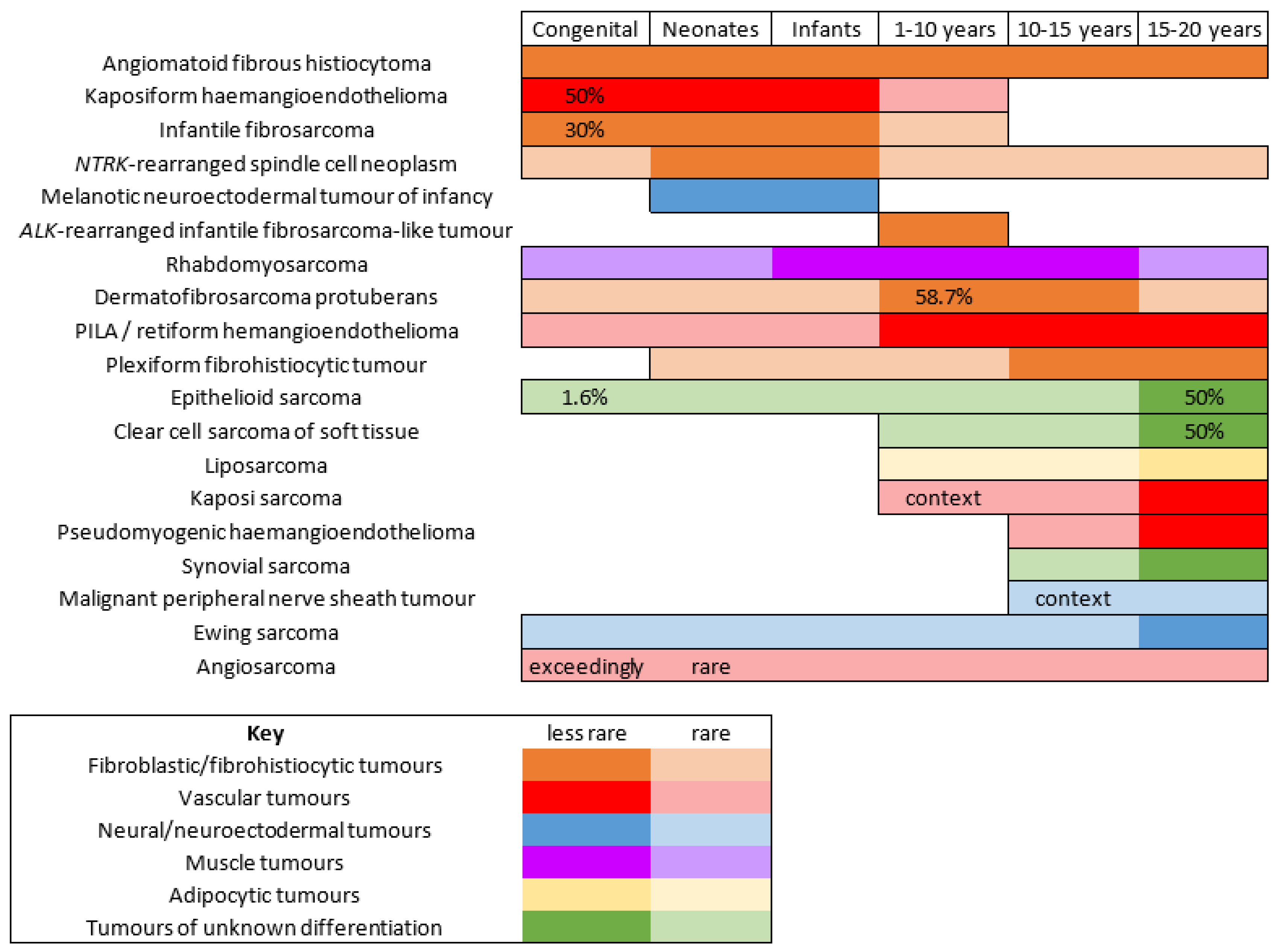
Malignant Superficial Mesenchymal Tumors in Children
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fibroblastic and Fibrohistiocytic Tumors
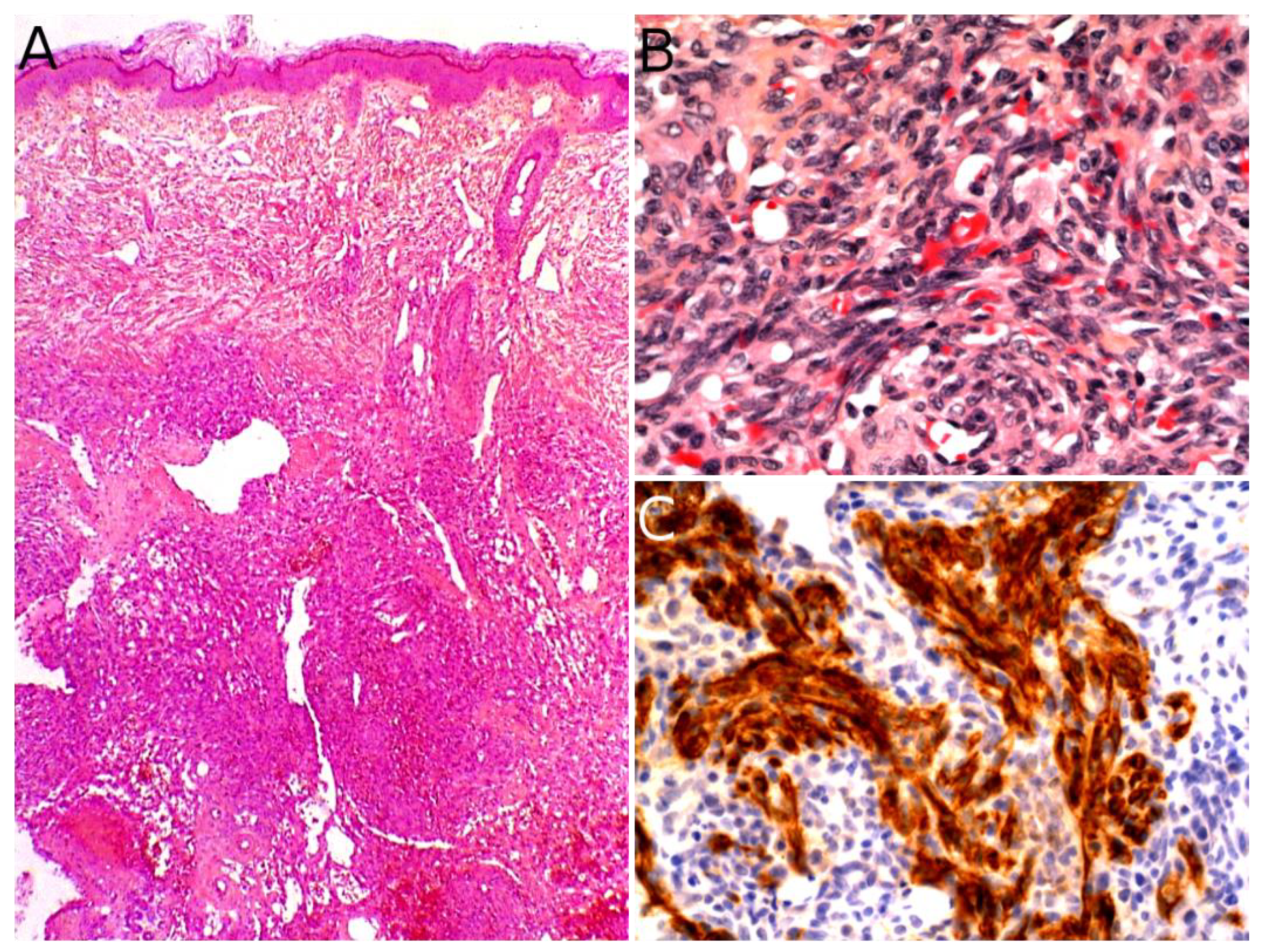
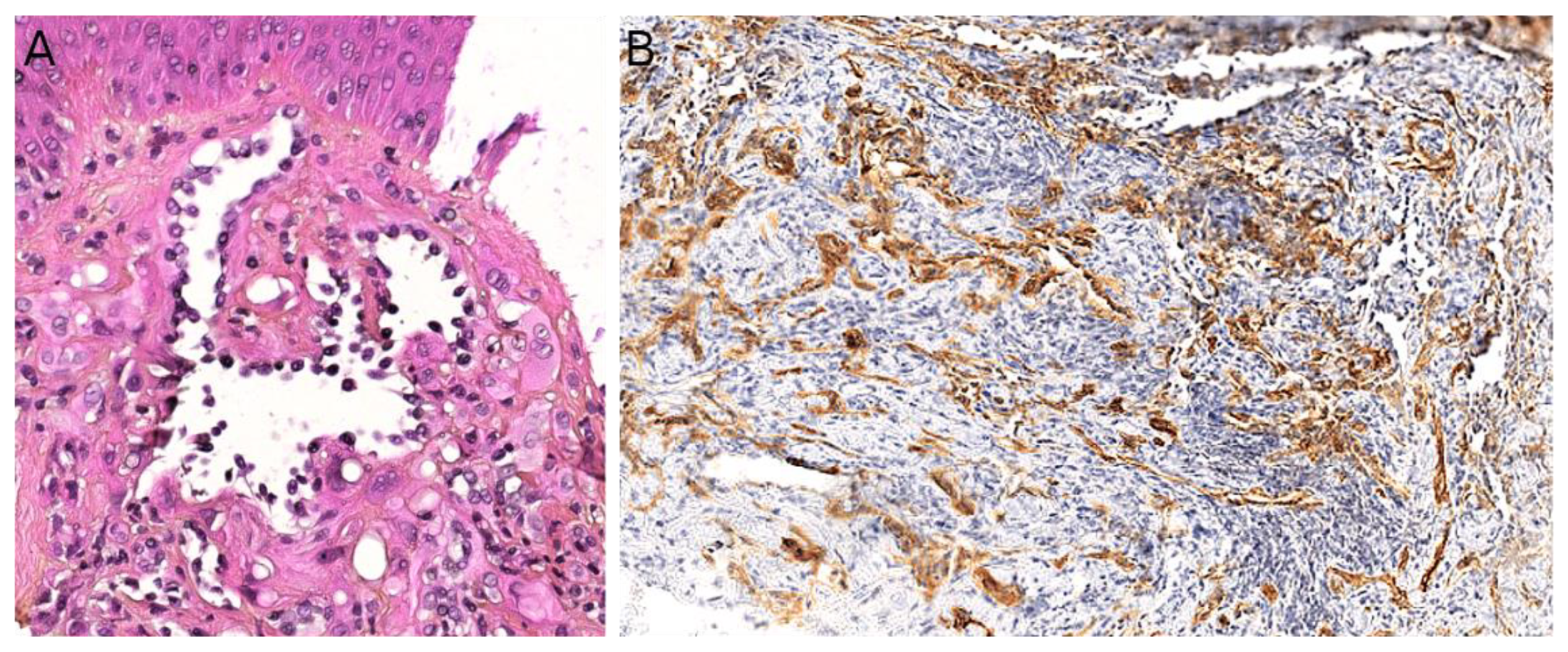
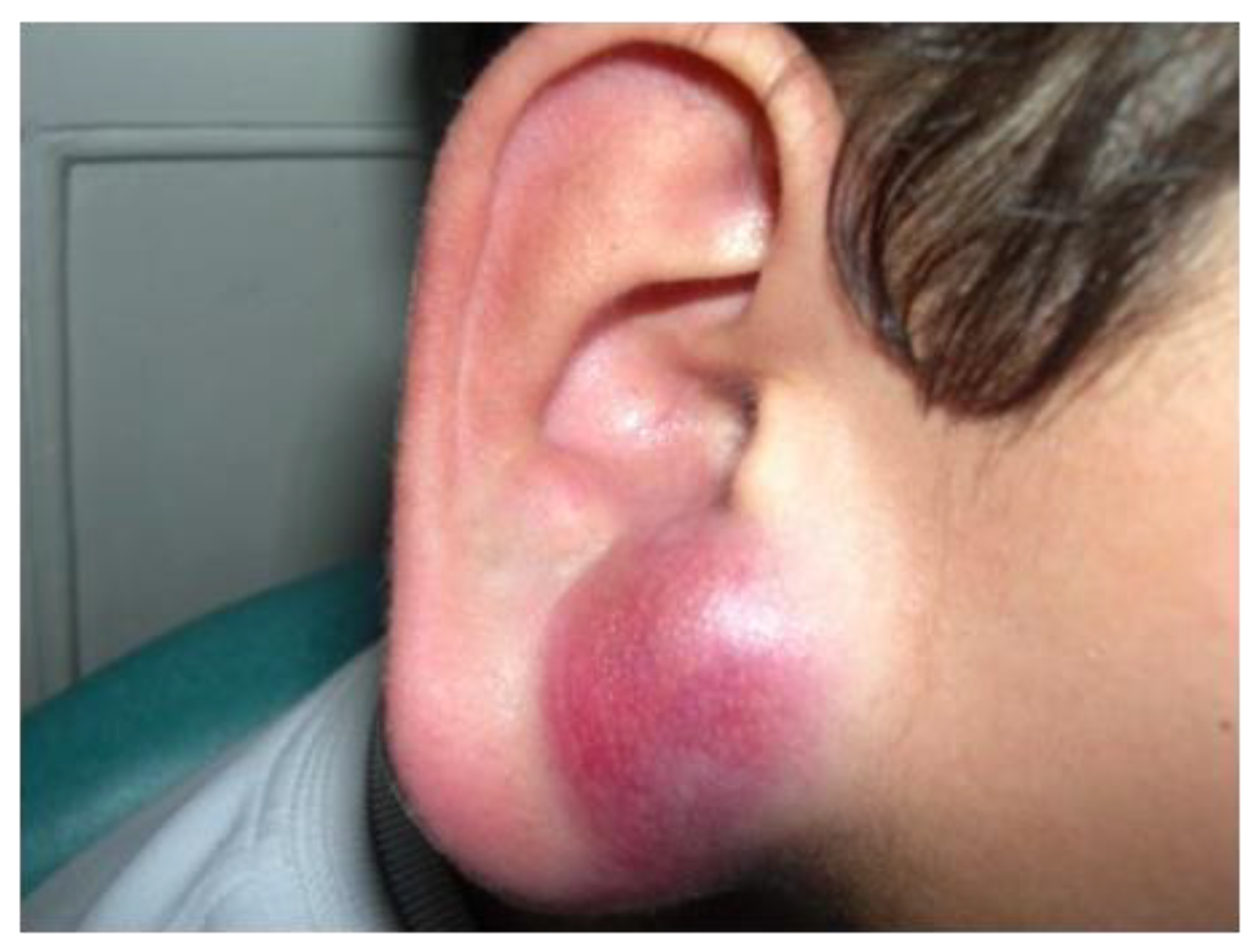
2.1. Angiomatoid Fibrous Histiocytoma
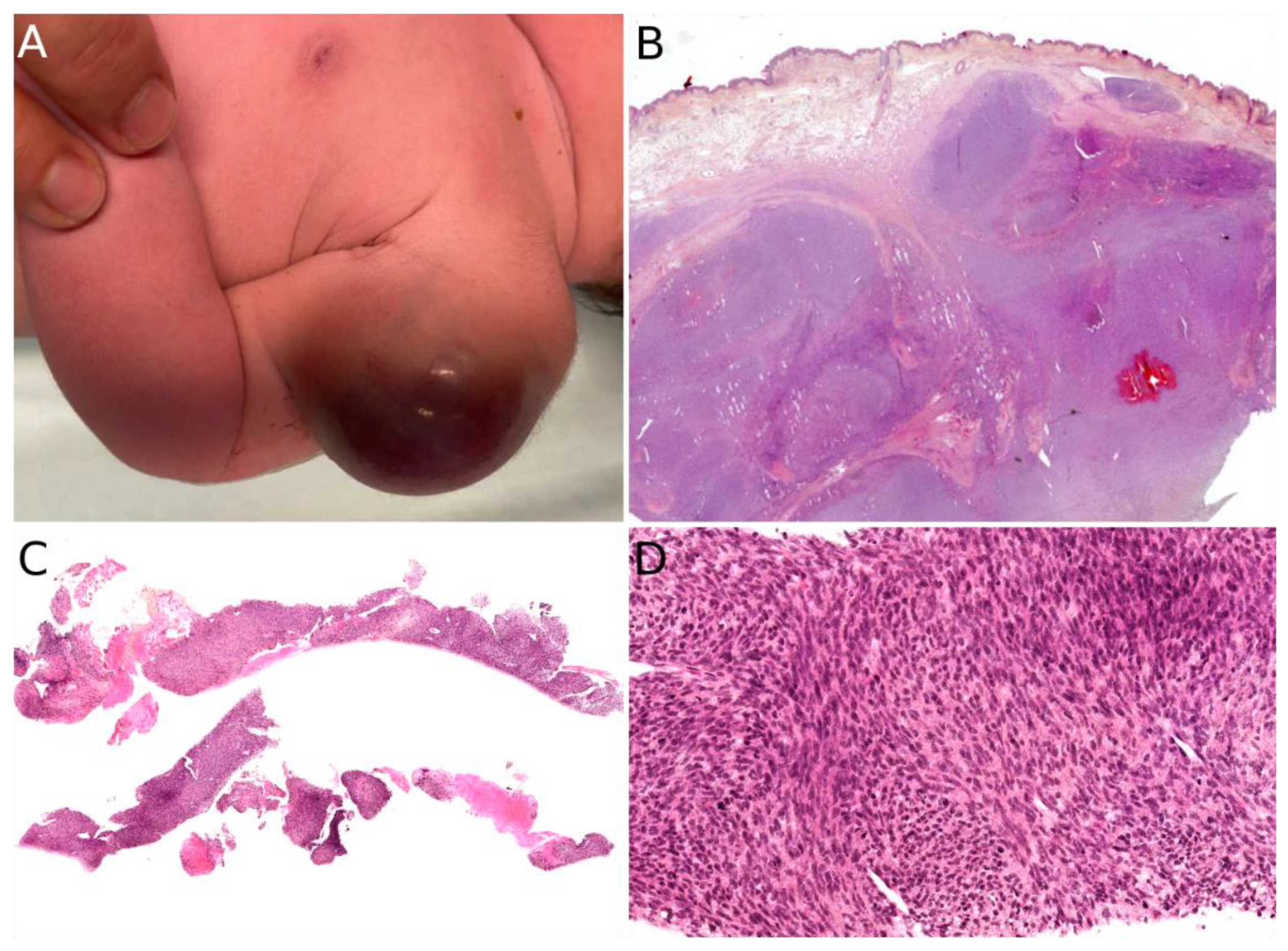
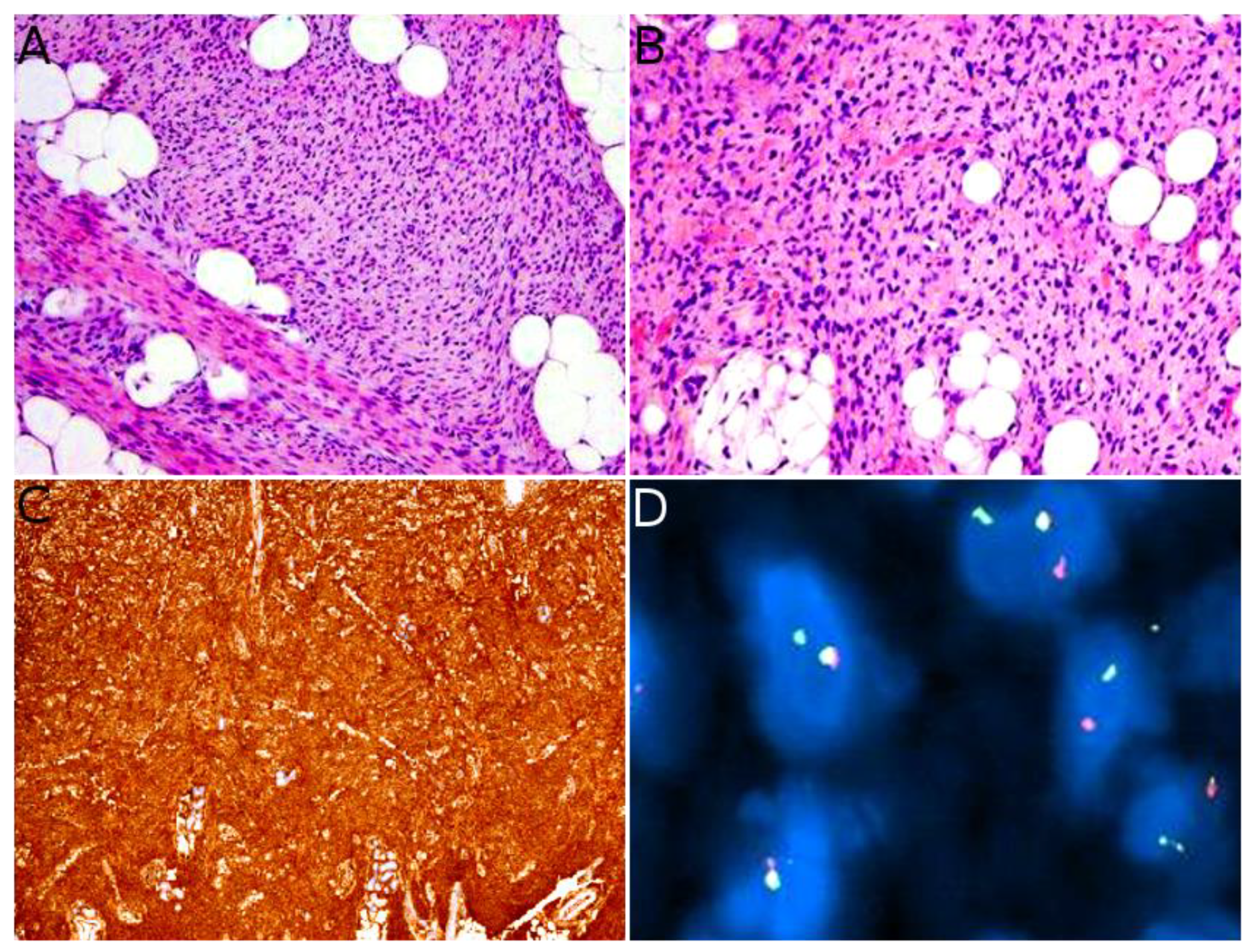
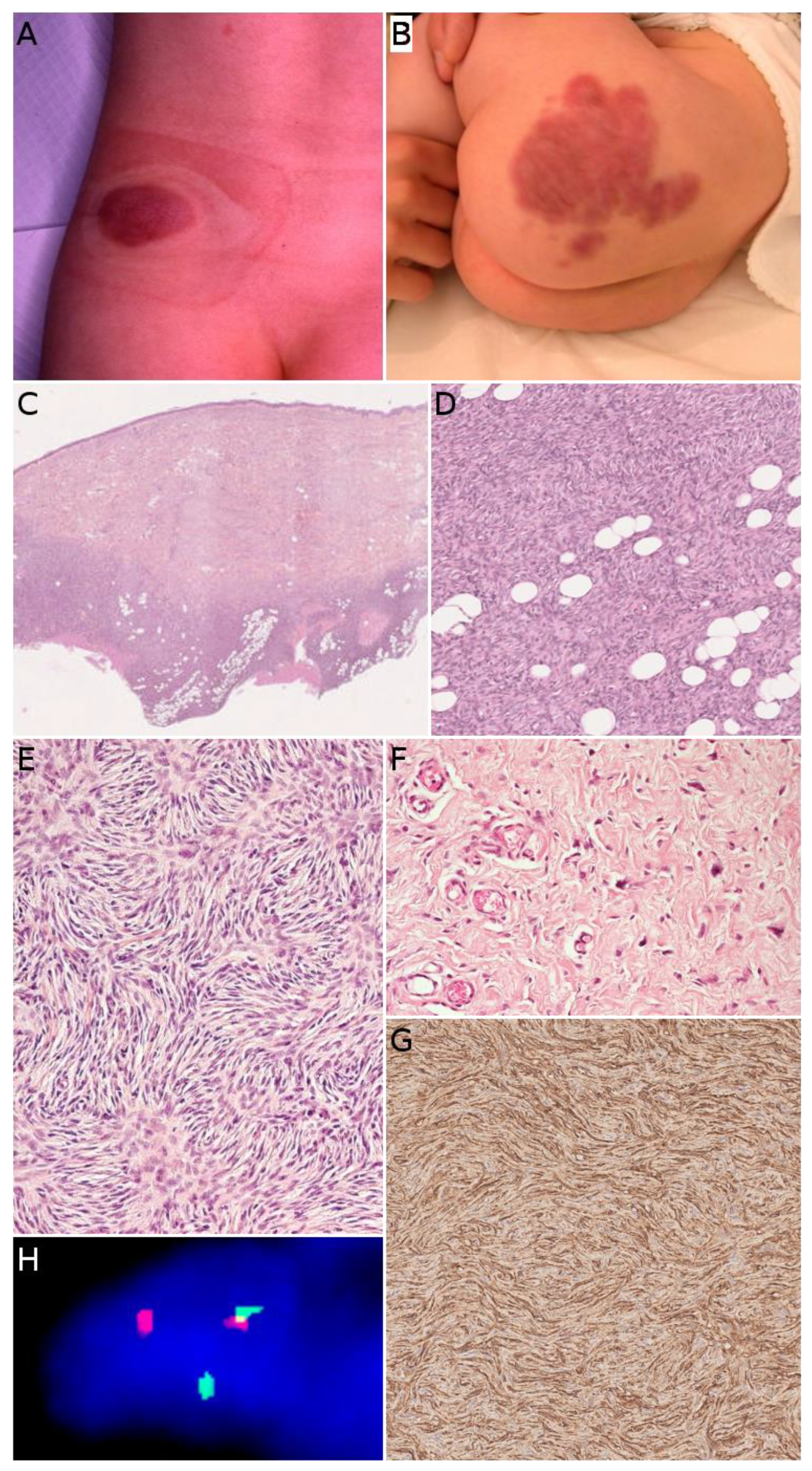
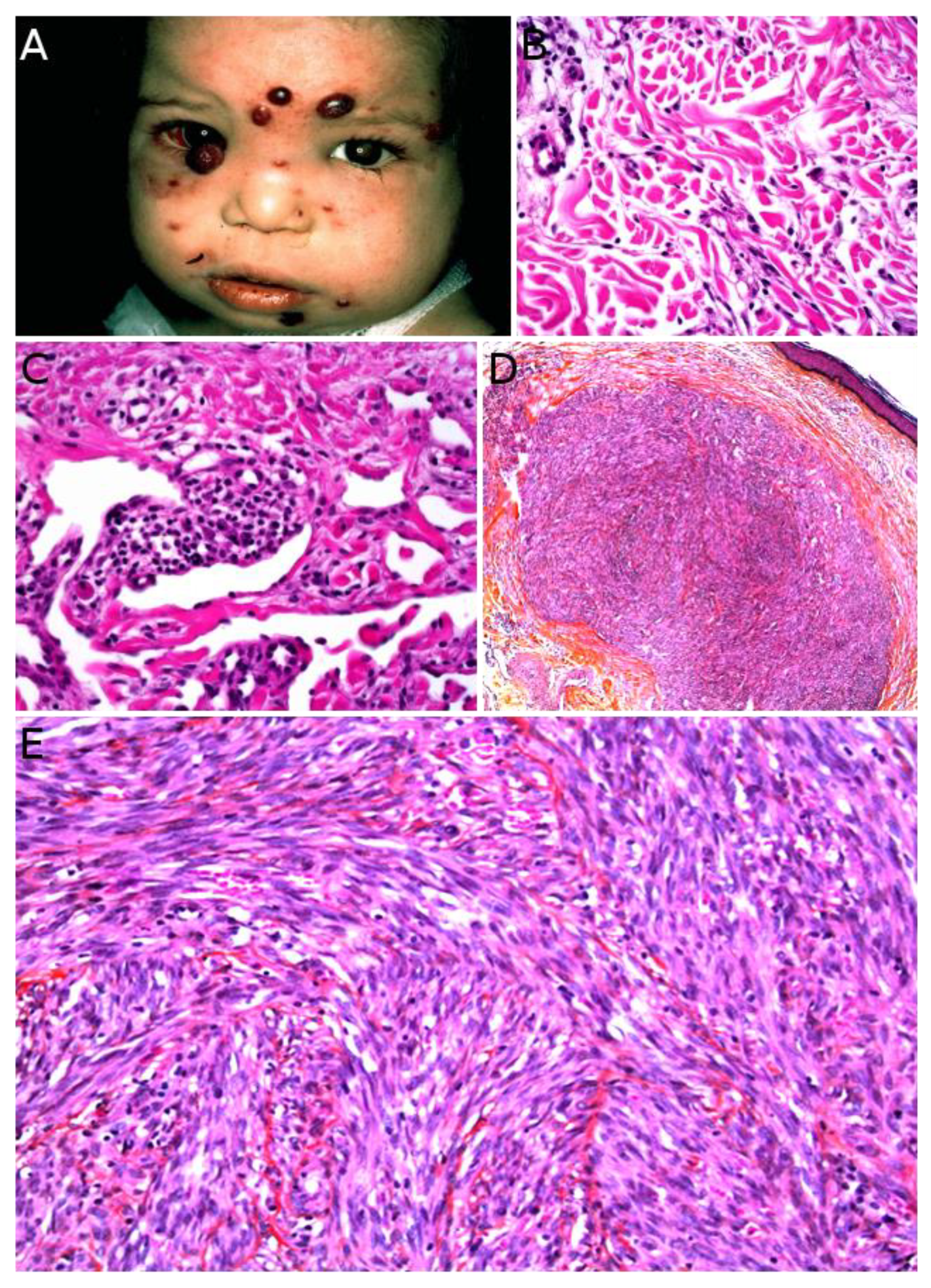
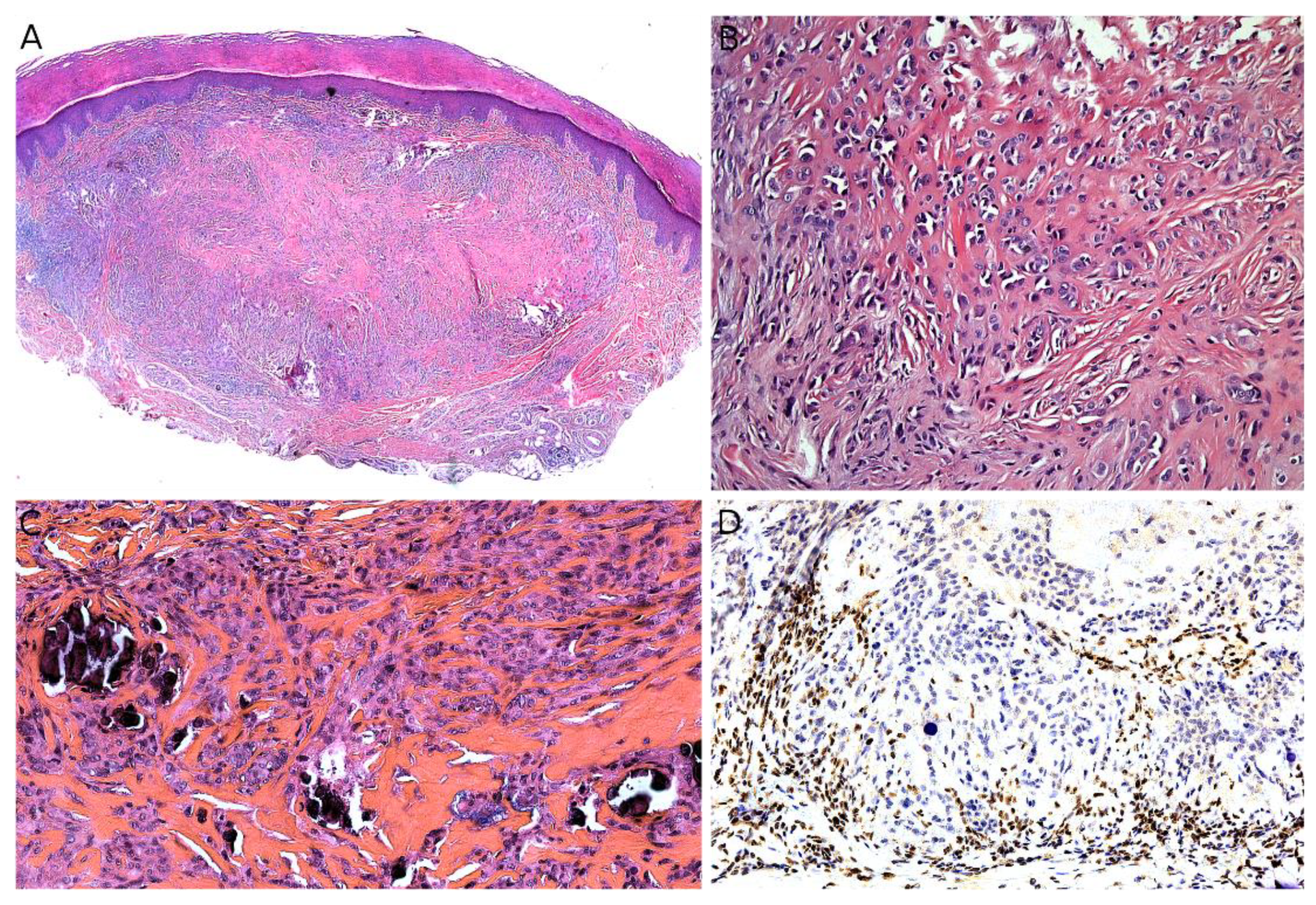
2.2. Infantile Fibrosarcoma
2.3. NTRK-Rearranged Spindle Cell Neoplasms
2.4. EWSR1-SMAD3-Rearranged Fibroblastic Tumor
2.5. ALK-Rearranged Infantile Fibrosarcoma-like Tumor
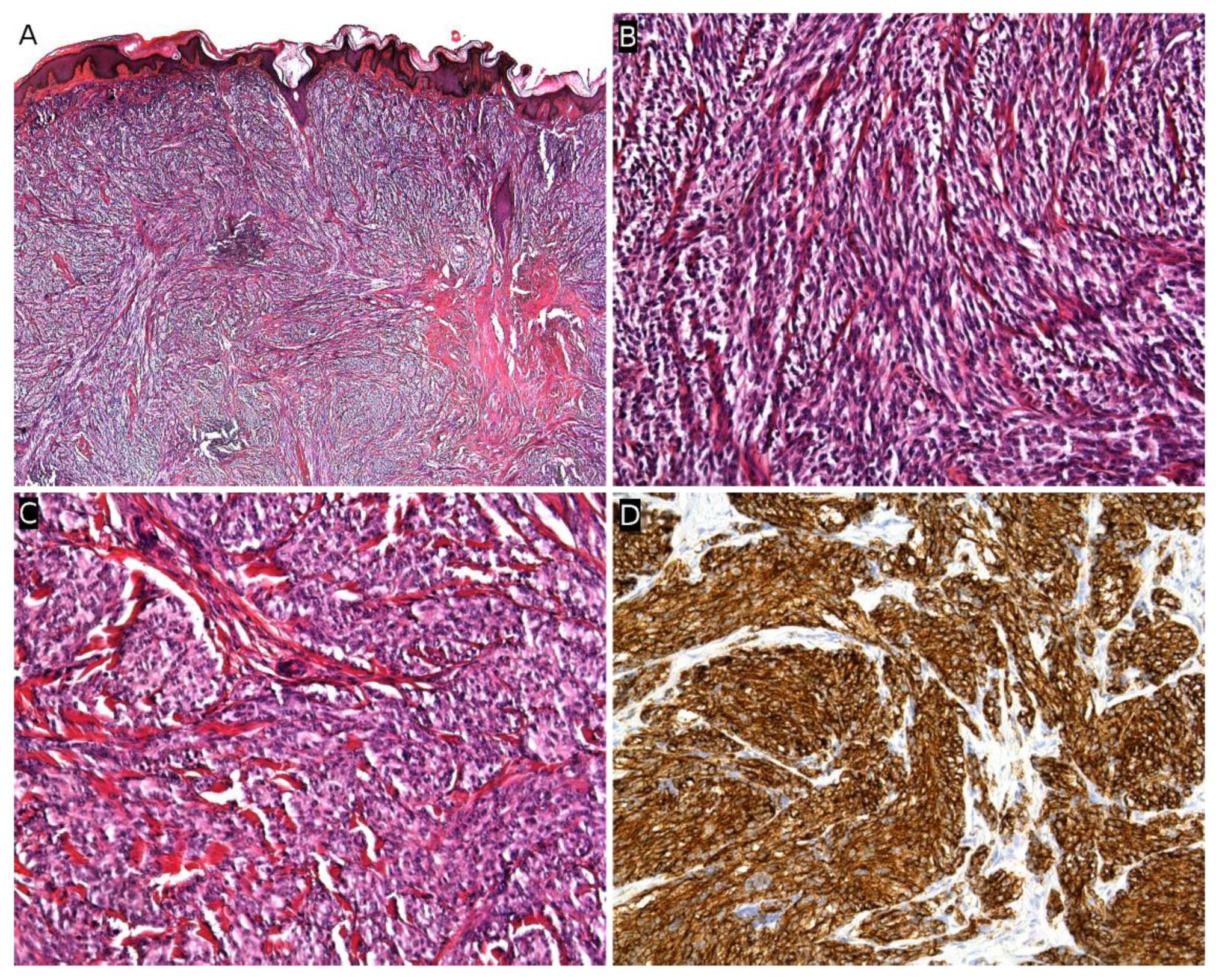
2.6. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans/Giant Cell Fibroblastoma
2.7. Plexiform Fibrohistiocytic Tumor
3. Vascular Tumors
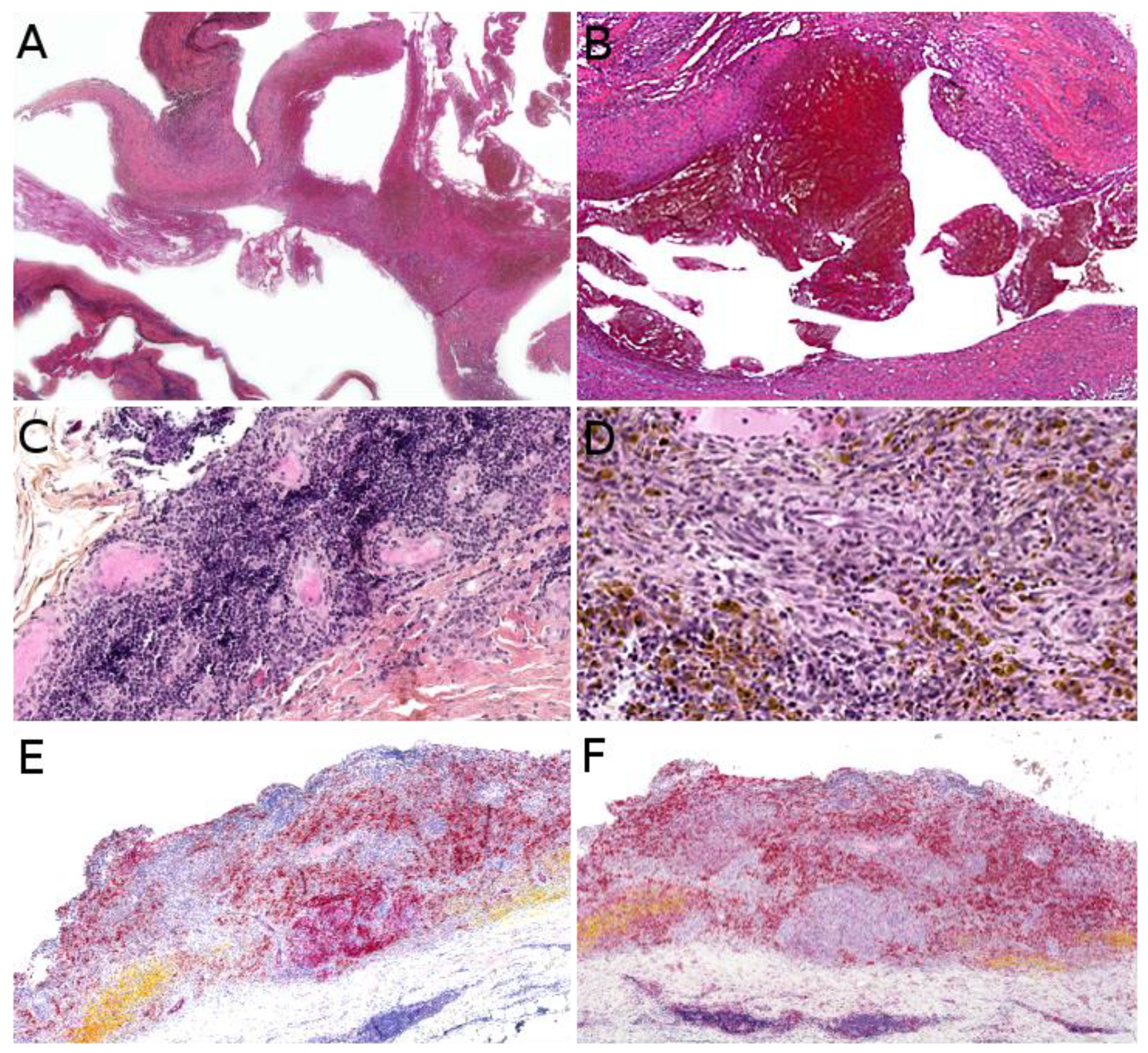
3.1. Kaposiform Hemangioendothelioma
3.2. Papillary Intralymphatic Angioendothelioma (PILA)/Retiform Hemangioendothelioma
3.3. Pseudomyogenic Haemangioendothelioma
3.4. Angiosarcoma
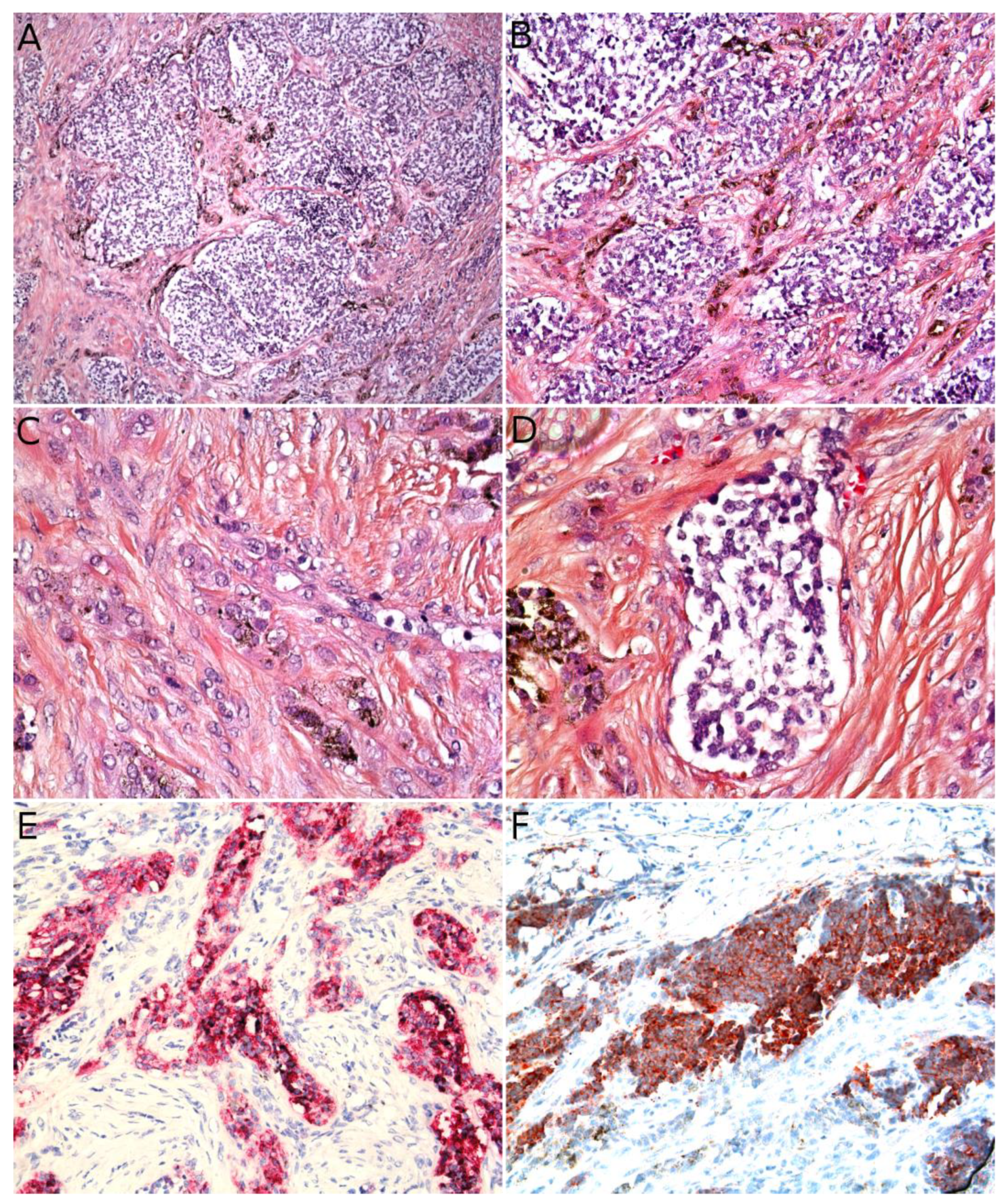
3.5. Kaposi Sarcoma
4. Muscular Tumors: Rhabdomyosarcomas
4.1. Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS)
4.2. Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS)
4.3. Rhabdomyosarcoma Risk Group Stratification and Treatment
5. Adipocytic Tumors: Liposarcomas
6. Neuroectodermal and Neural Tumors
6.1. Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy
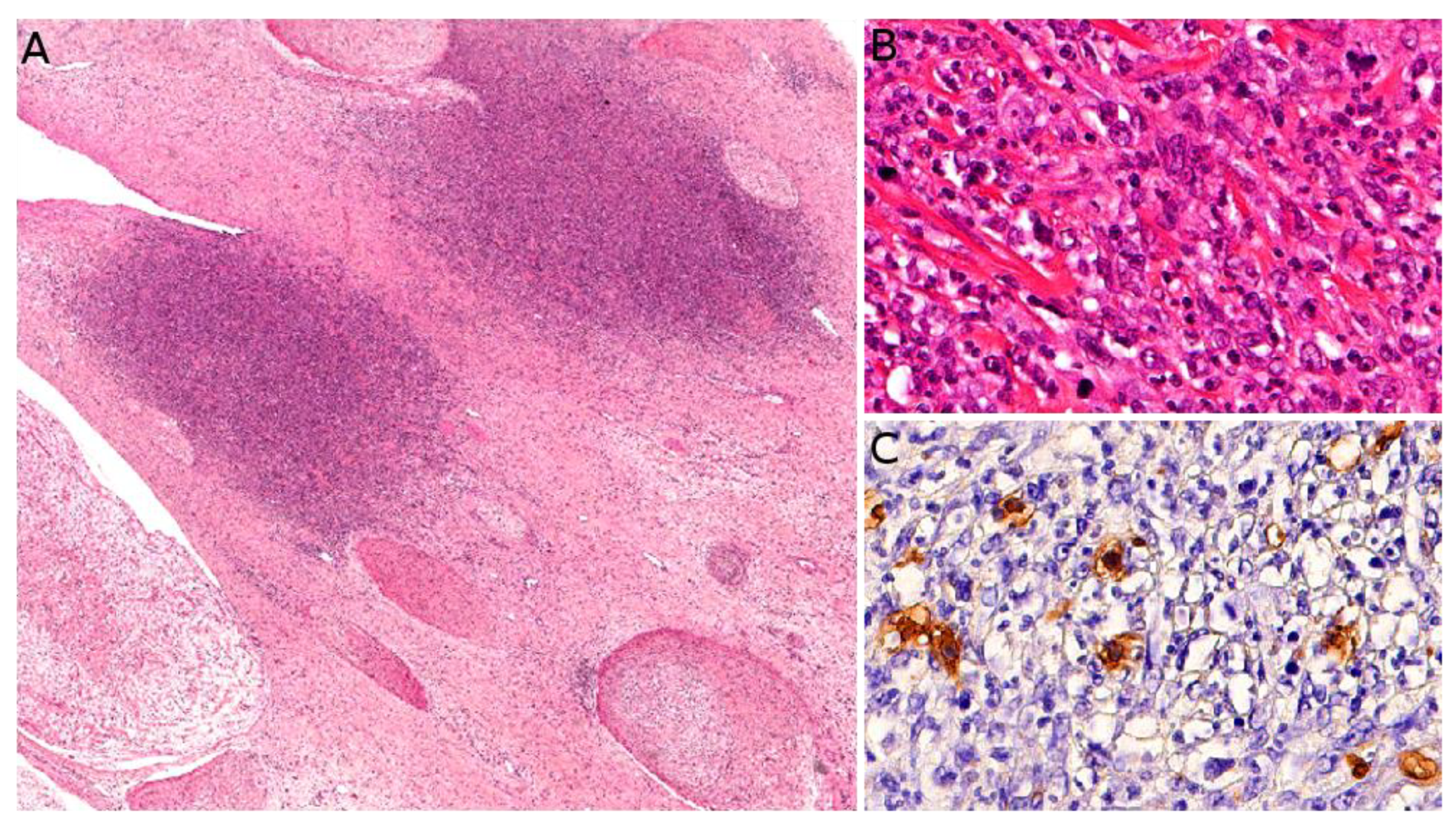
6.2. Ewing Sarcoma Family of Tumors
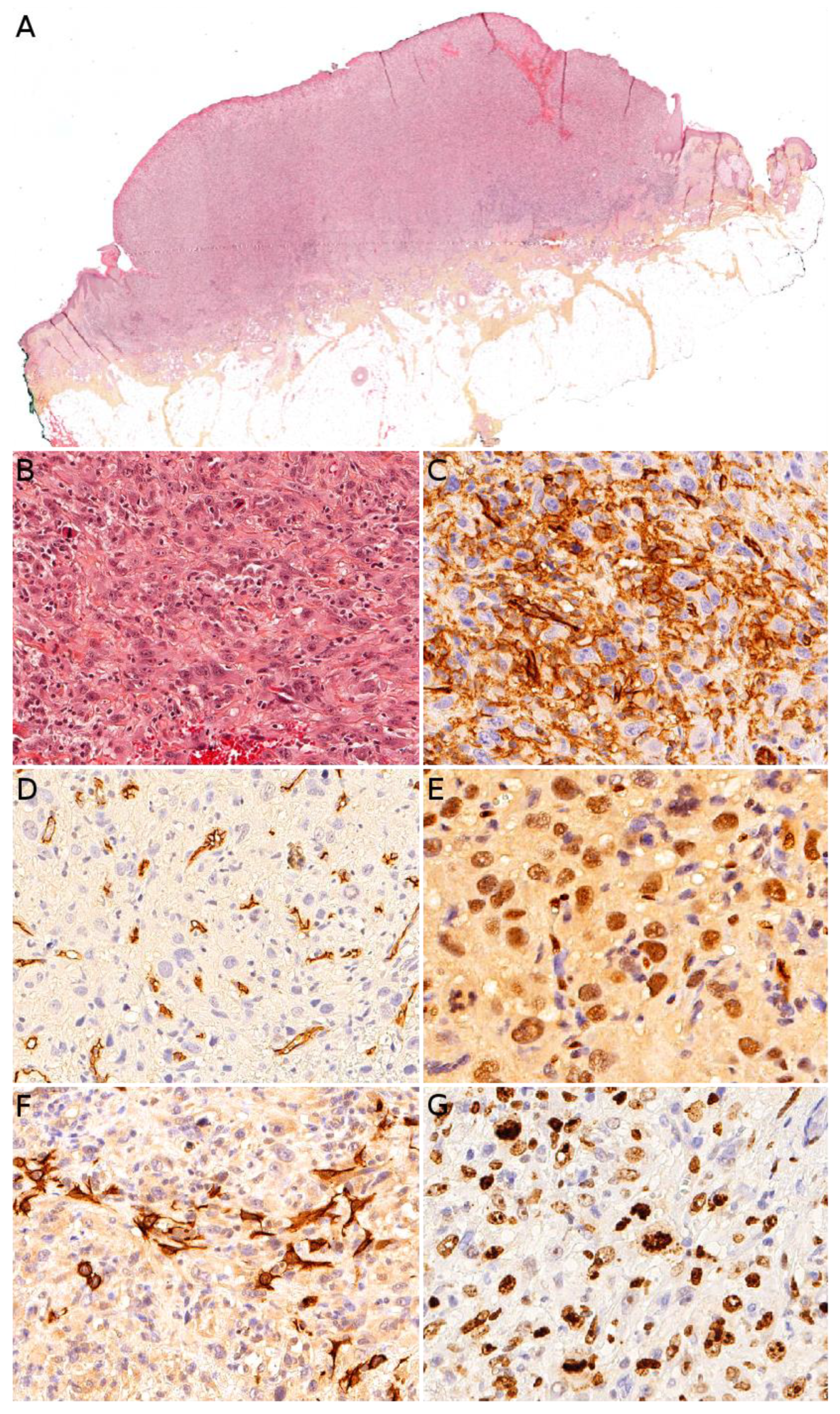
6.3. Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor (Associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 1)
7. Tumors of Unknown Differentiation
7.1. Epithelioid Sarcoma
7.2. Clear Cell Sarcoma of Soft Tissue
7.3. Synovial Sarcoma
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liszewski, W.; Maguiness, S.; Greengard, E.; Boull, C. The Incidence of Pediatric Malignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2018, 35, e427–e429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amadeo, B.; Penel, N.; Coindre, J.-M.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Ligier, K.; Delafosse, P.; Bouvier, A.-M.; Plouvier, S.; Gallet, J.; Lacourt, A.; et al. Incidence and Time Trends of Sarcoma (2000–2013): Results from the French Network of Cancer Registries (FRANCIM). BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohelay, G.; Kluger, N.; Battistella, M.; Biaggi-Frassati, A.; Plantier, F.; Harraudeau, A.; Avril, M.-F.; Pedeutour, F.; Fraitag, S. Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma in children: 6 cases. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 142, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thway, K.; Fisher, C. Angiomatoid Fibrous Histiocytoma: The Current Status of Pathology and Genetics. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2015, 139, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Kobayashi, E.; Yoshida, A.; Araki, Y.; Kubota, D.; Tanzawa, Y.; Kawai, A.; Yanagawa, T.; Takagishi, K.; Chuman, H. Angiomatoid Fibrous Histiocytoma: A Series of Seven Cases Including Genetically Confirmed Aggressive Cases and a Literature Review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.B.; Enzinger, F.M. Infantile Fibrosarcoma. Cancer 1976, 38, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbach, D.; Rey, A.; Cecchetto, G.; Oberlin, O.; Casanova, M.; Thebaud, E.; Scopinaro, M.; Bisogno, G.; Carli, M.; Ferrari, A. Infantile Fibrosarcoma: Management Based on the European Experience. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-92-832-4502-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth, K.E.; Chavhan, G.B.; Gupta, A.A.; Hopyan, S.; Taylor, G. Congenital Infantile Fibrosarcoma: Review of Imaging Features. Pediatr. Radiol. 2014, 44, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.C.; Chamlin, S.L.; Liang, M.G.; Hoffman, B.; Attiyeh, E.F.; Chang, B.; Honig, P.J. Congenital Infantile Fibrosarcoma: A Masquerader of Ulcerated Hemangioma. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2006, 23, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiadkiewicz, R.; Galmiche, L.; Belhous, K.; Boccara, O.; Fraitag, S.; Pedeutour, F.; Dadone, B.; Buis, J.; Picard, A.; Orbach, D.; et al. Congenital Infantile Fibrosarcoma Associated with a Lipofibromatosis-Like Component: One Train May Be Hiding Another. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2017, 39, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enos, T.; Hosler, G.A.; Uddin, N.; Mir, A. Congenital Infantile Fibrosarcoma Mimicking a Cutaneous Vascular Lesion: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2017, 44, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffin, C.M.; Alaggio, R. Fibroblastic and Myofibroblastic Tumors in Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2012, 15, 127–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.P.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Hornick, J.L. Evaluation of Pan-TRK Immunohistochemistry in Infantile Fibrosarcoma, Lipofibromatosis-like Neural Tumour and Histological Mimics. Histopathology 2018, 73, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, A.J.; Calicchio, M.L.; Nardi, V.; Skalova, A.; Pinto, A.; Dillon, D.A.; Gomez-Fernandez, C.R.; Manoj, N.; Haimes, J.D.; Stahl, J.A.; et al. Recurrent EML4-NTRK3 Fusions in Infantile Fibrosarcoma and Congenital Mesoblastic Nephroma Suggest a Revised Testing Strategy. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L.; Lockwood, C.M.; Stohr, B.; Boecking, C.; Al-Ibraheemi, A.; DuBois, S.G.; Vargas, S.O.; Black, J.O.; Cox, M.C.; Luquette, M.; et al. Expanding the Spectrum of Pediatric NTRK-Rearranged Mesenchymal Tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Kotch, C.; Fox, E.; Surrey, L.F.; Wertheim, G.B.; Baloch, Z.W.; Lin, F.; Pillai, V.; Luo, M.; Kreiger, P.A.; et al. NTRK Fusions Identified in Pediatric Tumors: The Frequency, Fusion Partners, and Clinical Outcome. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2021, 1, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-C.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Alaggio, R.; Wexler, L.; Zhang, L.; Sung, Y.-S.; Orhan, D.; Chang, W.-C.; Swanson, D.; Dickson, B.C.; et al. Recurrent BRAF Gene Fusions in a Subset of Pediatric Spindle Cell Sarcomas: Expanding the Genetic Spectrum of Tumors with Overlapping Features with Infantile Fibrosarcoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegert, J.; Vokuhl, C.; Collord, G.; Velasco-Herrera, M.D.C.; Farndon, S.J.; Guzzo, C.; Jorgensen, M.; Anderson, J.; Slater, O.; Duncan, C.; et al. Recurrent Intragenic Rearrangements of EGFR and BRAF in Soft Tissue Tumors of Infants. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L.; Vargas, S.O.; Rudzinski, E.R.; Marti, J.M.L.; Janeway, K.; Forrest, S.; Winsnes, K.; Pinto, N.; Yang, S.E.; VanSandt, M.; et al. Recurrent RET Gene Fusions in Paediatric Spindle Mesenchymal Neoplasms. Histopathology 2020, 76, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suurmeijer, A.J.H.; Dickson, B.C.; Swanson, D.; Zhang, L.; Sung, Y.-S.; Cotzia, P.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Antonescu, C.R. A Novel Group of Spindle Cell Tumors Defined by S100 and CD34 Co-Expression Shows Recurrent Fusions Involving RAF1, BRAF, and NTRK1/2 Genes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2018, 57, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankwiler, R.A.; Athey, P.A.; Lamki, N. Aggressive Infantile Fibromatosis. Pulmonary Metastases Documented by Plain Film and Computed Tomography. Clin. Imaging 1989, 13, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramphal, R.; Manson, D.; Viero, S.; Zielenska, M.; Gerstle, T.; Pappo, A. Retroperitoneal Infantile Fibrosarcoma: Clinical, Molecular, and Therapeutic Aspects of an Unusual Tumor. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2003, 20, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulibaly, B.; Barel, E.; Soulier, M.; Bouvier, C.; Chaumoitre, K.; D’Ercole, C.; Liprandi, A. Prenatal Diagnosis of Infantile Fibrosarcoma with Diffuse Metastases. Prenat. Diagn. 2008, 28, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, L.; Fernandez-Pineda, I.; Uffman, J.K.; Davidoff, A.M.; Krasin, M.J.; Pappo, A.; Rao, B.N. Clinical Management of Infantile Fibrosarcoma: A Retrospective Single-Institution Review. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2013, 29, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.-H.; Cheng, S.-N.; Lin, K.-T.; Jen, Y.-M. Successful Treatment of Infantile Fibrosarcoma Spinal Metastasis by Chemotherapy and Stereotactic Hypofractionated Radiotherapy. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2013, 54, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orbach, D.; Sparber-Sauer, M.; Laetsch, T.W.; Minard-Colin, V.; Bielack, S.S.; Casanova, M.; Corradini, N.; Koscielniak, E.; Scheer, M.; Hettmer, S.; et al. Spotlight on the Treatment of Infantile Fibrosarcoma in the Era of Neurotrophic Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase Inhibitors: International Consensus and Remaining Controversies. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 137, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.N.; Price, M.R.; Loeb, D.M. Cardiac Metastasis and Hypertrophic Osteoarthropathy in Recurrent Infantile Fibrosarcoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 59, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiradfar, A.; Pourlak, T.; Badebarin, D. Primary Pulmonary Fibrosarcoma With Bone Metastasis: A Successful Treatment with Post-Operation Adjuvant Chemotherapy. Iran. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 8, e2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laetsch, T.W.; DuBois, S.G.; Mascarenhas, L.; Turpin, B.; Federman, N.; Albert, C.M.; Nagasubramanian, R.; Davis, J.L.; Rudzinski, E.; Feraco, A.M.; et al. Larotrectinib for Paediatric Solid Tumours Harbouring NTRK Gene Fusions: Phase 1 Results from a Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 1/2 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, D.S.; DuBois, S.G. The Evolving Diagnostic and Treatment Landscape of NTRK-Fusion-Driven Pediatric Cancers. Pediatr. Drugs 2020, 22, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, K.J.; De La Cuesta, E.; Morin, C.; Pappo, A.; Helmig, S. A Newborn with a Large NTRK Fusion Positive Infantile Fibrosarcoma Successfully Treated with Larotrectinib. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, Y.; Suurmeijer, A.J.H.; Argani, P.; Dickson, B.C.; Zhang, L.; Sung, Y.; Agaram, N.P.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Antonescu, C.R. Soft Tissue Tumors Characterized by a Wide Spectrum of Kinase Fusions Share a Lipofibromatosis-like Neural Tumor Pattern. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2020, 59, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agaram, N.P.; Zhang, L.; Sung, Y.-S.; Chen, C.-L.; Chung, C.T.; Antonescu, C.R.; Fletcher, C.D. Recurrent NTRK1 Gene Fusions Define a Novel Subset of Locally Aggressive Lipofibromatosis-like Neural Tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drabent, P.; Fraitag, S. Update on Superficial Spindle Cell Mesenchymal Tumors in Children. Dermatopathology 2021, 8, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siozopoulou, V.; Smits, E.; De Winne, K.; Marcq, E.; Pauwels, P. NTRK Fusions in Sarcomas: Diagnostic Challenges and Clinical Aspects. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michal, M.; Hájková, V.; Skálová, A.; Michal, M. STRN-NTRK3-Rearranged Mesenchymal Tumor of the Uterus: Expanding the Morphologic Spectrum of Tumors with NTRK Fusions. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 1152–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L.; Lockwood, C.M.; Albert, C.M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Hawkins, D.S.; Rudzinski, E.R. Infantile NTRK-Associated Mesenchymal Tumors. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. Off. J. Soc. Pediatr. Pathol. Paediatr. Pathol. Soc. 2018, 21, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallegas, M.; Fraitag, S.; Binet, A.; Orbach, D.; Jourdain, A.; Reynaud, S.; Pierron, G.; Machet, M.-C.; Maruani, A. Novel KHDRBS1-NTRK3 Rearrangement in a Congenital Pediatric CD34-Positive Skin Tumor: A Case Report. Virchows Arch. Int. J. Pathol. 2019, 474, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-C.; Flucke, U.; Eijkelenboom, A.; Zhang, L.; Sung, Y.-S.; Suurmeijer, A.J.H.; Antonescu, C.R. Novel EWSR1-SMAD3 Gene Fusions in a Group of Acral Fibroblastic Spindle Cell Neoplasms. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michal, M.; Berry, R.S.; Rubin, B.P.; Kilpatrick, S.E.; Agaimy, A.; Kazakov, D.V.; Steiner, P.; Ptakova, N.; Martinek, P.; Hadravsky, L.; et al. EWSR1-SMAD3—Rearranged Fibroblastic Tumor: An Emerging Entity in an Increasingly More Complex Group of Fibroblastic/Myofibroblastic Neoplasms. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.Y.; Al-Ibraheemi, A.; Ahrens, W.A.; Oesterheld, J.E.; Fanburg-Smith, J.C.; Liu, Y.J.; Spunt, S.L.; Rudzinski, E.R.; Coffin, C.; Davis, J.L. ALK Rearrangements in Infantile Fibrosarcoma-like Spindle Cell Tumours of Soft Tissue and Kidney. Histopathology 2022, 80, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, G.A.; Alvarado, A.; Gerth, D.J.; Tashiro, J.; Thaller, S.R. Incidence and Outcomes of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans in the US Pediatric Population. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2017, 28, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, B.; Zanetti, I.; De Salvo, G.L.; Orbach, D.; Gallego, S.; Francotte, N.; Schifflers, S.; Van Noesel, M.; Kelsey, A.; Casanova, M.; et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans in Children and Adolescents: The European Paediatric Soft Tissue Sarcoma Study Group Prospective Trial (EpSSG NRSTS 2005). Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maire, G.; Fraitag, S.; Galmiche, L.; Keslair, F.; Ebran, N.; Terrier-Lacombe, M.-J.; de Prost, Y.; Pedeutour, F. A Clinical, Histologic, and Molecular Study of 9 Cases of Congenital Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans. Arch. Dermatol. 2007, 143, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrier-Lacombe, M.-J.; Guillou, L.; Maire, G.; Terrier, P.; Vince, D.R.; Somerhausen, N.D.S.A.; Collin, F.; Pedeutour, F.; Coindre, J.-M. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans, Giant Cell Fibroblastoma, and Hybrid Lesions in Children: Clinicopathologic Comparative Analysis of 28 Cases with Molecular Data—A Study from the French Federation of Cancer Centers Sarcoma Group. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2003, 27, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, B.; Wang, F.; Taher, A.; Aslam, R.; Madewell, J.E.; Spear, R.; Nassar, S. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: Pathological and Imaging Review. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 2021, 50, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.-H.; Huang, Q.; Yang, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.-J.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, R.-Q. Role of Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Primary and Recurrent Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llombart, B.; Monteagudo, C.; Sanmartín, O.; López-Guerrero, J.A.; Serra-Guillén, C.; Poveda, A.; Jorda, E.; Fernandez-Serra, A.; Pellín, A.; Guillén, C.; et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: A Clinicopathological, Immunohistochemical, Genetic (COL1A1-PDGFB), and Therapeutic Study of Low-Grade versus High-Grade (Fibrosarcomatous) Tumors. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 65, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Xu, X.; Jiang, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Xiang, B.; Ji, Y. Clinicopathological Features of Fibrosarcomatous Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans and the Construction of a Back-Propagation Neural Network Recognition Model. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowne, W.B.; Antonescu, C.R.; Leung, D.H.Y.; Katz, S.C.; Hawkins, W.G.; Woodruff, J.M.; Brennan, M.F.; Lewis, J.J. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: A Clinicopathologic Analysis of Patients Treated and Followed at a Single Institution. Cancer 2000, 88, 2711–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicaud, M.; Frassati-Biaggi, A.; Kaltenbach, S.; Karanian, M.; Orbach, D.; Fraitag, S. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans, Fibrosarcomatous Variant: A Rare Tumor in Children. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2021, 38, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirvent, N.; Maire, G.; Pedeutour, F. Genetics of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans Family of Tumors: From Ring Chromosomes to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2003, 37, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köster, J.; Arbajian, E.; Viklund, B.; Isaksson, A.; Hofvander, J.; Haglund, F.; Bauer, H.; Magnusson, L.; Mandahl, N.; Mertens, F. Genomic and Transcriptomic Features of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: Unusual Chromosomal Origin of the COL1A1-PDGFB Fusion Gene and Synergistic Effects of Amplified Regions in Tumor Development. Cancer Genet. 2020, 241, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Oda, Y. Current Update on the Molecular Biology of Cutaneous Sarcoma: Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2019, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saab, J.; Rosenthal, I.M.; Wang, L.; Busam, K.J.; Nehal, K.S.; Dickson, M.A.; Hameed, M.R.; Hollmann, T.J. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans-Like Tumor With COL1A1 Copy Number Gain in the Absence of t(17;22). Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2017, 39, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaput, B.; Filleron, T.; Le Guellec, S.; Meresse, T.; Courtade-Saïdi, M.; Grolleau, J.-L.; Chevreau, C.; Garrido, I.; Gangloff, D. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: Margins Reduction Using Slow-Mohs Micrographic Surgery. Experience with 35 Patients. Ann. Chir. Plast. Esthét. 2014, 59, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, C.; Ricard, A.S.; Cogrel, O.; Bondaz, M.; Carrier, S. Marges d’exérèse des dermatofibrosarcomes cervico-faciaux par technique de Slow-Mohs: Étude clinique rétrospective sur 20 cas. Ann. Chir. Plast. Esthét. 2018, 63, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asilian, A.; Honarjou, N.; Faghihi, G.; Saber, M.; Mozafarpoor, S.; Hafezi, H. An Experience of Slow-Mohs Micrographic Surgery for the Treatment of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: A Long-term Cohort Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 2701–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiwah, A.; Psomadakis, C.; Craythorne, E.; Stefanato, C.M.; Rickaby, W.; Robson, A.; Mellerio, J.E.; Greig, A. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans (DFSP) in Children: A Combined Multidisciplinary Approach. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2021, 38, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroozan, M.; Sei, J.-F.; Amini, M.; Beauchet, A.; Saiag, P. Efficacy of Mohs Micrographic Surgery for the Treatment of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: Systematic Review. Arch. Dermatol. 2012, 148, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malan, M.; Xuejingzi, W.; Quan, S.J. The Efficacy of Mohs Micrographic Surgery over the Traditional Wide Local Excision Surgery in the Cure of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2019, 33, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappell, A.G.; Doe, S.C.; Worley, B.; Yoo, S.S.; Gerami, P.; Alam, M.; Buck, D.W.; Kim, J.Y.S.; Wayne, J.D. Multidisciplinary Surgical Treatment Approach for Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: An Update. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2021, 313, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kérob, D.; Porcher, R.; Vérola, O.; Dalle, S.; Maubec, E.; Aubin, F.; D’Incan, M.; Bodokh, I.; Boulinguez, S.; Madelaine-Chambrin, I.; et al. Imatinib Mesylate as a Preoperative Therapy in Dermatofibrosarcoma: Results of a Multicenter Phase II Study on 25 Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 3288–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacchiotti, S.; Pedeutour, F.; Negri, T.; Conca, E.; Marrari, A.; Palassini, E.; Collini, P.; Keslair, F.; Morosi, C.; Gronchi, A.; et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans-Derived Fibrosarcoma: Clinical History, Biological Profile and Sensitivity to Imatinib. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, F.G.; Kairouz, V.F.; Sabri, A.N. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans (DFSP) Successfully Treated with Sorafenib: Case Report. Clin. Sarcoma Res. 2013, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugurel, S.; Mentzel, T.; Utikal, J.; Helmbold, P.; Mohr, P.; Pföhler, C.; Schiller, M.; Hauschild, A.; Hein, R.; Kämpgen, E.; et al. Neoadjuvant Imatinib in Advanced Primary or Locally Recurrent Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: A Multicenter Phase II DeCOG Trial with Long-Term Follow-Up. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Kang, H.; Zhao, H.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Du, N.; Huang, Y. Sunitinib for Patients with Locally Advanced or Distantly Metastatic Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans but Resistant to Imatinib. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 8288–8294. [Google Scholar]
- Miyagawa, T.; Kadono, T.; Kimura, T.; Saigusa, R.; Yoshizaki, A.; Miyagaki, T.; Yamada, D.; Masui, Y.; Fujita, H.; Sato, S. Pazopanib Induced a Partial Response in a Patient with Metastatic Fibrosarcomatous Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans without Genetic Translocations Resistant to Mesna, Doxorubicin, Ifosfamide and Dacarbazine Chemotherapy and Gemcitabine-Docetaxel Chemotherapy. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, e21–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Que, Y.; Peng, R.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wen, X.; Weng, D.; Zhang, X.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, X. A Favorable Outcome of Advanced Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans under Treatment with Sunitinib after Imatinib Failure. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 2439–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzar, B.; Calonje, E. Cutaneous Fibrohistiocytic Tumours—An Update. Histopathology 2010, 56, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuman, M.; Hwang, S.; Antonescu, C.R.; Panicek, D.M. Plexiform Fibrohistiocytic Tumor: Imaging Features and Clinical Findings. Skelet. Radiol. 2019, 48, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papke, D.J.; Al-Ibraheemi, A.; Fletcher, C.D.M. Plexiform Myofibroblastoma: Clinicopathologic Analysis of 36 Cases of a Distinctive Benign Tumor of Soft Tissue Affecting Mainly Children and Young Adults. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 44, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclerc-Mercier, S.; Brousse, N.; Fraitag, S. Is Plexiform Fibro-Histiocytic Tumor a Deep Form of Cellular Neurothekeoma? J. Cutan. Pathol. 2009, 36, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclerc-Mercier, S.; Pedeutour, F.; Fabas, T.; Glorion, C.; Brousse, N.; Fraitag, S. Plexiform Fibrohistiocytic Tumor with Molecular and Cytogenetic Analysis: Plexiform Fibrohistiocytic Tumor. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2011, 28, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yang, K.; Peng, S.; Chen, S.; Xiang, B.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Xia, C.; et al. Kaposiform Haemangioendothelioma: Clinical Features, Complications and Risk Factors for Kasabach-Merritt Phenomenon. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Broek, R.W.; Koelsche, C.; Eijkelenboom, A.; Mentzel, T.; Creytens, D.; Vokuhl, C.; van Gorp, J.M.; Versleijen-Jonkers, Y.M.; van der Vleuten, C.J.; Kemmeren, P.; et al. Kaposiform Hemangioendothelioma and Tufted Angioma—(Epi)Genetic Analysis Including Genome-Wide Methylation Profiling. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 44, 151434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, K.; Xia, C.; Li, L. Kaposiform Hemangioendothelioma: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Cheon, J.-E.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, I.-O.; Park, J.E.; Kim, Y.J. Imaging Findings of Kaposiform Hemangioendothelioma in Children. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 86, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, L.L.; North, P.E.; Mac-Moune Lai, F.; Stoler, M.H.; Folpe, A.L.; Weiss, S.W. Kaposiform Hemangioendothelioma: A Study of 33 Cases Emphasizing Its Pathologic, Immunophenotypic, and Biologic Uniqueness from Juvenile Hemangioma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2004, 28, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, V.; Lee, A.; Witman, P.M.; Anderson, P.A. Kasabach-Merritt Phenomenon: Case Series and Retrospective Review of the Mayo Clinic Experience. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2009, 31, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croteau, S.E.; Liang, M.G.; Kozakewich, H.P.; Alomari, A.I.; Fishman, S.J.; Mulliken, J.B.; Trenor, C.C. Kaposiform Hemangioendothelioma: Atypical Features and Risks of Kasabach-Merritt Phenomenon in 107 Referrals. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruman, A.; Liang, M.G.; Mulliken, J.B.; Fishman, S.J.; Burrows, P.E.; Kozakewich, H.P.W.; Blei, F.; Frieden, I.J. Kaposiform Hemangioendothelioma without Kasabach-Merritt Phenomenon. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 52, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drolet, B.A.; Trenor, C.C.; Brandão, L.R.; Chiu, Y.E.; Chun, R.H.; Dasgupta, R.; Garzon, M.C.; Hammill, A.M.; Johnson, C.M.; Tlougan, B.; et al. Consensus-Derived Practice Standards Plan for Complicated Kaposiform Hemangioendothelioma. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmenero, I.; Hoeger, P.H. Vascular Tumours in Infants. Part II: Vascular Tumours of Intermediate Dignity and Malignant Tumours. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Huu, A.R.; Jokinen, C.H.; Rubin, B.P.; Ruben, B.P.; Mihm, M.C.; Weiss, S.W.; North, P.E.; Dadras, S.S. Expression of Prox1, Lymphatic Endothelial Nuclear Transcription Factor, in Kaposiform Hemangioendothelioma and Tufted Angioma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.H.; Bacchiocchi, A.; Qiu, J.; Straub, R.; Bruckner, A.; Bercovitch, L.; Narayan, D.; Yale Center for Mendelian Genomics; McNiff, J.; Ko, C.; et al. GNA14 Somatic Mutation Causes Congenital and Sporadic Vascular Tumors by MAPK Activation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatt, J.; Stavas, J.; Moats-Staats, B.; Woosley, J.; Morrell, D.S. Treatment of Childhood Kaposiform Hemangioendothelioma with Sirolimus: Hemangioendothelioma and Sirolimus. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 55, 1396–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rössler, J.; Baselga, E.; Davila, V.; Celis, V.; Diociaiuti, A.; El Hachem, M.; Mestre, S.; Haeberli, D.; Prokop, A.; Hanke, C.; et al. Severe Adverse Events during Sirolimus “Off-label” Therapy for Vascular Anomalies. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e28936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, D.-D.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.-P. Initial Dose Recommendation for Sirolimus in Paediatric Kaposiform Haemangioendothelioma Patients Based on Population Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacogenomics. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 030006052094762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, K.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, X.; Xu, X.; Lu, G.; Qiu, L.; Kong, F.; et al. A Prospective Multicenter Study of Sirolimus for Complicated Vascular Anomalies. J. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 74, 1673–1681.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folpe, A.L.; Veikkola, T.; Valtola, R.; Weiss, S.W. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-3 (VEGFR-3): A Marker of Vascular Tumors with Presumed Lymphatic Differentiation, Including Kaposi’s Sarcoma, Kaposiform and Dabska-Type Hemangioendotheliomas, and a Subset of Angiosarcomas. Mod. Pathol. 2000, 13, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requena, L.; Kutzner, H. Hemangioendothelioma. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 30, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertini, A.-F.; Brousse, N.; Bodemer, C.; Calonje, E.; Fraitag, S. Retiform Hemangioendothelioma Developed on the Site of an Earlier Cystic Lymphangioma in a Six-Year-Old Girl. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2011, 33, e84–e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, M.; Wang, Z.-F. Prox1 Transcription Factor as a Marker for Vascular Tumors—Evaluation of 314 Vascular Endothelial and 1086 Nonvascular Tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, K.D.; Al-lbraheemi, A.; Rubin, B.P.; Jen, J.; Ren, H.; Jang, J.S.; Nair, A.; Davila, J.; Pambuccian, S.; Horvai, A.; et al. Composite Hemangioendothelioma with Neuroendocrine Marker Expression: An Aggressive Variant. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 1589–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, M. Expression of D2-40 in Lymphatic Endothelium of Normal Tissues and in Vascular Tumours. Histopathology 2005, 46, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, A.; Sheehan, D.J.; Sangueza, O.P. Retiform Hemangioendotheliomas Usually Do Not Express D2-40 and VEGFR-3. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2008, 30, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, R.A.; Dabski, C.; Dabska, M. The Dabska Tumor: A Thirty-Year Retrospect. Dermatology 2000, 201, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiler, S.A.; Honda, K.; Bordeaux, J.S. Retiform Hemangioendothelioma Treated with Mohs Micrographic Surgery. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 65, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsh, A.Z.; Yan, W.; Wei, L.; Wernicke, A.G.; Parashar, B. Unresectable Retiform Hemangioendothelioma Treated with External Beam Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Sarcoma 2010, 2010, 756246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Walther, C.; Tayebwa, J.; Lilljebjörn, H.; Magnusson, L.; Nilsson, J.; von Steyern, F.V.; Øra, I.; Domanski, H.A.; Fioretos, T.; Nord, K.H.; et al. A Novel SERPINE1-FOSB Fusion Gene Results in Transcriptional up-Regulation of FOSB in Pseudomyogenic Haemangioendothelioma: SERPINE1-FOSB Fusion in Pseudomyogenic Haemangioendothelioma. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raftopoulos, E.; Royer, M.; Warren, M.; Zhao, J.; Rush, W. Pseudomyogenic Hemangioendothelioma: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2018, 40, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.P.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Hornick, J.L. FOSB Is a Useful Diagnostic Marker for Pseudomyogenic Hemangioendothelioma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, G.A.; Roitman, P.D. Pseudomyogenic Hemangioendothelioma (Epithelioid Sarcoma-Like Hemangioendothelioma). Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 144, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requena, L.; Santonja, C.; Martinez-Amo, J.L.; Saus, C.; Kutzner, H. Cutaneous Epithelioid Sarcomalike (Pseudomyogenic) Hemangioendothelioma: A Little-Known Low-Grade Cutaneous Vascular Neoplasm. JAMA Dermatol. 2013, 149, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornick, J.L.; Fletcher, C.D.M. Pseudomyogenic Hemangioendothelioma: A Distinctive, Often Multicentric Tumor with Indolent Behavior. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2011, 35, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, D.; Magnusson, L.; von Steyern, F.V.; Hornick, J.L.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Mertens, F. Translocation t(7;19)(Q22;Q13)—A Recurrent Chromosome Aberration in Pseudomyogenic Hemangioendothelioma? Cancer Genet. 2011, 204, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agaram, N.P.; Zhang, L.; Cotzia, P.; Antonescu, C.R. Expanding the Spectrum of Genetic Alterations in Pseudomyogenic Hemangioendothelioma with Recurrent Novel ACTB-FOSB Gene Fusions. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Benayed, R.; Ho, C.; Mullaney, K.; Sukhadia, P.; Rios, K.; Berry, R.; Rubin, B.P.; Nafa, K.; Wang, L.; et al. Diagnosis of Known Sarcoma Fusions and Novel Fusion Partners by Targeted RNA Sequencing with Identification of a Recurrent ACTB-FOSB Fusion in Pseudomyogenic Hemangioendothelioma. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, I.; Lobmaier, I.; Gorunova, L.; Heim, S. Fusion of the Genes WWTR1 and FOSB in Pseudomyogenic Hemangioendothelioma. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2019, 16, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, J.A.; Sumegi, J.; Royce, T.; Baker, M.; Linos, K. A Novel CLTC-FOSB Gene Fusion in Pseudomyogenic Hemangioendothelioma of Bone. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2021, 60, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakar, M.H.; White, K.; Hansford, B.G.; Swensen, J.; Davis, J.L. Novel EGFL7-FOSB Fusion in Pseudomyogenic Haemangioendothelioma with Widely Metastatic Disease. Histopathology 2021, 79, 888–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirra, J.M.; Kessler, S.; Bhuta, S.; Eckardt, J. The Fibroma-like Variant of Epithelioid Sarcoma. A Fibrohistiocytic/Myoid Cell Lesion Often Confused with Benign and Malignant Spindle Cell Tumors. Cancer 1992, 69, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, S.D.; Folpe, A.L.; Weiss, S.W. Epithelioid Sarcoma-like Hemangioendothelioma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2003, 27, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozeki, M.; Nozawa, A.; Kanda, K.; Hori, T.; Nagano, A.; Shimada, A.; Miyazaki, T.; Fukao, T. Everolimus for Treatment of Pseudomyogenic Hemangioendothelioma. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 39, e328–e331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabor, K.M.; Sapi, Z.; Tiszlavicz, L.G.; Fige, A.; Bereczki, C.; Bartyik, K. Sirolimus Therapy in the Treatment of Pseudomyogenic Hemangioendothelioma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e26781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyrup, A.T.; Miettinen, M.; Khoury, J.D.; Parham, D.M.; Shehata, B.M. Pediatric Cutaneous Angiosarcomas: A Clinicopathologic Study of 10 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2011, 35, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinne, S.J.; Sipilä, L.J.; Sulo, P.; Jouanguy, E.; Béziat, V.; Abel, L.; Casanova, J.-L.; Parvaneh, N.; Balighi, K.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; et al. Candidate Predisposition Variants in Kaposi Sarcoma as Detected by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofz337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyango, W.; Villiera, J.; Silverstein, A.; Peckham-Gregory, E.; Campbell, L.R.; El-Mallawany, N.K. Navigating the Heterogeneous Landscape of Pediatric Kaposi Sarcoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019, 38, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.; Azurara, L.; Monteiro, A.F.; Miroux-Catarino, A.; Amaro, C.; Viana, I. Pediatric Kaposi’s Sarcoma Associated with Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2020, 37, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, C.; Mellouli, F.; Duprez, R.; Chédeville, G.; Neven, B.; Fraitag, S.; Delaunay, J.; Le Deist, F.; Fischer, A.; Blanche, S.; et al. Kaposi’s Sarcoma in a Child with Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2006, 165, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunn, B.K.; Carvalho, M.d.V.; Louw, M.; Vargas, P.A.; van Heerden, W.F. Microscopic Diversity in Oral Kaposi Sarcoma. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2013, 115, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyneux, E.; Davidson, A.; Orem, J.; Hesseling, P.; Balagadde-Kambugu, J.; Githanga, J.; Israels, T. The Management of Children with Kaposi Sarcoma in Resource Limited Settings. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, Y.M. Primary Cutaneous Rhabdomyosarcoma: Case Report and Review of Published Work. J. Dermatol. 2015, 42, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökdemir, G.; Ekmen, S.; Gungor, S.; Singer, R. Perianal Rhabdomyosarcoma: Report of a Case in an Infant and Review of the Literature: A Polypoid Anal Mass as Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2013, 30, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekhi, B.; Qureshi, S.S.; Narula, G.; Gujral, S.; Kurkure, P. Rapidly Progressive Congenital Rhabdomyosarcoma Presenting with Multiple Cutaneous Lesions: An Uncommon Diagnosis and a Therapeutic Challenge. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2014, 210, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilova, M.; Cabezas Macian, M.; Martin-Gorgojo, A.; Beteta, L.G.; Posadas, V.; Jorda-Cuevas, E. A Rapidly Enlarging Mass on the Right Leg. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2015, 32, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piersigilli, F.; Auriti, C.; Mondì, V.; Francalanci, P.; Salvatori, G.; Danhaive, O. Decreased CDKN1C Expression in Congenital Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma Associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome. Indian J. Pediatr. 2016, 83, 1476–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, I.; Di Paolo, V.; Gurnari, C.; Mastronuzzi, A.; Del Bufalo, F.; Di Paolo, P.L.; Di Giannatale, A.; Boldrini, R.; Milano, G.M. Congenital Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Different Clinical Presentation in Two Cases. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Chao, J.; Bauer, B.; Sun, X.; Chou, P.M. Primary Cutaneous Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Perineum. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2002, 126, 982–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, R.; Anderson, J.; Gaze, M.; Gerrard, M.; Glaser, A.; Gordon, A.; Malone, M.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; Michalski, A. Congenital Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcomam: Clinical and Molecular Distinction from Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma in Older Children. Cancer 2001, 91, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualman, S.; Lynch, J.; Bridge, J.; Parham, D.; Teot, L.; Meyer, W.; Pappo, A. Prevalence and Clinical Impact of Anaplasia in Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report from the Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee of the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer 2008, 113, 3242–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Cerrillo, D.M.; Diaz-Perez, J.A.; Velez-Torres, J.M.; Montgomery, E.A.; Rosenberg, A.E. Novel Fusion Genes in Spindle Cell Rhabdomyosarcoma: The Spectrum Broadens. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2021, 60, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroiwa, M.; Sakamoto, J.; Shimada, A.; Suzuki, N.; Hirato, J.; Park, M.-J.; Sotomatsu, M.; Hayashi, Y. Manifestation of Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma as Primary Cutaneous Lesions in a Neonate with Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2009, 44, e31–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraitag, S.; Boccara, O. What to Look Out for in a Newborn with Multiple Papulonodular Skin Lesions at Birth. Dermatopathology 2021, 8, 390–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecher, A.R.; Reyes-Mugica, M.; Kamino, H.; Chang, M.W. Congenital Primary Cutaneous Rhabdomyosarcoma in a Neonate. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2003, 20, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skapek, S.X.; Ferrari, A.; Gupta, A.A.; Lupo, P.J.; Butler, E.; Shipley, J.; Barr, F.G.; Hawkins, D.S. Rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2019, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marburger, T.B.; Gardner, J.M.; Prieto, V.G.; Billings, S.D. Primary Cutaneous Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Clinicopathologic Review of 11 Cases: Cutaneous Rhabdomyosarcoma. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2012, 39, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, H.; Azimpouran, M. Congenital Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma; Multiple Lesions. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2017, 31, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitjadi, T.M.; Wadee, R.; Grayson, W. Rhabdomyosarcoma Arising in a Giant Congenital Melanocytic Naevus: Case Report and Literature Review. Dermatopathology 2019, 6, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sisoudiya, S.D.; Martin-Giacalone, B.A.; Khayat, M.M.; Dugan-Perez, S.; Marquez-Do, D.A.; Scheurer, M.E.; Muzny, D.; Boerwinkle, E.; Gibbs, R.A.; et al. Germline Cancer Predisposition Variants in Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yechieli, R.L.; Mandeville, H.C.; Hiniker, S.M.; Bernier-Chastagner, V.; McGovern, S.; Scarzello, G.; Wolden, S.; Cameron, A.; Breneman, J.; Fajardo, R.D.; et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e28254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, W.W.; Yuen, C.; Munsell, M.; Hayes-Jordan, A.; Lazar, A.J.; Patel, S.; Wang, W.-L.; Barahmani, N.; Okcu, M.F.; Hicks, J.; et al. Liposarcoma in Children and Young Adults: A Multi-Institutional Experience. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2011, 57, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, J.; Al-Ibraheemi, A. Adipocytic Tumors in Children: A Contemporary Review. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 36, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariño-Enriquez, A.; Nascimento, A.F.; Ligon, A.H.; Liang, C.; Fletcher, C.D.M. Atypical Spindle Cell Lipomatous Tumor: Clinicopathologic Characterization of 232 Cases Demonstrating a Morphologic Spectrum. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.M.; Dandekar, M.; Thomas, D.; Goldblum, J.R.; Weiss, S.W.; Billings, S.D.; Lucas, D.R.; McHugh, J.B.; Patel, R.M. Cutaneous and Subcutaneous Pleomorphic Liposarcoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of 29 Cases with Evaluation of MDM2 Gene Amplification in 26. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Nunez, O.; Alaggio, R.; John, I.; Ciolfi, A.; Pedace, L.; Mastronuzzi, A.; Gianno, F.; Giangaspero, F.; Rossi, S.; Donofrio, V.; et al. Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy (MNTI) and Pineal Anlage Tumor (PAT) Harbor A Medulloblastoma Signature by DNA Methylation Profiling. Cancers 2021, 13, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creytens, D.; Ferdinande, L.; Lecoutere, E.; Van Dorpe, J. Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumour of Infancy Presenting as an Undifferentiated Round Cell Tumour in the Soft Tissue of the Forearm. Pathology 2017, 49, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zheng, J.; Yang, S.; Zhu, H.; Dong, K.; Xiao, X.; Chen, L. Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy in the Soft Tissue of the Forearm: Report of a Case. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 13584–13589. [Google Scholar]
- Rekhi, B.; Suryavanshi, P.; Desai, S.; Gulia, A.; Desai, S.; Juvekar, S.L.; Puri, A.; Jambhekar, N.A. Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy in Thigh of an Infant—A Rare Case Report with Diagnostic Implications. Skelet. Radiol. 2011, 40, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Marzooq, Y.M.; Al-Bagshi, M.H.; Chopra, R.; Hashish, H. Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy in the Soft Tissues of the Arm: Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy and Histologic Correlation-a Case Report. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2003, 29, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, A.; Galmiche, L.; Minard-Colin, V.; Rachwalski, M.; Belhous, K.; Orbach, D.; Joly, A.; Picard, A.; Kadlub, N. Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy (MNTI) of the Head and Neck: A French Multicenter Study. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, C.C.; Diniz, M.G.; de Menezes, G.H.F.; Castro, W.H.; Gomez, R.S. BRAFV600E Mutation in Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy: Toward Personalized Medicine? Pediatrics 2015, 136, e267–e269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, D.J.; Hookway, E.; Athanasou, N.; Kashima, T.; Oppermann, U.; Hughes, S.; Swan, D.; Lueerssen, D.; Anson, J.; Hassan, A.B. A Germline Mutation of CDKN2A and a Novel RPLP1-C19MC Fusion Detected in a Rare Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy: A Case Report. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judd, P.L.; Harrop, K.; Becker, J. Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1990, 69, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giannatale, A.; Frezza, A.M.; Le Deley, M.-C.; Marec-Bérard, P.; Benson, C.; Blay, J.-Y.; Bui, B.; Judson, I.; Oberlin, O.; Whelan, J.; et al. Primary Cutaneous and Subcutaneous Ewing Sarcoma: Primary Cutaneous/Subcutaneous Ewing Sarcoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Shen, L.; Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Wei, L. Congenital Cutaneous Peripheral Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor/Ewing Sarcoma: A Rare Case in a Male Neonate. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekeuleneer, V.; El Nemnom, P.; Vervier, J.; Brichard, B.; Libert, J.; Van Eeckhout, P.; Marot, L.; Tennstedt, D.; Levy, G.; De Ville De Goyet, M.; et al. Primary Cutaneous Ewing Sarcoma in a Young Girl. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2019. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, S.; Lessnick, S.L. Promiscuous Partnerships in Ewing’s Sarcoma. Cancer Genet. 2011, 204, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Deniz, K.; Sung, Y.-S.; Zhang, L.; Dry, S.; Antonescu, C.R. Ewing Sarcoma with ERG Gene Rearrangements: A Molecular Study Focusing on the Prevalence of FUS-ERG and Common Pitfalls in Detecting EWSR1-ERG Fusions by FISH. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2016, 55, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-L.; Patel, N.R.; Caragea, M.; Hogendoorn, P.C.W.; López-Terrada, D.; Hornick, J.L.; Lazar, A.J. Expression of ERG, an Ets Family Transcription Factor, Identifies ERG-Rearranged Ewing Sarcoma. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilpatrick, S.E.; Reith, J.D.; Rubin, B. Ewing Sarcoma and the History of Similar and Possibly Related Small Round Cell Tumors: From Whence Have We Come and Where Are We Going? Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2018, 25, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, L.D.; Orman, G.M.; Bridge, J.A.; Bajaj, G.; Gardner, J.M.; Douglass, D.P. Primary Superficial Ewing Sarcoma: A Unique Entity? A Case Report Including Novel Findings of ELF3 and TNFRSF14 Copy Number Loss. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2020, 47, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacot, L.; Vidaud, D.; Sabbagh, A.; Laurendeau, I.; Briand-Suleau, A.; Coustier, A.; Maillard, T.; Barbance, C.; Morice-Picard, F.; Sigaudy, S.; et al. Severe Phenotype in Patients with Large Deletions of NF1. Cancers 2021, 13, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legius, E.; Messiaen, L.; Wolkenstein, P.; Pancza, P.; Avery, R.A.; Berman, Y.; Blakeley, J.; Babovic-Vuksanovic, D.; Cunha, K.S.; Ferner, R.; et al. Revised Diagnostic Criteria for Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and Legius Syndrome: An International Consensus Recommendation. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2021, 23, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehrer-Sawatzki, H.; Cooper, D.N. Challenges in the Diagnosis of Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) in Young Children Facilitated by Means of Revised Diagnostic Criteria Including Genetic Testing for Pathogenic NF1 Gene Variants. Hum. Genet. 2022, 141, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.G.R.; Salvador, H.; Chang, V.Y.; Erez, A.; Voss, S.D.; Schneider, K.W.; Scott, H.S.; Plon, S.E.; Tabori, U. Cancer and Central Nervous System Tumor Surveillance in Pediatric Neurofibromatosis 1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, e46–e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, S.; Blakeley, J.O.; Langmead, S.; Belzberg, A.J.; Fayad, L.M. Current Status and Recommendations for Imaging in Neurofibromatosis Type 1, Neurofibromatosis Type 2, and Schwannomatosis. Skelet. Radiol. 2020, 49, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, K.M.; Kim, A.; Blakely, J.; Ferner, R.E.; Gutmann, D.H.; Legius, E.; Miettinen, M.M.; Randall, R.L.; Ratner, N.; Jumbé, N.L.; et al. Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated MPNST State of the Science: Outlining a Research Agenda for the Future. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djx124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spunt, S.L.; Francotte, N.; De Salvo, G.L.; Chi, Y.-Y.; Zanetti, I.; Hayes-Jordan, A.; Kao, S.C.; Orbach, D.; Brennan, B.; Weiss, A.R.; et al. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Young Patients with Epithelioid Sarcoma: An Analysis from the Children’s Oncology Group and the European Paediatric Soft Tissue Sarcoma Study Group Prospective Clinical Trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 112, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armah, H.B.; Parwani, A.V. Epithelioid Sarcoma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2009, 133, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornick, J.L.; Dal Cin, P.; Fletcher, C.D.M. Loss of INI1 Expression Is Characteristic of Both Conventional and Proximal-Type Epithelioid Sarcoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2009, 33, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, G.; Krausz, T.; Stricker, T.P.; Szendrői, M.; Sápi, Z. SMARCB1 Expression in Epithelioid Sarcoma Is Regulated by MiR-206, MiR-381, and MiR-671-5p on Both MRNA and Protein Levels. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014, 53, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sápi, Z.; Papp, G.; Szendrői, M.; Pápai, Z.; Plótár, V.; Krausz, T.; Fletcher, C.D.M. Epigenetic Regulation of SMARCB1 By MiR-206, -381 and -671-5p Is Evident in a Variety of SMARCB1 Immunonegative Soft Tissue Sarcomas, While MiR-765 Appears Specific for Epithelioid Sarcoma. A MiRNA Study of 223 Soft Tissue Sarcomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2016, 55, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, F.; Bashashati, A.; Shumansky, K.; Dickson, B.; Gokgoz, N.; Wunder, J.S.; Andrulis, I.L.; Lazar, A.J.; Shah, S.P.; Huntsman, D.G.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of Epithelioid Sarcoma Cell Lines and Tumours. J. Pathol. 2016, 238, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohashi, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Yamada, Y.; Kinoshita, I.; Taguchi, T.; Iwamoto, Y.; Oda, Y. SWI/SNF Chromatin-Remodeling Complex Status in SMARCB1/INI1-Preserved Epithelioid Sarcoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C. Epithelioid Sarcoma of Enzinger. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2006, 13, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thway, K.; Jones, R.L.; Noujaim, J.; Fisher, C. Epithelioid Sarcoma: Diagnostic Features and Genetics. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2016, 23, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzaga, M.I.; Grant, L.; Curtin, C.; Gootee, J.; Silberstein, P.; Voth, E. The Epidemiology and Survivorship of Clear Cell Sarcoma: A National Cancer Database (NCDB) Review. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, C.D.M.; McKEE, P.H. Sarcomas-a Clinicopathological Guide with Special Reference to Cutaneous Manifestation IV. Extraskeletal Osteosarcoma, Extraskeletal Chondrosarcoma, Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma, Clear Cell Sarcoma and Discussion. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1985, 10, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.M.; Jensen, S.S.; Juel, J. Clear Cell Sarcoma-A Review. J. Orthop. 2018, 15, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dim, D.C.; Cooley, L.D.; Miranda, R.N. Clear Cell Sarcoma of Tendons and Aponeuroses: A Review. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2007, 131, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahira, T.; Oda, Y.; Tamiya, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Kawaguchi, K.; Kobayashi, C.; Iwamoto, Y.; Tsuneyoshi, M. Alterations of the P16INK4a/P14ARF Pathway in Clear Cell Sarcoma. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Hu, W.; Gao, X.; Liu, G.; Li, D.; Ding, Y.; Wen, X.; et al. Whole-exome Sequencing in Clear Cell Sarcoma of Soft Tissue Uncovers Novel Prognostic Categorization and Drug Targets. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thway, K.; Fisher, C. Synovial Sarcoma: Defining Features and Diagnostic Evolution. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 18, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerouanton, A.; Jimenez, I.; Cellier, C.; Laurence, V.; Helfre, S.; Pannier, S.; Mary, P.; Freneaux, P.; Orbach, D. Synovial Sarcoma in Children and Adolescents. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 36, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Tumor | Major Genetic Anomalies | Other Genetic Anomalies |
|---|---|---|
| Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma | EWSR1-CREB1 | EWSR1-ATF1, FUS-ATF1 |
| Infantile fibrosarcoma | ETV6-NTRK3 | EML4-NTRK3, RBPMS-NTRK3, SPECC1L-NTRK3 Other gene fusions involving NTRK1, NTRK2, MET, RET, RAF1 |
| NTRK-rearranged spindle cell neoplasms | LMNA-NTRK1 TPM3-NTRK1 TPR-NTRK1 | SQSTM1-NTRK1 EML4-NTRK3 KHDRBS1-NTRK3 Other gene fusions involving NTRK1,2,3 |
| EWSR1-SMAD3-rearranged fibroblastic tumor | EWSR1-SMAD3 | |
| ALK-rearranged infantile fibrosarcoma-like tumor | ALK-AK5, ALK-ERC1 | Other gene fusions involving ALK? |
| Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans/giant cell fibroblastoma | COL1A1-PDGFB | COL1A2-PDGFB, COL6A3-PDGFD, EMILIN2-PDGFD |
| Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor | Unknown | |
| Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma | - | Mutations in GNA14 |
| Papillary intralymphatic angioendothelioma (PILA)/retiform hemangioendothelioma | - | |
| Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma | SERPINE1-FOSB | ACTB-FOSB, WWTR1-FOSB, CLTC-FOSB, EGFL7-FOSB |
| Angiosarcoma | Complex anomalies (high grade tumor) | |
| Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS) | PAX7-FOXO1, PAX3-FOXO1, or no FOXO1 fusion | |
| Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) | Unknown | |
| Myxoid liposarcoma | FUS-DDIT3 | EWSR1-DDIT3 |
| Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy | unknown | BRAFV600E mutation (one case) |
| Ewing sarcoma | EWSR1-FLI1, EWSR1-ERG | EWSR1-ETV1, EWSR1-ETV4, EWSR1-FEV, FUS-ERG, FUS-FEV |
| Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) | Unknown | Loss of function mutations in SUZ12 or EED |
| Epithelioid sarcoma | SMARCB1 deletion, mutation or epigenetic silencing | SMARCA4, SMARCC1, SMARCC2 deletions |
| Clear cell sarcoma of soft tissue | EWSR1-ATF1 | EWSR1-CREB1 |
| Synovial sarcoma | SS18-SSX1, SS18-SSX2, SS18-SSX4 | SS18L1-SSX1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drabent, P.; Fraitag, S. Malignant Superficial Mesenchymal Tumors in Children. Cancers 2022, 14, 2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092160
Drabent P, Fraitag S. Malignant Superficial Mesenchymal Tumors in Children. Cancers. 2022; 14(9):2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092160
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrabent, Philippe, and Sylvie Fraitag. 2022. "Malignant Superficial Mesenchymal Tumors in Children" Cancers 14, no. 9: 2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092160
APA StyleDrabent, P., & Fraitag, S. (2022). Malignant Superficial Mesenchymal Tumors in Children. Cancers, 14(9), 2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092160







