Recent Advances in Adult Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathogenesis
3. Pathologic Classification
4. Clinical Features
5. Diagnosis and Staging
6. Risk Factors
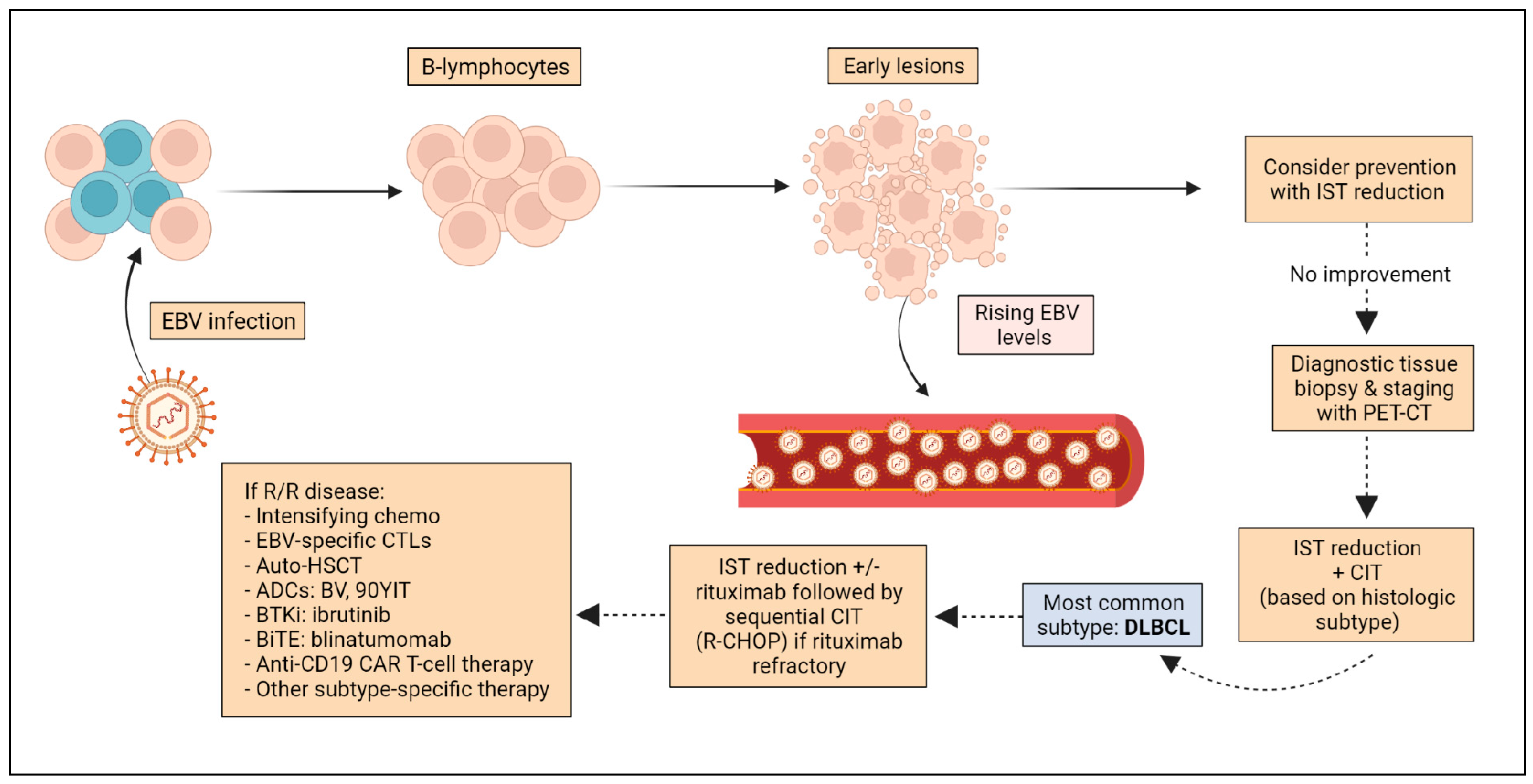
7. Surveillance and Prevention
8. Pre-Emptive Therapy
9. Treatment
9.1. SOT Recipients
9.1.1. Reduction in IST
9.1.2. Rituximab
9.1.3. Rituximab and Chemotherapy
9.2. AlloHSCT Recipients
9.3. Treatment of Relapsed Disease
9.4. Novel Approaches
9.4.1. EBV-Specific Cytotoxic Lymphocytes
9.4.2. Antibody Drug Conjugates
9.4.3. Targeted Therapies
9.4.4. Antiviral Therapies
9.4.5. Serotype-Dependent Recombinant Adeno-Associated Vector (AAV)
9.4.6. T-Cell-Redirecting Bispecific Antibodies
9.4.7. Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapies
9.5. Radiation Therapy
9.6. Treatment of Rare Histologic Subtypes
9.6.1. CNS PTLD
9.6.2. Burkitt-like PTLD
9.6.3. Plasmacytic PTLD
9.6.4. Plasmablastic PTLD
9.6.5. Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL)-like PTLD
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samant, H.; Vaitla, P.; Kothadia, J.P. Post Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders; StatPearls: Adelaide SA, Australia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Adami, J.; Gäbel, H.; Lindelöf, B.; Ekström, K.; Rydh, B.; Glimelius, B.; Ekbom, A.; Adami, H.O.; Granath, F. Cancer Risk Following Organ Transplantation: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Sweden. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, I. Cancers Complicating Organ Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 1767–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Johnson, W.T.; Kartan, S.; Gonsalves, A.S.; Fenkel, J.M.; Gong, J.Z.; Porcu, P. Durable Response to Brentuximab Vedotin Plus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, and Prednisone (BV-CHP) in a Patient with CD30-Positive PTCL Arising as a Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD). Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herreman, A.; Dierickx, D.; Morscio, J.; Camps, J.; Bittoun, E.; Verhoef, G.; De Wolf-Peeters, C.; Sagaert, X.; Tousseyn, T. Clinicopathological Characteristics of Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders of T-Cell Origin: Single-Center Series of Nine Cases and Meta-Analysis of 147 Reported Cases. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 2190–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opelz, G.; Henderson, R. Incidence of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Kidney and Heart Transplant Recipients. Lancet 1993, 342, 1514–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, F.; El Kossi, M.; Shaheen, I.S.; Sharma, A.; Halawa, A. Post-Transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorders: Current Concepts and Future Therapeutic Approaches. World J. Transplant. 2020, 10, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, U.D.; Preiksaitis, J.K. Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders, Epstein-Barr Virus Infection, and Disease in Solid Organ Transplantation: Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.; Remacha, E.F.; Canizales, J.T.; Bravo-Gallego, L.Y.; Fitzpatrick, E.; Melgar, A.A.; Bartolo, G.M.; Guereta, L.G.; Boluda, E.R.; Mozo, Y.; et al. Current Practices on Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment of Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder in Pediatric Patients after Solid Organ Transplantation: Results of ERN TransplantChild Healthcare Working Group Survey. Children 2021, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Bowles, K.; Bradley, J.A.; Emery, V.; Featherstone, C.; Gupte, G.; Marcus, R.; Parameshwar, J.; Ramsay, A.; Newstead, C. Diagnosis of Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients-BCSH and BTS Guidelines. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 149, 675–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourse, J.P.; Jones, K.; Gandhi, M.K. Epstein–Barr Virus-Related Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders: Pathogenetic Insights for Targeted Therapy. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferla, V.; Rossi, F.G.; Goldaniga, M.C.; Baldini, L. Biological Difference Between Epstein–Barr Virus Positive and Negative Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Their Clinical Impact. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierickx, D.; Habermann, T.M. Post-Transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorders in Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.L.; Marcus, R.; Bradley, J.A. Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders (PTLD) after Solid Organ Transplantation. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2005, 56, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finalet Ferreiro, J.; Morscio, J.; Dierickx, D.; Vandenberghe, P.; Gheysens, O.; Verhoef, G.; Zamani, M.; Tousseyn, T.; Wlodarska, I. EBV-Positive and EBV-Negative Posttransplant Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphomas Have Distinct Genomic and Transcriptomic Features. Am. J. Transpl. 2016, 16, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopwood, P.; Crawford, D.H. The Role of EBV in Post-Transplant Malignancies: A Review. J. Clin. Pathol. 2000, 53, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morscio, J.; Finalet Ferreiro, J.; Vander Borght, S.; Bittoun, E.; Gheysens, O.; Dierickx, D.; Verhoef, G.; Wlodarska, I.; Tousseyn, T. Identification of Distinct Subgroups of EBV-Positive Post-Transplant Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, H.A.; Bernheim, A.; Schneider, A.; Meddeb, M.; Choquet, S.; Leblond, V.; Charlotte, F.; Davi, F.; Canioni, D.; Macintyre, E.; et al. Characteristic Pattern of Chromosomal Imbalances in Posttransplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorders: Correlation with Histopathological Subcategories and EBV Status. Transplantation 2005, 80, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.; Kwee, I.; Poretti, G.; Mensah, A.; Pruneri, G.; Capello, D.; Rossi, D.; Zucca, E.; Ponzoni, M.; Catapano, C.; et al. Comparative Genome-Wide Profiling of Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 134, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.; Capello, D.; Scandurra, M.; Greiner, T.C.; Chan, W.C.; Bhagat, G.; Rossi, D.; Morra, E.; Paulli, M.; Rambaldi, A.; et al. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism-Arrays Provide New Insights in the Pathogenesis of Post-Transplant Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 149, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, T.; Juskevicius, D.; Alikian, M.; Steiger, J.; Dirnhofer, S.; Tzankov, A.; Naresh, K.N. Mutational Landscape of B-Cell Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 178, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeStefano, C.B.; Desai, S.H.; Shenoy, A.G.; Catlett, J.P. Management of Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 182, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.R.; Nalesnik, M.A.; Swerdlow, S.H. Impact of Epstein-Barr Virus in Monomorphic B-Cell Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders: A Histogenetic Study. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2006, 30, 1604–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, D.; Rossi, D.; Gaidano, G. Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders: Molecular Basis of Disease Histogenesis and Pathogenesis. Hematol. Oncol. 2005, 23, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luskin, M.R.; Heil, D.S.; Tan, K.S.; Choi, S.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; Schuster, S.J.; Porter, D.L.; Vonderheide, R.H.; Bagg, A.; Heitjan, D.F.; et al. The Impact of EBV Status on Characteristics and Outcomes of Posttransplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorder. Am. J. Transpl. 2015, 15, 2665–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblond, V.; Davi, F.; Charlotte, F.; Dorent, R.; Bitker, M.O.; Sutton, L.; Gandjbakhch, I.; Binet, J.L.; Raphael, M. Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders Not Associated with Epstein-Barr Virus: A Distinct Entity? J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, D.E.; Hardy, C.L.; Tomaszewski, J.E.; Kotloff, R.M.; Oltoff, K.M.; Somer, B.G.; Schuster, S.J.; Porter, D.L.; Montone, K.T.; Stadtmauer, E.A. Reduction in Immunosuppression as Initial Therapy for Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder: Analysis of Prognostic Variables and Long-Term Follow-up of 42 Adult Patients. Transplantation 2001, 71, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.; Riches, M.; Hari, P.; Kim, S.; Chen, M.; Bachier, C.; Shaughnessy, P.; Hill, J.; Ljungman, P.; Battiwalla, M.; et al. Survival Outcomes of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplants with EBV-Positive or EBV-Negative Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder, A CIBMTR Study. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2019, 21, e13145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Lee Harris, N.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 Revision of the World Health Organization Classification of Lymphoid Neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobrial, I.M.; Habermann, T.M.; Maurer, M.J.; Geyer, S.M.; Ristow, K.M.; Larson, T.S.; Walker, R.C.; Ansell, S.M.; Macon, W.R.; Gores, G.G.; et al. Prognostic Analysis for Survival in Adult Solid Organ Transplant Recipients with Post-Transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorders. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7574–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.S.; Tsodikov, A.; Cibrik, D.M.; Ross, C.W.; Kaminski, M.S.; Blayney, D.W. Lymphoma after Solid Organ Transplantation: Risk, Response to Therapy, and Survival at a Transplantation Center. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3354–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courville, E.L.; Yohe, S.; Chou, D.; Nardi, V.; Lazaryan, A.; Thakral, B.; Nelson, A.C.; Ferry, J.A.; Sohani, A.R. EBV-Negative Monomorphic B-Cell Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders Are Pathologically Distinct from EBV-Positive Cases and Frequently Contain TP53 Mutations. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 1200–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakiani, E.; Basso, K.; Klein, U.; Mansukhani, M.M.; Narayan, G.; Smith, P.M.; Murty, V.V.; Dalla-Favera, R.; Pasqualucci, L.; Bhagat, G. Genetic and Phenotypic Analysis of B-Cell Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders Provides Insights into Disease Biology. Hematol. Oncol. 2008, 26, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morscio, J.; Dierickx, D.; Ferreiro, J.F.; Herreman, A.; Van Loo, P.; Bittoun, E.; Verhoef, G.; Matthys, P.; Cools, J.; Wlodarska, I.; et al. Gene Expression Profiling Reveals Clear Differences between EBV-Positive and EBV-Negative Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Am. J. Transpl. 2013, 13, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotti, G.; Fiocchi, R.; Motta, T.; Gamba, A.; Gotti, E.; Gridelli, B.; Borleri, G.; Manzoni, C.; Viero, P.; Remuzzi, G.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus-Negative Lymphoproliferate Disorders in Long-Term Survivors after Heart, Kidney, and Liver Transplant. Transplantation 2000, 69, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koff, J.L.; Li, J.X.; Zhang, X.; Switchenko, J.M.; Flowers, C.R.; Waller, E.K. Impact of the Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder Subtype on Survival. Cancer 2018, 124, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, F.; Orjuela-Grimm, M. Joining Efforts for PTLD: Lessons Learned from Comparing the Approach and Treatment Strategies across the Pediatric and Adult Age Spectra. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2021, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrara, M.R.; Giunco, S.; Serraino, D.; Dolcetti, R.; De Rossi, A. Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders: From Epidemiology to Pathogenesis-Driven Treatment. Cancer Lett. 2015, 369, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.S.Y.; Hwang, Y.Y.; Gill, H.; Au, W.Y.; Leung, A.Y.H.; Tse, E.; Chim, C.S.; Loong, F.; Kwong, Y.L. Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Diseases in Asian Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: Late Onset and Favorable Response to Treatment. Clin. Transplant. 2012, 26, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, M.; Coupes, B.; Roberts, S.A.; Klapper, P.E.; Byers, R.J.; Vallely, P.J.; Ryan, K.; Picton, M.L. Epidemiology of Posttransplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorder in Adult Renal Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2013, 95, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakanay, Ş.M.; Kaygusuz, G.; Topçuoǧlu, P.; Şengül, Ş.; Tunçali, T.; Keven, K.; Kuzu, I.; Uysal, A.; Arat, M. Epstein-Barr Virus-Negative Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Diseases: Three Distinct Cases from a Single Center. Turkish J. Hematol. 2014, 31, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, R.E.; Travis, L.B.; Rowlings, P.A.; Socié, G.; Kingma, D.W.; Banks, P.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Sale, G.E.; Horowitz, M.M.; Witherspoon, R.P.; et al. Risk of Lymphoproliferative Disorders after Bone Marrow Transplantation: A Multi-Institutional Study. Blood 1999, 94, 2208–2216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.; Ramsay, N.K.C.; Steinbuch, M.; Dusenbery, K.E.; Shapiro, R.S.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Robison, L.L.; Miller, J.S.; Neglia, J.P. Malignant Neoplasms Following Bone Marrow Transplantation. Blood 1996, 87, 3633–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblond, V.; Dhedin, N.; Bruneel, M.F.M.; Choquet, S.; Hermine, O.; Porcher, R.; Qouc, S.N.; Davi, F.; Charlotte, F.; Dorent, R.; et al. Identification of Prognostic Factors in 61 Patients with Posttransplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorders. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evens, A.M.; David, K.A.; Helenowski, I.; Nelson, B.; Kaufman, D.; Kircher, S.M.; Gimelfarb, A.; Hattersley, E.; Mauro, L.A.; Jovanovic, B.; et al. Multicenter Analysis of 80 Solid Organ Transplantation Recipients With Post-Transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disease: Outcomes and Prognostic Factors in the Modern Era. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asleh, R.; Alnsasra, H.; Habermann, T.M.; Briasoulis, A.; Kushwaha, S.S. Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder Following Cardiac Transplantation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 787975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, E.; Moyers, J.T.; Wang, B.C.; Jeong, I.S.D.; Lee, J.; Liu, L.; Kim, M.; Villicana, R.; Kim, B.; Mitchell, J.; et al. Analysis of Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD) Outcomes with Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Assessments—A Single Tertiary Referral Center Experience and Review of Literature. Cancers 2021, 13, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshef, R.; Vardhanabhuti, S.; Luskin, M.R.; Heitjan, D.F.; Hadjiliadis, D.; Goral, S.; Krok, K.L.; Goldberg, L.R.; Porter, D.L.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; et al. Reduction of Immunosuppression as Initial Therapy for Posttransplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorder(★). Am. J. Transpl. 2011, 11, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Eyre, T.A.; Tucker, D.; Kassam, S.; Parmar, J.; Featherstone, C.; Andrews, P.; Asgari, E.; Chaganti, S.; Menne, T.F.; et al. Front-Line Management of Post-Transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorder in Adult Solid Organ Recipient Patients—A British Society for Haematology Guideline. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 193, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoon Kim, J.; Cho, H.; Sung, H.; Ra Jung, A.; Sei Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Ryu, J.-S.; Jin Chae, E.; Won Kim, K.; Huh, J.; et al. Reappraisal of the Prognostic Value of Epstein-Barr Virus Status in Monomorphic Post-Transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorders-Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierickx, D.; Tousseyn, T.; Requilé, A.; Verscuren, R.; Sagaert, X.; Morscio, J.; Wlodarska, I.; Herreman, A.; Kuypers, D.; Van Cleemput, J.; et al. The Accuracy of Positron Emission Tomography in the Detection of Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder. Haematologica 2013, 98, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balfour, H.H.; Sifakis, F.; Sliman, J.A.; Knight, J.A.; Schmeling, D.O.; Thomas, W. Age-Specific Prevalence of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection among Individuals Aged 6-19 Years in the United States and Factors Affecting Its Acquisition. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharnidharka, V.R.; Lamb, K.E.; Gregg, J.A.; Meier-Kriesche, H.U. Associations Between EBV Serostatus and Organ Transplant Type in PTLD Risk: An Analysis of the SRTR National Registry Data in the United States. Am. J. Transplant. 2012, 12, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opelz, G.; Daniel, V.; Naujokat, C.; Döhler, B. Epidemiology of Pretransplant Ebv and Cmv Serostatus in Relation to Posttransplant Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Transplantation 2009, 88, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.C.; Akinwumi, M.S.; Cervera, C.; Mabilangan, C.; Ghosh, S.; Lai, R.; Iafolla, M.; Doucette, K.; Preiksaitis, J.K. The Changing Epidemiology of Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder in Adult Solid Organ Transplant Recipients Over 30 Years: A Single-Center Experience. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, C.; Schuchmann, M.; Zimmermann, T. Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disease in Liver Transplant Patients. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2011, 13, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Ahn, C.M.; Lee, D.Y.; Paik, H.C. Two Cases of Post Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder in Lung Transplant Recipients. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2004, 19, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillard, S.; Dharnidharka, V.; Agodoa, L.; Bohen, E.; Abbott, K. Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders after Renal Transplantation in the United States in Era of Modern Immunosuppression. Transplantation 2005, 80, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharnidharka, V.R.; Kenneth Sullivan, E.; Stablein, D.M.; Tejani, A.H.; Harmon, W.E. Risk Factors for Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD) in Pediatric Kidney Transplantation: A Report of the North American Pediatric Renal Transplant Cooperative Study (NAPRTCS). Transplantation 2001, 71, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nee, R.; Hurst, F.P.; Dharnidharka, V.R.; Jindal, R.M.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Abbott, K.C. Racial Variation in the Development of Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders after Renal Transplantation. Transplantation 2011, 92, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opelz, G.; Döhler, B. Lymphomas after Solid Organ Transplantation: A Collaborative Transplant Study Report. Am. J. Transpl. 2004, 4, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, L.; Hsi, E.D. The Clinicopathologic Spectrum of Posttransplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2007, 131, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, R.A.; Smith, J.M.; Ho, M.; Lindblad, R.; Ikle, D.; Grimm, P.; Wyatt, R.; Arar, M.; Liereman, D.; Bridges, N.; et al. Incidence of PTLD in Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients Receiving Basiliximab, Calcineurin Inhibitor, Sirolimus and Steroids. Am. J. Transpl. 2008, 8, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, F.; Kunitake, H.; Laks, H.; Odim, J. Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder Following Pediatric Heart Transplantation. Pediatr. Transplant. 2006, 10, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, J.G.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, D.J. Different Causes of Early and Late-Onset Post Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder in Kidney Transplantation Patients after 2000. Asian J. Surg. 2019, 42, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldman, M.R.; Edlefsen, K.L.; Pepper, G.; Kapnadak, S.G.; Rakita, R.M.; Fisher, C.E.; Limaye, A.P. Combined Assessment of Epstein-Barr Virus Viral Capsid Antigen and Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen-1 Serology for Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder Risk Stratification in Adult Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2022. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, A.; Hiramoto, N.; Yamasaki, S.; Inamoto, Y.; Uchida, N.; Maeda, T.; Mori, T.; Kanda, Y.; Kondo, T.; Shiratori, S.; et al. Risk Factors and Predictive Scoring System For Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.N.; Lin, J.; Wang, L.J.; Li, F.; Li, H.H.; Wang, S.H.; Huang, W.R.; Gao, C.J.; Yu, L.; Liu, D.H. Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Epstein–Barr Virus DNAemia and Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders after Haploidentical and Matched-Sibling PBSCT in Patients with Hematologic Malignancies. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgren, O.; Gilbert, E.S.; Rizzo, J.D.; Socié, G.; Banks, P.M.; Sobocinski, K.A.; Horowitz, M.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Kingma, D.W.; Travis, L.B.; et al. Risk Factors for Lymphoproliferative Disorders after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Blood 2009, 113, 4992–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaia, J.; Baden, L.; Boeckh, M.J.; Chakrabarti, S.; Einsele, H.; Ljungman, P.; McDonald, G.B.; Hirsch, H. Viral Disease Prevention after Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009, 44, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasche, L.; Kapp, M.; Einsele, H.; Mielke, S. EBV-Induced Post Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders: A Persisting Challenge in Allogeneic Hematopoetic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014, 49, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styczynski, J.; Reusser, P.; Einsele, H.; de la Camara, R.; Cordonnier, C.; Ward, K.N.; Ljungman, P.; Engelhard, D. Management of HSV, VZV and EBV Infections in Patients with Hematological Malignancies and after SCT: Guidelines from the Second European Conference on Infections in Leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009, 43, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlin, M.; Wikell, H.; Sundin, M.; Blennow, O.; Maeurer, M.; Ringden, O.; Winiarski, J.; Ljungman, P.; Remberger, M.; Mattsson, J. Risk Factors for Epstein-Barr Virus-Related Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Haematologica 2014, 99, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Esser, J.W.J.; Van Der Holt, B.; Meijer, E.; Niesters, H.G.M.; Trenschel, R.; Thijsen, S.F.T.; Van Loon, A.M.; Frassoni, F.; Bacigalupo, A.; Schaefer, U.W.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Reactivation Is a Frequent Event after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation (SCT) and Quantitatively Predicts EBV-Lymphoproliferative Disease Following T-Cell–Depleted SCT. Blood 2001, 98, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, D.E.; Douglas, L.; Andreadis, C.; Vogl, D.T.; Arnoldi, S.; Kotloff, R.; Svoboda, J.; Bloom, R.D.; Olthoff, K.M.; Brozena, S.C.; et al. EBV PCR in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder: Results of a Two-Arm Prospective Trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styczynski, J.; Van Der Velden, W.; Fox, C.P.; Engelhard, D.; De La Camara, R.; Cordonnier, C.; Ljungman, P. Management of Epstein-Barr Virus Infections and Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders in Patients after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Sixth European Conference on Infections in Leukemia (ECIL-6) Guidelines. Haematologica 2016, 101, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Hsu, T.C.; Kuo, C.C.; Liu, M.A.; Abdelfattah, A.M.; Chang, C.N.; Yao, M.; Li, C.C.; Wu, K.H.; Chen, T.C.; et al. Validation of a Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder Risk Prediction Score and Derivation of a New Prediction Score Using a National Bone Marrow Transplant Registry Database. Oncologist 2021, 26, e2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Juan, R.; Comoli, P.; Caillard, S.; Moulin, B.; Hirsch, H.H.; Meylan, P. Epstein-Barr Virus-Related Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, E.; Kwong, Y.L. Epstein Barr Virus-Associated Lymphoproliferative Diseases: The Virus as a Therapeutic Target. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, A.; Roessner, C.; Jupp, J.; Williamson, T.; Tellier, R.; Chaudhry, A.; Khan, F.; Taparia, M.; Jimenez-Zepeda, V.H.; Stewart, D.A.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus DNAemia Monitoring for the Management of Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder. Cytotherapy 2018, 20, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaes, A.H.; Cao, Q.; Wagner, J.E.; Young, J.A.H.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Brunstein, C.G. Monitoring and Preemptive Rituximab Therapy for Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation after Antithymocyte Globulin Containing Nonmyeloablative Conditioning for Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010, 16, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styczynski, J.; Einsele, H.; Gil, L.; Ljungman, P. Outcome of Treatment of Epstein-Barr Virus-Related Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Recipients: A Comprehensive Review of Reported Cases. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2009, 11, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinch, A.; Hallböök, H.; Arvidson, J.; Sällström, K.; Bondeson, K.; Pauksens, K. Long-Term Outcome of Epstein–Barr Virus DNAemia and PTLD with the Use of Preemptive Rituximab Following Allogeneic HSCT. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choquet, S.; Varnous, S.; Deback, C.; Golmard, J.L.; Leblond, V. Adapted Treatment of Epstein–Barr Virus Infection to Prevent Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder After Heart Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2014, 14, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oertel, S.H.K.; Verschuuren, E.; Reinke, P.; Zeidler, K.; Papp-Váry, M.; Babel, N.; Trappe, R.U.; Jonas, S.; Hummel, M.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; et al. Effect of Anti-CD 20 Antibody Rituximab in Patients with Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD). Am. J. Transpl. 2005, 5, 2901–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choquet, S.; Leblond, V.; Herbrecht, R.; Socié, G.; Stoppa, A.M.; Vandenberghe, P.; Fischer, A.; Morschhauser, F.; Salles, G.; Feremans, W.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Rituximab in B-Cell Post-Transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorders: Results of a Prospective Multicenter Phase 2 Study. Blood 2006, 107, 3053–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Barca, E.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; Capote, F.J.; Gómez-Codina, J.; Salar, A.; Bauen, A.; Ribera, J.M.; López, A.; Briones, J.; Muñoz, A.; et al. Prospective Phase II Trial of Extended Treatment with Rituximab in Patients with B-Cell Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease. Haematologica 2007, 92, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Barca, E.; Capote, F.J.; Gómez-Codina, J.; Panizo, C.; Salar, A.; Sancho, J.M.; López, A.; Briones, J.; Muñoz, A.; Encuentra, M.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up of a Prospective Phase 2 Clinical Trial of Extended Treatment with Rituximab in Patients with B Cell Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease and Validation in Real World Patients. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 100, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choquet, S.; Oertel, S.; LeBlond, V.; Riess, H.; Varoqueaux, N.; Dörken, B.; Trappe, R. Rituximab in the Management of Post-Transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorder after Solid Organ Transplantation: Proceed with Caution. Ann. Hematol. 2007, 86, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.; Hawkes, E.A.; Jack, A.; Qian, W.; Smith, P.; Mouncey, P.; Pocock, C.; Ardeshna, K.M.; Radford, J.A.; McMillan, A.; et al. Rituximab plus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, and Prednisolone in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Diffuse Large B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Phase 3 Comparison of Dose Intensification with 14-Day versus 21-Day Cycles. Lancet 2013, 381, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappe, R.; Oertel, S.; Leblond, V.; Mollee, P.; Sender, M.; Reinke, P.; Neuhaus, R.; Lehmkuhl, H.; Horst, H.A.; Salles, G.; et al. Sequential Treatment with Rituximab Followed by CHOP Chemotherapy in Adult B-Cell Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD): The Prospective International Multicentre Phase 2 PTLD-1 Trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2012, 13, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappe, R.U.; Choquet, S.; Dierickx, D.; Mollee, P.; Zaucha, J.M.; Dreyling, M.H.; Dührsen, U.; Tarella, C.; Shpilberg, O.; Sender, M.; et al. International Prognostic Index, Type of Transplant and Response to Rituximab Are Key Parameters to Tailor Treatment in Adults With CD20-Positive B Cell PTLD: Clues From the PTLD-1 Trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trappe, R.U.; Dierickx, D.; Zimmermann, H.; Morschhauser, F.; Mollee, P.; Zaucha, J.M.; Dreyling, M.H.; Dührsen, U.; Reinke, P.; Verhoef, G.; et al. Response to Rituximab Induction Is a Predictive Biomarker in Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD) and Allows Successful Treatment Stratification in an International Phase II Trial Including 152 Patients. Blood 2015, 126, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappe, R.U.; Dierickx, D.; Zimmermann, H.; Morschhauser, F.; Mollee, P.; Zaucha, J.M.; Dreyling, M.H.; Dührsen, U.; Reinke, P.; Verhoef, G.; et al. Response to Rituximab Induction Is a Predictive Marker in B-Cell Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder and Allows Successful Stratification into Rituximab or r-Chop Consolidation in an International, Prospective, Multicenter Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, H.; Koenecke, C.; Dreyling, M.H.; Pott, C.; Dührsen, U.; Hahn, D.; Meidenbauer, N.; Hauser, I.A.; Rummel, M.J.; Wolf, D.; et al. Modified Risk-Stratified Sequential Treatment (Subcutaneous Rituximab with or without Chemotherapy) in B-Cell Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD) after Solid Organ Transplantation (SOT): The Prospective Multicentre Phase II PTLD-2 Trial. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radeski, D.; Hoehn, D.; Montanari, F.; Alobeid, B.; Zhang, Y.; Amengual, J.E.; Sawas, A.; Deng, C.; O’Connor, O.A.; Bhagat, G. The Impact of Immunophenotypic Subtypes and Treatment Regimens on Patient Outcomes in Monomorphic Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders (Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma). Blood 2014, 124, 4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prockop, S.; Doubrovina, E.; Suser, S.; Heller, G.; Barker, J.; Dahi, P.; Perales, M.A.; Papadopoulos, E.; Sauter, C.; Castro-Malaspina, H.; et al. Off-the-Shelf EBV-Specific T Cell Immunotherapy for Rituximab-Refractory EBV-Associated Lymphoma Following Transplantation. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prockop, S.; Mahadeo, K.M.; Beitinjaneh, A.; Choquet, S.; Stiff, P.; Reshef, R.; Satyanarayana, G.; Dahiya, S.; Parmar, H.; Ye, W.; et al. Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study of Tabelecleucel for Solid Organ or Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients with Epstein-Barr Virus-Driven Post Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease after Failure of Rituximab or Rituximab and Chemotherapy (ALLELE). Blood 2021, 138, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prockop, S.; Gamelin, L.; Dinavahi, R.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, W.; Galderisi, F.; Mehta, A. Overall Survival By Best Overall Response with Tabelecleucel in Patients with Epstein-Barr Virus-Driven Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease Following Solid Organ or Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplant. Blood 2021, 138, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Y.; Zhao, S.S.; Wang, X.K.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.Y.; Fang, S.; Liu, Z.X.; Guan, L.X.; Liu, Y.C.; Ding, Y.; et al. Outcome of Rituximab-Based Treatment for Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Single-Center Experience. Ann. Transplant. 2019, 24, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagno, F.; Basso, S.; Panigari, A.; Bagnarino, J.; Stoppini, L.; Maiello, A.; Mina, T.; Zelini, P.; Perotti, C.; Baldanti, F.; et al. Management of PTLD After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Immunological Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styczynski, J.; Gil, L.; Tridello, G.; Ljungman, P.; Donnelly, J.P.; Van Der Velden, W.; Omar, H.; Martino, R.; Halkes, C.; Faraci, M.; et al. Response to Rituximab-Based Therapy and Risk Factor Analysis in Epstein Barr Virus-Related Lymphoproliferative Disorder after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant in Children and Adults: A Study from the Infectious Diseases Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Watson, C.; Garib, S.A.; Forsythe, A.; Barlev, A. Treatment Patterns for Patients with Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder Who Fail Rituximab after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Findings from a Systematic Literature Review. Blood 2018, 132, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertel, S.H.; Papp-Váry, M.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Hummel, M.W.; Jonas, S.; Riess, H.B. Salvage Chemotherapy for Refractory or Relapsed Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder in Patients after Solid Organ Transplantation with a Combination of Carboplatin and Etoposide. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 123, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappe, R.U.; Choquet, S.; Reinke, P.; Dreyling, M.; Mergenthaler, H.G.; Jäger, U.; Kebelmann-Betzing, C.; Jonas, S.; Lehmkuhl, H.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; et al. Salvage Therapy for Relapsed Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders (PTLD) with a Second Progression of PTLD after Upfront Chemotherapy: The Role of Single-Agent Rituximab. Transplantation 2007, 84, 1708–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre, T.A.; Caillard, S.; Finel, H.; Boumendil, A.; Kothari, J.; Zimmermann, H.; Trappe, R.U.; De Wilde, V.; Tholouli, E.; Kanfer, E.; et al. Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation for Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders after Solid Organ Transplantation: A Retrospective Analysis from the Lymphoma Working Party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021, 56, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, J.; Terriou, L.; Robu, D.; Willekens, C.; Hivert, B.; Pascal, L.; Guieze, R.; Trappe, R.; Baillet, C.; Huglo, D.; et al. Radioimmunotherapy ((90) Y-Ibritumomab Tiuxetan) for Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders After Prior Exposure to Rituximab. Am. J. Transpl. 2015, 15, 1976–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schecter, J.M.; Hoehn, D.; Imus, P.; Alma, E.; Lentzsch, S.; Alobeid, B.; Orjuela, M.; O’Connor, O.A.; Bhagat, G. Pathologic and Clinical Features Of CD30+ Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders: A Large Retrospective Single Institutional Study. Blood 2013, 122, 4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vase, M.O.; Maksten, E.F.; Bendix, K.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.; Andersen, C.; Moller, M.B.; Sorensen, S.S.; Jespersen, B.; Kampmann, J.; Sondergård, E.; et al. Occurrence and Prognostic Relevance of CD30 Expression in Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinch, A.; Amini, R.M.; Hollander, P.; Molin, D.; Sundström, C.; Enblad, G. CD30 Expression and Survival in Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Acta Oncol. 2020, 59, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, T.; Strate, K.; Ladigan, S.; Aigner, C.; Schlegel, U.; Tischoff, I.; Tischer-Zimmermann, S.; Eiz-Vesper, B.; Maecker-Kolhoff, B.; Schroers, R. Refractory Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-Related Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease: Cure by Combined Brentuximab Vedotin and Allogeneic EBV-Specific T-Lymphocytes. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearse, W.; Pro, B.; Gordon, L.I.; Karmali, R.; Winter, J.N.; Ma, S.; Behdad, A.; Klein, A.; Petrich, A.M.; Jovanovic, B.; et al. A Phase I/II Trial of Brentuximab Vedotin (BV) Plus Rituximab (R) As Frontline Therapy for Patients with Immunosuppression-Associated CD30+ and/or EBV+ Lymphomas. Blood 2019, 134, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaganti, S.; Maycock, S.; McIlroy, G.; Iqbal, W.A.; Mason, J.; Kanfer, E.; Kassam, S.; Cwynarski, K.; Wrench, D.; Arumainathan, A.K.; et al. Risk-Stratified Sequential Treatment with Ibrutinib and Rituximab (IR) and IR-CHOP for De-Novo Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder: Results of the Tidal Trial. Blood 2021, 138, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrine, S.P.; Hermine, O.; Small, T.; Suarez, F.; O’Reilly, R.; Boulad, F.; Fingeroth, J.; Askin, M.; Levy, A.; Mentzer, S.J.; et al. A Phase 1/2 Trial of Arginine Butyrate and Ganciclovir in Patients with Epstein-Barr Virus–Associated Lymphoid Malignancies. Blood 2007, 109, 2571–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.J.; Iempridee, T.; Wang, X.; Lee, H.C.; Mertz, J.E.; Kenney, S.C.; Lin, H.C.; Baladandayuthapani, V.; Dawson, C.W.; Shah, J.J.; et al. Lenalidomide, Thalidomide, and Pomalidomide Reactivate the Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Cycle through Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Signaling and Ikaros Expression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4901–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granato, M.; Romeo, M.A.; Tiano, M.S.; Santarelli, R.; Gonnella, R.; Gilardini Montani, M.S.; Faggioni, A.; Cirone, M. Bortezomib Promotes KHSV and EBV Lytic Cycle by Activating JNK and Autophagy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostetler, K.Y. Synthesis and Early Development of Hexadecyloxypropyl-Cidofovir: An Oral Antipoxvirus Nucleoside Phosphonate. Viruses 2010, 2, 2213–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Bowles, D.E.; Van Dyke, T.; Samulski, R.J. Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors: Potential Applications for Cancer Gene Therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2005, 12, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, E.; Ravanshad, M.; Xie, J.; Panigrahi, R.; Jubbal, S.S.; Guru, S.K.; Guangping, G.; Ziyaeyan, M.; Fingeroth, J. Serotype-Dependent Recombinant Adeno-Associated Vector (AAV) Infection of Epstein–Barr Virus-Positive B-Cells, towards Recombinant AAV-Based Therapy of Focal EBV + Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendtner, C.M.; Kofler, D.M.; Mayr, C.; Bund, D.; Hallek, M. The Potential of Gene Transfer into Primary B-CLL Cells Using Recombinant Virus Vectors. Leuk. Lymphoma 2004, 45, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janardan, S.; Horwitz, E.; Watkins, B.; Williams, K.; Chandrakasan, S.; Qayed, M.; Parikh, S.; Arnold, S.; Keller, F.; Alazraki, A.; et al. Blinatumomab Induces Complete Response in Refractory PTLD after Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, S.; Ghobadi, A.; Santos, R.D.; Schilling, J.D.; Malone, A.F.; Murad, H.; Bartlett, N.L.; Alhamad, T. CAR-T Therapy in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients with Treatment Refractory Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder. Am. J. Transplant 2021, 21, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernani, R.; Sancho, A.; Amat, P.; Hernández-Boluda, J.C.; Pérez, A.; Piñana, J.L.; Carretero, C.; Goterris, R.; Gómez, M.; Saus, A.; et al. CAR-T Therapy in Solid Transplant Recipients with Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease: Case Report and Literature Review. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2021, 69, 103304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamlouk, O.; Nair, R.; Iyer, S.P.; Edwards, A.; Neelapu, S.S.; Steiner, R.E.; Adkins, S.A.; Hawkins, M.; Saini, N.; Devashish, K.; et al. Safety of CAR T-Cell Therapy in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Blood 2021, 137, 2558–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, S.; Malone, A.; Santos, R.D.; Murad, H.; Alhamad, T. Role of CAR-T Cell Therapy in Post Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder. Available online: https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/role-of-car-t-cell-therapy-in-post-transplant-lymphoproliferative-disorder/ (accessed on 26 September 2022).
- Luttwak, E.; Hagin, D.; Perry, C.; Wolach, O.; Itchaki, G.; Amit, O.; Bar-On, Y.; Freund, T.; Kay, S.; Eshel, R.; et al. Anti-CD19 CAR-T Therapy for EBV-Negative Posttransplantation Lymphoproliferative Disease—A Single Center Case Series. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020, 56, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Wang, N.; Zhang, P.; Wang, G.; Mao, X.; Peng, D.; Kuang, D.; Chen, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, J.; et al. Case Report: Successful Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Haploidentical-Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant Patients With Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, E.; Iorio, G.C.; Bartoncini, S.; Gallio, E.; Cavallo, F.; Santoro, F.; Ricardi, U.; Levis, M. Role of Radiotherapy in Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders: Three Case Reports and Review of the Literature. Clin. Lymphoma. Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, e309–e316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evens, A.M.; Choquet, S.; Kroll-Desrosiers, A.R.; Jagadeesh, D.; Smith, S.M.; Morschhauser, F.; Leblond, V.; Roy, R.; Barton, B.; Gordon, L.I.; et al. Primary CNS Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disease (PTLD): An International Report of 84 Cases in the Modern Era. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taj, M.M.; Maecker-Kolhoff, B.; Ling, R.; Bomken, S.; Burkhardt, B.; Chiang, A.K.S.; Csoka, M.; Füreder, A.; Haouy, S.; Lazic, J.; et al. Primary Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder of the Central Nervous System: Characteristics, Management and Outcome in 25 Paediatric Patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 193, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, F.; Zhou, H.; Fan, Z.; Xuan, L.; Yu, G.; Guo, X.; Dai, M.; et al. Intrathecal Rituximab for EBV-Associated Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder with Central Nervous System Involvement Unresponsive to Intravenous Rituximab-Based Treatments: A Prospective Study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016, 51, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallam, A.; Hansen, N.; Bierman, P. Central Nervous System Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder: Response to Ibrutinib. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020, 20, e930–e933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, A.J.; Bajwa, R.; Bishnoi, R.; Skelton, W.P.; Patel, N.; Slayton, W.B.; Dang, N.H.; Bobillo, S.; Abrisqueta, P.; Sánchez-González, B.; et al. Post-Transplant Monomorphic Burkitt’s Lymphoma: Clinical Characteristics and Outcome of a Multicenter Series. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 349–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.Z.; Stenzel, T.T.; Bennett, E.R.; Lagoo, A.S.; Dunphy, C.H.; Moore, J.O.; Rizzieri, D.A.; Tepperberg, J.H.; Papenhausen, P.; Buckley, P.J. Burkitt Lymphoma Arising in Organ Transplant Recipients: A Clinicopathologic Study of Five Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2003, 27, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xicoy, B.; Ribera, J.-M.; Esteve, J.; Brunet, S.; Sanz, M.-A.; Fernández-Abellán, P.; Feliu, E. Post-Transplant Burkit t’s Leukemia or Lymphoma. Study of Five Cases Treated with Specific Intensive Therapy (PETHEMA ALL-3/97 Trial). Leuk. Lymphoma 2003, 44, 1541–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, H.; Reinke, P.; Neuhaus, R.; Lehmkuhl, H.; Oertel, S.; Atta, J.; Planker, M.; Gärtner, B.; Lenze, D.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; et al. Burkitt Post-Transplantation Lymphoma in Adult Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Cancer 2012, 118, 4715–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierickx, D.; Tousseyn, T.; Gheysens, O. How I Treat Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Blood 2015, 126, 2274–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trappe, R.; Zimmermann, H.; Fink, S.; Reinke, P.; Dreyling, M.; Pascher, A.; Lehmkuhl, H.; Gärtner, B.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Riess, H. Plasmacytoma-like Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder, a Rare Subtype of Monomorphic B-Cell Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferation, Is Associated with a Favorable Outcome in Localized as Well as in Advanced Disease: A Prospective Analysis of 8 Cases. Haematologica 2011, 96, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuturi, M.; Shah, N.; Frank, D.; Fasan, O.; Reshef, R.; Ahya, V.N.; Bromberg, M.; Faust, T.; Goral, S.; Schuster, S.J.; et al. Plasmacytic Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder: A Case Series of Nine Patients. Transpl. Int. 2013, 26, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, D.; Dower, J.; Comenzo, R.L.; Varga, C. Evaluating Daratumumab in the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma: Safety, Efficacy and Place in Therapy. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 7891–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulagain, C.P.; Diacovo, J.M.; Elson, L.; Comenzo, R.L.; Samaras, C.; Anwer, F.; Khouri, J.; Landau, H.; Valent, J. Daratumumab-Based Regimen in Treating Clonal Plasma Cell Neoplasms in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Clin. Lymphoma. Myeloma Leuk. 2020, 20, e137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman-Neill, R.J.; Soderquist, C.R.; Montanari, F.; Raciti, P.; Park, D.; Radeski, D.; Mansukhani, M.M.; Murty, V.V.; Hsiao, S.; Alobeid, B.; et al. Phenogenomic Heterogeneity of Post-Transplant Plasmablastic Lymphomas. Haematologica 2022, 107, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, H.; Oschlies, I.; Fink, S.; Pott, C.; Neumayer, H.H.; Lehmkuhl, H.; Hauser, I.A.; Dreyling, M.; Kneba, M.; Gärtner, B.; et al. Plasmablastic Posttransplant Lymphoma: Cytogenetic Aberrations and Lack of Epstein-Barr Virus Association Linked with Poor Outcome in the Prospective German Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder Registry. Transplantation 2012, 93, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, A.S.; Klein, A.K.; Ruthazer, R.; Evens, A.M. Hodgkin Lymphoma Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder: A Comparative Analysis of Clinical Characteristics, Prognosis, and Survival. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbins, R.J.; Mabilangan, C.; Rojas-Vasquez, M.; Lai, R.L.; Zhu, J.; Preiksaitis, J.P.; Peters, A.C. Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders (PTLD) Are Often Preceded by Discordant PTLD Subtypes. Leuk. Lymphoma 2020, 61, 3319–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumata, H.; Nakanishi, C.; Murakami, K.; Miyagi, S.; Fukuhara, N.; Carreras, J.; Nakamura, N.; Ichinohasama, R.; Unno, M.; Kamei, T.; et al. Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma-Type and Monomorphic-Type Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder Following Liver Transplantation: A Case Report. Surg. Case Rep. 2018, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgkin Lymphoma-Like Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder (HL-Like PTLD) Simulates Monomorphic B-Cell PTLD Both Clinically and Pathologically. The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/ajsp/Abstract/2006/04000/Hodgkin_Lymphoma_Like_Posttransplant.7.aspx (accessed on 23 November 2022).
| Pathologic Subtype of PTLD | Location | LN Architecture | Latency from Transplant | Clonality | Further Histologic Subclassification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Non-destructive forms i. Plasmacytic hyperplasia ii. Infectious Mononucleosis-like PTLD iii. Florid follicular hyperplasia | Nodal | Preserved | Almost all cases early onset | Polyclonal | |
| 2. Polymorphic PTLD | Nodal and Extranodal | Destructed | Typically early onset | Polyclonal | |
| 3. Monomorphic PTLD | Nodal and Extranodal | Destructed | Both early and late onset | Monoclonal | Per WHO criteria for NHL (most common type is DLBCL) |
| 4. Classic Hodgkin lymphoma like-PTLD | Nodal and Extranodal | Destructed | Both early and late onset | Monoclonal | Per WHO criteria for HL |
| Post-SOT | Post-alloHSCT |
|---|---|
| Strong Evidence: | Strong Evidence: |
| 1. Type of Graft: | 1. High degree of HLA mismatch |
| Intestinal > Lung > Heart > others | HLA-mismatched or unrelated donor |
| Multivisceral grafts or graft from deceased donors | Haploidentical donor |
| 2. EBV Seronegative/naive EBV recipient pre-SOT | Umbilical cord blood graft use |
| 3. High intensity IST | 2. Type of conditioning regimen |
| 4. Anti-thymocyte globulin use as part of induction IST | T-cell-depleting strategies (in vivo and ex vivo) |
| Weak Evidence: | Anti-thymocyte globulin use |
| a. Non-white ethnicity | Non-myeloablative conditioning regimens |
| b. Young recipient and old donor age | 3. Recipient old age > 50 years |
| c. Non-EBV infection | Weak Evidence: |
| d. Recipient HLA-A26 and B38 status | a. Acute GVHD |
| b. History of splenectomy | |
| c. Diagnosis of Aplastic Anemia | |
| d. Non-EBV infection |
| NCT Number (Name) | Phase | N | Study Population & Type of Disease | Therapeutic Regimen | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT01458548 (PTLD-1 trial) [91] | II | 70 | Newly diagnosed CD20+ PTLD | R induction, followed by CHOP consolidation | ▪ R induction: ORR 60%, CR 20% ▪ CHOP consolidation: ORR 90%, CR 68% ▪ 3 and 5-yr OS: 65% and 57% ▪ mPFS 4 mo, mOS 6.6 years ▪ CHOP-TRM 11% |
| NCT00590447 (PTLD-1/3) [93,94] | II | 152 | Newly diagnosed CD20+ PTLD | R-induction followed by response assessment to determine consolidation: (response adapted strategy) ▪ CR to R-induction: repeat R ▪ less than CR to R-induction: R-CHOP | ▪ R-induction: CR 25% ▪ R-CHOP consolidation: ORR 85%, CR 60% ▪ Entire cohort: final ORR 88%, CR 70% ▪ 3-yr TTP 78%, mOS 6.6 years ▪ TRM 7% |
| NCT02042391 (PTLD-2 trial) [95] | II | 48 | Newly diagnosed CD20+ PTLD | R-induction followed by response assessment to determine consolidation: (response adapted strategy) ▪ Low risk (CR or PR w/ IPI 0–2) group: repeat R, n = 21 ▪ High risk (PR w/ IPI 3–5 or SD or PD but not heart or lung recipient) group: R-CHOP, n = 22 ▪ Very high risk (heart, lung or multiorgan recipients with PD) group: alternating R-CHOP and R-DHAOx, n = 5 | ▪ R-induction: ORR 45%, CR 9% ▪ Entire cohort outcomes at final staging: ORR 94%, 2-yr OS 68%, mPFS 3.8 yrs, 2-yr PFS 56%, 2-yr TTP 78%, TRM 7% ▪ Outcomes by group at final staging: - Low risk: ORR 95%, 2-yr EFS 66%, 2 & 3-yr both TTP & PFS 85%, 2 & 3-yr OS 100%, no TRM - High risk: ORR 100%, 2- and 3-yr TTP 81%, 2 & 3-yr PFS 54%, 2 & 3-yr OS 59%, Grade 3/4 toxicity 50%, TRM 8% - Very high risk: ORR 60%, CR 40%, 2-yr TTP 33%, 2-yr PFS 11%, mOS 7.4 m, 2-yr OS 30%, grade 3/4 toxicity 63%, TRM 25% |
| NCT01498484 NCT00002663 [97] | II | 46 | EBV (+) PTLD patients who have failed frontline R -n = 33 post alloHSCT -n = 12 post SOT | EBV-specific T cells CTLs from normal HLA-compatible or partially-matched third-party donor | ▪ >PR: 68% (alloHSCT), 54% (SOT) ▪ 1-yr OS for pts who responded (CR/PR) to cycle 1: 88.9% ▪ 1-yr OS for pts with SD post cycle 1: 81.8% ▪ PD: 5 patients, 3/5 responded to CTLs from other donors and achieved CR or durable PR, 1-yr OS 100% ▪ Maximum response: after a median of 2 cycles ▪ No significant toxicity |
| NCT03394365 (ALLELE) [98,99] | III | 66 | EBV(+) PTLD patients who have failed frontline R and chemotherapy -n = 14 post alloHSCT -n = 24 post SOT | Tabelecleucel after R or R + chemotherapy failure in post-SOT and post-alloHSCT patients |
Interim results of 38 patients (May 2021): ▪ ORR: 50% (50% post-SOT and 50% post-HSCT) ▪ CR: n = 5 post-SOT, n = 5 post-HSCT ▪ Overall mTTR 1.1 mo ▪ 11/19 responders had DOR >6 mo, and mDOR was NR ▪ mOS: 18.4 mo (entire cohort), 16.4 mo for post-SOT, and NR for post-HSCT patients. ▪ 1-yr OS: 61.1% (entire cohort), 57.4% for post-SOT, and 66.8% post HSCT patients. ▪ Responders had longer OS vs. non-responders: mOS: NR vs 5,7 mo, 1-yr OS 89.2% vs 32.4% ▪ Serious TEAEs: 62.5% post-SOT and 57.1% post-HSCT; Fatal TEAEs: 16.7% post-SOT and 7.1% post-HSCT, none from study treatment. |
| NCT04337827 | II | 62 | Newly Diagnosed B-cell PTLD | Rituximab and Acalabrutinib | Ongoing, no available results |
| NCT02900976 | II | 18 | Newly Diagnosed B-cell PTLD | Rituximab and Allogeneic LMP1/LMP2-Specific Cytotoxic T-Lymphocytes | Ongoing, no available results |
| NCT03131934 | I | 18 | EBV(+) PTLD post-SOT | Tacrolimus-Resistant EBV CTLs | Ongoing, no available results |
| NCT04989491 (REPLY) | IV | 120 | EBV(-) recipients who receive EBV(+) kidney allograft | Single dose of R (375 mg/m2) for prevention of PTLD | Ongoing, no available results |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markouli, M.; Ullah, F.; Omar, N.; Apostolopoulou, A.; Dhillon, P.; Diamantopoulos, P.; Dower, J.; Gurnari, C.; Ahmed, S.; Dima, D. Recent Advances in Adult Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder. Cancers 2022, 14, 5949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235949
Markouli M, Ullah F, Omar N, Apostolopoulou A, Dhillon P, Diamantopoulos P, Dower J, Gurnari C, Ahmed S, Dima D. Recent Advances in Adult Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder. Cancers. 2022; 14(23):5949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235949
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkouli, Mariam, Fauzia Ullah, Najiullah Omar, Anna Apostolopoulou, Puneet Dhillon, Panagiotis Diamantopoulos, Joshua Dower, Carmelo Gurnari, Sairah Ahmed, and Danai Dima. 2022. "Recent Advances in Adult Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder" Cancers 14, no. 23: 5949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235949
APA StyleMarkouli, M., Ullah, F., Omar, N., Apostolopoulou, A., Dhillon, P., Diamantopoulos, P., Dower, J., Gurnari, C., Ahmed, S., & Dima, D. (2022). Recent Advances in Adult Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder. Cancers, 14(23), 5949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235949





