Inhibition of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Protects against the Development of Oxaliplatin-Induced Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome in Wild-Type but Not in CD39-Null Mice
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In-Vivo Model of Oxaliplatin-Induced Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome
2.2. Processing of Liver Specimen: Histological Assessment of SOS, Liver Regeneration and Quantitative PCR
2.3. Plasma Analysis of Parameters of Liver Damage and Other Analytes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
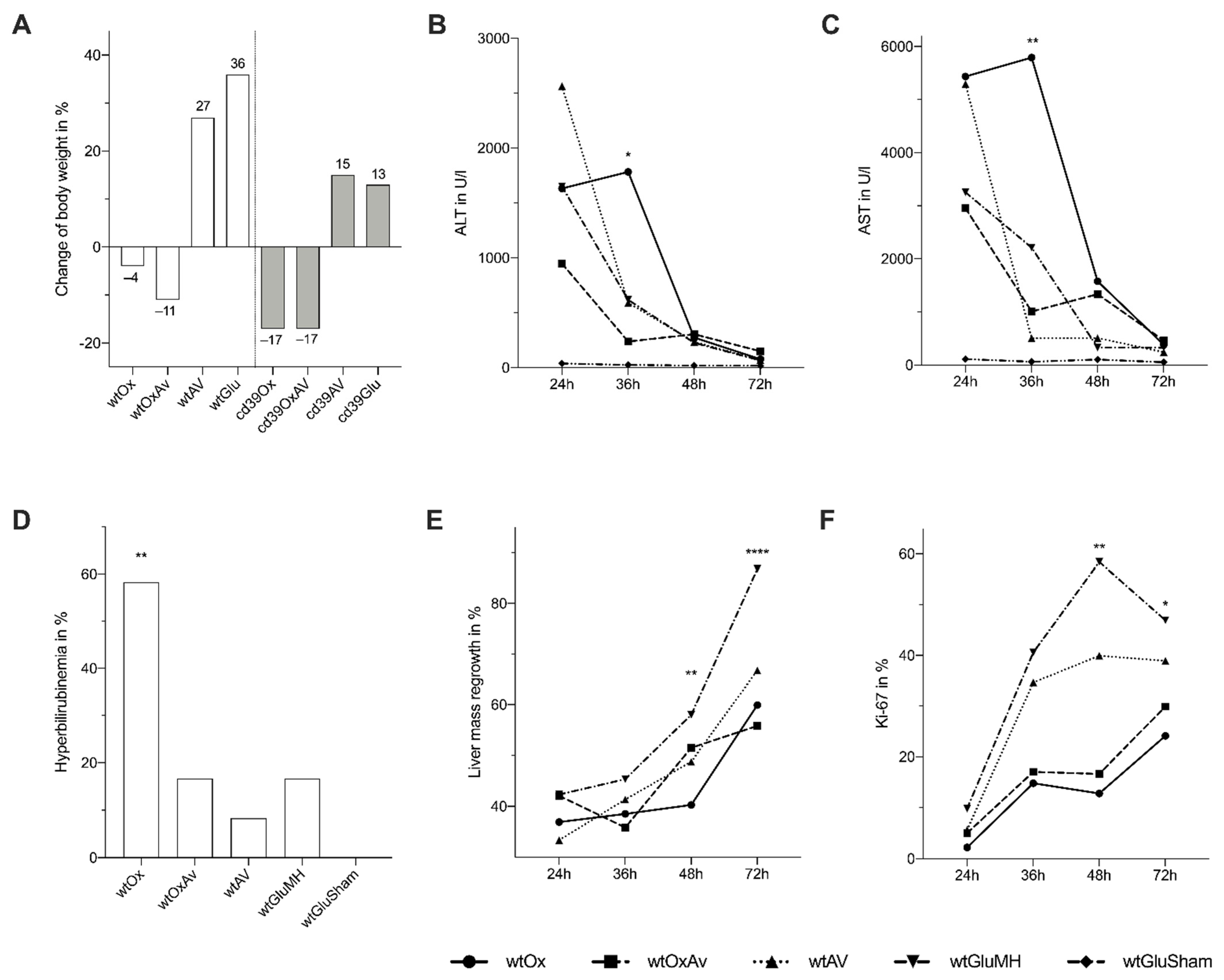
3.1. Establishment of a New Murine Model of Oxaliplatin-Induced SOS and the Effect of VEGF-Inhibition on the Development of SOS
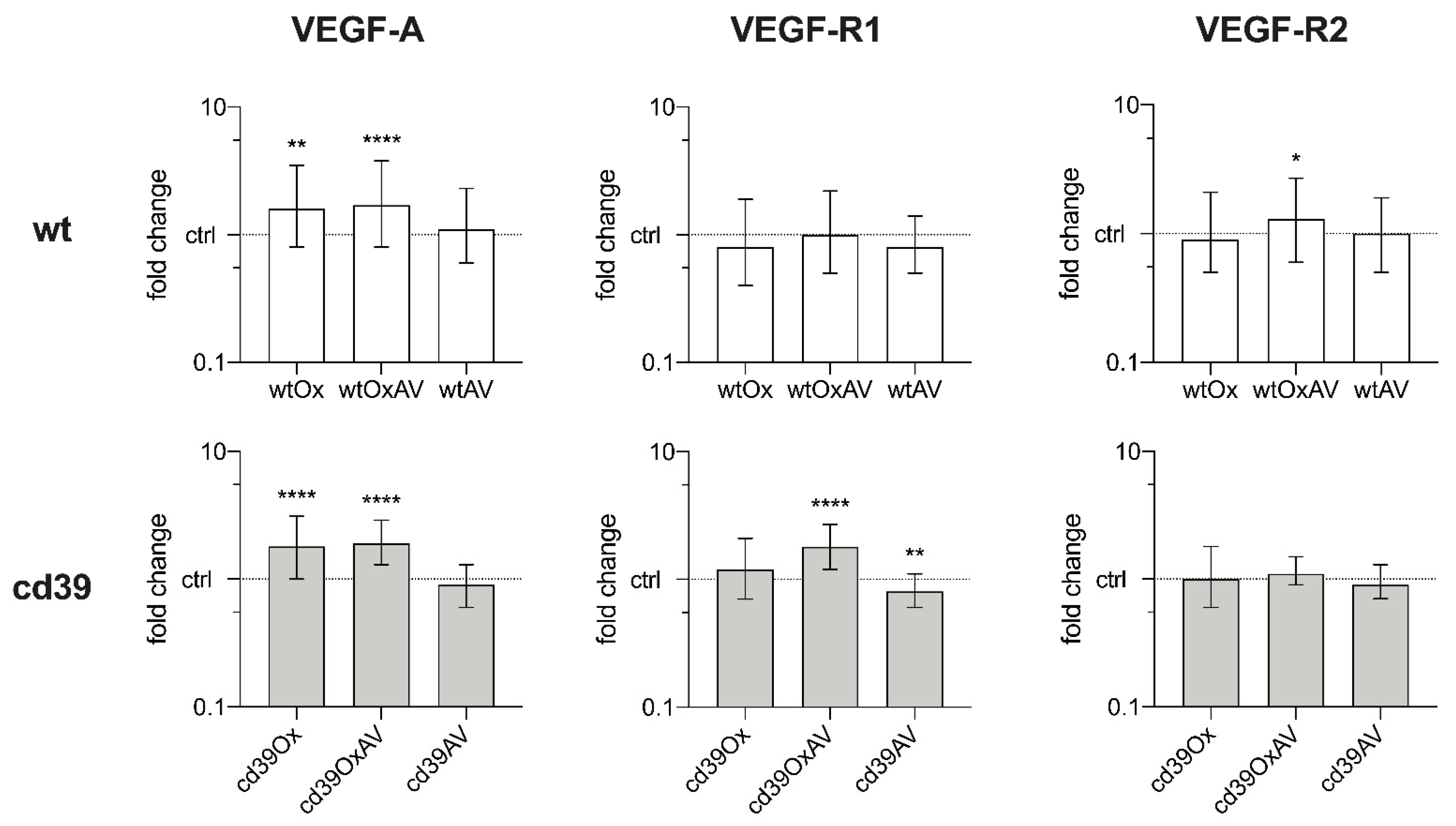
3.2. Pathogenesis of SOS: Quantitative PCR of Liver Tissue and Blood Plasma Analysis
3.3. Impact of SOS on Liver Damage and Liver Regeneration after Major Partial Hepatectomy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Administration of Chemotherapy, Major Partial Hepatectomy and Postoperative Care
Appendix B. Processing of Specimen Including Histology, Liver Regeneration, Quantitative PCR, and Plasma Analysis
Appendix C. Detailed Results of Quantitative PCR Analysis
| Groups | Cycle Threshold Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| VEGF-A | VEGF-R1 | VEGF-R2 | |
| wtOx | 23.41, 22.58, 22.47, 23.14, 22.52, 22.98, 23.12, 23.62, 22.09, 23.15, 22.89, 22.81, 22.83, 22.72, 21.48, 22.84, 22.91, 22.93, 22.65, 23.03, 22.32, 23.26, 22.59, 22.64, 23.64, 22.46, 21.3, 22.38, 22.33, 22.66, 23.43, 22.9, 22.25, 22.91, 22.44, 22.33, 22.46, 22.41, 22.84, 21.89 | 28.7, 27.05, 26.75, 27.21, 27.18, 27.97, 27.47, 29.01, 27.84, 27.88, 27.62, 27.18, 27.14, 28.32, 26.63, 27.21, 26.69, 26.64, 26.41, 26.97, 26.49, 27.09, 26.97, 26.39, 28.17, 26.69, 26.6, 26.51, 25.87, 27.29, 27.54, 27.28, 26.45, 27.57, 27.1, 27.36, 28.03, 26.36, 27.23, 26.06 | 25.68, 24.54, 24.69, 24.88, 24.73, 24.65, 25.59, 26.2, 24.31, 24.96, 24.89, 24.95, 24.71, 25.21, 24.65, 24.85, 24.55, 24.94, 24.3, 24.84, 24.83, 25.06, 25.23, 24.42, 26.02, 24.9, 26.45, 24.44, 23.92, 24.73, 25.17, 24.57, 24.13, 24.83, 24.83, 25, 25.09, 24.18, 24.86, 24.01 |
| wtOxAV | 23.03, 24.83, 24.42, 22.74, 22.08, 22.2, 23.27, 23.79, 23.39, 23.37, 23.68, 23.17, 23.61, 22.8, 23.7, 22.27, 22.72, 23.58, 22.59, 23.07, 22.69, 23.37, 22.73, 23.1, 22.5, 22.94, 23.43, 21.89, 22.47, 22.69, 22.78, 21.72, 22.84, 22.96, 22.78, 22.85, 22.76, 22.66 | 28.24, 29.08, 30.11, 27.95, 26.19, 27.63, 27.34, 28.71, 27.12, 27.14, 27.61, 27.74, 27.83, 26.81, 26.96, 24.78, 26.04, 27.03, 26.94, 27.51, 28.15, 27.55, 27.28, 27.98, 26.67, 27.35, 28.45, 26.97, 27.17, 27.4, 26.96, 25.29, 27.83, 27.73, 27.35, 27.58, 26.94, 26.94 | 25.52, 26.62, 27.02, 24.6, 24.41, 25.11, 24.69, 26.03, 24.86, 25.42, 25.14, 25.01, 24.98, 24.32, 24.87, 24.76, 23.71, 24.51, 23.68, 25, 24.69, 25.01, 24.93, 25.11, 24.21, 25.16, 25.88, 24.34, 24.53, 24.41, 24.29, 23.54, 24.87, 24.8, 24.38, 24.98, 24.05, 23.95 |
| wtAV | 23.9, 23.41, 24.2, 23.64, 22.77, 23.49, 23.44, 23.85, 23.92, 23.67, 23.55, 23.73 | 26.79, 27.77, 27.39, 27.35, 27.45, 27.49, 27.28, 27.9, 28.26, 27.4, 27.01, 27.86 | 24.61, 25.45, 25.39, 25.15, 24.41, 25.69, 25, 25.29, 25.47, 25.25, 25.12, 25.42 |
| wtGlu | 23.78, 24.35, 24.73, 23.61, 23.82, 23.23, 23.79, 23.56, 23.3, 23.33, 24.38, 23.16 | 27.47, 28, 28.07, 27.74, 28.04, 26.69, 26.85, 26.8, 26.01, 26.92, 27.72, 26.37 | 24.59, 25.83, 25.79, 25.33, 24.76, 24.92, 24.91, 24.56, 24.66, 24.71, 25.56, 24.27 |
| cd39Ox | 22.15, 22.06, 22.95, 22.99, 22.91, 23.49, 22.85, 22.36, 22.48, 23.96, 22.68, 22.61, 21.96, 21.73, 22.11, 22.03, 21.79, 22.33, 21.44, 21.97, 23.29, 21.07, 22.33, 21.34 | 26.15, 26.73, 27.58, 27.76, 29.48, 28.74, 26.96, 26.35, 26.31, 27.91, 26.64, 27.45, 26.65, 26.64, 26.99, 27.33, 26.59, 27.41, 26.18, 26.81, 28.3, 27.02, 28.07, 26.39 | 24.57, 24.9, 25.05, 25.07, 26.99, 25.54, 24.96, 24.6, 24.33, 24.92, 24.27, 24.87, 23.98, 24.09, 24.68, 24.57, 24.48, 24.62, 24.2, 25.93, 26.03, 25.88, 25.36, 25.27 |
| cd39OxAV | 21.25, 20.53, 21.83, 21.05, 20.98, 21.56, 22.73, 21.94, 22.02, 22.28, 22.95, 21.49 | 25.47, 24.86, 25.85, 25.53, 25.26, 25.92, 26.78, 26.34, 26.24, 26.55, 28.26, 26.44 | 23.96, 23.32, 23.95, 23.45, 23.75, 24.4, 25.22, 24.9, 24.13, 25.07, 26.04, 24.56 |
| cd39AV | 22.27, 23.77, 22.92, 23.43, 22.37, 22.88, 22.82, 23.21, 24.67, 21.87, 22.99, 23.51 | 26.34, 27.64, 27.45, 27.56, 26.35, 26.71, 26.55, 27.95, 29.82, 26.64, 27.94, 28.84 | 23.92, 25.56, 24.96, 24.69, 23.61, 24.02, 23.94, 25.07, 27.38, 23.92, 25.14, 26.22 |
| cd39Glu | 23, 23.03, 23.37, 23.99, 23.78, 24.01, 23.68, 22.75, 22.91, 23.25, 23.44, 23.32, 22.81, 24, 22.47, 22.98, 21.99, 22.15, 22.77, 22.27, 22.94, 22.94 | 26.91, 26.9, 27.46, 28.03, 28.24, 27.83, 27.64, 26.76, 26.98, 27.83, 27.91, 27.79, 27.41, 27.87, 26.74, 27.23, 26.41, 27.25, 27.44, 26.88, 27.14, 27.34 | 24.33, 24.44, 25.38, 25.94, 26.61, 25.36, 25.35, 24.22, 24.49, 25.43, 25.21, 24.82, 24.5, 25.31, 23.91, 24.89, 23.95, 24.95, 25.17, 24.22, 24.89, 25.02 |
Appendix D. Detailed Results of Magnetic Bead-Based Blood Plasma Analysis
References
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Sobrero, A.; van Krieken, J.H.; Aderka, D.; Aguilar, E.A.; Bardelli, A.; Benson, A.; Bodoky, G.; et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1386–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Audard, V.; Sartoretti, P.; Roth, A.D.; Brezault, C.; Le Charpentier, M.; Dousset, B.; Morel, P.; Soubrane, O.; Chaussade, S.; et al. Severe hepatic sinusoidal obstruction associated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.M.; Wilson, C.H.; Burt, A.; Manas, D.M.; White, S.A. Chemotherapy-Associated Liver Injury in Patients with Colorectal Liver Metastases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 4287–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duwe, G.; Knitter, S.; Pesthy, S.; Beierle, A.S.; Bahra, M.; Schmelzle, M.; Schmuck, R.B.; Lohneis, P.; Raschzok, N.; Öllinger, R.; et al. Hepatotoxicity following systemic therapy for colorectal liver metastases and the impact of chemotherapy-associated liver injury on outcomes after curative liver resection. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 43, 1668–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloia, T.; Sebagh, M.; Plasse, M.; Karam, V.; Lévi, F.; Giacchetti, S.; Azoulay, D.; Bismuth, H.; Castaing, D.; Adam, R. Liver Histology and Surgical Outcomes After Preoperative Chemotherapy with Fluorouracil Plus Oxaliplatin in Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4983–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, H.; Oussoultzoglou, E.; Rosso, E.; Casnedi, S.; Chenard-Neu, M.-P.; Dufour, P.; Bachellier, P.; Jaeck, D. Sinusoidal Injury Increases Morbidity after Major Hepatectomy in Patients with Colorectal Liver Metastases Receiving Preoperative Chemotherapy. Ann. Surg. 2008, 247, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karoui, M.; Penna, C.; Amin-Hashem, M.; Mitry, E.; Benoist, S.; Franc, B.; Rougier, P.; Nordlinger, B. Influence of Preoperative Chemotherapy on the Risk of Major Hepatectomy for Colorectal Liver Metastases. Ann. Surg. 2006, 243, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, S.; Antoine, B.; Stéphane, Z.; Benoît, T.; Catherine, B.; Vincent, M.; François, G.; Olivier, S. Predicting high grade lesions of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome related to oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for colorectal liver metastases: Correlation with post-hepatectomy outcome. Ann. Surg. 2010, 251, 454–460. [Google Scholar]
- Tamandl, D.; Klinger, M.; Eipeldauer, S.; Herberger, B.; Kaczirek, K.; Gruenberger, B.; Gruenberger, T. Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome Impairs Long-Term Outcome of Colorectal Liver Metastases Treated with Resection after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 18, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreuls, C.P.; Van Den Broek, M.A.; Winstanley, A.; Koek, G.H.; Wisse, E.; Dejong, C.H.; Damink, S.W.M.O.; Bosman, F.T.; Driessen, A. Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS) reduces the effect of oxaliplatin in colorectal liver metastases. Histopathology 2012, 61, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Tauzin, S.; Brezault, C.; Delucinge-Vivier, C.; Descombes, P.; Dousset, B.; Majno, P.E.; Mentha, G.; Terris, B. Gene expression profiling provides insights into pathways of oxaliplatin-related sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in humans. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostini, J.; Benoist, S.; Seman, M.; Julié, C.; Imbeaud, S.; Letourneur, F.; Cagnard, N.; Rougier, P.; Brouquet, A.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; et al. Identification of molecular pathways involved in oxaliplatin-associated sinusoidal dilatation. J. Hepatol. 2011, 56, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribero, D.; Wang, H.; Donadon, M.; Zorzi, D.; Thomas, M.B.; Eng, C.; Chang, D.Z.; Curley, S.A.; Abdalla, E.K.; Ellis, L.M.; et al. Bevacizumab improves pathologic response and protects against hepatic injury in patients treated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for colorectal liver metastases. Cancer 2007, 110, 2761–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukulski, F.; Lévesque, S.A.; Lavoie, G.; Lecka, J.; Bigonnesse, F.; Knowles, A.F.; Robson, S.C.; Kirley, T.L.; Sévigny, J. Comparative hydrolysis of P2 receptor agonists by NTPDases 1, 2, 3 and 8. Purinergic Signal. 2005, 1, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yegutkin, G.G. Nucleotide- and nucleoside-converting ectoenzymes: Important modulators of purinergic signalling cascade. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2008, 1783, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, S.C.; Sévigny, J.; Zimmermann, H. The E-NTPDase family of ectonucleotidases: Structure function relationships and pathophysiological significance. Purinergic Signal. 2006, 2, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, R.; Sohail, M.A.; Salhanick, S.; Malik, A.F.; Ghani, A.; Robson, S.C.; Mehal, W.Z. P2X7 receptor-mediated purinergic signaling promotes liver injury in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G1171–G1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beldi, G.; Wu, Y.; Sun, X.; Imai, M.; Enjyoji, K.; Csizmadia, E.; Candinas, D.; Erb, L.; Robson, S.C. Regulated catalysis of extracellular nucleotides by vascular CD39/ENTPD1 is required for liver regeneration. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schmelzle, M.; Duhme, C.; Junger, W.; Salhanick, S.D.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Toxavidis, V.; Csizmadia, E.; Han, L.; Bian, S.; et al. CD39 Modulates Hematopoietic Stem Cell Recruitment and Promotes Liver Regeneration in Mice and Humans after Partial Hepatectomy. Ann. Surg. 2013, 257, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, K.; Stephenson, C.; Filshie, I. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease produced experimentally in rats by the injection of monocrotaline. Lancet 1958, 271, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoental, R.; Head, M.A. Pathological Changes in Rats as a Result of Treatment with Monocrotaline. Br. J. Cancer 1955, 9, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- DeLeve, L.D.; McCuskey, R.S.; Wang, X.; Hu, L.; McCuskey, M.K.; Epstein, R.B.; Kanel, G.C. Characterization of a reproducible rat model of hepatic veno-occlusive disease. Hepatology 1999, 29, 1779–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Kanel, G.C.; DeLeve, L.D. Support of sinusoidal endothelial cell glutathione prevents hepatic veno-occlusive disease in the rat. Hepatology 2000, 31, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffer, E.; Frossard, J.-L.; Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Mentha, G.; Pastor, C.M. Hepatic regeneration is decreased in a rat model of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. J. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 99, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, A.; Wehner, S.; Kalff, J.C.; Manekeller, S. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in the animal model: Influence on liver surgery. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2016; 402, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Nordlinger, B.; Sorbye, H.; Glimelius, B.; Poston, G.J.; Schlag, P.M.; Rougier, P.; Bechstein, W.O.; Primrose, J.N.; Walpole, E.T.; Finch-Jones, M.; et al. Perioperative chemotherapy with FOLFOX4 and surgery versus surgery alone for resectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer (EORTC Intergroup trial 40983): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2008, 371, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.M.; Mann, D.A.; Manas, D.M.; Oakley, F.; Mann, J.; White, S.A. The potential contribution of tumour-related factors to the development of FOLFOX-induced sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2396–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.; Mann, J.; Vasilaki, A.; Mathers, J.; Burt, A.; Oakley, F.; White, S.; Mann, D. Pathogenesis of FOLFOX induced sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in a murine chemotherapy model. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, C.; Sempoux, C.; Humblet, Y.; Eynde, M.V.D.; Zech, F.; Leclercq, I.; Gigot, J.-F. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS) related to chemotherapy for colorectal liver metastases: Factors predictive of severe SOS lesions and protective effect of bevacizumab. HPB 2013, 15, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Shimizu, K.; Oonishi, I.; Hasebe, K.; Takamura, H.; Inoue, T.; Muraoka, K.; Tani, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Yagi, M. Genistein suppresses cellular injury following hepatic ischemia/reperfusion. Transplant. Proc. 1996, 28, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.H.; Arao, Y.; Sun, S.J.; Kikuchi, A.; Kayama, F. Oral administration of soy-derived genistin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver inflammation but does not induce thymic atrophy in the rat. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzu, N.; Metin, K.; Dagli, A.F.; Akdemir, F.; Orhan, C.; Yalniz, M.; Ozercan, I.H.; Sahin, K.; Bahcecioglu, I.H. Protective Role of Genistein in Acute Liver Damage Induced by Carbon Tetrachloride. Mediat. Inflamm. 2007, 2007, 36381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salih, S.M.; Nallasamy, P.; Muniyandi, P.; Periyasami, V.; Venkatraman, A.C. Retracted: Genistein improves liver function and attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a rat model of insulin resistance. J. Diabetes 2009, 1, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, R.; Zhang, S.; Lin, J.; Wei, L.; He, M.; Zhou, L.; Lin, X. Protective effect of genistein isolated from Hydrocotyle sibthorpioides on hepatic injury and fibrosis induced by chronic alcohol in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 217, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinger, M.; Eipeldauer, S.; Hacker, S.; Herberger, B.; Tamandl, D.; Dorfmeister, M.; Koelblinger, C.; Gruenberger, T. Bevacizumab protects against sinusoidal obstruction syndrome and does not increase response rate in neoadjuvant XELOX/FOLFOX therapy of colorectal cancer liver metastases. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 35, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Wang, H.; Majno, P.E.; Tanabe, K.; Zhu, A.X.; Brezault, C.; Soubrane, O.; Abdalla, E.A.; Vauthey, J.-N.; et al. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome and nodular regenerative hyperplasia are frequent oxaliplatin-associated liver lesions and partially prevented by bevacizumab in patients with hepatic colorectal metastasis. Histopathology 2010, 56, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Pool, A.E.; Marsman, H.A.; Verheij, J.; Ten Kate, F.J.; Eggermont, A.M.; IJzermans, J.N.; Verhoef, C. Effect of bevacizumab added preoperatively to oxaliplatin on liver injury and complications after resection of colorectal liver metastases. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 106, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, A.M.; Fritzmann, J.; Reissfelder, C.; Weber, G.F.; Weitz, J.; Rahbari, N.N. Impact of Bevacizumab on parenchymal damage and functional recovery of the liver in patients with colorectal liver metastases. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.; Matthaei, H.; Wehner, S.; Tonguc, T.; Kalff, J.C.; Manekeller, S. Bevacizumab exacerbates sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS) in the animal model and increases MMP 9 production. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 21797–21810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, J.C.; Haworth, L.; Sherry, R.M.; Hwu, P.; Schwartzentruber, D.J.; Topalian, S.L.; Steinberg, S.M.; Chen, H.X.; Rosenberg, S.A. A randomized trial of bevacizumab, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody, for metastatic renal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alidzanovic, L.; Starlinger, P.; Schauer, D.; Maier, T.; Feldman, A.; Buchberger, E.; Stift, J.; Koeck, U.; Pop, L.; Gruenberger, B.; et al. The VEGF rise in blood of bevacizumab patients is not based on tumor escape but a host-blockade of VEGF clearance. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57197–57212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocci, G.; Man, S.; Green, S.K.; Francia, G.; Ebos, J.M.L.; du Manoir, J.M.; Weinerman, A.; Emmenegger, U.; Ma, L.; Thorpe, P.; et al. Increased Plasma Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) as a Surrogate Marker for Optimal Therapeutic Dosing of VEGF Receptor-2 Monoclonal Antibodies. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6616–6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Loupakis, F.; Falcone, A.; Masi, G.; Fioravanti, A.; Kerbel, R.S.; Del Tacca, M.; Bocci, G. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels in Immunodepleted Plasma of Cancer Patients As a Possible Pharmacodynamic Marker for Bevacizumab Activity. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1816–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starlinger, P.; Alidzanovic, L.; Schauer, D.; Maier, T.; Nemeth, C.; Perisanidis, B.; Tamandl, D.; Gruenberger, B.; Brostjan, C. Neoadjuvant bevacizumab persistently inactivates VEGF at the time of surgery despite preoperative cessation. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tabernero, J.; Yoshino, T.; Cohn, A.L.; Obermannova, R.; Bodoky, G.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Portnoy, D.C.; Cutsem, E.V.; Grothey, A.; et al. Ramucirumab versus placebo in combination with second-line FOLFIRI in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma that progressed during or after first-line therapy with bevacizumab, oxaliplatin, and a fluoropyrimidine (RAISE): A randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 499–508. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.; Hatano, E.; Narita, M.; Miyagawa-Hayashino, A.; Koyama, Y.; Nagata, H.; Iwaisa, K.; Taura, K.; Uemoto, S. Sorafenib attenuates monocrotaline-induced sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in rats through suppression of JNK and MMP-9. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLeve, L.D.; Wang, X.; Tsai, J.; Kanel, G.; Strasberg, S.; Tokes, Z.A. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (veno-occlusive disease) in the rat is prevented by matrix metalloproteinase inhibition. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbacioglu, S.; Carreras, E.; Ansari, M.; Balduzzi, A.; Cesaro, S.; Dalle, J.-H.; Dignan, F.; Gibson, B.; Guengoer, T.; Gruhn, B.; et al. Diagnosis and severity criteria for sinusoidal obstruction syndrome/veno-occlusive disease in pediatric patients: A new classification from the European society for blood and marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017, 53, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taub, R. Liver regeneration: From myth to mechanism. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, C.; Dahrenmoller, C.; Marique, L.; Jabbour, N.; Gianello, P.; Leclercq, I. Hepatic regeneration in a rat model is impaired by chemotherapy agents used in metastatic colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 41, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppell, J.A.; Richardson, P.G.; Soiffer, R.; Martin, P.L.; Kernan, N.A.; Chen, A.; Guinan, E.; Vogelsang, G.; Krishnan, A.; Giralt, S.; et al. Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease following Stem Cell Transplantation: Incidence, Clinical Course, and Outcome. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010, 16, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.J.; Lee, K.S.; Beschorner, W.E.; Vogel, V.G.; Grochow, L.B.; Braine, H.G.; Vogelsang, G.B.; Sensenbrenner, L.L.; Santos, G.W.; Saral, R. Venoocclusive disease of the liver following bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 1987, 44, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, G.B.; Sharma, P.; Matthews, D.E.; Shulman, H.M.; Thomas, E.D. Venocclusive disease of the liver after bone marrow transplantation: Diagnosis, incidence, and predisposing factors. Hepatology 1984, 4, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohty, M.; Malard, F.; Abecassis, M.; Aerts, E.; Alaskar, A.S.; Aljurf, M.; Arat, M.; Bader, P.; Baron, F.; Bazarbachi, A.; et al. Revised diagnosis and severity criteria for sinusoidal obstruction syndrome/veno-occlusive disease in adult patients: A new classification from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016, 51, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, N.; Michel, R.P.; Marcus, V.A. Pathology of Gastrointestinal and Liver Complications of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Lee, C.V.; LeCouter, J.; Campa, C.; Fuh, G.; Lowman, H.; Ferrara, N. Interaction between Bevacizumab and Murine VEGF-A: A Reassessment. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollanders, K.; Van Bergen, T.; Van de Velde, S.; Sijnave, D.; Vandewalle, E.; Moons, L.; Stalmans, I. Bevacizumab Revisited: Its Use in Different Mouse Models of Ocular Pathologies. Curr. Eye Res. 2014, 40, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folprecht, G.; Gruenberger, T.; Bechstein, W.O.; Raab, H.-R.; Lordick, F.; Hartmann, J.T.; Lang, H.; Frilling, A.; Stoehlmacher, J.; Weitz, J.; et al. Tumour response and secondary resectability of colorectal liver metastases following neoadjuvant chemotherapy with cetuximab: The CELIM randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modest, D.P.; Denecke, T.; Pratschke, J.; Ricard, I.; Lang, H.; Bemelmans, M.; Becker, T.; Rentsch, M.; Seehofer, D.; Gebauer, B.; et al. Surgical treatment options following chemotherapy plus cetuximab or bevacizumab in metastatic colorectal cancer-central evaluation of FIRE-3. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 88, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremolini, C.; Antoniotti, C.; Rossini, D.; Lonardi, S.; Loupakis, F.; Pietrantonio, F.; Bordonaro, R.; Latiano, T.P.; Tamburini, E.; Santini, D.; et al. Upfront FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab and reintroduction after progression versus mFOLFOX6 plus bevacizumab followed by FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab in the treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (TRIBE2): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 497–507. [Google Scholar]
- Wessendorf, M.D.S.; Ettrich, M.D.T.; Kanzler, M.D.S.; Nörenberg, M.D.D.; Ricke, M.D.J. FOLFOXIRI Plus Panitumumab As First-Line Treatment of RAS Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: The Randomized, Open-Label, Phase II VOLFI Study (AIO KRK0109). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3401–3411. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, G.M. Experimental pathology of the liver. I. Restoration of the liver of the white rat following partial surgical removal. Arch Pathol. 1931, 12, 186–202. [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Horgan, G.W.; Dempfle, L. Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameters | wtOx (n = 40) | wtOxAV (n = 40) | wtAV (n = 12) | wtGlu (n = 24) | p | cd39Ox (n = 24) | cd39OxAV (n = 12) | cd39AV (n = 12) | cd39Glu (n = 22) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sinusoidal dilation, n (%) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||||||
| absent | 4 (10) | 17 (42) | 12 (100) | 24 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 12 (100) | 22 (100) | ||
| present | 36 (90) | 23 (58) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 24 (100) | 12 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Grading of sinusoidal dilation, n (%) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||||||
| Grade 0 | 5 (12) | 18 (45) | 12 (100) | 24 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 12 (100) | 22 (100) | ||
| Grade 1 | 32 (80) | 21 (53) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 16 (66) | 10 (83) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Grade 2 | 3 (8) | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 (17) | 2 (17) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Grade 3 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 (17) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Perisinusoidal hemorrhage, n (%) | 0.019 | 0.233 | ||||||||
| absent | 35 (88) | 40 (100) | 12 (100) | 24 (100) | 22 (92) | 12 (100) | 10 (83) | 17 (77) | ||
| present | 5 (12) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (8) | 0 (0) | 2 (17) | 5 (23) | ||
| Nodularity, n (%) | - | - | ||||||||
| Grade 0 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 24 (100) | 12 (100) | 12 (100) | 22 (100) | ||
| Grade 1 | 40 (100) | 40 (100) | 12 (100) | 24 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Grade 2 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Grade 3 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Steatosis, n (%) | <0.0001 | 0.782 | ||||||||
| absent | 24 (60) | 32 (80) | 12 (100) | 24 (100) | 23 (83) | 12 (100) | 12 (100) | 21 (96) | ||
| present | 16 (40) | 8 (20) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | ||
| Grading of steatosis, n (%) | 0.045 | 0.529 | ||||||||
| Grade 0 | 28 (70) | 33 (82) | 12 (100) | 24 (100) | 24 (100) | 12 (100) | 12 (100) | 21 (96) | ||
| Grade 1 | 6 (15) | 4 (10) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | ||
| Grade 2 | 2 (5) | 3 (8) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Grade 3 | 4 (10) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Steatohepatitis, n (%) | - | - | ||||||||
| absent | 40 (100) | 40 (100) | 12 (100) | 24 (100) | 24 (100) | 12 (100) | 12 (100) | 22 (100) | ||
| present | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Hepatocellular damage, n (%) | 0.001 | 0.062 | ||||||||
| absent | 25 (63) | 33 (82) | 12 (100) | 24 (100) | 12 (50) | 3 (25) | 6 (50) | 16 (73) | ||
| present | 15 (37) | 7 (18) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 12 (50) | 9 (75) | 6 (50) | 6 (27) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knitter, S.; Duwe, G.; Beierle, A.S.; Pesthy, S.; Ritschl, P.V.; Hillebrandt, K.H.; Arnold, A.; Malinka, T.; Modest, D.P.; Bahra, M.; et al. Inhibition of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Protects against the Development of Oxaliplatin-Induced Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome in Wild-Type but Not in CD39-Null Mice. Cancers 2022, 14, 5992. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235992
Knitter S, Duwe G, Beierle AS, Pesthy S, Ritschl PV, Hillebrandt KH, Arnold A, Malinka T, Modest DP, Bahra M, et al. Inhibition of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Protects against the Development of Oxaliplatin-Induced Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome in Wild-Type but Not in CD39-Null Mice. Cancers. 2022; 14(23):5992. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235992
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnitter, Sebastian, Gregor Duwe, Anika Sophie Beierle, Sina Pesthy, Paul Viktor Ritschl, Karl Herbert Hillebrandt, Alexander Arnold, Thomas Malinka, Dominik Paul Modest, Marcus Bahra, and et al. 2022. "Inhibition of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Protects against the Development of Oxaliplatin-Induced Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome in Wild-Type but Not in CD39-Null Mice" Cancers 14, no. 23: 5992. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235992
APA StyleKnitter, S., Duwe, G., Beierle, A. S., Pesthy, S., Ritschl, P. V., Hillebrandt, K. H., Arnold, A., Malinka, T., Modest, D. P., Bahra, M., Pratschke, J., Sauer, I. M., Schmelzle, M., & Andreou, A. (2022). Inhibition of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Protects against the Development of Oxaliplatin-Induced Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome in Wild-Type but Not in CD39-Null Mice. Cancers, 14(23), 5992. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235992







