Golgi Protein 73 (GP73) Serum Levels Predict Outcome after Resection of Biliary Tract Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Cohort
2.2. Measurements of GP73
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Golgi Protein 73 Serum Levels Are Elevated in Patients with Biliary Tract Cancer
3.3. Golgi Protein 73 Serum Levels Are Unaltered between Different Tumor and Patient Characteristics
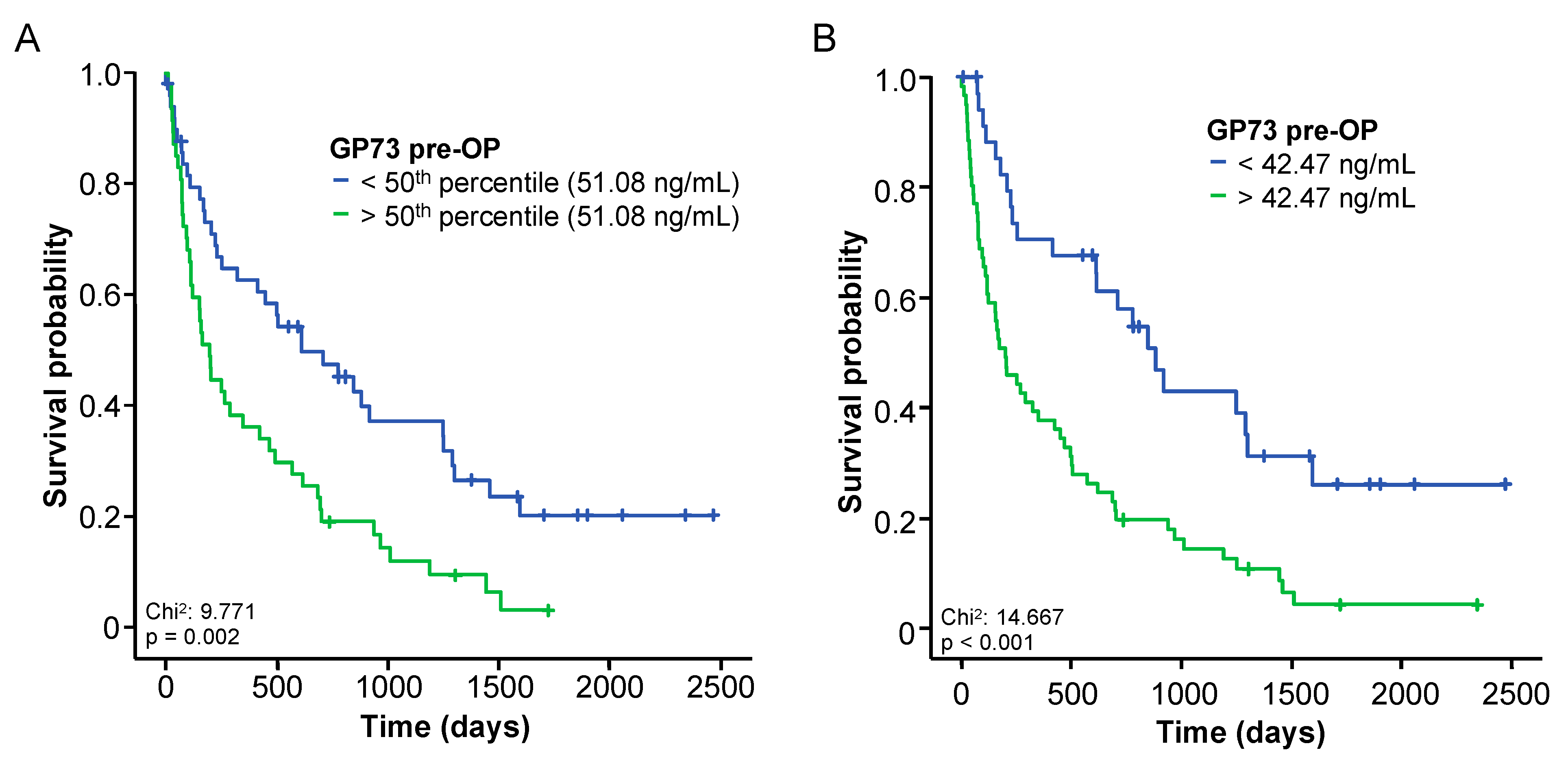
3.4. Elevated Baseline Levels of GP73 Predict an Impaired Overall Survival following BTC Resection
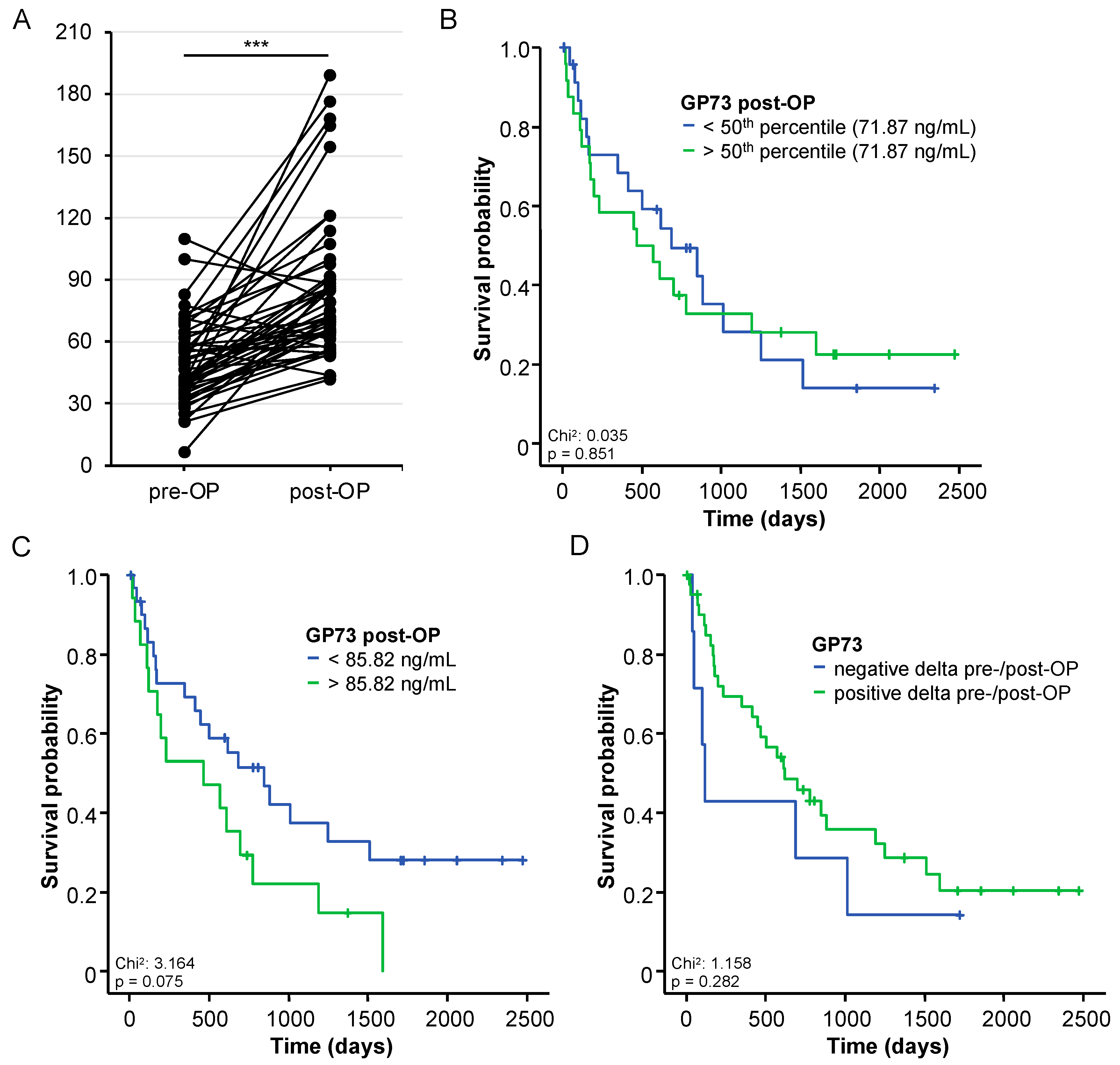
3.5. Postoperative GP73 Serum Levels and Patients’ Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Razumilava, N.; Gores, G.J. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet 2014, 383, 2168–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, J.W.; Kelley, R.K.; Nervi, B.; Oh, D.Y.; Zhu, A.X. Biliary Tract Cancer. Lancet 2021, 397, 428–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primrose, J.N.; Fox, R.P.; Palmer, D.H.; Malik, H.Z.; Prasad, R.; Mirza, D.; Anthony, A.; Corrie, P.; Falk, S.; Finch-Jones, M.; et al. Capecitabine Compared With Observation in Resected Biliary Tract Cancer (BILCAP): A Randomised, Controlled, Multicentre, Phase 3 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stremitzer, S.; Jones, R.P.; Quinn, L.M.; Fenwick, S.W.; Diaz-Nieto, R.; Poston, G.J.; Malik, H.Z. Clinical Outcome after Resection of Early-Stage Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 45, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kladney, R.D.; Bulla, G.A.; Guo, L.; Mason, A.L.; Tollefson, A.E.; Simon, D.J.; Koutoubi, Z.; Fimmel, C.J. GP73, a Novel Golgi-Localized Protein Upregulated by Viral Infection. Gene 2000, 249, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riener, M.O.; Stenner, F.; Liewen, H.; Soll, C.; Bretenstein, S.; Pestalozzi, B.C.; Samaras, P.; Probst-Hensch, N.; Hellerbrand, C.; Müllhaupt, B.; et al. Golgi Phosphoprotein 2 (GOLPH2) Expression in Liver Tumors and Its Value as a Serum Marker in Hepatocellular Carcinomas. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.H.; Zhu, W.W.; Zhang, J.B.; Qin, Y.; Lu, M.; Lin, G.L.; Guo, L.; Zhang, B.; Lin, Z.H.; Roessler, S.; et al. GOLM1 Modulates EGFR/RTK Cell-Surface Recycling to Drive Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Tao, J.; Shi, Y.; Gai, X.; Huang, F.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. MTORC1 Up-Regulates GP73 to Promote Proliferation and Migration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells and Growth of Xenograft Tumors in Mice. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 741.e14–752.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, A.; Li, N. Dynamic Changes in Serum Markers and Their Utility in the Early Diagnosis of All Stages of Hepatitis B-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, M.Y.; Wu, X.N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Lv, Y.; Dong, J. Serum GP73 Predicts Posthepatectomy Outcomes in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loosen, S.H.; Roderburg, C.; Kauertz, K.L.; Pombeiro, I.; Leyh, C.; Benz, F.; Vucur, M.; Longerich, T.; Koch, A.; Braunschweig, T.; et al. Elevated Levels of Circulating Osteopontin Are Associated with a Poor Survival after Resection of Cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmi, A.; Ruzzenente, A.; Campagnaro, T.; Pachera, S.; Valdegamberi, A.; Nicoli, P.; Cappellani, A.; Malfermoni, G.; Iacono, C. Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Prognostic Factors after Surgical Resection. World J. Surg. 2009, 33, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, R.; Kladney, R.D.; Havlioglu, N.; Schmitt-Gräff, A.; Gusmirovic, I.; Solomon, H.; Luxon, B.A.; Bacon, B.R.; Fimmel, C.J. Disease- and Cell-Specific Expression of GP73 in Human Liver Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Jia, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Ya, S.; Mao, R.; Ailijiang, T.; et al. GP73 Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion Partly by Activating TGF-Β1/Smad2 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.; Shi, J.; Xu, Y.; He, J.; Lin, F.; Wei, A.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Z. Knockdown of Golgi Phosphoprotein 73 Blocks the Trafficking of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells and Inhibits Cell Invasion. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 2399–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loosen, S.H.; Vucur, M.; Trautwein, C.; Roderburg, C.; Luedde, T. Circulating Biomarkers for Cholangiocarcinoma. Dig. Dis. 2018, 36, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Deng, S.; Jin, K.; Gong, Y.; Cheng, H.; Fan, Z.; Qian, Y.; Huang, Q.; Ni, Q.; Luo, G.; et al. Lewis Antigen-negative Pancreatic Cancer: An Aggressive Subgroup. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Long, M.; Zhang, X.; Lei, S.; Dou, W.; Hu, J.; Du, X.; Liu, L. The Diagnostic Value of the Combination of Golgi Protein 73, Glypican-3 and Alpha-Fetoprotein in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Diagnostic Meta-Analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Block, T.M.; Wang, M.; Nefsky, B.; Long, R.; Hafner, J.; Mehta, A.S.; Marrero, J.; Gish, R.; Norton, P.A. Interleukin-6 and Oncostatin M Are Elevated in Liver Disease in Conjunction with Candidate Hepatocellular Carcinoma Biomarker GP73. Cancer Biomark. Sect. A Dis. Markers 2012, 11, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| BTC Patients | Healthy Controls | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BTC patients | n = 97 | n = 31 | |
| Gender [%]: | |||
| Male | 53.1 | 76.7 | 0.033 |
| Female | 46.9 | 23.3 | |
| Age [years, median and range] | 68 [37–84] | 33 [19–74] | <0.001 |
| BMI [kg/m2, median and range] | 26.23 [18.83–46.36] | ||
| Anatomic location of BTC [%]: | |||
| Intrahepatic CCA | 39.2 | ||
| Perihilar | 38.1 | ||
| Distal CCA | 13.4 | ||
| Gallbladder | 9.3 | ||
| Staging [%]: | |||
| T1-T2-T3-T4 | 6.3-41.3-35.0-17.5 | ||
| N0-N1 | 43.2-56.8 | ||
| M0-M1 | 77.9-22.1 | ||
| G2-G3 | 53.7-46.3 | ||
| R0-R1 | 60.3-39.7 | ||
| ECOG PS [%]: | |||
| ECOG 0 | 50.5 | ||
| ECOG 1 | 40.0 | ||
| ECOG 2 | 9.5 | ||
| Deceased during follow up [%]: | |||
| Yes | 81.4 | ||
| No | 18.6 |
| Univariate Cox-Regression | Multivariate Cox-Regression | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | p-Value | Hazard-Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Hazard-Ratio (95% CI) |
| GP73 pre-OP >42.47 ng/mL | <0.001 | 2.559 (1.556–4.209) | 0.009 | 2.457 (1.255–4.808) |
| CEA | 0.059 | 1.004 (1.000–1.008) | 0.006 | 1.009 (1.002–1.015) |
| Leukocyte count | 0.451 | 1.024 (0.962–1.091) | ||
| CRP | <0.001 | 1.012 (1.006–1.018) | 0.469 | 1.003 (0.994–1.013) |
| Platelets | 0.902 | 1.000 (0.999–1.002) | ||
| Sodium | 0.210 | 0.959 (0.889–1.024) | ||
| Potassium | 0.904 | 1.029 (0.641–1.653) | ||
| AST | 0.407 | 0.999 (0.998–1.001) | ||
| Bilirubin | 0.325 | 0.967 (0.903–1.034) | ||
| ALP | 0.797 | 1.000 (0.999–1.001) | ||
| GGT | 0.514 | 1.000 (0.999–1.000) | ||
| Creatinine | 0.104 | 1.918 (0.874–4.208) | 0.328 | 0.588 (0.202–1.706) |
| BMI | 0.061 | 1.048 (0.998–1.100) | 0.026 | 1.070 (1.008–1.136) |
| ECOG PS | 0.085 | 1.371 (0.957–1.964) | 0.108 | 1.500 (0.915–2.461) |
| Age | 0.014 | 1.027 (1.005–1.050) | 0.058 | 1.029 (0.999–1.060) |
| Sex | 0.984 | 1.005 (0.643–1.579) | ||
| T-stage | 0.004 | 1.633 (1.171–2.278) | 0.051 | 1.461 (0.999–2.136) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loosen, S.H.; Halpaap, J.; Labuhn, S.; Bednarsch, J.; Alizai, P.H.; Roeth, A.A.; Lang, S.A.; Vucur, M.; Kather, J.N.; Knoefel, W.T.; et al. Golgi Protein 73 (GP73) Serum Levels Predict Outcome after Resection of Biliary Tract Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4428. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184428
Loosen SH, Halpaap J, Labuhn S, Bednarsch J, Alizai PH, Roeth AA, Lang SA, Vucur M, Kather JN, Knoefel WT, et al. Golgi Protein 73 (GP73) Serum Levels Predict Outcome after Resection of Biliary Tract Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(18):4428. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184428
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoosen, Sven H., Justus Halpaap, Simon Labuhn, Jan Bednarsch, Patrick H. Alizai, Anjali A. Roeth, Sven A. Lang, Mihael Vucur, Jakob N. Kather, Wolfram T. Knoefel, and et al. 2022. "Golgi Protein 73 (GP73) Serum Levels Predict Outcome after Resection of Biliary Tract Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 18: 4428. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184428
APA StyleLoosen, S. H., Halpaap, J., Labuhn, S., Bednarsch, J., Alizai, P. H., Roeth, A. A., Lang, S. A., Vucur, M., Kather, J. N., Knoefel, W. T., Ulmer, T. F., Neumann, U. P., Roderburg, C., & Luedde, T. (2022). Golgi Protein 73 (GP73) Serum Levels Predict Outcome after Resection of Biliary Tract Cancer. Cancers, 14(18), 4428. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184428







