Clinical Features, Gene Alterations, and Outcomes in Prefibrotic and Overt Primary and Secondary Myelofibrotic Patients
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Molecular and Cytogenetic Studies
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Cytogenetic Features of Patients with Prefibrotic PMF, Overt PMF, and Secondary MF
3.2. Genetic Features of Patients with Prefibrotic PMF, Overt PMF, and Secondary MF
3.3. Correlation of Genetic and Clinical Features
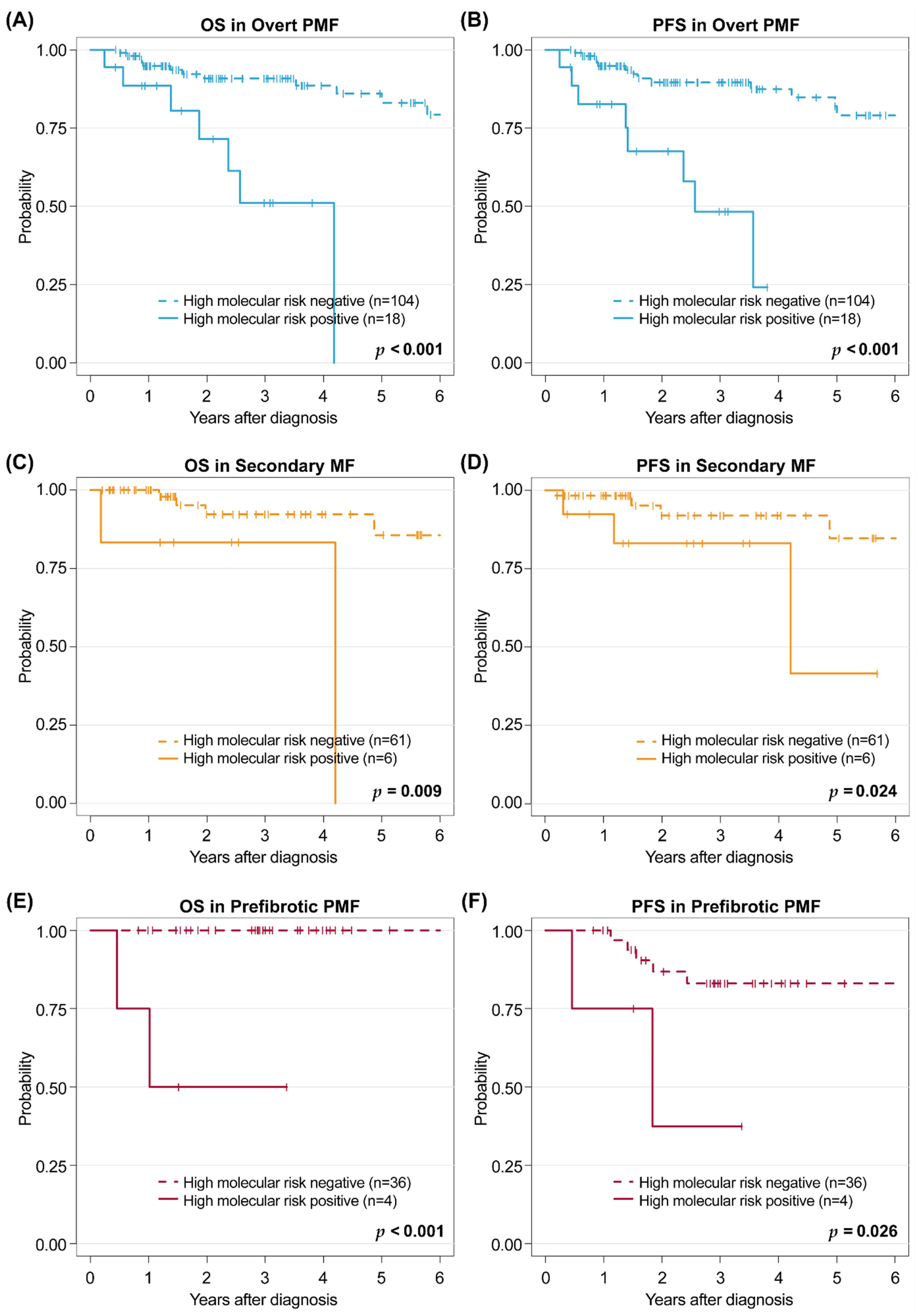
3.4. Distribution of Risk Categories, Outcomes, and Prognostic Effect of Risk Stratification Systems in Each Subgroup
3.5. Univariate and Multivariate Analyses for OS and PFS in Each Subgroup
3.6. Genomic Subgroups in Myelofibrosis by Nondriver Mutations
3.7. Proposal of High-Risk Mutation Groups Predicting Survival Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cervantes, F.; Dupriez, B.; Pereira, A.; Passamonti, F.; Reilly, J.T.; Morra, E.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Mesa, R.A.; Demory, J.-L.; Barosi, G.; et al. New prognostic scoring system for primary myelofibrosis based on a study of the International Working Group for Myelofibrosis Research and Treatment. Blood 2009, 113, 2895–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefferi, A. Myeloproliferative neoplasms: A decade of discoveries and treatment advances: Myeloproliferative neoplasms. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, I.C.; Yeon, S.H.; Lee, M.W.; Ryu, H.; Lee, H.J.; Yun, H.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Jo, D.Y. Thrombotic and hemorrhagic events in 2016 World Health Organization-defined Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasm. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nangalia, J.; Green, A.R. Myeloproliferative neoplasms: From origins to outcomes. Blood 2017, 130, 2475–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nangalia, J.; Massie, C.E.; Baxter, E.J.; Nice, F.L.; Gundem, G.; Wedge, D.C.; Avezov, E.; Li, J.; Kollmann, K.; Kent, D.G.; et al. Somatic CALR mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms with nonmutated JAK2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmelli, P.; Pacilli, A.; Rotunno, G.; Rumi, E.; Rosti, V.; Delaini, F.; Maffioli, M.; Fanelli, T.; Pancrazzi, A.; Pietra, D.; et al. Presentation and outcome of patients with 2016 WHO diagnosis of prefibrotic and overt primary myelofibrosis. Blood 2017, 129, 3227–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Lasho, T.L.; Finke, C.; Belachew, A.A.; Wassie, E.A.; Ketterling, R.P.; Hanson, C.A.; Pardanani, A. Type 1 vs type 2 calreticulin mutations in primary myelofibrosis: Differences in phenotype and prognostic impact. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1568–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Lasho, T.L.; Finke, C.M.; Knudson, R.A.; Ketterling, R.; Hanson, C.H.; Maffioli, M.; Caramazza, D.; Passamonti, F.; Pardanani, A. CALR vs JAK2 vs MPL-mutated or triple-negative myelofibrosis: Clinical, cytogenetic and molecular comparisons. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1472–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmelli, P.; Rotunno, G.; Fanelli, T.; Pacilli, A.; Brogi, G.; Calabresi, L.; Pancrazzi, A.; Vannucchi, A.M. Validation of the differential prognostic impact of type 1/type 1-like versus type 2/type 2-like CALR mutations in myelofibrosis. Blood Cancer J. 2015, 5, e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumi, E.; Pietra, D.; Pascutto, C.; Guglielmelli, P.; Martínez-Trillos, A.; Casetti, I.; Colomer, D.; Pieri, L.; Pratcorona, M.; Rotunno, G.; et al. Clinical effect of driver mutations of JAK2, CALR, or MPL in primary myelofibrosis. Blood 2014, 124, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucchi, A.M.; Lasho, T.L.; Guglielmelli, P.; Biamonte, F.; Pardanani, A.; Pereira, A.; Finke, C.; Score, J.; Gangat, N.; Mannarelli, C.; et al. Mutations and prognosis in primary myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmelli, P.; Biamonte, F.; Rotunno, G.; Artusi, V.; Artuso, L.; Bernardis, I.; Tenedini, E.; Pieri, L.; Paoli, C.; Mannarelli, C.; et al. Impact of mutational status on outcomes in myelofibrosis patients treated with ruxolitinib in the COMFORT-II study. Blood 2014, 123, 2157–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefferi, A.; Paola, G.; Terra, L.L.; Naseema, G.; Rhett, P.K.; Animesh, P.; Alessandro, M.V. MIPSS70+ version 2.0: Mutation and karyotype-enhanced international prognostic scoring system for primary myelofibrosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1769–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortmann, C.A.; Kent, D.G.; Nangalia, J.; Silber, Y.; Wedge, D.C.; Grinfeld, J.; Baxter, E.J.; Massie, C.E.; Papaemmanuil, E.; Menon, S.; et al. Effect of Mutation Order on Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylonas, E.; Yoshida, K.; Frick, M.; Hoyer, K.; Christen, F.; Kaeda, J.; Obenaus, M.; Noerenberg, D.; Hennch, C.; Chan, W.; et al. Single-cell analysis based dissection of clonality in myelofibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.; Lee, J.; Mitchell, E.; Moore, L.; Baxter, E.J.; Hewinson, J.; Dawson, K.J.; Menzies, A.; Godfrey, A.L.; Green, A.R.; et al. Life histories of myeloproliferative neoplasms inferred from phylogenies. Nature 2022, 602, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Elias, C.; Stefano, A.P.; Nancy, L.H.; Harald, S.; Reiner, S.; Ranjana, A.; Michele, G.; Gilles, A.S.; Andrew, D.Z.; et al. The 2016 Revision of the World Health Organization Classification of Lymphoid Neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan-Jordan, J.; Simons, A.; Schmid, M. An International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-318-05857-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, S.S.; Han, E.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y. Simultaneous monitoring of mutation and chimerism using next-generation sequencing in myelodysplastic syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamonti, F.; Cervantes, F.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Morra, E.; Rumi, E.; Pereira, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Pungolino, E.; Caramella, M.; Maffioli, M.; et al. A dynamic prognostic model to predict survival in primary myelofibrosis: A study by the IWG-MRT (International Working Group for Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Research and Treatment). Blood 2010, 115, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangat, N.; Caramazza, D.; Vaidya, R.; George, G.; Begna, K.; Schwager, S.; Dyke, D.V.; Hanson, C.; Wu, W.; Pardanani, A.; et al. DIPSS plus: A refined Dynamic International Prognostic Scoring System for primary myelofibrosis that incorporates prognostic information from karyotype, platelet count, and transfusion status. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmelli, P.; Lasho, T.L.; Rotunno, G.; Mudireddy, M.; Mannarelli, C.; Nicolosi, M.; Pacilli, A.; Pardanani, A.; Rumi, E.; Rosti, V.; et al. MIPSS70: Mutation-enhanced international prognostic score system for transplantation-age patients with primary myelofibrosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefferi, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Nicolosi, M.; Mannelli, F.; Mudireddy, M.; Bartalucci, N.; Finke, C.M.; Lasho, T.L.; Hanson, C.A.; Ketterling, R.P.; et al. GIPSS: Genetically inspired prognostic scoring system for primary myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamonti, F.; Giorgino, T.; Mora, B.; Guglielmelli, P.; Rumi, E.; Maffioli, M.; Rambaldi, A.; Caramella, M.; Komrokji, R.; Gotlib, J.; et al. A clinical-molecular prognostic model to predict survival in patients with post polycythemia vera and post essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2726–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartels, S.; Faisal, M.; Büsche, G.; Schlue, J.; Hasemeier, B.; Schipper, E.; Vogtmann, J.; Westphal, L.; Lehmann, U.; Kreipe, H. Mutations associated with age-related clonal hematopoiesis in PMF patients with rapid progression to myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, P.L.; Stone, R.M.; Al-Kali, A.; Barta, S.K.; Bejar, R.; Bennett, J.M.; Carraway, H.; De Castro, C.M.; Deeg, H.J.; DeZern, A.E.; et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes, version 2.2017, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2017, 15, 60–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeryczynski, G.; Thiele, J.; Gisslinger, B.; Wölfler, A.; Schalling, M.; Gleiß, A.; Burgstaller, S.; Buxhofer-Ausch, V.; Sliwa, T.; Schlögl, E.; et al. Pre-fibrotic/early primary myelofibrosis vs. WHO-defined essential thrombocythemia: The impact of minor clinical diagnostic criteria on the outcome of the disease. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudireddy, M.; Shah, S.; Lasho, T.; Barraco, D.; Hanson, C.A.; Ketterling, R.P.; Gangat, N.; Pardanani, A.; Tefferi, A. Prefibrotic versus overtly fibrotic primary myelofibrosis: Clinical, cytogenetic, molecular and prognostic comparisons. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 182, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masarova, L.; Bose, P.; Daver, N.; Pemmaraju, N.; Newberry, K.J.; Manshouri, T.; Cortes, J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Verstovsek, S. Patients with post-essential thrombocythemia and post-polycythemia vera differ from patients with primary myelofibrosis. Leuk. Res. 2017, 59, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triviai, I.; Zeschke, S.; Rentel, J.; Spanakis, M.; Scherer, T.; Gabdoulline, R.; Panagiota, V.; Thol, F.; Heuser, M.; Stocking, C.; et al. ASXL1/EZH2 mutations promote clonal expansion of neoplastic HSC and impair erythropoiesis in PMF. Leukemia 2019, 33, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, C.J.; Panzarella, T.; Kennedy, J.A.; Arruda, A.; Claudio, J.O.; Daher-Reyes, G.; Ho, J.; Siddiq, N.; Devlin, R.; Tsui, H.; et al. The mutational landscape of accelerated- and blast-phase myeloproliferative neoplasms impacts patient outcomes. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2658–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucchi, A.M.; Antonioli, E.; Guglielmelli, P.; Rambaldi, A.; Barosi, G.; Marchioli, R.; Marfisi, R.M.; Finazzi, G.; Guerini, V.; Fabris, F.; et al. Clinical profile of homozygous JAK2 617V>F mutation in patients with polycythemia vera or essential thrombocythemia. Blood 2007, 110, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtier, F.; Garnier, S.; Carbuccia, N.; Guille, A.; Adélaide, J.; Chaffanet, M.; Hirsch, P.; Paz, D.L.; Slama, B.; Vey, N.; et al. Targeted molecular characterization shows differences between primary and secondary myelofibrosis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2019, 59, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, A.; Yang, Y.; Le, B.T.; Zhang, Y.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Zang, C.; Mohi, G. U2AF1 is required for survival and function of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2382–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefferi, A.; Finke, C.M.; Lasho, T.L.; Wassie, E.A.; Knudson, R.; Ketterling, R.P.; Hanson, C.A.; Pardanani, A. U2AF1 mutations in primary myelofibrosis are strongly associated with anemia and thrombocytopenia despite clustering with JAK2V617F and normal karyotype. Leukemia 2014, 28, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinfeld, J.; Nangalia, J.; Baxter, E.J.; Wedge, D.C.; Angelopoulos, N.; Cantrill, R.; Godfrey, A.L.; Papaemmanuil, E.; Gundem, G.; MacLean, C.; et al. Classification and personalized prognosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1416–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skov, V. Next Generation Sequencing in MPNs. Lessons from the Past and Prospects for Use as Predictors of Prognosis and Treatment Responses. Cancers 2020, 12, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoda, A.; Morishita, D.; Mizutani, A.; Satoh, Y.; Ochi, Y.; Nannya, Y.; Makishima, H.; Miyake, H.; Ogawa, S. CTX-712, a Novel Clk inhibitor targeting myeloid neoplasms with SRSF2 mutation. Blood 2019, 134, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavidij, O.; Keller, P.; Cui, J.; Mertz, J.; Salama, M.; Olteanu, H.; Chiu, A.; Chen, D.; Hanson, C.A.; Chen, Z.; et al. MPN-343: The BET inhibitor pelabresib decreases inflammatory cytokines, improves bone marrow fibrosis and function, and demonstrates clinical response irrespective of mutation status in myelofibrosis patients in the phase 2 MANIFEST Trial. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, S363–S364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable | SMF | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (n = 229) | PPV-MF (n = 21) | PET-MF (n = 46) | SMF (n = 67) | PMF (n = 122) | Pre-PMF (n = 40) | SMF vs. PMF p | SMF vs. Pre-PMF p | PMF vs. Pre-PMF p | |
| Age at diagnosis (years), mean ± SD | 56.8 ± 12.1 | 62.8 ± 10.1 | 59.6 ± 11.9 | 60.6 ± 11.4 | 55.9 ± 11.8 | 53.4 ± 12.6 | 0.008 | 0.003 | 0.250 |
| Sex, male, n (%) | 119 (52.0) | 9 (42.9) | 20 (43.5) | 29 (43.3) | 73 (59.8) | 17 (42.5) | 0.042 | >0.999 | 0.083 |
| White blood cells (109/L), mean ± SD | 14.7 ± 2.6 | 23.0 ± 18.9 | 12.1 ± 9.2 | 15.5 ± 1.4 | 14.3 ± 33.6 | 14.4 ± 12.3 | 0.721 | 0.678 | 0.969 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL), mean ± SD | 10.6 ± 2.8 | 11.5 ± 3.4 | 9.9 ± 2.0 | 10.4 ± 2.6 | 10.0 ± 2.7 | 12.7 ± 2.3 | 0.306 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Platelet (109/L), mean ± SD | 442.7 ± 357.8 | 396.7 ± 232.4 | 487.5 ± 243.2 | 459.0 ± 241.8 | 350.9 ± 345.8 | 695.5 ± 431.6 | 0.013 | 0.002 | <0.001 |
| Peripheral blast proportion (%) | 1.0 ± 1.9 | 1.2 ± 2.2 | 1.2 ± 2.3 | 1.2 ± 2.2 | 1.2 ± 1.9 | 0.1 ± 0.5 | 0.819 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| Spleen size (cm) mean ± SD | 15.6 ± 4.8 | 17.9 ± 5.5 | 13.7 ± 3.5 | 14.9 ± 4.6 | 16.7 ± 4.9 | 13.1 ± 3.2 | 0.018 | 0.017 | <0.001 |
| Constitutional symptoms, n (%) | 112 (48.9) | 11 (52.4) | 24 (52.2) | 35 (52.2) | 70 (57.4) | 7 (17.5) | 0.598 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| Allogeneic HSCT, n (%) | 48 (21.0) | 3 (14.3) | 10 (21.7) | 13 (19.4) | 27 (22.1) | 8 (20.0) | 0.800 | >0.999 | 0.895 |
| Ruxolitinib exposure before HSCT, n (%) | 33 (14.4) | 2 (9.5) | 10 (21.7) | 12 (17.9) | 21 (17.2) | 0 (0.0) | >0.999 | 0.012 | 0.017 |
| Treatment of non-transplant patients, n (%) | 181 (79.0) | 18 (85.7) | 36 (78.3) | 54 (80.6) | 95 (77.9) | 32 (80.0) | 0.8 | >0.999 | 0.895 |
| Ruxolitinib | 136 (59.6) | 17 (81.0) | 29 (63.0) | 46 (68.7) | 82 (67.8) | 8 (20.0) | >0.999 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Androgens | 47 (20.6) | 3 (14.3) | 8 (17.4) | 11 (16.4) | 31 (25.6) | 5 (12.5) | 0.205 | 0.787 | 0.124 |
| Hydroxyurea | 91 (39.9) | 14 (66.7) | 26 (56.5) | 40 (59.7) | 31 (25.6) | 20 (50.0) | <0.001 | 0.437 | <0.001 |
| Anagrelide | 67 (29.4) | 4 (19.0) | 26 (56.5) | 30 (44.8) | 14 (11.6) | 23 (57.5) | <0.001 | 0.283 | <0.001 |
| Thalidomide | 1 (0.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.8) | 0 (0.0) | >0.999 | - | 0.641 |
| Investigational agent | 13 (5.7) | 2 (9.5) | 2 (4.3) | 4 (6.0) | 5 (4.1) | 4 (10.0) | 0.835 | 0.699 | 0.379 |
| Leukemic transformation, n (%) | 8 (3.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.2) | 1 (1.5) | 6 (4.9) | 1 (2.5) | 0.429 | >0.999 | 0.838 |
| DIPSS Karyotype, n (%) | |||||||||
| Unfavorable * | 17 (7.4) | 2 (9.5) | 4 (8.7) | 6 (9.0) | 11 (9.0) | 0 (0.0) | >0.999 | 0.130 | 0.109 |
| MIPSS Karyotype, n (%) | 0.035 | 0.123 | 0.016 | ||||||
| Favorable † | 184 (80.3) | 18 (85.7) | 38 (82.6) | 56 (83.5) | 90 (73.8) | 38 (95.0) | |||
| Intermediate | 33 (14.4) | 2 (9.5) | 3 (6.5) | 5 (7.5) | 26 (21.3) | 2 (5.0) | |||
| Very High risk †† | 12 (5.2) | 1 (4.8) | 5 (10.9) | 6 (9.0) | 6 (4.9) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| Mutation, n (%) | |||||||||
| JAK2V617F | 117 (51.1) | 21 (100.0) | 22 (47.8) | 43 (64.2) | 54 (44.3) | 20 (50.0) | 0.014 | 0.215 | 0.653 |
| CALR | 60 (26.2) | 0 (0.0) | 18 (39.1) | 18 (26.9) | 35 (28.7) | 7 (17.5) | 0.922 | 0.383 | 0.233 |
| Type1/like | 39 (17.0) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (19.6) | 9 (13.4) | 25 (20.5) | 5 (12.5) | 0.320 | 0.377 | 0.534 |
| Type2/like | 16 (7.0) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (17.4) | 8 (11.9) | 7 (5.7) | 1 (2.5) | |||
| Others | 5 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.2) | 1 (1.5) | 3 (2.5) | 1 (2.5) | |||
| MPL | 10 (4.4) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (6.5) | 3 (4.5) | 5 (4.1) | 2 (5.0) | >0.999 | >0.999 | >0.999 |
| ASXL1 | 66 (28.8) | 3 (14.3) | 16 (34.8) | 19 (28.4) | 44 (36.1) | 3 (7.5) | 0.361 | 0.020 | 0.001 |
| CBL | 5 (2.2) | 1 (4.8) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.5) | 4 (3.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0.796 | >0.999 | 0.567 |
| CUX1 | 4 (1.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (3.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0.332 | 0.567 | |
| DNMT3A | 11 (4.8) | 3 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (4.5) | 4 (3.3) | 4 (10.0) | 0.988 | 0.475 | 0.200 |
| EZH2 | 5 (2.2) | 1 (4.8) | 2 (4.3) | 3 (4.5) | 2 (1.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0.491 | 0.452 | >0.999 |
| IDH1 | 4 (1.7) | 1 (4.8) | 1 (2.2) | 2 (3.0) | 2 (1.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0.931 | 0.715 | >0.999 |
| IDH2 | 4 (1.7) | 1 (4.8) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.5) | 1 (0.8) | 2 (5.0) | >0.999 | 0.647 | 0.305 |
| NOTCH1 | 3 (1.3) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.2) | 1 (1.5) | 1 (0.8) | 1 (2.5) | >0.999 | >0.999 | 0.992 |
| NRAS | 5 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (2.5) | 2 (5.0) | 0.493 | 0.267 | 0.780 |
| RUNX1 | 8 (3.5) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (6.5) | 3 (4.5) | 4 (3.3) | 1 (2.5) | 0.988 | >0.999 | >0.999 |
| SETBP1 | 5 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (2.5) | 2 (5.0) | 0.493 | 0.267 | 0.780 |
| SF3B1 | 17 (7.4) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (10.9) | 5 (7.5) | 8 (6.6) | 4 (10.0) | >0.999 | 0.922 | 0.709 |
| SRSF2 | 5 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (2.5) | 2 (5.0) | 0.493 | 0.267 | 0.780 |
| TET2 | 28 (12.2) | 4 (19.0) | 5 (10.9) | 9 (13.4) | 12 (9.8) | 7 (17.5) | 0.610 | 0.771 | 0.306 |
| TP53 | 8 (3.5) | 2 (9.5) | 1 (2.2) | 3 (4.5) | 5 (4.1) | 0 (0.0) | >0.999 | 0.452 | 0.439 |
| U2AF1 | 11 (4.8) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.2) | 1 (1.5) | 8 (6.6) | 2 (5.0) | 0.227 | 0.647 | >0.999 |
| U2AF1Q157 | 3 (1.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (2.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0.493 | 0.745 | |
| ZRSR2 | 4 (1.7) | 1 (4.8) | 1 (2.2) | 2 (3.0) | 1 (0.8) | 1 (2.5) | 0.595 | >0.999 | 0.992 |
| Variable | All (n = 229) | SMF (n = 67) | PMF (n = 122) | pre-PMF (n = 40) | SMF vs. PMF p | SMF vs. pre-PMF p | PMF vs. pre-PMF p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPSS Score, mean ± SD | 1.8 ± 1.2 | 2.1 ± 1.2 | 2.0 ± 1.2 | 0.7 ± 1.0 | 0.574 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| IPSS Risk Group, n (%) | 0.721 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Low | 44 (19.2) | 6 (9.0) | 15 (12.3) | 23 (57.5) | |||
| Intermediate-1 | 54 (23.6) | 15 (22.4) | 30 (24.6) | 9 (22.5) | |||
| Intermediate-2 | 62 (27.1) | 23 (34.3) | 33 (27.0) | 6 (15.0) | |||
| High | 69 (30.1) | 23 (34.3) | 44 (36.1) | 2 (5.0) | |||
| DIPSS Score, mean ± SD | 2.3 ± 1.6 | 2.6 ± 1.5 | 2.5 ± 1.5 | 0.8 ± 1.2 | 0.734 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| DPSS Risk Group, n (%) | 0.813 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Low | 44 (19.2) | 6 (9.0) | 15 (12.3) | 23 (57.5) | |||
| Intermediate-1 | 77 (33.6) | 24 (35.8) | 42 (34.4) | 11 (27.5) | |||
| Intermediate-2 | 92 (40.2) | 30 (44.8) | 56 (45.9) | 6 (15.0) | |||
| High | 16 (7.0) | 7 (10.4) | 9 (7.4) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| DIPSS-plus Score, mean ± SD | 1.8 ± 1.4 | 1.9 ± 1.1 | 2.1 ± 1.4 | 0.7 ± 1.1 | 0.153 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| DIPSS-plus Risk Group, n (%) | 0.051 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Low | 43 (18.8) | 5 (7.5) | 15 (12.3) | 23 (57.5) | |||
| Intermediate-1 | 66 (28.8) | 23 (34.3) | 33 (27.0) | 10 (25.0) | |||
| Intermediate-2 | 92 (40.2) | 35 (52.2) | 51 (41.8) | 6 (15.0) | |||
| High | 28 (12.2) | 4 (6.0) | 23(18.9) | 1 (2.5) | |||
| MYSEC-PM Score, mean ± SD | 12.3 ± 3.0 | 13.1 ± 2.5 | 12.5 ± 3.0 | 10.4 ± 2.6 | 0.159 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| MYSEC-PM Risk Group, n (%) | 0.336 | <0.001 | 0.002 | ||||
| Low | 68 (29.7) | 12 (17.9) | 35 (28.7) | 21 (52.5) | |||
| Intermediate-1 | 84 (36.7) | 26 (38.8) | 42 (34.4) | 16 (40.0) | |||
| Intermediate-2 | 53 (23.1) | 18 (26.9) | 32 (26.2) | 3 (7.5) | |||
| High | 24 (10.5) | 11 (16.4) | 13 (10.7) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| MIPSS70 Score, mean ± SD | 3.8 ± 2.0 | 4.0 ± 1.6 | 4.4 ± 1.9 | 1.8 ± 1.7 | 0.164 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| MIPSS70 Risk Group, n (%) | 0.025 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Low | 34 (14.8) | 1 (1.5) | 5 (4.1) | 28 (70.0) | |||
| Intermediate | 111 (48.5) | 46 (68.7) | 59 (48.4) | 6 (15.0) | |||
| High | 84 (36.7) | 20 (29.9) | 58 (47.5) | 6 (15.0) | |||
| MIPSS70 + Ver2 Score, mean ± SD | 5.0 ± 2.9 | 5.1 ± 2.6 | 5.6 ± 3.1 | 2.9 ± 2.0 | 0.260 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| MIPSS70 + Ver2 Risk Group, n (%) | 0.418 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Very low | 7 (3.1) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (3.3) | 3 (7.5) | |||
| Low | 54 (23.6) | 13 (19.4) | 17 (13.9) | 24 (60.0) | |||
| Intermediate | 48 (21.0) | 15 (22.4) | 28 (23.0) | 5 (12.5) | |||
| High | 87 (38.0) | 30 (44.8) | 50 (41.0) | 7 (17.5) | |||
| Very high | 33 (14.4) | 9 (13.4) | 23 (18.9) | 1 (2.5) | |||
| GIPSS Score, mean ± SD | 1.4 ± 0.9 | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 1.0 ± 0.6 | 0.410 | 0.208 | <0.001 |
| GIPSS Risk Group, n (%) | 0.697 | 0.121 | 0.018 | ||||
| Low | 21 (9.2) | 5 (7.5) | 11 (9.0) | 5 (12.5) | |||
| Intermediate-1 | 127 (55.5) | 38 (56.7) | 60 (49.2) | 29 (72.5) | |||
| Intermediate-2 | 54 (23.6) | 17 (25.4) | 32 (26.2) | 5 (12.5) | |||
| High | 27 (11.8) | 7 (10.4) | 19 (15.6) | 1 (2.5) | |||
| Variable | Overall Survival | Progression-Free Survival * | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | |
| pre-PMF | ||||||
| Risk stratification | ||||||
| IPSS, INT2 or high | - | - | >0.999 | 9.69 | 2.03, 46.1 | 0.004 |
| DIPSS, INT2 or high | - | - | >0.999 | 11.2 | 2.40, 52.2 | 0.002 |
| DIPSS plus, INT2 or high | - | - | >0.999 | 5.44 | 1.20, 24.7 | 0.028 |
| MIPSS70, high | - | - | >0.999 | 6.11 | 1.32, 28.3 | 0.021 |
| MIPSS70 +Ver2, high or very high | - | - | >0.999 | 3.93 | 0.86, 18.0 | 0.078 |
| GIPSS, INT2 or high | 5.93 | 0.37, 94.8 | 0.2 | 3.37 | 0.63, 18.0 | 0.2 |
| MYSECPM, INT2 or high | - | - | >0.999 | 16.7 | 2.71, 103 | 0.002 |
| PMF | ||||||
| Risk stratification | ||||||
| IPSS, INT2 or high | 6.73 | 1.94, 23.3 | 0.003 | 6.92 | 2.02, 23.7 | 0.002 |
| DIPSS, INT2 or high | 10.9 | 3.06, 38.7 | <0.001 | 7.71 | 2.51, 23.7 | <0.001 |
| DIPSS plus, INT2 or high | 6.21 | 1.82, 21.3 | 0.004 | 4.64 | 1.57, 13.7 | 0.006 |
| MIPSS70, high | 6.62 | 2.39, 18.4 | <0.001 | 5.41 | 2.11, 13.9 | <0.001 |
| MIPSS70 +Ver2, high or very high | 9.05 | 2.10, 39.0 | 0.003 | 9.72 | 2.27, 41.5 | 0.002 |
| GIPSS, INT2 or high | 2.68 | 1.12, 6.43 | 0.027 | 3.1 | 1.32, 7.28 | 0.009 |
| MYSEC-PM, INT2 or high | 2.37 | 0.91, 6.18 | 0.079 | 2.62 | 1.07, 6.37 | 0.034 |
| SMF | ||||||
| Risk stratification | ||||||
| IPSS, INT2 or high | 3.63 | 0.42, 31.4 | 0.2 | 4.15 | 0.49, 34.9 | 0.2 |
| DIPSS, INT2 or high | 4.59 | 0.54, 39.4 | 0.2 | 5.48 | 0.66, 45.6 | 0.12 |
| DIPSS plus, INT2 or high | 4.46 | 0.52, 38.3 | 0.2 | 5.25 | 0.63, 43.8 | 0.13 |
| MIPSS70, high | 5.04 | 0.92, 27.6 | 0.062 | 3.33 | 0.74, 14.9 | 0.12 |
| MIPSS70 +Ver2, high or very high | - | - | >0.999 | - | >0.999 | |
| GIPSS, INT2 or high | 3.26 | 0.59, 17.9 | 0.2 | 4.18 | 0.81, 21.6 | 0.088 |
| MYSECPM, INT2 or high | 4.18 | 0.75, 23.5 | 0.1 | 4.98 | 0.94, 26.3 | 0.059 |
| Variable | Univariate | Multivariate Model I | Multivariate Model II | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | |
| pre-PMF | |||||||||
| Clinical variable | |||||||||
| Age at diagnosis (years) | 2.34 | 0.45, 12.1 | 0.3 | ||||||
| Sex, male vs. female | 0.23 | 0.04, 1.20 | 0.081 | ||||||
| White blood cells (109/L) > 25 | 1.71 | 0.20, 14.4 | 0.6 | ||||||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) < 10 | 5.6 | 1.23, 25.4 | 0.026 | 6.30 | 1.02, 39.1 | 0.048 | |||
| Platelet (109/L) < 100 | 1.72 | 0.21, 14.3 | 0.6 | ||||||
| Peripheral blast (%) > 1 | 6.45 | 1.14, 36.5 | 0.035 | ||||||
| Splenomegaly (cm) | 0.94 | 0.18, 4.85 | >0.999 | ||||||
| Constitutional symptom, yes | 4.7 | 1.04, 21.3 | 0.044 | 4.47 | 0.75, 26.6 | 0.1 | |||
| Genetic variable | |||||||||
| JAK2V617F | 0.47 | 0.09, 2.41 | 0.4 | ||||||
| CALR Type1/like | 0.94 | 0.11, 7.85 | >0.999 | ||||||
| MPL | 3.29 | 0.38, 28.4 | 0.3 | ||||||
| ASXL1 | 8.68 | 1.57, 48.1 | 0.013 | 11.4 | 1.59, 81.5 | 0.015 | 3.69 | 0.55, 24.8 | 0.2 |
| DNMT3A | 1.68 | 0.20, 14.1 | 0.6 | ||||||
| RUNX1 | - | - | >0.999 | ||||||
| SETBP1 | 4.36 | 0.52, 36.4 | 0.2 | ||||||
| SF3B1 | - | - | >0.999 | ||||||
| SRSF2 | 13.7 | 1.22, 154 | 0.034 | 2.23 | 0.10, 50.9 | 0.6 | 19.5 | 1.29, 294 | 0.032 |
| TET2 | 1.94 | 0.38, 10.0 | 0.4 | ||||||
| U2AF1 | 2.86 | 0.34, 23.9 | 0.3 | ||||||
| ZRSR2 | - | - | >0.999 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.-Y.; Kwag, D.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Min, G.-J.; Park, S.-S.; Park, S.; Jeon, Y.-W.; Yoon, J.-H.; Shin, S.-H.; et al. Clinical Features, Gene Alterations, and Outcomes in Prefibrotic and Overt Primary and Secondary Myelofibrotic Patients. Cancers 2022, 14, 4485. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184485
Kim T-Y, Kwag D, Lee J-H, Lee J, Min G-J, Park S-S, Park S, Jeon Y-W, Yoon J-H, Shin S-H, et al. Clinical Features, Gene Alterations, and Outcomes in Prefibrotic and Overt Primary and Secondary Myelofibrotic Patients. Cancers. 2022; 14(18):4485. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184485
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Tong-Yoon, Daehun Kwag, Jong-Hyuk Lee, Joonyeop Lee, Gi-June Min, Sung-Soo Park, Silvia Park, Young-Woo Jeon, Jae-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hawn Shin, and et al. 2022. "Clinical Features, Gene Alterations, and Outcomes in Prefibrotic and Overt Primary and Secondary Myelofibrotic Patients" Cancers 14, no. 18: 4485. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184485
APA StyleKim, T.-Y., Kwag, D., Lee, J.-H., Lee, J., Min, G.-J., Park, S.-S., Park, S., Jeon, Y.-W., Yoon, J.-H., Shin, S.-H., Yahng, S.-A., Cho, B.-S., Eom, K.-S., Kim, Y.-J., Lee, S., Kim, H.-J., Min, C.-K., Cho, S.-G., Lee, J.-W., ... Lee, S.-E. (2022). Clinical Features, Gene Alterations, and Outcomes in Prefibrotic and Overt Primary and Secondary Myelofibrotic Patients. Cancers, 14(18), 4485. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184485







