Ultrasensitive Detection of GRP78 in Exosomes and Observation of Migration and Proliferation of Cancer Cells by Application of GRP78-Containing Exosomes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Exosome Isolation
2.3. Ultrasensitive Thio-NAD Cycling ELISA
2.4. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. MTT Assay
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Wound Healing Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ultrasensitive Determination of GRP78
3.2. Characterization of Isolated Exosomes by Western Blotting and Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
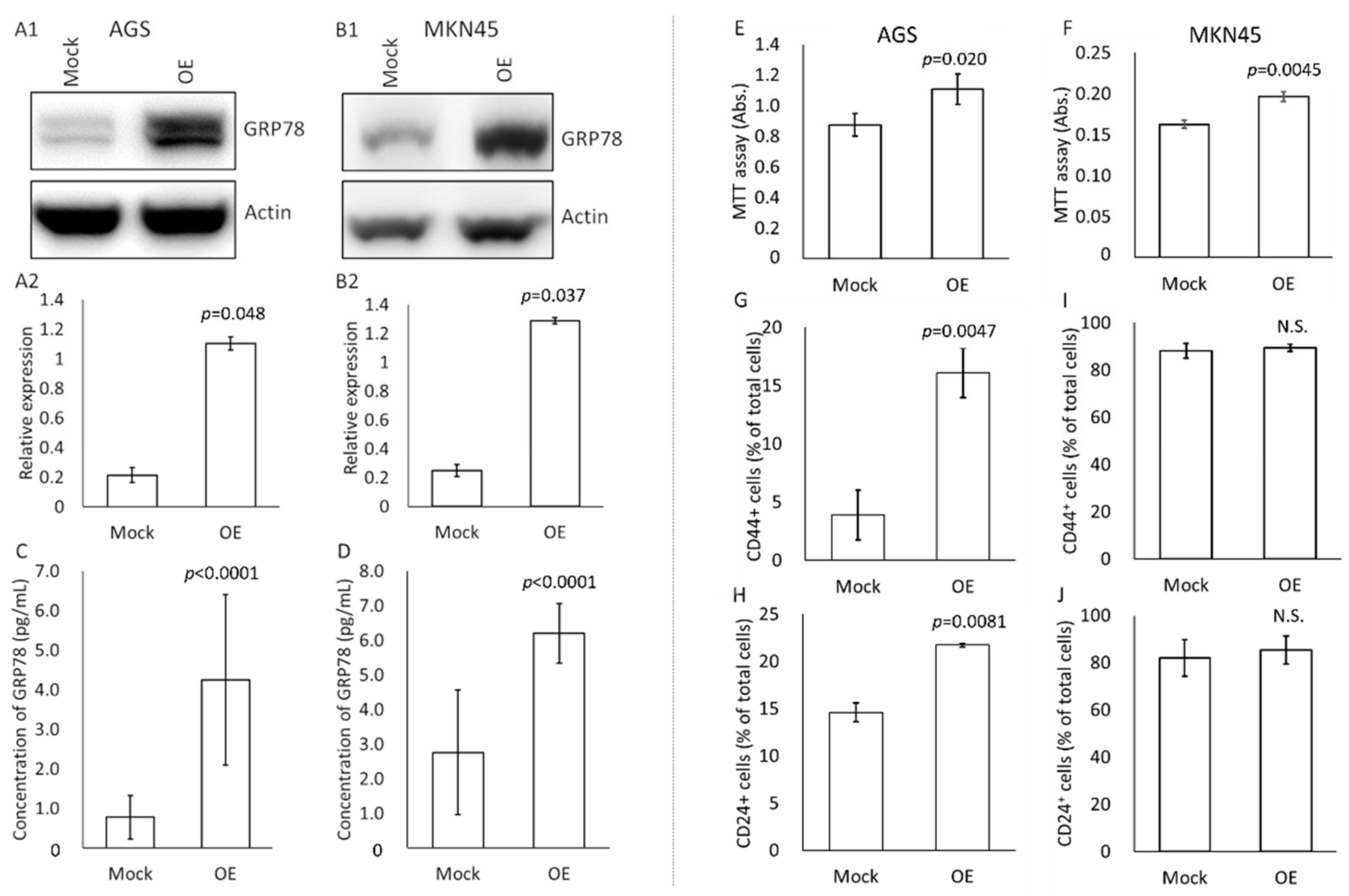
3.3. Effects of High-GRP78-Containing Exosomes on Profiles of Untreated Cultured Gastric Cancer Cells
3.4. Change in Migration and Proliferation of Cultured Gastric Cancer Cells by the Application of GRP78-Containing Exosomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Shi, P.; Zhao, G.; Xu, J.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Dong, Z.; Chen, F.; et al. Targeting cancer stem cell pathways for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.D.; Holzapfel, B.M.; Liu, J.; Lee, T.K.; Ma, S.; Jovanovic, L.; An, J.; Russell, P.J.; Clements, J.A.; Hutmacher, D.W.; et al. Tie-2 regulates the stemness and metastatic properties of prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 2572–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, G.; Aziz, S.G.; Jaghi, N.Z.Z. EMT, cancer stem cells and autophagy; The three main axes of metastasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajewski, T.F.; Schreiber, H.; Fu, Y.X. Innate and adaptive immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, R.A. The Biology of Cancer, 2nd ed.; W.W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Zheng, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, B. Exosome theranostics: Biology and translational medicine. Theranostics 2018, 8, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Ding, Z.; Xu, S.; Gao, B.; et al. Exosomes immunity strategy: A novel approach for ameliorating intervertebral disc degeneration. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2022, 9, 822149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Yang, J.C.; Rau, C.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Lu, T.H.; Lin, M.W.; Tzeng, S.L.; Wu, Y.C.; Wu, C.J.; Hsieh, C.H. Profiling circulating microRNA expression in experimental sepsis using cecal ligation and puncture. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, F.T.; Reis, L.A.; Schor, N. Extracellular vesicles: Structure, function, and potential clinical uses in renal diseases. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2013, 46, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Wang, W.; Lan, X.L.; Zeng, Z.C.; Liang, Y.S.; Yan, Y.R.; Song, F.Y.; Wang, F.F.; Zhu, X.H.; Liao, W.J.; et al. CAFs secreted exosomes promote metastasis and chemotherapy resistance by enhancing cell stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osteikoetxea, X.; Németh, A.; Sódar, B.W.; Vukman, K.V.; Buzás, E.I. Extracellular vesicles in cardiovascular disease: Are they Jedi or Sith? J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 2881–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iha, K.; Inada, M.; Kawada, N.; Nakaishi, K.; Watabe, S.; Tan, Y.H.; Shen, C.; Ke, L.Y.; Yoshimura, T.; Ito, E. Ultrasensitive ELISA developed for diagnosis. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iha, K.; Kyosei, Y.; Namba, M.; Makioka, D.; Yamura, S.; Watabe, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Ito, E. Zeptomole detection of an enzyme by a simple colorimetric method. Anal. Sci. 2021, 37, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, A.S. Beyond the endoplasmic reticulum: Atypical GRP78 in cell viability, signalling and therapeutic targeting. Biochem. J. 2011, 434, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z. Glucose regulated protein 78: A critical link between tumor microenvironment and cancer hallmarks. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1826, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Cheng, C.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Wu, D.C.; Hsieh, J.S.; Lee, S.C.; Wang, W.M. Discovery of tumor markers for gastric cancer by proteomics. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watabe, S.; Kodama, H.; Kaneda, M.; Morikawa, M.; Nakaishi, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Iwai, A.; Miura, T.; Ito, E. Ultrasensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of proteins by combination with the thio-NAD cycling method. Biophysics 2014, 10, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, E.; Iha, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Nakaishi, K.; Watabe, S. Early diagnosis with ultrasensitive ELISA. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2021, 101, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyosei, Y.; Yamura, S.; Namba, M.; Yoshimura, T.; Watabe, S.; Ito, E. Antigen tests for COVID-19. Biophys. Physicobiol. 2021, 18, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurusawa, N.; Chang, J.; Namba, M.; Makioka, D.; Yamura, S.; Iha, K.; Kyosei, Y.; Watabe, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Ito, E. Modified ELISA for ultrasensitive diagnosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyosei, Y.; Namba, M.; Yamura, S.; Watabe, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Sasaki, T.; Shioda, T.; Ito, E. Improved detection sensitivity of an antigen test for SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid proteins with thio-NAD cycling. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 44, 1332–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyosei, Y.; Namba, M.; Makioka, D.; Kokubun, A.; Watabe, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Sasaki, T.; Shioda, T.; Ito, E. Ultrasensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins using the thio-NAD cycling reaction: A preliminary study before clinical trials. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyosei, Y.; Namba, M.; Yamura, S.; Takeuchi, R.; Aoki, N.; Nakaishi, K.; Watabe, S.; Ito, E. Proposal of de novo antigen test for COVID-19: Ultrasensitive detection of spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Takeuchi, R.; Jain, S.H.; Jiang, Y.H.; Watanuki, S.; Ohtaki, Y.; Nakaishi, K.; Watabe, S.; Lu, P.L.; Ito, E. A novel, rapid (within hours) culture-free diagnostic method for detecting live Mycobacterium tuberculosis with high sensitivity. EBioMedicine 2020, 60, 103007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Guo, W.; Yang, S.; Zhu, X.; Xiang, J.; Li, H. Serum GRP78 as a tumor marker and its prognostic significance in non-small cell lung cancers: A retrospective study. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 814670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himbert, D.; Zeuschner, P.; Ayoubian, H.; Heinzelmann, J.; Stöckle, M.; Junker, K. Characterization of CD147, CA9, and CD70 as tumor-specific markers on extracellular vesicles in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Zhan, W.; Gao, Y.; Huang, L.; Gong, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Gao, S.; Kang, T. RAB31 marks and controls an ESCRT-independent exosome pathway. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, X.H.; Wang, D.; Luo, C.L.; Chen, L.X. Bladder cancer cell-derived exosomes inhibit tumor cell apoptosis and induce cell proliferation in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.P.; Wong, C.C.; Kai, A.K.; Ho, D.W.; Lau, E.Y.; Tsui, Y.M.; Chan, L.K.; Cheung, T.T.; Chok, K.S.; Chan, A.C.Y.; et al. SENP1 promotes hypoxia-induced cancer stemness by HIF-1α deSUMOylation and SENP1/HIF-1α positive feedback loop. Gut 2017, 66, 2149–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Dong, C.; Ruan, X.; Yan, W.; Cao, M.; Pizzo, D.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, L.; Ren, X.; et al. Chemotherapy-induced extracellular vesicle miRNAs promote breast cancer stemness by targeting ONECUT2. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3608–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.H.; Ro, E.J.; Yoon, J.S.; Mizutani, T.; Kang, D.W.; Park, J.C.; Il Kim, T.; Clevers, H.; Choi, K.Y. 5-FU promotes stemness of colorectal cancer via p53-mediated WNT/β-catenin pathway activation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhuang, X.; Lin, L.; Yu, P.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Hu, G.; Sun, Y. New horizons in tumor microenvironment biology: Challenges and opportunities. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Lin, M.W.; Rau, C.S.; Jeng, S.F.; Lu, T.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Tzeng, S.L.; Wu, C.J.; Hsieh, C.H. Altered exosomal protein expression in the serum of NF-κB knockout mice following skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, X.; Yang, P.; Li, Z. Acetylation modification regulates GRP78 secretion in colon cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Xiao, H.; Fu, R.; Zhao, C.; Wu, H.; Li, Z. Cell-surface GRP78 facilitates colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, U.K.; Deedwania, R.; Pizzo, S.V. Binding of activated alpha2-macroglobulin to its cell surface receptor GRP78 in 1-LN prostate cancer cells regulates PAK-2-dependent activation of LIMK. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26278–26286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida-Ruiz, D.; Wuillemin, C.; Pederencino, A.; Yaron, M.; Martinez de Tejada, B.; Pizzo, S.V.; Cohen, M. Activated α2-macroglobulin binding to cell surface GRP78 induces trophoblastic cell fusion. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, D.; Shi, G.; Xu, Q.; Shen, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Hou, Y. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by transferring exosomal lncRNA H19. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3932–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yang, F.; Yu, L.; Yu, Z.; Pan, J.; Wang, L.; Cao, X.; Wang, J. Immunosuppressive exosomes from TGF-β1 gene-modified dendritic cells attenuate Th17-mediated inflammatory autoimmune disease by inducing regulatory T cells. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, C.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, L. Exosomes derived from siRNA against GRP78 modified bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells suppress Sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, S.H.; Kim, B.; Sul, H.J.; Choi, B.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Zang, D.Y. Foretinib inhibits cancer stemness and gastric cancer cell proliferation by decreasing CD44 and c-MET signaling. Onco. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrami, H.; Moradi, B.; Borzabadi Farahani, D.; Mehdizadeh, K. Ibuprofen reduces cell proliferation through inhibiting Wnt/β catenin signaling pathway in gastric cancer stem cells. Cell. Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi, M.; Asadi, J.; Ebrahimi, M.; Moradi, A.V.; Hajimoradi, M. Increased expression of miR-146a, miR-10b, and miR-21 in cancer stem-like gastro-spheres. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 16589–16599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ding, H.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.B.; Wang, X.; Zheng, J.; Xue, T.; Amin, H.M.; Song, Y.H.; et al. DAXX inhibits cancer stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, S.; da Costa, D.S.; Freitas, D.; Reis, C.A.; Reis, R.L.; Pashkuleva, I.; Pires, R.A. Molecular weight of surface immobilized hyaluronic acid influences CD44-mediated binding of gastric cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzioğlu, G.; Türksoy, Ö.; Bayrak, Ö.F. Identification of an mtDNA setpoint associated with highest levels of CD44 positivity and chemoresistance in HGC-27 and MKN-45 gastric cancer cell lines. Cell J. 2018, 20, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.T.; Wang, Y.K.; Tseng, Y.J. Exosomal proteins and lipids as potential biomarkers for lung cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Cancers 2022, 14, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Tsai, H.Y.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, J.L.; Lu, C.C.; Fang, Y.P.; Wu, D.C.; Huang, Y.B.; Lin, M.W. Isoliquiritigenin inhibits gastric cancer stemness, modulates tumor microenvironment, and suppresses tumor growth through glucose-regulated protein 78 downregulation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iha, K.; Tsurusawa, N.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Lin, M.-W.; Sonoda, H.; Watabe, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Ito, E. Ultrasensitive ELISA detection of proteins in separated lumen and membrane fractions of cancer cell exosomes. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 654, 114831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsurusawa, N.; Iha, K.; Sato, A.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Sonoda, H.; Watabe, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Wu, D.-C.; Lin, M.-W.; Ito, E. Ultrasensitive Detection of GRP78 in Exosomes and Observation of Migration and Proliferation of Cancer Cells by Application of GRP78-Containing Exosomes. Cancers 2022, 14, 3887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163887
Tsurusawa N, Iha K, Sato A, Tsai H-Y, Sonoda H, Watabe S, Yoshimura T, Wu D-C, Lin M-W, Ito E. Ultrasensitive Detection of GRP78 in Exosomes and Observation of Migration and Proliferation of Cancer Cells by Application of GRP78-Containing Exosomes. Cancers. 2022; 14(16):3887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163887
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsurusawa, Naoko, Kanako Iha, Akane Sato, Hsin-Yi Tsai, Hikaru Sonoda, Satoshi Watabe, Teruki Yoshimura, Deng-Chyang Wu, Ming-Wei Lin, and Etsuro Ito. 2022. "Ultrasensitive Detection of GRP78 in Exosomes and Observation of Migration and Proliferation of Cancer Cells by Application of GRP78-Containing Exosomes" Cancers 14, no. 16: 3887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163887
APA StyleTsurusawa, N., Iha, K., Sato, A., Tsai, H.-Y., Sonoda, H., Watabe, S., Yoshimura, T., Wu, D.-C., Lin, M.-W., & Ito, E. (2022). Ultrasensitive Detection of GRP78 in Exosomes and Observation of Migration and Proliferation of Cancer Cells by Application of GRP78-Containing Exosomes. Cancers, 14(16), 3887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163887






