TNF Receptor Associated Factor 2 (TRAF2) Signaling in Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
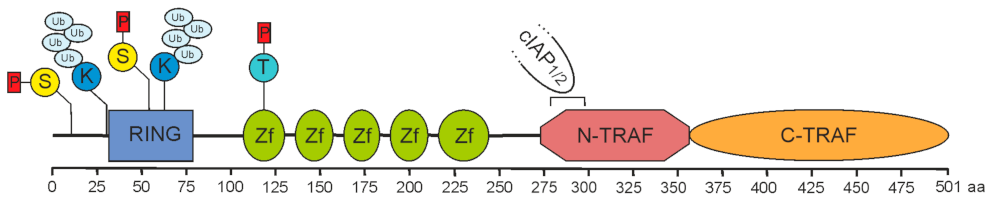
2. Role of TRAF2 in Immune Signaling Pathways
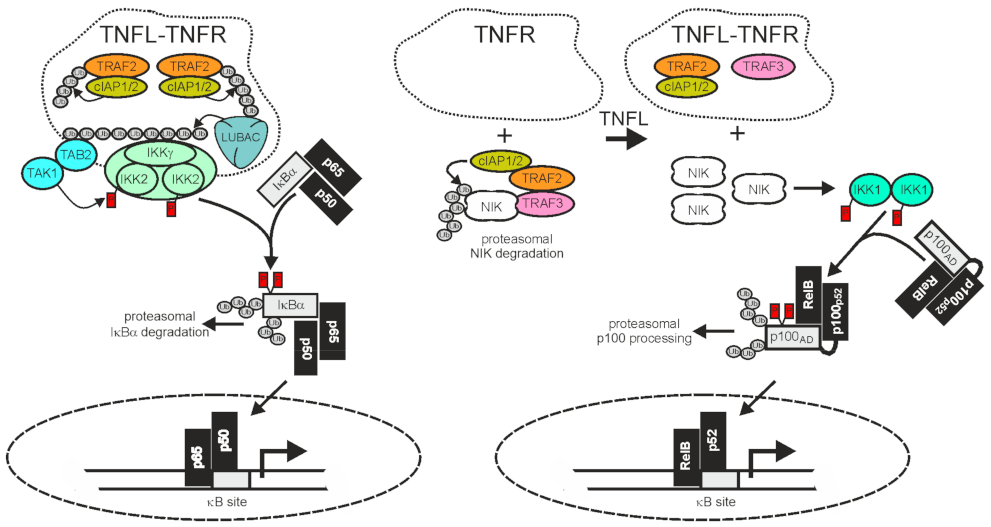
2.1. TRAF2 and Activation of the Classical NFκB Pathway
2.2. TRAF2 and Activation of the Alternative NFκB Pathway
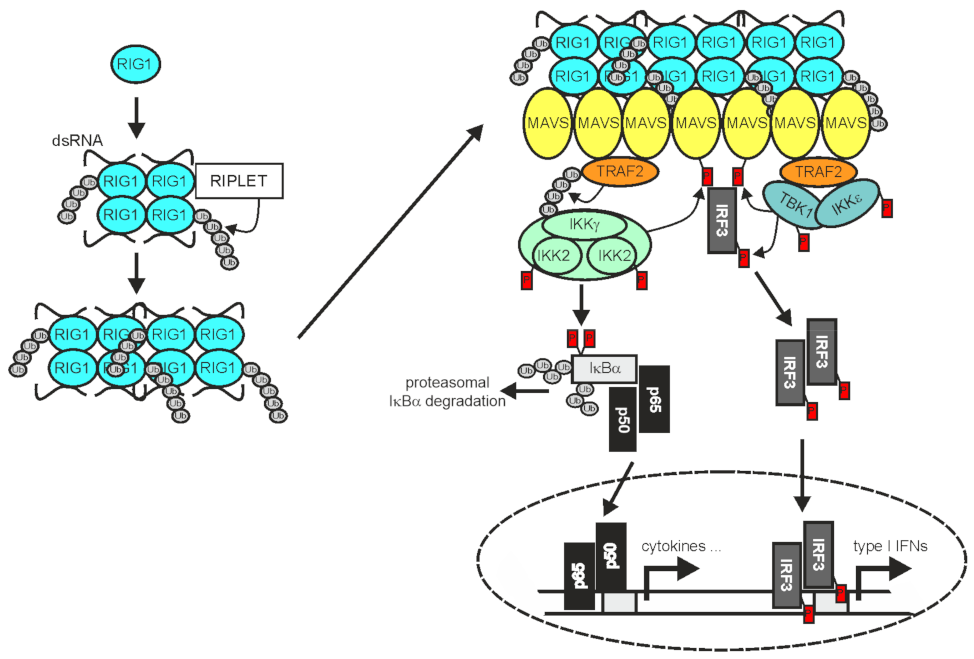
2.3. TRAF2 in RLR Signaling
3. TRAF2 in the Control and Integration of Cell Death Programs, ER Stress and Autophagy
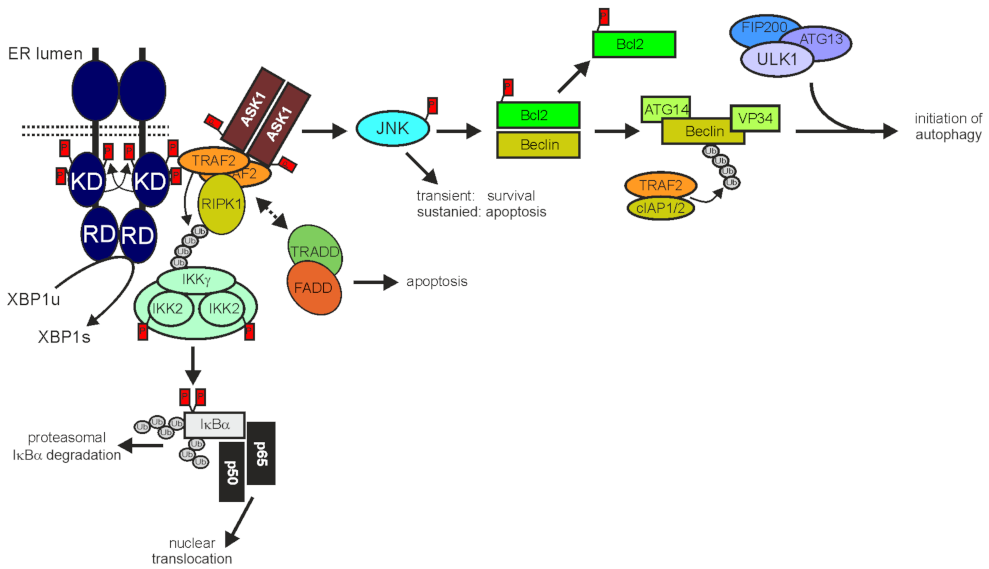
3.1. TRAF2 and Programmed Cell Death
3.2. TRAF2 in ER Stress and Autophagy
4. TRAF2 and the NFκB System in Oncogenesis
4.1. TRAF2 in EBV-associated Oncogenesis
4.2. TRAF2 and the Alternative NFκB Pathway in Multiple Myeloma and B-cell Lymphoma
4.3. TRAF2 and Wnt/β-catenin Signaling
4.4. TRAF2 in Breast Cancer and Other Solid Tumors
5. TRAF2 and the Response to Immune Checkpoint Blockade
6. Therapeutic TRAF2 Targeting Strategies
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rothe, M.; Pan, M.G.; Henzel, W.J.; Ayres, T.M.; Goeddel, D.V. The TNFR2-TRAF signaling complex contains two novel proteins related to baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. Cell 1995, 83, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothe, M.; Wong, S.C.; Henzel, W.J.; Goeddel, D.V. A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell 1994, 78, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajant, H.; Grell, M.; Scheurich, P. TNF receptor associated factors in cytokine signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1999, 10, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vince, J.E.; Pantaki, D.; Feltham, R.; Mace, P.D.; Cordier, S.M.; Schmukle, A.C.; Davidson, A.J.; Callus, B.A.; Wong, W.W.; Gentle, I.E.; et al. TRAF2 must bind to cellular inhibitors of apoptosis for tumor necrosis factor (tnf) to efficiently activate nf-{kappa}b and to prevent tnf-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35906–35915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Workman, L.M.; Zhang, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Habelhah, H. TRAF2 Ser-11 Phosphorylation Promotes Cytosolic Translocation of the CD40 Complex To Regulate Downstream Signaling Pathways. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 40, e00429-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yao, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Feng, D.; Li, Y.; Qasim, W.; Tan, W.; Ning, S.; et al. PKCζ phosphorylates TRAF2 to protect against intestinal ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, G.S.; Zhang, L.; Blackwell, K.; Habelhah, H. Phosphorylation of TRAF2 within its RING domain inhibits stress-induced cell death by promoting IKK and suppressing JNK activation. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3665–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H.; Lei, T.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, W.; Wu, X.; Zuo, L.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. TRIM47 is a novel endothelial activation factor that aggravates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice via K63-linked ubiquitination of TRAF2. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Dorf, M.E. PKC phosphorylation of TRAF2 mediates IKKalpha/beta recruitment and K63-linked polyubiquitination. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Berman, M.A.; Zhang, Y.; Dorf, M.E. RNAi screen in mouse astrocytes identifies phosphatases that regulate NF-kappaB signaling. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.S.; Nedospasov, S.A.; Liu, Z.G. TRAF2 plays a key, nonredundant role in LIGHT-lymphotoxin beta receptor signaling. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arch, R.H.; Thompson, C.B. 4-1BB and Ox40 are members of a tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-nerve growth factor receptor subfamily that bind TNF receptor-associated factors and activate nuclear factor kappaB. Mol. Cell Biol. 1998, 18, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawamata, S.; Hori, T.; Imura, A.; Takaori-Kondo, A.; Uchiyama, T. Activation of OX40 signal transduction pathways leads to tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 2- and TRAF5-mediated NF-kappaB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 5808–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothe, M.; Sarma, V.; Dixit, V.M.; Goeddel, D.V. TRAF2-mediated activation of NF-kappa B by TNF receptor 2 and CD40. Science 1995, 269, 1424–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiba, H.; Nakano, H.; Nishinaka, S.; Shindo, M.; Kobata, T.; Atsuta, M.; Morimoto, C.; Ware, C.F.; Malinin, N.L.; Wallach, D.; et al. CD27, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, activates NF-kappaB and stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase via TRAF2, TRAF5, and NF-kappaB-inducing kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 13353–13358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gravestein, L.A.; Amsen, D.; Boes, M.; Calvo, C.R.; Kruisbeek, A.M.; Borst, J. The TNF receptor family member CD27 signals to Jun N-terminal kinase via Traf-2. Eur J. Immunol. 1998, 28, 2208–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Kishimoto, T.; Minamoto, S. NF-kappaB activation in CD27 signaling: Involvement of TNF receptor-associated factors in its signaling and identification of functional region of CD27. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 4753–4759. [Google Scholar]
- Gedrich, R.W.; Gilfillan, M.C.; Duckett, C.S.; Van Dongen, J.L.; Thompson, C.B. CD30 contains two binding sites with different specificities for members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor family of signal transducing proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 12852–12858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.Y.; Park, C.G.; Choi, Y. T cell receptor-dependent cell death of T cell hybridomas mediated by the CD30 cytoplasmic domain in association with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, I.K.; Lee, Z.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kwon, B.S. Human 4-1BB (CD137) signals are mediated by TRAF2 and activate nuclear factor-kappa B. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 242, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoulli, K.; Lee, S.Y.; Cannons, J.L.; Yeh, W.C.; Santana, A.; Goldstein, M.D.; Bangia, N.; DeBenedette, M.A.; Mak, T.W.; Choi, Y.; et al. CD28-independent, TRAF2-dependent costimulation of resting T cells by 4-1BB ligand. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 1849–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnay, B.G.; Haridas, V.; Ni, J.; Moore, P.A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Characterization of the intracellular domain of receptor activator of NF-kappaB (RANK). Interaction with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors and activation of NF-kappab and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 20551–20555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galibert, L.; Tometsko, M.E.; Anderson, D.M.; Cosman, D.; Dougall, W.C. The involvement of multiple tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-associated factors in the signaling mechanisms of receptor activator of NF-kappaB, a member of the TNFR superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 34120–34127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, B.R.; Josien, R.; Lee, S.Y.; Vologodskaia, M.; Steinman, R.M.; Choi, Y. The TRAF family of signal transducers mediates NF-kappaB activation by the TRANCE receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 28355–28359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiley, S.R.; Cassiano, L.; Lofton, T.; Davis-Smith, T.; Winkles, J.A.; Lindner, V.; Liu, H.; Daniel, T.O.; Smith, C.A.; Fanslow, W.C. A novel TNF receptor family member binds TWEAK and is implicated in angiogenesis. Immunity 2001, 15, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.Z.; Treanor, J.; Senaldi, G.; Khare, S.D.; Boone, T.; Kelley, M.; Theill, L.E.; Colombero, A.; Solovyev, I.; Lee, F.; et al. TACI is a TRAF-interacting receptor for TALL-1, a tumor necrosis factor family member involved in B cell regulation. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marsters, S.A.; Ayres, T.M.; Skubatch, M.; Gray, C.L.; Rothe, M.; Ashkenazi, A. Herpesvirus entry mediator, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) family, interacts with members of the TNFR-associated factor family and activates the transcription factors NF-kappaB and AP-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 14029–14032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, X.; Mehlen, P.; Rabizadeh, S.; VanArsdale, T.; Zhang, H.; Shin, H.; Wang, J.J.; Leo, E.; Zapata, J.; Hauser, C.A.; et al. TRAF family proteins interact with the common neurotrophin receptor and modulate apoptosis induction. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30202–30208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatzoglou, A.; Roussel, J.; Bourgeade, M.F.; Rogier, E.; Madry, C.; Inoue, J.; Devergne, O.; Tsapis, A. TNF receptor family member BCMA (B cell maturation) associates with TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 1, TRAF2, and TRAF3 and activates NF-kappa B, elk-1, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esparza, E.M.; Arch, R.H. Glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor, a costimulatory receptor on naive and activated T cells, uses TNF receptor-associated factor 2 in a novel fashion as an inhibitor of NF-kappa B activation. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 7875–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, B.; Yu, K.Y.; Ni, J.; Yu, G.L.; Jang, I.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Xing, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, S.X.; Kwon, B.S. Identification of a novel activation-inducible protein of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily and its ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 6056–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eby, M.T.; Jasmin, A.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, K.; Chaudhary, P.M. TAJ, a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family, activates the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and mediates caspase-independent cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 15336–15342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereno, R.; Giron-Michel, J.; Gaggero, A.; Cazes, E.; Meazza, R.; Monetti, M.; Monaco, E.; Mishal, Z.; Jasmin, C.; Indiveri, F.; et al. IL-15/IL-15Ralpha intracellular trafficking in human melanoma cells and signal transduction through the IL-15Ralpha. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5153–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.H.; Murti, A.; Pfeffer, L.M. Interferon induces NF-kappa B-inducing kinase/tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-dependent NF-kappa B activation to promote cell survival. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31530–31536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaye, K.M.; Devergne, O.; Harada, J.N.; Izumi, K.M.; Yalamanchili, R.; Kieff, E.; Mosialos, G. Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 2 is a mediator of NF-kappa B activation by latent infection membrane protein 1, the Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 11085–11090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosialos, G.; Birkenbach, M.; Yalamanchili, R.; VanArsdale, T.; Ware, C.; Kieff, E. The Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 engages signaling proteins for the tumor necrosis factor receptor family. Cell 1995, 80, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, H.Y.; Rothe, M.; Goeddel, D.V. The tumor necrosis factor-inducible zinc finger protein A20 interacts with TRAF1/TRAF2 and inhibits NF-kappaB activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6721–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Luo, Y.; D’Alessio, A.; Pober, J.S.; Min, W. AIP1/DAB2IP, a novel member of the Ras-GAP family, transduces TRAF2-induced ASK1-JNK activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44955–44965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.W.; Kim, D.G.; Park, M.C.; Um, J.Y.; Han, J.M.; Park, S.G.; Choi, E.C.; Kim, S. AIMP2 promotes TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis via ubiquitin-mediated degradation of TRAF2. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 2710–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hupalowska, A.; Pyrzynska, B.; Miaczynska, M. APPL1 regulates basal NF-κB activity by stabilizing NIK. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4090–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, E.J.; Ha, J.; Kang, S.S.; Lee, Z.H.; Kim, H.H. AWP1 binds to tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) and is involved in TRAF2-mediated nuclear factor-kappaB signaling. Int J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, T.; Imaizumi, K.; Maeda, M.; Yui, D.; Manabe, T.; Katayama, T.; Sato, N.; Gomi, F.; Morihara, T.; Mori, Y.; et al. Regulatory mechanisms of TRAF2-mediated signal transduction by Bcl10, a MALT lymphoma-associated protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 11114–11120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; He, H.W.; Zhao, W.L.; Shao, R.G. SPHK1 (sphingosine kinase 1) induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition by promoting the autophagy-linked lysosomal degradation of CDH1/E-cadherin in hepatoma cells. Autophagy 2017, 13, 900–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamkanfi, M.; D’Hondt, K.; Vande Walle, L.; van Gurp, M.; Denecker, G.; Demeulemeester, J.; Kalai, M.; Declercq, W.; Saelens, X.; Vandenabeele, P. A novel caspase-2 complex containing TRAF2 and RIP1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 6923–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoneda, T.; Imaizumi, K.; Oono, K.; Yui, D.; Gomi, F.; Katayama, T.; Tohyama, M. Activation of caspase-12, an endoplastic reticulum (ER) resident caspase, through tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2-dependent mechanism in response to the ER stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 13935–13940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, R.; Zhu, H.; Huang, P.; Yang, M.; Shen, M.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, X.; Li, H.; Ke, X.; et al. Liquidambaric acid inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling and colon cancer via targeting TNF receptor-associated factor 2. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Gaeta, M.L.; Madge, L.A.; Yang, J.H.; Bradley, J.R.; Pober, J.S. Caveolin-1 associates with TRAF2 to form a complex that is recruited to tumor necrosis factor receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8341–8349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, K.W.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Jin, T.; Choi, E.Y.; Jeon, H.J.; Kim, E.; Han, Y.S.; Chung, J.H. Ubiquitin ligase CHIP induces TRAF2 proteasomal degradation and NF-κB inactivation to regulate breast cancer cell invasion. J. Cell Biochem. 2011, 112, 3612–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalenko, A.; Chable-Bessia, C.; Cantarella, G.; Israël, A.; Wallach, D.; Courtois, G. The tumour suppressor CYLD negatively regulates NF-kappaB signalling by deubiquitination. Nature 2003, 424, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.; Chiu, L.L.; Tan, T.H. TRAF2-mediated Lys63-linked ubiquitination of DUSP14/MKP6 is essential for its phosphatase activity. Cell Signal. 2016, 28, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Washburn, M.P.; Florens, L.; Wu, M.; Huang, C.; Hou, Z.; Mohan, M. K63-linked ubiquitination of DYRK1A by TRAF2 alleviates Sprouty 2-mediated degradation of EGFR. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakely, C.M.; Pazarentzos, E.; Olivas, V.; Asthana, S.; Yan, J.J.; Tan, I.; Hrustanovic, G.; Chan, E.; Lin, L.; Neel, D.S.; et al. NF-κB-activating complex engaged in response to EGFR oncogene inhibition drives tumor cell survival and residual disease in lung cancer. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.M.; Devkota, S.; Sung, Y.H.; Lee, H.W. EI24 regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tumor progression by suppressing TRAF2-mediated NF-κB activity. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 2383–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.J.; Back, S.H.; Kim, V.; Ryu, I.; Jang, S.K. Sequestration of TRAF2 into stress granules interrupts tumor necrosis factor signaling under stress conditions. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 2450–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohtsu, N.; Nakatani, Y.; Yamashita, D.; Ohue, S.; Ohnishi, T.; Kondo, T. Eva1 Maintains the Stem-like Character of Glioblastoma-Initiating Cells by Activating the Noncanonical NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Silva, S.D.; Xu, B.; Maschietto, M.; Marchi, F.A.; Alkailani, M.I.; Bijian, K.; Xiao, D.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.A. TRAF2 Cooperates with Focal Adhesion Signaling to Regulate Cancer Cell Susceptibility to Anoikis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leonardi, A.; Ellinger-Ziegelbauer, H.; Franzoso, G.; Brown, K.; Siebenlist, U. Physical and functional interaction of filamin (actin-binding protein-280) and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, C.S.; Leonardi, A.; Kyriakis, J.; Siebenlist, U.; Kehrl, J.H. TNF-mediated activation of the stress-activated protein kinase pathway: TNF receptor-associated factor 2 recruits and activates germinal center kinase related. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 3279–3285. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, E.K.; Kang, D.H.; Lee, J.; Hong, S.H.; Jeong, W.; Kang, S.W. Glutathione peroxidase-1 regulates ASK1-dependent apoptosis via interaction with TRAF2 in RIPK3-negative cancer cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangaré, L.O.; Yang, N.; Konstantinou, E.K.; Lu, D.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Young, L.H.; Saeij, J.P.J. Toxoplasma GRA15 Activates the NF-κB Pathway through Interactions with TNF Receptor-Associated Factors. mBio 2019, 10, e00808-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Xue, B.; Luo, L.; Shen, J.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Yin, Z. Human glutathione S-transferase P1-1 interacts with TRAF2 and regulates TRAF2-ASK1 signals. Oncogene 2006, 25, 5787–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chuang, H.C.; Sheu, W.H.; Lin, Y.T.; Tsai, C.Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Cheng, Y.J.; Huang, P.Y.; Li, J.P.; Chiu, L.L.; Wang, X.; et al. HGK/MAP4K4 deficiency induces TRAF2 stabilization and Th17 differentiation leading to insulin resistance. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambert, B.; Vandeputte, J.; Remacle, S.; Bergiers, I.; Simonis, N.; Twizere, J.C.; Vidal, M.; Rezsohazy, R. Protein interactions of the transcription factor Hoxa1. BMC Dev. Biol. 2012, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, S.; Jiang, L.; Wang, G.; Zhou, X.; Wei, X.; Cheng, H.; Wu, Z.; Wei, D. HSP70 interacts with TRAF2 and differentially regulates TNFalpha signalling in human colon cancer cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 710–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devin, A.; Lin, Y.; Yamaoka, S.; Li, Z.; Karin, M.; Liu, Z. The alpha and beta subunits of IkappaB kinase (IKK) mediate TRAF2-dependent IKK recruitment to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 1 in response to TNF. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 3986–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, A.Y.; Shen, R.R.; Kim, E.; Lock, Y.J.; Xu, M.; Chen, Z.J.; Hahn, W.C. IKKε-mediated tumorigenesis requires K63-linked polyubiquitination by a cIAP1/cIAP2/TRAF2 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urano, F.; Wang, X.; Bertolotti, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chung, P.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science 2000, 287, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothe, M.; Xiong, J.; Shu, H.B.; Williamson, K.; Goddard, A.; Goeddel, D.V. I-TRAF is a novel TRAF-interacting protein that regulates TRAF-mediated signal transduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8241–8246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oukka, M.; Kim, S.T.; Lugo, G.; Sun, J.; Wu, L.C.; Glimcher, L.H. A mammalian homolog of Drosophila schnurri, KRC, regulates TNF receptor-driven responses and interacts with TRAF2. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisien, J.P.; Lenoir, J.J.; Mandhana, R.; Rodriguez, K.R.; Qian, K.; Bruns, A.M.; Horvath, C.M. RNA sensor LGP2 inhibits TRAF ubiquitin ligase to negatively regulate innate immune signaling. EMBO Rep. 2018, 19, e45176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Xu, Y.; Schultz, R.D.; Chen, H.; Xie, J.; Deng, M.; Liu, X.; Gui, X.; John, S.; Lu, Z.; et al. LILRB3 supports acute myeloid leukemia development and regulates T-cell antitumor immune responses through the TRAF2-cFLIP-NF-κB signaling axis. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 1170–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Chu, Y.; Song, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Snail enhances arginine synthesis by inhibiting ubiquitination-mediated degradation of ASS1. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e51780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.G.; Wang, Y.Y.; Han, K.J.; Li, L.Y.; Zhai, Z.; Shu, H.B. VISA is an adapter protein required for virus-triggered IFN-beta signaling. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.; Jiang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C.; Guan, Y.; Tao, J.; Xi, J.; Feng, J.M.; Jiang, Z. MAVS activates TBK1 and IKKε through TRAFs in NEMO dependent and independent manner. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baud, V.; Liu, Z.G.; Bennett, B.; Suzuki, N.; Xia, Y.; Karin, M. Signaling by proinflammatory cytokines: Oligomerization of TRAF2 and TRAF6 is sufficient for JNK and IKK activation and target gene induction via an amino-terminal effector domain. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Yan, J.; Jiang, S.; Wen, J.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, A. Site-specific ubiquitination is required for relieving the transcription factor Miz1-mediated suppression on TNF-α-induced JNK activation and inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korchnak, A.C.; Zhan, Y.; Aguilar, M.T.; Chadee, D.N. Cytokine-induced activation of mixed lineage kinase 3 requires TRAF2 and TRAF6. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sondarva, G.; Kundu, C.N.; Mehrotra, S.; Mishra, R.; Rangasamy, V.; Sathyanarayana, P.; Ray, R.S.; Rana, B.; Rana, A. TRAF2-MLK3 interaction is essential for TNF-alpha-induced MLK3 activation. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roh, K.H.; Choi, E.J. TRAF2 functions as an activator switch in the reactive oxygen species-induced stimulation of MST1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 91, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, J.M.; Pawlowski, K.; Haas, E.; Ware, C.F.; Godzik, A.; Reed, J.C. A diverse family of proteins containing tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 24242–24252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, K.A.; Abbas, W.; Varin, A.; Kumar, A.; Di Martino, V.; Dichamp, I.; Herbein, G. HIV-1 Nef interacts with HCV Core, recruits TRAF2, TRAF5 and TRAF6, and stimulates HIV-1 replication in macrophages. J. Innate Immun. 2013, 5, 639–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangino, G.; Percario, Z.A.; Fiorucci, G.; Vaccari, G.; Acconcia, F.; Chiarabelli, C.; Leone, S.; Noto, A.; Horenkamp, F.A.; Manrique, S.; et al. HIV-1 Nef induces proinflammatory state in macrophages through its acidic cluster domain: Involvement of TNF alpha receptor associated factor 2. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lieberson, R.; Mowen, K.A.; McBride, K.D.; Leautaud, V.; Zhang, X.; Suh, W.K.; Wu, L.; Glimcher, L.H. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF)2 represses the T helper cell type 2 response through interaction with NFAT-interacting protein (NIP45). J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bagchi, P.; Bhowmick, R.; Nandi, S.; Kant Nayak, M.; Chawla-Sarkar, M. Rotavirus NSP1 inhibits interferon induced non-canonical NFκB activation by interacting with TNF receptor associated factor 2. Virology 2013, 444, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, M.; Luo, Q.; Alitongbieke, G.; Chong, S.; Xu, C.; Xie, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Celastrol-Induced Nur77 Interaction with TRAF2 Alleviates Inflammation by Promoting Mitochondrial Ubiquitination and Autophagy. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 141–153.e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henn, I.H.; Bouman, L.; Schlehe, J.S.; Schlierf, A.; Schramm, J.E.; Wegener, E.; Nakaso, K.; Culmsee, C.; Berninger, B.; Krappmann, D.; et al. Parkin mediates neuroprotection through activation of IkappaB kinase/nuclear factor-kappaB signaling. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 1868–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorokin, A.V.; Nair, B.C.; Wei, Y.; Aziz, K.E.; Evdokimova, V.; Hung, M.C.; Chen, J. Aberrant Expression of proPTPRN2 in Cancer Cells Confers Resistance to Apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1846–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wixted, J.H.; Rothstein, J.L.; Eisenlohr, L.C. Identification of functionally distinct TRAF proinflammatory and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase (PI3K/MEK) transforming activities emanating from RET/PTC fusion oncoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 3691–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, M.; Rothe, M.; Goeddel, D.V. Anatomy of TRAF2. Distinct domains for nuclear factor-kappaB activation and association with tumor necrosis factor signaling proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 19935–19942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thome, M.; Hofmann, K.; Burns, K.; Martinon, F.; Bodmer, J.L.; Mattmann, C.; Tschopp, J. Identification of CARDIAK, a RIP-like kinase that associates with caspase-1. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, M.; Wu, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, L. Stress-induced RNASET2 overexpression mediates melanocyte apoptosis via the TRAF2 pathway in vitro. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.; Zhu, F.; Wen, W.; Yao, K.; Li, S.; Zykova, T.; Liu, K.; Li, X.; Ma, W.Y.; Bode, A.M.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor family protein 2 is a key mediator of the epidermal growth factor-induced ribosomal S6 kinase 2/cAMP-responsive element-binding protein/Fos protein signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 25881–25892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Busca, A.; Konarski, Y.; Gajanayaka, N.; O’Hara, S.; Angel, J.; Kozlowski, M.; Kumar, A. cIAP1/2-TRAF2-SHP-1-Src-MyD88 Complex Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced IL-27 Production through NF-κB Activation in Human Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 1593–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin Ensign, S.P.; Mathews, I.T.; Eschbacher, J.M.; Loftus, J.C.; Symons, M.H.; Tran, N.L. The Src homology 3 domain-containing guanine nucleotide exchange factor is overexpressed in high-grade gliomas and promotes tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis-fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14-induced cell migration and invasion via tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21887–21897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y. SHARPIN negatively associates with TRAF2-mediated NFκB activation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habelhah, H.; Frew, I.J.; Laine, A.; Janes, P.W.; Relaix, F.; Sassoon, D.; Bowtell, D.D.; Ronai, Z. Stress-induced decrease in TRAF2 stability is mediated by Siah2. Embo. J. 2002, 21, 5756–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Ikeda, K.; Ito, K. Traf2 interacts with Smad4 and regulates BMP signaling pathway in MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, I.; Coornaert, B.; Beyaert, R. Smurf2 is a TRAF2 binding protein that triggers TNF-R2 ubiquitination and TNF-R2-induced JNK activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 374, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Xiao, C.; Su, Z.; Su, H.; Zhong, W.; Mao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.Z. SMYD2-mediated TRAF2 methylation promotes the NF-κB signaling pathways in inflammatory diseases. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Wang, L.; Moretti, P.A.; Albanese, N.; Chai, F.; Pitson, S.M.; D’Andrea, R.J.; Gamble, J.R.; Vadas, M.A. Sphingosine kinase interacts with TRAF2 and dissects tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 7996–8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanamori, M.; Suzuki, H.; Saito, R.; Muramatsu, M.; Hayashizaki, Y. T2BP, a novel TRAF2 binding protein, can activate NF-kappaB and AP-1 without TNF stimulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vliet, C.; Bukczynska, P.E.; Puryer, M.A.; Sadek, C.M.; Shields, B.J.; Tremblay, M.L.; Tiganis, T. Selective regulation of tumor necrosis factor-induced Erk signaling by Src family kinases and the T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliopoulos, A.G.; Davies, C.; Blake, S.S.; Murray, P.; Najafipour, S.; Tsichlis, P.N.; Young, L.S. The oncogenic protein kinase Tpl-2/Cot contributes to Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent infection membrane protein 1-induced NF-kappaB signaling downstream of TRAF2. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 4567–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.; Lim, S.; Li, A.G.; Lee, C.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, E.K.; Park, S.H.; Wang, X.J.; Kim, S.J. Smad7 binds to the adaptors TAB2 and TAB3 to block recruitment of the kinase TAK1 to the adaptor TRAF2. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.A.; Shen, M.; Huang, B.C.; Lasaga, J.; Payan, D.G.; Luo, Y. TNIK, a novel member of the germinal center kinase family that activates the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and regulates the cytoskeleton. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30729–30737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, H.; Shu, H.B.; Pan, M.G.; Goeddel, D.V. TRADD-TRAF2 and TRADD-FADD interactions define two distinct TNF receptor 1 signal transduction pathways. Cell 1996, 84, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.H.; Yeh, D.W.; Lai, C.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Huang, L.R.; Lee, A.Y.; Jin, S.C.; Chuang, T.H. USP17 mediates macrophage-promoted inflammation and stemness in lung cancer cells by regulating TRAF2/TRAF3 complex formation. Oncogene 2018, 37, 6327–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wen, Z.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Song, M.; Wang, E.; Mi, X. TRAF2 regulates the cytoplasmic/nuclear distribution of TRAF4 and its biological function in breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 436, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasai, M.; Tatematsu, M.; Oshiumi, H.; Funami, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Hatakeyama, S.; Seya, T. Direct binding of TRAF2 and TRAF6 to TICAM-1/TRIF adaptor participates in activation of the Toll-like receptor 3/4 pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Li, H.; Luo, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, P. Ubiquitin-specific protease 4 (USP4) targets TRAF2 and TRAF6 for deubiquitination and inhibits TNFα-induced cancer cell migration. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C. UXT-V1 protects cells against TNF-induced apoptosis through modulating complex II formation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaMonica, R.; Kocer, S.S.; Nazarova, J.; Dowling, W.; Geimonen, E.; Shaw, R.D.; Mackow, E.R. VP4 differentially regulates TRAF2 signaling, disengaging JNK activation while directing NF-kappa B to effect rotavirus-specific cellular responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 19889–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prinz, E.; Aviram, S.; Aronheim, A. WDR62 mediates TNFα-dependent JNK activation via TRAF2-MLK3 axis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2018, 29, 2470–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalvez, F.; Lawrence, D.; Yang, B.; Yee, S.; Pitti, R.; Marsters, S.; Pham, V.C.; Stephan, J.P.; Lill, J.; Ashkenazi, A. TRAF2 Sets a threshold for extrinsic apoptosis by tagging caspase-8 with a ubiquitin shutoff timer. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, X.; Che, X.; Guo, T.; Li, C.; Ma, R.; Fan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Hou, K.; et al. DR5-Cbl-b/c-Cbl-TRAF2 complex inhibits TRAIL-induced apoptosis by promoting TRAF2-mediated polyubiquitination of caspase-8 in gastric cancer cells. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 1733–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, J.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, H.; Zou, Q.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ge, W.; Cheng, X.; Sun, S.C. Proinflammatory TLR signalling is regulated by a TRAF2-dependent proteolysis mechanism in macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, W.W.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J.G.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, L.; Qin, Y.; Liu, B.; Shi, J.H. TRAF3 promotes ROS production and pyroptosis by targeting ULK1 ubiquitination in macrophages. Faseb. J. 2020, 34, 7144–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.C.; Ma, X.; Liu, H.; Murphy, J.; Barger, P.M.; Mann, D.L.; Diwan, A. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 mediates mitochondrial autophagy. Circ. Heart Fail. 2015, 8, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zachari, M.; Gudmundsson, S.R.; Li, Z.; Manifava, M.; Cugliandolo, F.; Shah, R.; Smith, M.; Stronge, J.; Karanasios, E.; Piunti, C.; et al. Selective Autophagy of Mitochondria on a Ubiquitin-Endoplasmic-Reticulum Platform. Dev. Cell 2019, 50, 627–643.e625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.C. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lenardo, M.J.; Baltimore, D. 30 Years of NF-κB: A Blossoming of Relevance to Human Pathobiology. Cell 2017, 168, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brummelkamp, T.R.; Nijman, S.M.; Dirac, A.M.; Bernards, R. Loss of the cylindromatosis tumour suppressor inhibits apoptosis by activating NF-kappaB. Nature 2003, 424, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesio, M.; Tang, Y.; Müdder, K.; Saini, M.; von Paleske, L.; Macintyre, E.; Pasparakis, M.; Waisman, A.; Trumpp, A. Hematopoietic stem cell quiescence and function are controlled by the CYLD-TRAF2-p38MAPK pathway. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trompouki, E.; Hatzivassiliou, E.; Tsichritzis, T.; Farmer, H.; Ashworth, A.; Mosialos, G. CYLD is a deubiquitinating enzyme that negatively regulates NF-kappaB activation by TNFR family members. Nature 2003, 424, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lork, M.; Verhelst, K.; Beyaert, R. CYLD, A20 and OTULIN deubiquitinases in NF-κB signaling and cell death: So similar, yet so different. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borghi, A.; Haegman, M.; Fischer, R.; Carpentier, I.; Bertrand, M.J.M.; Libert, C.; Afonina, I.S.; Beyaert, R. The E3 ubiquitin ligases HOIP and cIAP1 are recruited to the TNFR2 signaling complex and mediate TNFR2-induced canonical NF-κB signaling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 153, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafont, E.; Kantari-Mimoun, C.; Draber, P.; De Miguel, D.; Hartwig, T.; Reichert, M.; Kupka, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Taraborrelli, L.; Spit, M.; et al. The linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex regulates TRAIL-induced gene activation and cell death. Embo. J. 2017, 36, 1147–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, F.; Nakagawa, T.; Nakahara, M.; Saeki, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Sakata, S.; Tanaka, K.; Nakano, H.; Iwai, K. SHARPIN is a component of the NF-κB-activating linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex. Nature 2011, 471, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varfolomeev, E.; Goncharov, T.; Maecker, H.; Zobel, K.; Kömüves, L.G.; Deshayes, K.; Vucic, D. Cellular inhibitors of apoptosis are global regulators of NF-κB and MAPK activation by members of the TNF family of receptors. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Hostager, B.S.; Munroe, M.E.; Moore, C.R.; Bishop, G.A. Cooperation between TNF receptor-associated factors 1 and 2 in CD40 signaling. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 5388–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowland, S.L.; Tremblay, M.M.; Ellison, J.M.; Stunz, L.L.; Bishop, G.A.; Hostager, B.S. A novel mechanism for TNFR-associated factor 6-dependent CD40 signaling. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 4645–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vallabhapurapu, S.; Matsuzawa, A.; Zhang, W.; Tseng, P.H.; Keats, J.J.; Wang, H.; Vignali, D.A.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Karin, M. Nonredundant and complementary functions of TRAF2 and TRAF3 in a ubiquitination cascade that activates NIK-dependent alternative NF-kappaB signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zarnegar, B.J.; Wang, Y.; Mahoney, D.J.; Dempsey, P.W.; Cheung, H.H.; He, J.; Shiba, T.; Yang, X.; Yeh, W.C.; Mak, T.W.; et al. Noncanonical NF-kappaB activation requires coordinated assembly of a regulatory complex of the adaptors cIAP1, cIAP2, TRAF2 and TRAF3 and the kinase NIK. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fotin-Mleczek, M.; Henkler, F.; Samel, D.; Reichwein, M.; Hausser, A.; Parmryd, I.; Scheurich, P.; Schmid, J.A.; Wajant, H. Apoptotic crosstalk of TNF receptors: TNF-R2-induces depletion of TRAF2 and IAP proteins and accelerates TNF-R1-dependent activation of caspase-8. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 2757–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vince, J.E.; Chau, D.; Callus, B.; Wong, W.W.; Hawkins, C.J.; Schneider, P.; McKinlay, M.; Benetatos, C.A.; Condon, S.M.; Chunduru, S.K.; et al. TWEAK-FN14 signaling induces lysosomal degradation of a cIAP1-TRAF2 complex to sensitize tumor cells to TNFalpha. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 182, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ablasser, A.; Hur, S. Regulation of cGAS- and RLR-mediated immunity to nucleic acids. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena, C.; Ahmad, S.; Xavier, A.; Willemsen, J.; Park, S.; Park, J.W.; Oh, S.W.; Fujita, T.; Hou, F.; Binder, M.; et al. Ubiquitin-Dependent and -Independent Roles of E3 Ligase RIPLET in Innate Immunity. Cell 2019, 177, 1187–1200.e1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Kinch, L.N.; Brautigam, C.A.; Chen, X.; Du, F.; Grishin, N.V.; Chen, Z.J. Ubiquitin-induced oligomerization of the RNA sensors RIG-I and MDA5 activates antiviral innate immune response. Immunity 2012, 36, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peisley, A.; Wu, B.; Yao, H.; Walz, T.; Hur, S. RIG-I forms signaling-competent filaments in an ATP-dependent, ubiquitin-independent manner. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.; Peisley, A.; Tetrault, D.; Li, Z.; Egelman, E.H.; Magor, K.E.; Walz, T.; Penczek, P.A.; Hur, S. Molecular imprinting as a signal-activation mechanism of the viral RNA sensor RIG-I. Mol. Cell 2014, 55, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Cai, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.T.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.J. MAVS recruits multiple ubiquitin E3 ligases to activate antiviral signaling cascades. Elife 2013, 2, e00785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cai, X.; Wu, J.; Cong, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, T.; Du, F.; Ren, J.; Wu, Y.T.; Grishin, N.V.; et al. Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3 activation. Science 2015, 347, aaa2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shu, H.B.; Takeuchi, M.; Goeddel, D.V. The tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 signal transducers TRAF2 and c-IAP1 are components of the tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 signaling complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 13973–13978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.Y.; Mayo, M.W.; Korneluk, R.G.; Goeddel, D.V.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. NF-kappaB antiapoptosis: Induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 1998, 281, 1680–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, T.; Grell, M.; Siemienski, K.; Mühlenbeck, F.; Dürkop, H.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Scheurich, P.; Wajant, H. TNFR80-dependent enhancement of TNFR60-induced cell death is mediated by TNFR-associated factor 2 and is specific for TNFR60. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 3136–3142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yeh, W.C.; Shahinian, A.; Speiser, D.; Kraunus, J.; Billia, F.; Wakeham, A.; de la Pompa, J.L.; Ferrick, D.; Hum, B.; Iscove, N.; et al. Early lethality, functional NF-kappaB activation, and increased sensitivity to TNF-induced cell death in TRAF2-deficient mice. Immunity 1997, 7, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, F.K.; Lenardo, M.J. A crucial role for p80 TNF-R2 in amplifying p60 TNF-R1 apoptosis signals in T lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckett, C.S.; Thompson, C.B. CD30-dependent degradation of TRAF2: Implications for negative regulation of TRAF signaling and the control of cell survival. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 2810–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Ashwell, J.D. TNF-RII and c-IAP1 mediate ubiquitination and degradation of TRAF2. Nature 2002, 416, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiss, T.; Grell, M.; Hessabi, B.; Bourteele, S.; Müller, G.; Scheurich, P.; Wajant, H. Enhancement of TNF receptor p60-mediated cytotoxicity by TNF receptor p80: Requirement of the TNF receptor-associated factor-2 binding site. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 2398–2404. [Google Scholar]
- Wicovsky, A.; Henkler, F.; Salzmann, S.; Scheurich, P.; Kneitz, C.; Wajant, H. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-1 enhances proinflammatory TNF receptor-2 signaling and modifies TNFR1-TNFR2 cooperation. Oncogene 2009, 28, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wicovsky, A.; Salzmann, S.; Roos, C.; Ehrenschwender, M.; Rosenthal, T.; Siegmund, D.; Henkler, F.; Gohlke, F.; Kneitz, C.; Wajant, H. TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis inhibits proinflammatory TNF receptor-1 signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 1445–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanov, V.N.; Fodstad, O.; Ronai, Z. Expression of ring finger-deleted TRAF2 sensitizes metastatic melanoma cells to apoptosis via up-regulation of p38, TNFalpha and suppression of NF-kappaB activities. Oncogene 2001, 20, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kucharczak, J.; Simmons, M.J.; Fan, Y.; Gélinas, C. To be, or not to be: NF-kappaB is the answer--role of Rel/NF-kappaB in the regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8961–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Blackwell, K.; Altaeva, A.; Shi, Z.; Habelhah, H. TRAF2 phosphorylation promotes NF-κB-dependent gene expression and inhibits oxidative stress-induced cell death. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orning, P.; Lien, E. Multiple roles of caspase-8 in cell death, inflammation, and innate immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 109, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, I.; Jossberger-Werner, M.; Schmidt, N.; Horn, S.; Goebeler, M.; Leverkus, M.; Wajant, H.; Giner, T. TRAF2 inhibits TRAIL- and CD95L-induced apoptosis and necroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, S.L.; Chen, T.T.; Lawrence, D.A.; Marsters, S.A.; Gonzalvez, F.; Ashkenazi, A. TRAF2 is a biologically important necroptosis suppressor. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 1846–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anany, M.A.; Kreckel, J.; Füllsack, S.; Rosenthal, A.; Otto, C.; Siegmund, D.; Wajant, H. Soluble TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) enhances poly(I:C)-induced RIPK1-mediated necroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, M.; Brandl, A.; Siegmund, D.; Mottok, A.; Schäfer, V.; Biehl, M.; Kraus, S.; Bäuerlein, C.A.; Ritz, M.; Mattenheimer, K.; et al. Blocking TWEAK-Fn14 interaction inhibits hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-induced intestinal cell death and reduces GVHD. Blood 2015, 126, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabinger, T.; Bode, K.J.; Demgenski, J.; Seitz, C.; Delgado, M.E.; Kostadinova, F.; Reinhold, C.; Etemadi, N.; Wilhelm, S.; Schweinlin, M.; et al. Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein-1 Regulates Tumor Necrosis Factor-Mediated Destruction of Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lawlor, K.E.; Feltham, R.; Yabal, M.; Conos, S.A.; Chen, K.W.; Ziehe, S.; Graß, C.; Zhan, Y.; Nguyen, T.A.; Hall, C.; et al. XIAP Loss Triggers RIPK3- and Caspase-8-Driven IL-1β Activation and Cell Death as a Consequence of TLR-MyD88-Induced cIAP1-TRAF2 Degradation. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin-Sanchez, D.; Fontecha-Barriuso, M.; Carrasco, S.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Mässenhausen, A.V.; Linkermann, A.; Cannata-Ortiz, P.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Egido, J.; Ortiz, A.; et al. TWEAK and RIPK1 mediate a second wave of cell death during AKI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4182–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ivanov, V.N.; Kehrl, J.H.; Ronai, Z. Role of TRAF2/GCK in melanoma sensitivity to UV-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2000, 19, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhanasekaran, D.N.; Reddy, E.P. JNK signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6245–6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeflich, K.P.; Yeh, W.C.; Yao, Z.; Mak, T.W.; Woodgett, J.R. Mediation of TNF receptor-associated factor effector functions by apoptosis signal-regulating kinase-1 (ASK1). Oncogene 1999, 18, 5814–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagai, H.; Noguchi, T.; Takeda, K.; Ichijo, H. Pathophysiological roles of ASK1-MAP kinase signaling pathways. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 40, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitoh, H.; Matsuzawa, A.; Tobiume, K.; Saegusa, K.; Takeda, K.; Inoue, K.; Hori, S.; Kakizuka, A.; Ichijo, H. ASK1 is essential for endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal cell death triggered by expanded polyglutamine repeats. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishitoh, H.; Saitoh, M.; Mochida, Y.; Takeda, K.; Nakano, H.; Rothe, M.; Miyazono, K.; Ichijo, H. ASK1 is essential for JNK/SAPK activation by TRAF2. Mol. Cell 1998, 2, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Nishitoh, H.; Ichijo, H.; Kyriakis, J.M. Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) by tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 requires prior dissociation of the ASK1 inhibitor thioredoxin. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 2198–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, K.W.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, J.K.; Kang, Y.H.; Chae, J.S.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, S.E.; Baik, J.H.; et al. CIB1 functions as a Ca(2+)-sensitive modulator of stress-induced signaling by targeting ASK1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17389–17394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.H.; Lee, M.K.; Yoon, K.W.; Lee, J.; Cho, S.G.; Choi, E.J. Arginine methylation-dependent regulation of ASK1 signaling by PRMT1. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galan, J.A.; Avruch, J. MST1/MST2 Protein Kinases: Regulation and Physiologic Roles. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 5507–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almanza, A.; Carlesso, A.; Chintha, C.; Creedican, S.; Doultsinos, D.; Leuzzi, B.; Luís, A.; McCarthy, N.; Montibeller, L.; More, S.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling—From basic mechanisms to clinical applications. Febs. J. 2019, 286, 241–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C. The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C.; Glimcher, L.H. Fine-tuning of the unfolded protein response: Assembling the IRE1alpha interactome. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maurel, M.; Chevet, E.; Tavernier, J.; Gerlo, S. Getting RIDD of RNA: IRE1 in cell fate regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Ikushiro, H.; Seo, H.S.; Shin, K.O.; Kim, Y.I.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, Y.M.; Yano, T.; Holleran, W.M.; Elias, P.; et al. ER stress stimulates production of the key antimicrobial peptide, cathelicidin, by forming a previously unidentified intracellular S1P signaling complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1334–E1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Weng, H.; Quon, M.J.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.Y.; Hueber, A.O.; Yang, P. Dominant negative FADD dissipates the proapoptotic signalosome of the unfolded protein response in diabetic embryopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E861–E873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; Strudwick, N.; Suwara, M.; Sutcliffe, L.K.; Mihai, A.D.; Ali, A.A.; Watson, J.N.; Schröder, M. An initial phase of JNK activation inhibits cell death early in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 2317–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, G.P.; O’Connor, H.; Henry, C.M.; Davidovich, P.; Clancy, D.M.; Albert, M.L.; Cullen, S.P.; Martin, S.J. TRAIL Receptors Serve as Stress-Associated Molecular Patterns to Promote ER-Stress-Induced Inflammation. Dev. Cell 2020, 52, 714–730.e715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Han, Z.; Couvillon, A.D.; Kaufman, R.J.; Exton, J.H. Autocrine tumor necrosis factor alpha links endoplasmic reticulum stress to the membrane death receptor pathway through IRE1alpha-mediated NF-kappaB activation and down-regulation of TRAF2 expression. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 3071–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mauro, C.; Crescenzi, E.; De Mattia, R.; Pacifico, F.; Mellone, S.; Salzano, S.; de Luca, C.; D’Adamio, L.; Palumbo, G.; Formisano, S.; et al. Central role of the scaffold protein tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 in regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 2811, 2631–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lalaoui, N.; Lindqvist, L.M.; Sandow, J.J.; Ekert, P.G. The molecular relationships between apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 39, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.S.; Ryan, K.M. New frontiers in promoting tumour cell death: Targeting apoptosis, necroptosis and autophagy. Oncogene 2012, 31, 5045–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stengel, S.; Messner, B.; Falk-Paulsen, M.; Sommer, N.; Rosenstiel, P. Regulated proteolysis as an element of ER stress and autophagy: Implications for intestinal inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q. Apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and cancer metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pattingre, S.; Tassa, A.; Qu, X.; Garuti, R.; Liang, X.H.; Mizushima, N.; Packer, M.; Schneider, M.D.; Levine, B. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell 2005, 122, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maiuri, M.C.; Zalckvar, E.; Kimchi, A.; Kroemer, G. Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattingre, S.; Bauvy, C.; Carpentier, S.; Levade, T.; Levine, B.; Codogno, P. Role of JNK1-dependent Bcl-2 phosphorylation in ceramide-induced macroautophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 2719–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castillo, K.; Rojas-Rivera, D.; Lisbona, F.; Caballero, B.; Nassif, M.; Court, F.A.; Schuck, S.; Ibar, C.; Walter, P.; Sierralta, J.; et al. BAX inhibitor-1 regulates autophagy by controlling the IRE1α branch of the unfolded protein response. Embo. J. 2011, 30, 4465–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, W.; Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Xu, X.; Padilla, M.T.; Ren, G.; Gou, X.; Lin, Y. Attenuation of TNFSF10/TRAIL-induced apoptosis by an autophagic survival pathway involving TRAF2- and RIPK1/RIP1-mediated MAPK8/JNK activation. Autophagy 2012, 8, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lisbona, F.; Rojas-Rivera, D.; Thielen, P.; Zamorano, S.; Todd, D.; Martinon, F.; Glavic, A.; Kress, C.; Lin, J.H.; Walter, P.; et al. BAX inhibitor-1 is a negative regulator of the ER stress sensor IRE1alpha. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Zhao, H.; Jin, M.; Zhu, H.; Shan, B.; Geng, J.; Dziedzic, S.A.; Amin, P.; Mifflin, L.; Naito, M.G.; et al. Modulating TRADD to restore cellular homeostasis and inhibit apoptosis. Nature 2020, 587, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, C.; De Luca, A.; Rosato, N.; Forgione, M.; Rotili, D.; Caccuri, A.M. c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation by nitrobenzoxadiazoles leads to late-stage autophagy inhibition. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultheiss, U.; Püschner, S.; Kremmer, E.; Mak, T.W.; Engelmann, H.; Hammerschmidt, W.; Kieser, A. TRAF6 is a critical mediator of signal transduction by the viral oncogene latent membrane protein 1. Embo. J. 2001, 20, 5678–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Münz, C. Latency and lytic replication in Epstein-Barr virus-associated oncogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsang, C.M.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bruce, J.P.; Pugh, T.J.; Lo, K.W. Translational genomics of nasopharyngeal cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 61, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devergne, O.; Hatzivassiliou, E.; Izumi, K.M.; Kaye, K.M.; Kleijnen, M.F.; Kieff, E.; Mosialos, G. Association of TRAF1, TRAF2, and TRAF3 with an Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 domain important for B-lymphocyte transformation: Role in NF-kappaB activation. Mol. Cell Biol. 1996, 16, 7098–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izumi, K.M.; Kaye, K.M.; Kieff, E.D. The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 amino acid sequence that engages tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factors is critical for primary B lymphocyte growth transformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arcipowski, K.M.; Stunz, L.L.; Graham, J.P.; Kraus, Z.J.; Vanden Bush, T.J.; Bishop, G.A. Molecular mechanisms of TNFR-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) utilization by the oncogenic viral mimic of CD40, latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 9948–9955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Busch, L.K.; Bishop, G.A. Multiple carboxyl-terminal regions of the EBV oncoprotein, latent membrane protein 1, cooperatively regulate signaling to B lymphocytes via TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF)-dependent and TRAF-independent mechanisms. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 5805–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soni, V.; Cahir-McFarland, E.; Kieff, E. LMP1 TRAFficking activates growth and survival pathways. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 597, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.P.; Arcipowski, K.M.; Bishop, G.A. Differential B-lymphocyte regulation by CD40 and its viral mimic, latent membrane protein 1. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 237, 226–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Hostager, B.S.; Bishop, G.A. Requirement for TRAF3 in signaling by LMP1 but not CD40 in B lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luftig, M.; Prinarakis, E.; Yasui, T.; Tsichritzis, T.; Cahir-McFarland, E.; Inoue, J.; Nakano, H.; Mak, T.W.; Yeh, W.C.; Li, X.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 activation of NF-kappaB through IRAK1 and TRAF6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15595–15600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, G.T.; Lou, W.P.; Chow, C.; To, K.F.; Choy, K.W.; Leung, A.W.; Tong, C.Y.; Yuen, J.W.; Ko, C.W.; Yip, T.T.; et al. Constitutive activation of distinct NF-κB signals in EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2013, 231, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliopoulos, A.G.; Blake, S.M.; Floettmann, J.E.; Rowe, M.; Young, L.S. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 activates the JNK pathway through its extreme C terminus via a mechanism involving TRADD and TRAF2. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenfeld, H.; Takasaki, K.; Walsh, M.J.; Ersing, I.; Bernhardt, K.; Ma, Y.; Fu, B.; Ashbaugh, C.W.; Cabo, J.; Mollo, S.B.; et al. TRAF1 Coordinates Polyubiquitin Signaling to Enhance Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1-Mediated Growth and Survival Pathway Activation. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fries, K.L.; Miller, W.E.; Raab-Traub, N. The A20 protein interacts with the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) and alters the LMP1/TRAF1/TRADD complex. Virology 1999, 264, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laherty, C.D.; Hu, H.M.; Opipari, A.W.; Wang, F.; Dixit, V.M. The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 gene product induces A20 zinc finger protein expression by activating nuclear factor kappa B. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 24157–24160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewurz, B.E.; Towfic, F.; Mar, J.C.; Shinners, N.P.; Takasaki, K.; Zhao, B.; Cahir-McFarland, E.D.; Quackenbush, J.; Xavier, R.J.; Kieff, E. Genome-wide siRNA screen for mediators of NF-κB activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2467–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grech, A.P.; Amesbury, M.; Chan, T.; Gardam, S.; Basten, A.; Brink, R. TRAF2 differentially regulates the canonical and noncanonical pathways of NF-kappaB activation in mature B cells. Immunity 2004, 21, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, K.D.; Hostager, B.S.; Bishop, G.A. Differential signaling and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) degradation mediated by CD40 and the Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1). J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hostager, B.S.; Haxhinasto, S.A.; Rowland, S.L.; Bishop, G.A. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2)-deficient B lymphocytes reveal novel roles for TRAF2 in CD40 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 45382–45390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graham, J.P.; Moore, C.R.; Bishop, G.A. Roles of the TRAF2/3 binding site in differential B cell signaling by CD40 and its viral oncogenic mimic, LMP1. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2966–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderwood, M.A.; Venkatesan, K.; Xing, L.; Chase, M.R.; Vazquez, A.; Holthaus, A.M.; Ewence, A.E.; Li, N.; Hirozane-Kishikawa, T.; Hill, D.E.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus and virus human protein interaction maps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7606–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagemeier, S.R.; Barlow, E.A.; Kleman, A.A.; Kenney, S.C. The Epstein-Barr virus BRRF1 protein, Na, induces lytic infection in a TRAF2- and p53-dependent manner. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4318–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Annunziata, C.M.; Davis, R.E.; Demchenko, Y.; Bellamy, W.; Gabrea, A.; Zhan, F.; Lenz, G.; Hanamura, I.; Wright, G.; Xiao, W.; et al. Frequent engagement of the classical and alternative NF-kappaB pathways by diverse genetic abnormalities in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demchenko, Y.N.; Glebov, O.K.; Zingone, A.; Keats, J.J.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Kuehl, W.M. Classical and/or alternative NF-kappaB pathway activation in multiple myeloma. Blood 2010, 115, 3541–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jourdan, M.; Moreaux, J.; Vos, J.D.; Hose, D.; Mahtouk, K.; Abouladze, M.; Robert, N.; Baudard, M.; Rème, T.; Romanelli, A.; et al. Targeting NF-kappaB pathway with an IKK2 inhibitor induces inhibition of multiple myeloma cell growth. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 138, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keats, J.J.; Fonseca, R.; Chesi, M.; Schop, R.; Baker, A.; Chng, W.J.; Van Wier, S.; Tiedemann, R.; Shi, C.X.; Sebag, M.; et al. Promiscuous mutations activate the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gardam, S.; Turner, V.M.; Anderton, H.; Limaye, S.; Basten, A.; Koentgen, F.; Vaux, D.L.; Silke, J.; Brink, R. Deletion of cIAP1 and cIAP2 in murine B lymphocytes constitutively activates cell survival pathways and inactivates the germinal center response. Blood 2011, 117, 4041–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Hideshima, T.; Xing, L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, W.; Samur, M.K.; Sewastianik, T.; Ogiya, D.; An, G.; Gao, S.; et al. ERK signaling mediates resistance to immunomodulatory drugs in the bone marrow microenvironment. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahal, R.; Frick, M.; Romero, R.; Korn, J.M.; Kridel, R.; Chan, F.C.; Meissner, B.; Bhang, H.E.; Ruddy, D.; Kauffmann, A.; et al. Pharmacological and genomic profiling identifies NF-κB-targeted treatment strategies for mantle cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compagno, M.; Lim, W.K.; Grunn, A.; Nandula, S.V.; Brahmachary, M.; Shen, Q.; Bertoni, F.; Ponzoni, M.; Scandurra, M.; Califano, A.; et al. Mutations of multiple genes cause deregulation of NF-kappaB in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2009, 459, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, P.P.; Zhong, H.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Gao, X.D.; Zhao, X.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, S.; Huang, J.Y.; Chen, S.J.; Wang, L.; et al. B-cell Function Gene Mutations in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma: A Retrospective Cohort Study. EBioMedicine 2017, 16, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Galen, J.C.; Muris, J.J.; Giroth, C.P.; Vos, W.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Meijer, C.J.; Oudejans, J.J. Expression of TNF-receptor associated factor 2 correlates with poor progression-free survival time in ABC-like primary nodal diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Histopathology 2008, 52, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontan, L.; Goldstein, R.; Casalena, G.; Durant, M.; Teater, M.R.; Wilson, J.; Phillip, J.; Xia, M.; Shah, S.; Us, I.; et al. Identification of MALT1 feedback mechanisms enables rational design of potent antilymphoma regimens for ABC-DLBCL. Blood 2021, 137, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Wood, S.; Namiranian, S.; Mizukoshi, R.; Weng, S.; Jang, I.S.; Fontanillo, C.; Baughman, J.M.; Silva-Torres, A.; Slade, M.; et al. Deciphering the mechanisms of CC-122 resistance in DLBCL via a genome-wide CRISPR screen. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Stunz, L.L.; Larison, K.D.; Yang, B.; Bishop, G.A. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 is a critical regulator of B cell homeostasis in secondary lymphoid organs. Immunity 2007, 27, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moore, C.R.; Liu, Y.; Shao, C.; Covey, L.R.; Morse, H.C., 3rd; Xie, P. Specific deletion of TRAF3 in B lymphocytes leads to B-lymphoma development in mice. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zapata, J.M.; Krajewska, M.; Morse, H.C., 3rd; Choi, Y.; Reed, J.C. TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) domain and Bcl-2 cooperate to induce small B cell lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16600–16605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Chacón, G.; Llobet, D.; Pardo, C.; Pindado, J.; Choi, Y.; Reed, J.C.; Zapata, J.M. TNFR-associated factor 2 deficiency in B lymphocytes predisposes to chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma in mice. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.W.; Son, H.J.; Choi, E.J.; Yoo, N.J.; Lee, S.H. Brief Research Report Regional Difference in TRAF2 and TRAF3 Gene Mutations in Colon Cancers. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2021, 27, 625438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürch, C.; Riether, C.; Matter, M.S.; Tzankov, A.; Ochsenbein, A.F. CD27 signaling on chronic myelogenous leukemia stem cells activates Wnt target genes and promotes disease progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.H. The nuclear factor-kappa B pathway and response to treatment in breast cancer. Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 1697–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velloso, F.J.; Bianco, A.F.; Farias, J.O.; Torres, N.E.; Ferruzo, P.Y.; Anschau, V.; Jesus-Ferreira, H.C.; Chang, T.H.; Sogayar, M.C.; Zerbini, L.F.; et al. The crossroads of breast cancer progression: Insights into the modulation of major signaling pathways. Onco. Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 5491–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durand, J.K.; Zhang, Q.; Baldwin, A.S. Roles for the IKK-Related Kinases TBK1 and IKKε in Cancer. Cells 2018, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, R.R.; Zhou, A.Y.; Kim, E.; Lim, E.; Habelhah, H.; Hahn, W.C. IκB kinase ε phosphorylates TRAF2 to promote mammary epithelial cell transformation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 4756–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peramuhendige, P.; Marino, S.; Bishop, R.T.; de Ridder, D.; Khogeer, A.; Baldini, I.; Capulli, M.; Rucci, N.; Idris, A.I. TRAF2 in osteotropic breast cancer cells enhances skeletal tumour growth and promotes osteolysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papanastasiou, A.D.; Sirinian, C.; Kalofonos, H.P. Identification of novel human receptor activator of nuclear factor-kB isoforms generated through alternative splicing: Implications in breast cancer cell survival and migration. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sirinian, C.; Papanastasiou, A.D.; Schizas, M.; Spella, M.; Stathopoulos, G.T.; Repanti, M.; Zarkadis, I.K.; King, T.A.; Kalofonos, H.P. RANK-c attenuates aggressive properties of ER-negative breast cancer by inhibiting NF-κB activation and EGFR signaling. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5101–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.J.; Liu, N.; Wang, A.L.; Ren, H.Y.; Yang, F.; Diao, K.X.; Fu, W.N.; Wan, E.H.; et al. Suppressive role of miR-502-5p in breast cancer via downregulation of TRAF2. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Yu, L.; Zhang, X.; Lei, F.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Zhu, J.; Wu, G.; Cao, L.; et al. miR-892b Silencing Activates NF-κB and Promotes Aggressiveness in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.Y.; Li, Y.; Yin, H.Z.; Yin, H.; Qu, Y.Y.; Xu, Q.Y. TNFAIP8 Promotes Cisplatin Chemoresistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Repressing p53-Mediated miR-205-5p Expression. Mol. Ther. Nucleic. Acids 2020, 22, 640–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, P.; Chen, W.; Guo, F. The ubiquitin ligase CHIP inactivates NF-κB signaling and impairs the ability of migration and invasion in gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, H.; Chen, H.; Xu, J.; Zhou, J.; Shan, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhou, X.; Guo, F. The ubiquitin ligase CHIP modulates cellular behaviors of gastric cancer cells by regulating TRAF2. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Youn, H.; Seong, K.M.; Jin, Y.W.; Kim, J.; Youn, B. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S3 and antiapoptotic TRAF2 protein mediates radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 2965–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vredevoogd, D.W.; Kuilman, T.; Ligtenberg, M.A.; Boshuizen, J.; Stecker, K.E.; de Bruijn, B.; Krijgsman, O.; Huang, X.; Kenski, J.C.N.; Lacroix, R.; et al. Augmenting Immunotherapy Impact by Lowering Tumor TNF Cytotoxicity Threshold. Cell 2019, 178, 585–599.e515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, K.; Reading, J.L.; Puttick, C.; Thakkar, K.; Abbosh, C.; Bentham, R.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Rosenthal, R.; Biswas, D.; Rowan, A.; et al. Meta-analysis of tumor- and T cell-intrinsic mechanisms of sensitization to checkpoint inhibition. Cell 2021, 184, 596–614.e514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrish, E.; Brumatti, G.; Silke, J. Future Therapeutic Directions for Smac-Mimetics. Cells 2020, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lombrea, A.; Scurtu, A.D.; Avram, S.; Pavel, I.Z.; Turks, M.; Lugiņina, J.; Peipiņš, U.; Dehelean, C.A.; Soica, C.; Danciu, C. Anticancer Potential of Betulonic Acid Derivatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearney, C.J.; Vervoort, S.J.; Hogg, S.J.; Ramsbottom, K.M.; Freeman, A.J.; Lalaoui, N.; Pijpers, L.; Michie, J.; Brown, K.K.; Knight, D.A.; et al. Tumor immune evasion arises through loss of TNF sensitivity. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaar3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Protein | Type of Protein | Experimental Evidence | Target Domain in TRAF | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNFR2 | TNFRSF | THS, GST, endo Co-IP | CTD | [2] |
| LTβR | TNFRSF | endo Co-IP | [11] | |
| OX40 | TNFRSF | THS, Co-IP | [12,13] | |
| CD40 | TNFRSF | THS, GST, endo Co-IP | [14] | |
| CD27 | TNFRSF | THS, Co-IP | [15,16,17] | |
| CD30 | TNFRSF | THS, GST | [18,19] | |
| 4-1BB | TNFRSF | THS, GST, endo Co-IP | [12,20,21] | |
| RANK | TNFRSF | GST, Co-IP | [22,23,24] | |
| Fn14 | TNFRSF | GST | [25] | |
| TACI | TNFRSF | THS, Co-IP | [26] | |
| HVEM | TNFRSF | GST | [27] | |
| NGFR | TNFRSF | Co-IP | [28] | |
| BCMA | TNFRSF | Co-IP | [29] | |
| GITR | TNFRSF | THS, endo Co-IP | [30,31] | |
| TROY | TNFRSF | Co-IP | [32] | |
| IL15R | receptor | Co-IP | [33] | |
| IFNαR1 | receptor | GST, Co-IP | [34] | |
| LMP1 | viral oncogen | GST, Co-IP | [35,36] | |
| A20 | DUB, E3 ligase | THS, Co-IP | [37] | |
| AIP1 | Ras-GAP | Co-IP | RING/zinc | [38] |
| AIMP2 | adaptor | THS, GST, endo Co-IP | [39] | |
| APPL1 | adaptor | GST, endo Co-IP | [40] | |
| AWP1 | adaptor | THS, Co-IP | TD | [41] |
| Bcl10 | adaptor | THS, Co-IP | [42] | |
| Beclin | autophagy | GST, endo Co-IP | RING | [43] |
| Caspase-2 | caspase | Endo Co-IP | [44] | |
| Caspase-12 | caspase | Co-IP | NTD | [45] |
| β-catenin | proto-oncogene | Co-IP, MST | TD | [46] |
| caveolin-1 | plasma membrane protein | endo Co-IP | [47] | |
| CHIP | E3 ligase | endo Co-IP | [48] | |
| cIAP1 | E3 ligase | THS, Co-IP | NTD | [1] |
| cIAP2 | E3 ligase | THS, Co-IP | NTD | [1] |
| CYLD | DUB | THS, Co-IP | TD | [49] |
| DUSP14 | phosphatase | Co-IP | [50] | |
| DYRK1A | kinase | endo Co-IP | TD | [51] |
| EGFR | kinase | endo Co-IP | [52] | |
| EI24 | E3 ligase | Co-IP | [53] | |
| eIF4GI | scaffold | THS, GST, Co-IP | TD | [54] |
| Eva1 | adhesion protein | endo Co-IP | [55] | |
| FAK | kinase | endo Co-IP | [56] | |
| Filamin | actin binder | Co-IP | RZ | [57] |
| GCKR | kinase | endo Co-IP | TD | [58] |
| Gpx1 | peroxidase | Co-IP | TD | [59] |
| GRA15 | virulence factor | Co-IP | [60] | |
| GSTP1-1 | gluthation transferase | Co-IP | [61] | |
| HGK | Kinase | Co-IP | [62] | |
| Hoxa1 | transcription factor | THS, Co-IP | [63] | |
| HSP70 | Chaperon | Co-IP | TD | [64] |
| IKK1 | kinase | GST, endo Co-IP | RING | [65] |
| IKK2 | kinase | GST, endo Co-IP | RING | [65] |
| IKKe | kinase | Co-IP | [66] | |
| IRE1 | kinase, nuclease | endo Co-IP | [67] | |
| I-TRAF | adaptor | THS, GST, Co-IP | TD | [68] |
| JIK | kinase | Co-IP | [45] | |
| KRC | DNA binding | endo Co-IP | TD | [69] |
| LGP2 | RLR | Co-IP | CTD | [70] |
| LILRB3 | receptor | endo Co-IP | [71] | |
| LRPPRC | RNA regulation | Co-IP | [72] | |
| MAVS | adaptor | Co-IP | CTD | [73,74] |
| MEKK1 | kinase | Co-IP | [75] | |
| MIZ | transcription factor | GST, endo Co-IP | RING | [76] |
| MLK3 | kinase | Co-IP | NTD | [77,78] |
| MST1 | kinase | endo Co-IP | Zn fingers | [79] |
| TRIM37 | E3 ligase | Co-IP | TD | [80] |
| Nef | virulence factor | GST | [81,82] | |
| HCV core | virulence factor | GST | [81] | |
| NIP45 | transcription factor associated | endo Co-IP | [83] | |
| NSP1 | virulence factor | Co-IP | [84] | |
| Nur77 | nuclear receptor | Co-IP | RING, NTD | [85] |
| parkin | E3 ligase | endo Co-IP | [86] | |
| proPTPRN2 | phosphatase | Co-IP | RING | [87] |
| RET/PTC3 | oncogenic RTK fusion protein | Co-IP | [88] | |
| RIPK1 | kinase | Co-IP | NTD, CTD | [89] |
| RIP2 | kinase | Co-IP | [90] | |
| RNAseT2 | ribonuclease | Co-IP | [91] | |
| RSK2 | kinase | Co-IP | [92] | |
| SHP-1 | phosphatase | Co-IP | [93] | |
| SGEF | GEF | Co-IP | TD | [94] |
| Sharpin | scaffold | Co-IP | [95] | |
| SIAH-2 | E3 ligase | GST | [96] | |
| SMAD4 | signaling protein | THS, endo Co-IP | [97] | |
| SMURF-2 | E3 ligase | THS, Co-IP | [98] | |
| SMYD2 | methyltransferase | Co-IP, SPR | [99] | |
| SphK1 | kinase | GST, Co-IP | [100] | |
| T2BP / TIFA | adaptor | THS, Co-IP | TD | [101] |
| TCPTP | phosphatase | endo Co-IP | [102] | |
| TPL2/COT1 | kinase | Co-IP | [103] | |
| TAK1 | kinase | Co-IP | [104] | |
| TBK1 | kinase | endo Co-IP | NTD | [74] |
| TNIK | kinase | Co-IP | TD | [105] |
| TRADD | adaptor | THS, Co-IP | CTD | [89,106] |
| TRAF1 | adaptor | THS, Co-IP | NTD, CTD | [2,89] |
| TRAF2 | E3 ligase, adaptor | THS, Co-IP | CTD | [2,89] |
| TRAF3 | E3 ligase, adaptor | Co-IP | [107] | |
| TRAF4 | E3 ligase, adaptor | endo Co-IP | [108] | |
| TRIF | adaptor | THS, Co-IP | [109] | |
| UBC13 | E2 | endo Co-IP | RING | [76] |
| USP4 | DUB | Co-IP | [110] | |
| USP7 | DUB | GST | [80] | |
| USP17 | DUB | Co-IP | [107] | |
| UXT-V1 | transcriptional cofactor | endo Co-IP | [111] | |
| VP4 | rotavirus capsid protein | THS, Co-IP | [112] | |
| WDR62 | scaffold | Co-IP | [113] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siegmund, D.; Wagner, J.; Wajant, H. TNF Receptor Associated Factor 2 (TRAF2) Signaling in Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4055. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14164055
Siegmund D, Wagner J, Wajant H. TNF Receptor Associated Factor 2 (TRAF2) Signaling in Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(16):4055. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14164055
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiegmund, Daniela, Jennifer Wagner, and Harald Wajant. 2022. "TNF Receptor Associated Factor 2 (TRAF2) Signaling in Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 16: 4055. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14164055
APA StyleSiegmund, D., Wagner, J., & Wajant, H. (2022). TNF Receptor Associated Factor 2 (TRAF2) Signaling in Cancer. Cancers, 14(16), 4055. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14164055






