Prognostic Impact of MAFLD Following Surgical Resection of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Outcomes of the Study
2.3. Definition of Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Patients
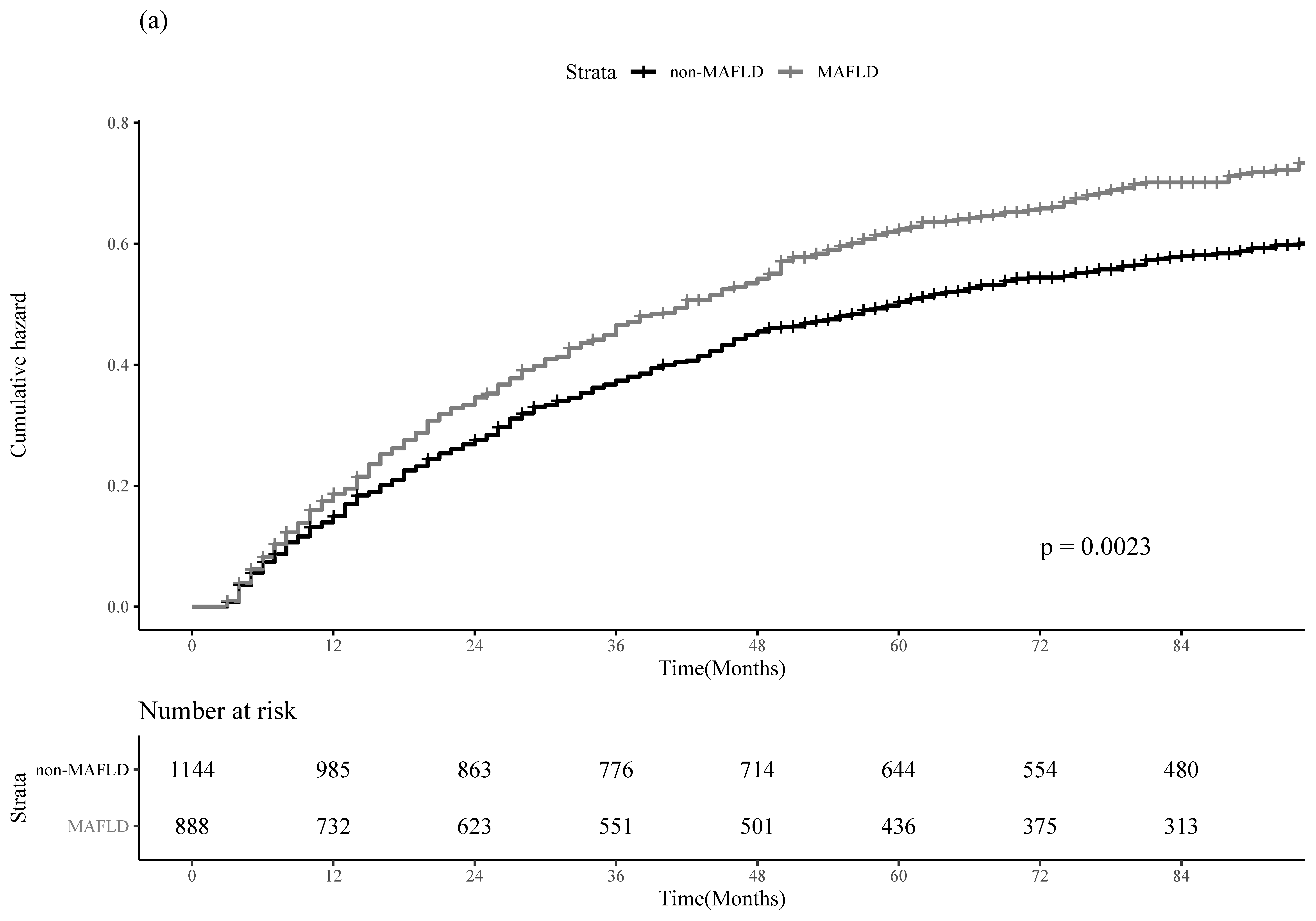
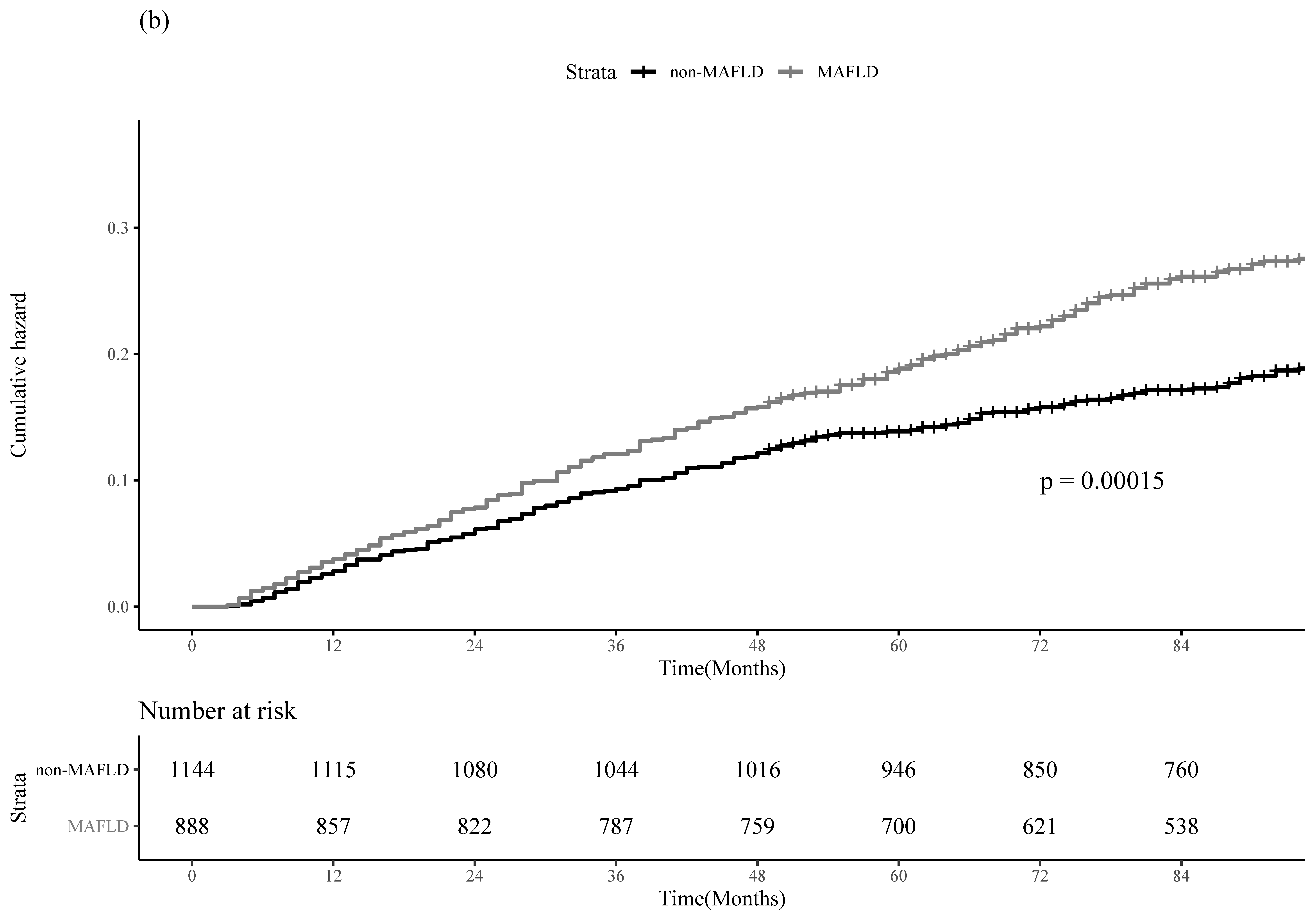
3.2. Clinical Outcomes of HCC Recurrence and All-Cause Mortality between the MAFLD and Non-MAFLD Groups in the Entire Cohort
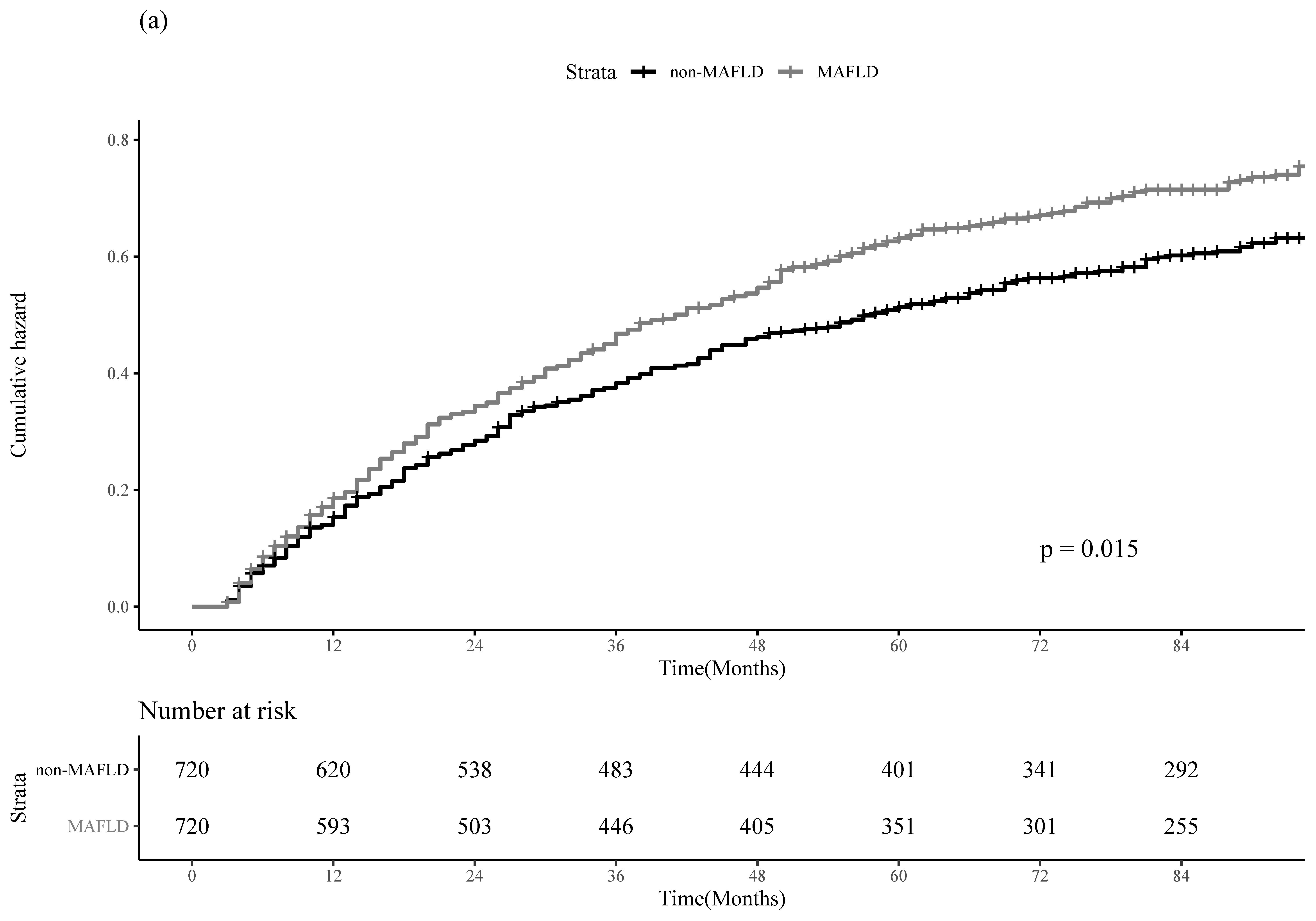
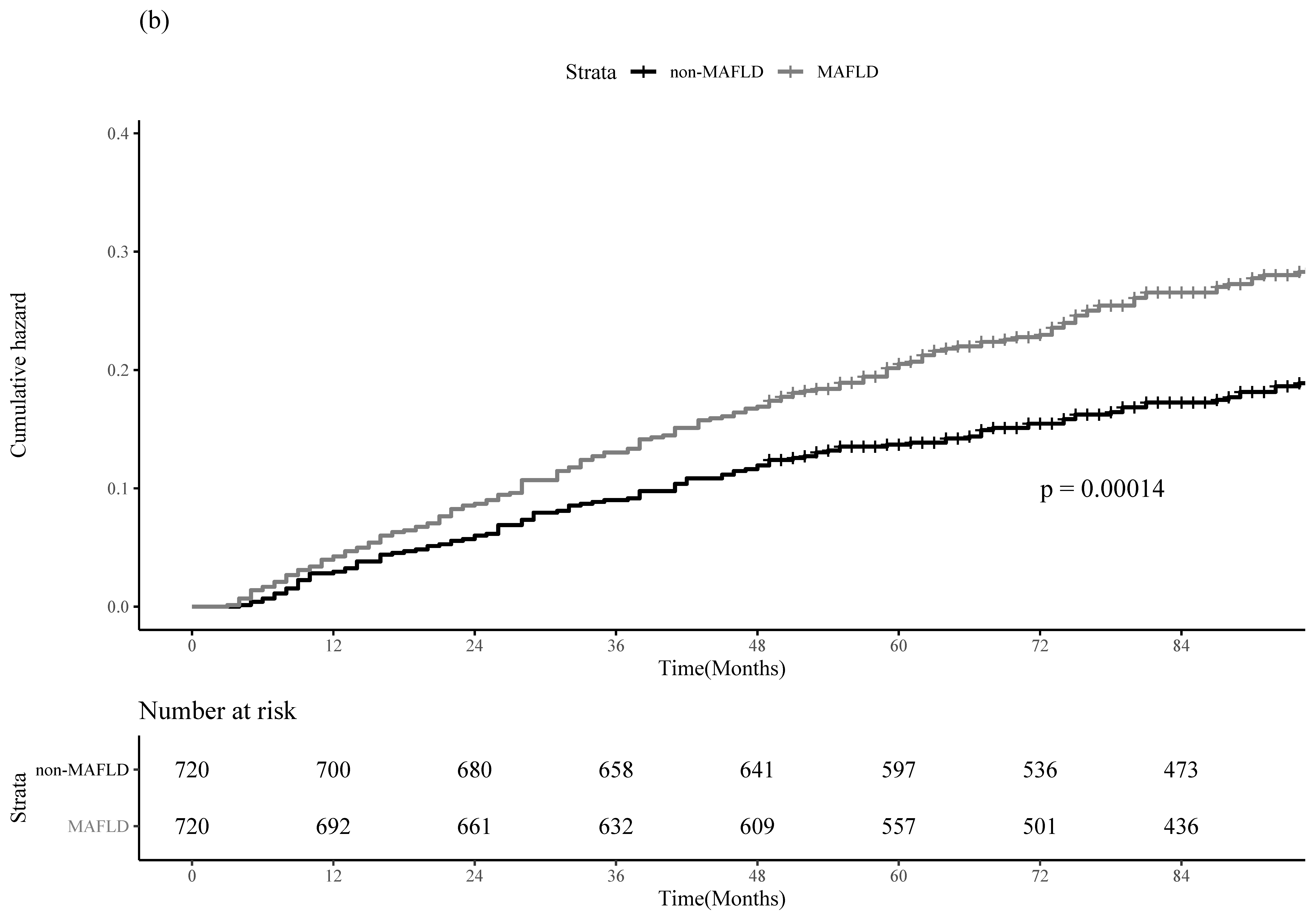
3.3. PS-Matching and IPTW Analyses
3.4. Sensitivity Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paik, J.M.; Younossi, Y.; Henry, L.; Mishra, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Recent trends in the global burden of hepatitis b virus: 2007–2017. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1845–1846.e1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis b: Aasld 2018 hepatitis b guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association For The Study of The Liver. EASL 2017 clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis b virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Plank, L.D.; Suk, K.T.; Park, Y.E.; Lee, J.; Choi, J.H.; Heo, N.Y.; Park, J.; Kim, T.O.; Moon, Y.S.; et al. Trends in the prevalence of chronic liver disease in the korean adult population, 1998–2017. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in globocan 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcellin, P.; Gane, E.; Buti, M.; Afdhal, N.; Sievert, W.; Jacobson, I.M.; Washington, M.K.; Germanidis, G.; Flaherty, J.F.; Aguilar Schall, R.; et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis b: A 5-year open-label follow-up study. Lancet 2013, 381, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Yang, H.I.; Su, J.; Jen, C.L.; You, S.L.; Lu, S.N.; Huang, G.T.; Iloeje, U.H. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis b virus DNA level. JAMA 2006, 295, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Yoon, E.L.; Park, H.; Kwon, J.H.; Sinn, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.W. Comparison of clinical practice guidelines for the management of chronic hepatitis b: When to start, when to change, and when to stop. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stickel, F.; Hellerbrand, C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as a risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanisms and implications. Gut 2010, 59, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoulfas, G. Hepatocellular carcinoma and metabolic syndrome: The times are changing and so should we. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 3842–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.N.; Han, K.; Yoo, J.; Hwang, S.G.; Ahn, S.H. Increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and mortality in chronic viral hepatitis with concurrent fatty liver. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 55, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roayaie, S.; Obeidat, K.; Sposito, C.; Mariani, L.; Bhoori, S.; Pellegrinelli, A.; Labow, D.; Llovet, J.M.; Schwartz, M.; Mazzaferro, V. Resection of hepatocellular cancer ≤2 cm: Results from two western centers. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kang, W.; Sinn, D.H.; Gwak, G.Y.; Paik, Y.H.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Koh, K.C.; Paik, S.W. Substantial risk of recurrence even after 5 recurrence-free years in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamai, H.; Okamura, J. New next-generation microwave thermosphere ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Ho, H.J.; Hsu, Y.C.; Kuo, K.N.; Wu, M.S.; Lin, J.T. Association between nucleoside analogues and risk of hepatitis b virus–related hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence following liver resection. JAMA 2012, 308, 1906–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.L.; Tse, Y.K.; Chan, H.L.; Yip, T.C.; Tsoi, K.K.; Wong, V.W. Oral nucleos(t)ide analogues reduce recurrence and death in chronic hepatitis b-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, K.S.; Choi, J.S.; Moon, B.S.; Han, K.H.; Chon, C.Y.; Moon, Y.M.; et al. Persistent hepatitis b viral replication affects recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2008, 28, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of nafld and nash: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, C.K.; Zinman, B.; Retnakaran, R. Are metabolically healthy overweight and obesity benign conditions? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 159, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Schick, F.; Häring, H.U. Causes, characteristics, and consequences of metabolically unhealthy normal weight in humans. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, W.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, S.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, M.W.; Park, C.H.; Yoon, S.K. Obesity and the risk of primary liver cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J. Mafld: A consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.H.; Cho, Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Kim, S.U.; Lee, J.W. From nonalcoholic fatty liver disease to metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: Big wave or ripple? Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Konyn, P.; Sandhu, K.K.; Dennis, B.B.; Cheung, A.C.; Ahmed, A. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease is associated with increased all-cause mortality in the united states. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, H.C. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and incident cardiovascular disease risk: A nationwide cohort study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2021, 19, 2138–2147.e2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment Guidelines, Republic of Korera. Available online: https://livercancer.Or.Kr/study/guidelines.Php (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Torimura, T.; Iwamoto, H. Optimizing the management of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: Current trends and prospects. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Lim, Y.S.; Kim, K.M.; Shim, J.H.; Lee, D.; An, J.; Jung, J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.C. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for small (≤5 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma not amenable to curative treatment: Results of a single-arm, phase ii clinical trial. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, G.; Bellentani, S.; Miglioli, L.; Masutti, F.; Passalacqua, M.; Castiglione, A.; Tiribelli, C. The fatty liver index: A simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.G.; Kim, D.Y.; Kang, D.W.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, C.K.; Kim, Y.; Yang, W.; Park, E.S.; Lee, S.H. Physical activity frequency and the risk of stroke: A nationwide cohort study in Korea. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Yoon, C.H.; Youn, T.J.; Chae, I.H. Mortality reduction with physical activity in patients with and without cardiovascular disease. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3547–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Physical activity guidelines advisory committee report, 2008. To the secretary of health and human services. Part a: Executive summary. Nutr. Rev. 2009, 67, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, A. Ethnic-specific criteria for classification of body mass index: A perspective for asian indians and american diabetes association position statement. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2015, 17, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.B.; Moon, H.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, E.J.; Yu, S.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Zoulim, F.; Lee, J.; Yoon, J.H. Association of metabolic risk factors with risks of cancer and all-cause mortality in patients with chronic hepatitis b. Hepatology 2021, 73, 2266–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.W.; Lin, C.L.; Liu, C.J.; Yang, S.H.; Tseng, Y.L.; Wu, C.F. Influence of metabolic risk factors on risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver-related death in men with chronic hepatitis b: A large cohort study. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1006–1017.e1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, J.W.; Hyun, J.J.; Kim, B.; Han, K.D. Influence of metabolic syndrome on cancer risk in hbv carriers: A nationwide population based study using the national health insurance service database. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, H.I.; Yeh, M.L.; Le, M.H.; Le, A.K.; Yeo, Y.H.; Dai, C.Y.; Barnett, S.; Zhang, J.Q.; Huang, J.F.; et al. Association between fatty liver and cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and hepatitis b surface antigen seroclearance in chronic hepatitis b. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, K.M.; Prieto, M.; Cheong, C.K.; Di Martino, M.; Ielpo, B.; Goh, B.K.P.; Koh, Y.X. Outcomes after curative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis and review of current literature. HPB Off. J. Int. Hepato Pancreato Biliary Assoc. 2021, 23, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, N.K.; Sharma, D.; Ding, X.; Lin, S.; Marra, F.; Merlin, D.; Anania, F.A. Concomitant activation of the jak/stat, pi3k/akt, and erk signaling is involved in leptin-mediated promotion of invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2497–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalamaga, M.; Diakopoulos, K.N.; Mantzoros, C.S. The role of adiponectin in cancer: A review of current evidence. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 547–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Loo, T.M.; Atarashi, K.; Kanda, H.; Sato, S.; Oyadomari, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Oshima, K.; Morita, H.; Hattori, M.; et al. Obesity-induced gut microbial metabolite promotes liver cancer through senescence secretome. Nature 2013, 499, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Tanaka, Y. Novel biomarkers for the management of chronic hepatitis b. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.W.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, H.S.; Tak, K.Y.; Nam, H.; Sung, P.S.; Bae, S.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoon, S.K.; Roberts, L.R. Persistence of intrahepatic hepatitis b virus DNA integration in patients developing hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatitis b surface antigen seroclearance. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.S.; Chang, D.R.; Kim, H.; Kim, M.J. Comparison of li-rads 2018 and klca-ncc 2018 for noninvasive diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma using magnetic resonance imaging. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.W.; Kao, J.H.; Tseng, T.C. Three heads are better than two: Hepatitis b core-related antigen as a new predictor of hepatitis b virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cho, E.H.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, R. Prognosis after intrahepatic recurrence in the patients who underwent curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Surg. 2020, 24, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, C.G.; Yim, S.Y.; Um, S.H.; Lee, Y.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, T.H.; Goh, H.G.; Lee, Y.S.; Suh, S.J.; Han, N.Y.; et al. Survival according to recurrence patterns after resection for transplantable hepatocellular carcinoma in hbv endemic area: Appraisal of liver transplantation strategy. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2020, 44, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabrizian, P.; Jibara, G.; Shrager, B.; Schwartz, M.; Roayaie, S. Recurrence of hepatocellular cancer after resection: Patterns, treatments, and prognosis. Ann. Surg. 2015, 261, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Bang, H.; Park, Y.M.; Bae, J.C.; Lee, B.W.; Kang, E.S.; Cha, B.S.; Lee, H.C.; Balkau, B.; Lee, W.Y.; et al. Non-laboratory-based self-assessment screening score for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Development, validation and comparison with other scores. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.J. Hepatitis b virus mutations related to liver disease progression of korean patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| The Entire Cohort (n = 2032) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-MAFLD (n = 1144) | MAFLD (n = 888) | p-Value | |
| Age | 0.355 | ||
| 55.1 (8.8) | 54.8 (8.4) | ||
| Sex | <0.001 | ||
| Male | 788 (68.9%) | 795 (89.5%) | |
| Female | 356 (31.1%) | 93 (10.5%) | |
| Hypertension | <0.001 | ||
| No | 768 (67.1%) | 448 (50.4%) | |
| Yes | 376 (32.9%) | 440 (49.6%) | |
| Diabetes | <0.001 | ||
| No | 900 (78.7%) | 572 (64.4%) | |
| Yes | 244 (21.3%) | 316 (35.6%) | |
| Dyslipidemia | 0.007 | ||
| No | 871 (76.1%) | 629 (70.8%) | |
| Yes | 273 (23.9%) | 259 (29.2%) | |
| Liver cirrhosis | 0.955 | ||
| No | 407 (35.6%) | 317 (35.7%) | |
| Yes | 737 (64.4%) | 571 (64.3%) | |
| Metformin use | <0.001 | ||
| No | 1013 (88.6%) | 697 (78.4%) | |
| Yes | 131 (11.4%) | 191 (21.5%) | |
| Statin use | <0.001 | ||
| No | 1009 (88.2%) | 697 (78.5%) | |
| Yes | 135 (11.8%) | 191 (21.5%) | |
| Antiviral therapy | 0.292 | ||
| No | 243 (21.2%) | 206 (23.2%) | |
| Yes | 901 (78.8%) | 682 (76.8%) | |
| Smoking history | <0.001 | ||
| Non-smoker | 564 (49.3%) | 296 (33.3%) | |
| Ex-smoker | 303 (26.5%) | 274 (30.9%) | |
| Current smoker | 277 (24.2%) | 318 (35.8%) | |
| Alcohol drink | <0.001 | ||
| None | 805 (70.4%) | 405 (45.6%) | |
| Moderate | 247 (21.6%) | 276 (31.1%) | |
| Heavy | 92 (8.0%) | 207 (23.3%) | |
| Physical activity | 0.037 | ||
| 0 to <3 METs-hour/week | 344 (30.1%) | 297 (33.4%) | |
| 3 to <9 METs-hour/week | 272 (23.8%) | 202 (22.8%) | |
| 9 to <18 METs-hour/week | 330 (28.8%) | 273 (30.7%) | |
| ≥18 METs-hour/week | 198 (17.3%) | 116 (13.1%) | |
| HCC Recurrence | All-Cause Mortality | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| MAFLD | ||||
| No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | ||
| Yes | 1.20 (1.04–1.37) | 0.01 | 1.44 (1.17–1.76) | 0.001 |
| MAFLD | HCC Recurrence | All-Cause Mortality | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted HR (95% CI) | p-Value | ||
| PS-Matching | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | ||
| Yes | 1.22 (1.05–1.42) | 0.01 | 1.52 (1.21–1.91) | <0.001 | |
| IPTW | No | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | ||
| Yes | 1.26 (1.16–1.36) | <0.001 | 1.44 (1.28–1.61) | <0.001 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yun, B.; Ahn, S.H.; Oh, J.; Yoon, J.-H.; Kim, B.K. Prognostic Impact of MAFLD Following Surgical Resection of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 5002. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205002
Yun B, Ahn SH, Oh J, Yoon J-H, Kim BK. Prognostic Impact of MAFLD Following Surgical Resection of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Cancers. 2022; 14(20):5002. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205002
Chicago/Turabian StyleYun, Byungyoon, Sang Hoon Ahn, Juyeon Oh, Jin-Ha Yoon, and Beom Kyung Kim. 2022. "Prognostic Impact of MAFLD Following Surgical Resection of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Nationwide Cohort Study" Cancers 14, no. 20: 5002. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205002
APA StyleYun, B., Ahn, S. H., Oh, J., Yoon, J.-H., & Kim, B. K. (2022). Prognostic Impact of MAFLD Following Surgical Resection of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Cancers, 14(20), 5002. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205002






