, Y.S.; Li, S.M.; Bago, J.R.; Klyachko, N.L.; Kabanov, A.V.; Batrakova, E.V. Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Delivery Systems for Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Therapy. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. Off. J. Soc. NeuroImmune Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severic, M.; Ma, G.; Pereira, S.G.T.; Ruiz, A.; Cheung, C.C.L.; Al-Jamal, W.T. Genetically-engineered anti-PSMA exosome mimetics targeting advanced prostate cancer in vitro and in vivo. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2021, 330, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wan, Z.; Yang, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, F.; Tang, J. Sonodynamical reversion of immunosuppressive microenvironment in prostate cancer via engineered exosomes. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Ding, W.; Qian, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, C.; Yu, Q.; Tai, Z.; Xu, K. Immunotherapy Strategy Targeting Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 and CD73 with Macrophage-Derived Mimetic Nanovesicles to Treat Bladder Cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 4015–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helissey, C.; Guitard, N.; Théry, H.; Goulinet, S.; Mauduit, P.; Girleanu, M.; Favier, A.L.; Drouet, M.; Parnot, C.; Chargari, C.; et al. Two New Potential Therapeutic Approaches in Radiation Cystitis Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Extracellular Vesicles and Conditioned Medium. Biology 2022, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Hai, B.; Kelly, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, F. Extracellular vesicle mimics made from iPS cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, J.; Boleij, A.; Pieters, B.C.H.; Feitsma, A.L.; van Neerven, R.J.J.; Ten Klooster, J.P.; M’Rabet, L.; Arntz, O.J.; Koenders, M.I.; van de Loo, F.A.J. Flood Control: How Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Can Help to Improve the Intestinal Barrier Function and Break the Gut-Joint Axis in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 703277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecocci, S.; Pietrucci, D.; Milanesi, M.; Pascucci, L.; Filippi, S.; Rosato, V.; Chillemi, G.; Capomaccio, S.; Cappelli, K. Transcriptomic Characterization of Cow, Donkey and Goat Milk Extracellular Vesicles Reveals Their Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Rong, Y.; Tang, X.; Yi, K.; Qi, P.; Hou, J.; Liu, W.; He, Y.; Gao, X.; Yuan, C.; et al. Engineered exosomes as an in situ DC-primed vaccine to boost antitumor immunity in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zuo, B.; Jing, R.; Gao, X.; Rao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Qi, H.; Guo, H.; Yin, H. Dendritic cell-derived exosomes elicit tumor regression in autochthonous hepatocellular carcinoma mouse models. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.Y.; Li, N.; Yao, N.; Xu, X.F.; Wang, H.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y. CD8+ T cells stimulated by exosomes derived from RenCa cells mediate specific immune responses through the FasL/Fas signaling pathway and, combined with GM-CSF and IL-12, enhance the anti-renal cortical adenocarcinoma effect. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 866–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parenky, A.C.; Akalkotkar, A.; Mulla, N.S.; D’Souza, M.J. Harnessing T-cell activity against prostate cancer: A therapeutic microparticulate oral cancer vaccine. Vaccine 2019, 37, 6085–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Lin, H.; Xie, W.; Li, J.; Tan, W. Antitumor efficacy of interferon-γ-modified exosomal vaccine in prostate cancer. Prostate 2020, 80, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Mechanism | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultracentrifugation | Density | Gold standard; Low cost | Time consuming; low specificity |
| Density gradients | Density | Gold standard; High specificity | Low production; Time consuming |
| Precipitation | Solubility | Quikly | Low specificity, presence of protein |
| Immuno-capture | Antigen | Quikly | High cost; High specificity |
| Size exclusion chromatography | Size | Quikly | Contaminated protein |
| Type | Disease | Source | Cargoes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA | RCC | Serum | miR-4525, miR-155 | Muramatsu-Maekawa et al., Meng et al. [80,81] |
| Plasma | miR-301a-3p, miR-1293, miR-92a-1-5p, miR-149-3p, miR-424-3p | Dias et al., Xiao et al. [82,83] | ||
| Urine | miR-224-5p, miR-204-5p, miR-30c-5p | Qin et al., Kurahashi et al., Song et al. [84,85,86] | ||
| PCa | Serum | miR-93, miR-181a-5p | Iinuma et al., Wang et al. [87,88] | |
| Plasma | miR-145, miR-221, mIR-451a, miR-141 | Zabegina et al., Kim et al. [89,90] | ||
| Urine | miR-375, miR-574, miR-30b, miR-126 | Davey et al., Matsuzaki et al. [91,92] | ||
| BC | Plasma | miR-185, miR-106a, miR-10b | Sabo et al. [93] | |
| Urine | miR-96-5p, miR-183-5p | El-Shal et al. [94] | ||
| lncRNA | PCa | Urine | lncRNA PCA3, lncRNA-p21 | Li et al., Işın et al. [95,96] |
| Serum | lncRNA HOXD-AS1 | Jiang et al. [97] | ||
| BC | Plasma | lncRNA PTENP1 | Zheng et al. [98] | |
| Urine | lncRNA ANRIL | Abbastabar et al. [99] | ||
| CircRNA | RCC | Plasma | circ_400068 | Xiao et al. [100] |
| PCa | Blood | circ_0044516 | Li et al. [101] | |
| Protein | RCC | Cells | Rab 27b | Tsuruda et al. [102] |
| Plasma | MTDH | Iliuk et al. [103] | ||
| Urine | PTRF | Zhao et al. [104] | ||
| PCa | Plasma | CA IX | Logozzi et al. [105] | |
| BCa | Urine | Hsp 90, CEACAM | Tomiyama et al. [106] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L.; Mao, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, Z. Current Status of Research on Small Extracellular Vesicles for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Urological Tumors. Cancers 2023, 15, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010100
Zhang M, Lu Y, Wang L, Mao Y, Hu X, Chen Z. Current Status of Research on Small Extracellular Vesicles for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Urological Tumors. Cancers. 2023; 15(1):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010100
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Mengting, Yukang Lu, Lanfeng Wang, Yiping Mao, Xinyi Hu, and Zhiping Chen. 2023. "Current Status of Research on Small Extracellular Vesicles for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Urological Tumors" Cancers 15, no. 1: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010100
APA StyleZhang, M., Lu, Y., Wang, L., Mao, Y., Hu, X., & Chen, Z. (2023). Current Status of Research on Small Extracellular Vesicles for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Urological Tumors. Cancers, 15(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010100







