Safety and Efficacy of Allogeneic Natural Killer Cells in Combination with Pembrolizumab in Patients with Chemotherapy-Refractory Biliary Tract Cancer: A Multicenter Open-Label Phase 1/2a Trial
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Study Protocol
2.3. Preparation and Ex Vivo Expansion of Allogeneic NK Cells
2.4. Characterization of NK Cells
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
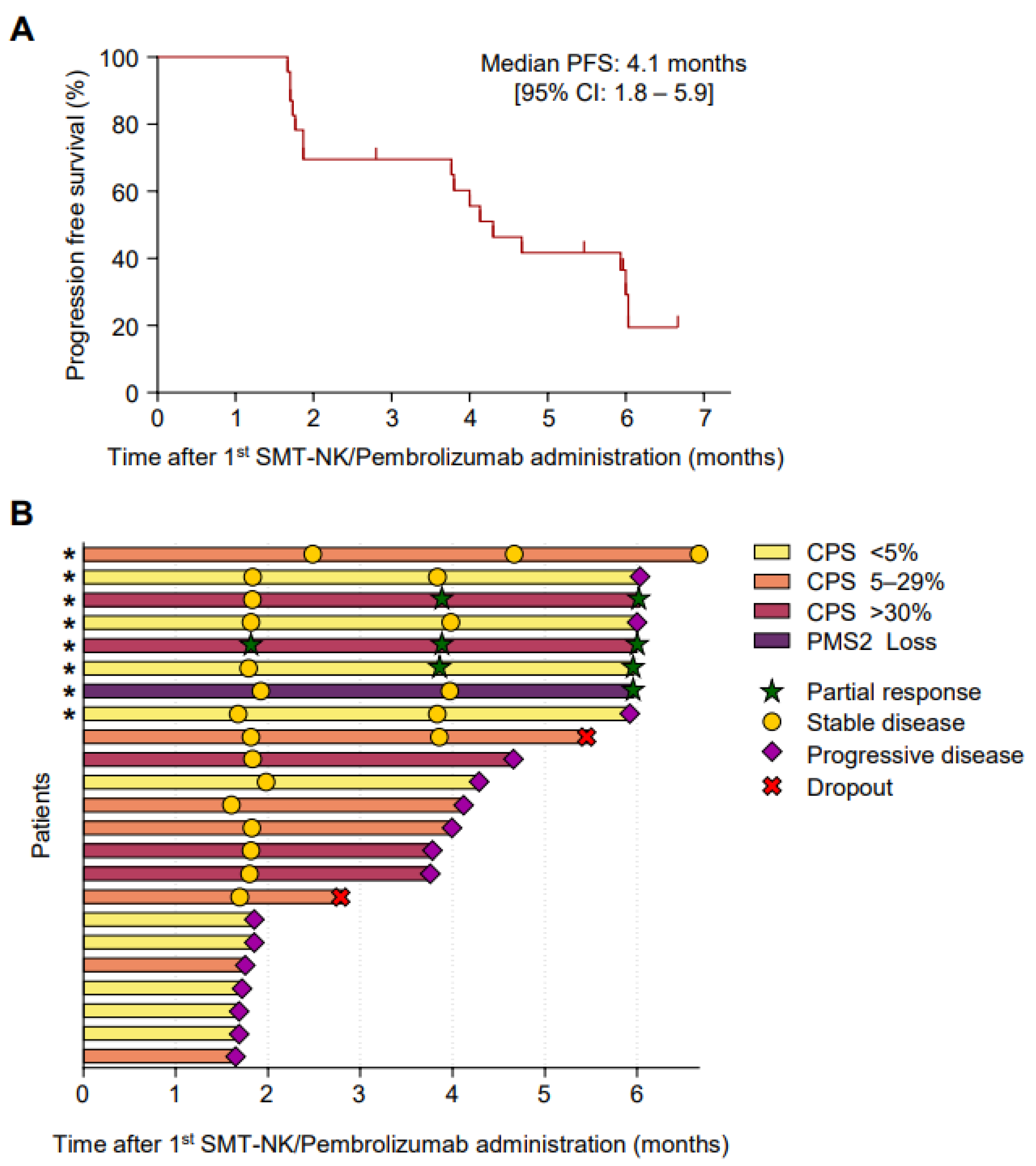
3.2. Tumor Response
3.3. Safety and Tolerability
3.4. Biomarkers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banales, J.M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Lamarca, A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Khan, S.A.; Roberts, L.R.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Andersen, J.B.; Braconi, C.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: The next horizon in mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 557–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, J.W.; Kelley, R.K.; Nervi, B.; Oh, D.-Y.; Zhu, A.X. Biliary tract cancer. Lancet 2021, 397, 428–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, J.; Wasan, H.; Palmer, D.H.; Cunningham, D.; Anthoney, A.; Maraveyas, A.; Madhusudan, S.; Iveson, T.; Hughes, S.; Pereira, S.P.; et al. Cisplatin plus Gemcitabine versus Gemcitabine for Biliary Tract Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Hepatobiliary Cancers (Version 5.2021). 2021. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/hepatobiliary.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2021).
- Alabraba, E.; Joshi, H.; Bird, N.; Griffin, R.; Sturgess, R.; Stern, N.; Sieberhagen, C.; Cross, T.; Camenzuli, A.; Davis, R.; et al. Increased multimodality treatment options has improved survival for Hepatocellular carcinoma but poor survival for biliary tract cancers remains unchanged. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamarca, A.; Hubner, R.A.; David Ryder, W.; Valle, J.W. Second-line chemotherapy in advanced biliary cancer: A systematic review. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 2328–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malka, D.; Cervera, P.; Foulon, S.; Trarbach, T.; de la Fouchardière, C.; Boucher, E.; Fartoux, L.; Faivre, S.; Blanc, J.; Viret, F.; et al. Gemcitabine and oxaliplatin with or without cetuximab in advanced biliary-tract cancer (BINGO): A randomised, open-label, non-comparative phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved Survival with Ipilimumab in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Tykodi, S.S.; Chow, L.Q.M.; Hwu, W.-J.; Topalian, S.L.; Hwu, P.; Drake, C.G.; Camacho, L.H.; Kauh, J.; Odunsi, K.; et al. Safety and Activity of Anti–PD-L1 Antibody in Patients with Advanced Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Rini, B.I.; McDermott, D.F.; Redman, B.G.; Kuzel, T.M.; Harrison, M.R.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; Drabkin, H.A.; George, S.; Logan, T.F.; et al. Nivolumab for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Results of a Randomized Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (Version 7.2021). 2021. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2021).
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Melanoma: Cutaneous (Version 2.2021). 2021. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cutaneous_melanoma.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2021).
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Melanoma: Uveal (Version 2.2021). 2021. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/uveal.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Kidney Cancer (Version 2.2022). 2021. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Ueno, M.; Chung, H.C.; Nagrial, A.; Marabelle, A.; Kelley, R.K.; Xu, L.; Mahoney, J.; Pruitt, S.K.; Oh, D.-Y. Pembrolizumab for advanced biliary adenocarcinoma: Results from the multicohort, phase II KEYNOTE-158 study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, viii210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, Y.-J.; Ueno, M.; Malka, D.; Chung, H.C.; Nagrial, A.; Kelley, R.K.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Ros, W.; Italiano, A.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Pembrolizumab (pembro) for advanced biliary adenocarcinoma: Results from the KEYNOTE-028 (KN028) and KEYNOTE-158 (KN158) basket studies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. S15), 4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, M.; Ikeda, M.; Morizane, C.; Kobayashi, S.; Ohno, I.; Kondo, S.; Okano, N.; Kimura, K.; Asada, S.; Namba, Y.; et al. Nivolumab alone or in combination with cisplatin plus gemcitabine in Japanese patients with unresectable or recurrent biliary tract cancer: A non-randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 1 study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Jeong, J.H.; Hwang, H.S.; Lee, S.S.; Park, D.H.; Oh, D.W.; Song, T.J.; Kim, K.; Hwang, S.; Hwang, D.W. Efficacy and Safety of Pembrolizumab in Patients with Refractory Advanced Biliary Tract Cancer: Tumor Proportion Score as a Potential Biomarker for Response. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 52, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivier, E.; Tomasello, E.; Baratin, M.; Walzer, T.; Ugolini, S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol. 2008, 9, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, A.M.; Yang, C.; Thakar, M.S.; Malarkannan, S. Natural Killer Cells: Development, Maturation, and Clinical Utilization. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, A.K.; Campbell, K.S. Natural killer cells and cancer: Regulation by the killer cell Ig-like receptors (KIR). Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 2211–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, E.O.; Kim, H.S.; Liu, D.; Peterson, M.E.; Rajagopalan, S. Controlling natural killer cell responses: Integration of signals for activation and inhibition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 227–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amand, M.; Iserentant, G.; Poli, A.; Sleiman, M.; Fievez, V.; Sanchez, I.P.; Sauvageot, N.; Michel, T.; Aouali, N.; Janji, B.; et al. Human CD56(dim)CD16(dim) Cells as an Individualized Natural Killer Cell Subset. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, G.; Cheon, S.; Lee, H.; Choi, S.J.; Jeong, S.; Kim, E.S.; Jeong, H.W.; Jeong, H.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.; et al. Abnormality in the NK-cell population is prolonged in severe COVID-19 patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 996–1006.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, L.; Capanni, M.; Urbani, E.; Perruccio, K.; Shlomchik, W.D.; Tosti, A.; Posati, S.; Rogaia, D.; Frassoni, F.; Aversa, F.; et al. Effectiveness of Donor Natural Killer Cell Alloreactivity in Mismatched Hematopoietic Transplants. Science 2002, 295, 2097–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lim, O.; Kim, T.M.; Ahn, Y.O.; Choi, H.; Chung, H.; Min, B.; Her, J.H.; Cho, S.Y.; Keam, B.; et al. Phase I Study of Random Healthy Donor-Derived Allogeneic Natural Killer Cell Therapy in Patients with Malignant Lymphoma or Advanced Solid Tumors. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Luo, H.; Liang, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, A.; Niu, L.; Jiang, Y. Pembrolizumab plus allogeneic NK cells in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2560–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.H.; Kim, D.H.; Yoo, D.K.; Baek, S.Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Jung, D.E.; Park, S.W.; Chung, Y. In Vivo Study of Natural Killer (NK) Cell Cytotoxicity Against Cholangiocarcinoma in a Nude Mouse Model. In Vivo 2018, 32, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Du, X.; Li, C.; Peng, J.; Gao, L.; Liang, X.; Ma, C. Increased expression of programmed cell death protein 1 on NK cells inhibits NK-cell-mediated anti-tumor function and indicates poor prognosis in digestive cancers. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6143–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Li, M.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xu, D.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Cui, J. PD-1-positive Natural Killer Cells have a weaker antitumor function than that of PD-1-negative Natural Killer Cells in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piha-Paul, S.A.; Oh, D.Y.; Ueno, M.; Malka, D.; Chung, H.C.; Nagrial, A.; Kelley, R.K.; Ros, W.; Italiano, A.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab for the treatment of advanced biliary cancer: Results from the KEYNOTE-158 and KEYNOTE-028 studies. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 2190–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparica, R.; Lengele, A.; Bekolo, W.; Hendlisz, A. FOLFIRI as second-line treatment of metastatic biliary tract cancer patients. Autopsy Case Rep. 2019, 9, e2019087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarca, A.; Palmer, D.H.; Wasan, H.S.; Ross, P.J.; Ma, Y.T.; Arora, A.; Falk, S.; Gillmore, R.; Wadsley, J.; Patel, K.; et al. ABC-06|A randomised phase III, multi-centre, open-label study of active symptom control (ASC) alone or ASC with oxaliplatin/5-FU chemotherapy (ASC+mFOLFOX) for patients (pts) with locally advanced/metastatic biliary tract cancers (ABC) previously-treated with cisplatin/gemcitabine (CisGem) chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. S15), 4003. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Patel, A.; Normolle, D.; Patel, K.; Ohr, J.; Lee, J.J.; Bahary, N.; Chu, E.; Streeter, N.; Drummon, S.D. A phase 2 trial of regorafenib as a single agent in patients with chemotherapy-refractory, advanced, and metastatic biliary tract adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2019, 125, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wu, X.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Nalin, A.P.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Benson, D.M.; He, K.; Caligiuri, M.A.; et al. The Mechanism of Anti-PD-L1 Antibody Efficacy against PD-L1-Negative Tumors Identifies NK Cells Expressing PD-L1 as a Cytolytic Effector. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1422–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pesce, S.; Greppi, M.; Grossi, F.; Del Zotto, G.; Moretta, L.; Sivori, S.; Genova, C.; Marcenaro, E. PD/1-PD-Ls Checkpoint: Insight on the Potential Role of NK Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quatrini, L.; Mariotti, F.R.; Munari, E.; Tumino, N.; Vacca, P.; Moretta, L. The Immune Checkpoint PD-1 in Natural Killer Cells: Expression, Function and Targeting in Tumour Immunotherapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Full Analysis Set (N = 23) | Per-Protocol Set (N = 8) | |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor response | ||
| CR | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| PR | 4 (17.4) | 4 (50.0) |
| SD | 3 (13.0) | 1 (12.5) |
| PD | 16 (69.6) | 3 (37.5) |
| Objective response rate a | 4 (17.4) | 4 (50.0) |
| (95% CI) | (5.0–38.8%) | (15.7–84.3%) |
| Disease control rate b | 7 (30.4) | 5 (62.5) |
| (95% CI) | (13.9–54.9%) | (24.5–91.5%) |
| Phase 1 (N = 6) | Phase 2a (N = 34) | |
|---|---|---|
| Patients with any AE | 4 (66.7) (22.3–95.7%) | 29 (85.3) (68.9–95.1%) |
| Number of events | 7 | 126 |
| Patient characteristics | ||
| Patients with serious AE | 1 (16.7) (0.4–64.1%) | 16 (47.1) (29.8–64.9%) |
| Patients with ADR | 2 (33.3) (4.3–77.7%) | 7 (20.6) (8.7–37.9%) |
| Patients with serious ADR | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.9) (0.1–15.3%) |
| Patients with unexpected ADR | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Grade | ||
| Grade 1/mild AE | 4 (66.7) | 23 (67.6) |
| Grade 2/moderate AE | 0 (0.0) | 18 (52.9) |
| Grade 3/severe AE | 1 (16.7) | 13 (38.2) |
| Grade 4/life-threatening or disabling AE | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Grade 5/death related to AE | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.9) |
| Outcome | ||
| Recovered | 3 (50.0) | 24 (70.6) |
| Recovered with sequelae | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.9) |
| Recovering | 0 (0.0) | 7 (20.6) |
| Not yet recovered | 2 (33.3) | 14 (41.2) |
| Lost to follow-up | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Death | 1 (16.7) | 3 (8.8) |
| Action taken with NP | ||
| Dose not changed | 4 (66.7) | 25 (73.5) |
| Dose delayed | 1 (16.7) | 5 (5.9) |
| IP withdrawn | 1 (16.7) | 12 (35.3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leem, G.; Jang, S.-I.; Cho, J.-H.; Jo, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Chung, M.J.; Park, J.Y.; Bang, S.; Yoo, D.-K.; Cheon, H.-C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Allogeneic Natural Killer Cells in Combination with Pembrolizumab in Patients with Chemotherapy-Refractory Biliary Tract Cancer: A Multicenter Open-Label Phase 1/2a Trial. Cancers 2022, 14, 4229. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174229
Leem G, Jang S-I, Cho J-H, Jo JH, Lee HS, Chung MJ, Park JY, Bang S, Yoo D-K, Cheon H-C, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Allogeneic Natural Killer Cells in Combination with Pembrolizumab in Patients with Chemotherapy-Refractory Biliary Tract Cancer: A Multicenter Open-Label Phase 1/2a Trial. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4229. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174229
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeem, Galam, Sung-Ill Jang, Jae-Hee Cho, Jung Hyun Jo, Hee Seung Lee, Moon Jae Chung, Jeong Youp Park, Seungmin Bang, Da-Kyung Yoo, Hyo-Cheon Cheon, and et al. 2022. "Safety and Efficacy of Allogeneic Natural Killer Cells in Combination with Pembrolizumab in Patients with Chemotherapy-Refractory Biliary Tract Cancer: A Multicenter Open-Label Phase 1/2a Trial" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4229. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174229
APA StyleLeem, G., Jang, S.-I., Cho, J.-H., Jo, J. H., Lee, H. S., Chung, M. J., Park, J. Y., Bang, S., Yoo, D.-K., Cheon, H.-C., Kim, J.-E., Lim, K.-P., Jung, I.-H., Im, J.-M., Chung, Y.-Y., & Park, S. W. (2022). Safety and Efficacy of Allogeneic Natural Killer Cells in Combination with Pembrolizumab in Patients with Chemotherapy-Refractory Biliary Tract Cancer: A Multicenter Open-Label Phase 1/2a Trial. Cancers, 14(17), 4229. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174229






