A Biomarker Panel Based upon AFP, Fucosylated Kininogen and PEG-Precipitated IgG Is Highly Accurate for the Early Detection Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Cirrhosis in Phase II and Phase III Biomarker Evaluation
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Samples and Ethics Statements
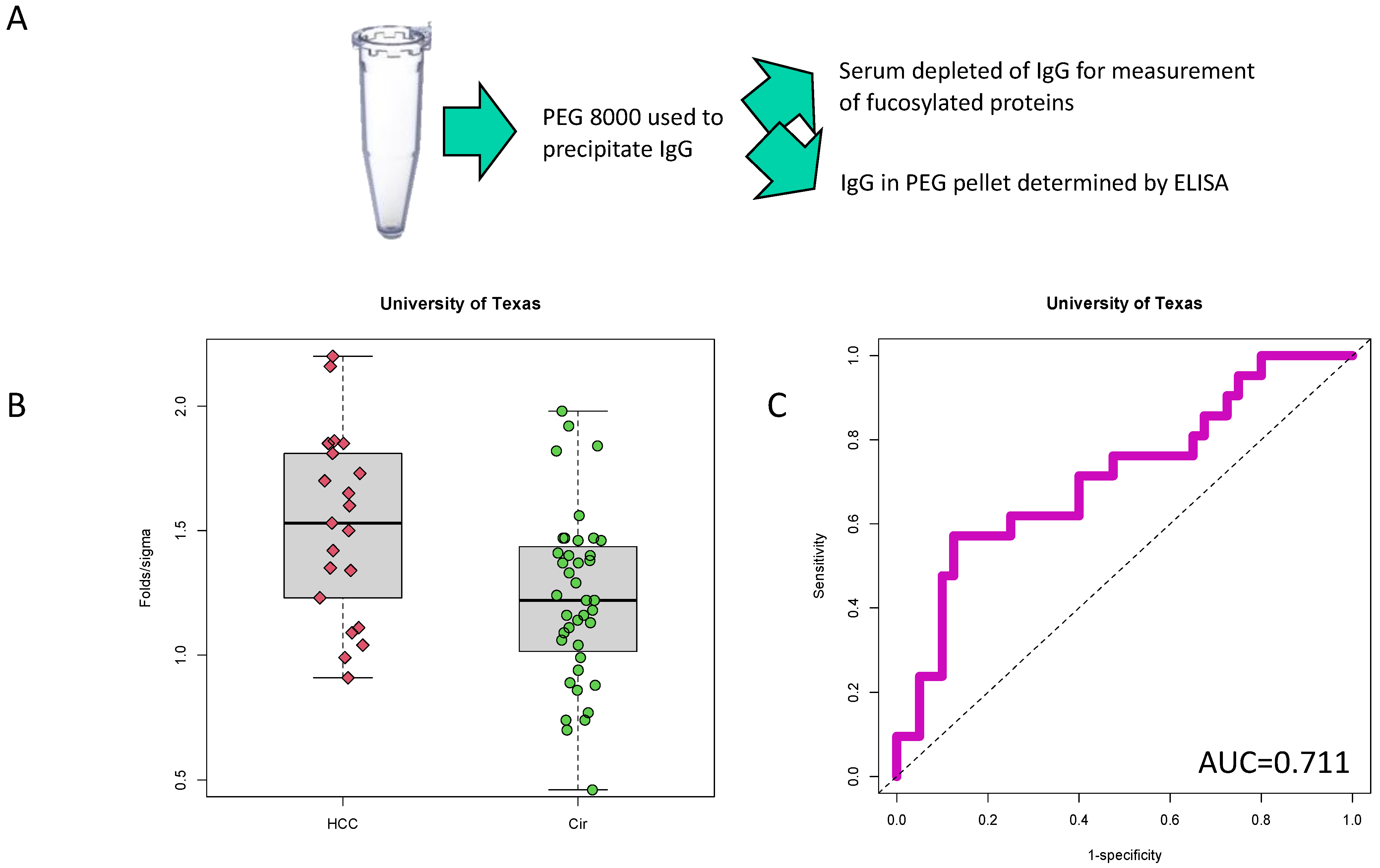
2.2. PEG-Precipitation of Serum
2.3. Analysis of IgG Levels in PEG-Precipitated Material with Indirect, Direct, Competitive and Sandwhich ELISA
2.4. Analysis of Fucosylated Kininogen
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
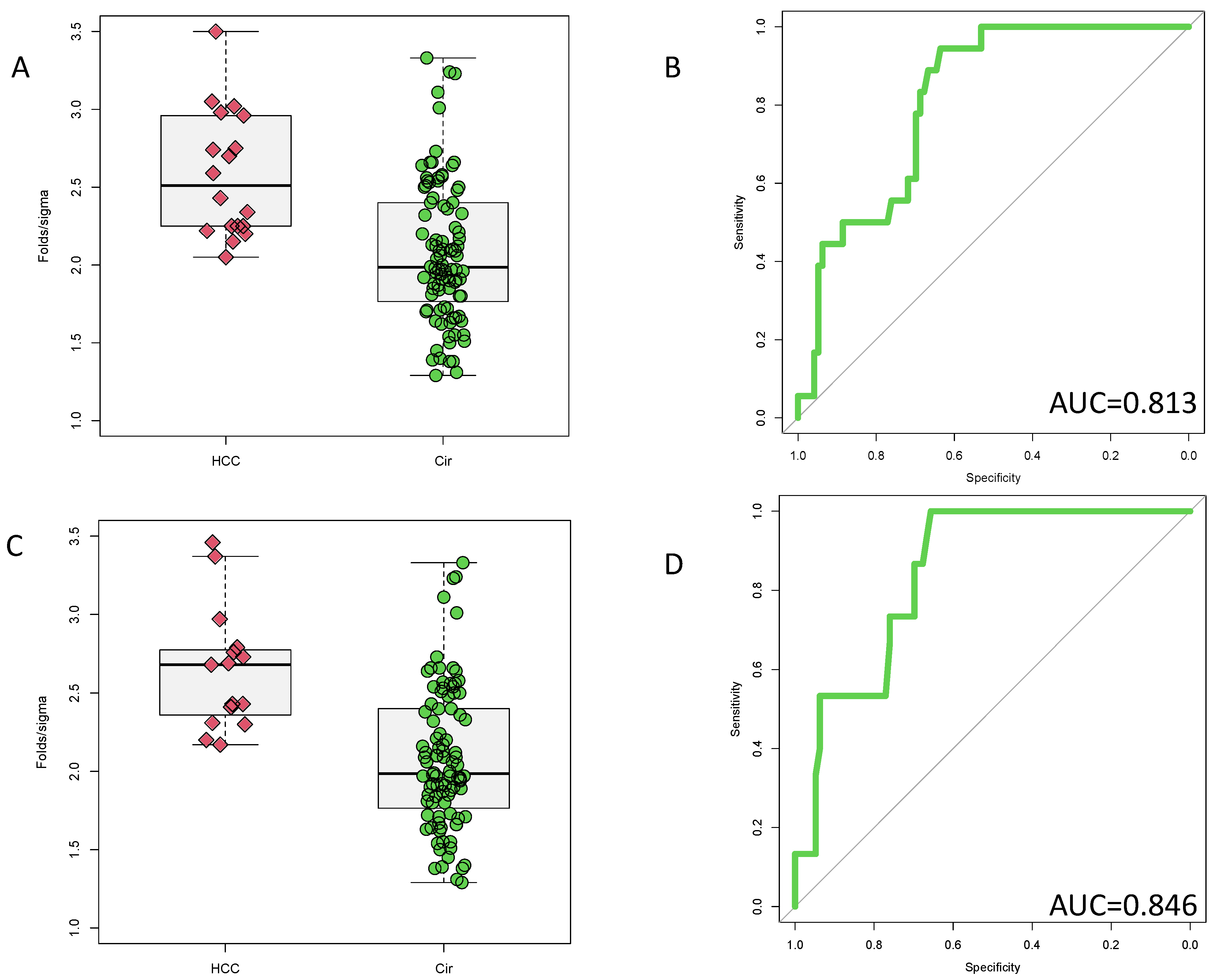
3.1. Identification of PEG-Precipitated IgG as a Biomarker of HCC
3.2. Validation of PEG-Precipitated IgG as a Biomarker of HCC at Time of Cancer Detection
3.3. Potential Prognostic Value of PEG-Precipitated IgG
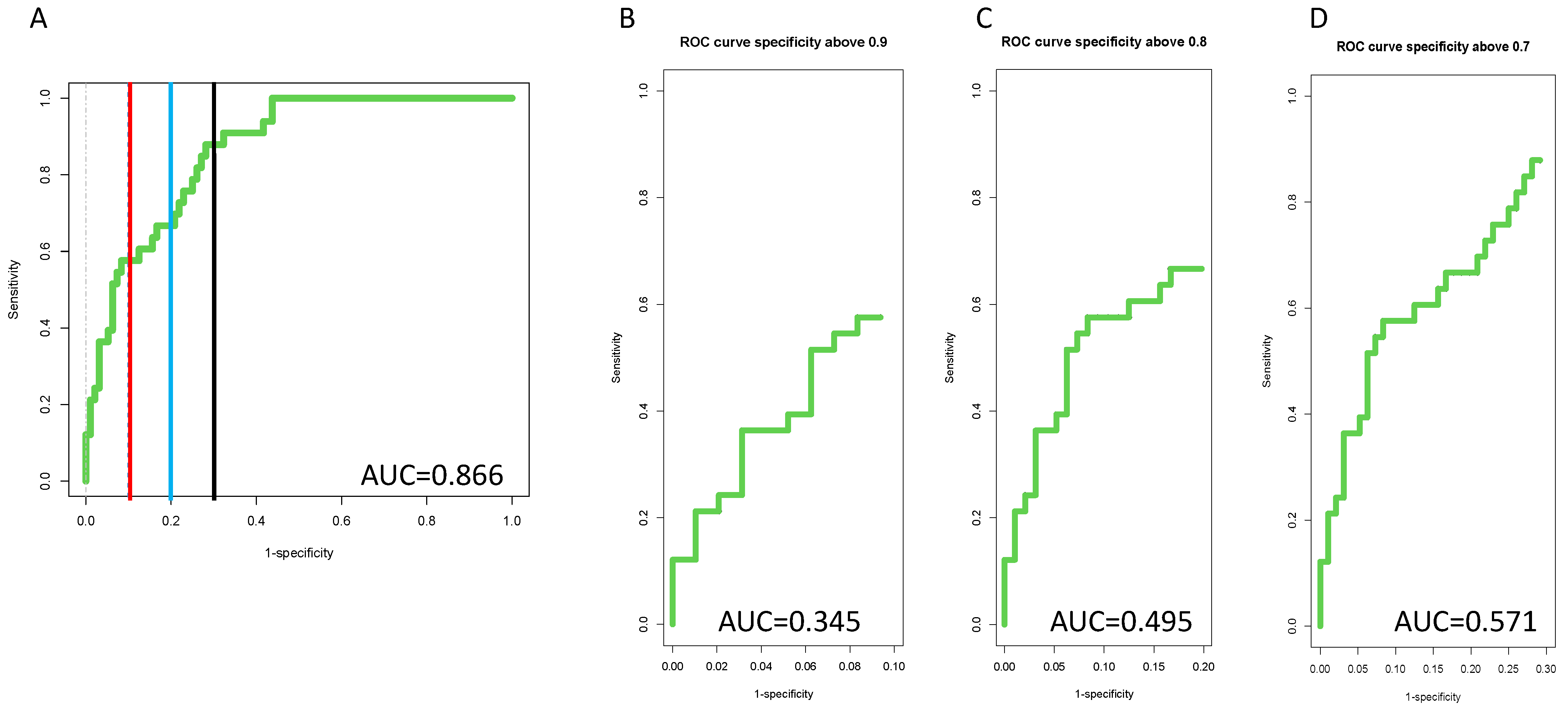
3.4. Inclusion of PEG-IgG into a Biomarker Algorithm
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Block, T.M.; Mehta, A.S.; Fimmel, C.J.; Jordan, R. Molecular viral oncology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2003, 22, 5093–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singal, A.G.; El-Serag, H.B. Hepatocellular Carcinoma From Epidemiology to Prevention: Translating Knowledge into Practice. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 2140–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiq, O.; Tiro, J.; Yopp, A.C.; Muffler, A.; Marrero, J.A.; Parikh, N.D.; Murphy, C.; McCallister, K.; Singal, A.G. HCC Surveillance: Striving for a Better Balance of Benefits and Harms. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1002–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwal, F.; Khaderi, S.; Singal, A.G.; Marrero, J.A.; Loo, N.; Asrani, S.K.; Amos, C.I.; Thrift, A.P.; Gu, X.; Luster, M.; et al. Risk factors for HCC in contemporary cohorts of patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.Q.; Singal, A.G.; Kono, Y.; Tan, D.J.; El-Serag, H.B.; Loomba, R. Changing global epidemiology of liver cancer from 2010 to 2019: NASH is the fastest growing cause of liver cancer. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 969–977.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, N.D.; Mehta, A.S.; Singal, A.G.; Block, T.; Marrero, J.A.; Lok, A.S. Biomarkers for the Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 2495–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.G.; Zhang, E.; Narasimman, M.; Rich, N.E.; Waljee, A.K.; Hoshida, Y.; Yang, J.D.; Reig, M.; Cabibbo, G.; Nahon, P.; et al. HCC surveillance improves early detection, curative treatment receipt, and survival in patients with cirrhosis: A meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, M. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology, risk factors, and screening. Semin. Liver Dis. 2005, 25, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzartzeva, K.; Obi, J.; Rich, N.E.; Parikh, N.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Yopp, A.; Waljee, A.K.; Singal, A.G. Surveillance Imaging and Alpha Fetoprotein for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Cirrhosis: A Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1706–1718.e1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comunale, M.A.; Lowman, M.; Long, R.E.; Krakover, J.; Philip, R.; Seeholzer, S.; Evans, A.A.; Hann, H.W.L.; Block, T.M.; Mehta, A.S. Proteomic analysis of serum associated fucosylated glycoproteins in the development of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 6, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comunale, M.A.; Wang, M.; Hafner, J.; Krakover, J.; Rodemich, L.; Kopenhaver, B.; Long, R.E.; Junaidi, O.; Bisceglie, A.M.; Block, T.M.; et al. Identification and development of fucosylated glycoproteins as biomarkers of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J Proteome Res 2009, 8, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.S.; Long, R.E.; Comunale, M.A.; Wang, M.; Rodemich, L.; Krakover, J.; Philip, R.; Marrero, J.A.; Dwek, R.A.; Block, T.M. Increased levels of galactose-deficient anti-Gal immunoglobulin G in the sera of hepatitis C virus-infected individuals with fibrosis and cirrhosis. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Comunale, M.A.; Herrera, H.; Betesh, L.; Kono, Y.; Mehta, A. Identification of IgM as a contaminant in lectin-FLISA assays for HCC detection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 476, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Shen, J.; Herrera, H.; Singal, A.; Swindell, C.; Renquan, L.; Mehta, A. Biomarker analysis of fucosylated kininogen through depletion of lectin reactive heterophilic antibodies in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Immunol. Methods 2018, 462, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singal, A.G.; Hoshida, Y.; Pinato, D.J.; Marrero, J.; Nault, J.C.; Paradis, V.; Tayob, N.; Sherman, M.; Lim, Y.S.; Feng, Z.; et al. International Liver Cancer Association (ILCA) White Paper on Biomarker Development for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2572–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Regalia, E.; Doci, R.; Andreola, S.; Pulvirenti, A.; Bozzetti, F.; Montalto, F.; Ammatuna, M.; Morabito, A.; Gennari, L. Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comunale, M.A.; Wang, M.; Anbarasan, N.; Betesh, L.; Karabudak, A.; Moritz, E.; Devarajan, K.; Marrero, J.; Block, T.M.; Mehta, A. Total serum glycan analysis is superior to lectin-FLISA for the early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2013, 7, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Long, R.E.; Comunale, M.A.; Junaidi, O.; Marrero, J.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Block, T.M.; Mehta, A.S. Novel fucosylated biomarkers for the early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; (Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA). Personal communication, 2022.
- Singal, A.G.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Volk, M.L.; Fu, S.; Fontana, R.J.; Askari, F.; Su, G.L.; Lok, A.S.; Marrero, J.A. Effectiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance in patients with cirrhosis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. A Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2012, 21, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sanda, M.; Comunale, M.A.; Herrera, H.; Swindell, C.; Kono, Y.; Singal, A.G.; Marrero, J.; Block, T.; Goldman, R.; et al. Changes in the Glycosylation of Kininogen and the Development of a Kininogen-Based Algorithm for the Early Detection of HCC. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2017, 26, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Block, T.M.; Marrero, J.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Devarajan, K.; Mehta, A. Improved biomarker performance for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma by inclusion of clinical parameters. Proceedings (IEEE Int. Conf. Bioinform. Biomed.) 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Devarajan, K.; Singal, A.G.; Marrero, J.A.; Dai, J.; Feng, Z.; Rinaudo, J.A.; Srivastava, S.; Evans, A.; Hann, H.W.; et al. The Doylestown Algorithm: A Test to Improve the Performance of AFP in the Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Prev. Res. 2016, 9, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Mehta, A.; Block, T.M.; Marrero, J.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Devarajan, K. A comparison of statistical methods for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma based on serum biomarkers and clinical variables. BMC Med. Genom. 2013, 6 (Suppl. 3), S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roza, M.A.; Lamba, M.; Goh, G.B.; Lum, J.H.; Cheah, M.C.; Ngu, J.H.J. Immunoglobulin G in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis predicts clinical outcome: A prospective multi-centre cohort study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 7563–7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, S.L.; He, T.; Tscheliessnig, A.; Mueller, M.; Tan, R.B.; Jungbauer, A. Branched polyethylene glycol for protein precipitation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, S.L.; He, T.; Tscheliessnig, A.; Mueller, M.; Tan, R.B.; Jungbauer, A. Protein precipitation by polyethylene glycol: A generalized model based on hydrodynamic radius. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 157, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atha, D.H.; Ingham, K.C. Mechanism of precipitation of proteins by polyethylene glycols. Analysis in terms of excluded volume. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 12108–12117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.G.; Tayob, N.; Mehta, A.; Marrero, J.A.; Jin, Q.; Lau, J.; Parikh, N.D. Doylestown Plus and GALAD Demonstrate High Sensitivity for HCC Detection in Patients with Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 20, 953–955.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| University of Texas 1 | Saint Louis University 1 | UCSD 1 | University of Michigan 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 61 | 74 | 339 | 97 |
| UCC:Cirrhosis: Other 3 | 21:40:0 | 40:34:0 | 107:184:48 | 37:60 |
| Early stage HCC 4 | 0% | 100% | 42% | 75% |
| Gender (Male:Female) | 38:23 | 39:35 | 195:144 | 60:37 |
| Age (Mean, SD) 5 | 58.23, 6.64 | 55.86, 11.93 | 60.32, 10.45 | 54.46, 8.39 |
| ALK (Mean, SD) 6 | 144.51, 92.75 | NA | 145.33, 90.88 | 163.23, 98.57 |
| ALT (Mean, SD) 7 | NA | NA | 47.89, 61.35 | 59.09, 43.74 |
| AST (Mean, SD) 8 | 69.13, 50.23 | NA | 66.92, 67.67 | 79.58, 57.22 |
| AFP (Mean, SD) 9 | 3101.29, 12910.51 | 65.07, 98.76 | 169.97, 998.85 | 13.24, 30.30 |
| PER-IgG (Mean, SD) 10 | 1.32, 0.37 | 1.62, 0.44 | 1.50, 0.23 | 2.24, 0.47 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Singal, A.G.; Parikh, N.; Kono, Y.; Marrero, J.; Mehta, A. A Biomarker Panel Based upon AFP, Fucosylated Kininogen and PEG-Precipitated IgG Is Highly Accurate for the Early Detection Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Cirrhosis in Phase II and Phase III Biomarker Evaluation. Cancers 2022, 14, 5970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235970
Wang M, Singal AG, Parikh N, Kono Y, Marrero J, Mehta A. A Biomarker Panel Based upon AFP, Fucosylated Kininogen and PEG-Precipitated IgG Is Highly Accurate for the Early Detection Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Cirrhosis in Phase II and Phase III Biomarker Evaluation. Cancers. 2022; 14(23):5970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235970
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mengjun, Amit G. Singal, Neehar Parikh, Yuko Kono, Jorge Marrero, and Anand Mehta. 2022. "A Biomarker Panel Based upon AFP, Fucosylated Kininogen and PEG-Precipitated IgG Is Highly Accurate for the Early Detection Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Cirrhosis in Phase II and Phase III Biomarker Evaluation" Cancers 14, no. 23: 5970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235970
APA StyleWang, M., Singal, A. G., Parikh, N., Kono, Y., Marrero, J., & Mehta, A. (2022). A Biomarker Panel Based upon AFP, Fucosylated Kininogen and PEG-Precipitated IgG Is Highly Accurate for the Early Detection Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Cirrhosis in Phase II and Phase III Biomarker Evaluation. Cancers, 14(23), 5970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235970





