Simple Summary
Prostate cancer progression is mainly driven by the androgen receptor (AR) signaling pathway and its inhibition has been the cornerstone in the treatment of patients harboring this disease. However, during the course of prostate cancer, various resistance mechanisms have been defined as responsible for tumor progression and the lack of response to current antiandrogen drugs. These resistance mechanisms act directly over the AR signaling pathway, but also over other bypassing pathways that could potentially be targetable. Therefore, the improvement in the molecular knowledge of prostate cancer progression and the development of new active therapies may overcome the current limits in prolonging the survival of patients with prostate cancer.
Abstract
The androgen signaling pathway is the cornerstone in the treatment of high risk or advanced prostate cancer patients. However, in recent years, different mechanisms of resistance have been defined in this field, limiting the efficacy of the currently approved antiandrogen drugs. Different therapeutic approaches are under research to assess the role of combination therapies against escape signaling pathways or the development of novel antiandrogen drugs to try to solve the primary or acquired resistance against androgen dependent or independent pathways. The present review aims to summarize the current state of androgen inhibition in the therapeutic algorithm of patients with advanced prostate cancer and the mechanisms of resistance to those available drugs. In addition, this review conducted a comprehensive overview of the main present and future research approaches in the field of androgen receptor inhibition to overcome these resistances and the potential new drugs under research coming into this setting.
1. Introduction
Prostate cancer is the second most common solid tumor diagnosed in men with an estimated incidence for 2020 of 1.4 million new cases worldwide. Therefore, patients diagnosed with prostate cancer represent a major health clinical concern, and research focused on developing early and precise diagnostic tools as well as optimal treatment approaches is key [1]. Different clinical settings have been defined in prostate cancer that harbor a particular management according to their distinct prognosis and approved therapies. In the advanced disease, androgen deprivation therapy has been a cornerstone in the management of these patients. Unfortunately, patients will finally progress at some point of this therapy and new drugs have been developed to improve the oncological results by inhibiting the androgen receptor pathway more effectively, or by targeting bypassing pathways [1,2,3]. During the last years, the improvement in the molecular characteristics of prostate cancer has increased the relevance for a biomarker-driven therapeutic approach and, in this sense, the role of continuing AR signaling during the oncological progression as a key pathway [1]. Thus, deepening the knowledge in AR upstream and downstream signaling as well as potential targets with antitumoral activity is a constant field of research to keeping the blockade of the ARSI beyond the already AR signaling inhibitor (ARSI) approved drugs such as enzalutamide, apalutamide, darolutamide, or abiraterone acetate.
Overall, the aim of this review is to provide molecular insights on AR signaling in metastatic castration resistance prostate cancer (mCRPC) as well as current and future perspectives on drug development to adequately inhibit this key pathway and overcome potential resistance mechanisms to, finally, improve the patient survival. For this purpose, the relevant literature was searched through an automatized search in the PubMed bibliographic database published between 2000 and 2022 using the combination terms: “prostate cancer” OR “androgen receptor” OR “castration resistance” OR “metastatic prostate cancer” OR “antiandorgens”, “novel hormone agents”, “androgen receptor signaling inhibitors” OR “resistance mechanisms”.
2. Molecular Characterization of Metastatic Castration Resistance Prostate Cancer Focusing on Androgen Receptor Signaling Pathway
In an effort to understand the molecular landscape of mCRPC, Robinson and colleagues conducted a whole exome and transcriptome sequencing from 150 tumor samples of patients with mCRPC [1]. A driver genomic aberration was identified in almost all cases, the most prevalent being alterations in AR, suggesting that most mCRPC are dependent on AR signaling. The AR gene is located on chromosome X and consists of eight exons that encode for the AR nuclear receptor, a member of the steroid hormone nuclear receptor family [1,2,3]. AR has four functional regions: an NH2 terminal transactivation domain (NTD), a DNA-binding domain (DBD), a hinge region, and a C-terminal ligand binding domain (LBD). Given its ubiquitous distribution, it exerts a diverse range of biological actions including the development and regulation of the reproductive, cardiovascular, immune, neural, and hemopoietic systems.
In particular, AR signaling plays a major role in the development and homeostasis of the prostate [2]. In normal prostatic tissue, epithelial AR provides the prostate gland with several secretory proteins including prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and stromal AR facilitates prostate growth. Stromal AR-knockout mice have reduced epithelium proliferation, extracellular matrix remodeling, immune cell infiltration, and angiogenesis [3]. AR accumulates in the cytoplasm and is bound to a heat shock protein, cytoskeletal proteins, and other chaperones. Their role is to preserve AR in a conformation that allows for ligand binding and also to protect it from proteolysis.
Testosterone is produced primarily by the testes with a small contribution from the adrenal glands. 5α-Reductase is an enzyme that converts testosterone to DHT and is widely expressed within the prostate [4]. AR is activated after the binding of testosterone or 5 alpha dihydrotestosterone, which induces a conformational change in AR, facilitating interaction between the NTD and the LBD, which results in the dimerization of AR. The receptor is subsequently translocated into the nucleus [5]. There, the DBD tethers the AR to the promoter and enhancer regions of targeted genes through zinc fingers [6]. Once bound to the DNA, the AR dimer forms a complex with coregulatory proteins including SRC1, SRC2, SRC3, and p300/CBP, among others. Of note, the p160 coactivator complex formed by SRC1, TIF2, and SRC3 interacts with the NTS and the LBD, enhancing ligand-independent AR-mediated transcription of the target genes [7]. AR regulates the expression of genes that play an important role in prostate cancer such as KLK3, KLK2, TMPRSS2-ERG, IGFR-1, FKBP5, FOXp1, TACC2, and UGT1A1 [8]. It has been well-established that AR is the backbone of prostate cancer tumorigenesis by facilitating cell survival, proliferation, migration, and invasion [9]. Several decades ago, Huggins and Hodges demonstrated the sensitivity of prostate cancer to androgen deprivation [10]. Indeed, ADT has been the cornerstone therapy in metastatic prostate cancer ever since. Nonetheless, over time, most tumors develop mechanisms that enable them to escape ADT. It appears that genomic aberrancies affecting AR signaling are responsible for resistance to treatment. Interestingly, despite low levels of serum testosterone, AR signaling persists in the castration-resistance setting. In other words, ADT-refractory prostate cancer remains androgen-driven [11], probably due to activating AR mutations or amplifications that result in increased protein expression. The clinical proof-of-principle would be that novel antiandrogens abiraterone and enzalutamide are active in mCRPC. However, both intrinsic and acquired resistance to these novel agents are occurring and the current focus is on developing strategies to overcome these mechanisms of resistance.
Other putatively clinically actionable alterations identified by Robinson et al. included aberrations in the PI3K pathway (49%), DNA repair pathway (19%), MAP kinases (3%), cell cycle pathways (7%), and the WNT pathway (5%) [1]. A cross analysis with primary prostate cancer samples was performed, finding AR and GN17AS mutations to arise exclusively in mCRPC patients.
A later study performed whole generation sequencing in 197 mCRPC samples. They defined eight distinct genomic clusters including a microsatellite instability (MSI) subgroup with high tumor mutational burden associated with mismatch repair deficiency, homologous recombination deficient (HRD) tumors involving genetic alterations in BRCA-related genes, a tandem duplication genotype associated with biallelic loss of CDK12, and a chromothripsis-enriched group [12].
3. Current Treatment Based on Next-Generation Androgen Receptor Inhibition in Prostate Cancer
The primary axis of prostate cancer development is the androgen receptor (AR) signaling system, which controls the expression of genes involved in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and prostate cancer cell survival. Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), which lowers circulating testosterone to castration levels and provides disease control, has long been the go-to treatment for metastatic prostate cancer [13]. Castration resistance develops over time despite ADT. Castration resistance is determined by biochemical progression (three consecutive increases in prostate-specific antigen [PSA] spaced by one week that result in two 50% increases over the nadir, with PSA >2 ng/mL) or radiological progression (the presence of two or more new bone lesions on a bone scan or the enlargement of a soft tissue lesion using serum testosterone levels below 50 ng/dL or 1.7 nmol/L) [14]. The role of these ARSI has expanded beyond non-metastatic or mCRPC to metastatic hormone sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC) [15,16,17,18,19,20], and, even more, in high risk non-metastatic prostate cancer. Overall, the blockade of the AR axis either by the suppression of androgen synthesis (abiraterone) or the inhibition of AR by second generation AR antagonists (enzalutamide, darolutamide, apalutamide) is key in different settings [21].
3.1. Abiraterone
Abiraterone is a selective cytochrome P450 (CYP)17 inhibitor (CYP17A1) that permanently inhibits the manufacture of androgen in the testicles, adrenal tissue, and tumor cells. Due to reduced endogenous glucocorticoid synthesis, prednisone must be administered concurrently in the mCPRC context. In both docetaxel-pretreated (COU-AA-301) and chemotherapy-naive (COU-AA-302) mCRPC patients, two phase 3 trials have shown the benefit of abiraterone (Table 1) [22,23,24,25]. Various trials have investigated the function of abiraterone in mHSPC. De novo high risk mHSPC patients having at least two aggressive characteristics such as a Gleason score more than 8, at least three bone metastatic lesions, and/or visceral metastases were included in the LATITUDE study. PFS and OS both saw a substantial improvement with the addition of abiraterone to ADT (Table 1). Overproduction of mineralocorticoids was the cause of the majority of adverse events (AEs), which included hypertension, nausea, edema, and hypokalemia. However, other toxicities, most of which were grade 1–2, were also reported including fatigue, hot flushes, diarrhea, vomiting, and abnormal liver function [18]. In several clinical contexts, the STAMPEDE Protocol platform assessed the interaction of ADT with abiraterone acetate and enzalutamide. The ADT + abiraterone acetate doublet had no discernible anticancer efficacy in individuals with mHSPC and high risk prostate cancer, although it significantly increased toxicity (Table 1) [21,26]. Finally, the PEACE-1 study, which was focused on the de novo mHSPC situation, randomized 710 patients in a 2 × 2 factorial design to assess the impact of abiraterone in addition to ADT and docetaxel (Table 1) [16]. The trial indicated that the triplet treatment subgroup of individuals with large volume illness improved by 19 months in OS and 30 months in rPFS.
3.2. Apalutamide
An oral nonsteroidal antiandrogen called apalutamide (ARN-509) binds specifically to the AR’s ligand-binding domain and inhibits the AR from translocating, binding to DNA, or mediating transcription. Apalutamide has shown benefits in metastasis free survival (MFS) in the SPARTAN trial in nmCPRC. This study included patients with high risk for disease progression (PSA level of ≥8 ng/mL or a PSA doubling time of ≤10 months) (Table 1) [27]. MFS was 40.5 months in the apalutamide group compared to 16.2 months in the placebo group (HR for metastasis or death was 0.28; 95% CI 0.23–0.35; p < 0.001). Apalutamide also proved to be beneficial in all secondary end points such as OS with a median increase of 14 months [28]. The most frequent AE were rash (23.8% vs. 5.5%), hypothyroidism (8.1% vs. 2.0%), and fractures (11.7% vs. 6.5%), being the majority grade 1 or 2. In the mHSPC setting, apalutamide was studied in the phase III TITAN trial with a significant improvement in the co-primary endpoints of radiographic PFS and OS (Table 1) [15,29]. The addition of apalutamide has also been evaluated in first line mCRPC in combination with abiraterone and prednisone in a phase III trial (ACIS; NCT02257736) (Table 1) [30]. The primary outcome of rPFS was achieved with no clear impact on OS. Thus, we still need to define whether there is a patient subgroup that could potentially benefit from this combination.
3.3. Darolutamide
Darolutamide (ODM-201) is a new generation AR inhibitor with higher AR affinity than enzalutamide or apalutamide, blocking nuclear translocation of the AR receptor. Its main characteristic is that its structure differs from AR antagonists such as enzalutamide or apalutamide, leading to a differential profile of AE as it does not penetrate through the blood–brain barrier [31]. The ARADES phase 1–2 trial was designed to assess the safety and tolerability of this molecule in mCRPC patients [32]. After showing a favorable safety profile, antitumor activity and decrease in PSA levels, clinical development started in men with non-metastatic CRPC (nmCRPC) (ARAMIS trial) and metastatic hormone-sensitive PC (ARASENS trial) (Table 1) [17,33]. ARAMIS was a phase 3 trial that involved 1509 nmCRPC patients with a PSA doubling time of 10 months or less [33]. The primary endpoint, MFS, was achieved at 40.4 months in the darolutamide group and 18.4 months in the placebo group (the darolutamide group’s HR for metastasis or death was 0.41; 95% CI 0.34–0.50; p = 0.001). The darolutamide group outperformed all secondary objectives including OS, time to pain progression, time to first symptomatic skeletal event, and time to next cytotoxic treatment. The majority of the grade 1–2 adverse events (AE) in both groups had a comparable frequency (83.2% vs. 76.9%). Fatigue was the most frequent AE, and fracture frequency was similar in both groups. In the ARASENS study, the addition of darolutamide to ADT and docetaxel significantly improved the patient survival in those with de novo mHSPC [17].
3.4. Enzalutamide
Enzalutamide is a second-generation, nonsteroidal AR inhibitor that binds to the AR with greater affinity than bicalutamide, impairs AR nuclear translocation, and prevents the recruitment of AR cofactors [34]. Its efficacy was initially evaluated in the post-docetaxel and chemo-naïve setting of mCRPC patients included in the AFFIRM and PREVAIL trials, respectively (Table 1) [35,36]. Safety and efficacy was proven in patients over 75 years and in those with visceral metastasis [37]. The most frequent adverse event (AE) was fatigue, hypertension, diarrhea, hot flashes, and headache; a small proportion of seizures in the enzalutamide group was described (0.6%). In the nmCRPC setting, enzalutamide was tested in the PROSPER phase III trial, showing a significant improvement not only in the primary endpoint of metastases free survival, but also in OS (Table 1) [38]. In the mHSPC setting, the role of enzalutamide has been evaluated in two different clinical trials: the ARCHES and ENZAMET studies, showing a benefit from the addition of enzalutamide to ADT over ADT alone or in combination with standard nonsteroidal antiandrogen therapy, respectively (Table 1) [19,20,39,40].

Table 1.
Main clinical trials evaluating the role of currently approved androgen receptor signaling inhibitors (ARSI).
Table 1.
Main clinical trials evaluating the role of currently approved androgen receptor signaling inhibitors (ARSI).
| Clinical Trial | Setting and Median Follow Up (Months; m) | Number of Patients | Treatment Arms | PFS (Median Months; HR 95%CI) | OS (Median Months) (HR; 95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENZALUTAMIDE (ENZA) | |||||
| AFFIRM [41] | mCRPC post-doc (14.4 m) | 1199 (2:1) | ADT + ENZA vs. PBO | 8.3 vs. 2.9 (0.40; 0.35–0.47) | 18.4 vs. 13.6 (0.63; 0.53 to 0.75) |
| PREVAIL [36] | mCRPC (12 & 22 m) | 1717 (1:1) | ADT + ENZA vs. PBO | 20.0 vs. 5.4 (0.19; 0.15–0.23) | 35.3 vs. 31.3 (0.77; 0.67–0.88) |
| PROSPER [38,42] | NM CRPC (48 m) | 1401 (2:1) | ADT + ENZA vs. PBO | MFS = 36.6 vs. 14.7 (0.29; 0.24–0.35) | 67 vs. 56.3 (0.73; 0.61–0.89) |
| ENZAMET [20] | mHSPC (34 m & 40 m) | 1125 (1:1) | ADT + TSAA +/− ENZA+/− DOC | 3-y-PFS = 68% vs. 41% (0.40; 0.33–0.49) | NR vs. 73.2 (0.70; 0.58–0.84) |
| ARCHES [19,39] | mHSPC (14.4 m & 44.6 m) | 1150 (1:1) | ADT + ENZA vs. PBO (+/− DOC) | 49.8 vs. 38.9 (0.63; 0.52–0.76) | NR vs. NR (0.66; 0.53–0.81) |
| DAROLUTAMIDE (DARO) | |||||
| ARAMIS [33] | NM CRPC (29 m) | 1509 (2:1) | ADT + DARO vs. PBO | MFS = 40.4 vs. 18.4 (0.41; 0.34–0.5) | NR vs. NR (0.69; 0.53–0.88) |
| ARASENS [17] | mHSPC (43.7 m) | 1305 (1:1) | ADT + DOC +/− DARO | - | NR vs. 48.9 (0.68; 0.57–0.8) |
| APALUTAMIDE (APA) | |||||
| SPARTAN [28] | NM CRPC (52 m) | 1207 (2:1) | ADT + APA vs. PBO | MFS = 40.5 vs. 16.2 (0.28; 0.23–0.35) | 73.9 vs. 59.9 (0.78; 0.64–0.96) |
| TITAN [39,40] | mHSPC (22.7 m & 44 m) | 1052 (1:1) | ADT + APA vs. PBO (+/− DOC) | NR vs. 22.1 (0.48; 0.39–0.60) | NR v 52.2 (0.65; 0.53–0.79) |
| ABIRATERONE ACETATE/PREDNISONE (AA/P) | |||||
| COU-AA-301 [22,25] | mCRPC post-doc (20.2 m) | 1195 (2:1) | ADT + AA/P vs. PBO/P | 5.6 vs. 3.6 (0.66; 0.58–0.76) | 15.8 vs. 11.2 (0.74; 0.64–0.86) |
| COU-AA-302 [23,24] | mCRPC (22.2 m & 49.2 m) | 1088 (2:1) | ADT + AA/P vs. PBO/P | 16.5 vs. 8.2 (0.53; 0.45–0.62) | 34.7 vs. 30.3 (0.81; 0.70–0.93) |
| ACIS [30] | mCRPC (54.8 m) | 982 (1:1) | ADT + AA/P +/− APA | 24.0 vs. 16.6 (0.70; 0.60–0.83) | 36.2 vs. 33.7 (0·95; 0·81–1·11) |
| LATITUDE [18] | mHSPC (30.4 & 51.8 m) | 1209 (1:1) | ADT + AA/P vs. PBO | NR vs. 34.7 (0.62; 0.51–0.76) | 53.3 vs. 36.5 (0·66; 0.56–0.78) |
| PEACE-1 [16] | mHSPC (36 m/45.6 m) | 710 (1:1) | ADT + DOC +/− AA/P (+/− RT) | 54 vs. 24 (0.50; 0.40–0.62) | NR vs. 52.8 (0.75; 0.59–0.95) |
| STAMPEDE (Arm G) [43] | mHSPC (40 m) | 1917 (1:1) | AA/P vs. PBO | 3-y-FFS = 75% vs. 45% (0.29; 0.25 to 0.34) | 3-y-OS = 83% vs. 76% (0.63; 0.52–0.76) |
| STAMPEDE (Arm G & J) [26] | mHSPC (95.8 m/71.7 m) | 1003 (1:1) | ADT +/− AA/P +/− ENZA | - | ADT + AA/P + ENZA (0.65; 0.55–0.7) ADT + AA/P (0.62; 0.53–0.73) |
| STAMPEDE (Arm G & J) [21] | NM high risk PC (72 m) | 1974 (1:1) | ADT +/− AA +/− ENZA | MFS = 0.53 (0.44–0.64) | 0.60 (0.48–0.73) |
PFS: progression free survival; OS: overall survival; mCRPC: metastatic castration resistance prostate cancer; post-doc: post-docetaxel; ADT: androgen deprivation therapy; NM CRPC: non-metastatic castration resistance prostate cancer; MFS: metastasis free survival; mHSPC: metastatic hormone sensitive prostate cancer; 3-y-PFS: 3 years progression free survival; NR: non reached; PBO: placebo.
4. Molecular Events on Resistance Mechanisms to AR Signaling Pathway Inhibition
Despite the initial response to ADT in the hormone-naïve setting, which usually achieves rapid decline in PSA levels, this therapy does not completely wean tumor cells of androgens because prostate cancer cells can employ alternative routes to generate AR ligands [44]. Additionally, under the selective pressure from hormonal treatment, prostate cancer cells rely on different steroid hormone receptors including the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) [45] and the progesterone receptor (PR) [46]. During the course of ADT/antiandrogen treatment, AR develops amplifications that lead to AR overactivation as well as point mutations causing ligand promiscuity [47]. Other genomic aberrancies involving the AR, but also coregulator complexes, the selection of AR spicing variants (AR-V), intratumoral steroid hormone synthesis, or posttranscriptional AR regulation are well-known events that occur during ADT/antiandrogen treatment, leading to castration resistance and, eventually, disease progression [48]. Understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms driving tumors to castration resistance has revealed the continuous role of AR signaling in metastatic CRPC. Furthermore, it has set the background for the development of novel therapeutic approaches.
4.1. Structural Changes in AR (Figure 1)
4.1.1. Amplification/Overexpression
Amplification of the AR has been found in up to 30% of patients with CPRC, being virtually non-existent in hormone-sensitive disease [49]. Amplification may be due to the selective overgrowth of PC cells [50]. Chen et al. found that the overexpression of AR mRNA in prostate cancer xenograft models was sufficient to explain the transition from a hormone-sensitive to a hormone-refractory stage [51]. Overall, the consequence of AR amplification and/or overexpression is to enhance the PC cells’ sensitivity to low levels of androgens, which leads to disease progression [52].
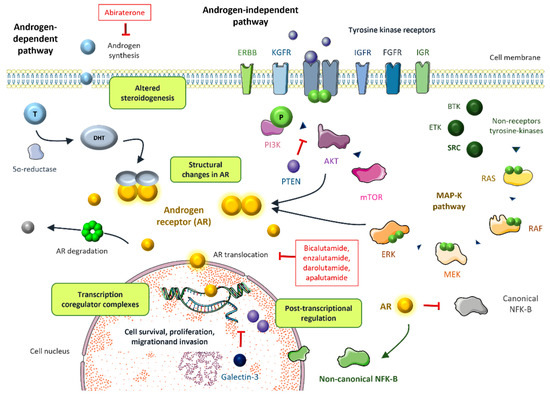
Figure 1.
The most relevant mechanisms of resistance to androgen targeted therapy including androgen-dependent and androgen-independent pathways [6,9,11].
4.1.2. Mutations
Several mutations have been identified within the AR gene, predominantly in the ligand-binding domain (LBD), which occur in 15–20% of CRPC. The same as in AR amplification, rather than conveying constitutive activation, gain of function mutations lead to increased AR activity in the presence of low levels of androgens. Two patients with an AR T877A mutation experienced a drastic fall in PSA levels upon withdrawal of the antiandrogen, suggesting thar this mutation may play a role in antiandrogen withdrawal syndrome [53]. Point mutations have also been associated with resistance to novel hormonal agents. For instance, the AR F876L mutation was found to drive resistance to enzalutamide by conferring an antagonist-to-agonist switch [54]. The double mutation F877L/T878A also converts enzalutamide into an AR agonist. Interestingly, this can be overcome by the action of another next-generation antiandrogen such as darolutamide [55]. Moreover, two recent studies have shown that structural disturbances of AR enhancers may decrease sensitivity to hormonal treatments and precipitate castration resistance. In the first study, Takeda et al. characterized a somatically acquired enhancer of AR expression that is activated in the metastatic setting. They demonstrated that a knock-in of a single additional copy of this enhancer was sufficient to foster proliferation in a low-androgen milieu and confer resistance to enzalutamide. Interestingly, disruption of this enhancer caused decreased proliferation by suppressing AR levels [56]. Viswanathan and colleagues analyzed 23 biopsies and cell-free DNA from 86 patients with mCRPC, finding complex rearrangements of the AR locus in most cases, particularly recurrent tandem duplications of an AR upstream enhancer in up to 70–87% of cases, compared to <2% of primary tumors [57]. Targeting epigenetics could be a therapeutic avenue worth exploring in mCRPC.
4.1.3. AR Splice Variants
AR splice variants (AR-Vs) are truncated forms of the AR protein that lack the C-terminal LBD but still have an intact N-terminal domain and a partial or complete DNA binding domain (DBD). These proteins are constitutively active and can activate AR signaling pathways by activating AR targeted genes without the need for ligands [58]. There have been reports of up to 22 AR-Vs including ARV1, ARV7, ARV 567, and ARV8 [59]. Second-generation AR signaling inhibitors such as abiraterone and enzalutamide [60] are resistant to AR-Vs, either as primary resistance in up to 20–40% of cases or as secondary resistance in almost all ones [61]. This is likely due to the fact that both abiraterone and enzalutamide work by binding to the LBD, which AR-Vs lack. The most well-described AR-V is still AR-V7. In CRPC, a recent meta-analysis revealed that AR-V7-positive is linked to greater ECOG performance, metastatic spread, higher Gleason scores, and worse pain management [62].
AR-Vs are transcription factors that join co-regulators to bind DNA and carry out their downstream genomic activities. HOXB13 and AR-V7 interact to activate target oncogenes. It is interesting to note that suppressing HOXB13 in AR-V7-expressing cells prevents AR-V7 from having an oncogenic effect [63]. It is difficult to attempt to inactivate AR signaling since AR-V7 lacks a ligand-binding domain.
This indicates that RNA splicing is essential for the expression of AR-V7 [59]. The RNA helicase DDX39, which is ATP-dependent, controls the expression of AR-V7 and is involved in RNA splicing. The AR-V7 was downregulated in cells that expressed the AR variant after DDX39 was knocked down [64]. An RNA-binding protein called LIN28 is involved in prostate cancer AR signaling. AR mutations and treatment resistance increase as a result of LIN28 overexpression. However, blocking LIN28 can enhance prostate cancer cells sensitive to antiandrogens [65]. Overexpression of a-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) in prostate cancer has become an immunohistochemical marker.
Dual treatment with docetaxel and an AMARC inhibitor decreased AR-7 expression probably via downregulating HSP27, a cytoprotective chaperone protein that ensures AR stability [66]. In a recent study, castration in mice and prostate cancer cell models led to the activation of NF-KB and the subsequent increase in AR-V7 expression. The NF-KB inhibitor dimethylaminoparthenolide downregulated AR-V7, delaying castration resistance [67]. After depletion of AR-V7, vasopressin 1A receptor (AVPR1A) was found to be the most downregulated gene. Therefore, suppressing APVR1A may decrease cell proliferation [68]. In an AR-V7 enriched environment, there is an overexpression of MAO-A, which results in the alteration of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α signals, contributing to enzalutamide resistance. Targeting MAO-A with antidepressants could restore sensitivity to enzalutamide [69]. As stated by Wang et al. [70], other agents have been identified as AR-V7 inhibitors in CRPC models such as the fatty acid synthase inhibitor IPI-9119, lutelolin, triterpenoid anti-oxidant drugbardoxolone methyl(CDDO-Me), and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist degarelix [71,72,73,74].
Targeting AR-V7 degradation could potentially entail clinical relevance. HSP70 is a shock protein family member that interacts with ubiquitin ligase STUB1. Suppression of HSP70 reverted enzalutamide resistance by decreasing the AR-V7 levels [75]. Xu and colleagues showed that AR-V7 positively regulates E2F1 expression in docetaxel and enzalutamide resistant prostate cancer cells. Auranofin, an FDA-approved drug for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, is known to promote AR protein degradation. Auranofin was able to circumvent castration resistance both in vitro and in vivo by downregulating the E2F1-AR3 axis, setting the molecular rationale for drug development in this context [76]. Antimalarial agent bruceantin inhibits both AR full length (AR-FL) and AR-V7 activity by disrupting the interaction of HSP90 with AR-FL/AR-V7, leading to their degradation by the proteasome [77]. Nobiletin, a polymethoxylated flavonoid, induced proteasomal degradation of AR-V7 in vitro, enhancing the sensitivity of AR-V7 positive cells to enzalutamide [78]. Other agents including BCL2 protein inhibitor ABT263 or AKR1C3 inhibitor indomethacin have shown to increase the proteasome-dependent degradation of AR-V7 [79,80].
4.2. Coregulator Complexes
The transcriptional function of AR is controlled by over 150 co-regulators [81]). These molecules either enhance (co-activators) or suppress (co-repressors) transcriptional activity. They have a variety of roles including RNA splicing, the recruitment of transcriptional machinery or the modulation of other proteins in the transcriptional complex by phosphorylation, methylation, or ubiquitination [82,83]. The increased activity of co-activators and diminished influence of co-repressors facilitate castration resistance.
Co-activator FKBP51 is a Hsp90 cochaperone that has been proven to be upregulated in castrated mice. This leads to the formation of a superchaperone complex that associates with AR, stimulating androgen binding [84]. Interestingly, patients with a high expression of AR-V7 have increased FKBP51 levels [85]. Depletion of either FKBP51 or FKBP52—another AR co-activator—by using specific inhibitors, reduced the AR dimer formation [86,87].
The steroid receptor coactivators (SRC) enhance AR-induced transcription in a hormone-dependent fashion. The SCR family contains three homologous members, SRC1, SRC2, and SRC3, that have been associated with prostate cancer progression [88] (Figure 1). Under the influence of IL-6, SRC1 phosphorylation leads to AR activation [89,90]. Disrupting the interaction between SRC1/2 and the AR inhibits AR activity in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells [91]. Additionally, miR-137 selectively depleted the expression of SRC1, SRC2, and SRC3 in prostate cancer cells, supporting the potential role of epigenetic targeting in prostate cancer [92].
CBP and p300 are paralogous histone acetyltransferase proteins that precipitate AR activation. Perturbation of p300/CBP function decreases AR activity and reduces tumor cell growth in prostate cancer models [93,94]. CCS1477, a new selective inhibitor of the p300/CBP bromodomain, blocks AR and AR-Vs signaling in the cell line, patient-derive xenografts [95], and in serial tumor biopsies from an ongoing phase I clinical trial [96].
Galectin-3 has been proven to enhance AR transcriptional activity, leading to the overexpression of several AR-target genes such as KLK3 and TMPRSS2. This supports the role of galectin-3 as a potential target molecule in CRPC [97].
4.3. Altered Steroidogenesis
Castration resistance develops within a low circulating androgen environment. However, CPRC models show high levels of intra-tumoral androgens. This supports the existence of alternative androgen production involving the adrenal glands but also the prostate cancer cells. Prostate tumor cells overexpress enzymes responsible for androgen synthesis. This allows for the conversion of adrenal precursors such as dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) [98]. In the absence of ADT, testosterone acts an intermediary to transform androstenedione (AD) into DHT. However, in an androgen deprived environment, 5α-dione serves as the intermediary between AD and DHT, hence bypassing testosterone [99] (Figure 1). Interestingly, intracrine steroidogenesis not only occurs within the primary prostate cancer, but also in distant metastases [44]. Abiraterone is an orally active inhibitor of the steroidal enzyme CYP17A1, blocking the synthesis of androgens in the adrenal glands as well as in the tumor. A recent study showed that prostate cancer cell lines exposed to abiraterone accumulate steroidogenesis substrates. These precursors are able to activate AR, independent of CYP17A1-mediated conversion into testosterone, leading to cell growth. Interestingly, the potent AR antagonist RD162 was able to reverse proliferation. This supports the rationale for combining CYP17A1 inhibitors (i.e., abiraterone) with potent antiandrogens to suppress AR activation mediated by steroid substrates [100]. The enzyme 3βHSD1 regulates steroidogenesis and abiraterone metabolism and it may be responsible for resistance to abiraterone and enzalutamide [101]. A gain of function mutation of this enzyme has recently been identified as a negative predictive biomarker for response to novel antiandrogens and as a biomarker of poor prognosis [102,103]. Biochanin A is able to overcome resistance to novel antiandrogens by inhibiting 3βHSD1. Daidzein, a biochanin A analogue, showed meaningful PSA reduction in patients with abiraterone-resistant metastatic CRPC [104].
4.4. Posttranscriptional Regulation
Posttranscriptional regulation of AR through acetylation, phosphorylation, methylation, SUMOylation, and ubiquitination enhances AR signaling, which leads to cell growth and survival [105]. Arrest-defect-1 protein (ARD1) is an acetyltransferase that forms a complex with AR and Hsp90, leading to AR acetylation, resulting in AR nuclear translocation, AR target gene expression, and prostate cancer tumorigenesis [106]. In vitro and in vivo models have shown that ARD1 activates AR, and ARD1 knockdown inhibits the nuclear translocation of AR [107]. AR phosphorylation at serine 81 (S81) is associated with AR re-activation [108], which is sustained by CDK1 and CDK9, supporting the potential role of CDK inhibitors in the castration resistant setting [109]. Recently, a methylation signature revealed that patients with hypermethylation of AR-associated genes had low AR activity and worse prognosis after ADT [110]. SUMOylation refers to the binding of small ubiquitin like modifiers (SUMO) to AR, typically repressing AR transcriptional activity. An imbalance between SUMOylation and deSUMOylation can lead to tumor progression [111]. Finally, AR ubiquitination induced by different ER ubiquitin ligases can modulate the expression of AR target genes [112]. Siah2 and RNF6 enhance the expression of AR target genes by local turnover of AR and the recruitment of AR co-activators, respectively [113,114], and SPOP represses AR target gene expression by promoting the degradation of AR [115] (Figure 1).
4.5. Androgen-Independent Activation
Multiple cytokines, growth factors, and kinase pathways activate AR signaling in a ligand-independent fashion, leading to castration resistance.
The non-receptor tyrosine kinase Src fosters the proliferation of prostate cancer cells through activation of the MAPK cascade. In fact, Src kinase activation is associated with androgen-independent cell growth and tumor invasion [116,117]. Although Src inhibitors have been successful in preclinical models [118], their performance in clinical trials has been disappointing thus far [119]. Other non-receptor tyrosine kinases such as Btk and Etk have been targeted in recent years [120,121] (Figure 1).
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway also plays an important role. Almost all metastatic prostate cancer show loss of PTEN, which is an inhibitor of this cascade. The activation of the downstream effectors of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway leads to castration resistance [122] (Figure 1). Interestingly, this pathway interacts with AR signaling through several reciprocal inhibitory loops [123]. The AKT inhibitor capivasertib, in addition to docetaxel, improved outcomes in a phase II trial with CRPC patients, particularly in patients that had received drugs targeting the androgen receptor [124]. A phase III trial of capivasertib and abiraterone vs. placebo and abiraterone in PTEN deficient mHSPC is ongoing (CAPItello-281, NCT04493853) [125]. As discussed above, the AKT inhibitor ipatasertib in combination with abiraterone seems to improve the survival outcomes in PTEN-loss tumors.
NF-kB is a transcription factor that has been associated with prostate cell survival and tumor proliferation [126]. There is a relevant crosstalk between NF-KB and androgen receptor signaling [127]. The AR blocks canonical NF-kB expression but induces non-canonical NF-kB activation [128] (Figure 1). This could be of major importance in driving androgen independence, since the loss of androgen repression of NF-kB target genes is linked to poor prognosis [129]. Inhibition of NF-kB signaling resensitizes castrate-resistant prostate cancer cells to androgen receptor targeted therapies [130]. Additionally, a key role has recently been identified on cancer stemness in prostate cancer cells related to SOX2/OCT4 expression, and the PI3K/Akt downstream signaling has been associated with playing a role in keeping this pathway. This molecular activation has been related to tumor progression irrespective to AR signaling as well as a potential resistance mechanism to therapy [131,132].
Growth factor pathways such as IGF, KGF, or FGF activate AR in a castrate resistance setting. Several RTKs such as EGFR, IGR, or HER-2 can also enhance AR activity (Figure 1). It is known that MYB overexpression plays an important role in androgen-depletion resistance and prostate cancer aggressiveness [133]. Recently, it has been discovered that there is a close interaction between MYB and the AR. MYB-overexpressing prostate cancer cells retain AR in the nucleus, even in androgen-deprived conditions, leading to enhanced transcriptional activity [134].
5. Novel Agents under Research That to Overcome Those Resistance Mechanisms
5.1. Galeterone
Galeterone is a multitargeted, selective drug that alters androgen signaling in a variety of ways. It works as a powerful AR antagonist and a selective CYP17 inhibitor, inducing an increase in AR protein breakdown and lowering AR expression in prostate cancer cells. Galeterone therapy in prostate cancer models has led to a considerable decrease in the levels of both full-length AR and AR-V7, according to preclinical in vitro and in vivo findings. Galeterone is also effective against AR point mutations T878A, and early findings indicate that it may also successfully target cells with F876L mutations [135]. Galeterone-based Androgen Receptor Modulation Optimized for Response (ARMOR) Phase I and Phase II trials on patients with metastatic and non-metastatic CRPC showed sufficient tolerance and potential efficacy [60].
In the ARMOR1 trial, 49.0% of patients had a 30% drop in PSA and 22.4% had a 50% reduction. These findings led to the development of a phase 3 clinical study (ARMOR3-SV) [136] that focused on the splice variant AR-V7. Patients with mCRPC who exhibited AR-V7 were given the option of receiving enzalutamide 160 mg or galeterone 2550 mg on a random basis. Sadly, the research was stopped after it was determined that its survival endpoints were unlikely to be met.
5.2. ODM-204
ODM-204 is a non-steroidal compound constructed as a potent dual inhibitor of both the CYP17A1 enzyme and AR-mediated signaling at the receptor level [6,9,11]. Following favorable outcomes in xenograft models, phase I–II studies were planned in patients with progressive mCRPC [137]. In the DUALIDES study, escalating doses of ODM-204 together with prednisone were administered orally twice a day. ODM-204 was well-tolerated and preliminary antitumor activity was observed in some patients [137]. Unfortunately, pharmacokinetic difficulties have stalled the development of this molecule.
5.3. ODM-208
Recently, the phase I/II CYPIDES trial explored ODM-208, a CYP11A1 inhibitor able to suppress the synthesis of all steroid hormones and precursors in heavily pretreated patients with an activating AR LBD mutation. ODM-208 showed meaningful PSA reductions and up to four partial responses in 17 evaluable patients [138].
5.4. Proxalutamide (GT-0918)
In contrast to bicalutamide and enzalutamide, proxalutamide is a new non-steroidal AR antagonist that suppresses AR-mediated gene transcription more potently while maintaining quiet antagonism in CRPC cells [139]. Studies have shown that it can downregulate AR protein levels and impede the transcriptional activity of both wild-type and clinically significant mutant ARs. Additionally, it has been discovered to suppress the AR, which suggests that it may be more effective than other second-generation AR antagonists. Currently, this drug is being developed in a phase I multicenter, open-label clinical study for men with progressive mCRPC treated with chemotherapy (docetaxel) and hormone treatment (abiraterone or enzalutamide) (NCT02826772).
5.5. Bipolar Androgen Therapy (BAT)
BAT is an emerging approach to androgen inhibition in the mCRPC setting. As already mentioned, CRPC remains dependent on AR signaling. Preclinical models suggest that supratherapeutic testosterone levels could reduce CRPC growth and promote cell death [140]. BAT aims to disrupt the CRPC cells’ ability to adapt to a low-androgen environment by alternating cycles of high-dose testosterone with cycles of androgen inhibition, resulting in the minimum testosterone levels and cell death. RESTORE is a multicohort phase 2 study that includes patients who have progressed to hormone therapy (including enzalutamide or abiraterone). BAT showed clinical activity by decreasing PSA levels, but did not reach statistical significance [141]. A cohort of this study analyzed results from 29 patients after first hormonal treatment excluding patients receiving second generation antiandrogens. In this setting, BAT resulted in PSA and radiologic responses, both in mCRPC and in non-metastatic CRPC. Response to abiraterone and enzalutamide at progression was favorable [142]. The TRANSFORMER trial [143] recruited men with asymptomatic mCRPC progressing on abiraterone and compared BAT treatment with enzalutamide. The results showed no superiority of BAT compared to enzalutamide in terms of PFS and PSA response. However, BAT improved the magnitude and duration of response to enzalutamide after treatment with abiraterone, suggesting again the presence of a sensitizing effect and a potential role for sequential BAT and enzalutamide as a single therapy.
5.6. Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras (PROTACs)
This is a novel technology targeting the degradation of the AR. PROTACs are molecules that work as a trimeric complex between a target protein and an E3 ubiquitin ligase, enabling target ubiquitination and subsequent degradation [144]. ARCC-4 is one of these AR degraders. It also prevents cell proliferation, even in enzalutamide resistant cells, becoming a potential therapeutic option in these patients. PROTAC-mediated AR degradation can overcome AR resistance mechanisms such as AR amplifications, AR mutations, and intra-tumoral androgen synthesis [145]. The phase I clinical trial of ARV-110 [146], an orally bioavailable PROTAC, included 18 patients that had progressed to at least two previous lines of treatment. Anti-proliferative activity was observed including PSA reduction of ≥50% in two patients. Toxicity was manageable with two patients developing grade 3–4 elevated AST/ALT levels. The expansion cohort of the phase I/II clinical trial has shown promising activity in heavily pretreated mCRPC, particularly in patients with AR T878 and/or H875 mutations [147].
5.7. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
The identification of different mCRPC phenotypes may prove to be clinically relevant. Aside from the agnostic FDA approval of pembrolizumab [148] and dostarlimab for MSI-H or dMMR/TMB-H [149] and for dMMR tumors [150], respectively, there are clinical trials ongoing testing immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in selected patients with mCRPC. In the KEYNOTE-199 trial, pembrolizumab in PD-L1 positive mCRPC previously treated with docetaxel and endocrine therapy showed a disease control rate (DCR) of 10% and a median OS of 9.5 months [151]. Recently, we learned from the phase III clinical trial KEYNOTE-921, that pembrolizumab does not provide a survival benefit when combined with docetaxel versus chemotherapy alone in unselected mCRPC [152]. Hence, it seems that adequate patient selection is key to finding the subset of patients that could potentially benefit from ICIs. In prostate cancer, MSI-H seems to be a more reliable biomarker than TMB. A prospective comparison between ICI vs. taxane-based therapy showed that patients with a TMB ≥10 mutations per Mb achieved better survival outcomes when treated with immunotherapy [153]. Combination schemes with antiandrogens have also been explored. Unfortunately, the phase III trial IMbassador 250 of enzalutamide plus atezolizumab versus enzalutamide alone was stopped early due to futility [154]. The results of the ongoing KEYNOTE 641 trial of enzalutamide plus pembrolizumab [155] are awaited after promising data from the phase II trial [156]. Interestingly, the combination of apalutamide and anti-PD-1 cetrelimab is being evaluated in small cell neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NCTNCT04926181). Thus, biomarker selection and treatment combination will be key in this setting [157].
5.8. PARP Inhibition
PARP inhibitors have recently entered the therapeutic landscape of mCRPC. Olaparib has been approved by regulatory agencies for the treatment of germline or somatic homologous recombination repair (HRR) gene-mutated mCRPC following the results of the phase III PROfound trial [158]. However, a subgroup analysis of this trial showed that for almost all of the HRR mutations other than BRCA, olaparib did not offer a clear benefit. For this reason, the optimal treatment approach in these patients is yet to be elucidated. Additionally, the PARP inhibitor rucaparib has been approved for BRCA-mutated mCRPC based on the results of the TRITON2 trial [159]. Trials exploring the combination of PARP inhibitors with ARSI are currently ongoing. Recently, the PROpel and MAGNITUDE phase III trials exploring the combination of abiraterone with olaparib and niraparib, respectively, proved meaningful rPFS improvement for the experimental arm, along with a trend toward OS in the PROpel study [160,161]. On a similar note, the phase III trial TALAPRO-2 of talazoparib plus enzalutamide versus enzalutamide has achieved its primary endpoint of rPFS [162]. The potential synergy from this combination was assessed in the BRCAAway trial, a phase 2 randomized study in patients with inactivating BRCA1, BRCA2, and/or ATM alterations. The first results presented at the ASCO Congress 2022 showed a significant improvement on the median PFS from the abiraterone acetate and olaparib combination over either agent alone. The possibility to crossover at disease progression will also offer data on sequencing compared with the combination [163].
5.9. PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK Pathway Inhibition
As for the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, preclinical studies in mice have established that loss of PTEN promotes resistance to castration [164], hence upregulating the PI3K pathway. Interestingly, inhibition of the PI3K pathway in PTEN negative prostate cancers activates the AR pathway [165]. Since AR and PI3K seem to compensate each other’s inhibition, simultaneous targeting of AR and PI3K has been the proof-of-concept for developing clinical trials in this setting. The phase III clinical trial IPATential150 randomized unselected mCRPC patients to receive the PI3K inhibitor ipatasertib plus abiraterone and prednisolone or the placebo plus abiraterone and prednisolone. Although the primary endpoint of PFS was not met in the intention-to-treat population, ipatasertib improved PFS in PTEN-loss tumors [166]. The phase III trial Capitello280 in mHSPC is ongoing [167]. As for cell cycle targeting in mCRPC, a phase Ib/II clinical trial with ribociclib and docetaxel in ARSI-pretreated mCRPC, showed a favorable toxicity profile and encouraging results (median rPFS of 8.1 months) [168]. Clinical trials with drugs targeting MAPK downstream proteins (i.e., BRAF/MEK inhibitors) or the WNT pathway (i.e., porcupine inhibitors) are yet to be designed.
5.10. Cell Cycle Pathway Inhibition
Approximately 20% alterations in cell cycle genes have been identified in CRPC with RB1 loss, CCND1 amplification, and other alterations in CDKN2A/B, CDKN1B, and CDK4 as the main genes affected [1]. Preclinical data have demonstrated the ability from abemaciclib to enhance effective senescence in prostate cancer cells expressing AR. These data have also been obtained with AR+ Prostate 22RV1 Xenograft models showing a tumor reduction with abemaciclib treatment [169]. Therefore, clinical trials have been designed and are currently ongoing with CDK4/6 inhibitors in monotherapy [170,171], but also in combination [172,173,174,175,176] in prostate cancer.
5.11. Radionuclides
Different attempts have been reported trying to combine Radium223 with new hormone agents. The most relevant data came from the prospective phase III ERA trial in which the addition of abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone to Radium223 reported an earlier and higher rate of SRE (HR 1.12 [95% CI 0.917–1.374]; p = 0.2636) than with Radium223 monotherapy [177]. Based on this increase in bone fractures and death, some regulatory agencies such as the European Medicines Agency in July 2018 decided to modify the recommendation in the use of Radium223 to patients that had received two previous regimens in the metastatic setting or to patients that were not candidates for other treatments. This restriction raised relevant issues such as the adequate identification of those patients unfit for chemotherapy and/or novel hormone agents, the concern regarding bone health maintenance, the impact of a prolonged use of corticoids, and how to optimize the therapeutic sequences in patients with mCRPC. The key role of bone protective agents has been demonstrated in the PEACE III trial. Gillessen S et al. reported a reduction in the cumulative risk of fracture at 1.5 years to practically zero with the use of those agents at least 6 weeks before the initiation of Radium223, both in the enzalutamide and the combination group compared with the previously reported risk without antiresorptive agents of 22.3% and 45.9%, respectively [178]. The combination of ARSI with radionuclides is improving as in the mHSPC setting, 177LuPSMA-617 is being combined with ARSI in a phase III clinical trial (NCT04689828).
5.12. Continuing AR Blockade upon Progression
As in breast cancer, maintaining hormonal treatment after disease progression is being explored in prostate cancer. The randomized phase II ABIDO trial compared abiraterone plus docetaxel versus docetaxel alone following progression to first line abiraterone. This study was unable to demonstrate a significant clinical benefit of abiraterone maintenance [179]. Surprisingly, the PRESIDE phase III trial, testing enzalutamide in the same clinical setting, did meet its primary endpoint of PFS [180]. It is important to note that the ABIDO trial, but not the PRESIDE study, allowed for the inclusion of patients with primary resistance to ARSI. Additionally, there were some differences between the two trials regarding the consideration of progressive disease to first line ARSI. These factors could, to some extent, explain the different outcomes [181]. Nonetheless, considering the PEACE-1 trial results, the population depicted in the PRESIDE study will not be representative of clinical practice in the near future (Table 2).

Table 2.
Ongoing trials for emerging drugs in prostate cancer.
6. Discussion
Metastatic prostate cancer treatment is initially based on androgen inhibition to reach undetectable testosterone levels. However, recent findings highlight the continuous role of androgen receptor signaling in disease progression in up to 70% of patients whose tumor show different AR aberrations [1]. Indeed, even though patients reach the castration resistance stage, androgen inhibition is still effective with novel antiandrogens that have come in the field such as abiraterone acetate, apalutamide, enzalutamide, or darolutamide [11]. Moreover, other pathways are also involved in this tumor progression such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway activation in 30–40% of patients, DDR gene alterations in 20–30% of patients, cell cycle alterations in 20% of patients, or the Wnt signaling pathway in 18% of patients [1]. Thus, key questions arise as to whether to sequence with a different therapeutic strategy, but with which treatment or combination strategy. This is an important question as prostate cancer has entered the precision medicine era, so current research is moving forward to overcome the primary or acquired resistance mechanisms involved in prostate cancer to allow physicians to improve the strength of their clinical decisions. Multiple drugs are showing activity in metastatic prostate cancer, but the main question remains on how to sequence them in each patient.
As AR signaling plays a key role along the disease of prostate cancer and ARSI has dramatically modified the natural history of this disease in different clinical settings, AR aberrations are still an essential target to inhibit during the continuum of care in prostate cancer.
7. Conclusions
Novel drugs with potential activity in patients harboring tumors whose AR-related alterations are resistant to current ARSI, but can be targetable with these new agents, offer an exceptional opportunity to continue with androgen inhibition and, hopefully, survival contribution to patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Alone or in combination with effective therapies will require further answers as research in this field is rapidly increasing.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.A.-G. and J.P.; Methodology, J.P., S.Á.R. and J.M.-C.; Software, J.P.; Validation, J.P. and S.Á.R.; Formal analysis, V.A.F. and T.A.-G.; Investigation, J.P.; Resources, S.Á.R.; Data curation, J.P. and V.A.F.; Writing—original draft preparation, J.P., S.Á.R., J.M.-C. and J.B.; Writing—review and editing, V.A.F., T.A.-G., M.S. and R.M.K.; Visualization, V.A.F.; Supervision, J.M.-C. and T.A.-G.; Project administration, J.P., J.B. and T.A.-G.; Funding acquisition, Not applicable. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
S.A.R. has received research funding, honoraria, and non-financial or other support from Bayer, Janssen, and Astellas; V.A.F declares no conflicts of interest; J.B. has received research funding, honoraria, and non-financial or other support from Bayer, Janssen and Astellas; R.M.K declares a consulting or advisory role from IPSEN, Pfizer, Jannsen, Astellas, Sanofi, Novartis, MSD, BMS. JMC declares consultant, advisory, or speaker roles for IPSEN, Roche, Pfizer, Sanofi, Janssen, and BMS. JMC has received research grants from Pfizer, IPSEN and Roche; T.A.G. has received research funding, honoraria, and non-financial or other support from Lilly, IPSEN, Adacap, Pfizer, Sanofi, EISAI, Bayer, Janssen, BMS, Astellas, Novartis, and Roche. The rest of authors declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Robinson, D.; Van Allen, E.M.; Wu, Y.-M.; Schultz, N.; Lonigro, R.J.; Mosquera, J.-M.; Montgomery, B.; Taplin, M.-E.; Pritchard, C.C.; Attard, G.; et al. Integrative clinical genomics of advanced prostate cancer. Cell 2015, 161, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Bohl, C.E.; Dalton, J.T. Chemistry and Structural Biology of Androgen Receptor. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 3352–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.-P.; Yamashita, S.; Huang, C.-K.; Yeh, S.; Chang, C. Loss of stromal androgen receptor leads to suppressed prostate tumourigenesis via modulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines/chemokines. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 791–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.D. The role of 5alpha-reduction in steroid hormone physiology. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2001, 13, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Myers, M.; Brown, M. Formation of the androgen receptor transcription complex. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.H.E.; Li, J.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K.; Yong, E. Androgen receptor: Structure, role in prostate cancer and drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alen, P.; Claessens, F.; Verhoeven, G.; Rombauts, W.; Peeters, B. The androgen receptor amino-terminal domain plays a key role in p160 coactivator-stimulated gene transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 6085–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Nonomura, N. Role of Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer: A Review. World J. Mens Health 2019, 37, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culig, Z.; Santer, F.R. Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014, 33, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggins, C.; Hodges, C.V. Studies on prostatic cancer. I. The effect of castration, of estrogen and androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 1972, 22, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonergan, P.E.; Tindall, D.J. Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer development and progression. J. Carcinog. 2011, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dessel, L.F.; van Riet, J.; Smits, M.; Zhu, Y.; Hamberg, P.; van der Heijden, M.S.; Bergman, A.M.; van Oort, I.M.; de Wit, R.; Voest, E.E.; et al. The genomic landscape of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancers reveals multiple distinct genotypes with potential clinical impact. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez Rodríguez, S.; Alonso Gordoa, T.; Burgos Revilla, F.J. Current status of androgen deprivation therapy in hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. Arch. Esp. Urol. 2018, 71, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scher, H.I.; Morris, M.J.; Stadler, W.M.; Higano, C.; Basch, E.; Fizazi, K.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Beer, T.M.; Carducci, M.A.; Chi, K.N.; et al. Trial Design and Objectives for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Updated Recommendations from the Prostate Cancer Clinical Trials Working Group 3. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1402–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, K.N.; Chowdhury, S.; Bjartell, A.; Chung, B.H.; Pereira de Santana Gomes, A.J.; Given, R.; Juárez, A.; Merseburger, A.S.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Uemura, H.; et al. Apalutamide in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer: Final Survival Analysis of the Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III TITAN Study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2294–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizazi, K.; Foulon, S.; Carles, J.; Roubaud, G.; McDermott, R.; Fléchon, A.; Tombal, B.; Supiot, S.; Berthold, D.; Ronchin, P.; et al. Abiraterone plus prednisone added to androgen deprivation therapy and docetaxel in de novo metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (PEACE-1): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study with a 2 × 2 factorial design. Lancet 2022, 399, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R.; Hussain, M.; Saad, F.; Fizazi, K.; Sternberg, C.N.; Crawford, E.D.; Kopyltsov, E.; Park, C.H.; Alekseev, B.; Montesa-Pino, Á.; et al. Darolutamide and Survival in Metastatic, Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizazi, K.; Tran, N.; Fein, L.; Matsubara, N.; Rodriguez-Antolin, A.; Alekseev, B.Y.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ye, D.; Feyerabend, S.; Protheroe, A.; et al. Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone in patients with newly diagnosed high-risk metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (LATITUDE): Final overall survival analysis of a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.J.; Szmulewitz, R.Z.; Petrylak, D.P.; Holzbeierlein, J.; Villers, A.; Azad, A.; Alcaraz, A.; Alekseev, B.; Iguchi, T.; Shore, N.D.; et al. ARCHES: A Randomized, Phase III Study of Androgen Deprivation Therapy with Enzalutamide or Placebo in Men with Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2974–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, I.D.; Martin, A.J.; Stockler, M.R.; Begbie, S.; Chi, K.N.; Chowdhury, S.; Coskinas, X.; Frydenberg, M.; Hague, W.E.; Horvath, L.G.; et al. Enzalutamide with Standard First-Line Therapy in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, G.; Murphy, L.; Clarke, N.W.; Cross, W.; Jones, R.J.; Parker, C.C.; Gillessen, S.; Cook, A.; Brawley, C.; Amos, C.L.; et al. Abiraterone acetate and prednisolone with or without enzalutamide for high-risk non-metastatic prostate cancer: A meta-analysis of primary results from two randomised controlled phase 3 trials of the STAMPEDE platform protocol. Lancet 2022, 399, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bono, J.S.; Logothetis, C.J.; Molina, A.; Fizazi, K.; North, S.; Chu, L.; Chi, K.N.; Jones, R.J.; Goodman, O.B.; Saad, F.; et al. Abiraterone and Increased Survival in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, C.J.; Smith, M.R.; de Bono, J.S.; Molina, A.; Logothetis, C.J.; de Souza, P.; Fizazi, K.; Mainwaring, P.; Piulats, J.M.; Ng, S.; et al. Abiraterone in metastatic prostate cancer without previous chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, C.J.; Smith, M.R.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Mulders, P.F.A.; Sternberg, C.N.; Miller, K.; Logothetis, C.J.; Shore, N.D.; Small, E.J.; et al. Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone versus placebo plus prednisone in chemotherapy-naive men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (COU-AA-302): Final overall survival analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fizazi, K.; Scher, H.I.; Molina, A.; Logothetis, C.J.; Chi, K.N.; Jones, R.J.; Staffurth, J.N.; North, S.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Saad, F.; et al. Abiraterone acetate for treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Final overall survival analysis of the COU-AA-301 randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, G.; Murphy, L.R.; Clarke, N.W.; Cross, W.R.; Gillessen, S.; Amos, C.L.; Brawley, C.D.; Jones, R.J.; Pezaro, C.; Malik, Z.; et al. LBA62—Comparison of abiraterone acetate and prednisolone (AAP) or combination enzalutamide (ENZ) + AAP for metastatic hormone sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC) starting androgen deprivation therapy (ADT): Overall survival (OS) results of 2 randomised phase III trials from the STAMPEDE protocol. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S808–S869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R.; Saad, F.; Chowdhury, S.; Oudard, S.; Hadaschik, B.A.; Graff, J.N.; Olmos, D.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Lee, J.Y.; Uemura, H.; et al. Apalutamide Treatment and Metastasis-free Survival in Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R.; Saad, F.; Chowdhury, S.; Oudard, S.; Hadaschik, B.A.; Graff, J.N.; Olmos, D.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Lee, J.Y.; Uemura, H.; et al. Apalutamide and Overall Survival in Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.N.; Agarwal, N.; Bjartell, A.; Chung, B.H.; Pereira de Santana Gomes, A.J.; Given, R.; Juárez Soto, Á.; Merseburger, A.S.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Uemura, H.; et al. Apalutamide for Metastatic, Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, F.; Efstathiou, E.; Attard, G.; Flaig, T.W.; Franke, F.; Goodman, O.B.; Oudard, S.; Steuber, T.; Suzuki, H.; Wu, D.; et al. Apalutamide plus abiraterone acetate and prednisone versus placebo plus abiraterone and prednisone in metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer (ACIS): A randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multinational, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1541–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moilanen, A.-M.; Riikonen, R.; Oksala, R.; Ravanti, L.; Aho, E.; Wohlfahrt, G.; Nykänen, P.S.; Törmäkangas, O.P.; Palvimo, J.J.; Kallio, P.J. Discovery of ODM-201, a new-generation androgen receptor inhibitor targeting resistance mechanisms to androgen signaling-directed prostate cancer therapies. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fizazi, K.; Massard, C.; Bono, P.; Jones, R.; Kataja, V.; James, N.; Garcia, J.A.; Protheroe, A.; Tammela, T.L.; Elliott, T.; et al. Activity and safety of ODM-201 in patients with progressive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (ARADES): An open-label phase 1 dose-escalation and randomised phase 2 dose expansion trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fizazi, K.; Shore, N.; Tammela, T.L.; Ulys, A.; Vjaters, E.; Polyakov, S.; Jievaltas, M.; Luz, M.; Alekseev, B.; Kuss, I.; et al. Darolutamide in Nonmetastatic, Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadal, R.; Bellmunt, J. The evolving role of enzalutamide on the treatment of prostate cancer. Future Oncol. 2016, 12, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, H.I.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Taplin, M.-E.; Sternberg, C.N.; Miller, K.; de Wit, R.; Mulders, P.; Chi, K.N.; Shore, N.D.; et al. Increased Survival with Enzalutamide in Prostate Cancer after Chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, T.M.; Armstrong, A.J.; Rathkopf, D.E.; Loriot, Y.; Sternberg, C.N.; Higano, C.S.; Iversen, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Carles, J.; Chowdhury, S.; et al. Enzalutamide in Metastatic Prostate Cancer before Chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.N.; Baciarello, G.; Armstrong, A.J.; Higano, C.S.; Iversen, P.; Flaig, T.W.; Forer, D.; Parli, T.; Phung, D.; Tombal, B.; et al. Efficacy and safety of enzalutamide in patients 75 years or older with chemotherapy-naive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Results from PREVAIL. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2016, 27, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Rathenborg, P.; Shore, N.; Ferreira, U.; Ivashchenko, P.; Demirhan, E.; Modelska, K.; Phung, D.; et al. Enzalutamide in Men with Nonmetastatic, Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.J.; Azad, A.A.; Iguchi, T.; Szmulewitz, R.Z.; Petrylak, D.P.; Holzbeierlein, J.; Villers, A.; Alcaraz, A.; Alekseev, B.; Shore, N.D.; et al. Improved Survival with Enzalutamide in Patients with Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, C.J.; Martin, A.J.; Stockler, M.R.; Begbie, S.; Chi, K.N.; Chowdhury, S.; Coskinas, X.; Frydenberg, M.; Hague, W.E.; Horvath, L.G.; et al. Overall Survival of Men with Metachronous Metastatic Hormone-sensitive Prostate Cancer Treated with Enzalutamide and Androgen Deprivation Therapy. Eur. Urol. 2021, 80, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loriot, Y.; Fizazi, K.; de Bono, J.S.; Forer, D.; Hirmand, M.; Scher, H.I. Enzalutamide in castration-resistant prostate cancer patients with visceral disease in the liver and/or lung: Outcomes from the randomized controlled phase 3 AFFIRM trial. Cancer 2017, 123, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternberg, C.N.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Shore, N.D.; De Giorgi, U.; Penson, D.F.; Ferreira, U.; Efstathiou, E.; Madziarska, K.; Kolinsky, M.P.; et al. Enzalutamide and Survival in Nonmetastatic, Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, N.D.; de Bono, J.S.; Spears, M.R.; Clarke, N.W.; Mason, M.D.; Dearnaley, D.P.; Ritchie, A.W.S.; Amos, C.L.; Gilson, C.; Jones, R.J.; et al. Abiraterone for Prostate Cancer Not Previously Treated with Hormone Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, R.B.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Vessella, R.; Hess, D.L.; Kalhorn, T.F.; Higano, C.S.; True, L.D.; Nelson, P.S. Maintenance of Intratumoral Androgens in Metastatic Prostate Cancer: A Mechanism for Castration-Resistant Tumor Growth. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4447–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, V.K.; Schenkein, E.; Murali, R.; Subudhi, S.K.; Wongvipat, J.; Balbas, M.D.; Shah, N.; Cai, L.; Efstathiou, E.; Logothetis, C.; et al. Glucocorticoid receptor confers resistance to antiandrogens by bypassing androgen receptor blockade. Cell 2013, 155, 1309–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grindstad, T.; Andersen, S.; Al-Saad, S.; Donnem, T.; Kiselev, Y.; Nordahl Melbø-Jørgensen, C.; Skjefstad, K.; Busund, L.-T.; Bremnes, R.M.; Richardsen, E. High Progesterone Receptor Expression in Prostate Cancer Is Associated with Clinical Failure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Visakorpi, T.; Hyytinen, E.; Koivisto, P.; Tanner, M.; Keinänen, R.; Palmberg, C.; Palotie, A.; Tammela, T.; Isola, J.; Kallioniemi, O.P. In vivo amplification of the androgen receptor gene and progression of human prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 1995, 9, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.P.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Nelson, P.S.; Montgomery, B. Androgen deprivation therapy: Progress in understanding mechanisms of resistance and optimizing androgen depletion. Nat. Clin. Pract. Urol. 2009, 6, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linja, M.J.; Savinainen, K.J.; Saramäki, O.R.; Tammela, T.L.; Vessella, R.L.; Visakorpi, T. Amplification and overexpression of androgen receptor gene in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3550–3555. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekar, T.; Yang, J.C.; Gao, A.C.; Evans, C.P. Mechanisms of resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.D.; Welsbie, D.S.; Tran, C.; Baek, S.H.; Chen, R.; Vessella, R.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Sawyers, C.L. Molecular determinants of resistance to antiandrogen therapy. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, C.W.; Johnson, R.T.; Mohler, J.L.; French, F.S.; Wilson, E.M. Androgen receptor stabilization in recurrent prostate cancer is associated with hypersensitivity to low androgen. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2892–2898. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, H.; Akakura, K.; Komiya, A.; Aida, S.; Akimoto, S.; Shimazaki, J. Codon 877 mutation in the androgen receptor gene in advanced prostate cancer: Relation to antiandrogen withdrawal syndrome. Prostate 1996, 29, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpal, M.; Korn, J.M.; Gao, X.; Rakiec, D.P.; Ruddy, D.A.; Doshi, S.; Yuan, J.; Kovats, S.G.; Kim, S.; Cooke, V.G.; et al. An F876L Mutation in Androgen Receptor Confers Genetic and Phenotypic Resistance to MDV3100 (Enzalutamide). Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgmann, H.; Lallous, N.; Ozistanbullu, D.; Beraldi, E.; Paul, N.; Dalal, K.; Fazli, L.; Haferkamp, A.; Lejeune, P.; Cherkasov, A.; et al. Moving Towards Precision Urologic Oncology: Targeting Enzalutamide-resistant Prostate Cancer and Mutated Forms of the Androgen Receptor Using the Novel Inhibitor Darolutamide (ODM-201). Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, D.Y.; Spisák, S.; Seo, J.-H.; Bell, C.; O’Connor, E.; Korthauer, K.; Ribli, D.; Csabai, I.; Solymosi, N.; Szállási, Z.; et al. A Somatically Acquired Enhancer of the Androgen Receptor Is a Noncoding Driver in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cell 2018, 174, 422–432.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.R.; Ha, G.; Hoff, A.M.; Wala, J.A.; Carrot-Zhang, J.; Whelan, C.W.; Haradhvala, N.J.; Freeman, S.S.; Reed, S.C.; Rhoades, J.; et al. Structural alterations driving castration-resistant prostate cancer revealed by linked-read genome sequencing. Cell 2018, 174, 433–447.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehm, S.M.; Schmidt, L.J.; Heemers, H.V.; Vessella, R.L.; Tindall, D.J. Splicing of a novel androgen receptor exon generates a constitutively active androgen receptor that mediates prostate cancer therapy resistance. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5469–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Brown, L.C.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Armstrong, A.J.; Luo, J. Androgen receptor variant-driven prostate cancer II: Advances in laboratory investigations. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2020, 23, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, E.; Bastos, D. Galeterone for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer: The evidence to date. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 2289–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, F.; Sterpi, M.; Buckley, C.; Margetich, L.; Handa, S.; Dovey, Z. A Review of the Pathophysiological Mechanisms Underlying Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Res. Rep. Urol. 2021, 13, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yi, J.; Shen, H.; Yang, Z.; Yan, L.; Xie, L. Clinicopathological characteristics of androgen receptor splicing variant 7 (AR-V7) expression in patients with castration resistant prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, D.; Thomas-Ahner, J.M.; Lu, C.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Q.; Geraghty, C.; Yan, P.S.; Hankey, W.; Sunkel, B.; et al. Diverse AR-V7 cistromes in castration-resistant prostate cancer are governed by HoxB13. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6810–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, D.; Nakao, S.; Nakayama, K.; Araki, S.; Nakayama, Y.; Aparicio, S.; Hara, T.; Nakanishi, A. The RNA helicase DDX39B and its paralog DDX39A regulate androgen receptor splice variant AR-V7 generation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tummala, R.; Nadiminty, N.; Lou, W.; Evans, C.P.; Gao, A.C. Lin28 induces resistance to anti-androgens via promotion of AR splice variant generation. Prostate 2016, 76, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, A.; Takahara, K.; Saruta, M.; Zennami, K.; Nukaya, T.; Fukaya, K.; Ichino, M.; Fukami, N.; Niimi, A.; Sasaki, H.; et al. Combined α-methylacyl-CoA racemase inhibition and docetaxel treatment reduce cell proliferation and decrease expression of heat shock protein 27 in androgen receptor-variant-7-positive prostate cancer cells. Prostate Int. 2021, 9, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, K.L.; Hamid, A.A.; Clohessy, J.G.; Pandell, N.; Ellis, L.; Sweeney, C.J. NF-κB Blockade with Oral Administration of Dimethylaminoparthenolide (DMAPT), Delays Prostate Cancer Resistance to Androgen Receptor (AR) Inhibition and Inhibits AR Variants. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2021, 19, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Peacock, S.O.; Lo, C.H.; Heidman, L.M.; Rice, M.A.; Fahrenholtz, C.D.; Greene, A.M.; Magani, F.; Copello, V.A.; Martinez, M.J.; et al. Arginine vasopressin receptor 1a is a therapeutic target for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Luo, J.; Yeh, S.; You, B.; Meng, J.; Chang, P.; Niu, Y.; Li, G.; Lu, C.; Zhu, Y.; et al. The MAO inhibitors phenelzine and clorgyline revert enzalutamide resistance in castration resistant prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Ding, W.; Gao, S.; Gao, Y.; Xu, C. Mechanisms of enzalutamide resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer and therapeutic strategies to overcome it. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucchiara, V.; Yang, J.C.; Liu, C.; Adomat, H.H.; Tomlinson Guns, E.S.; Gleave, M.E.; Gao, A.C.; Evans, C.P. GnRH Antagonists Have Direct Inhibitory Effects on Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Via Intracrine Androgen and AR-V7 Expression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, N.; Chandra, P.K.; Kim, H.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Mondal, D.; Sikka, S.C. Bardoxolone-Methyl (CDDO-Me) Suppresses Androgen Receptor and Its Splice-Variant AR-V7 and Enhances Efficacy of Enzalutamide in Prostate Cancer Cells. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naiki-Ito, A.; Naiki, T.; Kato, H.; Iida, K.; Etani, T.; Nagayasu, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Inaguma, S.; Onishi, M.; et al. Recruitment of miR-8080 by luteolin inhibits androgen receptor splice variant 7 expression in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadra, G.; Ribeiro, C.F.; Chetta, P.; Ho, Y.; Cacciatore, S.; Gao, X.; Syamala, S.; Bango, C.; Photopoulos, C.; Huang, Y.; et al. Inhibition of de novo lipogenesis targets androgen receptor signaling in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Lou, W.; Yang, J.C.; Liu, L.; Armstrong, C.M.; Lombard, A.P.; Zhao, R.; Noel, O.D.V.; Tepper, C.G.; Chen, H.-W.; et al. Proteostasis by STUB1/HSP70 complex controls sensitivity to androgen receptor targeted therapy in advanced prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, X.; Deshmukh, D.; Chen, H.; Fang, S.; Qiu, Y. The Role of Crosstalk between AR3 and E2F1 in Drug Resistance in Prostate Cancer Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.J.; Jeong, B.C.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, J.E.; Kim, H.-J.; Kwon, G.Y.; Jackman, J.A.; Kim, J.H. Bruceantin targets HSP90 to overcome resistance to hormone therapy in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Theranostics 2021, 11, 958–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, C.; Shao, Z.; Xia, X.; Hu, T.; Kong, W.; He, X.; Sun, W.; Deng, Y.; Liao, Y.; et al. Selective degradation of AR-V7 to overcome castration resistance of prostate cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Sun, Y.; Huang, C.-P.; You, B.; Ye, D.; Chang, C. Preclinical Study Using ABT263 to Increase Enzalutamide Sensitivity to Suppress Prostate Cancer Progression Via Targeting BCL2/ROS/USP26 Axis Through Altering ARv7 Protein Degradation. Cancers 2020, 12, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, J.C.; Armstrong, C.M.; Lou, W.; Liu, L.; Qiu, X.; Zou, B.; Lombard, A.P.; D’Abronzo, L.S.; Evans, C.P.; et al. AKR1C3 Promotes AR-V7 Protein Stabilization and Confers Resistance to AR-Targeted Therapies in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1875–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heemers, H.V.; Tindall, D.J. Androgen receptor (AR) coregulators: A diversity of functions converging on and regulating the AR transcriptional complex. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 778–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, I.M.; Heitzer, M.D.; Grubisha, M.; DeFranco, D.B. Coactivators and nuclear receptor transactivation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 104, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culig, Z. Androgen Receptor Coactivators in Regulation of Growth and Differentiation in Prostate Cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Yang, C.-S.; Gioeli, D.; Frierson, H.; Toft, D.O.; Paschal, B.M. FKBP51 promotes assembly of the Hsp90 chaperone complex and regulates androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Sun, L.; Hao, T.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, S.; Quan, C.; Niu, Y.; et al. Restoration of FKBP51 protein promotes the progression of castration resistant prostate cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Habara, M.; Kawaguchi, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Hanaki, S.; Masaki, T.; Sato, Y.; Matsuyama, H.; Kunieda, K.; Nakagawa, H.; et al. FKBP51 and FKBP52 regulate androgen receptor dimerization and proliferation in prostate cancer cells. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 940–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, D.; He, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Lu, J.; Gui, H.; Wang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Rapamycin inhibits AR signaling pathway in prostate cancer by interacting with the FK1 domain of FKBP51. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2020, 23, 100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, R.-C.; O’Malley, B.W. Normal and cancer-related functions of the p160 steroid receptor co-activator (SRC) family. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, T.; Mawji, N.R.; Bruchovsky, N.; Sadar, M.D. Ligand-independent activation of the androgen receptor by interleukin-6 and the role of steroid receptor coactivator-1 in prostate cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 38087–38094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Ju, Q.; Ding, Z.; Ge, X.; Shi, Q.-M.; Zhou, J.-L.; Zhou, X.-L.; Zhang, J.-P.; Zhang, M.-R.; et al. The co-regulators SRC-1 and SMRT are involved in interleukin-6-induced androgen receptor activation. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2016, 27, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakka, M.; Agoulnik, I.U.; Weigel, N.L. Targeted disruption of the p160 coactivator interface of androgen receptor (AR) selectively inhibits AR activity in both androgen-dependent and castration-resistant AR-expressing prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eedunuri, V.K.; Rajapakshe, K.; Fiskus, W.; Geng, C.; Chew, S.A.; Foley, C.; Shah, S.S.; Shou, J.; Mohamed, J.S.; Coarfa, C.; et al. miR-137 Targets p160 Steroid Receptor Coactivators SRC1, SRC2, and SRC3 and Inhibits Cell Proliferation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 1170–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, M.; Ferrone, L.; Puhr, M.; Santer, F.R.; Furlan, T.; Eder, I.E.; Sampson, N.; Schäfer, G.; Handle, F.; Culig, Z. p300 is upregulated by docetaxel and is a target in chemoresistant prostate cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2020, 27, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Garcia, J.; Chan, E.; de la Cruz, C.; Segal, E.; Merchant, M.; Kharbanda, S.; Raisner, R.; Haverty, P.M.; Modrusan, Z.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting of the CBP/p300 Bromodomain Blocks the Growth of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5564–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welti, J.; Sharp, A.; Brooks, N.; Yuan, W.; McNair, C.; Chand, S.N.; Pal, A.; Figueiredo, I.; Riisnaes, R.; Gurel, B.; et al. Targeting the p300/CBP Axis in Lethal Prostate Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1118–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CellCentric Ltd. An Open-Label Phase I/IIa Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of CCS1477 as Monotherapy and in Combination, in Patients with Advanced Solid/Metastatic Tumours. Report No.: NCT03568656. June 2022. clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03568656 (accessed on 22 September 2022).
- Dondoo, T.-O.; Fukumori, T.; Daizumoto, K.; Fukawa, T.; Kohzuki, M.; Kowada, M.; Kusuhara, Y.; Mori, H.; Nakatsuji, H.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Galectin-3 Is Implicated in Tumor Progression and Resistance to Anti-androgen Drug Through Regulation of Androgen Receptor Signaling in Prostate Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Titus, M.A.; Gregory, C.W.; Ford, O.H.; Schell, M.J.; Maygarden, S.J.; Mohler, J.L. Steroid 5alpha-reductase isozymes I and II in recurrent prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 4365–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-H.; Li, R.; Papari-Zareei, M.; Watumull, L.; Zhao, Y.D.; Auchus, R.J.; Sharifi, N. Dihydrotestosterone synthesis bypasses testosterone to drive castration-resistant prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13728–13733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, J.M.; Kumagai, J.; van Royen, M.E.; Teubel, W.J.; van Soest, R.J.; French, P.J.; Homma, Y.; Jenster, G.; de Wit, R.; van Weerden, W.M. A bypass mechanism of abiraterone-resistant prostate cancer: Accumulating CYP17A1 substrates activate androgen receptor signaling. Prostate 2019, 79, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Huang, S.; Li, Z. Androgens in prostate cancer: A tale that never ends. Cancer Lett. 2021, 516, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, D.J.; Aragón, I.M.; Annala, M.; Lozano, R.; Taavitsainen, S.; Lorente, D.; Finch, D.L.; Romero-Laorden, N.; Vergidis, J.; Cendón, Y.; et al. HSD3B1 (1245A>C) germline variant and clinical outcomes in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients treated with abiraterone and enzalutamide: Results from two prospective studies. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Terbuch, A.; Dolling, D.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Fountain, J.; Bertan, C.; Sharp, A.; Carreira, S.; et al. Treatment with abiraterone and enzalutamide does not overcome poor outcome from metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer in men with the germline homozygous HSD3B1 c.1245C genotype. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hou, Z.; Zhuang, Q.; He, D.; Zhang, X.; Tan, Q.; Zhu, X.; et al. Management of prostate cancer by targeting 3βHSD1 after enzalutamide and abiraterone treatment. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffey, K.; Robson, C.N. Regulation of the androgen receptor by post-translational modifications. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 215, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePaolo, J.S.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Zhang, G.; Qian, C.; Zhang, H.; Zabaleta, J.; Liu, W. Acetylation of androgen receptor by ARD1 promotes dissociation from HSP90 complex and prostate tumorigenesis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 71417–71428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhns, K.J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W. ARD1/NAA10 acetylation in prostate cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, J.W.; Liu, X.; Ye, H.; Calagua, C.; Chen, S.; Voznesensky, O.; Condulis, J.; Ma, F.; Taplin, M.-E.; Einstein, D.J.; et al. Phosphorylation of androgen receptor serine 81 is associated with its reactivation in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 438, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, P.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Ma, F.; Calagua, C.; Ye, H.; et al. Phosphorylation of the androgen receptor at Ser81 is co-sustained by CDK1 and CDK9 and leads to AR-mediated transactivation in prostate cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1901–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylitalo, E.B.; Thysell, E.; Landfors, M.; Brattsand, M.; Jernberg, E.; Crnalic, S.; Widmark, A.; Hultdin, M.; Bergh, A.; Degerman, S.; et al. A novel DNA methylation signature is associated with androgen receptor activity and patient prognosis in bone metastatic prostate cancer. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, W. Roles of Ubiquitination and SUMOylation on Prostate Cancer: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 4560–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Fan, L.; Hussain, A. Ubiquitin Ligases in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2015, 27, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Tripathi, M.; Mishra, R.; Sahgal, N.; Fazli, L.; Fazil, L.; Ettinger, S.; Placzek, W.J.; Claps, G.; Chung, L.W.K.; et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase Siah2 contributes to castration-resistant prostate cancer by regulation of androgen receptor transcriptional activity. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Shimelis, H.; Linn, D.E.; Jiang, R.; Yang, X.; Sun, F.; Guo, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; et al. Regulation of androgen receptor transcriptional activity and specificity by RNF6-induced ubiquitination. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Rajapakshe, K.; Shah, S.S.; Shou, J.; Eedunuri, V.K.; Foley, C.; Fiskus, W.; Rajendran, M.; Chew, S.A.; Zimmermann, M.; et al. Androgen receptor is the key transcriptional mediator of the tumor suppressor SPOP in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5631–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Yao, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Bourne, P.A.; Quinn, A.M.; di Sant’Agnese, P.A.; Reeder, J.E. Differential Expression of Interleukin-8 and Its Receptors in the Neuroendocrine and Non-Neuroendocrine Compartments of Prostate Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Recchia, I.; Rucci, N.; Festuccia, C.; Bologna, M.; MacKay, A.R.; Migliaccio, S.; Longo, M.; Susa, M.; Fabbro, D.; Teti, A. Pyrrolopyrimidine c-Src inhibitors reduce growth, adhesion, motility and invasion of prostate cancer cells in vitro. Eur. J. Cancer 2003, 39, 1927–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-M.; Bai, L.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.C.; Kung, H.-J.; Evans, C.P. Src family kinase oncogenic potential and pathways in prostate cancer as revealed by AZD0530. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6365–6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, J.C.; Trudel, G.C.; Saad, F.; Armstrong, A.J.; Yu, E.Y.; Bellmunt, J.; Wilding, G.; McCaffrey, J.; Serrano, S.V.; Matveev, V.B.; et al. Docetaxel and dasatinib or placebo in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (READY): A randomised, double-blind phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, R.; Bhardwaj, G.; Yang, J.C.; Changou, C.; Ma, A.-H.; Mazloom, A.; Chintapalli, S.; Xiao, K.; Xiao, W.; et al. Targeting Btk/Etk of prostate cancer cells by a novel dual inhibitor. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Ling, L.; Qi, L.; Chong, Y.; Xue, L. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Inhibitor (Ibrutinib)-Suppressed Migration and Invasion of Prostate Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 4113–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toren, P.; Zoubeidi, A. Targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway in prostate cancer: Challenges and opportunities (review). Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorning, B.Y.; Dass, M.S.; Smalley, M.J.; Pearson, H.B. The PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway and Prostate Cancer: At the Crossroads of AR, MAPK, and WNT Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabb, S.J.; Griffiths, G.; Dunkley, D.; Downs, N.; Ellis, M.; Radford, M.; Light, M.; Northey, J.; Whitehead, A.; Wilding, S.; et al. Overall Survival Update for Patients with Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer Treated with Capivasertib and Docetaxel in the Phase 2 ProCAID Clinical Trial. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Phase III Trial of Capivasertib and Abiraterone versus Placebo and Abiraterone in Patients with De Novo Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer Characterized by PTEN Deficiency (CAPItello-281).|Journal of Clinical Oncology. Available online: https://ascopubs.org/doi/abs/10.1200/JCO.2021.39.6_suppl.TPS178 (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Garg, R.; Blando, J.; Perez, C.J.; Wang, H.; Benavides, F.J.; Kazanietz, M.G. Activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) in prostate cancer is mediated by protein kinase C epsilon (PKCepsilon). J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 37570–37582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staal, J.; Beyaert, R. Inflammation and NF-κB Signaling in Prostate Cancer: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Cells 2018, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, L.; Saad, F.; Le Page, C.; Diallo, J.-S.; Péant, B.; Delvoye, N.; Mes-Masson, A.-M. NF-kappaB2 processing and p52 nuclear accumulation after androgenic stimulation of LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Cell. Signal. 2007, 19, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, V.M.; Baltziskueta, E.; Bengoa-Vergniory, N.; Gorroño-Etxebarria, I.; Wesołowski, R.; Waxman, J.; Kypta, R.M. A screen for transcription factor targets of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 highlights an inverse correlation of NFκB and Androgen Receptor Signaling in Prostate Cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8173–8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Yamashita, H.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Franco, O.E.; Wang, Y.; Hayward, S.W.; Matusik, R.J. Inhibition of NF-kappa B signaling restores responsiveness of castrate-resistant prostate cancer cells to anti-androgen treatment by decreasing androgen receptor-variant expression. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3700–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaddi, P.K.; Stamnes, M.A.; Cao, H.; Chen, S. Elimination of SOX2/OCT4-Associated Prostate Cancer Stem Cells Blocks Tumor Development and Enhances Therapeutic Response. Cancers 2019, 11, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, D.; Senbanjo, L.; Majumdar, S.; Franklin, R.B.; Chellaiah, M.A. Androgen receptor expression reduces stemness characteristics of prostate cancer cells (PC3) by repression of CD44 and SOX2. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 120, 2413–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, S.; Arora, S.; McClellan, S.; Grizzle, W.E.; Reed, E.; Singh, A.P. Myb overexpression overrides androgen depletion–induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells, and confers aggressive malignant traits: Potential role in castration resistance. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Khan, M.A.; Anand, S.; Zubair, H.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Patel, G.K.; Singh, S.; Andrews, J.; Wang, B.; Carter, J.E.; et al. MYB interacts with androgen receptor, sustains its ligand-independent activation and promotes castration resistance in prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Nakouzi, N.; Wang, C.; Jacoby, D.; Gleave, M.E.; Zoubeidi, A. Abstract C89: Galeterone suppresses castration-resistant and enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer growth in vitro. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, C89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; De Bono, J.S.; Ferrante, K.J.; Horgan, K.; Luo, J.; Saad, F.; Taplin, M.-E. Randomized, open-label, multicenter, controlled study of galeterone vs enzalutamide in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) expressing AR-V7 splice variant (ARMOR3-SV). J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, TPS5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltola, K.J.; Bono, P.; Jones, R.H.; Vjaters, E.; Nykänen, P.; Vuorela, A.; Oksala, R.; Pohjanjousi, P.; Mustonen, M.V.J.; Fizazi, K.; et al. ODM-204, a Novel Dual Inhibitor of CYP17A1 and Androgen Receptor: Early Results from Phase I Dose Escalation in Men with Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus 2020, 6, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizazi, K.; Cook, N.; Barthélémy, P.; Bernard-Tessier, A.; Baldini, C.; Peters, N.; Nykänen, P.; Ikonen, T.; Pohjanjousi, P.; Mattila, L.; et al. Phase 1 results of the ODM-208 first-in-human phase 1-2 trial in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CYPIDES). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Yan, H.; Gao, X.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Q.; Hou, J.; Ren, S.; et al. Preclinical profile and phase I clinical trial of a novel androgen receptor antagonist GT0918 in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 134, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmeade, S.R.; Isaacs, J.T. Bipolar androgen therapy: The rationale for rapid cycling of supraphysiologic androgen/ablation in men with castration resistant prostate cancer. Prostate 2010, 70, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowski, M.C.; Wang, H.; Sullivan, R.; Rifkind, I.; Sinibaldi, V.; Schweizer, M.T.; Teply, B.A.; Ngomba, N.; Fu, W.; Carducci, M.A.; et al. A Multicohort Open-label Phase II Trial of Bipolar Androgen Therapy in Men with Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer (RESTORE): A Comparison of Post-abiraterone Versus Post-enzalutamide Cohorts. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, L.A.; Wang, H.; Lim ScM, S.J.; Rifkind, I.; Ngomba, N.; Isaacs, J.T.; Luo, J.; Pratz, C.; Sinibaldi, V.; Carducci, M.A.; et al. Bipolar androgen therapy sensitizes castration-resistant prostate cancer to subsequent androgen receptor ablative therapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 144, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmeade, S.R.; Wang, H.; Agarwal, N.; Smith, D.C.; Schweizer, M.T.; Stein, M.N.; Assikis, V.; Twardowski, P.W.; Flaig, T.W.; Szmulewitz, R.Z.; et al. TRANSFORMER: A Randomized Phase II Study Comparing Bipolar Androgen Therapy Versus Enzalutamide in Asymptomatic Men with Castration-Resistant Metastatic Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neklesa, T.K.; Winkler, J.D.; Crews, C.M. Targeted protein degradation by PROTACs. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 174, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salami, J.; Alabi, S.; Willard, R.R.; Vitale, N.J.; Wang, J.; Dong, H.; Jin, M.; McDonnell, D.P.; Crew, A.P.; Neklesa, T.K.; et al. Androgen receptor degradation by the proteolysis-targeting chimera ARCC-4 outperforms enzalutamide in cellular models of prostate cancer drug resistance. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrylak, D.P.; Gao, X.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Garfield, M.H.; Taylor, I.; Dougan Moore, M.; Peck, R.A.; Burris, H.A. First-in-human phase I study of ARV-110, an androgen receptor (AR) PROTAC degrader in patients (pts) with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) following enzalutamide (ENZ) and/or abiraterone (ABI). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Burris, H.A., III; Vuky, J.; Dreicer, R.; Sartor, A.O.; Sternberg, C.N.; Percent, I.J.; Hussain, M.H.A.; Rezazadeh Kalebasty, A.; Shen, J.; et al. Phase 1/2 study of ARV-110, an androgen receptor (AR) PROTAC degrader, in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannantuono, G.M.; Torino, F.; Rosenfeld, R.; Guerriero, S.; Carlucci, M.; Sganga, S.; Capotondi, B.; Riondino, S.; Roselli, M. The Role of Histology-Agnostic Drugs in the Treatment of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pembrolizumab FDA Approval and Genomic Testing in Cancer—NCI. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/news-events/cancer-currents-blog/2020/fda-pembrolizumab-tmb-approval-genomic-testing (accessed on 28 August 2022).
- Research C for DE and. FDA Grants Accelerated Approval to Dostarlimab-Gxly for dMMR Advanced Solid Tumors. FDA. 2 January 2022. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-dostarlimab-gxly-dmmr-advanced-solid-tumors (accessed on 28 August 2022).
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Piulats, J.M.; Gross-Goupil, M.; Goh, J.; Ojamaa, K.; Hoimes, C.J.; Vaishampayan, U.; Berger, R.; Sezer, A.; Alanko, T.; et al. Pembrolizumab for Treatment-Refractory Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Multicohort, Open-Label Phase II KEYNOTE-199 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merck Provides Update on Phase 3 KEYNOTE-921 Trial Evaluating KEYTRUDA® (Pembrolizumab) Plus Chemotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Available online: https://www.merck.com/news/merck-provides-update-on-phase-3-keynote-921-trial-evaluating-keytruda-pembrolizumab-plus-chemotherapy-in-patients-with-metastatic-castration-resistant-prostate-cancer/ (accessed on 28 August 2022).
- Graf, R.P.; Fisher, V.; Weberpals, J.; Gjoerup, O.; Tierno, M.B.; Huang, R.S.P.; Sayegh, N.; Lin, D.I.; Raskina, K.; Schrock, A.B.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors vs Chemotherapy by Tumor Mutational Burden in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e225394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMbassador250: A Phase III Trial Comparing Atezolizumab with Enzalutamide vs Enzalutamide Alone in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC). Available online: https://www.abstractsonline.com/pp8/#!/9045/presentation/10596 (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Graff, J.N.; Liang, L.W.; Kim, J.; Stenzl, A. KEYNOTE-641: A Phase III study of pembrolizumab plus enzalutamide for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Future Oncol. 2021, 17, 3017–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.N.; Beer, T.M.; Alumkal, J.J.; Slottke, R.E.; Redmond, W.L.; Thomas, G.V.; Thompson, R.F.; Wood, M.A.; Koguchi, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. A phase II single-arm study of pembrolizumab with enzalutamide in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer progressing on enzalutamide alone. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebuzzi, S.E.; Rescigno, P.; Catalano, F.; Mollica, V.; Vogl, U.M.; Marandino, L.; Massari, F.; Pereira Mestre, R.; Zanardi, E.; Signori, A.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Advanced Prostate Cancer: Current Data and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bono, J.; Mateo, J.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Shore, N.; Sandhu, S.; Chi, K.N.; Sartor, O.; Agarwal, N.; Olmos, D.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abida, W.; Patnaik, A.; Campbell, D.; Shapiro, J.; Bryce, A.H.; McDermott, R.; Sautois, B.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Bambury, R.M.; Voog, E.; et al. Rucaparib in Men with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Harboring a BRCA1 or BRCA2 Gene Alteration. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3763–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, F.; Armstrong, A.J.; Thiery-Vuillemin, A.; Oya, M.; Shore, N.D.; Procopio, G.; Arslan, C.; Mehra, N.; Parnis, F.; Brown, E.; et al. 1357O Biomarker analysis and updated results from the Phase III PROpel trial of abiraterone (abi) and olaparib (ola) vs. abi and placebo (pbo) as first-line (1L) therapy for patients (pts) with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.N.; Rathkopf, D.E.; Smith, M.R.; Efstathiou, E.; Attard, G.; Olmos, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Small, E.J.; Gomes, A.J.; Roubaud, G.; et al. Phase 3 MAGNITUDE study: First results of niraparib (NIRA) with abiraterone acetate and prednisone (AAP) as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) with and without homologous recombination repair (HRR) gene alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfizer Announces Positive Topline Results from Phase 3 TALAPRO-2 Trial|Pfizer. Available online: https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/pfizer-announces-positive-topline-results-phase-3-talapro-2 (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Hussain, M.H.A.; Kocherginsky, M.; Agarwal, N.; Zhang, J.; Adra, N.; Paller, C.J.; Picus, J.; Reichert, Z.R.; Szmulewitz, R.Z.; Tagawa, S.T.; et al. BRCAAWAY: A randomized phase 2 trial of abiraterone, olaparib, or abiraterone + olaparib in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) with DNA repair defects. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Wang, S.; Qiao, R.; Vivanco, I.; Watson, P.A.; Sawyers, C.L.; Wu, H. Murine cell lines derived from Pten null prostate cancer show the critical role of PTEN in hormone refractory prostate cancer development. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6083–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, B.S.; Chapinski, C.; Wongvipat, J.; Hieronymus, H.; Chen, Y.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Arora, V.K.; Le, C.; Koutcher, J.; Scher, H.; et al. Reciprocal feedback regulation of PI3K and androgen receptor signaling in PTEN-deficient prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, C.; Bracarda, S.; Sternberg, C.N.; Chi, K.N.; Olmos, D.; Sandhu, S.; Massard, C.; Matsubara, N.; Alekseev, B.; Parnis, F.; et al. Ipatasertib plus abiraterone and prednisolone in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (IPATential150): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AstraZeneca. A Phase III Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Study Assessing the Efficacy and Safety of Capivasertib + Docetaxel Versus Placebo + Docetaxel as Treatment for Patients with Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC). clinicaltrials.gov. Report No.: NCT05348577. October 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05348577 (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- De Kouchkovsky, I.; Rao, A.; Carneiro, B.A.; Zhang, L.; Lewis, C.; Phone, A.; Small, E.J.; Friedlander, T.; Fong, L.; Paris, P.L.; et al. A Phase Ib/II Study of the CDK4/6 Inhibitor Ribociclib in Combination with Docetaxel plus Prednisone in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Guzmán, R.; Baquero, C.; Ganado, M.P.; Marugán, C.; Bian, H.; Zeng, Y.; Rama, R.; Du, J.; Lallena, M.J. Abstract 4850: Targeting prostate cancer with the CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitor abemaciclib. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eli Lilly and Company. CYCLONE 1: A Phase 2 Study of Abemaciclib in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Pa-tients Previously Treated with a Novel Hormonal Agent and Taxane-based Chemotherapy. clinicaltrials.gov. Report No.: NCT04408924. June 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04408924 (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Canadian Cancer Trials Group. A Phase II Study of Palbociclib, A CDK4/6 Inhibitor, in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. clinicaltrials.gov. Report No.: NCT02905318. January 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02905318 (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Pfizer. A Phase 1 Dose Escalation and Expansion Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetic, Pharmacody-Namic, and Anti-Tumor Activity of PF-07248144 in Participants with Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors. clinical-trials.gov. Report No.: NCT04606446. October 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04606446 (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Eli Lilly and Company. A Phase 2/3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of Abiraterone Acetate Plus Prednisone with or without Abemaciclib in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Report No.: NCT03706365. clinicaltri-als.gov. October 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03706365 (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Eli Lilly and Company. CYCLONE 3: A Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of Abemaciclib in Combination with Abiraterone Plus Prednisone in Men with High-Risk Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. Report No.: NCT05288166. clinicaltrials.gov. October 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05288166 (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Koshkin, V.S. Phase I/II Study of CDK4/6 Inhibition with Abemaciclib to Upregulate PSMA Expression Prior to 177Lu-PSMA-617 Treatment in Patients with Metastatic Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC) Previously Treated with Novel Hormonal Agents and Chemotherapy. Report No.: NCT05113537. clinicaltrials.gov. September 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05113537 (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Zeng, H. Phase Ib/II Clinical Study of TQB3616 Capsules in Combination with Abiraterone Acetate Plus Prednisone in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Report No.: NCT05156450. clinicaltrials.gov. December 2021. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05156450 (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Smith, M.; Parker, C.; Saad, F.; Miller, K.; Tombal, B.; Ng, Q.S.; Boegemann, M.; Matveev, V.; Piulats, J.M.; Zucca, L.E.; et al. Addition of radium-223 to abiraterone acetate and prednisone or prednisolone in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer and bone metastases (ERA 223): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillessen, S.; Choudhury, A.; Rodriguez-Vida, A.; Nole, F.; Gallardo Diaz, E.; Roumeguere, T.A.; Daugaard, G.; Loriot, Y.; Saad, F.; McDermott, R.S.; et al. Decreased fracture rate by mandating bone protecting agents in the EORTC 1333/PEACEIII trial combining Ra223 with enzalutamide versus enzalutamide alone: An updated safety analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent Duran, M.A.; Font, A.; Duran, I.; Puente, J.; Castellano, D.; Sáez, M.I.; Mendez Vidal, M.J.J.; Santander, C.; Arranz Arija, J.A.; Gonzalez del Alba, A.; et al. Randomized phase II study of docetaxel (D) + abiraterone acetate (AA) versus D after disease progression to first-line AA in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC): ABIDO-SOGUG Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merseburger, A.S.; Attard, G.; Åström, L.; Matveev, V.B.; Bracarda, S.; Esen, A.; Feyerabend, S.; Senkus, E.; Piqueras, M.L.-B.; Boysen, G.; et al. Continuous enzalutamide after progression of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with docetaxel (PRESIDE): An international, randomised, phase 3b study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1398–1408. Available online: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanonc/article/PIIS1470-2045(22)00560-5/fulltext (accessed on 21 October 2022). [CrossRef]
- Shiota, M. Continuing enzalutamide with docetaxel in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1345–1347. Available online: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanonc/article/PIIS1470-2045(22)00614-3/fulltext (accessed on 26 October 2022). [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).