Structure–Activity Relationship of Benzofuran Derivatives with Potential Anticancer Activity
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Benzofuran Derivatives as Anticancer Agents
3.1. Halogenated Derivatives of Benzofuran
3.2. Hybrid Benzofuran as Anticancer Agents
3.2.1. Benzene-Sulfonamide-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
3.2.2. 6-Substituted Hexamethylene Amiloride (6-HMA)-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
3.2.3. Quinazolinone- and Imidazolium-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
3.2.4. Carbohydrazide- and Substituted Benzaldehydes-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
3.2.5. Trimethoxyacetophenone-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
3.2.6. N-Methylpiperidine-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
| Compound | Cell Line | IC50 (μM) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | HCT116 (p53-null) | 2.91 | [51] |
| MDA-MB-435s (p53-mutated) | 4.71 | ||
| 5 | uPA | 0.43 | [61] |
| 6a | MCF-7 | 7.70 | [47] |
| 6b | MCF-7 | 9.14 | |
| 6c | MCF-7 | 1.00 | |
| 6d | MCF-7 | 20.58 | |
| 6e | MCF-7 | inactive | |
| 6f | MCF-7 | 73.26 | |
| 6g | MCF-7 | 1.00 | |
| 6h | MCF-7 | 100 | |
| 6i | MCF-7 | 0.57 | |
| 8 | Tubulin | 0.43 | [74] |
| 8a | Tubulin | 0.76 | |
| 8b | Tubulin | ND | |
| 9 | SQ20B | 0.46 | [79] |
| 10 | ND | ND | [82] |
| 10a | PANC-1 | 1.52 | |
| BxPC3 | 1.08 | ||
| HCT116 | 2.39 | ||
| HCT116(p53−/−) | 1.66 | ||
| MCF-7 | 2.84 | ||
| A549 | 2.98 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | 3.73 | ||
| 10b | PANC-1 | 1.07 | |
| BxPC3 | 0.65 | ||
| HCT116 | 1.81 | ||
| HCT116(p53−/−) | 1.61 | ||
| MCF-7 | 2.39 | ||
| A549 | 2.68 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | 1.90 | ||
| 11a | A549 | 0.12 | [84] |
| Hela | 26.32 | ||
| SGC7901 | 2.75 | ||
| 11b | A549 | 6.25 | |
| Hela | 18.71 | ||
| SGC7901 | 36.23 | ||
| 11c | A549 | 8.11 | |
| Hela | 28.74 | ||
| SGC7901 | >40 | ||
| 11d | A549 | 34.13 | |
| Hela | 12.68 | ||
| SGC7901 | 7.45 | ||
| 12 | HT-1080 | 8.86 | [85] |
| 13a | HL60 | 2.34 | [86] |
| SMMC-7721 | 2.63 | ||
| A549 | 4.5 | ||
| MCF-7 | 3.24 | ||
| SW480 | 3.61 | ||
| 13b | HL60 | 0.64 | |
| SMMC-7721 | 2.10 | ||
| A549 | 3.34 | ||
| MCF-7 | 4.78 | ||
| SW480 | 5.56 | ||
| 13c | HL60 | 0.61 | [86] |
| SMMC-7721 | 2.30 | ||
| A549 | 5.35 | ||
| MCF-7 | 3.03 | ||
| SW480 | 3.14 | ||
| 13d | HL60 | 0.08 | |
| SMMC-7721 | 0.52 | ||
| A549 | 0.55 | ||
| MCF-7 | 0.51 | ||
| SW480 | 0.47 | ||
| 14a | ND | ND | [87] |
| 14b | ND | ND | |
| 14c | ND | ND | |
| 14d | ND | ND | |
| 15a | MCF-7 | 1.90 | [88] |
| A549 | 2.38 | ||
| Colo-205 | 2.11 | ||
| A2780 | 1.05 | ||
| 15b | MCF-7 | 3.90 | |
| A549 | 4.17 | ||
| Colo-205 | ND | ||
| A2780 | ND | ||
| 15c | MCF-7 | 0.011 | |
| A549 | 0.073 | ||
| Colo-205 | 0.10 | ||
| A2780 | 0.034 | ||
| 15d | MCF-7 | 7.23 | |
| A549 | 6.91 | ||
| Colo-205 | 2.84 | ||
| A2780 | 10.2 | ||
| 15e | MCF-7 | 12.5 | |
| A549 | 5.34 | ||
| Colo-205 | ND | ||
| A2780 | 9.55 | ||
| 15f | MCF-7 | 3.16 | |
| A549 | ND | ||
| Colo-205 | 7.10 | ||
| A2780 | 8.64 | ||
| 15g | MCF-7 | 10.76 | |
| A549 | 19.42 | ||
| Colo-205 | ND | ||
| A2780 | ND | ||
| 15h | MCF-7 | 1.55 | |
| A549 | 1.93 | ||
| Colo-205 | 1.28 | ||
| A2780 | 2.13 | ||
| 15i | MCF-7 | 0.21 | |
| A549 | 0.43 | ||
| Colo-205 | 0.17 | ||
| A2780 | 1.84 | ||
| 15j | MCF-7 | 0.14 | |
| A549 | 0.25 | ||
| Colo-205 | 0.12 | ||
| A2780 | 0.33 | ||
| 16 | K562 | ND | [89] |
| 17a | K562 | ND | |
| 17b | K562 | ND | |
| 18 | A549 | 9 | [90] |
| MCF-7 | 2 | ||
| PC-3 | 10 | ||
| 19 | A549 | 6.3 | [49] |
| 20a | A549 | 10.9 | |
| 20b | A549 | Inactive |
| Compound | CTC50 (μM/mL) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 7a | 35.5 | [71] |
| 7b | 472 | |
| 7c | 33.5 | |
| 7d | 33.75 | |
| 7e | 255 | |
| 7f | 43 | |
| 7g | 280 | |
| 7h | 365 | |
| 7i | 34 | |
| 7j | 49 | |
| 7k | 478 |
3.2.7. Piperazine-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
3.2.8. Neolignans-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
3.2.9. Imidazole-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
3.2.10. Pyrazole-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
3.2.11. Imidazopyridine-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
3.2.12. Aurones-Chromone- and -Coumarin-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
3.2.13. Chalcone-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
3.2.14. Oxadiazole- and Triazole-Based Benzofuran Derivatives
3.3. Cytotoxicity of Benzofurans’ Derivatives against Selected Cancer Cell Lines
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5FU | 5-fluorouracil |
| 6-HMA | 6-substituted hexamethylene amiloride |
| 6-HMA | 6- N, N-hexamethylene |
| ADME | Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion |
| AKT signaling | Serine–threonine kinase signaling |
| ATP | Adenosine 5′-triphosphate |
| A549 | Hypotriploid alveolar basal epithelial cell lines |
| A2780 | Ovarian cancer cell line |
| BNC105P | Disoduimphosphase ester derivative compound 8b |
| BxPC3 | Human pancreatic cancer cell lines |
| CB1 | 5-chlorobenzofuran-2-carboxamides |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CB1 modulator | Cannabinoid receptor type 1 modulator |
| CA-A4 | Combretastatin A-4 |
| CTC50 | cytotoxic concentration scores |
| Colo-205 | Colon cancer cell lines |
| EAC | Erlich ascites carcinoma cells |
| HT-29 | Human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell lines |
| HCT116 | Human colorectal carcinoma cell lines |
| HIF pathway | Hypoxia-inducible factor pathway |
| HUVEC | normal endothelial cancer cell lines |
| HT-1080 | Fibrosarcoma cell lines |
| HL60 | Human acute leukemia cells |
| HeLa | human cervical cancer cells |
| HTS | High-Throughput Screening |
| IC50 | half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| Ki | Dissociation constant |
| K562 | Human leukemia cell lines |
| MCF-7 | human breast cancer cells |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide |
| mTOR pathway | mammalian target of the rapamycin |
| mTORC1 | Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 |
| MDA-MB-23 | Metastatic adenocarcinoma cell lines |
| MCF-10A | human mammary gland epithelial cell line |
| MRC5 | normal breast cancer cells |
| NA | Not Applicable |
| Panc-1 | Human pancreatic cancer cell lines |
| P53 | Tumor protein |
| PADC | pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell lines |
| PC-3 | Prostate cancer cell lines |
| PLK1 PBD inhibitor | Polo-like kinase 1 Polo-Box Domain inhibitor |
| SAR | Structure–activity relationship |
| SRB | sulforhodamine B |
| SQ20B | head and neck cancer cell lines |
| SMMC-7721 | Hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines |
| SGC7901 | Colonic cancer cell lines |
| Src | Non-receptor tyrosine kinase protein |
| SW480 | Colon cancer cell lines |
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer cell lines |
| uPA | urokinase-type plasminogen activator |
| uPAR | urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor |
| ZAP-70 kinases | Zeta-chain-associated protein kinase 70 |
References
- Chand, K.; Hiremathad, A.; Singh, M.; Santos, M.A.; Keri, R.S. A Review on Antioxidant Potential of Bioactive Heterocycle Benzofuran: Natural and Synthetic Derivatives. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radadiya, A.; Shah, A. Bioactive Benzofuran Derivatives: An Insight on Lead Developments, Radioligands and Advances of the Last Decade. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 356–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, P.; Rodriguez, E. Chromenes and Benzofurans of the Asteraceae, Their Chemistry and Biological Significance. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 2335–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heravi, M.M.; Zadsirjan, V.; Hamidi, H.; Tabar Amiri, P.H. Total Synthesis of Natural Products Containing Benzofuran Rings. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 24470–24521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, G.; Höke, H. Benzofurans. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.W.; Park, J.H.; Seo, K.H.; Oh, E.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Lim, D.W.; Han, D.; Song, M.C.; Baek, N.I. New Hydroxy Fatty Acid from the Root Bark of Morus alba L. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2015, 58, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modell, A.E.; Blosser, S.L.; Arora, P.S. Systematic Targeting of Protein–Protein Interactions. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Lv, Z.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Bai, L.; Deng, J. Benzofuran Derivatives and Their Anti-Tubercular, Anti-Bacterial Activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 162, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevagi, R.J.; Dighe, S.N.; Dighe, S.N. Biological and Medicinal Significance of Benzofuran. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremathad, A.; Patil, M.R.; Chethana, K.R.; Chand, K.; Santos, M.A.; Keri, R.S. Benzofuran: An Emerging Scaffold for Antimicrobial Agents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 96809–96828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Peng, E.; Huang, N.; Huang, Q.; Huq, A.; Lau, M.; Colonno, R.; Li, L. Discovery of Novel Potent HCV NS5B Polymerase Non-Nucleoside Inhibitors Bearing a Fused Benzofuran Scaffold. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, D.; Kaur, A.; Goyal, B. Benzofuran and Indole: Promising Scaffolds for Drug Development in Alzheimer’s Disease. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 1275–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subair, T.I.; Soremekun, O.S.; Olotu, F.A.; Soliman, M.E.S. Therapeutic Path to Double Knockout: Investigating the Selective Dual-Inhibitory Mechanisms of Adenosine Receptors A1 and A2 by a Novel Methoxy-Substituted Benzofuran Derivative in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 79, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, T.; Tokunaga, N.; Tokumaru, K.; Ohra, T.; Koyama, N.; Hayashi, S.; Yamada, R.; Shirasaki, M.; Inui, Y.; Tsukamoto, T. Discovery of Benzofuran Derivatives That Collaborate with Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) to Promote Neuroprotection. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 5109–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashidhara, K.V.; Modukuri, R.K.; Sonkar, R.; Rao, K.B.; Bhatia, G. Hybrid Benzofuran-Bisindole Derivatives: New Prototypes with Promising Anti-Hyperlipidemic Activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 68, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, N.M.; Srour, A.M.; El-Karim, S.S.A.; Saleh, D.O.; Al-Omar, M.A. Synthesis and 2D-QSAR Study of Active Benzofuran-Based Vasodilators. Molecules 2017, 22, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, K.M. An Update on Benzofuran Inhibitors: A Patent Review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2019, 29, 841–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.H.; Hu, Y.H.; Yang, J.; Liu, T.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.J. Natural Source, Bioactivity and Synthesis of Benzofuran Derivatives. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 27510–27540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, C.; Martinelli, C.; Ciofani, G. Innovative Approaches for Cancer Treatment: Current Perspectives and New Challenges. Ecancermedicalscience 2019, 13, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today (accessed on 11 December 2021).
- Martins, P.; Jesus, J.; Santos, S.; Raposo, L.R.; Roma-Rodrigues, C.; Baptista, P.V.; Fernandes, A.R. Heterocyclic Anticancer Compounds: Recent Advances and the Paradigm Shift towards the Use of Nanomedicine’s Tool Box. Molecules 2015, 20, 16852–16891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodarahmi, G.; Asadi, P.; Hassanzadeh, F.; Khodarahmi, E. Benzofuran as a Promising Scaffold for the Synthesis of Antimicrobial and Antibreast Cancer Agents: A Review. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2015, 20, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Pu, X.J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, B.; Rao, G.X.; Wan, C.P.; Mao, Z.W. 2-Benzoylbenzofuran Derivatives Possessing Piperazine Linker as Anticancer Agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negalurmath, V.S.; Boda, S.K.; Kotresh, O.; Anantha Lakshmi, P.V.; Basanagouda, M. Benzofuran-Oxadiazole Hybrids: Design, Synthesis, Antitubercular Activity and Molecular Docking Studies. Chem. Data Collect. 2019, 19, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, Z.H.; Hu, A.X.; Yan, X.W.; Ding, N.; Ye, J. Design, Synthesis, and Antitumor Activity of (E,Z)-1-(Dihydrobenzofuran-5-Yl)-3-Phenyl-2-(1,2,4-Triazol-1-Yl)-2-Propen-1-Ones. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 86, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.P.; Xie, Q.; Huang, E.F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.Q.; Hu, J.S.; Wan, D.C.C.; Jin, Z.; Hu, C. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity of a Novel Series of Benzofuran Derivatives against Oestrogen Receptor-Dependent Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 95, 103566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Shen, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; Cao, J.; Shen, R.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Wan, H.; et al. Discovery of EBI-2511: A Highly Potent and Orally Active EZH2 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawiecka, M.; Kuran, B.; Kossakowski, J.; Cieslak, M.; Kazmierczak- Baranska, J.; Krolewska, K.; Nawrot, B. Synthesis and Cytotoxic Properties of Halogen and Aryl-/Heteroarylpiperazinyl Derivatives of Benzofurans. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 15, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, K.M.; Syam, Y.M.; Anwar, M.M.; Ali, H.I.; Abdel-Ghani, T.M.; Serry, A.M. Synthesis and Molecular Docking Study of New Benzofuran and Furo[3,2-g]Chromone-Based Cytotoxic Agents against Breast Cancer and P38α MAP Kinase Inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 76, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.S.; Wang, W.; Zhong, H.J.; Dong, Z.Z.; Huang, Q.; Mok, S.W.F.; Leung, C.H.; Wong, V.K.W.; Ma, D.L. An Anti-Prostate Cancer Benzofuran-Conjugated Iridium(III) Complex as a Dual Inhibitor of STAT3 and NF-ΚB. Cancer Lett. 2017, 396, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, M.C.; Ho, P.S. Computational Tools To Model Halogen Bonds in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 59, 1655–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcken, R.; Zimmermann, M.O.; Lange, A.; Joerger, A.C.; Boeckler, F.M. Principles and Applications of Halogen Bonding in Medicinal Chemistry and Chemical Biology. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1363–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfatah, S.; Berg, A.; Huang, Q.; Yang, L.J.; Hamdoun, S.; Klinger, A.; Greten, H.J.; Fleischer, E.; Berg, T.; Wong, V.K.W.; et al. MCC1019, a Selective Inhibitor of the Polo-Box Domain of Polo-like Kinase 1 as Novel, Potent Anticancer Candidate. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napiórkowska, M.; Cieślak, M.; Kaźmierczak-Barańska, J.; Królewska-Golińska, K.; Nawrot, B. Synthesis of New Derivatives of Benzofuran as Potential Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2019, 24, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, D.I.; Abdelal, A.M.M.; El-Sayed, M.A.; El Bialy, S.A.A. Novel Benzofuran Derivatives: Synthesis and Antitumor Activity. Heterocycl. Commun. 2013, 19, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.C.; Chen, W.; Liu, L.X.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.J.; Deng, X.Y.; Zhang, H.B.; Yang, X.D. Synthesis and Cytotoxic Activity of Novel Hybrid Compounds between 2-Alkylbenzofuran and Imidazole. Med. Chem. Res. 2014, 23, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Wan, W.C.; Deng, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.J.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.B. Design, Synthesis and Cytotoxic Activities of Novel Hybrid Compounds between 2-Phenylbenzofuran and Imidazole. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 2726–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Law, P.-Y.; Loh, H. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt Signaling: An Emerging Paradigm for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. Agents 2005, 5, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Jo, H.; Park, H.J.; Sateesh Kumar, A.; Lee, J.; Yun, J.; Kim, Y.; Han, S.B.; Jung, J.K.; Cho, J.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Benzofuran- and 2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran-2-Carboxylic Acid N-(Substituted)Phenylamide Derivatives as Anticancer Agents and Inhibitors of NF-ΚB. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2545–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.W.; Zheng, X.; Lin, Y.P.; Hu, C.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Wan, C.P.; Rao, G.X. Design, Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of Novel Hybrid Compounds between Benzofuran and N-Aryl Piperazine. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3421–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Feng, K.R.; Zhao, J.Y.; Zhang, J.W.; Shi, X.W.; Zhou, J.; Gao, D.; Lin, G.Q.; Tian, P. Identification of Novel STAT3 Inhibitors Bearing 2-Acetyl-7-Phenylamino Benzofuran Scaffold for Antitumour Study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssif, B.G.M.; Mohamed, A.M.; Osman, E.E.A.; Abou-Ghadir, O.F.; Elnaggar, D.H.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; Treamblu, L.; Gomaa, H.A.M. 5-Chlorobenzofuran-2-Carboxamides: From Allosteric CB1 Modulators to Potential Apoptotic Antitumor Agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 177, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riss, T.L.; Moravec, R.A.; Niles, A.L.; Duellman, S.; Benink, H.A.; Worzella, T.J.; Minor, L. Cell Viability Assays; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelhafez, O.M.; Amin, K.M.; Ali, H.I.; Abdalla, M.M.; Ahmed, E.Y. Design, Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of Benzofuran Derivatives Targeting VEGFR-2 Tyrosine Kinase. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 11569–11579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adem, F.A.; Kuete, V.; Mbaveng, A.T.; Heydenreich, M.; Ndakala, A.; Irungu, B.; Efferth, T.; Yenesew, A. Cytotoxic Benzylbenzofuran Derivatives from Dorstenia Kameruniana. Fitoterapia 2018, 128, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coşkun, D.; Tekin, S.; Sandal, S.; Coşkun, M.F. Synthesis, Characterization, and Anticancer Activity of New Benzofuran Substituted Chalcones. J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 7678486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, P.; Khodarahmi, G.; Jahanian-Najafabadi, A.; Saghaie, L.; Hassanzadeh, F. Biologically Active Heterocyclic Hybrids Based on Quinazolinone, Benzofuran and Imidazolium Moieties: Synthesis, Characterization, Cytotoxic and Antibacterial Evaluation. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etebari, M.; Khodarahmi, G.A.; Jafarian-Dehkordi, A.; Nokhodian, Z. Genotoxic Effects of Some L-[(Benzofuran-2-Yl)-Phenylmethyl]-Imidazoles on MCF-7 Cell Line. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 7, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Irfan, A.; Faiz, S.; Rasul, A.; Zafar, R.; Zahoor, A.F.; Kotwica-Mojzych, K.; Mojzych, M. Exploring the Synergistic Anticancer Potential of Benzofuran–Oxadiazoles and Triazoles: Improved Ultrasound-and Microwave-Assisted Synthesis, Molecular Docking, Hemolytic, Thrombolytic and Anticancer Evaluation of Furan-Based Molecules. Molecules 2022, 27, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, M.; Cao, Y.; Feng, W.; Li, X.; Xue, W.; Shi, H. Discovery of a Novel Benzenesulfonamide Analogue That Inhibits Proliferation and Metastasis against Ovarian Cancer OVCAR-8 Cells. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.R.; Wei, J.L.; Mo, X.F.; Yuan, Z.W.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.Y.; You, Q.D.; Sun, H.P. Discovery and Optimization of New Benzofuran Derivatives against P53-Independent Malignant Cancer Cells through Inhibition of HIF-1 Pathway. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2713–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. Defining the Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 in Cancer Biology and Therapeutics. Oncogene 2010, 29, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Yasui, Y.; Maruyama, M.; Minegishi, H.; Ban, H.S.; Sato, S. Development of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1α Inhibitors: Effect of Ortho-Carborane Substituents on HIF Transcriptional Activity under Hypoxia. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, N.; Mihalcioiu, C.; Rabbani, S.A. Multifaceted Role of the Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator (UPA) and Its Receptor (UPAR): Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Applications. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulisse, S.; Baldini, E.; Sorrenti, S.; D’Armiento, M. The Urokinase Plasminogen Activator System: A Target for Anti-Cancer Therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 32–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croucher, D.R.; Saunders, D.N.; Lobov, S.; Ranson, M. Revisiting the Biological Roles of PAI2 (SERPINB2) in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, H.; Ranson, M.; Tyndall, J.D.A.; Kelso, M.J. Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluation of Amiloride Analogs as Inhibitors of the Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator (UPA). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 6760–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.W.; Lyons, J.C.; Makepeace, C.M.; Griffin, R.J.; Cragoe, E.J. Effect’s of Hma, an Analog of Amiloride, on the Thermosensitivity of Tumors in Vivo. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994, 30, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Tannock, I.F. Inhibition of the Regulation of Intracellular PH: Potential of 5-(N,N-Hexamethylene) Amiloride in Tumour-Selective Therapy. Br. J. Cancer 1994, 70, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chemler, S.R.; Trauner, D.; Danishefsky, S.J. The B -Alkyl Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reaction: A Versatile C-C Bond-Forming Tool REVIEWS The B -Alkyl Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reaction: Development, Mechanistic Study, and Applications in Natural Product Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 4544–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, B.J.; Aboelela, A.; Minaei, E.; Jiang, L.X.; Xu, Z.; Ali, U.; Fildes, K.; Cheung, C.Y.; Cook, S.M.; Johnson, D.C.; et al. 6-Substituted Hexamethylene Amiloride (HMA) Derivatives as Potent and Selective Inhibitors of the Human Urokinase Plasminogen Activator for Use in Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 8299–8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ma, C.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Haimiti, X. BF12, a Novel Benzofuran, Exhibits Antitumor Activity by Inhibiting Microtubules and the PI3K/Akt/MTOR Signaling Pathway in Human Cervical Cancer Cells. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, A.; Asadi, J.; Rostami-Charati, F.; Gharaei, R. High Cytotoxicity and Apoptotic Effects of Natural Bioactive Benzofuran Derivative on the MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen 2015, 18, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S. Quinazolinone and Quinazoline Derivatives: Synthesis and Biological Application; Intechopen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, A.A.; Alanazi, F.K. Biological Activity of Quinazolinones; Intechopen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, E.; Khajouei, M.R.; Hassanzadeh, F.; Hakimelahi, G.H.; Khodarahmi, G.A. Quinazolinone and Quinazoline Derivatives: Recent Structures with Potent Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kuttan, R.; Bhanumathy, P.; Nirmala, K.; George, M.C. Potential Anticancer Activity of Turmeric (Curcuma Longa). Cancer Lett. 1985, 29, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.R.P.; Sharma, G.K.; Srinath, S.; Noor, M.; Suresh, B.; Srinivasa, B.R. Microwave-Assisted, Solvent-Free, Parallel Syntheses and Elucidation of Reaction Mechanism for the Formation of Some Novel Tetraaryl Imidazoles of Biological Interest. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2009, 46, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.K.; Pathak, D. Microwave-Assisted, Solvent-Free and Parallel Synthesis of Some Novel Substituted Imidazoles of Biological Interest. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, B.; Jalapathi, P.; Saikrishna, B.; Perugu, S.; Manga, V. Synthesis, Anti-Microbial Activity, Cytotoxicity of Some Novel Substituted (5-(3-(1H-Benzo[d]Imidazol-2-Yl)-4-Hydroxybenzyl)Benzofuran-2-Yl)(Phenyl)Methanone Analogs. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Saxena, R.; Kumar, P.; Varshney, S. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Newer Benzofuran Derivatives as Potential Anticancer and Antithelmintic Agents. World J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 3, 821. [Google Scholar]
- Khanam, H.; Shamsuzzaman. Bioactive Benzofuran Derivatives: A Review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 483–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.-H. Combretastatin A-4 Analogues as Antimitotic Antitumor Agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 10, 1697–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, B.L.; Gill, G.S.; Grobelny, D.W.; Chaplin, J.H.; Paul, D.; Leske, A.F.; Lavranos, T.C.; Chalmers, D.K.; Charman, S.A.; Kostewicz, E.; et al. Discovery of 7-Hydroxy-6-Methoxy-2-Methyl-3-(3,4,5-Trimethoxybenzoyl)Benzo[ b ]Furan (BNC105), a Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitor with Potent Antiproliferative and Tumor Vascular Disrupting Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6014–6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignot, S.; Faivre, S.; Aguirre, D.; Raymond, E. MTOR-Targeted Therapy of Cancer with Rapamycin Derivatives. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, S.; Serova, M.; Dreyer, C.; Sablin, M.P.; Faivre, S.; Raymond, E. New Inhibitors of the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling Pathway for Cancer. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2010, 19, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faivre, S.; Kroemer, G.; Raymond, E. Current Development of MTOR Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 671–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomé, C.; Narbonne, V.; Ribeiro, N.; Thuaud, F.; Serova, M.; De Gramont, A.; Faivre, S.; Raymond, E.; Désaubry, L. Benzofuran Derivatives as a Novel Class of Inhibitors of MTOR Signaling. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 74, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomé, C.; Ribeiro, N.; Chavagnan, T.; Thuaud, F.; Serova, M.; De Gramont, A.; Faivre, S.; Raymond, E.; Désaubry, L. Benzofuran Derivatives as Anticancer Inhibitors of MTOR Signaling. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 81, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Laguna, I.; Hidalgo, M. Pancreatic Cancer: From State-of-the-Art Treatments to Promising Novel Therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivak-Kroizman, T.R.; Hostetter, G.; Posner, R.; Aziz, M.; Hu, C.; Demeure, M.J.; Von Hoff, D.; Hingorani, S.R.; Palculict, T.B.; Izzo, J.; et al. Hypoxia Triggers Hedgehog-Mediated Tumor-Stromal Interactions in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3235–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-L.; Yang, Y.-R.; Mo, X.-F.; Wei, J.-L.; Zhang, X.-J.; You, Q.-D. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Benzofuran Derivatives as Novel Anti-Pancreatic Carcinoma Agents via Interfering the Hypoxia Environment by Targeting HIF-1α Pathway. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 137, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, R.; Harmalkar, D.S.; Xu, X.; Jang, K.; Lee, K. Bioactive Benzofuran Derivatives: Moracins A-Z in Medicinal Chemistry. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zheng, X.; Gao, H.; Wan, C.; Rao, G.; Mao, Z. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Benzofuran Derivatives Bearing N-Aryl Piperazine Moiety. Molecules 2016, 21, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.X.; Zhou, C.C.; Li, L.Z.; Peng, Y.; Lou, L.L.; Liu, S.; Li, D.M.; Ikejima, T.; Song, S.J. Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Dihydrobenzofuran Neolignans from the Seeds of Crataegus Pinnatifida. Fitoterapia 2013, 91, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Deng, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.J.; Wan, W.C.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, H.B.; Yang, X.D. Synthesis and Cytotoxic Activities of Novel Hybrid 2-Phenyl-3- Alkylbenzofuran and Imidazole/Triazole Compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4297–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Karim, S.S.; Anwar, M.M.; Mohamed, N.A.; Nasr, T.; Elseginy, S.A. Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Docking Studies of Novel Benzofuran-Pyrazole Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2015, 63, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, I.S.; Sireesha, R.; Deepti, K.; Srinivasa Rao, P.; Ramesh Raju, R. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Sulphonamide Derivatives of Benzofuran-Imidazopyridines as Anticancer Agents. Chem. Data Collect. 2021, 31, 100608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwergel, C.; Valente, S.; Salvato, A.; Xu, Z.; Talhi, O.; Mai, A.; Silva, A.; Altucci, L.; Kirsch, G. Novel Benzofuran-Chromone and -Coumarin Derivatives: Synthesis and Biological Activity in K562 Human Leukemia Cells. Med. Chem. Commun. 2013, 4, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, D.; Erkisa, M.; Ulukaya, E.; Coskun, M.F.; Ari, F. Novel 1-(7-Ethoxy-1-Benzofuran-2-Yl) Substituted Chalcone Derivatives: Synthesis, Characterization and Anticancer Activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 136, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghorbani, M.; Begum, B.A.; Mamatha, S.V.; Ara Khanum, S. Piperazine and Morpholine: Synthetic Preview and Pharmaceutical Applications. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 281–301. Available online: www.jocpr.com (accessed on 17 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Rathi, A.K.; Syed, R.; Shin, H.S.; Patel, R.V. Piperazine Derivatives for Therapeutic Use: A Patent Review (2010-Present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 777–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuca, L.E.; David Coy, E.; Alarcón, M.A.; Fernández, A.; Aristizábal, F.A. Cytotoxic Effect of Some Natural Compounds Isolated from Lauraceae Plants and Synthetic Derivatives. Biomédica 2011, 31, 335–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.H.; Liu, Y.P.; Huang, Z.H.; Wang, T.T.; Feng, X.Y.; Yue, H.; Guo, W.; Fu, Y.H. Cytotoxic Dihydrobenzofuran Neolignans from Mappianthus Iodoies. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 75, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, T.A.; Borralho, P.M.; Luo, X.; Mulhovo, S.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Ferreira, M.J.U. Apoptosis Inducing Activity of Benzophenanthridine-Type Alkaloids and 2-Arylbenzofuran Neolignans in HCT116 Colon Carcinoma Cells. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaraman, A.; Kim, J.S.; Harmalkar, D.S.; Min, K.H.; Park, J.W.; Choi, Y.; Kim, K.; Lee, K. Synthesis and Cytotoxicity Studies of Bioactive Benzofurans from Lavandula Agustifolia and Modified Synthesis of Ailanthoidol, Homoegonol, and Egonol. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 3354–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.B.; Luo, J.G.; Pan, K.; Shan, S.M.; Zhang, W.; Kong, L.Y. Bioactive Benzofuran Neolignans from Aristolochia Fordiana. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zálešák, F.; Bon, D.J.Y.D.; Pospíšil, J. Lignans and Neolignans: Plant Secondary Metabolites as a Reservoir of Biologically Active Substances. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 146, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Larosa, C.; Antwi, J.; Govindarajan, R.; Werbovetz, K.A. Imidazoles as Potential Anticancer Agents: An Update on Recent Studies. Molecules 2021, 26, 4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hranjec, M.; Sović, I.; Ratkaj, I.; Pavlović, G.; Ilić, N.; Valjalo, L.; Pavelić, K.; Kraljević Pavelić, S.; Karminski-Zamola, G. Antiproliferative Potency of Novel Benzofuran-2-Carboxamides on Tumour Cell Lines: Cell Death Mechanisms and Determination of Crystal Structure. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 59, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.J.; Yang, X.D.; Zeng, X.H.; Xu, X.L.; Zhang, G.L.; Zhang, H.B. Synthesis and Cytotoxic Activities of Novel Hybrid Compounds of Imidazole Scaffold-Based 2-Substituted Benzofurans. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 4612–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, X.D.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.J.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, G.L.; Zhang, H.B. Design, Synthesis and Cytotoxic Activities of Novel Hybrid Compounds between Dihydrobenzofuran and Imidazole. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4250–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Lone, M.N.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Imidazoles as Potential Anticancer Agents. Medchemcomm 2017, 8, 1742–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, D.M.; Dutia, M.; Birnberg, G.; Powell, D.; Boschelli, D.H.; Wang, Y.D.; Ravi, M.; Yaczko, D.; Golas, J.; Lucas, J.; et al. 4-Anilino-7,8-Dialkoxybenzo[g]Quinoline-3-Carbonitriles as Potent Src Kinase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5909–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, A.S.; He, D.; Saigal, B.; Liu, S.; Lee, J.J.; Bakkannagari, S.; Ordonez, N.G.; Waun, K.H.; Wistuba, I.; Johnson, F.M. Inhibition of C-Src Expression and Activation in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Tissues Leads to Apoptosis, Cell Cycle Arrest, and Decreased Migration and Invasion. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 1962–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summy, J.M.; Gallick, G.E. Src Family Kinases in Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhao, B.X. Progress of the Synthesis of Condensed Pyrazole Derivatives (from 2010 to Mid-2013). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 85, 311–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennani, F.E.; Doudach, L.; Cherrah, Y.; Ramli, Y.; Karrouchi, K.; Ansar, M.; Faouzi, M.E.A. Overview of Recent Developments of Pyrazole Derivatives as an Anticancer Agent in Different Cell Line. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, V.M.; Masand, N.; Verma, S.; Masand, V. Chromones: Privileged Scaffold in Anticancer Drug Discovery. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2021, 98, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Meerloo, J.; Kaspers, G.J.L.; Cloos, J. Cell Sensitivity Assays: The MTT Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 731, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsayari, A.; Muhsinah, A.B.; Hassan, M.Z.; Ahsan, M.J.; Alshehri, J.A.; Begum, N. Aurone: A Biologically Attractive Scaffold as Anticancer Agent. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 166, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Singla, R.; Jaitak, V. Coumarins as Anticancer Agents: A Review on Synthetic Strategies, Mechanism of Action and SAR Studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 101, 476–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumendjel, A. Aurones: A Subclass of Flavones with Promising Biological Potential. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 2621–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogiorgis, C.; Detsi, A.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Coumarin-Based Drugs: A Patent Review (2008-Present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwergel, C.; Gaascht, F.; Valente, S.; Diederich, M.; Bagrel, D.; Kirsch, G. Aurones: Interesting Natural and Synthetic Compounds with Emerging Biological Potential. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.; Zhang, W.; Sheng, C.; Zhang, W.; Xing, C.; Miao, Z. Chalcone: A Privileged Structure in Medicinal Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7762–7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Xing, C. Diverse Molecular Targets for Chalcones with Varied Bioactivities. Med. Chem. 2015, 5, 388–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, C.; Narayana Moorthy, N.S.H.; Ramasamy, S.; Vanam, U.; Manivannan, E.; Karunagaran, D.; Trivedi, P. Advances in Chalcones with Anticancer Activities. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Kaur, K. Triazole and Oxadiazole Containing Natural Products: A Review. Nat. Prod. J. 2014, 4, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Gaonkar, S.L.; Musad, E.A.; Dawsar, A.M.A. 1,3,4-Oxadiazole-Containing Hybrids as Potential Anticancer Agents: Recent Developments, Mechanism of Action and Structure-Activity Relationships. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, S.J.; Liu, Y. 1,2,3-Triazole-Containing Hybrids as Potential Anticancer Agents: Current Developments, Action Mechanisms and Structure-Activity Relationships. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 183, 111700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M. 1,2,3-Triazole Hybrids as Anticancer Agents: A Review. Arch. Pharm. 2022, 355, e2100158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervaram, S.; Ashok, D.; Sarasija, M.; Reddy, C.V.R.; Sridhar, G. Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Fused Benzofuran Derivatives. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2018, 88, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
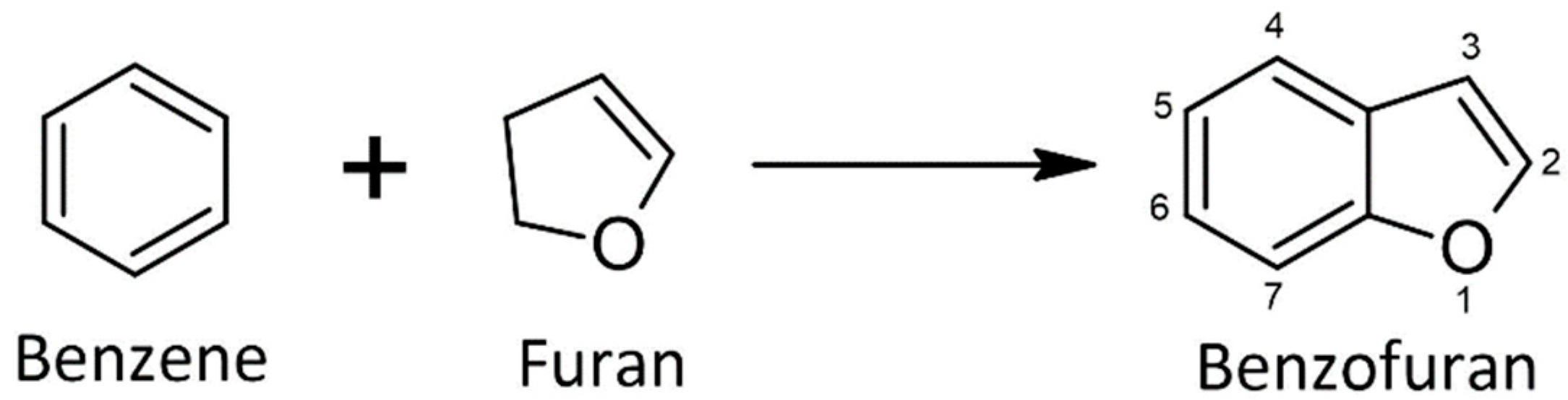
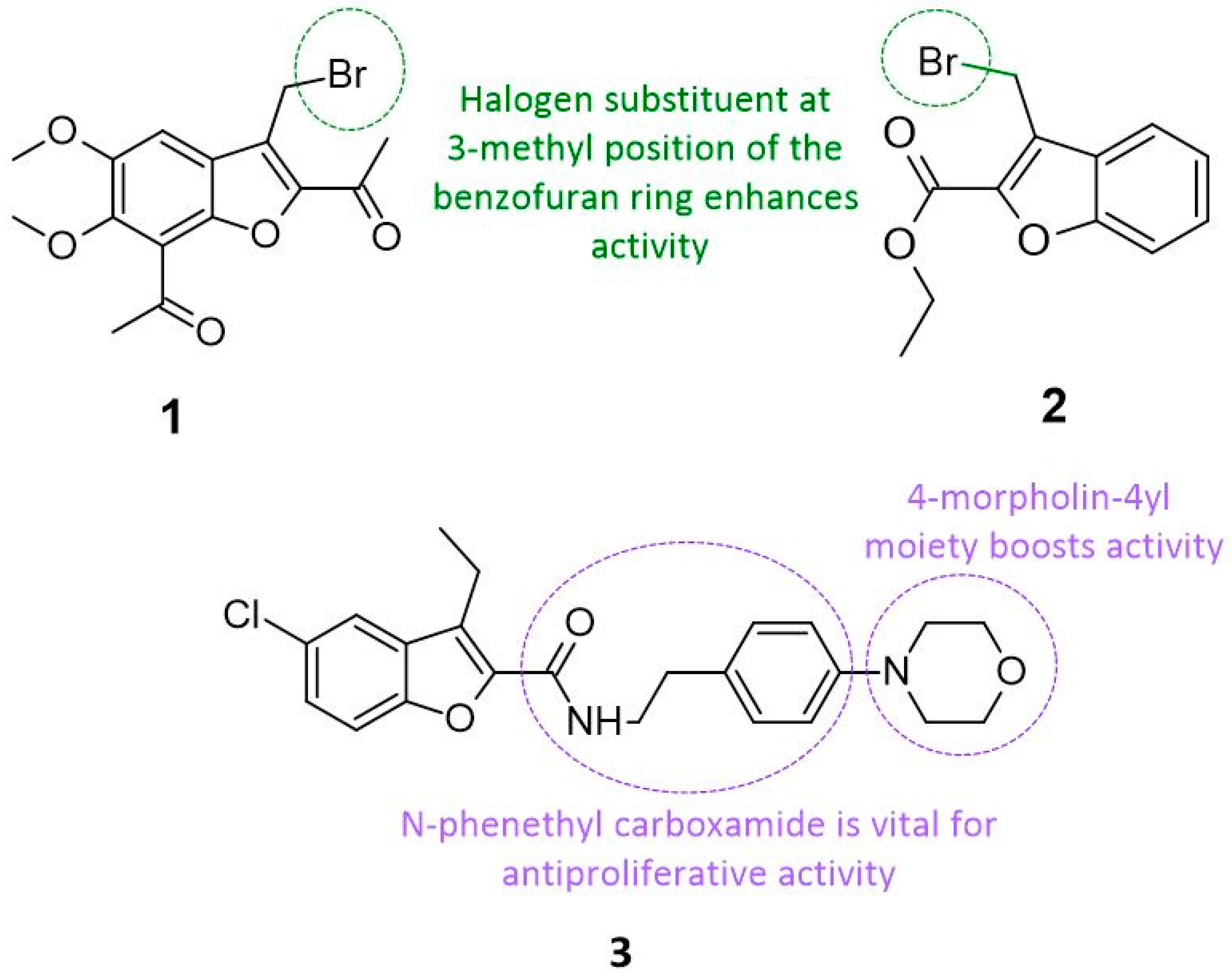

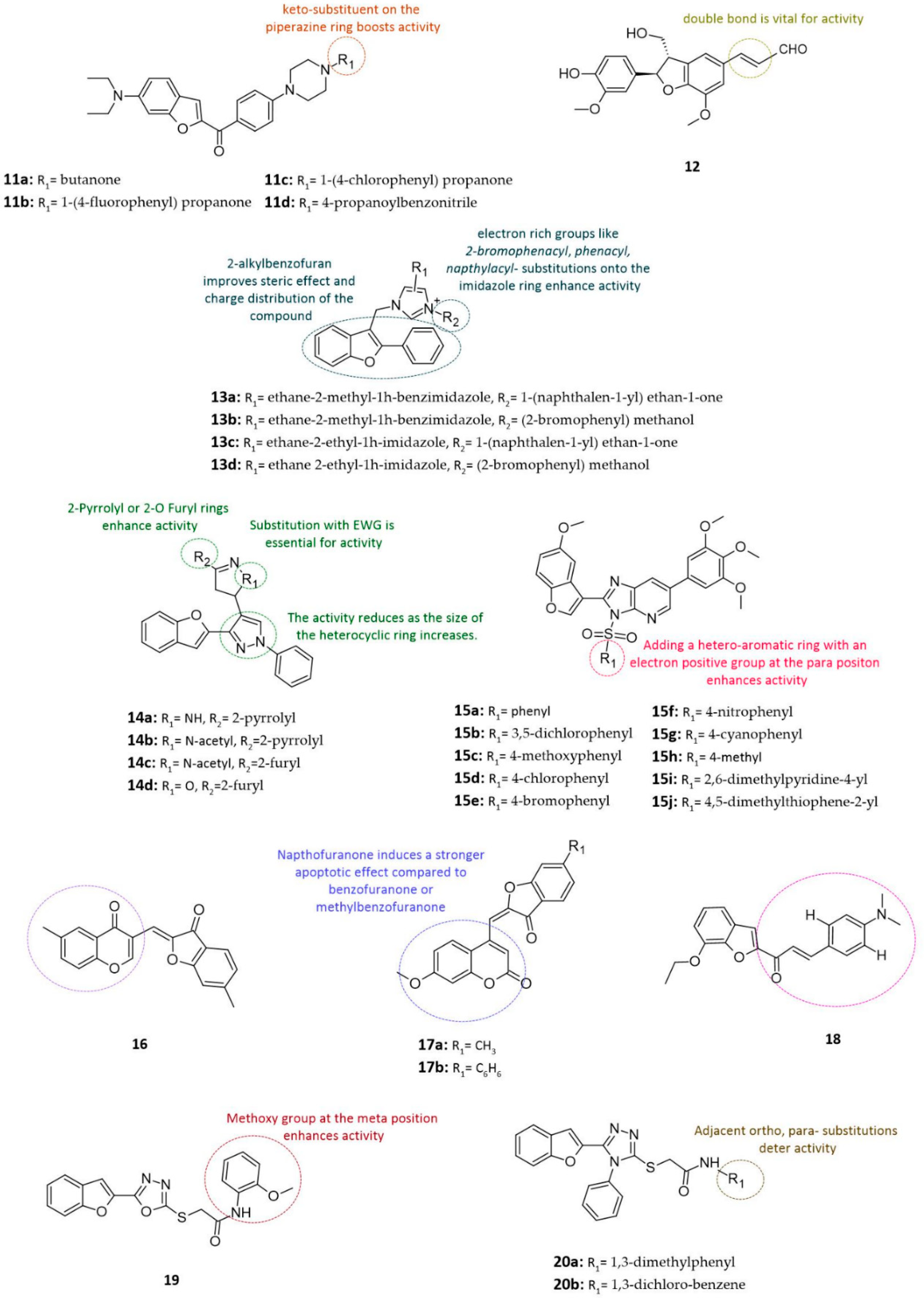
| Compound | Cell Line | IC50, μM | GI50, μM | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | K562 | 5 | ND | [28] |
| HL60 | 0.1 | ND | ||
| 2 | PLK1 PBD | 16.4 | ND | [33] |
| 3 | A-549 | ND | 1.8 | [42] |
| MCF-7 | ND | 0.7 | ||
| Panc-1 | ND | 1.3 | ||
| HT-29 | ND | 1.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farhat, J.; Alzyoud, L.; Alwahsh, M.; Al-Omari, B. Structure–Activity Relationship of Benzofuran Derivatives with Potential Anticancer Activity. Cancers 2022, 14, 2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092196
Farhat J, Alzyoud L, Alwahsh M, Al-Omari B. Structure–Activity Relationship of Benzofuran Derivatives with Potential Anticancer Activity. Cancers. 2022; 14(9):2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092196
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarhat, Joviana, Lara Alzyoud, Mohammad Alwahsh, and Basem Al-Omari. 2022. "Structure–Activity Relationship of Benzofuran Derivatives with Potential Anticancer Activity" Cancers 14, no. 9: 2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092196
APA StyleFarhat, J., Alzyoud, L., Alwahsh, M., & Al-Omari, B. (2022). Structure–Activity Relationship of Benzofuran Derivatives with Potential Anticancer Activity. Cancers, 14(9), 2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092196






