Screening for Biomarkers for Progression from Oral Leukoplakia to Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Evaluation of Diagnostic Efficacy by Multiple Machine Learning Algorithms
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2. Publicly Available Data Collection and Processing
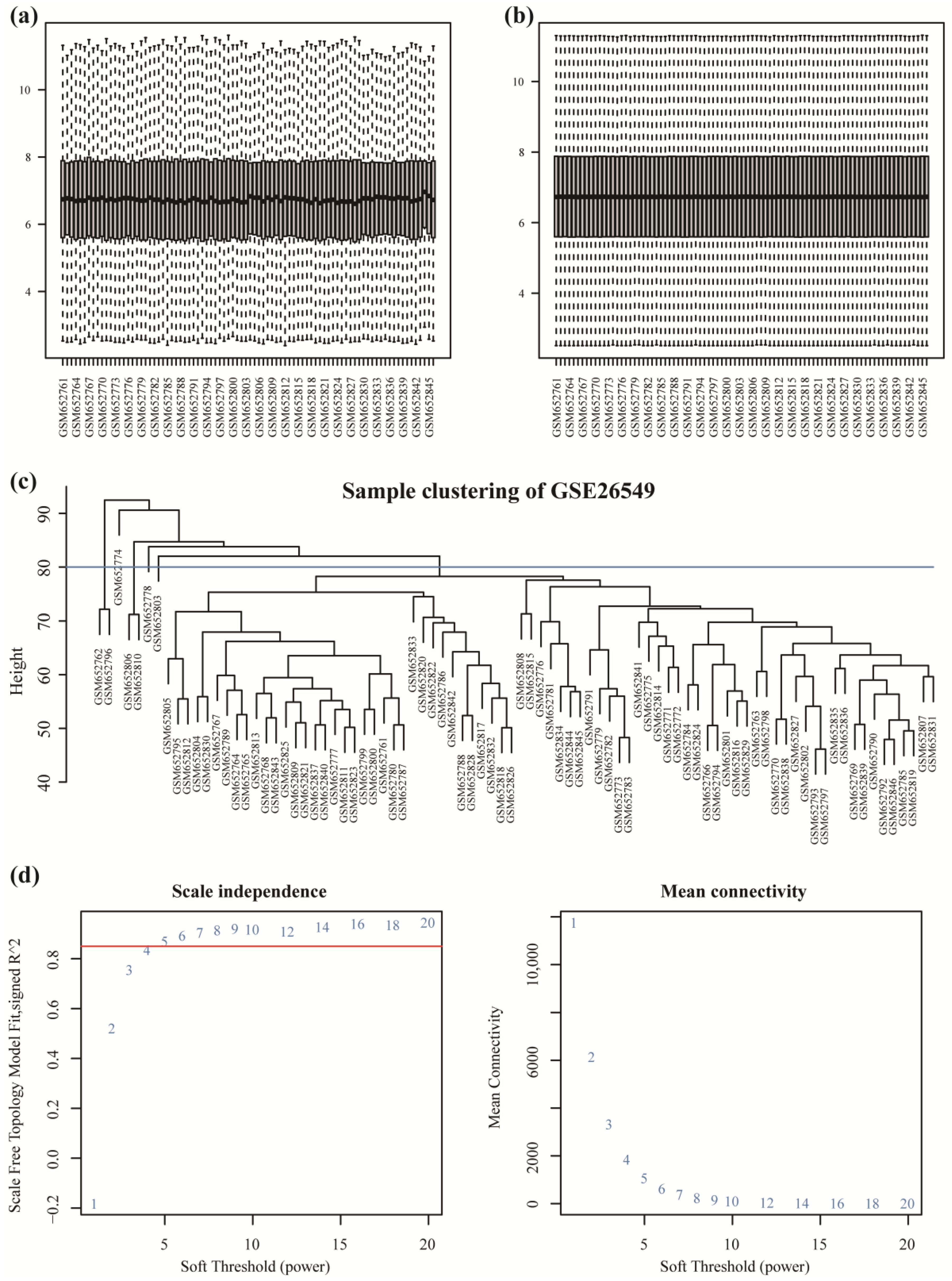
2.3. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
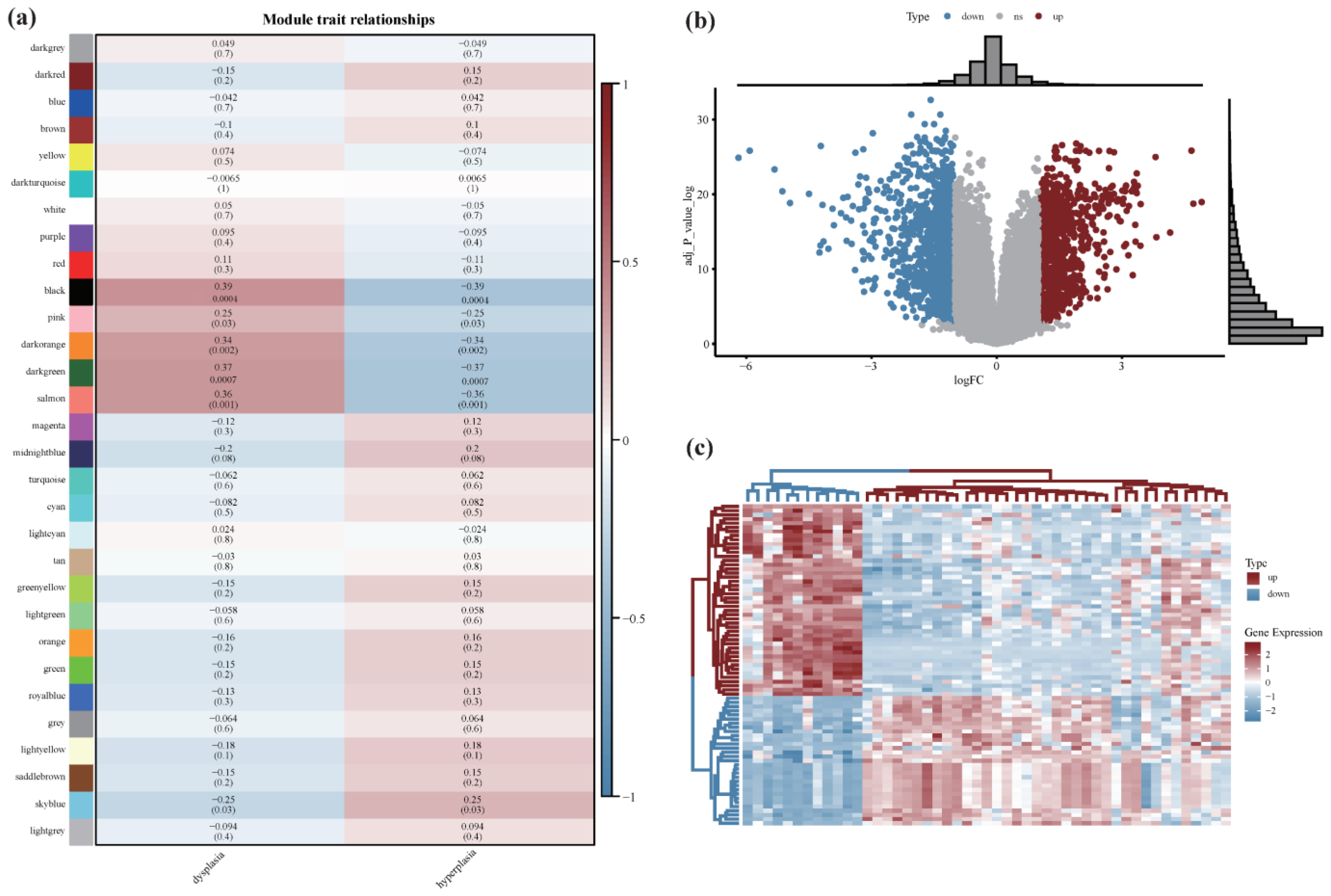
2.4. Differential Expression Analysis
2.5. Development of the Diagnostic Efficiency-Based Classifier Using Multiple Machine Learning Algorithms
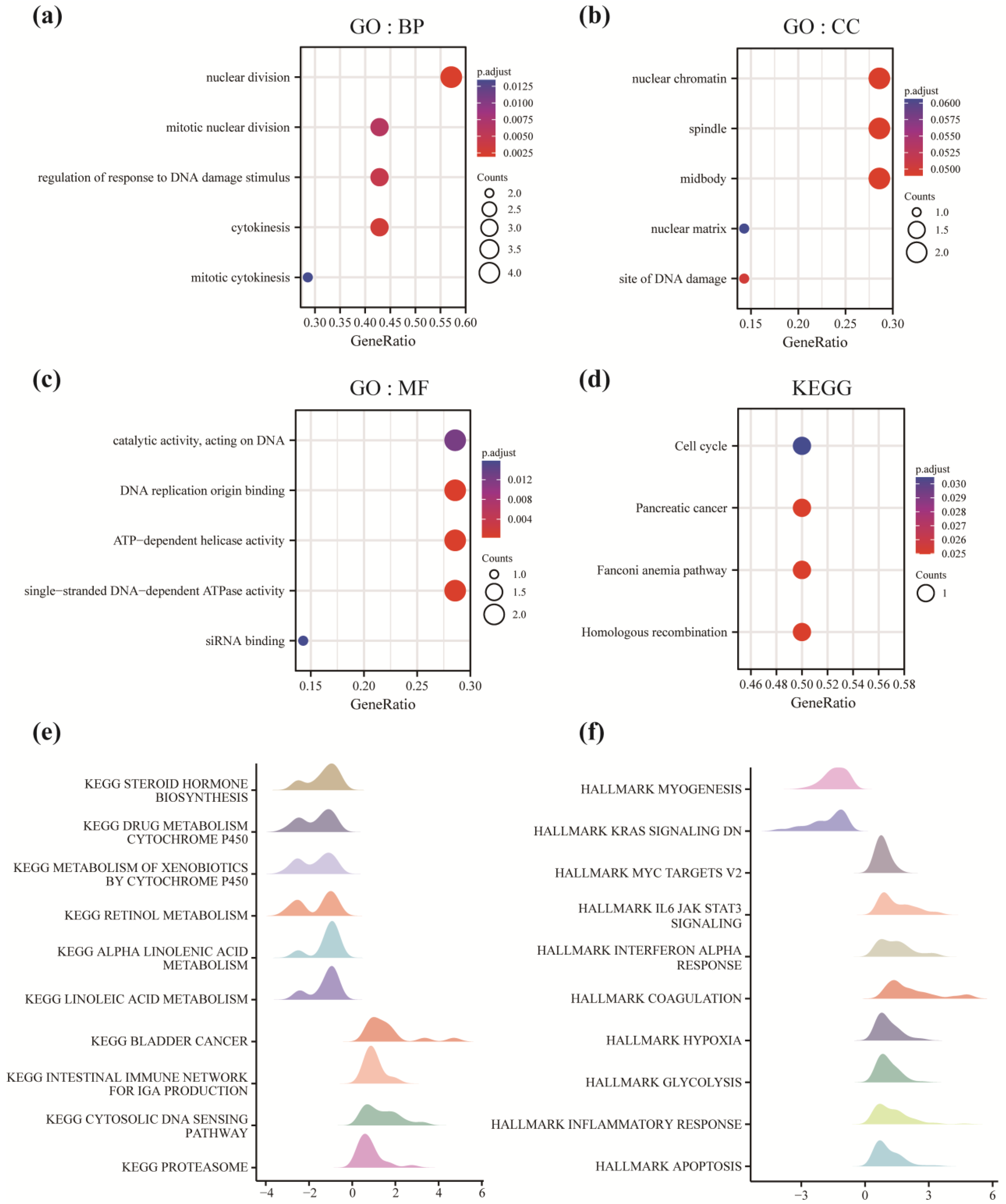
2.6. Enrichment Analysis
2.7. Cluster Analysis
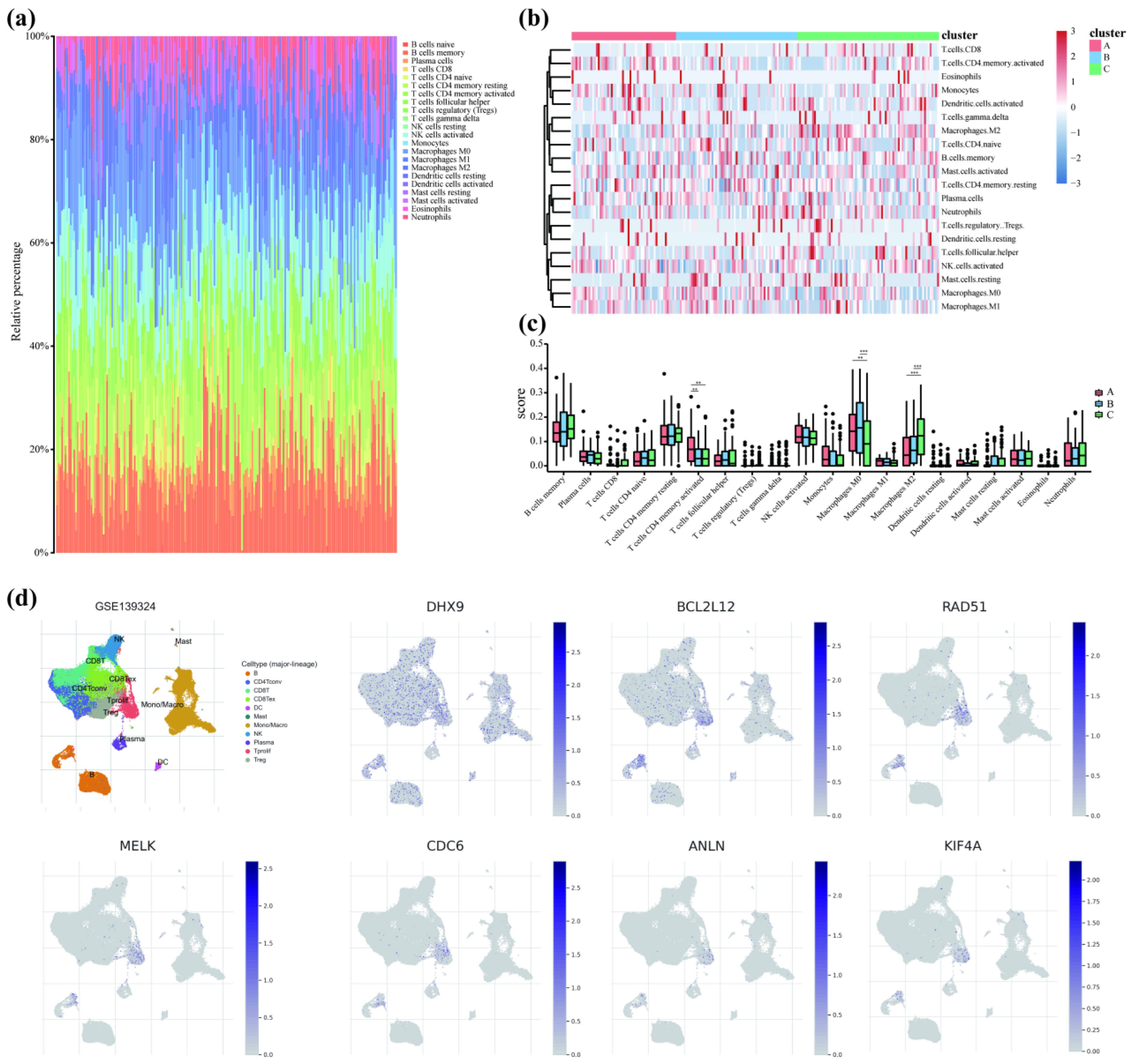
2.8. Immune Infiltration Analysis
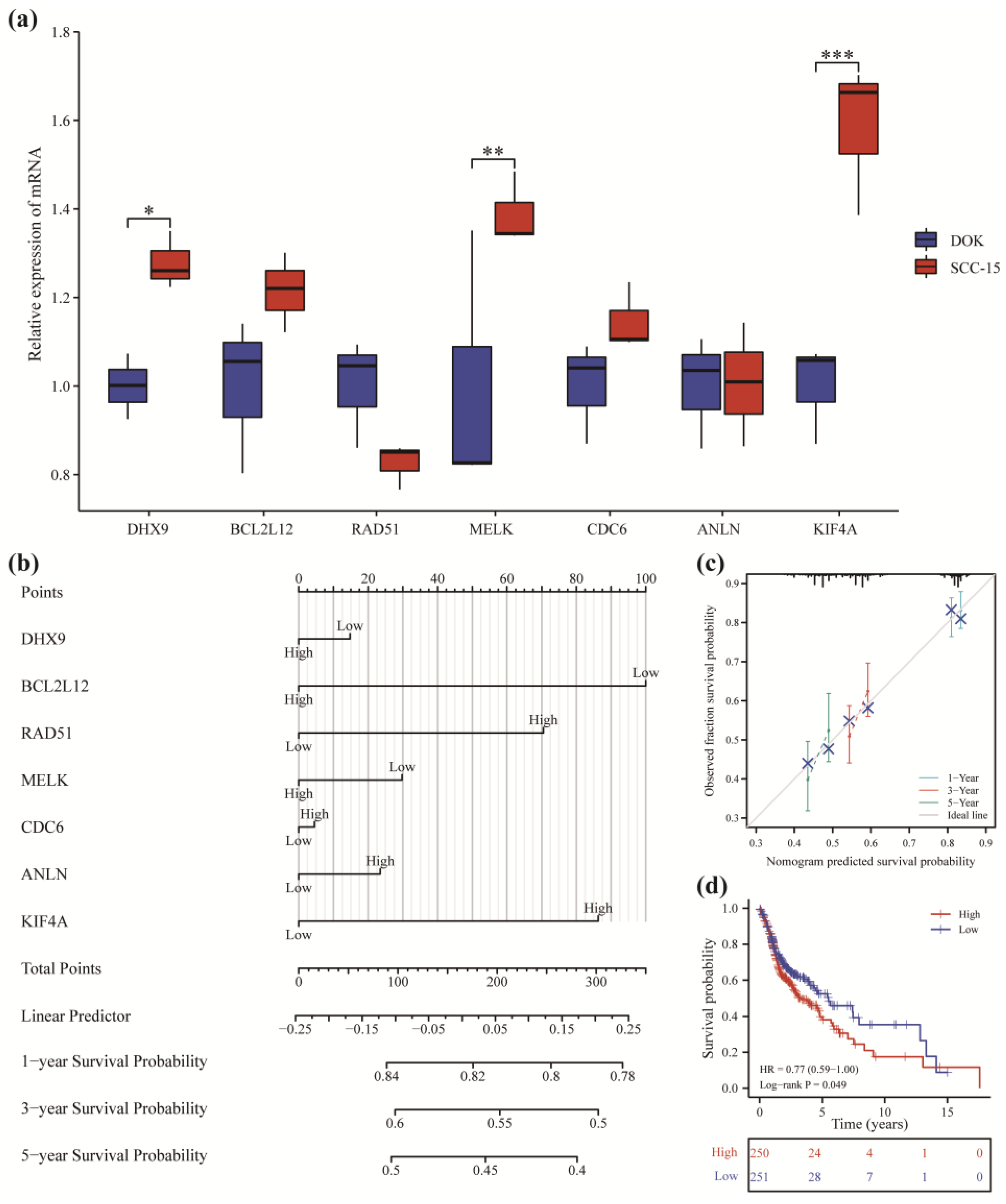
2.9. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.10. Prognostic Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gene Expression Modules Associated with OL
3.2. Differential Expression Analysis between OL and OSCC
3.3. Development and Verification of the Diagnostic-Efficiency-Based Classifier Using Multiple Machine Learning Algorithms
3.4. Enrichment Analysis
3.5. Subtype Analysis of the Model Genes
3.6. Model Genes Affect Immune Cell Infiltration
3.7. Prognostic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ota, A.; Miyamoto, I.; Ohashi, Y.; Chiba, T.; Takeda, Y.; Yamada, H. Diagnostic Accuracy of High-Grade Intraepithelial Papillary Capillary Loops by Narrow Band Imaging for Early Detection of Oral Malignancy: A Cross-Sectional Clinicopathological Imaging Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäwert, F.; Pettersson, H.; Jagefeldt, E.; Holmberg, E.; Kjeller, G.; Öhman, J. Clinicopathologic factors associated with malignant transformation of oral leukoplakias: A retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 50, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruegsanusak, K.; Peeravut, S.; Leelamanit, V.; Sinkijcharoenchai, W.; Jongsatitpaiboon, J.; Phungrassami, T.; Chuchart, K.; Thongsuksai, P. Survival and prognostic factors of different sites of head and neck cancer: An analysis from Thailand. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Clinical features and presentation of oral potentially malignant disorders. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2018, 125, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truchard, E.; Bertolus, C.; Martinez, P.; Thomas, E.; Saintigny, P.; Foy, J.P. Identification of a Gene-Expression-Based Surrogate of Genomic Instability during Oral Carcinogenesis. Cancers 2022, 14, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Oral potentially malignant disorders: A comprehensive review on clinical aspects and management. Oral Oncol. 2020, 102, 104550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Waal, I. Potentially malignant disorders of the oral and oropharyngeal mucosa, terminology, classification and present concepts of management. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petti, S. Pooled estimate of world leukoplakia prevalence: A systematic review. Oral Oncol. 2003, 39, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnakulasuriya, S.; Kujan, O.; Aguirre-Urizar, J.M.; Bagan, J.V.; González-Moles, M.Á.; Kerr, A.R.; Lodi, G.; Mello, F.W.; Monteiro, L.; Ogden, G.R.; et al. Oral potentially malignant disorders: A consensus report from an international seminar on nomenclature and classification, convened by the WHO Collaborating Centre for Oral Cancer. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1862–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Urizar, J.M.; Lafuente-Ibáñez de Mendoza, I.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the last 5 years. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1881–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odell, E.; Kujan, O.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Sloan, P. Oral epithelial dysplasia: Recognition, grading and clinical significance. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1947–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleskens, S.A.; Bergshoeff, V.E.; Voogd, A.C.; van Velthuysen, M.L.; Bot, F.J.; Speel, E.J.; Kremer, B.; Takes, R.; Slootweg, P. Interobserver variability of laryngeal mucosal premalignant lesions: A histopathological evaluation. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandio, M.; Brown, A.L.; Lock, C.; Morgan, P.R.; Coupland, V.H.; Madden, P.B.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Møller, H.; Odell, E.W. Predictive value of dysplasia grading and DNA ploidy in malignant transformation of oral potentially malignant disorders. Cancer Prev. Res. 2013, 6, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiloh, Y.; Kastan, M.B. ATM: Genome stability, neuronal development, and cancer cross paths. Adv. Cancer Res. 2001, 83, 209–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.G.; Carta, C.F.; de Barros, P.P.; Issa, J.S.; Nunes, F.D.; Almeida, J.D. Repair genes expression profile of MLH1, MSH2 and ATM in the normal oral mucosa of chronic smokers. Arch. Oral Biol. 2017, 73, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, S.; Klijanienko, J.; Giaginis, C.; Rodriguez, J.; Jouffroy, T.; Girod, A.; Point, D.; Tsourouflis, G.; Sastre-Garau, X. Expression of DNA repair proteins, MSH2, MLH1 and MGMT in mobile tongue squamous cell carcinoma: Associations with clinicopathological parameters and patients’ survival. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2011, 40, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saintigny, P.; Zhang, L.; Fan, Y.H.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Feng, L.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, E.S.; Ki Hong, W.; Mao, L. Gene expression profiling predicts the development of oral cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, P.G.; Cristea, S.; Ambatipudi, S.; Desai, R.S.; Kumar, R.; Patil, A.; Kane, S.; Borges, A.M.; Schäffer, A.A.; Beerenwinkel, N.; et al. Chromosomal Alterations and Gene Expression Changes Associated with the Progression of Leukoplakia to Advanced Gingivobuccal Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.; Meltzer, P.S. GEOquery: A bridge between the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1846–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaprico, A.; Silva, T.C.; Olsen, C.; Garofano, L.; Cava, C.; Garolini, D.; Sabedot, T.S.; Malta, T.M.; Pagnotta, S.M.; Castiglioni, I.; et al. TCGAbiolinks: An R/Bioconductor package for integrative analysis of TCGA data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonabend, R.; Király, F.J.; Bender, A.; Bischl, B.; Lang, M. mlr3proba: An R Package for Machine Learning in Survival Analysis. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 2789–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gene Ontology Consortium. Gene Ontology Consortium: Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D1049–D1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson, M.D.; Hayes, D.N. ConsensusClusterPlus: A class discovery tool with confidence assessments and item tracking. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1572–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Steen, C.B.; Liu, C.L.; Gentles, A.J.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Scherer, F.; Khodadoust, M.S.; Esfahani, M.S.; Luca, B.A.; Steiner, D.; et al. Determining cell type abundance and expression from bulk tissues with digital cytometry. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Dong, X.; Ge, J.; Zheng, R.; Shi, X.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Ren, P.; et al. TISCH: A comprehensive web resource enabling interactive single-cell transcriptome visualization of tumor microenvironment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1420–D1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Reinikainen, J.; Adeleke, K.A.; Pieterse, M.E.; Groothuis-Oudshoorn, C.G.M. Time-varying covariates and coefficients in Cox regression models. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.J.; Li, H.J.; Li, J.N.; Lu, Y.J.; Liao, G.Q. Expression of Mcm7 and Cdc6 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and precancerous lesions. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 3763–3769. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Du, L.; Wang, B.; Liu, W. Expression of RAD51 and Its Clinical Impact in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2020, 2020, 1827676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakawa, Y.; Kasamatsu, A.; Koike, H.; Higo, M.; Nakashima, D.; Kouzu, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Ogawara, K.; Shiiba, M.; Tanzawa, H.; et al. Kinesin family member 4A: A potential predictor for progression of human oral cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Qu, D.; Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Jing, X.; Li, C.; Wei, F.; Qu, X. Kif4A mediate the accumulation and reeducation of THP-1 derived macrophages via regulation of CCL2-CCR2 expression in crosstalking with OSCC. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xu, X.; Bin, X.; Zhou, J.; Tang, Z. Ectopic expression of MELK in oral squamous cell carcinoma and its correlation with epithelial mesenchymal transition. Aging 2021, 13, 13048–13060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Dai, Y. Tumor microenvironment and therapeutic response. Cancer Lett. 2017, 387, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Giraud, F.; Hafner, M.; Ries, C.H. In vitro generation of monocyte-derived macrophages under serum-free conditions improves their tumor promoting functions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.A.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinshaw, D.C.; Shevde, L.A. The Tumor Microenvironment Innately Modulates Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4557–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S. Prognostic significance of ANLN in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniwaki, M.; Takano, A.; Ishikawa, N.; Yasui, W.; Inai, K.; Nishimura, H.; Tsuchiya, E.; Kohno, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Daigo, Y. Activation of KIF4A as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 6624–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachechiladze, M.; Škarda, J.; Skanderová, D.; Überall, I.; Kolek, V.; Smičkova, P.; Vojta, P.; Vbrková, J.; Hajdúch, M.; Shani, I.; et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and their association with PD-L1 expression and DNA repair protein RAD51 in patients with resected non-small cell lung carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2020, 147, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, L.; Mao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, X.; Wang, X.; Shui, L.; Chen, X.; et al. CDC6 is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltrates in glioma. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, G.; Singh, P.; Kim, D.W. Integrative analysis of KIF4A, 9, 18A, and 23 and their clinical significance in low-grade glioma and glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Chen, X.; Hakizimana, O.; Mei, Y. Genetic interactions between ANLN and KDR are prognostic for breast cancer survival. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 2255–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kladi-Skandali, A.; Sideris, D.C.; Scorilas, A. BCL2L12: A multiply spliced gene with independent prognostic significance in breast cancer. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 57, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevappa, R.; Neves, H.; Yuen, S.M.; Bai, Y.; McCrudden, C.M.; Yuen, H.F.; Wen, Q.; Zhang, S.D.; Kwok, H.F. The prognostic significance of Cdc6 and Cdt1 in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, S. Comprehensive Analysis of Prognostic and Immune Infiltrates for RAD51 in Human Breast Cancer. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2021, 31, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Bolor-Erdene, E.; Li, Q.; Mei, Y.; Zhou, L. Identification of KIF4A as a prognostic biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Aging 2021, 13, 24050–24070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Hao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chu, X. Screening Hub Genes as Prognostic Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Bioinformatics Analysis. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28 (Suppl. 1), 76S–86S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Cao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Guo, W.; Zhang, S. High expression of DHX9 promotes the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e24052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Dong, C.; Dong, Z.; Liu, G.; Xu, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, W. Upregulate KIF4A Enhances Proliferation, Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Indicates poor prognosis Across Human Cancer Types. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Zheng, Q.; Niu, J.; Li, S. CCNB2, CDC20, AURKA, TOP2A, MELK, NCAPG, KIF20A, UBE2C, PRC1, and ASPM May Be Potential Therapeutic Targets for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Integrated Bioinformatic Analysis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 10185–10194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xiong, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Bai, D. Identification of Rad51 as a prognostic biomarker correlated with immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 2664–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florou, D.; Papadopoulos, I.N.; Scorilas, A. Molecular analysis and prognostic impact of the novel apoptotic gene BCL2L12 in gastric cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontos, C.K.; Papadopoulos, I.N.; Scorilas, A. Quantitative expression analysis and prognostic significance of the novel apoptosis-related gene BCL2L12 in colon cancer. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Wan, Z.; Shao, M.; Wu, S.; Wang, G. Potential Prognostic and Diagnostic Values of CDC6, CDC45, ORC6 and SNHG7 in Colorectal Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 11609–11621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, P.F.; Jiang, T.; Chen, F.; Shi, P.C.; Li, H.Q.; Bai, J.; Song, J. KIF4A facilitates cell proliferation via induction of p21-mediated cell cycle progression and promotes metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennstedt, P.; Fresow, R.; Simon, R.; Marx, A.; Terracciano, L.; Petersen, C.; Sauter, G.; Dikomey, E.; Borgmann, K. RAD51 overexpression is a negative prognostic marker for colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer. 2013, 132, 2118–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Bae, A.N.; Jung, A.S. Clinicopathological and Prognostic Characteristics of RAD51 in Colorectal Cancer. Medicina 2020, 56, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yicong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Denglong, W.; Baoying, H. Increased CDC6 Expression Associates with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 666418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, J.; Su, Z. KIF4A is a promising prognostic marker and correlates with immune infiltration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 7165–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
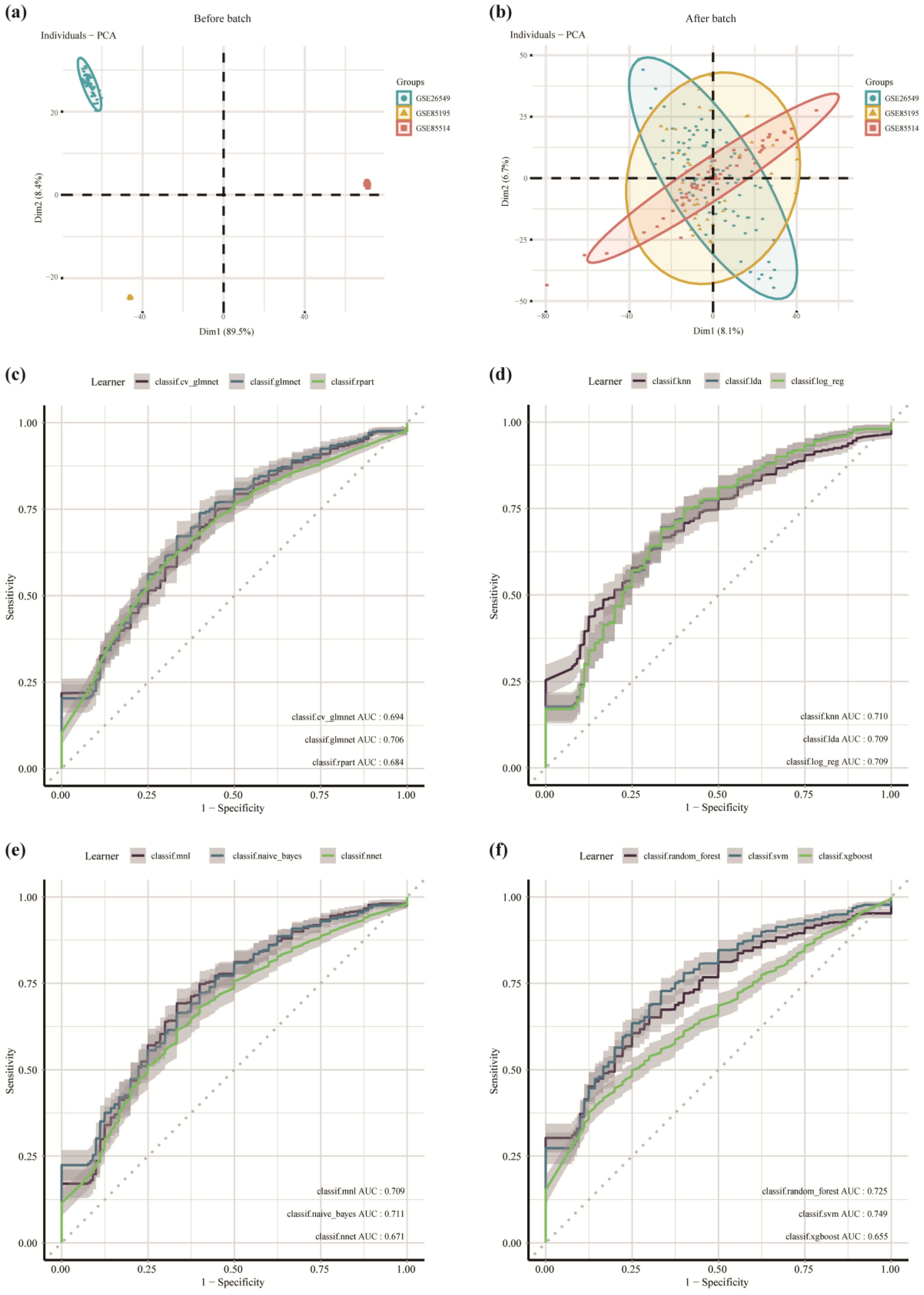

| Learner_Id | AUC_Train | AUC_Test |
|---|---|---|
| classif.cv_glmnet | 0.7163359 | 0.6935978 |
| classif.glmnet | 0.7451895 | 0.7058361 |
| classif.rpart | 0.8395653 | 0.6842594 |
| classif.knn | 0.962321 | 0.7103622 |
| classif.lda | 0.7493833 | 0.709229 |
| classif.log_reg | 0.749681 | 0.7086145 |
| classif.mnl | 0.7496823 | 0.7086145 |
| classif.naïve_Bayes | 0.7281341 | 0.7108963 |
| classif.nnet | 0.7839936 | 0.6708493 |
| classif.random_forest | 0.9985012 | 0.7248809 |
| classif.svm | 0.8655543 | 0.748687 |
| classif.xgboost | 0.9261073 | 0.6546356 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jing, F.; Zhang, J.; Cai, X.; Zhou, X.; Bai, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, T. Screening for Biomarkers for Progression from Oral Leukoplakia to Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Evaluation of Diagnostic Efficacy by Multiple Machine Learning Algorithms. Cancers 2022, 14, 5808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235808
Jing F, Zhang J, Cai X, Zhou X, Bai J, Zhang H, Li T. Screening for Biomarkers for Progression from Oral Leukoplakia to Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Evaluation of Diagnostic Efficacy by Multiple Machine Learning Algorithms. Cancers. 2022; 14(23):5808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235808
Chicago/Turabian StyleJing, Fengyang, Jianyun Zhang, Xinjia Cai, Xuan Zhou, Jiaying Bai, Heyu Zhang, and Tiejun Li. 2022. "Screening for Biomarkers for Progression from Oral Leukoplakia to Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Evaluation of Diagnostic Efficacy by Multiple Machine Learning Algorithms" Cancers 14, no. 23: 5808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235808
APA StyleJing, F., Zhang, J., Cai, X., Zhou, X., Bai, J., Zhang, H., & Li, T. (2022). Screening for Biomarkers for Progression from Oral Leukoplakia to Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Evaluation of Diagnostic Efficacy by Multiple Machine Learning Algorithms. Cancers, 14(23), 5808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235808





