Simple Summary
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as a prognostic indicator of patients treated with immunotherapy has been fully reported. However, the dynamics of NLR after immunotherapy and its association with efficacy of immunotherapy have been less frequently reported. This meta-analysis and systematic review study aimed to (a) summarize the early change in NLR after immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) treatment, (b) evaluate the association between the trend in NLR and efficacy of ICI treatment, and (c) analyze the prognostic value of baseline and post-treatment NLR.
Abstract
Background: A number of studies have reported an association between the dynamics of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and clinical efficacy in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), but there is still a lack of a meta-analysis or systematic review. Methods: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library were searched until September 2022 for studies reporting on the association between the change in NLR after ICI treatment and clinical outcomes. Outcome measures of interest included: change in NLR before and after treatment, overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and objective response rate (ORR). Results: A total of 4154 patients in 38 studies were included. The pooled percentage of patients with increased NLR was 49.7% (95CI%: 43.7–55.8%). Six studies discussing the change in NLR in patients with different tumor responses all showed that the NLR level in patients without response to immunotherapy may increase after ICI treatment. The upward trend in NLR was associated with shorter OS (pooled HR: 2.05, 95%CI: 1.79–2.35, p < 0.001) and PFS (pooled HR: 1.89, 95%CI: 1.66–2.14, p < 0.001) and higher ORR (pooled OR: 0.27, 95%CI: 0.19–0.39, p < 0.001), and downward trend in NLR was associated with longer OS (pooled HR: 0.49, 95%CI: 0.42–0.58, p < 0.001) and PFS (pooled HR: 0.55, 95%CI: 0.48–0.63, p < 0.001) and lower ORR (pooled OR: 3.26, 95%CI: 1.92–5.53, p < 0.001). In addition, post-treatment high NLR was associated with more impaired survival than baseline high NLR (pooled HR of baseline high NLR: 1.82, 95%CI: 1.52–2.18; pooled HR of post-treatment high NLR: 2.93, 95%CI: 2.26–3.81), but the NLR at different time points may have a similar predictive effect on PFS (pooled HR of baseline high NLR: 1.68, 95%CI: 1.44–1.97; pooled HR of post-treatment high NLR: 2.00, 95%CI: 1.54–2.59). Conclusions: The NLR level of tumor patients after ICI treatment is stable overall, but the NLR level in patients without response to immunotherapy may increase after ICI treatment. Patients with an upward trend in NLR after ICI treatment were associated with worse clinical outcomes; meanwhile, the downward trend in NLR was associated with better clinical outcomes. Post-treatment high NLR was associated with more impaired survival than baseline high NLR.
1. Introduction
For many decades, surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy were the main therapy for cancer [1]. Recent rapid developments in immunotherapy have attracted increased attention and have transformed practice in the treatment of many types of cancers; of special interest are immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) targeting programmed cell death-1/programmed death ligand-1 (PD-1/PD-L1) and T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) [2]. Despite the progress that has been achieved, the efficacy of ICI treatment is not totally satisfactory because only a part of patients responded to ICI treatment [3], and various immune-related adverse events (irAEs) during the course of therapy were not uncommon [4]. Therefore, it is essential to select appropriate biomarkers to identify the patients who may not benefit from ICI treatment to avoid useless, expensive, and possibly toxic treatments.
However, only PD-L1 expression, tumor mutational burden (TMB), and microsatellite instability (MSI) entered routine clinical practice in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) [5,6,7]. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) and immunohistochemical analysis were needed to confirm these biomarkers [8]. These tissue-based biomarkers are unsuitable for serial monitoring; meanwhile, biopsy site and specimen status may be bias factors affecting the results. Hence, it is necessary to find more readily available biomarkers suitable for diverse clinical settings (including low-resource settings) to predict the effect of ICI treatment in more types of tumors. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), a blood-based biomarker defined by the absolute counts of neutrophils and lymphocytes, has received more and more attention because of its relatively easy and inexpensive accessibility.
Inflammation is an important characteristic of cancer [9], and neutrophils have various important biological functions in innate and adaptive immunities, thus playing a key role in inflammation [10]. Activated neutrophils also were able to suppress T-lymphocyte function by secreting myeloperoxidase and arginase-1 and upregulating PD-L1, thus resulting in the delivery of a negative signal to T cells [11]. Therefore, neutrophils may help create an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment which reduces the efficacy of immunotherapy [12]. NLR could serve as a measure of the balance of adaptive immune surveillance and inflammation status; consequently, it was natural to explore the association between NLR and the efficacy of ICI treatment. There have been numerous systematic reviews and meta-analyses demonstrating that a high level of NLR at baseline was associated with poor prognosis in many types of cancers [13,14,15]. However, significant changes in serum cytokine concentrations were observed after the initial ICI treatment, and these changes were likely to be associated with treatment response [16,17].
Therefore, we hypothesized that systemic inflammatory status related to immune responses against tumors may be dynamic rather than static [18], and the early changes in NLR detected from peripheral blood could be the potential biomarkers of tumor burden and predict the very early efficacy of cancer immunotherapy in the initial weeks of ICI treatment before imaging evaluation or when it is not conclusive [16].
In fact, recently published studies about immunotherapy and the dynamics of NLR suggested the special role of early change in NLR in predicting the efficacy of immunotherapy and final survival outcomes [8,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]. Specifically, they observed the following three points: (1) The trend in NLR (upward or downward) may be associated with the outcome of tumor response after ICI treatment. (2) The different trends in NLR appear to be able to stratify the survival times of patients who received immunotherapy. (3) Compared with the baseline NLR, post-treatment high NLR was seemly associated with more impaired survival. Although a considerable number of studies discuss the early change in NLR after immunotherapy and its association with prognosis, there is still a lack of relevant review. Hence, we focused on the novel topic of dynamics of NLR in cancer patients who received ICI treatment, and we conducted this meta-analysis and systematic review study in an effort to comprehensively summarize the change in NLR after ICI treatment and its association with prognosis.
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
Literature review and data extraction followed established PRISMA guidelines [55], and we prospectively registered the protocol in the PROSPERO International Register of Systematic Reviews (CRD42022313394). We conducted comprehensive literature searches in PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library until 10 September 2022. The search terms were structured by combining the keywords including “neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio”, “NLR”, “immune checkpoint inhibitor”, “ICI”, “immunotherapy”, “cancer”, “tumor”, and “solid tumor”. An example of a search strategy used for PubMed is as follows: (NLR or (neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio)) and ((immune checkpoint inhibitor) or immunotherapy or ICI) and ((solid tumor) or cancer). After obtaining all results from four databases, we firstly deleted the duplicate results and then completed a manual search of potentially missing studies by screening the references of the studies.
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Two authors (Yusheng Guo and Jiayu Wan) independently conducted the literature search and preliminary screening of the literature from the databases by reading titles and abstracts. Studies meeting the inclusion criteria were included in this study: (1) studies written in English; (2) studies investigating the association between the dynamics of NLR and the prognosis of patients who received ICI treatment; (3) studies reporting overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), or the change in NLR before and after treatment. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) review studies, meta-analyses, conference or poster abstracts, case reports, comments, letters, and editorials; (2) studies on non-solid tumors; (3) duplicate reports and ongoing studies.
2.3. Data Extraction
Two authors independently assessed the quality and the risk of bias in each included study using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale. Any disagreements were resolved by a third author (Dongqiao Xiang or Lian Yang). The following data were extracted independently by two authors: year of publication, first author, region, treatment, type of tumor, number of patients, the time point for rechecking NLR after immunotherapy, outcome, gender, Newcastle–Ottawa Scale, study design (Table 1). In the case where multiple publications reported overlapping data, the study with the largest sample size was considered.

Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
All statistical analysis was conducted using R software (version 4.1.0). We assessed heterogeneity by using a chi-square test and the I2 metric before performing a meta-analysis. The I2 value indicates the percentage of variability across the pooled estimates attributable to statistical heterogeneity, and studies with I2 > 40% were considered as having high heterogeneity. We used a random effects model if high heterogeneity was present and used a fixed effects model in case of low heterogeneity. Next, forest plots were made to show the HR/OR and 95% CI of each study and the pooled HR/OR and 95% CI. We explored possible sources of heterogeneity by using Baujat plots and sensitivity analyses conducted by excluding the studies one by one. Finally, publication bias was assessed by funnel plot, Egger test, and Begg test. Wherever publication bias was detected, the trim-and-fill method was implemented to produce a model after accounting for any publication bias. Two-sided p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant for all statistical procedures.
3. Results
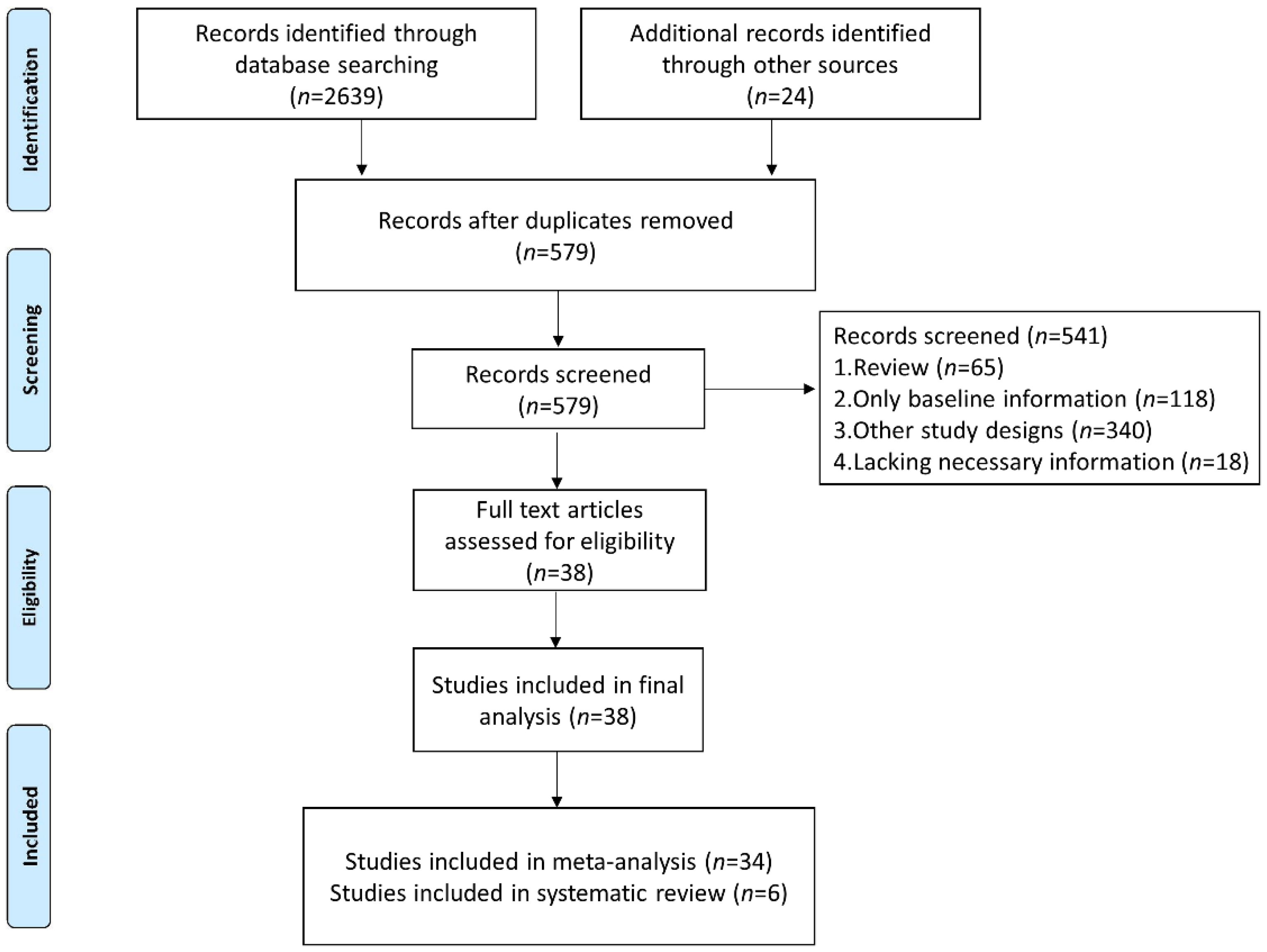
We identified 2663 studies in the database searches, and we excluded 2084 duplicated articles. After analysis of the title, abstract, and topic, 541 other articles were excluded (Figure 1). Finally, 38 studies were included (34 studies were included in the meta-analysis for quantitative analyses and 6 studies were included in the systematic review to analyze the dynamics of NLR level in patients without or with response to immunotherapy).
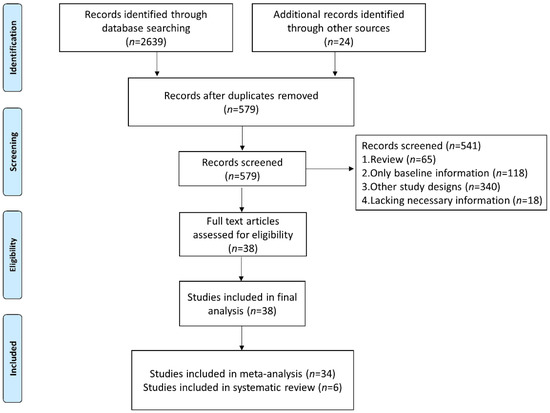
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of study selection for inclusion in this meta-analysis and systematic review.
3.1. Characteristics of Included Studies
In total, 38 studies involving 4154 patients were included in this meta-analysis and systematic review [8,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]. Thirty-seven studies had a retrospective study design, and only one study was prospective [24]. All the included studies received moderately high scores from the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale quality assessments. Of the 38 studies included, 6 studies [8,37,40,44,48,54] considered two or more types of tumors, and 32 studies dealt with specific types of cancer (non-small-cell lung cancer was the most frequently studied tumor). Seven studies [21,27,30,37,41,44,48] did not mention the specific drugs used, and the most widely used ICI is nivolumab, which was used in 24 studies [8,18,22,23,25,28,29,31,32,33,34,36,38,39,40,42,43,47,50,51,52,53,54]. Time points for rechecking NLR included 2 weeks to 8 weeks, after one to four cycles of treatment, after one to four infusions, and the most common time points were 4 weeks and 6 weeks.
3.2. Change in NLR before and after ICI Treatment
First, we investigated the studies that reported the proportion of patients with increased or decreased NLR after ICI treatment. A total of 12 studies [19,20,33,39,41,43,44,47,48,49,51,54] involving 1449 patients reported 726 patients (50.1%) with upward trend in NLR and 723 patients (49.9%) with downward trend in NLR. The proportion of patients with increased NLR ranged from 24.6% to 60.8% in 12 studies, and the pooled percentage of patients with increased NLR was 49.7% (95CI%: 43.7–55.8%) (Figure S1). Although ICI treatment did not influence the trend in NLR overall, six studies [27,32,37,42,45,53] reported that the NLR level in patients without response to immunotherapy tended to significantly increase after ICI treatment, and in contrast, patients who responded to ICI treatment have similar or lower NLR level before and after immunotherapy (Table S1). Notably, a retrospective study with data from a multicenter prospective trial using a mixed effects regression analysis with per-patient random intercept reported that patients with CR/PR/SD had a lower log-transformed NLR at study entry (p = 0.03) and the NLR level was stable during follow-up overall [37], which corresponded to our results.
3.3. Different Trends in NLR after ICI Treatment Were Associated with Different Prognoses
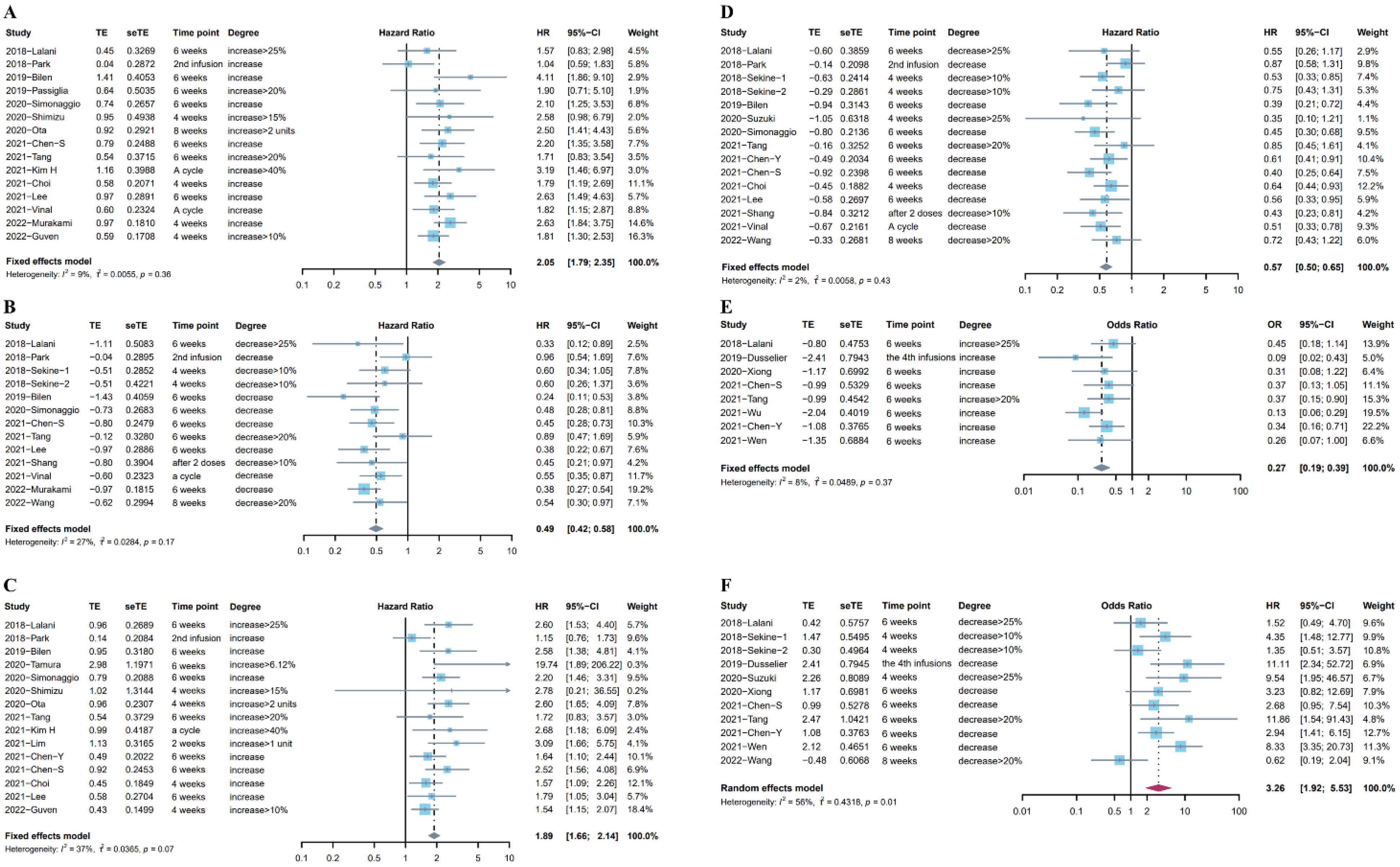
Eighteen studies (Sekine et al. reported two independent cohorts) [8,21,22,23,26,29,30,33,34,40,44,45,47,48,50,51,52,54] including 2324 patients looked at the association between OS and the different trends in NLR after ICI treatment. Fifteen studies [8,21,23,26,29,30,33,34,40,44,47,48,50,51,54] reported the relationship between the upward trend in NLR and OS, and the subsequent time points for rechecking NLR included 4–8 weeks, a treatment cycle after ICI treatment, or before the second infusion. Considering the low heterogeneity (I2= 9%), a fixed effects model was used for analysis. Results indicated the pooled HR was 2.05 (95%CI: 1.79–2.35, p < 0.001), suggesting the negative prognostic role of the upward trend in NLR in patients who received immunotherapy (Figure 2A). Twelve studies (13 cohorts) [21,22,29,30,40,44,45,47,48,51,52,54] investigated the association between the downward trend in NLR and OS. The time points for rechecking included 4–8 weeks, after the first treatment cycle, before the second infusion, or after two doses. Given the low heterogeneity (I2 = 27%), a fixed effects model showed that the pooled HR was 0.49 (95%CI: 0.42–0.58, p < 0.001, Figure 2B).
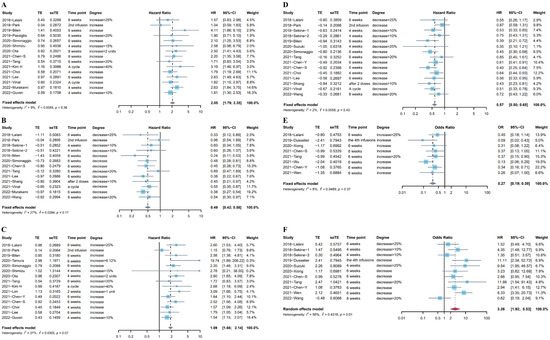
Figure 2.
(A) Forest plot for the association between upward trend in NLR after ICI treatment and OS. (B) Forest plot for the association between downward trend in NLR after ICI treatment and OS. (C) Forest plot for the association between upward trend in NLR after ICI treatment and PFS. (D) Forest plot for the association between downward trend in NLR after ICI treatment and PFS. (E) Forest plot for the association between upward trend in NLR after ICI treatment and ORR. (F) Forest plot for the association between downward trend in NLR after ICI treatment and ORR.
Twenty studies (Sekine et al. reported two independent cohorts) [8,18,20,21,22,23,26,28,29,30,33,40,44,45,46,47,48,50,52,54] including 2494 patients reported the association between PFS and the change in NLR after immunotherapy. Fifteen studies [8,18,20,21,23,26,29,30,33,40,44,46,47,50,54] reported the association between the increase in NLR after ICI treatment and PFS. The pooled HR from a fixed effects model was 1.89 (95%CI: 1.66–2.14, p < 0.001, I2 = 37%, Figure 2C). Fourteen studies (15 cohorts) [20,21,22,28,29,30,33,40,44,45,47,48,52,54] reported the association between the increase in NLR after ICI treatment and PFS. There was low heterogeneity (I2 = 2%) in these studies, and a fixed effects model indicated that the decrease in NLR was associated with longer PFS (pooled HR: 0.57, 95%CI: 0.50–0.65, p < 0.001, Figure 2D).
In addition, we investigated the association between the trends in NLR after ICI treatment and ORR, and 10 studies [19,20,21,28,30,39,41,43,45,47] provided data for ORR. Data from eight studies [19,20,21,30,39,41,43,47] on the increase in NLR after ICI treatment and ORR indicated that the upward trend in NLR after immunotherapy was significantly associated with worse tumor response (pooled OR: 0.27, 95%CI: 0.19–0.39, p < 0.001, I2 = 8%, Figure 2E). Meanwhile, a random effects model pooling OR from 10 studies [19,20,21,28,30,39,41,43,45,47] showed that the downward trend in NLR after immunotherapy was associated with better tumor response (pooled OR: 3.26, 95%CI: 1.92–5.53, p < 0.001, I2 = 56%, Figure 2F). The Baujat plot showed that the study by Wang et al. contributed the maximum heterogeneity and influence to the overall result (Figure S2). The results of the sensitivity analysis did not change after excluding the studies one by one (Figure S3). Table S2 in the Supplementary Materials lists more details about these studies.
3.4. Post-Treatment High NLR Was Associated with More Impaired Survival Than Baseline High NLR
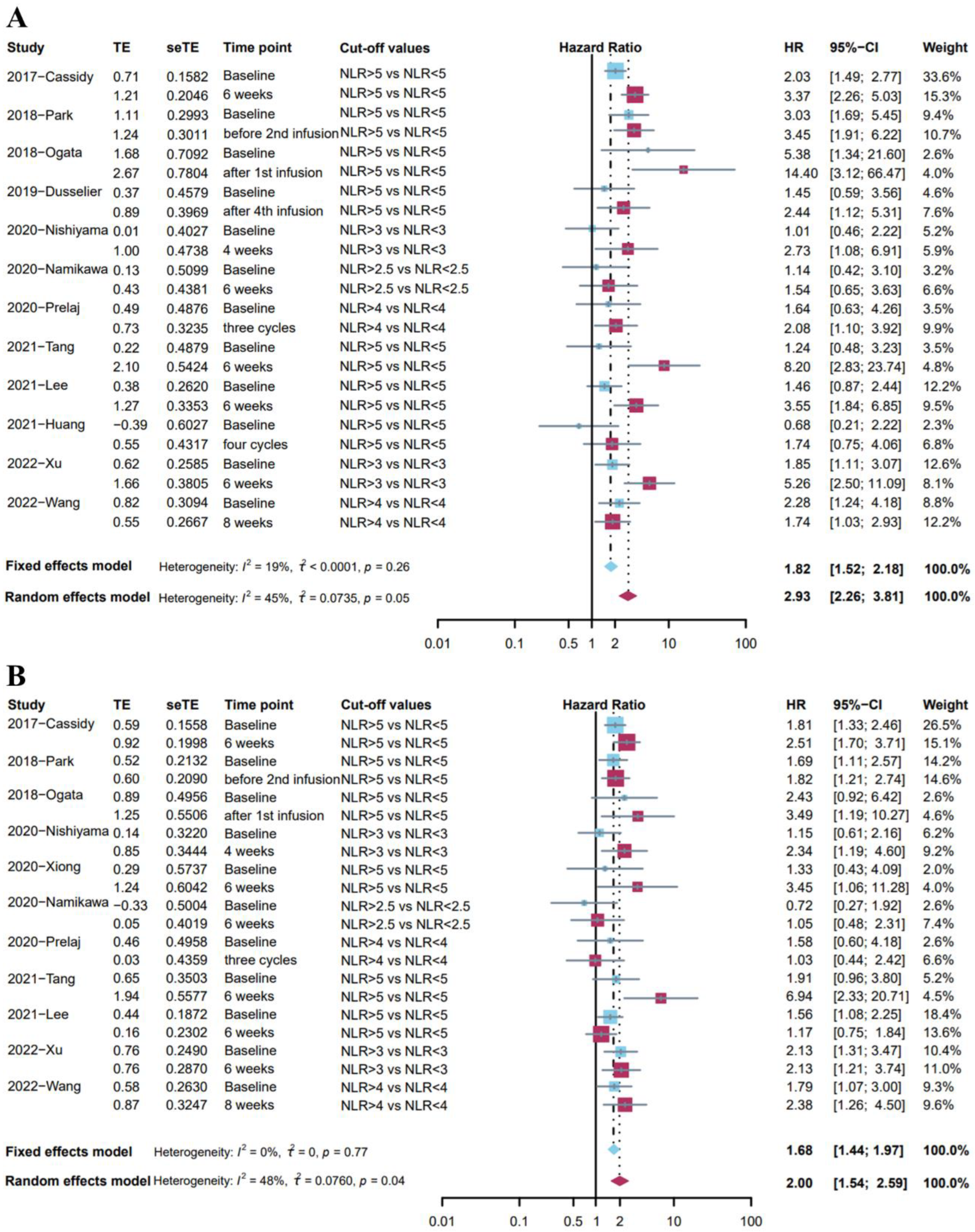
Among the previous studies, a considerable number of studies have demonstrated the negative impact of the elevation of the baseline (pre-treatment) NLR on the prognosis. Next, we compared the impact of NLR at baseline and after treatment on prognosis, based on those studies that gave both time points at the same time (Table S3).
Twelve studies [24,25,29,30,31,35,36,38,39,40,45,53] reported the association between OS and NLR at two different time points with the same cut-off values of NLR. Given the low heterogeneity (I2 = 19%), a fixed effects model was used for analysis, and the results showed that a high level of NLR at baseline was associated with poor overall survival (pooled HR: 1.82, 95%CI: 1.52–2.18, p < 0.001, Figure 3A). Meanwhile, a random effects model indicated that post-treatment high NLR level was associated with poor survival outcomes (pooled HR: 2.93, 95%CI: 2.26–3.81, p < 0.001, I2 = 45%, Figure 3A). The Baujat plot indicated that the biggest source was from the study by Wang et al. (Figure S4), and the sensitivity analysis found similar results (Figure S5). It was worth noting that post-treatment high NLR was associated with more impaired survival than baseline high NLR.
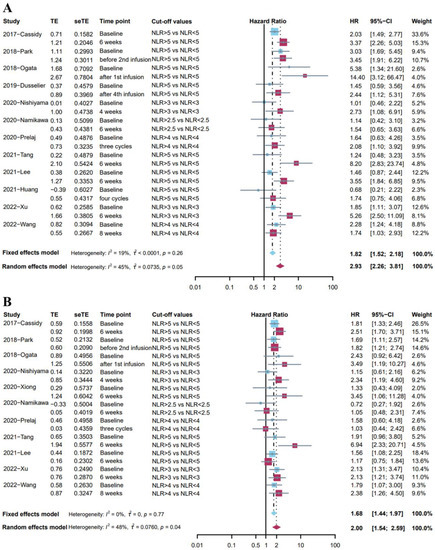
Figure 3.
(A) Forest plot for the association between high level of baseline NLR and OS (blue); the association between high level of post-treatment NLR and OS (red). (B) Forest plot for the association between high level of baseline NLR and PFS (blue); the association between high level of post-treatment NLR and PFS (red).
Eleven studies [24,29,30,31,35,36,38,40,43,45,53] investigated the association between PFS and NLR at two different time points with the same cut-off values of NLR. A fixed effects model indicated that baseline high NLR level was associated with shorter PFS (pooled HR: 1.68, 95%CI: 1.44–1.97, p < 0.001, I2 = 0%, Figure 3B). Moreover, a random effects model showed that post-treatment high NLR level was associated with shorter PFS (pooled HR: 2.00, 95%CI: 1.54–2.59, p < 0.001, I2 = 48%, Figure 3B). Sensitivity analysis demonstrated the stability of these results (Figure S6). However, the NLR at different time points may have a similar predictive effect on PFS.
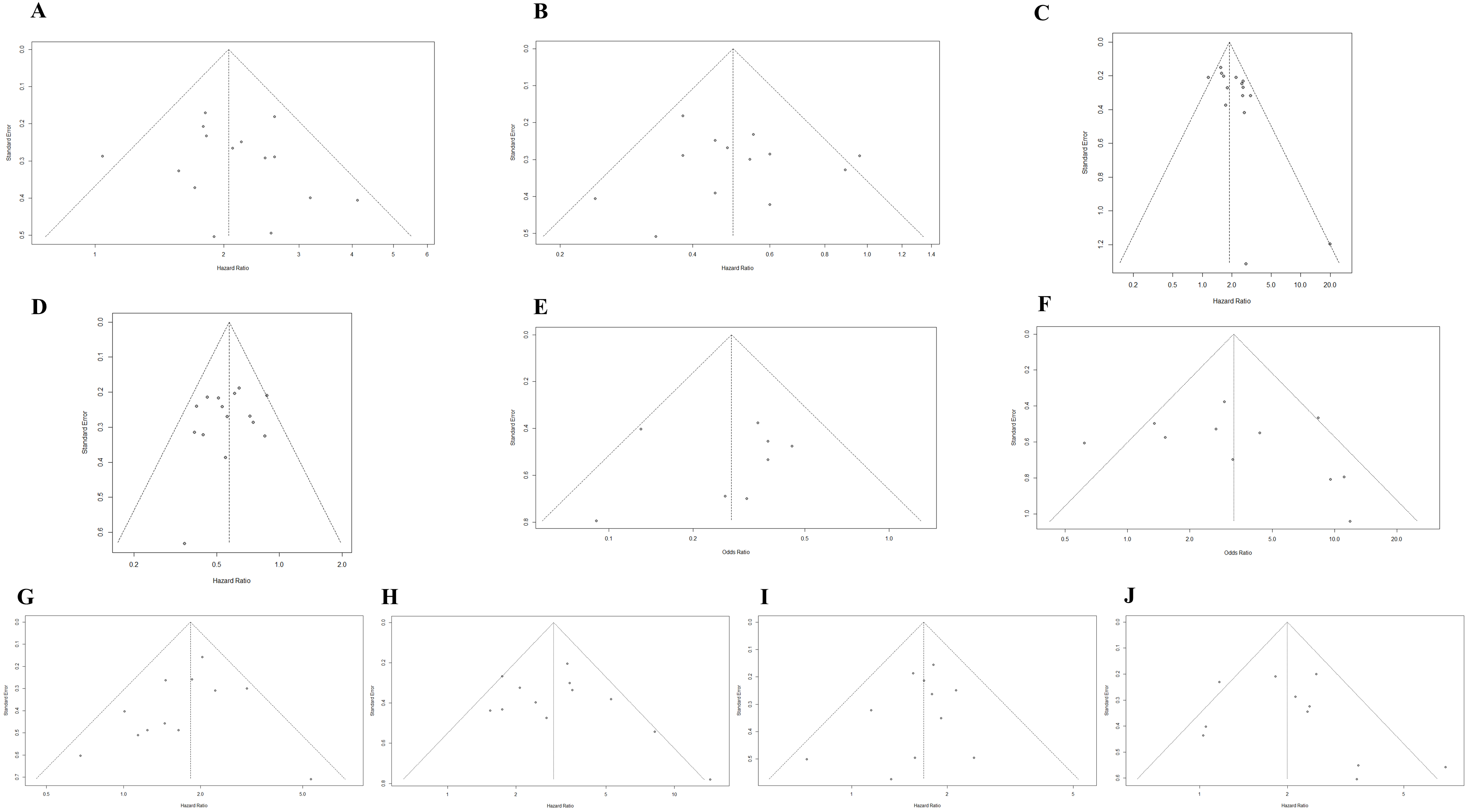
3.5. Publication Bias
Potential publication bias was assessed using funnel plots, the Egger test, and the Begg test. All funnel plots were approximately symmetrical (Figure 4A–J), and the results of the Egger test demonstrated that there was a publication bias in the studies reporting the association between the upward trend in NLR and PFS (Table 2). The trim-and-fill method showed that it was necessary to fill four potential unpublished studies in the funnel plot (Figure S7); the result was not relevantly changed with a pooled HR of 1.86 (95%CI: 1.58–2.19, p < 0.001).
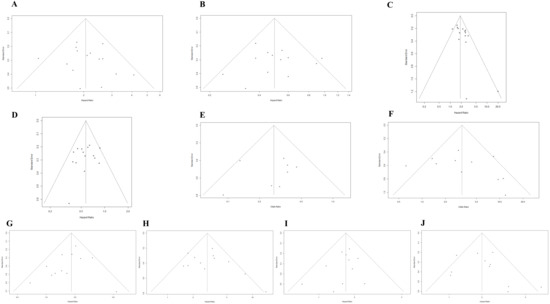
Figure 4.
(A) Funnel plot for the association between upward trend in NLR after ICI treatment and OS. (B) Funnel plot for the association between downward trend in NLR after ICI treatment and OS. (C) Funnel plot for the association between upward trend in NLR after ICI treatment and PFS. (D) Funnel plot for the association between downward trend in NLR after ICI treatment and PFS. (E) Funnel plot for the association between upward trend in NLR after ICI treatment and ORR. (F) Funnel plot for the association between downward trend in NLR after ICI treatment and ORR. (G) Funnel plot for the association between high level of baseline NLR and OS. (H) Funnel plot for the association between high level of post-treatment NLR and OS. (I) Funnel plot for the association between high level of baseline NLR and PFS. (J) Funnel plot for the association between high level of post-treatment NLR and PFS.

Table 2.
Publication bias.
4. Discussion
People have been looking for inexpensive and reproducible biomarkers that can accurately predict responses to immune checkpoint inhibition. Compared with biomarkers such as PD-L1, TMB, and MSI, routine blood samples are more readily available and do not require any other additional costs; thus, they have been easily applied in the real-world setting. [56]. More importantly, the prognostic role of NLR seems to be applicable to most patients with various tumors receiving ICI treatment [57,58,59]; therefore, it is necessary to conduct a further meta-analysis on NLR.
All previous meta-analyses about immunotherapy and NLR focused on the impact of baseline NLR on prognosis [60,61,62,63,64,65]. Although a small part of the meta-analyses included a few studies addressing the dynamics of NLR, they did not conduct quantitative analysis and did not arrive at a specific conclusion [60,61]. At present, this study is the first meta-analysis and systematic review focusing on the dynamics of NLR in cancer patients after ICI treatment and the relationship between the dynamics of NLR and prognosis. Our study yielded three key findings. First, we observed that ICI treatment was not associated with a significantly increased or decreased NLR level in the overall cohort; however, it seems that among patients who did not respond to immunotherapy, NLR may have a significant upward trend. Second, different trends in NLR after ICI treatment were associated with different prognoses. Results indicated that the upward trend in NLR was associated with worse clinical outcomes and that the downward trend in NLR was associated with better clinical outcomes. Finally, post-treatment high NLR associated was with more impaired survival than baseline high NLR.
Whether in daily clinical practice or clinical trials, imaging is often the standard to judge whether the tumor progression exists or not. However, patients often have their first imaging evaluation 6–12 weeks after treatment [66,67,68,69]. Imaging evaluation could be considered earlier when the NLR is relatively increased after ICI treatment, especially in patients with high levels of baseline or post-treatment NLR. Moreover, recently published studies indicated NLR (including baseline NLR and early change in NLR) is an important factor for hyperprogressive disease and pseudo-progression, suggesting the combination of NLR and imaging evaluation may help in reaching more accurate conclusions when imaging evaluation alone is not conclusive [33,70,71].
It is recognized that many components, including stromal cells, immune cells, and vasculature, together constitute a complex tumor microenvironment [72]. It has been widely reported that in the immune cells, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes play an important role in cancer immune surveillance and cytotoxic cell death and therefore inhibit the growth of tumors [73]. Checkpoint inhibitor therapies cannot come into play in patients with immunologically cold tumors which contain scarce tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes [74]. Previous studies indicated tumor cells secrete chemokines and growth factors such as IL-8 and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor recruiting neutrophils into tumors, aiding vascular invasion, and orchestrating the metastatic potential of tumor cells [42,75]. More importantly, neutrophils contribute to forming the immunosuppressive microenvironment by secreting myeloperoxidase and arginase-1 and upregulating PD-L1 and MDSC, a differentiation status of suppressive myeloid cells, preventing T-cell activation in the tumor and resulting in a decrease in the efficacy of immunotherapy [11]. The correlation between peripheral blood NLR and clinical outcomes may be attributed to the correlation between circulating neutrophils and neutrophils in the tumor microenvironment [76,77], and low levels of circulating lymphocytes may be associated with low levels of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and reduced anti-tumor T-cell responses [12,78,79]. A high level of NLR at baseline treatment implies an increase in neutrophil count and/or a decrease in lymphocyte count, probably indicating the repertoires of anti-tumor immunity are relatively absent; meanwhile, the occurrence of increased NLR after ICI treatment is more likely to imply the absence of response to ICI treatment, finally impairing survival benefit of patients.
This analysis has some limitations. First, most of the included studies are retrospective studies leading to inevitable selection bias. Second, there is no unified definition of critical value for the increase or decrease in NLR; this is also a potential source of heterogeneity. In addition, our study included a limited category of malignancies, mainly including NSCLC, renal cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Therefore, further large-scale prospective studies including more types of malignancies are needed. Despite these limitations, the results of the meta-analysis are reliable because among most of the results, low heterogeneity was detected and publication bias was not observed.
5. Conclusions
The NLR level of tumor patients after ICI treatment is stable overall, but the NLR level in patients without response to immunotherapy may increase after ICI treatment. Patients with an upward trend in NLR after ICI treatment were associated with worse clinical outcomes; meanwhile, the downward trend in NLR was associated with better clinical outcomes. Post-treatment high NLR was associated with more impaired survival than baseline high NLR. Monitoring the dynamics of NLR in patients treated with immunotherapy may contribute to the evaluation of tumor response, risk stratification, and patient management.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cancers14215297/s1, Figure S1: The pooled proportion of patients with increased NLR after immunotherapy; Figure S2: Baujat plot for studies reporting the association between the trends in NLR after ICI treatment and ORR; Figure S3: Sensitivity analysis for studies reporting the association between the trends in NLR after ICI treatment and ORR; Figure S4: Baujat plot for studies reporting the association between OS and NLR at two different time points with the same cut-off values of NLR; Figure S5: Sensitivity analysis for studies reporting the association between OS and NLR at two different time points with the same cut-off values of NLR; Figure S6: Sensitivity analysis for studies reporting the association between PFS and NLR at two different time points with the same cut-off values of NLR; Figure S7: Funnel plot plotted after application of the trim-and-fill method; Table S1: Studies reporting the association between the changes in NLR and the response to immunotherapy; Table S2: Studies reporting the association between trends in NLR and prognosis; Table S3: Studies that gave the values of baseline and post-treatment NLR with the same cut-off values.
Author Contributions
Conception and design: Y.G., L.Y. and C.Z.; administrative support: C.Z.; collection of data from literature: Y.G. and J.W.; data analysis and interpretation: Y.G. and D.X.; manuscript writing: Y.G., L.Y., J.W., D.X. and C.Z.; final approval of manuscript: Y.G., L.Y., J.W., D.X. and C.Z.; accountable for all aspects of the work: Y.G., L.Y., J.W., D.X. and C.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 81873919).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used and/or analyzed for this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Tianxiang Li (Peking Union Medical College Hospital) for her support in statistics. We also thank Xuefeng Kan and Licheng Zhu (Wuhan Union Hospital) for their scientific advice on this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- Hartmann, J.; Schüßler-Lenz, M.; Bondanza, A.; Buchholz, C.J. Clinical development of CAR T cells-challenges and opportunities in translating innovative treatment concepts. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 1183–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z. Local biomaterials-assisted cancer immunotherapy to trigger systemic antitumor responses. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 5506–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.A.; Minn, A.J. Combination Cancer Therapy with Immune Checkpoint Blockade: Mechanisms and Strategies. Immunity 2018, 48, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, E.P.; Mooradian, M.J.; Baruch, E.N.; Yilmaz, M.; Reynolds, K.L. Immune-Related Adverse Events (irAEs): Diagnosis, Management, and Clinical Pearls. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, T.; Shiu, K.K.; Kim, T.W.; Jensen, B.V.; Jensen, L.H.; Punt, C.; Smith, D.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Benavides, M.; Gibbs, P.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Microsatellite-Instability-High Advanced Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Giaccone, G.; de Marinis, F.; Reinmuth, N.; Vergnenegre, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Morise, M.; Felip, E.; Andric, Z.; Geater, S.; et al. Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of PD-L1-Selected Patients with NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büttner, R.; Longshore, J.W.; López-Ríos, F.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Normanno, N.; Rouleau, E.; Penault-Llorca, F. Implementing TMB measurement in clinical practice: Considerations on assay requirements. ESMO Open 2019, 4, e000442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, D.C.; Sahin, T.K.; Erul, E.; Cakir, I.Y.; Ucgul, E.; Yildirim, H.C.; Aktepe, O.H.; Erman, M.; Kilickap, S.; Aksoy, S.; et al. The Association between Early Changes in Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio and Survival in Patients Treated with Immunotherapy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.L.; Chen, Y.M.; Tang, K.T.; Chen, P.K.; Liu, H.J.; Chen, D.Y. MicroRNA-223 inhibits neutrophil extracellular traps formation through regulating calcium influx and small extracellular vesicles transmission. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberg, H.H.; Wesch, D.; Kalyan, S.; Kabelitz, D. Regulatory Interactions Between Neutrophils, Tumor Cells and T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valero, C.; Lee, M.; Hoen, D.; Weiss, K.; Kelly, D.W.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Paik, P.K.; Plitas, G.; Ladanyi, M.; Postow, M.A.; et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and mutational burden as biomarkers of tumor response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Zhou, S.; Lin, H.; Liao, Z.; Ding, Y.; Ling, L.; Wang, X. Prognostic Value of Baseline Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Outcome of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancer Investig. 2019, 37, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, D.; Li, W. Association of the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and clinical outcomes in patients with lung cancer receiving immunotherapy: A meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Jiang, J.; Tang, S.; Sun, G. Predictive value of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A meta-analysis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 85, 106677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmamed, M.F.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Schalper, K.A.; Fusco, J.P.; Gonzalez, A.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Oñate, C.; Perez, G.; Alfaro, C.; Martín-Algarra, S.; et al. Changes in serum interleukin-8 (IL-8) levels reflect and predict response to anti-PD-1 treatment in melanoma and non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1988–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutsikou, E.; Domvri, K.; Hardavella, G.; Tsiouda, D.; Zarogoulidis, K.; Kontakiotis, T. Tumour necrosis factor, interferon-gamma and interleukins as predictive markers of antiprogrammed cell-death protein-1 treatment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A pragmatic approach in clinical practice. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1758835918768238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.U.; Kang, H.S.; Yeo, C.D.; Kim, J.S.; Park, C.K.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.H. Predictability of early changes in derived neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 2824–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Du, X.; Chen, Y.; Xia, J.; Wang, R.; Zhu, M.; Peng, W.; Spitaleri, G.; Hofman, P.; Bironzo, P.; et al. Association between changes in thioredoxin reductase and other peripheral blood biomarkers with response to PD-1 inhibitor-based combination immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective study. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 757–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, S.; Xia, J.; Du, X.; Wu, Y.; Pan, B.; Zhu, W.; Shen, B. Association of Dynamic Changes in Peripheral Blood Indexes With Response to PD-1 Inhibitor-Based Combination Therapy and Survival Among Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 672271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalani, A.A.; Xie, W.; Martini, D.J.; Steinharter, J.A.; Norton, C.K.; Krajewski, K.M.; Duquette, A.; Bossé, D.; Bellmunt, J.; Van Allen, E.M.; et al. Change in Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in response to immune checkpoint blockade for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. ImmunoTherapy Cancer 2018, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, K.; Kanda, S.; Goto, Y.; Horinouchi, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Motoi, N.; Ohe, Y. Change in the lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio is an early surrogate marker of the efficacy of nivolumab monotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 124, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, Y.; Takahari, D.; Suzuki, T.; Osumi, H.; Nakayama, I.; Oki, A.; Wakatsuki, T.; Ichimura, T.; Ogura, M.; Shinozaki, E.; et al. Changes in the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio during nivolumab monotherapy are associated with gastric cancer survival. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2020, 85, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Fan, Q.; Shu, Y.; Yang, L.; Cui, T.; Gu, K.; Tao, M.; Wang, X.; Cui, C.; et al. Clinical and biomarker analyses of sintilimab versus chemotherapy as second-line therapy for advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A randomized, open-label phase 2 study (ORIENT-2). Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, F.; Liu, B.; Hong, X.; et al. Clinical Characteristics Correlate With Outcomes of Immunotherapy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 7137–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Miyake, M.; Hori, S.; Ichikawa, K.; Omori, C.; Iemura, Y.; Owari, T.; Itami, Y.; Nakai, Y.; Anai, S.; et al. Clinical Impact of Sarcopenia and Inflammatory/Nutritional Markers in Patients with Unresectable Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma Treated with Pembrolizumab. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zer, A.; Sung, M.R.; Walia, P.; Khoja, L.; Maganti, M.; Labbe, C.; Shepherd, F.A.; Bradbury, P.A.; Feld, R.; Liu, G.; et al. Correlation of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Absolute Neutrophil Count With Outcomes With PD-1 Axis Inhibitors in Patients With Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, 426–434.e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Terakawa, T.; Furukawa, J.; Harada, K.; Hinata, N.; Nakano, Y.; Fujisawa, M. C-reactive protein and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio are prognostic biomarkers in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with nivolumab. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Kwon, D.; Saravia, D.; Desai, A.; Vargas, F.; El Dinali, M.; Warsch, J.; Elias, R.; Chae, Y.K.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Developing a Predictive Model for Clinical Outcomes of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated With Nivolumab. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, 280–288.e284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Li, L.L.; Guan, Y.P.; Feng, D.F.; Yin, B.B.; Liang, X.F.; Yin, J.; Jiang, R.; Liang, J.; et al. Dynamics of Early Serum Tumour Markers and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predict Response to PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 8241–8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prelaj, A.; Rebuzzi, S.E.; Pizzutilo, P.; Bilancia, M.; Montrone, M.; Pesola, F.; Longo, V.; Del Bene, G.; Lapadula, V.; Cassano, F.; et al. EPSILoN: A Prognostic Score Using Clinical and Blood Biomarkers in Advanced Non-Small-cell Lung Cancer Treated With Immunotherapy. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, 365–377.e365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikarashi, D.; Kato, Y.; Kato, R.; Kanehira, M.; Takata, R.; Obara, W. Inflammatory markers for predicting responses to nivolumab in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Urol. Off. J. Jpn. Urol. Assoc. 2020, 27, 350–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Lee, D.; Shim, J.H.; Lim, Y.S.; Lee, H.C.; Yoo, C.; Ryu, M.H.; Ryoo, B.Y.; et al. Kinetics of the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio during PD-1 inhibition as a prognostic factor in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2021, 41, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passiglia, F.; Galvano, A.; Castiglia, M.; Incorvaia, L.; Calò, V.; Listì, A.; Mazzarisi, S.; Perez, A.; Gallina, G.; Rizzo, S.; et al. Monitoring blood biomarkers to predict nivolumab effectiveness in NSCLC patients. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919839928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, M.R.; Wolchok, R.E.; Zheng, J.; Panageas, K.S.; Wolchok, J.D.; Coit, D.; Postow, M.A.; Ariyan, C. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio is Associated With Outcome During Ipilimumab Treatment. EBioMedicine 2017, 18, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, N.; Hirobe, M.; Kikushima, T.; Matsuki, M.; Takahashi, A.; Yanase, M.; Ichimatsu, K.; Egawa, M.; Hayashi, N.; Negishi, T.; et al. The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio has a role in predicting the effectiveness of nivolumab in Japanese patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A multi-institutional retrospective study. BMC Urol. 2020, 20, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameratunga, M.; Chénard-Poirier, M.; Moreno Candilejo, I.; Pedregal, M.; Lui, A.; Dolling, D.; Aversa, C.; Ingles Garces, A.; Ang, J.E.; Banerji, U.; et al. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio kinetics in patients with advanced solid tumours on phase I trials of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 89, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, T.; Satake, H.; Ogata, M.; Hatachi, Y.; Inoue, K.; Hamada, M.; Yasui, H. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictive or prognostic factor for gastric cancer treated with nivolumab: A multicenter retrospective study. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 34520–34527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusselier, M.; Deluche, E.; Delacourt, N.; Ballouhey, J.; Egenod, T.; Melloni, B.; Vergnenègre, C.; Veillon, R.; Vergnenègre, A. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio evolution is an independent predictor of early progression of second-line nivolumab-treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancers. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.Y.; Oen, K.Q.X.; Lim, G.R.S.; Hartono, J.L.; Muthiah, M.; Huang, D.Q.; Teo, F.S.W.; Li, A.Y.; Mak, A.; Chandran, N.S.; et al. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Development of Immune-Related Adverse Events and Outcomes from Immune Checkpoint Blockade: A Case-Control Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Han, R.; Zhong, Y.; Weng, N.; Zhang, A. Post treatment NLR is a predictor of response to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khunger, M.; Patil, P.D.; Khunger, A.; Li, M.; Hu, B.; Rakshit, S.; Basu, A.; Pennell, N.; Stevenson, J.P.; Elson, P.; et al. Post-treatment changes in hematological parameters predict response to nivolumab monotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Huang, Z.; Xin, L.; Qin, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Shi, W.; Yang, B.; Zhang, G.; Hu, Y. Post-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) predicts response to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibody in SCLC patients at early phase. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2021, 70, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilen, M.A.; Martini, D.J.; Liu, Y.; Lewis, C.; Collins, H.H.; Shabto, J.M.; Akce, M.; Kissick, H.T.; Carthon, B.C.; Shaib, W.L.; et al. The prognostic and predictive impact of inflammatory biomarkers in patients who have advanced-stage cancer treated with immunotherapy. Cancer 2019, 125, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Mo, H.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, J.; Huang, J. Prognostic and predictive impact of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and HLA-I genotyping in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, D.; Jinnouchi, N.; Abe, M.; Ikarashi, D.; Matsuura, T.; Kato, R.; Maekawa, S.; Kato, Y.; Kanehira, M.; Takata, R.; et al. Prognostic outcomes and safety in patients treated with pembrolizumab for advanced urothelial carcinoma: Experience in real-world clinical practice. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Cui, P.; Jia, W.; Zhang, S.; Tao, H.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; et al. Prognostic value of baseline and change in neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for survival in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with poor performance status receiving PD-1 inhibitors. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viñal, D.; Gutierrez-Sainz, L.; Martinez, D.; Garcia-Cuesta, J.A.; Pedregosa, J.; Villamayor, J.; Ostios, L.; Sanchez-Cabrero, D.; Higuera, O.; Pinto, A.; et al. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in advanced cancer patients receiving immunotherapy. Clin. Transl. Oncol. Off. Publ. Fed. Span. Oncol. Soc. Natl. Cancer Inst. Mex. 2021, 23, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Yatsuda, J.; Shimokawa, M.; Fuji, N.; Aoki, A.; Sakano, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Suga, A.; Tei, Y.; Yoshihiro, S.; et al. Prognostic value of pre-treatment risk stratification and post-treatment neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio change for pembrolizumab in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 26, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Ahn, B.; Hong, S.M.; Jung, H.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, K.D.; Ahn, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Na, H.K.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Real-World Efficacy Data and Predictive Clinical Parameters for Treatment Outcomes in Advanced Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 54, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Tamiya, A.; Taniguchi, Y.; Adachi, Y.; Enomoto, T.; Azuma, K.; Inagaki, Y.; Kouno, S.; Matsuda, Y.; Okishio, K.; et al. Retrospective analysis of long-term survival factors in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Han, X.; Zha, H.; Tao, H.; Li, X.; Yuan, F.; Chen, G.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Hu, Y. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Changes of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio as Prognostic Biomarkers for Patients With Pancreatic Cancer Treated With Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 585271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namikawa, T.; Yokota, K.; Tanioka, N.; Fukudome, I.; Iwabu, J.; Munekage, M.; Uemura, S.; Maeda, H.; Kitagawa, H.; Kobayashi, M.; et al. Systemic inflammatory response and nutritional biomarkers as predictors of nivolumab efficacy for gastric cancer. Surg. Today 2020, 50, 1486–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonaggio, A.; Elaidi, R.; Fournier, L.; Fabre, E.; Ferrari, V.; Borchiellini, D.; Thouvenin, J.; Barthelemy, P.; Thibault, C.; Tartour, E.; et al. Variation in neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as predictor of outcomes in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) and non-small cell lung cancer (mNSCLC) patients treated with nivolumab. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2020, 69, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, K.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, M.; Keam, B.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, D.W.; Heo, D.S.; Lee, J.S. Post-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio at week 6 is prognostic in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancers treated with anti-PD-1 antibody. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2018, 67, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lin, N.; Mao, B.; Wu, Q. The efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis based on 40 cohorts incorporating 3697 individuals. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, Y.; Oya, R.; Takemoto, N.; Inohara, H. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: Meta-analysis. Head Neck 2022, 44, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Liu, S.; Liang, C.; Han, X.; Shi, Y. Pretreatment hematological markers predict clinical outcome in cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: A meta-analysis. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Mao, J.; Tao, P.; Chi, H.; Jia, W.; Dong, C. The relationship between NLR/PLR/LMR levels and survival prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Medicine 2022, 101, e28617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, T.; Mori, K.; Katayama, S.; Mostafaei, H.; Quhal, F.; Laukhtina, E.; Rajwa, P.; Motlagh, R.S.; Aydh, A.; König, F.; et al. Hematological prognosticators in metastatic renal cell cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A meta-analysis. Immunotherapy 2022, 14, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Meng, F.; Jiang, R. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Biomarker for Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 746976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunno, V.D.; Mollica, V.; Gatto, L.; Santoni, M.; Cosmai, L.; Porta, C.; Massari, F. Prognostic impact of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Immunotherapy 2019, 11, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platini, H.; Ferdinand, E.; Kohar, K.; Prayogo, S.A.; Amirah, S.; Komariah, M.; Maulana, S. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as Prognostic Markers for Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Immunotherapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicina 2022, 58, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, T.; Mori, K.; Katayama, S.; Mostafaei, H.; Quhal, F.; Laukhtina, E.; Rajwa, P.; Motlagh, R.S.; Aydh, A.; König, F.; et al. Pretreatment clinical and hematologic prognostic factors of metastatic urothelial carcinoma treated with pembrolizumab: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 27, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, P.R.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Zhu, A.X.; Kim, T.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sorafenib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (IMbrave150): An open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudier, B.; Sharma, P.; McDermott, D.F.; George, S.; Hammers, H.J.; Srinivas, S.; Tykodi, S.S.; Sosman, J.A.; Procopio, G.; Plimack, E.R.; et al. CheckMate 025 Randomized Phase 3 Study: Outcomes by Key Baseline Factors and Prior Therapy for Nivolumab Versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rini, B.I.; Powles, T.; Atkins, M.B.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; Suarez, C.; Bracarda, S.; Stadler, W.M.; Donskov, F.; Lee, J.L.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sunitinib in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (IMmotion151): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2404–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Mok, T.S.K.; Nishio, M.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower150): Key subgroup analyses of patients with EGFR mutations or baseline liver metastases in a randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriu, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Nagano, T.; Hazama, D.; Sekiya, R.; Katsurada, M.; Katsurada, N.; Tachihara, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Nishimura, Y. Pseudo-Progression and the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Case-Control Study. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 10559–10568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.G.; Kim, C.; Yoon, S.E.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, S.J.; Kang, B.; Kim, H.R.; Park, S.H.; Shin, E.C.; Kim, Y.Y.; et al. Hyperprogressive disease during PD-1 blockade in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.P.; Ju, L.; Chen, C.; Liu, T.; Li, S.; Wang, X. DNA Methylation-Based Panel Predicts Survival of Patients With Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma and Its Correlations With Genomic Metrics and Tumor Immune Cell Infiltration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 572628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Ye, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, X. Pretreatment Inflammatory Indexes as Prognostic Predictors for Survival in Colorectal Cancer Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, J.F.; Naseem, A.F.; Mok, H.; Schaeffer, A.J.; Abdulkadir, S.A.; Thumbikat, P. Multi-faceted immunomodulatory and tissue-tropic clinical bacterial isolate potentiates prostate cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalafati, L.; Mitroulis, I.; Verginis, P.; Chavakis, T.; Kourtzelis, I. Neutrophils as Orchestrators in Tumor Development and Metastasis Formation. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 581457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takakura, K.; Ito, Z.; Suka, M.; Kanai, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Odahara, S.; Matsudaira, H.; Haruki, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Saito, R.; et al. Comprehensive assessment of the prognosis of pancreatic cancer: Peripheral blood neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and immunohistochemical analyses of the tumour site. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohki, S.; Shibata, M.; Gonda, K.; Machida, T.; Shimura, T.; Nakamura, I.; Ohtake, T.; Koyama, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Ohto, H.; et al. Circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells are increased and correlate to immune suppression, inflammation and hypoproteinemia in patients with cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restifo, N.P.; Dudley, M.E.; Rosenberg, S.A. Adoptive immunotherapy for cancer: Harnessing the T cell response. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havel, J.J.; Chowell, D.; Chan, T.A. The evolving landscape of biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).