Copy Number Alteration and Mutational Profile of High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 Rearrangements, Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC-Rearrangement, and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC-Cluster Amplification
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Selection
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
2.4. Whole-Genome Copy Number Analysis
2.5. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Pathological Features
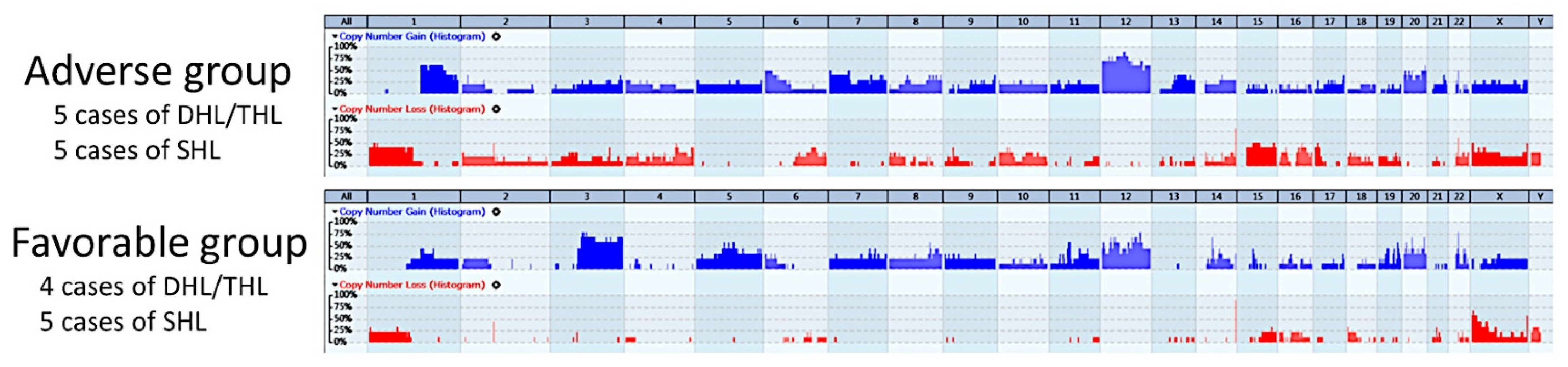
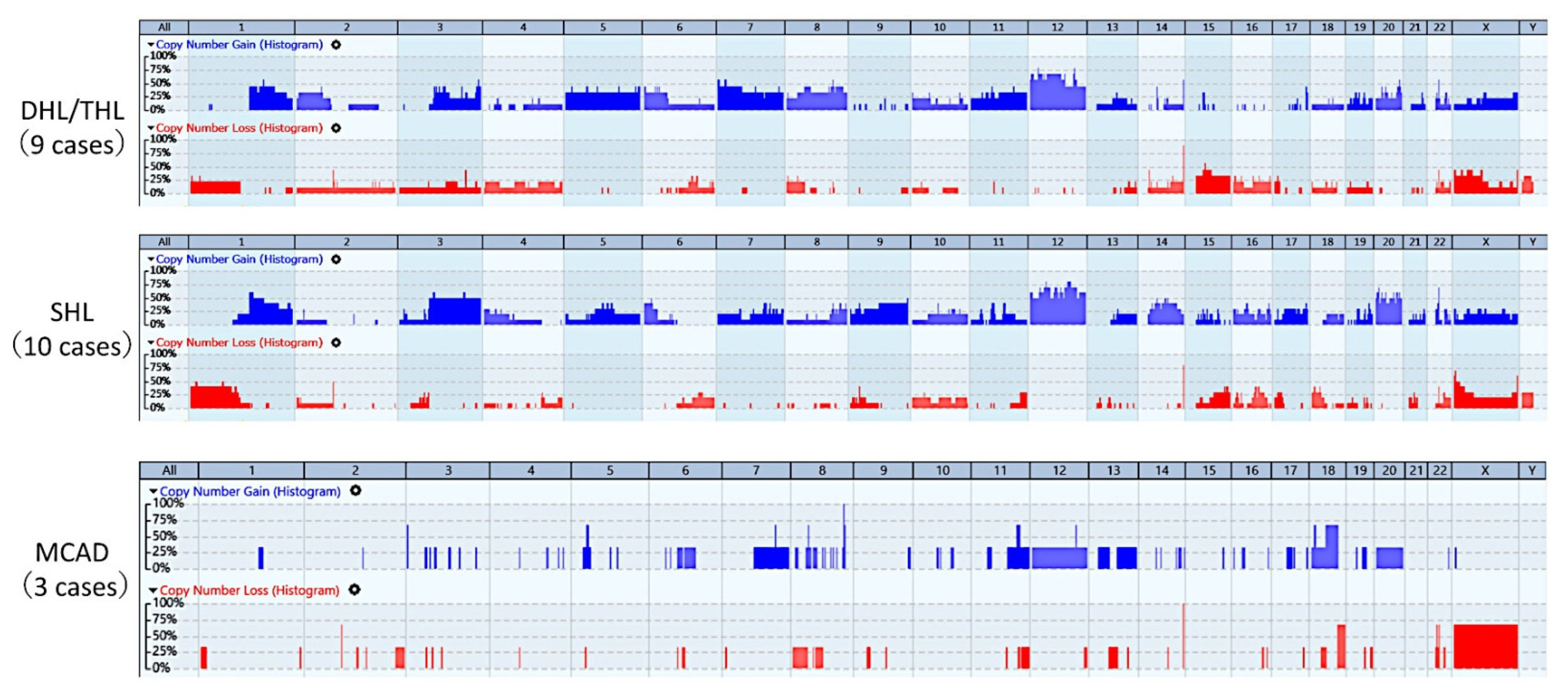
3.2. Whole-Genome Copy Number Profiles
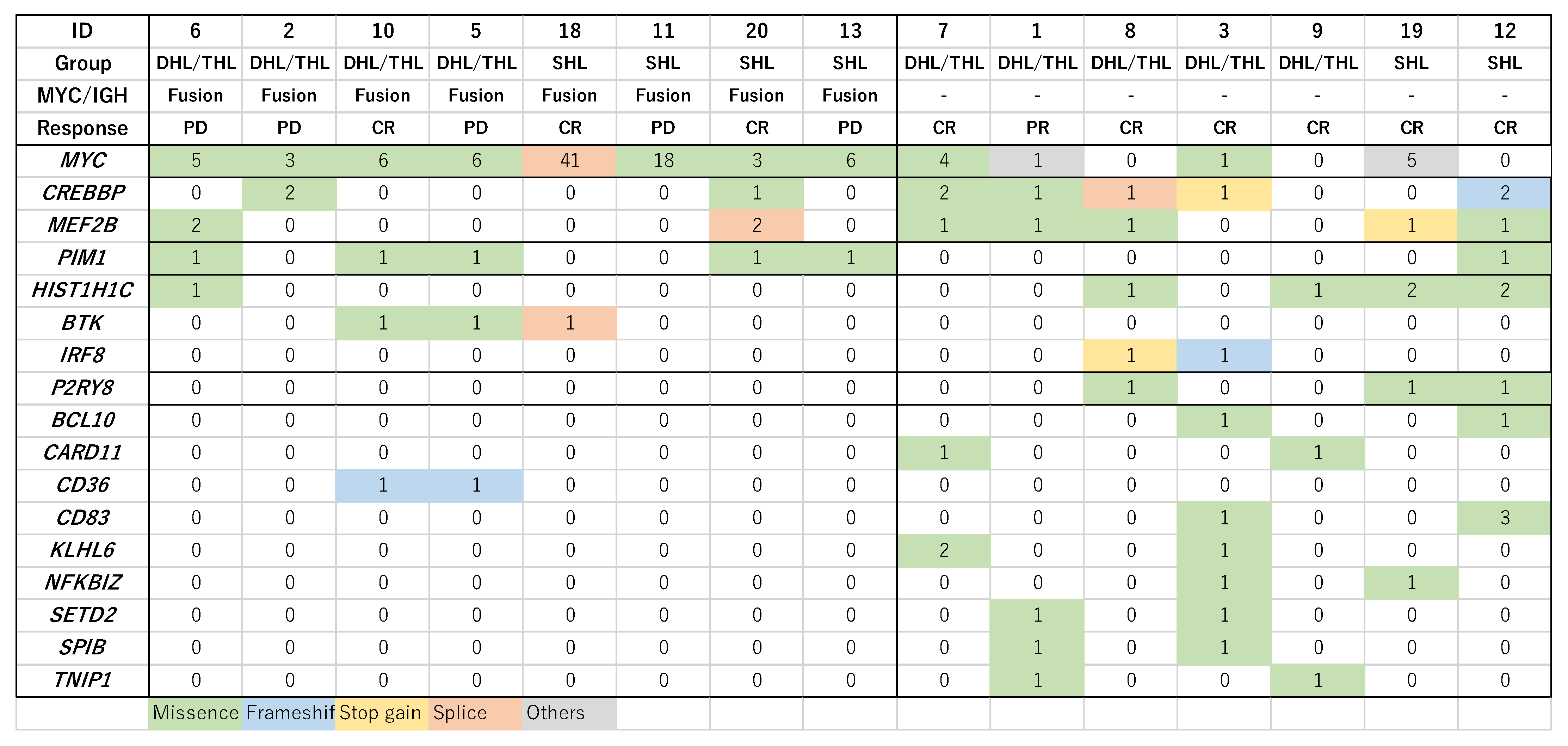
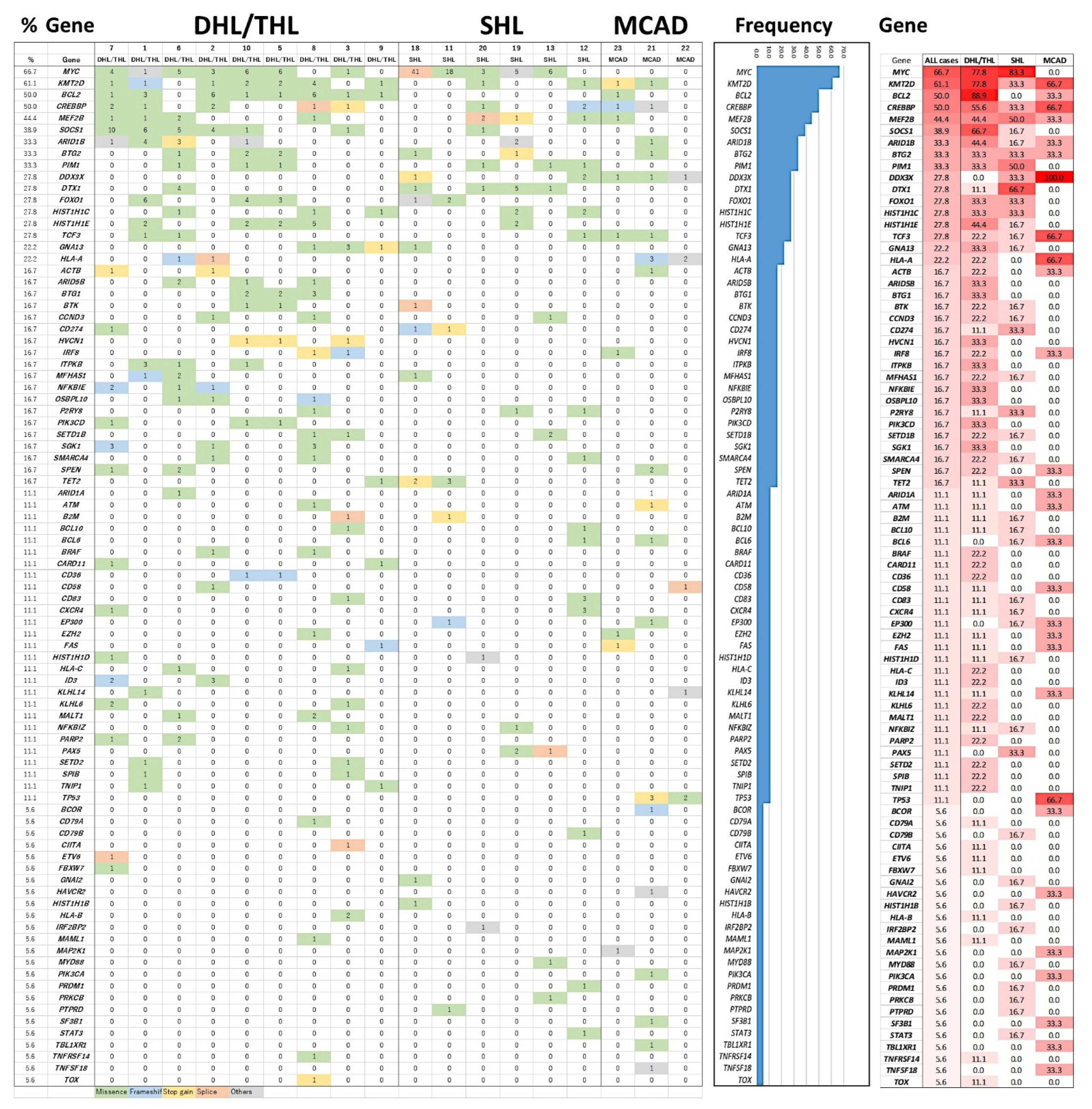
3.3. Mutational Profile with Targeted NGS
3.4. Combining Copy Number Alterations (CNA) and NGS Mutational Profiling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Id. | Subtype | Age | Gender | LDH | Stage | PS | BM | IPI | Therapy | Response to 1st Chemotherapy | OS | D/A | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DHL/THL | 69 | F | + | 4 | 0 | − | High | R-CHOP | Partial response | 69 | Dead | Adverse |
| 2 | DHL/THL | 63 | F | + | 4 | 2 | + | High | R-Hyper-CVAD | Progressive disease | 4 | Dead | Adverse |
| 3 | DHL/THL | 67 | M | + | 4 | 4 | − | High | R-COP | Relapse after 1st CR | 13 | Dead | Adverse |
| 4 | DHL/THL | 78 | M | − | 2 | 0 | − | Low | R-CHOP | Relapse after 1st CR | 55 | Dead | Adverse |
| 5 | DHL/THL | 55 | F | + | 4 | 0 | − | Low-intermediate | R-Hyper-CVAD | Progressive disease | 27 | Dead | Adverse |
| 6 | DHL/THL | 73 | F | + | 2 | 0 | − | Low-intermediate | DA-EPOCH-R | Progressive disease | 8 | Dead | Adverse |
| 7 | DHL/THL | 49 | F | No data | 2 | 0 | − | Low | R-CHOP | Complete response | 127 | Alive | Favorable |
| 8 | DHL/THL | 66 | M | + | 2 | 0 | − | Low-intermediate | R-CHOP | Complete response | 126 | Alive | Favorable |
| 9 | DHL/THL | 61 | F | + | 4 | 0 | − | High | R-CHP | Complete response | 97 | Alive | Favorable |
| 10 | DHL/THL | 57 | M | No data | 4 | 0 | + | Low | R-CHOP→DA-R-EPOCH | Complete response | 33 | Alive | Favorable |
| 11 | SHL | 67 | F | + | 2 | 0 | − | Low-intermediate | R-CHOP | Progressive disease | 10 | Dead | Adverse |
| 12 | SHL | 83 | F | + | 3 | 1 | − | High-intermediate | R-COP | Relapse after 1st CR | 23 | Dead | Adverse |
| 13 | SHL | 68 | M | + | 4 | 0 | + | High-intermediate | R-CHOP | Progressive disease | 32 | Dead | Adverse |
| 14 | SHL | 53 | M | + | 2 | 0 | − | Low-intermediate | R-CHO | Relapse after 1st PR | 12 | Dead | Adverse |
| 15 | SHL | 66 | F | + | 4 | 0 | + | High | DA-EPOCH-R | Progressive disease | 6 | Dead | Adverse |
| 16 | SHL | 62 | M | + | 2 | 0 | − | Low-intermediate | R-CHOP | Complete response | 167 | Alive | Favorable |
| 17 | SHL | 62 | M | − | 1 | 0 | − | Low | R-CHOP | Complete response | 109 | Alive | Favorable |
| 18 | SHL | 76 | M | + | 2 | 1 | No data | Low | R-CHOP | Complete response | 88 | Alive | Favorable |
| 19 | SHL | 58 | F | − | 3 | 0 | − | Low-intermediate | R-CHOP | Complete response | 105 | Alive | Favorable |
| 20 | SHL | 41 | F | − | 2 | 0 | − | Low | R-CHOP | Complete response | 99 | Alive | Favorable |
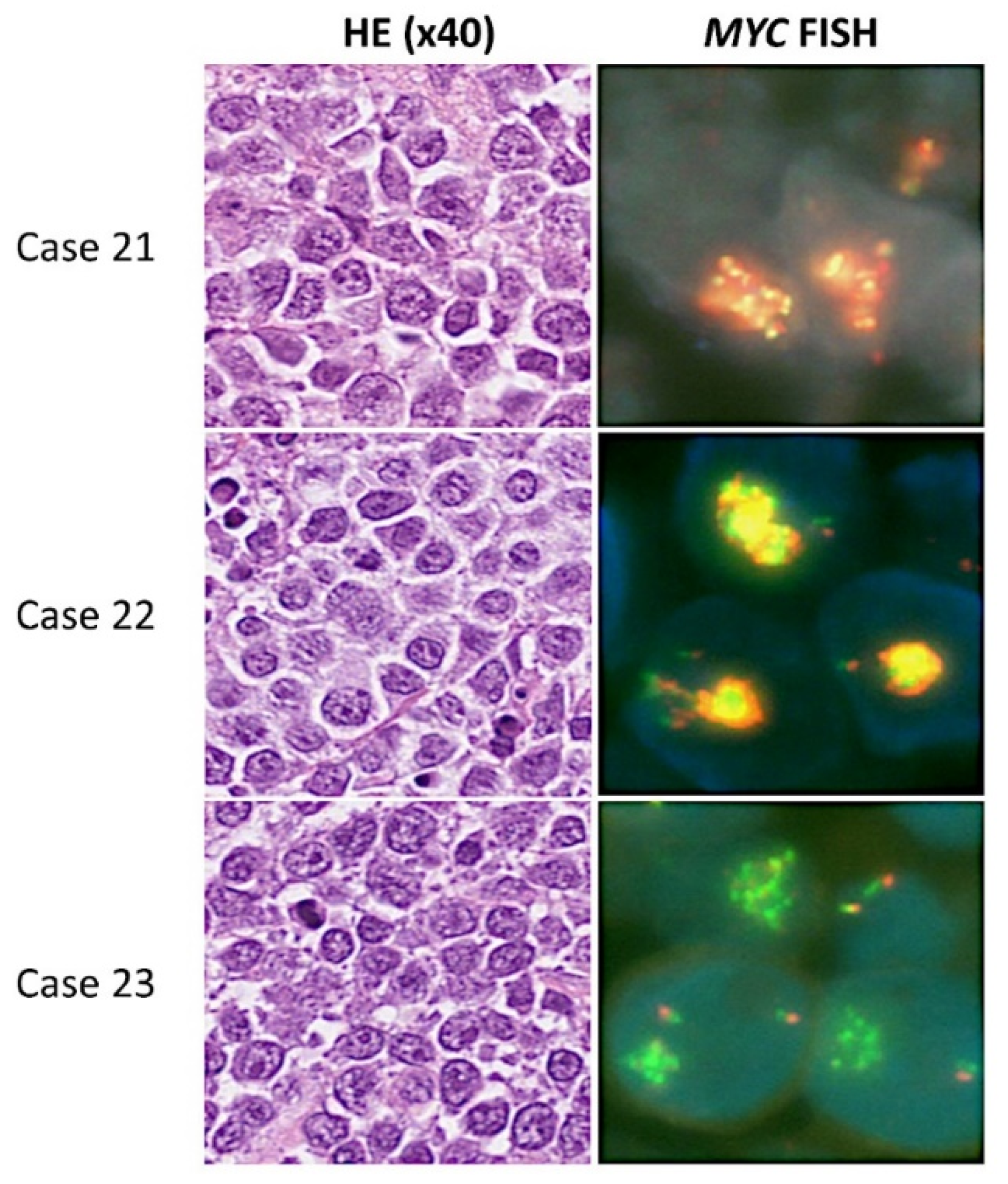
| 21 | MCAD | 51 | M | + | 3 | 1 | − | Low-intermediate | EPOCH-R | Partial response | 50 | Alive | N/A |
| 22 | MCAD | 72 | M | + | 4 | 1 | − | High | R-CHOP | Progressive disease | 6 | Dead | N/A |
| 23 | MCAD | 70 | M | + | 4 | 2 | − | High | MTX+R-CHOP | Partial response | 14 | Alive | N/A |
| Id. | Subtype | MYC F | MYC/IGH F | BCL2 F | BCL6 F | COO | MYC (%) | MIB-1 (%) | CD3 | CD5 | CD10 | CD20 | BCL2 | BCL6 | MUM1 | CNA | NGS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DHL/THL | + | − | + | − | non-GCB | 70 | 50 | − | − | − | + | + | − | − | + | + |
| 2 | DHL/THL | + | + | + | + | GCB | 90 | 60 | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| 3 | DHL/THL | + | − | + | No signal | non-GCB | 90 | 70 | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 4 | DHL/THL | + | − | − | + | non-GCB | 30 | 80 | − | − | − | + | − | − | + | + | No data |
| 5 | DHL/THL | + | + | + | + | GCB | 90 | 80 | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| 6 | DHL/THL | + | + | − | + | non-GCB | 10 | 90 | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | No data | + |
| 7 | DHL/THL | + | − | + | − | GCB | 70 | 80 | − | − | + | + | − | + | − | + | + |
| 8 | DHL/THL | + | − | + | − | GCB | 80 | 80 | − | − | + | + | − | + | − | + | + |
| 9 | DHL/THL | + | − | + | + | GCB | 80 | 70 | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| 10 | DHL/THL | + | + | + | + | GCB | 80 | 80 | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| 11 | SHL | + | + | − | − | GCB | 100 | 90 | − | − | + | + | − | + | − | + | + |
| 12 | SHL | + | − | − | − | non-GCB | 80 | 90 | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 13 | SHL | + | + | − | − | non-GCB | 60 | 70 | − | − | − | + | + | − | + | + | + |
| 14 | SHL | + | + | − | − | non-GCB | 80 | 90 | − | − | − | + | + | − | + | + | No data |
| 15 | SHL | + | + | − | − | GCB | 80 | 90 | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | No data |
| 16 | SHL | + | + | − | − | GCB | 90 | 80 | − | − | + | + | − | − | − | + | No data |
| 17 | SHL | + | − | − | − | non-GCB | 50 | 100 | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | No data |
| 18 | SHL | + | + | − | − | GCB | 90 | 90 | − | − | − | + | − | + | − | + | + |
| 19 | SHL | + | − | − | − | GCB | 60 | 90 | − | − | + | + | − | + | − | + | + |
| 20 | SHL | + | + | − | − | GCB | 50 | 80 | − | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | + |
| 21 | MCAD | − | No data | − | − | GCB | 90 | 90 | − | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | + |
| 22 | MCAD | − | No data | − | − | GCB | 80 | 90 | − | − | + | + | − | + | − | + | + |
| 23 | MCAD | − | No data | + | − | GCB | 80 | 80 | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + |
Appendix B. Immunohistochemical Procedures
Appendix C. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Procedures
Appendix D. Whole-Genome Copy Number Analysis Using OncoScan Platform
Appendix E. List of Genes in the custom NGS Panel
| ACTB | ARID1A | ARID1B | ARID5B | ATM | B2M | BCL10 | BCL2 | BCL6 | BCOR |
| BRAF | BTG1 | BTG2 | BTK | CARD11 | CCND3 | CD274 | CD36 | CD58 | CD70 |
| CD79A | CD79B | CD83 | CDKN2A | CDKN2B | CIITA | CREBBP | CXCR4 | DDX3X | DIS3 |
| DTX1 | EBF1 | EP300 | ETS1 | ETV6 | EZH2 | FAS | FBXW7 | FOXO1 | GNA13 |
| GNAI2 | HIST1H1B | HIST1H1C | HIST1H1D | HIST1H1E | HLA-A | HLA-B | HLA-C | HVCN1 | ID3 |
| IRF2BP2 | IRF4 | IRF8 | ITPKB | KLHL14 | KLHL6 | KMT2D | KRAS | MALT1 | MAML1 |
| MAP2K1 | MAPK1 | MCL1 | MEF2B | MFHAS1 | MIR17*92 | MYC | MYD88 | NFKBIA | NFKBIE |
| NFKBIZ | NOTCH1 | NOTCH2 | NRAS | OSBPL10 | P2RY8 | PARP2 | PAX5 | PCBP1 | PIK3CA |
| PIK3CD | PIM1 | POU2F2 | PRDM1 | PRKCB | PTEN | PTPRD | REL | RHOA | RRAGC |
| S1PR1 | S1PR2 | SETD1B | SETD2 | SF3B1 | SGK1 | SMARCA4 | SOCS1 | SPEN | SPIB |
| STAT3 | STAT6 | TBL1XR1 | TCF3 | TET2 | TMEM30A | TMSB4X | TNFAIP3 | TNFRSF14 | TNIP1 |
| TOX | TP53 | XBP1 | XPO1 | ZEB2 |
Appendix F
Appendix G
Appendix H
References
- Kanungo, A.; Medeiros, L.J.; Abruzzo, L.V.; Lin, P. Lymphoid neoplasms associated with concurrent t(14;18) and 8q24/c-MYC translocation generally have a poor prognosis. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Desai, P.; Lin, P.; Yin, C.C.; Tang, G.; Wang, X.J.; Konoplev, S.N.; Khoury, J.D.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Medeiros, L.J. MYC/BCL6 double-hit lymphoma (DHL): A tumour associated with an aggressive clinical course and poor prognosis. Histopathology 2016, 68, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, N.; Tokunaka, M.; Nakamura, N.; Takeuchi, K.; Koike, J.; Motomura, S.; Miyamoto, K.; Kikuchi, A.; Hyo, R.; Yakushijin, Y.; et al. Clinicopathological features of lymphoma/leukemia patients carrying both BCL2 and MYC translocations. Haematologica 2009, 94, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, N.A.; Slack, G.W.; Savage, K.J.; Connors, J.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Rogic, S.; Scott, D.W.; Tan, K.L.; Steidl, C.; Sehn, L.H.; et al. Concurrent Expression of MYC and BCL2 in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated With Rituximab Plus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, and Prednisone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3452–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. High-grade B-cell lymphoma. In WHO Classification of Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, revised 4th ed.; International Agency for Research Cancer Press: Lyon, France, 2017; pp. 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Ennishi, D.; Jiang, A.; Boyle, M.; Collinge, B.; Grande, B.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Rushton, C.; Tang, J.; Thomas, N.; Slack, G.W.; et al. Double-Hit Gene Expression Signature Defines a Distinct Subgroup of Germinal Center B-Cell-Like Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaoka, M.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Carreras, J.; Ikoma, H.; Hiraiwa, S.; Ichiki, A.; Kojima, M.; Ando, K.; Yokose, T.; Sakai, R.; et al. Clinicopathological and genomic analysis of double-hit follicular lymphoma: Comparison with high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenwald, A.; Bens, S.; Advani, R.; Barrans, S.; Copie-Bergman, C.; Elsensohn, M.-H.; Natkunam, Y.; Calaminici, M.; Sander, B.; Baia, M.; et al. Prognostic Significance of MYC Rearrangement and Translocation Partner in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Study by the Lunenburg Lymphoma Biomarker Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3359–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aukema, S.M.; Kreuz, M.; Kohler, C.W.; Rosolowski, M.; Hasenclever, D.; Hummel, M.; Küppers, R.; Lenze, D.; Ott, G.; Pott, C.; et al. Biological characterization of adult MYC-translocation-positive mature B-cell lymphomas other than molecular Burkitt lymphoma. Haematologica 2014, 99, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copie-Bergman, C.; Cuillière-Dartigues, P.; Baia, M.; Briere, J.; Delarue, R.; Canioni, D.; Salles, G.; Parrens, M.; Belhadj, K.; Fabiani, B.; et al. MYC-IG rearrangements are negative predictors of survival in DLBCL patients treated with immunochemotherapy: A GELA/LYSA study. Blood 2015, 126, 2466–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhail, E.D.; Maurer, M.J.; Macon, W.R.; Feldman, A.L.; Kurtin, P.J.; Ketterling, R.P.; Vaidya, R.; Cerhan, J.R.; Ansell, S.M.; Porrata, L.F.; et al. Inferior survival in high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements is not associated with MYC/IG gene rearrangements. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.A.; Savage, K.J.; Ludkovski, O.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Woods, R.; Steidl, C.; Dyer, M.J.S.; Siebert, R.; Kuruvilla, J.; Klasa, R.; et al. Lymphomas with concurrent BCL2 and MYC translocations: The critical factors associated with survival. Blood 2009, 114, 2273–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, M.; Gang, A.O.; Poulsen, T.S.; Knudsen, H.; Lauritzen, A.F.; Nielsen, S.L.; Klausen, T.W.; Nørgaard, P. MYC translocation partner gene determines survival of patients with large B-cell lymphoma with MYC- or double-hit MYC/BCL2 translocations. Eur. J. Haematol. 2014, 92, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Saksena, A.; Desai, P.; Xu, J.; Zuo, Z.; Lin, P.; Tang, G.; Yin, C.C.; Seegmiller, A.; Jorgensen, J.L.; et al. Prognostic impact of history of follicular lymphoma, induction regimen and stem cell transplant in patients with MYC/BCL2 double hit lymphoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 38122–38132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaoka, M.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Carreras, J.; Itou, A.; Ikoma, H.; Tomita, S.; Shiraiwa, S.; Ando, K.; Nakamura, N. AID is a poor prognostic marker of high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements. Pathol. Int. 2021; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Evrard, S.M.; Péricart, S.; Grand, D.; Amara, N.; Escudié, F.; Gilhodes, J.; Bories, P.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Dubois, R.; Pierre Brousset, P.; et al. Targeted next generation sequencing reveals high mutation frequency of CREBBP, BCL2 and KMT2D in high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements. Haematologica 2019, 104, e154–e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Arniani, S.; Crescenzi, B.; Ascani, S.; Flenghi, L.; Pierini, V.; Moretti, M.; Beacci, D.; Romoli, S.; Bardelli, V.; et al. High grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC, BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements: Unraveling the genetic landscape of a rare aggressive subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Künstner, A.; Witte, H.M.; Riedl, J.; Bernard, V.; Stölting, S.; Merz, H.; Olschewski, V.; Peter, W.; Ketzer, J.; Busch, Y.; et al. Mutational landscape of high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC-, BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements characterized by whole-exome sequencing. Haematologica, 2021; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, C.; Barrans, S.; Cucco, F.; Bentley, M.A.; Care, M.A.; Cummin, T.; Kennedy, H.; Thompson, J.S.; Uddin, R.; Worrillow, L.; et al. Molecular High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma: Defining a Poor-Risk Group That Requires Different Approaches to Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.W.; King, R.L.; Staiger, A.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Jiang, A.; Horn, H.; Mottok, A.; Farinha, P.; Slack, G.W.; Ennishi, D.; et al. High-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma morphology. Blood 2018, 131, 2060–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennishi, D.; Mottok, A.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Shulha, H.P.; Farinha, P.; Chan, F.C.; Meissner, B.; Boyle, M.; Hother, C.; Kridel, R.; et al. Genetic profiling of MYC and BCL2 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma determines cell-of-origin–specific clinical impact. Blood 2017, 129, 2760–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Carreras, J.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Miyaoka, M.; Kikuchi, T.; Amaki, J.; Sato, A.; Ogiya, D.; Ando, K.; Nakamura, N. A case of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with MYC gene cluster amplification related to chromothripsis. Leuk. Lymphoma. 2018, 59, 2460–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras, J.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Beà, S.; Miyaoka, M.; Hiraiwa, S.; Ikoma, H.; Nagao, R.; Tomita, S.; Martin-Garcia, D.; Salaverria, I.; et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and genomic profile of primary sinonasal tract diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) reveals gain at 1q31 and RGS1 encoding protein; high RGS1 immunohistochemical expression associates with poor overall survival in DLBCL not otherwise specified (NOS). Histopathology 2017, 70, 595–621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rivas-Delgado, A.; Nadeu, F.; Enjuanes, A.; Casanueva-Eliceiry, S.; Mozas, P.; Magnano, L.; Castrejón de Anta, N.; Rovira, J.; Dlouhy, I.; Martín, S.; et al. Mutational Landscape and Tumor Burden Assessed by Cell-free DNA in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in a Population-Based Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Molina, A.; Boss, I.W.; Canela, A.; Pan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, M.; Hu, D.; Agirre, X.; Niesvizky, I.; et al. The histone lysine methyltransferase KMT2D sustains a gene expression program that represses B cell lymphoma development. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucco, F.; Barrans, S.; Sha, C.; Clipson, A.; Crouch, S.; Dobson, R.; Chen, Z.; Thompson, J.S.; Care, M.A.; Cummin, T.; et al. Distinct genetic changes reveal evolutionary history and heterogeneous molecular grade of DLBCL with MYC/BCL2 double-hit. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; A Krupka, J.; Gao, J.; Grigoropoulos, N.F.; Giotopoulos, G.; Asby, R.; Screen, M.; Usheva, Z.; Cucco, F.; Barrans, S.; et al. Sequential inverse dysregulation of the RNA helicases DDX3X and DDX3Y facilitates MYC-driven lymphomagenesis. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 4059–4075.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouska, A.; Bi, C.; Lone, W.; Zhang, W.; Kedwaii, A.; Heavican, T.; Lachel, C.M.; Yu, J.; Ferro, R.; Eldorghamy, N.; et al. Adult high-grade B-cell lymphoma with Burkitt lymphoma signature: Genomic features and potential therapeutic targets. Blood 2017, 130, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, B.M.; Gerhard, D.S.; Jiang, A.; Griner, N.B.; Abramson, J.S.; Alexander, T.B.; Allen, H.; Ayers, L.W.; Bethony, J.M.; Bhatia, K.; et al. Genome-wide discovery of somatic coding and noncoding mutations in pediatric endemic and sporadic Burkitt lymphoma. Blood 2019, 133, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, C.; ICGC MMML-Seq Consortium; Kleinheinz, K.; Aukema, S.M.; Rohde, M.; Bernhart, S.H.; Hübschmann, D.; Wagener, R.; Toprak, U.H.; Raimondi, F.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic changes complement each other in the pathogenesis of sporadic Burkitt lymphoma. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.; Schlesner, M.; Hoffmann, S.; Kreuz, M.; Leich, E.; Burkhardt, B.; Rosolowski, M.; Ammerpohl, O.; Wagener, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; et al. Recurrent mutation of the ID3 gene in Burkitt lymphoma identified by integrated genome, exome and transcriptome sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1316–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, R.; Young, R.M.; Ceribelli, M.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, M.; Wright, G.; Shaffer, A.L.; Hodson, D.J.; Buras, E.; et al. Burkitt lymphoma pathogenesis and therapeutic targets from structural and functional genomics. Nature 2012, 490, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, J.; Secreto, C.R.; Rabe, K.G.; Van Dyke, D.L.; Kortum, K.M.; Slager, S.L.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Fonseca, R.; Kay, N.E.; Braggio, E. Identification of recurrent truncated DDX3X mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 169, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Hu, B.; Wang, F.; Yan, Y.; Kim, E.; Vitale, C.; Patel, K.P.; Strati, P.; Gumbs, C.; Little, L.; et al. Clinical implications of cancer gene mutations in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with lenalidomide. Blood 2018, 131, 1820–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Gu, Z.-H.; Yan, Z.-X.; Zhao, X.; Xie, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Pan, C.-M.; Hu, Y.; Cai, C.-P.; Dong, Y.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of DDX3X in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, H.; Xu, N.; Liang, S. A double-edged function of DDX3, as an oncogene or tumor suppressor, in cancer progression (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Rifo, R.; Rubilar, P.S.; Limousin, T.; de Breyne, S.; Décimo, D.; Ohlmann, T. DEAD-box protein DDX3 associates with eIF4F to promote translation of selected mRNAs. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 3745–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pophali, P.A.; Marinelli, L.M.; Ketterling, R.P.; Meyer, R.G.; McPhail, E.D.; Kurtin, P.J.; Mwangi, R.; Maurer, M.J.; Habermann, T.; King, R.L. High level MYC amplification in B-cell lymphomas: Is it a marker of aggressive disease? Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Schmitz, R. Molecular Subgroups of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma: Biology and Implications for Clinical Practice. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 551–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meléndez, B.; Van Campenhout, C.; Rorive, S.; Remmelink, M.; Salmon, I.; D’Haene, N. Methods of measurement for tumor mutational burden in tumor tissue. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, E.; Jaffe, E.S.; Cook, J.R.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Anderson, K.C.; Brousset, P.; Cerroni, L.; de Leval, L.; Dirnhofer, S.; et al. The International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms: A report from the Clinical Advisory Committee. Blood 2022, 140, 1229–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.D.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, J.; Yukie Kikuti, Y.; Miyaoka, M.; Hiraiwa, S.; Tomita, S.; Ikoma, H.; Kondo, Y.; Shiraiwa, S.; Ando, K.; Sato, S.; et al. Genomic Profile and Pathologic Features of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Subtype of Methotrexate-associated Lymphoproliferative Disorder in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 936–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, J.; Hamoudi, R.; Nakamura, N. Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Gene Expression Data Predicted the Prognosis of Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Tokai J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2020, 45, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Carreras, J.; Hiraiwa, S.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Miyaoka, M.; Tomita, S.; Ikoma, H.; Ito, A.; Kondo, Y.; Roncador, G.; Garcia, J.F.; et al. Artificial Neural Networks Predicted the Overall Survival and Molecular Subtypes of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Using a Pancancer Immune-Oncology Panel. Cancers 2021, 13, 6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, J.; Kikuti, Y.; Miyaoka, M.; Roncador, G.; Garcia, J.; Hiraiwa, S.; Tomita, S.; Ikoma, H.; Kondo, Y.; Ito, A.; et al. Integrative Statistics, Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Neural Network Analysis Correlated CSF1R with the Prognosis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Hemato 2021, 2, 182–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, A.; Rimsza, L. Genomics of aggressive B-cell lymphoma. Hematology 2018, 2018, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karube, K.; Enjuanes, A.; Dlouhy, I.; Jares, P.; Garcia, D.M.; Nadeu, F.; Ordóñez, G.R.; Rovira, J.; Clot, G.; Royo, C.; et al. Integrating genomic alterations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies new relevant pathways and potential therapeutic targets. Leukemia 2017, 32, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.; Zhang, J.; Davis, N.S.; Moffitt, A.; Love, C.L.; Waldrop, A.; Leppä, S.; Pasanen, A.; Meriranta, L.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.-L.; et al. Genetic and Functional Drivers of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cell 2017, 171, 481–494.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-C.; Su, Y.-C.; Bamodu, O.; Chen, B.-J.; Tsai, W.-C.; Cheng, W.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Hsieh, S.-M.; Liu, M.-L.; Fang, C.-L.; et al. High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma (HGBL) with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 Rearrangements Is Predominantly BCL6-Rearranged and BCL6-Expressing in Taiwan. Cancers 2021, 13, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, D.; Desai, A.; Yan, F.; Gong, T.; Ye, H.; Ahmed, M.; Nomie, K.; Romaguera, J.; Champlin, R.; Li, S.; et al. Challenges and Opportunities for High-grade B-Cell Lymphoma With MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 Rearrangement (Double-hit Lymphoma). Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 42, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, J.; Roncador, G.; Hamoudi, R. Artificial Intelligence Predicted Overall Survival and Classified Mature B-Cell Neoplasms Based on Immuno-Oncology and Immune Checkpoint Panels. Cancers 2022, 14, 5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, J.; Kikuti, Y.; Roncador, G.; Miyaoka, M.; Hiraiwa, S.; Tomita, S.; Ikoma, H.; Kondo, Y.; Ito, A.; Shiraiwa, S.; et al. High Expression of Caspase-8 Associated with Improved Survival in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Machine Learning and Artificial Neural Networks Analyses. BioMedInformatics 2021, 1, 18–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras, J.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Hiraiwa, S.; Miyaoka, M.; Tomita, S.; Ikoma, H.; Ito, A.; Kondo, Y.; Itoh, J.; Roncador, G.; et al. High PTX3 expression is associated with a poor prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolen, C.R.; Klanova, M.; Trneny, M.; Sehn, L.H.; He, J.; Tong, J.; Paulson, J.N.; Kim, E.; Vitolo, U.; Di Rocco, A.; et al. Prognostic impact of somatic mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and relationship to cell-of-origin: Data from the phase III GOYA study. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2298–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Function |
|---|---|
| MYC | Proto-oncogene and transcription factor that activates the transcription of growth-related genes |
| KMT2D | Histone methyltransferase with role in chromatin remodeling and DNA repair |
| BCL2 | Apoptosis regulator (suppressor) |
| CREBBP (CBP) | Acyltransferase with a role in the acetylation of histones and non-histone proteins, chromatin remodeling, and transcriptional co-activation of different transcription factors |
| MEF2B | DNA binding protein, gene expression regulator. |
| SOCS1 | Negative regulator of type I and II interferon signaling and other cytokines |
| ARID1B | Transcriptional activation and repression of select genes by chromatin remodeling, and cell cycle activation |
| BTG2 | Antiproliferative protein, regulation of B1/S transition of the cell cycle |
| PIM1 | Proto-oncogene with serine/threonine kinase activity, and involved in cell survival and cell proliferation |
| DDX3X | Multifunctional ATP-dependent RNA helicase. Role in transcriptional regulation |
| DTX1 | Ubiquitin ligase acts as a positive regulator of the Notch-signaling pathway (cell-cell communication, and cell-fate determination) |
| TCF3 | Critical role in lymphopoiesis, both B and T lymphocyte development |
| HLA-A | Antigen-presenting major histocompatibility complex class I (MHCI) molecule |
| TP53 | Tumor suppressor in many tumor cells, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, senescence, DNA repair, and metabolism changes. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyaoka, M.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Carreras, J.; Ito, A.; Ikoma, H.; Tomita, S.; Kawada, H.; Roncador, G.; Bea, S.; Campo, E.; et al. Copy Number Alteration and Mutational Profile of High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 Rearrangements, Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC-Rearrangement, and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC-Cluster Amplification. Cancers 2022, 14, 5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235849
Miyaoka M, Kikuti YY, Carreras J, Ito A, Ikoma H, Tomita S, Kawada H, Roncador G, Bea S, Campo E, et al. Copy Number Alteration and Mutational Profile of High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 Rearrangements, Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC-Rearrangement, and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC-Cluster Amplification. Cancers. 2022; 14(23):5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235849
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyaoka, Masashi, Yara Yukie Kikuti, Joaquim Carreras, Atsushi Ito, Haruka Ikoma, Sakura Tomita, Hiroshi Kawada, Giovanna Roncador, Silvia Bea, Elias Campo, and et al. 2022. "Copy Number Alteration and Mutational Profile of High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 Rearrangements, Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC-Rearrangement, and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC-Cluster Amplification" Cancers 14, no. 23: 5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235849
APA StyleMiyaoka, M., Kikuti, Y. Y., Carreras, J., Ito, A., Ikoma, H., Tomita, S., Kawada, H., Roncador, G., Bea, S., Campo, E., & Nakamura, N. (2022). Copy Number Alteration and Mutational Profile of High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 Rearrangements, Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC-Rearrangement, and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC-Cluster Amplification. Cancers, 14(23), 5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235849







