High-Frequency Pulsed Electric Field Ablation in Beagle Model for Treatment of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
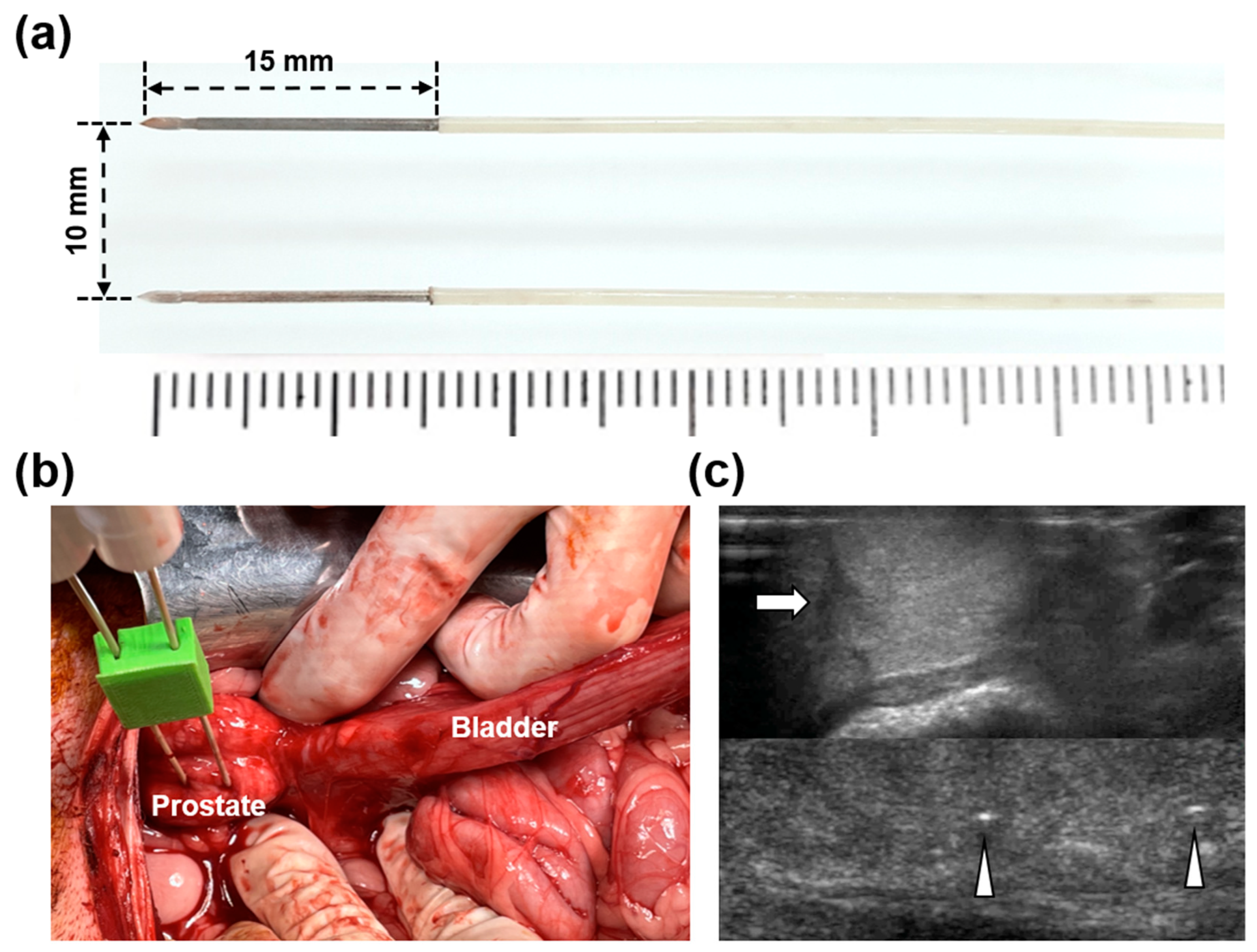
2.1. HF-PEF System and Electrodes
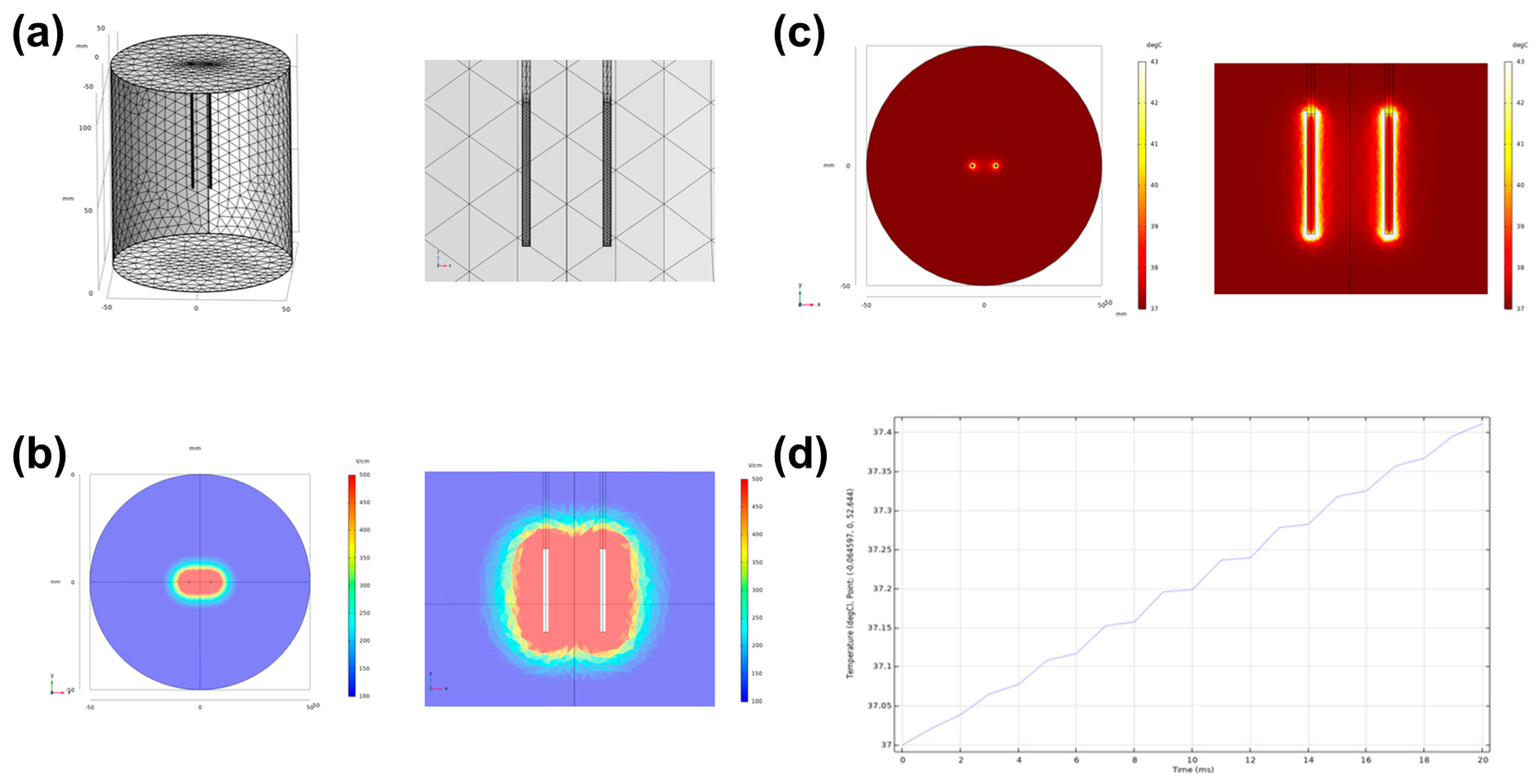
2.2. Simulation of Electrical Field and Temperature Distribution
2.3. Animal Study Design
2.4. IRE with HF-PEF in the Beagle Prostate
2.5. Electrocardiography
2.6. Hematological Examination
2.7. Gross and Histological Examinations
2.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Immunofluorescence
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Simulated Electric Field and Temperature Distribution
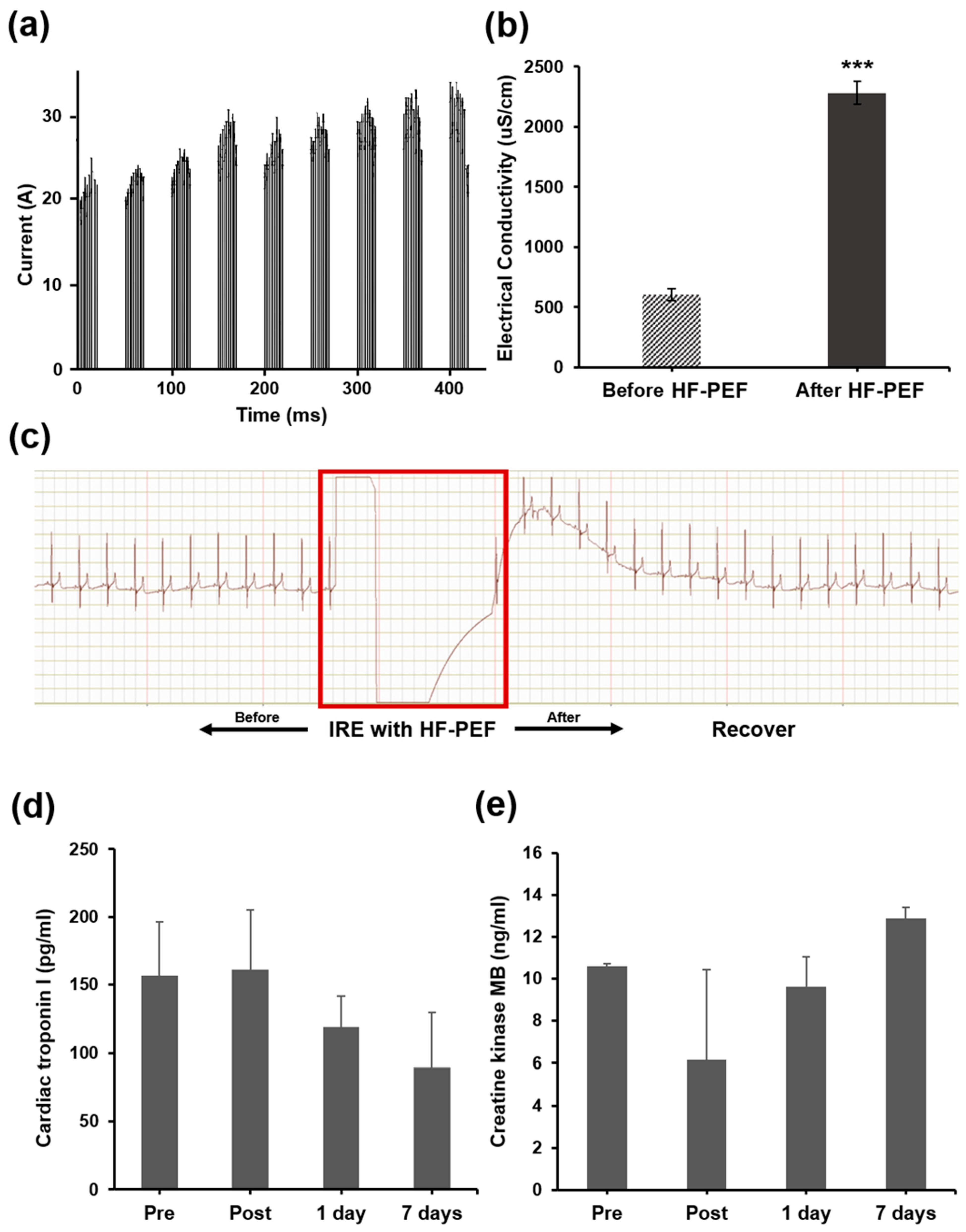
3.2. Procedural Outcomes
3.3. Cardiac Safety after IRE with HF-PEF
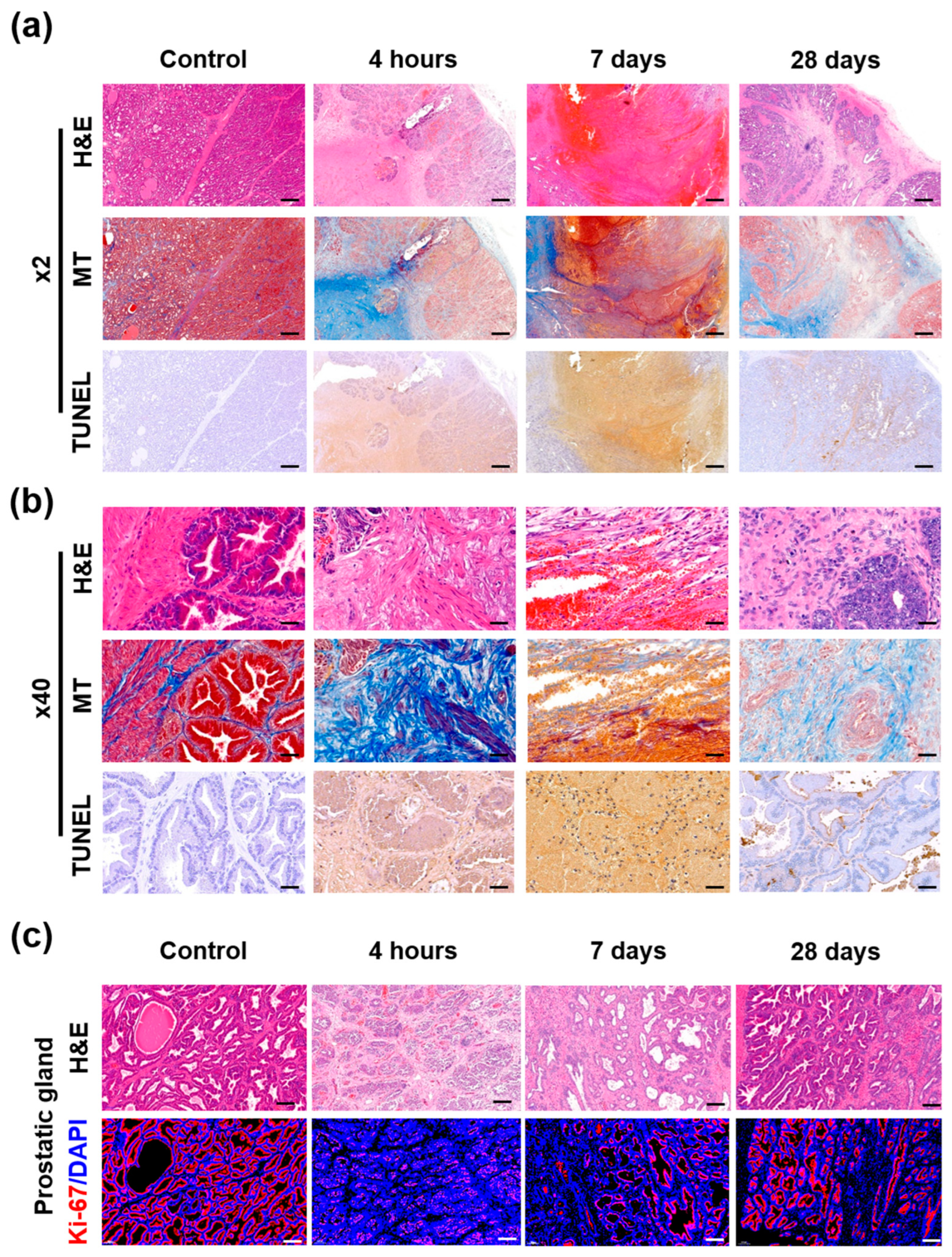
3.4. Gross and Histological Findings
3.5. Immunohistochemical Findings
3.6. Immunofluorescence Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, D.A.; O’Neil, M.E.; Richards, T.B.; Dowling, N.F.; Weir, H.K. Prostate Cancer Incidence and Survival, by Stage and Race/Ethnicity—United States, 2001–2017. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bill-Axelson, A.; Holmberg, L.; Garmo, H.; Rider, J.R.; Taari, K.; Busch, C.; Nordling, S.; Häggman, M.; Andersson, S.-O.; Spångberg, A.; et al. Radical Prostatectomy or Watchful Waiting in Early Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilt, T.J.; Brawer, M.K.; Jones, K.M.; Barry, M.J.; Aronson, W.J.; Fox, S.; Gingrich, J.R.; Wei, J.T.; Gilhooly, P.; Grob, B.M.; et al. Radical Prostatectomy versus Observation for Localized Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanda, M.G.; Dunn, R.L.; Michalski, J.; Sandler, H.M.; Northouse, L.; Hembroff, L.; Lin, X.; Greenfield, T.K.; Litwin, M.S.; Saigal, C.S.; et al. Quality of Life and Satisfaction with Outcome among Prostate-Cancer Survivors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1250–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Yang, Z.; Qi, L.; Chen, M. Robot-assisted and laparoscopic vs open radical prostatectomy in clinically localized prostate cancer: Perioperative, functional, and oncological outcomes: A Systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e15770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnick, M.J.; Koyama, T.; Fan, K.-H.; Albertsen, P.C.; Goodman, M.; Hamilton, A.S.; Hoffman, R.M.; Potosky, A.L.; Stanford, J.L.; Stroup, A.M.; et al. Long-Term Functional Outcomes after Treatment for Localized Prostate Cancer. N, Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahdoot, M.; Lebastchi, A.H.; Turkbey, B.; Wood, B.; Pinto, P.A. Contemporary treatments in prostate cancer focal therapy. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2019, 31, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasivisvanathan, V.; Emberton, M.; Ahmed, H. Focal Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Rationale and Treatment Opportunities. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, G. Irreversible Electroporation. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 32, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsivian, M.; Polascik, T.J. Bilateral focal ablation of prostate tissue using low-energy direct current (LEDC): A preclinical canine study. Br. J. Urol. 2013, 112, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, M.; Dickinson, L.; Ali, A.; Ramachandran, N.; Donaldson, I.; Freeman, A.; Ahmed, H.U.; Emberton, M. A prospective development study investigating focal irreversible electroporation in men with localised prostate cancer: Nanoknife Electroporation Ablation Trial (NEAT). Contemp. Clin. Trials 2014, 39, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerio, M.; Dickinson, L.; Ali, A.; Ramachadran, N.; Donaldson, I.; McCartan, N.; Freeman, A.; Ahmed, H.U.; Emberton, M. Nanoknife Electroporation Ablation Trial: A Prospective Development Study Investigating Focal Irreversible Electroporation for Localized Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2017, 197 Pt 1, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucihar, G.; Mir, L.; Miklavčič, D. The effect of pulse repetition frequency on the uptake into electropermeabilized cells in vitro with possible applications in electrochemotherapy. Bioelectrochemistry 2002, 57, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupanic, A.; Ribaric, S.; Miklavčič, D. Increasing the repetition frequency of electric pulse delivery reduces unpleasant sensations that occur in electrochemotherapy. Neoplasma 2007, 54, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rubinsky, B. Irreversible Electroporation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume xiv, p. 312. [Google Scholar]
- Miklavcic, D. Handbook of Electroporation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kiełbik, A.; Szlasa, W.; Novickij, V.; Szewczyk, A.; Maciejewska, M.; Saczko, J.; Kulbacka, J. Effects of high-frequency nanosecond pulses on prostate cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LackoviĆ, I.; MagjareviĆ, R.; Miklavčič, D. A multiphysics model for studying the influence of pulse repetition frequency on tissue heating during electrochemotherapy. In 4th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, Y.; Rui, S.; Li, C.; Yao, C.; Xu, J.; Bian, C.; Tang, X. Multi-parametric study of temperature and thermal damage of tumor exposed to high-frequency nanosecond-pulsed electric fields based on finite element simulation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 55, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aycock, K.N.; Vadlamani, R.A.; Jacobs, I.V.E.J.; Imran, K.M.; Verbridge, S.S.; Allen, I.C.; Manuchehrabadi, N.; Davalos, R.V. Experimental and numerical investigation of parameters affecting high-frequency irreversible electroporation for prostate cancer ablation. J. Biomech. Eng. 2022, 144, 061003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, B.; Kim, H.B.; Jeong, S.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, J.M.; Park, Y.; Won, D.-S.; Kim, J.W.; Ryu, D.S.; Kim, Y.; et al. Novel platinum bipolar electrode for irreversible electroporation in prostate cancer: Preclinical study in the beagle prostate. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Kim, H.; Park, J.; Kim, K.W.; Sim, S.B.; Chung, J.H. Evaluation of electroporated area using 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride in a potato model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinsky, J.; Onik, G.; Mikus, P.; Rubinsky, B. Optimal Parameters for the Destruction of Prostate Cancer Using Irreversible Electroporation. J. Urol. 2008, 180, 2668–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deodhar, A.; Dickfeld, T.; Single, G.W.; Hamilton, W.C.; Thornton, R.H.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Maybody, M.; Gónen, M.; Rubinsky, B.; Solomon, S.B. Irreversible Electroporation Near the Heart: Ventricular Arrhythmias Can Be Prevented With ECG Synchronization. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, W330–W335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, R.E., 2nd; Millar, J.L.; Kavnoudias, H.; Royce, P.; Rosenfeldt, F.; Pham, A.; Smith, R.; Davalos, R.V.; Thomson, K.R. In vivo characterization and numerical simulation of prostate properties for non-thermal irreversible electroporation ablation. Prostate 2014, 74, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerqueira, J.A.; Restan, W.A.Z.; Fonseca, M.G.; Catananti, L.A.; de Almeida, M.L.M.; Junior, W.H.F.; Pereira, G.T.; Carciofi, A.; Ferraz, G.D.C. Intense exercise and endurance-training program influence serum kinetics of muscle and cardiac biomarkers in dogs. Res. Veter- Sci. 2018, 121, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.; Kang, J.M.; Park, Y.; Won, D.-S.; Kim, J.W.; Ryu, D.S.; Zeng, C.H.; Chung, J.H.; et al. High-Frequency Pulsed Electric Field Ablation in Beagle Model for Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4987. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14204987
Jeong S, Kim SH, Kim H, Kang JM, Park Y, Won D-S, Kim JW, Ryu DS, Zeng CH, Chung JH, et al. High-Frequency Pulsed Electric Field Ablation in Beagle Model for Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(20):4987. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14204987
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Seung, Song Hee Kim, Hongbae Kim, Jeon Min Kang, Yubeen Park, Dong-Sung Won, Ji Won Kim, Dae Sung Ryu, Chu Hui Zeng, Jong Hoon Chung, and et al. 2022. "High-Frequency Pulsed Electric Field Ablation in Beagle Model for Treatment of Prostate Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 20: 4987. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14204987
APA StyleJeong, S., Kim, S. H., Kim, H., Kang, J. M., Park, Y., Won, D.-S., Kim, J. W., Ryu, D. S., Zeng, C. H., Chung, J. H., Lim, B., & Park, J.-H. (2022). High-Frequency Pulsed Electric Field Ablation in Beagle Model for Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Cancers, 14(20), 4987. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14204987







