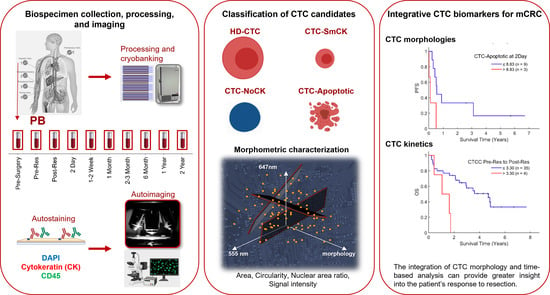
Circulating Tumor Cell Kinetics and Morphology from the Liquid Biopsy Predict Disease Progression in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Following Resection
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Study Overview
2.2. HDSCA Workflow
2.3. Statistical Analysis of Enumeration and Clinical Data
3. Results
3.1. Study Design
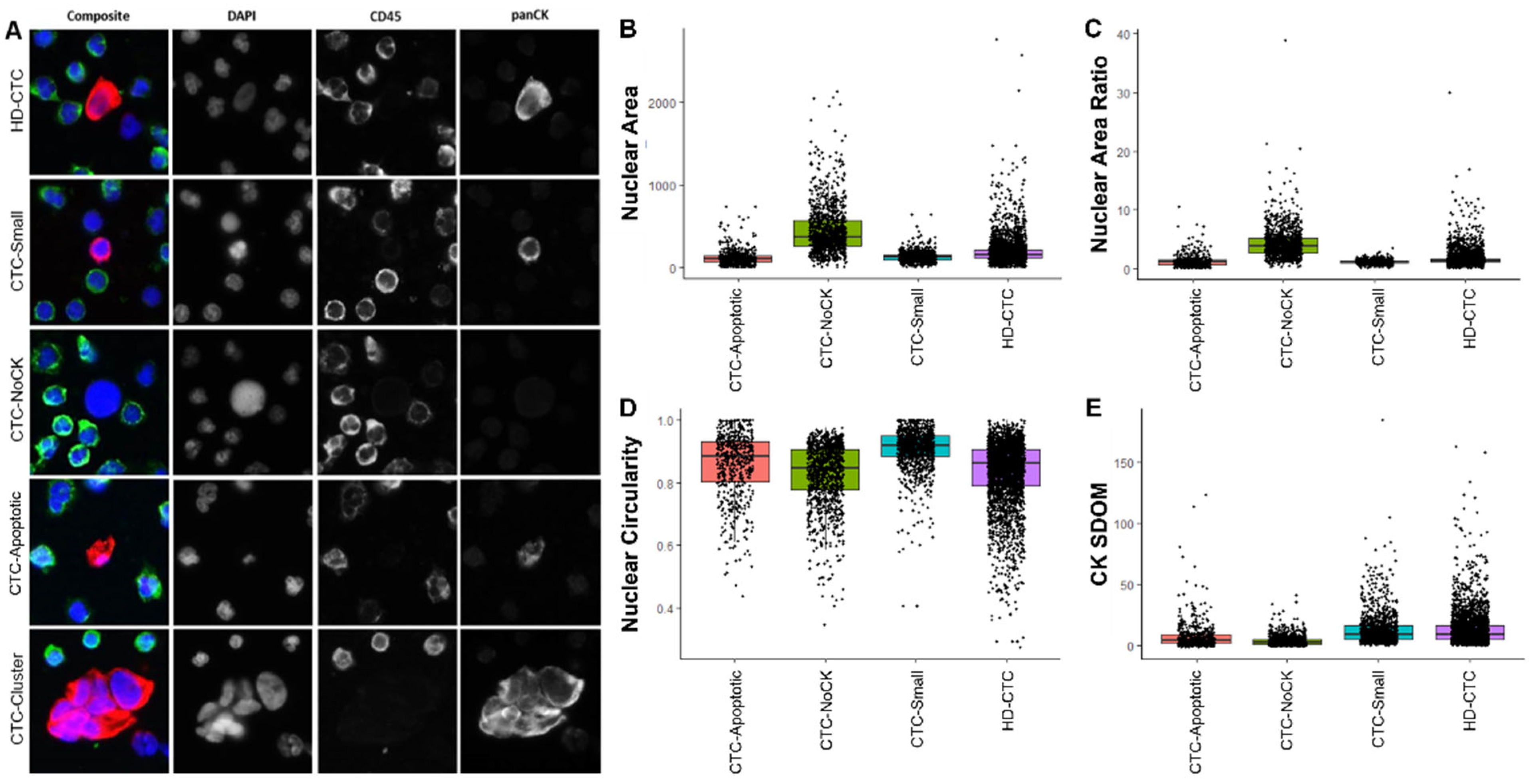
3.2. CTC Enumeration and Morphometric Analysis
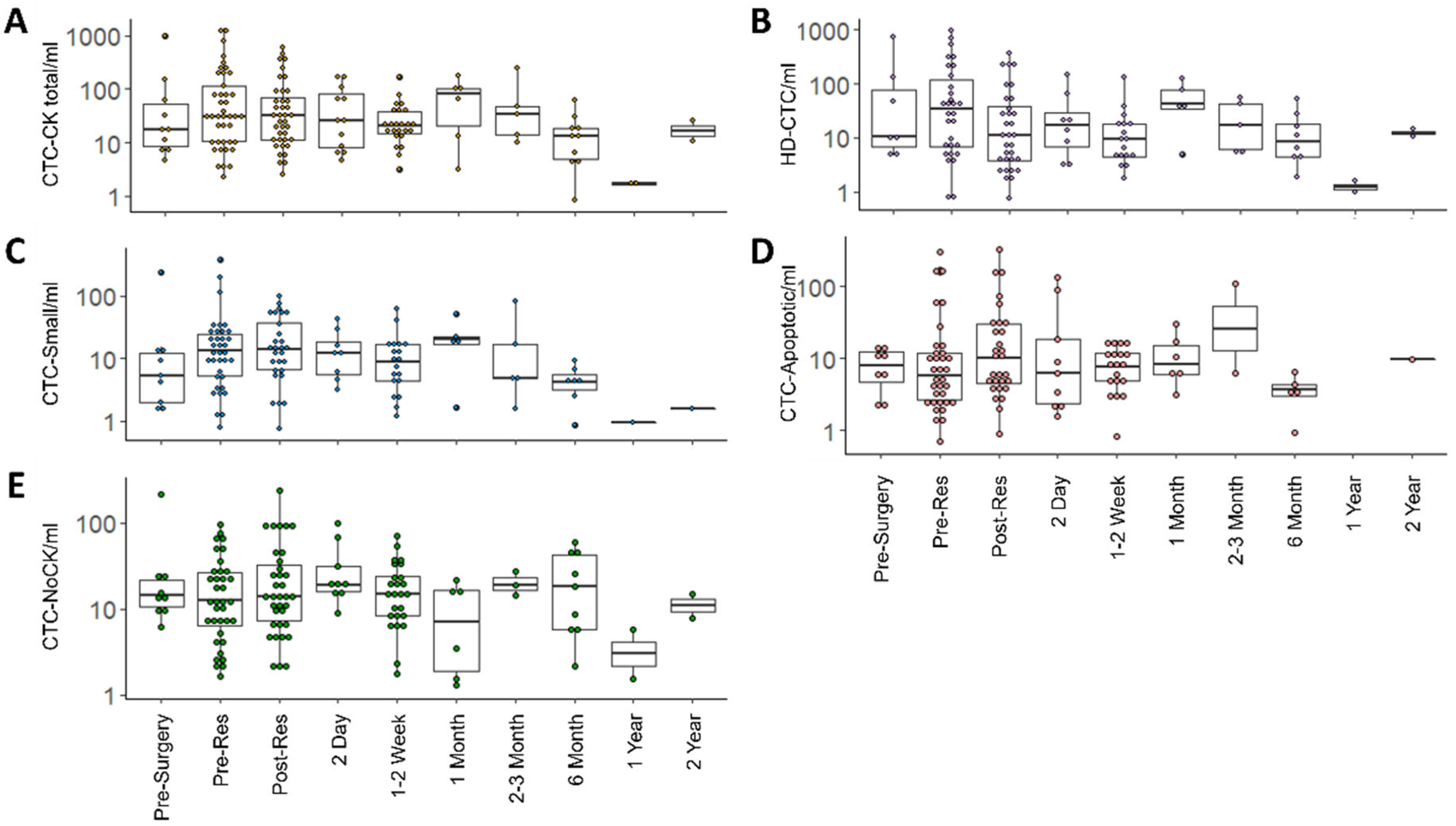
3.3. CTC Subtype Correlation with Clinical Data
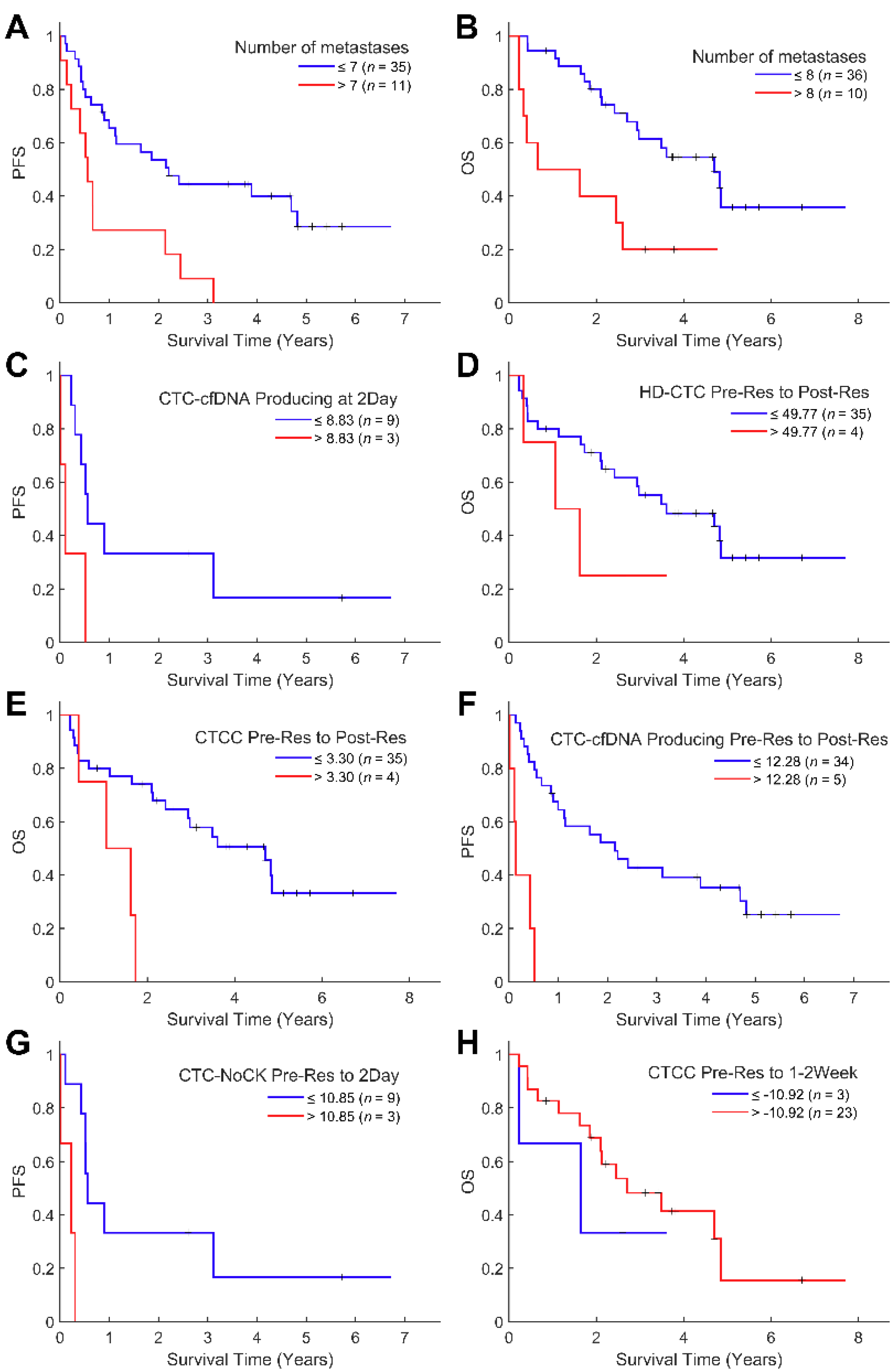
3.4. Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, E.; Nyamundanda, G.; Cunningham, D.; Tu, D.; Cheang, M.C.; Jonker, D.J.; Siu, L.L.; Sclafani, F.; Eason, K.; Ragulan, C.; et al. Intratumoral Transcriptome Heterogeneity Is Associated with Patient Prognosis and Sidedness in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Treated with Anti-EGFR Therapy from the CO.20 Trial. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Ng, S.B.; Chua, C.; Leow, W.Q.; Chng, J.; Liu, S.Y.; Ramnarayanan, K.; Gan, A.; Ho, D.L.; Ten, R.; et al. Multiregion ultra-deep sequencing reveals early intermixing and variable levels of intratumoral heterogeneity in colorectal cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 11, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Colon Cancer (Version 2.2021). Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/colon.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Nordlinger, B.; Arnold, D. Metastatic colorectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25 (Suppl. 3), iii1–iii9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, M.; Im, S.-A.; Senkus, E.; Xu, B.; Domchek, S.M.; Masuda, N.; Delaloge, S.; Li, W.; Tung, N.; Armstrong, A.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Breast Cancer in Patients with a Germline BRCA Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, C.; Castro, E.; Fizazi, K.; Heidenreich, A.; Ost, P.; Procopio, G.; Tombal, B.; Gillessen, S. Prostate cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendricks, A.; Brandt, B.; Geisen, R.; Dall, K.; Röder, C.; Schafmayer, C.; Becker, T.; Hinz, S.; Sebens, S. Isolation and enumeration of ctc in colorectal cancer patients: Introduction of a novel cell imaging approach and comparison to cellular and molecular detection techniques. Cancers 2020, 12, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza e Silva, V.; Chinen, L.T.D.; Abdallah, E.A.; Damascena, A.; Paludo, J.; Chojniak, R.; Dettino, A.L.A.; Lopes de Mello, C.A.; Alves, V.S.; Fanelli, M.F. Early detection of poor outcome in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: Tumor kinetics evaluated by circulating tumor cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 7503–7513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C.; Meropol, N.J.; Punt, C.J.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.A.; Mitchell, E.; et al. Relationship among circulating tumor cells, CEA and overall survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 24, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrazubi, V.; Mata, E.; Antelo, M.L.; Tarifa, A.; Herrera, J.; Zazpe, C.; Teijeira, L.; Viudez, A.; Suarez, J.; Hernández, I.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells in Patients Undergoing Resection of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases. Clinical Utility for Long-Term Outcome: A Prospective Trial. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 2805–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, D.H.; Kim, G.H.; Song, G.A.; Han, I.S.; Park, E.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jo, H.J.; Ko, S.H.; Park, D.Y.; Cho, Y.-K. Clinical Potential of Circulating Tumor Cells in Colorectal Cancer: A Prospective Study. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.-S.; Hung, W.-S.; Wang, T.-M.; Liu, H.; Yang, C.-Y.; Wu, S.-M.; Hsu, H.-L.; Hsiao, Y.-C.; Tsai, H.-J.; Tseng, C.-P. Circulating Tumor Cell Enumeration for Improved Screening and Disease Detection of Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Biomed. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Tanaka, F.; Yoneda, K.; Takuwa, T.; Kuroda, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Okumura, Y.; Kondo, N.; Tsujimura, T.; Nakano, T.; et al. The clinical value of circulating tumour cells (CTCs) in patients undergoing pulmonary metastasectomy for metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Yeh, P.-H.; Hsu, C.-J.; Chang, L.-W.; Chan, W.-J.; Lin, C.-P.; Lyu, Y.-Y.; Wu, W.-C.; Lee, C.-W.; et al. Highly Correlated Recurrence Prognosis in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer by Synergistic Consideration of Circulating Tumor Cells/Microemboli and Tumor Markers CEA/CA19-9. Cells 2021, 10, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, W.J.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.; Connelly, M.C.; Rao, C.; Tibbe, A.G.J.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Tumor cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.A.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Relationship of Circulating Tumor Cells to Tumor Response, Progression-Free Survival, and Overall Survival in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration. 510(k) Summary Cellsearch® Circulating Tumor Cell Kit; US Food and Drug Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Marrinucci, D.; Bethel, K.; Kolatkar, A.; Luttgen, M.S.; Malchiodi, M.; Baehring, F.; Voigt, K.; Lazar, D.; Nieva, J.J.; Bazhenova, L.; et al. Fluid biopsy in patients with metastatic prostate, pancreatic and breast cancers. Phys. Biol. 2012, 9, 016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Lee, M.; Kolatkar, A.; McCormick, M.; Dago, A.D.; Kendall, J.; Carlsson, N.A.; Bethel, K.; Greenspan, E.J.; Hwang, S.E.; Waitman, K.R.; et al. Effect of Blood Collection Tube Type and Time to Processing on the Enumeration and High-Content Characterization of Circulating Tumor Cells Using the High-Definition Single-Cell Assay. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishido, S.N.; Welter, L.; Rodriguez-Lee, M.; Kolatkar, A.; Xu, L.; Ruiz, C.; Gerdtsson, A.S.; Restrepo-Vassalli, S.; Carlsson, A.; Larsen, J.; et al. Preanalytical Variables for the Genomic Assessment of the Cellular and Acellular Fractions of the Liquid Biopsy in a Cohort of Breast Cancer Patients. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethel, K.; Luttgen, M.S.; Damani, S.; Kolatkar, A.; Lamy, R.; Sabouri-Ghomi, M.; Topol, S.; Topol, E.; Kuhn, P. Fluid phase biopsy for detection and characterization of circulating endothelial cells in myocardial infarction. Phys. Biol. 2014, 11, 016002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdtsson, A.S.; Thiele, J.-A.; Shishido, S.N.; Zheng, S.; Schaffer, R.; Bethel, K.; Curley, S.; Lenz, H.-J.; Hanna, D.L.; Nieva, J.; et al. Single cell correlation analysis of liquid and solid biopsies in metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 7016–7030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shishido, S.N.; Carlsson, A.; Nieva, J.; Bethel, K.; Hicks, J.B.; Bazhenova, L.; Kuhn, P. Circulating tumor cells as a response monitor in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welter, L.; Xu, L.; McKinley, D.; Dago, A.E.; Prabakar, R.K.; Restrepo-Vassalli, S.; Xu, K.; Rodriguez-Lee, M.; Kolatkar, A.; Nevarez, R.; et al. Treatment response and tumor evolution: Lessons from an extended series of multianalyte liquid biopsies in a metastatic breast cancer patient. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2020, 6, a005819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghatalia, P.; Smith, C.H.; Winer, A.; Gou, J.; Kiedrowski, L.A.; Slifker, M.; Saltzberg, P.D.; Bubes, N.; Anari, F.M.; Kasireddy, V.; et al. Clinical Utilization Pattern of Liquid Biopsies (LB) to Detect Actionable Driver Mutations, Guide Treatment Decisions and Monitor Disease Burden During Treatment of 33 Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mCRC) Patients (pts) at a Fox Chase Cancer Center GI Oncology Subspecialty Clinic. Front. Oncol. 2019, 8, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, R.L.; Dry, J.R.; Hanlon, S.E.; Johann, D.J.; Kolatkar, A.; Lee, J.S.H.; Meyer, C.; Salvatore, L.; Wells, W.; Leiman, L. BloodPAC Data Commons for Liquid Biopsy Data. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2021, 5, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, R.; Abel, B.; Angiuoli, S.; Barrett, J.; Bassett, D.; Bramlett, K.; Blumenthal, G.; Carlsson, A.; Cortese, R.; DiGiovanna, J.; et al. Collaborating to Compete: Blood Profiling Atlas in Cancer (BloodPAC) Consortium. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 101, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febbo, P.G.; Martin, A.; Scher, H.I.; Barrett, J.C.; Beaver, J.A.; Beresford, P.J.; Blumenthal, G.M.; Bramlett, K.; Compton, C.; Dittamore, R.; et al. Minimum Technical Data Elements for Liquid Biopsy Data Submitted to Public Databases. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 107, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godsey, J.H.; Silvestro, A.; Barrett, J.C.; Bramlett, K.; Chudova, D.; Deras, I.; Dickey, J.; Hicks, J.; Johann, D.J.; Leary, R.; et al. Generic Protocols for the Analytical Validation of Next-Generation Sequencing-Based ctDNA Assays: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the BloodPAC’s Analytical Variables Working Group. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dago, A.E.; Stepansky, A.; Carlsson, A.; Luttgen, M.; Kendall, J.; Baslan, T.; Kolatkar, A.; Wigler, M.; Bethel, K.; Gross, M.; et al. Rapid Phenotypic and Genomic Change in Response to Therapeutic Pressure in Prostate Cancer Inferred by High Content Analysis of Single Circulating Tumor Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, J.; Cohen, J.D.; Wang, Y.; Christie, M.; Simons, K.; Lee, M.; Wong, R.; Kosmider, S.; Ananda, S.; McKendrick, J.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Analyses as Markers of Recurrence Risk and Benefit of Adjuvant Therapy for Stage III Colon Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinert, T.; Henriksen, T.V.; Christensen, E.; Sharma, S.; Salari, R.; Sethi, H.; Knudsen, M.; Nordentoft, I.K.; Wu, H.-T.; Tin, A.S.; et al. Analysis of Plasma Cell-Free DNA by Ultradeep Sequencing in Patients with Stages I to III Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C.; Li, J.; Luttgen, M.S.; Kolatkar, A.; Kendall, J.T.; Flores, E.; Topp, Z.; Samlowski, W.E.; McClay, E.; Bethel, K.; et al. Limited genomic heterogeneity of circulating melanoma cells in advanced stage patients. Phys. Biol. 2015, 12, 016008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malihi, P.D.; Graf, R.P.; Rodriguez, A.; Ramesh, N.; Lee, J.; Sutton, R.; Jiles, R.; Velasco, C.R.; Sei, E.; Kolatkar, A.; et al. Single-Cell Circulating Tumor Cell Analysis Reveals Genomic Instability as a Distinctive Feature of Aggressive Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4143–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malihi, P.D.; Morikado, M.; Welter, L.; Liu, S.T.; Miller, E.T.; Cadaneanu, R.M.; Knudsen, B.S.; Lewis, M.S.; Carlsson, A.; Velasco, C.R.; et al. Clonal diversity revealed by morphoproteomic and copy number profiles of single prostate cancer cells at diagnosis. Converg. Sci. Phys. Oncol. 2018, 4, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdtsson, E.; Pore, M.; Thiele, J.-A.; Gerdtsson, A.S.; Malihi, P.D.; Nevarez, R.; Kolatkar, A.; Velasco, C.R.; Wix, S.; Singh, M.; et al. Multiplex protein detection on circulating tumor cells from liquid biopsies using imaging mass cytometry. Converg. Sci. Phys. Oncol. 2018, 4, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdtsson, A.; Setayesh, S.; Malihi, P.; Ruiz, C.; Carlsson, A.; Nevarez, R.; Matsumoto, N.; Gerdtsson, E.; Zurita, A.; Logothetis, C.; et al. Large Extracellular Vesicle Characterization and Association with Circulating Tumor Cells in Metastatic Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Circulating Tumor Cell Kinetics and Morphology from the Liquid Biopsy Predict Disease Progression in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Following Resection. Available online: https://pivot.usc.edu/pivot/CRC_Pilsen_Pivot_SN_20220118.html#%7B%22filters%22%3A%7B%7D%2C%22search%22%3Anull%2C%22sortBy%22%3A%22Timepoint%22%2C%22view%22%3A%22graph%22%7D (accessed on 3 November 2021).
| Clinical Factor | Median | Range | Clinical Factor | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at Resection | 63 | 34–82 | T Stage | ||
| Tumor Size | 5 | 1.5–9.0 | 1 | 1 | 2.1 |
| NA | n = 13 | 2 | 2 | 4.3 | |
| Metastatic Lesion Size | 3 | 0.4–18.5 | 3 | 30 | 63.8 |
| NA | n = 7 | 4 | 7 | 14.9 | |
| Number of Metastases | 2 | 1–10 | NA | 7 | 14.9 |
| NA | n = 13 | N Stage | |||
| Clinical Factor | n | % | 0 | 12 | 25.5 |
| Sex | 1 | 10 | 21.3 | ||
| Male | 25 | 53.2 | 2 | 18 | 38.3 |
| Female | 22 | 46.8 | NA | 7 | 14.9 |
| Synchronous Disease | M Stage | ||||
| Yes | 28 | 59.6 | 0 | 12 | 25.5 |
| No | 18 | 38.3 | 1 | 32 | 68.1 |
| NA | 1 | 2.1 | NA | 3 | 6.4 |
| Pre-Op Chemotherapy | Grade | ||||
| Yes | 16 | 34.0 | 1 | 8 | 17.0 |
| No | 18 | 38.3 | 2 | 21 | 44.7 |
| NA | 13 | 27.7 | 3 | 5 | 10.6 |
| Resection Type | NA | 13 | 27.7 | ||
| Primary | 21 | 44.7 | KRAS | ||
| Metastasis | 24 | 51.1 | WT | 13 | 27.7 |
| Both | 2 | 4.3 | Mutant | 10 | 21.3 |
| Primary Tumor Location | NA | 24 | 51.1 | ||
| Descending | 29 | 61.7 | CEA > 5ng/mL | ||
| Transverse | 7 | 14.9 | Yes | 23 | 48.9 |
| Ascending | 10 | 21.3 | No | 16 | 34.0 |
| NA | 1 | 2.1 | NA | 8 | 17.0 |
| Liver Metastasis Location | MSI | ||||
| Left | 14 | 29.8 | Stable | 11 | 23.4 |
| Right | 21 | 44.7 | Instable | 1 | 2.1 |
| All Over | 8 | 17.0 | NA | 35 | 74.5 |
| NA | 4 | 8.5 | Necrosis | ||
| 1 Year Progression | Yes | 3 | 6.4 | ||
| No | 25 | 53.2 | No | 20 | 42.6 |
| Yes | 21 | 44.7 | NA | 24 | 51.1 |
| NA | 1 | 2.1 |
| Variable1 | Variable2 | p Value | Median | Range | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD-CTCs/mL pre-res | KRAS mutant | 0.021 | 18.56 | 0.00–968.70 | 139.87 |
| HD-CTCs/mL pre-res | KRAS WT | 0.021 | 0.00 | 0.00–37.52 | 5.56 |
| CTCCs/mL pre res | KRAS mutant | 0.029 | 1.3 | 0.00–63.40 | 9.11 |
| HD-CTCs/mL pre-res | transverse colon | 0.0123 | 193.76 | 9.58–968.70 | 321.84 |
| HD-CTCs/mL pre-res | Ascending colon | 0.0123 | 0 | 0.00–694.89 | 82.89 |
| HD-CTCs/mL pre-res | Descending colon | 0.0123 | 5.38 | 0.00–278.77 | 41.56 |
| CCTCs/mL pre res | transverse colon | 0.0436 | 2.73 | 0.00–63.40 | 13.37 |
| CCTCs/mL pre res | Ascending colon | 0.0436 | 0 | 0.00–22.18 | 2.46 |
| CCTCs/mL pre-res | Descending colon | 0.0436 | 0 | 0.00–15.87 | 2.23 |
| CTC-NoCK/mL pre-res | NACT | 0.0325 | 4.81 | 0.00–27.28 | 9.25 |
| CTC-NoCK/mL pre-res | NACT | 0.0325 | 13.94 | 2.05–234.84 | 37.73 |
| CTC-NoCK/mL pre-res | Left liver metastases | 0.0305 | 23.07 | 1.67–96.10 | 30.94 |
| CTC-NoCK/mL pre-res | Right liver metastases | 0.0305 | 7.42 | 0.00–49.02 | 11.07 |
| CTC-Apoptotic/mL pre-res | Synchronous disease | 0.0256 | 2.52 | 0.00–295.70 | 16.06 |
| CTC-Apoptotic/mL pre-res | Asynchronous disease | 0.0256 | 5.79 | 0.71–171.57 | 29.59 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolenčík, D.; Narayan, S.; Thiele, J.-A.; McKinley, D.; Gerdtsson, A.S.; Welter, L.; Hošek, P.; Ostašov, P.; Vyčítal, O.; Brůha, J.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Kinetics and Morphology from the Liquid Biopsy Predict Disease Progression in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Following Resection. Cancers 2022, 14, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030642
Kolenčík D, Narayan S, Thiele J-A, McKinley D, Gerdtsson AS, Welter L, Hošek P, Ostašov P, Vyčítal O, Brůha J, et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Kinetics and Morphology from the Liquid Biopsy Predict Disease Progression in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Following Resection. Cancers. 2022; 14(3):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030642
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolenčík, Drahomír, Sachin Narayan, Jana-Aletta Thiele, Dillon McKinley, Anna Sandström Gerdtsson, Lisa Welter, Petr Hošek, Pavel Ostašov, Ondřej Vyčítal, Jan Brůha, and et al. 2022. "Circulating Tumor Cell Kinetics and Morphology from the Liquid Biopsy Predict Disease Progression in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Following Resection" Cancers 14, no. 3: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030642
APA StyleKolenčík, D., Narayan, S., Thiele, J.-A., McKinley, D., Gerdtsson, A. S., Welter, L., Hošek, P., Ostašov, P., Vyčítal, O., Brůha, J., Fiala, O., Šorejs, O., Liška, V., Pitule, P., Kuhn, P., & Shishido, S. N. (2022). Circulating Tumor Cell Kinetics and Morphology from the Liquid Biopsy Predict Disease Progression in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Following Resection. Cancers, 14(3), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030642